CA Inter Taxation GST Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) – CA Inter Taxation Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
CA Inter Taxation GST Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) – CA Inter Taxation Study Material
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
GST Council has been established under ………. of the Constitution of India.
(a) Article 246
(b) Article 254
(c) Article 279
(d) Article 279A
Answer:
(d) Article 279A
Question 2.
At present, the ‘alcoholic liquor for human consumption’ is subjected to which of the following?
(a) GST
(b) State excise duty
(c) Central Sales Tax/Value Added Tax
(d) Article 279A
Answer:
(d) Article 279A

Question 3.
Consequent to section 118 of the Finance Act, 2020, the section 2(114) of the CGST Act, 2017 has been amended. Which of the following Union Territories have been merged into a single Union Territory?
(i) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(ii) Lakshadweep
(iii) Dadra and Nagar Haveli
(iv) Daman and Diu
(v) Chandigarh
(vi) Ladakh
(a) (i)and(ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (v)and(vi)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(b) (iii) and (iv)
Question 4.
The erstwhile state “Jammu and Kashmir” has been removed as state and framed into two Union Territories of Jammu and Kashmir and UT of Ladakh. Which of these two has its own legislative body?
(a) UT of Jammu and Kashmir
(b) UT of Ladakh
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) UT of Jammu and Kashmir
Question 5.
In accordance with Article 279A(9), the vote of the Central Government shall have a weightage of ………. of the total votes cast.
(a) One half
(b) One third
(c) One fourth
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) One third
Question 6.
The functions of GST Council include
(a) To decide policy matters
(b) To formulate principles for administration
(c) The implementation of GST
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 7.
As per section 2(52) of the CGST Act, 2017, the term “Goods” includes ………..
(a) Actionable claims
(b) Growing crops, Grass
(c) Every kind of movable property other than money and securities
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 8.
……….. Are consumption based taxes on goods and services
(a) Direct Taxes
(b) Indirect Taxes
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Indirect Taxes
Question 9.
Which of the following is an example of transaction in money under GST laws?
(a) Deposit of principal amount in bank
(b) Amount withdrawn from bank
(c) Exchange of ₹ 2,000 note for 10 notes of ₹ 200 (without consideration)
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above

Question 10.
The section 2(52) defines goods. Which of the following is not considered in this definition of ‘goods’?
(a) Sale of shares of unlisted company
(b) Sale of perishable items of goods
(c) Sale of lottery tickets
(d) Sale of old twenty five-paisa coin at ₹ 25
Answer:
(a) Sale of shares of unlisted company
Question 11.
Which of the following countries was the first to introduce GST?
(a) United States
(b) Britain
(c) Canada
(d) France
Answer:
(d) France
Question 12.
As per Schedule II of CGST Act, 2017, which of the following is a supply of services?
(a) Transfer of title in goods
(b) Title in goods to be passed in future, as per existing agreement
(c) Repairing of Mobile Phone
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Repairing of Mobile Phone
Question 13.
Which of the following has been omit-ted at the time of introduction of GST?
(a) Article 268(1)
(b) Article 268(2)
(c) Article 268A
(d) Article 269
Answer:
(c) Article 268A
Question 14.
Which of the following is not a supply of services?
(a) Renting of immovable property
(b) Payment of Non-Compete Fee by an ex-employee to his previous employer
(c) Repairing of Laptop
(d) Transfer of title in goods at a future date
Answer:
(d) Transfer of title in goods at a future date
Question 15.
………. was the first state to pass State GST Bill.
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Assam
(d) Telangana
Answer:
(d) Telangana
Question 16.
Which of the following transactions does not qualify as supply under GST law?
(a) Import of services by Suresh without consideration for the purposes of his business from his son “Mukesh” living outside India.
(b) Supplies made by the principal to his agent (registered) situated within the same State.
(c) Disposal of car without consideration (ITC has not been claimed)
(d) Supply of service by Head Office (Delhi) to its own branch situated in Mumbai
Answer:
(c) Disposal of car without consideration (ITC has not been claimed)
Question 17.
GST Council has its headquarters in
(a) Delhi
(b) Mumbai
(c) Madras
(d) Kolkata
Answer:
(a) Delhi
Question 18.
Considering the definition of exempt goods given under section 2(47) of CGST Act, 2017, which of the following is
treated as exempt supply?
(a) Supply of electricity
(b) Sale of liquor
(c) Supply of health care services
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 19.
Who amongst the following is the chairperson of GST Council?
(a) Union Finance Minister
(b) President
(c) State Finance Minister
(d) Prime Minister
Answer:
(a) Union Finance Minister

Question 20.
Which of the following services received without consideration will not considered as supply under GST?
(a) Import of services by a person in India from his sister (wholly dependent on such person in India) in America
(b) Import of services by a person in India from his brother well-settled in Japan (Independent)
(c) Import of services by a person in India from his son (wholly dependent on such person in India) in China
(d) Import of services by a person in India from his son well-settled in Germany
Answer:
(b) Import of services by a person in India from his brother well-settled in Japan (Independent)
Question 21.
As per Article 279A, ……… Of the total number of members of GST Council shall constitute the quorum at its meetings?
(a) One third
(b) One half
(c) One fourth
(d) One tenth
Answer:
(b) One half
Question 22.
The Schedule III of CGST Act, 2017 specifies the transactions and activities which shall be neither treated as supply neither of goods nor as services. Which of the following will not be included in this category?
(a) Salary paid to director under em-ployment agreement
(b) Sitting fees to independent direc-tors for attending AGMs
(c) Payment to employee for providing broking services to the employer for purchase of commercial property. Such services do not form part of the employment contract entered into by the employer with the employee.
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 23.
The major reason for implementation of GST was:
(a) Plethora of taxes
(b) Plenty of taxable events
(c) Double taxation
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 24.
As per Government notification the services by way of transportation of passengers by a …….. shall be considered under section 9(5).
(a) Radio Taxi
(b) Motor Cab and maxi cab
(c) Motor Cycle
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 25.
Under GST, the final tax is borne by
(a) The end consumer
(b) The interim parties
(c) The supplier
(d) Partly by Government and balance by Supplier
Answer:
(a) The end consumer
Question 26.
Mr. Kamal is interested to opt for composition scheme. Which of the following goods can be supplied by Kamal under Composition scheme?
(a) Milk
(b) Aerated water
(c) Pan masala
(d) Tobacco
Answer:
(a) Milk
Question 27.
For intra-State sales, the GST is divided between Centre and the State in the ratio
(a) Equally
(b) 60:40
(c) 40:60
(d) 25:75
Answer:
(a) Equally

Question 28.
Which of the following has been kept out of the GST levy?
(a) Generator
(b) Computer
(c) Jewellery
(d) Electricity
Answer:
(d) Electricity
Question 29.
Shiv Steels is a renowned furniture house. As a part of their business policy, the firm donated 5 office tables to charitable school. The ITC has been taken in respect of these goods. Under GST:
(a) It is supply of goods as per Schedule I
(b) It is supply of services as per Schedule I
(c) It is supply of goods as per Schedule II
(d) It is not supply as per Schedule III
Answer:
(a) It is supply of goods as per Schedule I
Question 30.
Mr. Vikas, a registered supplier of Himachal Pradesh, wants to opt for composition levy. The turnover limit for composition levy is
(a) ₹ 50 lakh
(b) ₹ 75 lakh
(c) ₹ 1.5 crore
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) ₹ 1.5 crore
Question 31.
In which of the following case, GST is payable by recipient of services?
(a) Services supplied by a recovering agent to ICICI Bank
(b) Insurance Agent services
(c) Services provided by way of sponsorship to Reliance Industries Ltd.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 32.
When employer gifts goods to his employees, it will not be considered as taxable supply for the purpose of GST if the value of supply to an employee does not exceed:
(a) ₹ 5,000
(b) ₹ 20,000
(c) ₹ 50,000
(d) ₹ 1,00,000
Answer:
(c) ₹ 50,000
Question 33.
A hotel provides 5 days-4 nights pack-age wherein the facility of breakfast and dinner is provided along with the room accommodation. This supply is
(a) Composite Supply
(b) Mixed Supply
(c) Neither Composite nor Mixed Supply
(d) Both Composite and Mixed Supply
Answer:
(a) Composite Supply
Question 34.
A service would be called as “con-tinuous supply of service”, if the service under a contract is provided continuously or on recurrent basis exceeding:
(a) One year
(b) 6 months
(c) 3 months
(d) 1 month
Answer:
(c) 3 months
Question 35.
Mr. A of Delhi supplied goods to Mr. B of Chandigarh (Union-Territory). Which law will govern this transaction?
(a) CGST
(b) SGST
(c) UTGST
(d) IGST
Answer:
(d) IGST
Question 36.
The payment of tax by electronic operator who does not have physical presence in taxable territory in India be made by ………
(a) ECO himself
(b) His appointed representative in India
(c) The person who receives supply
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(b) His appointed representative in India
Question 37.
A registered person of Delhi is buying and selling goods only in Puducherry. The applicable law for GST ¡n this case
will be:
(a) SGST & CGST
(b) UTGST&CGST
(c) SGST & UTGST
(d) IGST
Answer:
(a) SGST & CGST
Question 38.
Section 8 deals with taxability of Composite and Mixed Supplies. What would be the tax rate in case of Mixed Supply?
(a) Tax rate as applicable on supply attracting the lowest rate of tax
(b) Tax rate as applicable on supply attracting the highest rate of tax
(c) Flat rate@ 1896
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Tax rate as applicable on supply attracting the highest rate of tax
Question 39.
In case of Goods Transport Agency (GTA) services, tax Is to be paid under forward charge If:
(a) Services supplied to body corporate established under law (GST is payable @ 596)
(b) Services supplied to Casual Taxable Person located in taxable territory (GST is payable @ 5%)
(c) Services supplied to cooperative society established under law (GST is payable @ 5%)
(d) Services supplied to factory registered under Factories Act (GST is payable @ 12%)
Answer:
(d) Services supplied to factory registered under Factories Act (GST is payable @ 12%)

Question 40.
Schedule I of CGST Act, 2017 deals with
(a) Supplies made with consideration
(b) Supplies made without consider-ation
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Supplies made with consideration
Question 41.
In which of the following cases, the RCM provision is optional subject to fulfilment of certain conditions?
(a) Services by director
(b) Recovery agent services
(c) Services by an author by way of transfer of copyright
(d) Services provided by business facilitator to a banking company
Answer:
(c) Services by an author by way of transfer of copyright
Question 42.
There are some products which have temporarily been kept out of GST and GST Council shall decide the date from which these shall be included in GST. These products are:
(a) Petroleum Crude
(b) High Speed Diesel & Motor Spirit
(c) Natural Gas and ATF
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 43.
Which of the following services does not fall under reverse charge provisions as contained under section 9(3) of the CGST Act?
(a) Services supplied by arbitral tribunal to business entity
(b) Sponsorship provided to any partnership firm
(c) Sponsorship provided to anybody corporate
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 44.
Which of the following activities are exempt from GST?
(a) Religious pilgrimage organised by Ajmer Charitable Trust.
(b) Milling of paddy into rice.
(c) Loading, packing and warehousing of jaggery and pulses.
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 45.
Sumit has opted for composition scheme in the financial year 2019-2020. His aggregate turnover in Financial Year 2018-2019 is ₹ 90 Lakh. In Financial Year 2019-2020, Mr. Sumit can supply services (other than restaurant services) up to a value
(a) ₹ 5,00,000
(b) ₹ 9,00,000
(c) ₹ 50,00,000
(d) Nil
Answer:
(b) ₹ 9,00,000
Question 46.
As per the amendment made in sec-tion 10 through CGST (Amendment) Act, 2017, a composition dealer can provide supply of services (other than restaurant services) not exceeding:
I. 10% of turnover in preceding finan-cial year
II. 10% of taxable supplies in preceding financial year
III. ₹ 5,00,000
IV. ₹ 10,00,000
(a) I or III, whichever is Lower
(b) I or III, whichever is Higher
(c) II or IV, whichever is Lower
(d) II or IV, whichever is Higher
Answer:
(a) I or III, whichever is Lower

Question 47.
The following categories of registered persons are not being eligible for the Composition Scheme under the CGST Act, 2017:
(i) Supplier of the Restaurant Services
(ii) Manufacturer of notified goods
(iii) Non-resident taxable persons
(iv) Casual taxable person
(a) (iii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Question 48.
As per Entry No. 17, service of transportation of passengers by ……….. is exempt from GST.
(a) Railway (Other than first class and AC)
(b) Metro, monorail and tramway
(c) Inland waterways
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 49.
A registered supplier under composi-tion levy can withdraw at any time and be required to file the Form for withdrawal from composition levy in :
(a) GST CMP-03
(b) GST CMP-04
(c) GST MIS-01
(d) GST PCT-02
Answer:
(b) GST CMP-04
Question 50.
Which of the following form of classical art or folk is included under exemption in Entry 78?
(a) Music
(b) Dance
(c) Theater
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 51.
Mr. Jethalal was registered taxpayer (in Delhi) under composition scheme during 2018-2019. His aggregate turnover in financial year 2018-2019 was ₹ 40,00,000. In view of Second Proviso inserted to section 10(1) w.e.f. 1 -4-2019, the taxpayer is willing to supply services in Financial Year 2019-2020. What is the maximum value of services (other than restaurant) which may be provided in such a manner so that he may continue to remain in composition scheme?
(a) ₹ 4,00,000
(b) ₹ 5,00,000
(c) ₹ 6,00,000
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) ₹ 5,00,000
Question 52.
For the purpose of eligibility for composition scheme, the following particulars are given:
(i) Intra-State supply of 46,00,000 NIL rated goods
(ii) Intra-state supplies 95,00,000 made under forward charge
(iii) Intra-state supplies of 9,00,000 exempted goods
(iv) Inward supplies of 4,00,000 goods on which tax is payable under RCM
The aggregate turnover is ……. And composition scheme is ………
(a) ₹ 1.5 Crore; available
(b) ₹ 1.5 Crore; Not available
(c) ₹ 1.54 Crore; Not available
(d) ₹ 1.54 Crore; Not available
Answer:
(a) ₹ 1.5 Crore; available
Question 53.
Mr. S, a manufacturer of medicines, whose turnover for financial year 2018-19 was of ₹ 1.2 Crore opted to pay under GST as per composition scheme from 1st April, 2019. His turnover crosses ₹ 1.5 Crore on 30th November, 2019. Will he be allowed to pay tax under composition scheme for the remainder of year i.e. from 1st December, 2019 to 31st March, 2020?
(a) Yes, he can avail the benefit till 31 st March, 2020
(b) No, the option availed shall lapse from the day on which his aggre-gate turnover during the financial year 2019-2020 exceeds ₹ 1.5 Crore
(c) Yes, the option can be availed up to completion of financial year i.e. till 30th September, 2019
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) No, the option availed shall lapse from the day on which his aggre-gate turnover during the financial year 2019-2020 exceeds ₹ 1.5 Crore
Question 54.
The supply of lottery is covered under reverse charge mechanism vide section 9(3), if the supplier of goods is …….
& recipient is ……….
I. State Government; Union Territory or any Local Authority
II. Lottery Distributor or selling agent
III. Registered person
IV. Manufacturer
(a) I; II
(b) I; III
(c) II; I
(d) I; IV
Answer:
(a) I; II
Question 55.
Which of the following services, subject to respective conditions, are covered under section 9(3) i.e. reverse charge mechanism?
I. Goods Transport Agency
II. Sponsorship Services
III. Services by Director
IV. Insurance Agent Services
V. Recovery Agent Services
VI. Services by business facilitator to a banking company
(a) I & II
(b) I, II & III
(c) I, II, III & IV
(d) All the six services
Answer:
(d) All the six services
Question 56.
What is the limit on consideration for exemption of services by way of right to admission to circus, dance or theater?
(a) ₹ 250 per person
(b) ₹ 500 per person
(c) ₹ 750 per person
(d) ₹ 1,000 per person
Answer:
(b) ₹ 500 per person

Question 57.
Kapil and Jaithmalani are partners in a firm of advocates. The firm has provided legal professional services to the following:
I. An advocate of Delhi High Court
II. A firm of Five advocates
III. ABC Limited, a business entity whose turnover of the preceding year is more than ₹ 20 Lakhs
IV. Rakesh Kumar, an individual Out of above, which service(s) is/are not exempted and Reverse Charge Mechanism is applicable.
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer:
(c) III
Question 58.
Kalyan Limited, a trader has aggre-gate turnover of outward supply up to 12th July, 2019 is ₹ 7,00,000. The company is under threshold limit, hence not registered under GST. Kalyan has taken sponsorship services from Mr. Rahul on 21 st July, 2019. Who is liable to pay GST on the amount of sponsorship services.
(a) Kalyan limited under reverse charge mechanism
(b) Mr. Rahul under forward charge mechanism
(c) Both Kalyan and Rahul
(d) It is exempt
Answer:
(a) Kalyan limited under reverse charge mechanism
Question 59.
Indusind bank located in Delhi, appointed Mr. Bahubali as a recovery agent for collecting outstanding balance amount of loan from a customer, Bal- labhdev. Bahubali provided service to the bank for which he charged ₹ 20,000 as fee. Who is liable to pay GST on ₹ 20,000?
(a) Bahubali
(b) Ballabhdev
(c) Indusind bank
(d) No one as it is exempt
Answer:
(c) Indusind bank
Question 60.
Which of the following service is not exempt under GST?
(a) Loading and unloading of tea bags
(b) Loading and unloading of sugar-cane
(c) Loading and unloading of paddy
(d) Loading and unloading of potato
Answer:
(a) Loading and unloading of tea bags
Question 61.
Tyagi Limited availed services of “Jaipur Golden”, (GTA) for transporta-tion of goods by road from warehouse (Delhi) to its factory (Delhi) and paid freight ₹ 2,40,000. Which of the following statement is true?
(a) If GTA pays tax @ 1296 with ITC, then GTA is liable to pay tax
(b) If GTA pays tax @ 1296 with ITC, then Tyagi Limited is liable to pay tax
(c) If GTA pays tax @ 596 without benefit of ITC, then GTA is liable to pay tax
(d) Irrespective of tax rate availed (z.e. with or without ITC)
Answer:
(a) If GTA pays tax @ 1296 with ITC, then GTA is liable to pay tax
Question 62.
The CGST (Amendment) Act, 2018 has amended section 9(4), which is ef-fective from 1-2-2019. As per amended provisions of section 9(4), the tax under reverse charge mechanism is payable:
I. By registered persons
II. By notified class of registered persons
III. By notified categories of intra-State supplies of goods and/or services
IV. On all intra-State supplies of goods and/or services
V. Received by such registered persons from any unregistered supplier
VI. Received by unregistered persons from registered supplier
(a) I, III and V
(b) I, IV and VI
(c) II, III and V
(d) II, IV and VI
Answer:
(a) I, III and V
Question 63.
On 4th September, 2019, A.R. Rehman, a famous music composer, received ₹ 4 Crore as consideration from T Series Limited for sale of copyright of his original music album “LARA”. Who is liable to pay GST?
(a) A.R. Rehman under forward charge mechanism
(b) A. R. Rehman under reverse charge mechanism
(c) T Series Limited under forward charge mechanism
(d) T Series Limited under forward charge mechanism
Answer:
(d) T Series Limited under forward charge mechanism

Question 64.
Transportation of …….. by rail from Delhi to Haryana are exempt from GST.
(a) Defence equipments
(b) Organic manure
(c) Milk, salt and food grain
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 65.
Services by way of warehousing of …….. is exempt from
(a) processed coffee
(b) Processed tea
(c) Rice
(d) Jaggery
Answer:
(c) Rice
Question 66.
Services by way of admission to …….. are exempt from GST.
(a) Museum
(b) National park
(c) Tiger reserve
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 67.
Which of the following goods have been notified by the Government under reverse charge mechanism under section 9(3);
(a) Shelled cashew nuts
(b) Peeled cashew nuts
(c) Silk yarn
(d) Fabricated cotton
Answer:
(c) Silk yarn
Question 68.
G D Goenka school is an educational institution providing education up to higher secondary school. The school is covered under Entry No. 66. Identify which of the following services is not covered in exemption notification?
(a) Transportation of students, faculty and staff
(b) Catering services
(c) Cleaning services performed in such educational institution
(d) All of the above are exempt
Answer:
(d) All of the above are exempt
Question 69.
The time of supply in case of voucher is “time of issue of voucher”, if the supply is ……… against the voucher.
(a) Identifiable
(b) Not identifiable
(c) Variable
(d) Indecisive
Answer:
(a) Identifiable

Question 70.
The Government has exempted the payment of tax by any taxable person on supply of footwear costing less than ₹ 100. It is
(a) Absolute Exemption
(b) Conditional Exemption
(c) Special Exemption
(d) Ancillary Exemption
Answer:
(b) Conditional Exemption
Question 71.
Mr. Kalakar is a famous painter registered under GST in UP. In an art exhibition organised by “Lalit Kala Academy” in Delhi, he sends his art work. The visitor is allowed to purchase any painting exhibited for cash immediately. Suppose, the painting of Mr. Kalakar is purchased by one visitor, then at what point of time, supply is considered to have been made under GST?
(a) When painting is completed by Mr. Kalakar
(b) When painting is sent from UP to Delhi for exhibition
(c) When painting is displayed at the exhibition by Lalit Kala Academy
(d) When painting is sold to one of the visitors in the exhibition
Answer:
(d) When painting is sold to one of the visitors in the exhibition
Question 72.
Mr. Krishna has received an advance of ₹ 1,00,000 from his client in respect of service to be provided. But, Mr. Krishna is not sure about the rate of tax and the nature of supply of this service, which will be determined at the time of provision of service only. What will be the rate of tax and nature of supply of a service?
(a) 10%, Inter-State supply
(b) 10%, Intra-State supply
(c) 18%, Inter-State supply
(d) 18%, Intra-State supply
Answer:
(c) 18%, Inter-State supply
Question 73.
Which of the following goods is not exempt from GST?
(a) Fish seed
(b) Ice Cream
(c) Pappad
(d) Plastic Bangles
Answer:
(b) Ice Cream
Question 74.
“GM Sales Ltd.” is a public limited company duly incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 with its registered office in Delhi, where it ordinarily carries on its business of taxable goods. The company has a warehouse in NOID A for storage of such taxable goods. What will be the place of business of “GM Sales Ltd.” under GST laws?
(a) Delhi only
(b) NOIDA only
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 75.
Transport of passengers by …….. Are exempt from GST.
(a) Railway in First Class
(b) Railway in an air conditioner coach
(c) Metro rail
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Metro rail

Question 76.
Mr. Roshan Singh is employed as a full time teacher in a Government school in Ghaziabad, UP. He has to purchase a laptop for his son. He visited the computer market situated in Nehru Place, Delhi. At the time of purchase, the shopkeeper insisted on demand draft instead of cash. Mr. Roshan got the demand draft generated at State Bank of India, registered in Delhi against cash. Mr. Roshan does not have a bank account in State Bank of India. Determine the place of supply of service provided by State Bank of India, Delhi to Mr. Roshan.
(a) Ghaziabad
(b) Delhi
(c) Any of the above
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Delhi
Question 77.
What is the rate of interest as per Rule 37(3) applicable in case of reversal of ITC in case of non-payment of consideration within 180 days.
(a) 5% p.a.
(b) 10% p.a.
(c) 12% p.a.
(d) 18% p.a.
Answer:
(d) 18% p.a.
Question 78.
Which of the following services provided by Department of Posts are exempt from GST?
(a) Speed Post
(b) Life Insurance
(c) Express Parcel Posts
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 79.
The liability of taxable person, as reflected in the Electronic Liability Register can be paid through …………..
(a) Debit in Electronic Debit Ledger
(b) Credit in Electronic Debit Ledger
(c) Debit in Electronic Cash Ledger
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Question 80.
Select the goods not exempt from GST, out of the following:
(a) Puja Samagri
(b) Betel Leaves
(c) Precious Metal Bangles
(d) Hearing Aids
Answer:
(c) Precious Metal Bangles

Question 81.
What is the threshold limit for registration under Notification No. 10/2019 dated 7-3-2019?
(a) ₹ 10 lakhs
(b) ₹ 20 lakhs
(c) ₹ 30 lakhs
(d) ₹ 40 lakhs
Answer:
(d) ₹ 40 lakhs
Question 82.
Mr. Amitabh Bachchan is the brand ambassador of GST in India. The con-sideration charged by him up to is
exempt vide entry No. 78.
(a) ₹ 75,000
(b) ₹ 1,50,000
(c) ₹ 2,50,000
(d) Nil (ie. 100% is taxable)
Answer:
(d) Nil (ie. 100% is taxable)
Question 83.
The section 30 of CGST Act, 2017 read with Rule 23 of CGST Rules, 2017 provide that an application for revocation of cancellation of registration can be made within …………….. days from the date of . ……………of the cancellation order
(a) 7, service
(b) 15, issue
(c) 30, service
(d) 45, issue
Answer:
(c) 30, service
Question 84.
The limit of nautical miles from base line of sea coast into the sea in order to determine the supply in territorial water as per section 9 of the IGST Act, 2017 is:
(a) Upto 7 nautical miles
(b) Upto 10 nautical miles
(c) Upto 12 nautical miles
(d) Upto 20 nautical miles
Answer:
(c) Upto 12 nautical miles
Question 85.
Which one of the following is inter-State supply?
(a) Supplier and Recipient are in same State
(b) Supplier and Recipient are in same Union Territory
(c) Supplier and Recipient are in different States/Union Territory
(d) All are intra-State supplies
Answer:
(c) Supplier and Recipient are in different States/Union Territory

Question 86.
Mr. Ram supplied goods to Mr. Laxman. The invoice is dated 30-7-2018. Payment was received for the supply on 30-10-2018. The goods were dispatched on 5-8-2018. What is the time of supply under CGST Act?
(a) 5-8-2018
(b) 30-7-2018
(c) 30-10-2018
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) 30-7-2018
Question 87.
ABC Ltd. of Mumbai supplied goods to XYZ Ltd. of Delhi under a contract for the goods to be delivered at the factory of the buyers. Goods removed from the factory of ABC Ltd. on 09-08-2018 and were delivered in the factory of XYZ Ltd. of Delhi on 16-08-2018. Invoice for the supplies was raised by ABC Ltd. on 18-08-2018. Payment of the bill was received on 20-09-2018. The time of supply in this case under GST be taken as :
(a) 09-08-2018
(b) 16-08-2018
(c) 18-08-2018
(d) 20-09-2018
Answer:
(a) 09-08-2018
Question 88.
Section 12(6) prescribes that the time of supply to the extent it relates to an addition in the value of supply by way of interest, late fee or penalty for delayed payment of any consideration shall be the date on which ………
(a) the supplier receives such addition in value
(b) the supplier becomes entitled to such addition in value
(c) Earlier of (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) the supplier receives such addition in value
Question 89.
What is the time of supply of service if the invoice is not issued within 30 days from the date of provision of service?
(a) Date of issue of invoice
(b) Date on which the supplier receives payment
(c) Date of provision of service
(d) Earlier of (b) & (c)
Answer:
(d) Earlier of (b) & (c)
Question 90.
Allahabad Bank has provided the following detail in respect of a service provided by it.
1. Date of Supply of Ser- 6-12-2017 vices
2. Date of issue of Invoice 10-1-2018 (Within 45 days of provision of service)
3. Date of receipt of pay- 18-12-2017 ment
Determine the time of supply of service:
(a) 6-12-2017
(b) 10-1-2018
(c) 18-12-2017
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) 18-12-2017
Question 91.
Jindal Consultancy services, provides the following details:
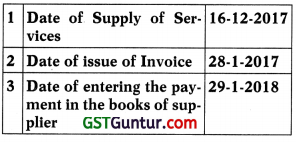

Determine the time of supply of service:
(a) 16-12-2017
(b) 29-1-2018
(c) 1-2-2018
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) 16-12-2017

Question 92.
Determine the time of supply from the following information:

(a) 4 May
(b) 4 June
(c) 12 June
(d) 3 July
Answer:
(b) 4 June
Question 93.
Discount given after the supply is deducted from the value of supply, if:
(a) Such discount is given as per the agreement entered into at/or be-fore the supply
(b) Such discount is linked to the relevant invoices
(c) Proportionate input tax credit is reversed by the recipient of supply
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 94.
Subsidy given by the Central Gov-ernment or a State Government while determining value of taxable supply under Goods and Services Tax (GST) as per section 15 of the CGST Act, 2017 :
(a) Included in the transaction value ie. (value of taxable supply)
(b) Just ignored no treatment
(c) Shall not be included in transaction value Le. (value of taxable supply)
(d) Deducted from the transaction value Le. (value of taxable supply)
Answer:
(c) Shall not be included in transaction value Le. (value of taxable supply)
Question 95.
Which of the following though shown in bill not be included in determining the value of supply for the purpose of GST?
(a) Packing
(b) Discount
(c) Interest for late payment
(d) Installation Charges
Answer:
(b) Discount
Question 96.
In respect of supplies notified by the Central Government, on the recommen-dation of GST Council, the valuation is done as per
(a) Section 15(5)
(b) Rule 32
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both (a) & (b)
Question 97.
When supplier and recipient are related and price is NOT the sole con-sideration, the valuation is done as per:
(a) Section 15(1)/(2)/(3)
(b) Section 15(4) and Rules (27 to 31)
(c) Section 15(5) and Rule 32
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Section 15(4) and Rules (27 to 31)

Question 98.
A film training Institute has subsi-dized its course on account of subsidies received. Which of the following shall be included in the value of supply?
(a) Subsidy from Cine Association, Mumbai
(b) Subsidy from US Government
(c) Subsidy from Warren Brothers of Hollywood
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 99.
Where a laptop is supplied for ₹ 40,000 along with the barter of a printer that is manufactured by the recipient and the value of the printer known at the time of supply is ₹ 4,000 but the open market value of the laptop is not known, the value of the supply of the laptop is ……….
(a) ₹ 44,000
(b) ₹ 40,000
(c) ₹ 6,000
(d) ₹ 4,000
Answer:
(a) ₹ 44,000
Question 100.
As per Notification No. 2/2017, the Supply of lottery is exempt from GST if:
(a) The Supplier of lottery is any person other than Government/Union territory/Local authority.
(b) The appropriate GST was paid when lottery was supplied by Government/Union territory/ Local authority to the authorized distributor.
(c) Both (a) and (b) conditions are satisfied
(d) No such condition is there
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b) conditions are satisfied
Question 101.
Shivani Enterprises has sold goods with list price ₹ 40,000 to a customer. A discount of 10% is given to the customer, which is reflected in invoice, to arrive at the final price of ₹ 36,000. The transaction value is ……….
(a) ₹ 40,000
(b) ₹ 36,000
(c) ₹ 44,000
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) ₹ 36,000
Question 102.
X Limited and Y Limited are related person as per explanation to section 15 of CGST Act, 2017. X Limited sold goods to Y Limited at ₹ 80,000. The similar goods are sold by X Limited in the open market at ₹ 1,25,000. Is the valuation possible as per section 15? Also find out the transaction value as per the applicable provisions:
(a) Yes, ₹ 1,25,000
(b) No, ₹ 1,25,000
(c) Yes, ₹ 80,000
(d) No, ₹ 80,000
Answer:
(b) No, ₹ 1,25,000
Question 103.
“Santosh Interiors” have charged ₹ 3,77,600 from their client in respect of services provided in the month of Febru-ary, 2018. The rate of GST is 18%. The amount ₹ 3,77,600 is inclusive of GST and Tax has not been shown separately in the invoice. Determine the amount of total Tax included in invoice:
(a) ₹ 3,77,600
(b) ₹ 2,15,000
(c) ₹ 65,000
(d) ₹ 57,600
Answer:
(d) ₹ 57,600
Question 104.
The selling price of a notebook is ₹ 50. For notebooks sold to students in Government schools, a company uses its CSR funds to pay the seller ₹ 30, so that the students pay only ₹ 20 per note book.
The value of the notebook will be ……….., as this is a non-government subsidy.
(a) ₹ 20
(b) ₹ 30
(c) ₹ 50
(d) ₹ 80
Answer:
(c) ₹ 50

Question 105.
A supply priced at ₹ 10,000 is made, with a credit period of 1 month for payment. Thereafter interest of 12% is charged. The payment is received after the lapse of three months from the date of supply. The amount of 12% p.a. (i.e. 1 % per month) on ₹ 10,000 for two months after the free credit period is ₹ 300. Such interest will be to the value.
(a) Added
(b) Deducted
(c) Added at 50%
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Added
Question 106.
The amount of ITC shall be
(a) Credited to the Electronic Cash Ledger
(b) Credited to the Electronic Credit Ledger
(c) Debited to the Electronic Cash Ledger
(d) Debited to the Electronic Credit Ledger
Answer:
(b) Credited to the Electronic Credit Ledger
Question 107.
As per section 16(1) of CGST Act, 2017, ITC is available:
I. Only to registered person
II. Only to unregistered person
III. Both registered and unregistered person
IV. Supplies are used in the course or furtherance of business
V. Supplies are intended to be used in the course or furtherance of business
VI. No condition of use of supply in business
Which of the following combination is correct?
(a) I, IV & V
(b) II, V & V
(c) III, IV, V& VI
(d) I, IV & VI
Answer:
(a) I, IV & V
Question 108.
If the goods are received in lots/ instalment,………
(a) 50% of ITC can be taken on receipt of 1st instalment and balance 50% on receipt of last instalment
(b) ITC can be availed upon receipt of last instalment
(c) 100% ITC can be taken on receipt of 1st Instalment
(d) Proportionate ITC can be availed on receipt of each lot/instalment
Answer:
(b) ITC can be availed upon receipt of last instalment
Question 109.
As per section 16(2) of CGST Act, 2017, the registered person is entitled to the credit of any Input Tax Credit on fulfilment of conditions:
I. Possession of Tax Invoice or Debit Note
II. Receipt of goods and services
III. Payment of tax to the Government
IV. Filing of valid return under section 39
V. Filing of valid return under section
VI. Payment of invoice by recipient to supplier
(a) I & II
(b) I, II, III & IV
(c) I, II, III & V
(d) I, III, V&VI
Answer:
(b) I, II, III & IV
Question 110.
As per second Proviso to section 16(2) of CGST Act, 2017, the time limit to pay the value of supply with taxes to avail the ITC is:
(a) 3 months
(b) 6 months
(c) 180 days
(d) Till the date of filing of Annual Return
Answer:
(c) 180 days
Question 111.
Where the registered person has claimed depreciation on the ……. Of the Capital Goods, ITC shall not be allowed.
(a) Cost
(b) Tax component of cost
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Tax component of cost

Question 112.
ABC Limited purchased a machine for ₹ 10,00,000 plus GST @ 18%. It has been capitalized in the books at ₹ 11,80,000 (i.e. inclusive of GST paid). Accordingly, the depreciation was claimed @ 15% on ₹ 11,80,000 under the Income Tax Act. What is the amount of ITC to be allowed?
(a) ₹ 1,80,000
(b) 15% of ₹ 1,80,000
(c) 85% of ₹ 1,80,000
(d) ITC will not be allowed
Answer:
(d) ITC will not be allowed
Question 113.
A manufacturer takes deduction of depreciation on the GST component of the cost of capital goods as per Income- tax Act, 1961. The manufacturer
(a) Can avail only 25% of the said tax component as ITC
(b) Can avail only 50% of the said tax component as ITC
(c) Can avail only 100% of the said tax component as ITC
(d) Cannot avail ITC on the said tax component
Answer:
(d) Cannot avail ITC on the said tax component
Question 114.
If debit note is issued in respect of an invoice subsequently, in the next financial year, ……. will be relevant in
determining the time limit.
(a) Date of invoice
(b) Date of debit note
(c) Date of debit note, if issued within 6 months
(d) Time limit is one year after the issue of debit note
Answer:
(a) Date of invoice
Question 115.
If the payment is not made by the re -cipient to the supplier within …….. from the date of invoice, then the taxpayer needs to reverse the credit already taken.
(a) 45 Days
(b) 90 Days
(c) 180 Days
(d) 200 Days
Answer:
(c) 180 Days
Question 116.
What is the time limit for reclaiming ITC reversed due to non-payment within 180 days?
(a) 3 months
(b) 1 financial year
(c) 2 financial years
(d) No time limit, as section 16(4) is not applicable in this case
Answer:
(d) No time limit, as section 16(4) is not applicable in this case
Question 117.
Mukesh purchased goods for the business, in respect of which ITC ad-missible is ₹ 36,000. 20% of such goods have been used for personal purposes, 60% sold and 20% goods are still lying in godown. Considering section 17(1) of CGST Act, ITC will be available for
(a) ₹ 36,000
(b) 20% of ₹ 36,000
(c) 60% of ₹ 36,000
(d) 8096 of ₹ 36,000
Answer:
(d) 8096 of ₹ 36,000

Question 118.
The turnover of taxable and exempt-ed goods are ₹ 6,00,000 and ₹ 4,00,000 respectively. The common inputs on which GST paid is ₹ 1,08,000. The common inputs on which GST paid is ₹ 1,08,000. The eligible ITC on common input as per section 17(2) is:
(a) ₹ 1,08,000
(b) 6096 of ₹ 1,08,000
(c) 4096 of ₹ 1,08,000
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) 6096 of ₹ 1,08,000
Question 119.
What is the time limit for availing the ITC, as given in section 16(4)
(a) Due date of furnishing of return under section 39 for the month of September following the end of financial year to which such invoice or invoice relating to such debit note pertains
(b) Furnishing of the relevant Annual Return
(c) Earlier of (a) or (b)
(d) Later of (a) or (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Earlier of (a) or (b)
Question 120.
Determine the amount of ITC, available to ABC Bank as per section 17(4)
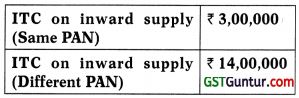
(a) ₹ 10,00,000
(b) ₹ 15,50,000
(c) ₹ 17,00,000
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) ₹ 10,00,000
Question 121.
ITC on aircraft purchased by an aviation school providing training on flying aircraft is ………
(a) Allowed
(b) Allowed but 8096 only
(c) Allowed but 5096 only
(d) Not allowed
Answer:
(a) Allowed
Question 122.
A company has paid for membership of a health club Centre for employees. The related ITC is
(a) Allowed, if provided by employer to its employees under statutory obligation
(b) Allowed, if it is provided by others working in the same industry
(c) Not allowed, in case it is provided under voluntary move
(d) Not Allowed, in any case
Answer:
(a) Allowed, if provided by employer to its employees under statutory obligation
Question 123.
Raj & Co., applied for voluntary registration under CGST Act, 2017 on 5th July, 2017 and the registration was granted on 15th July, 2017. Raj & Co., was having the stock available against the invoices for a period of 3 months old. Raj & Co., shall be eligible for input tax credit on such stock as held as on :
(a) 30th June, 2017
(b) 5th July, 2017
(c) 15th July, 2017
(d) 14th July, 2017
Answer:
(d) 14th July, 2017

Question 124.
Capital goods were brought in the factory on 1-10-2017 worth 110,00,000 on which IGST of 18% was paid. These capital goods were sold at 17,80,000 on 2-2-2019. The ITC to be reversed is
(a) Nil
(b) ₹ 1,26,000
(c) ₹ 1,40,000
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) ₹ 1,40,000
Question 125.
Calculate the amount of ITC avail able from the following Information:

The above ITC includes ITC on input and input services used:
(a) Exclusively for Non-Business Purpose = ₹ 70,000
(b) Exclusively for Exempt Supplies = ₹ 30,000
(a) ₹ 3,00,000
(b) ₹ 4,80,000
(c) ₹ 4,10,000
(d) ₹ 3,80,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 3,80,000
Question 126.
X Limited purchased goods on 20-2-20 18. A debit note was issued in respect of the same invoice on 7-4-2018. The last date for claiming ITC will be:
I. Due date of furnishing of return under section 39 for the month of September following financial year 2017-20 18
II. Due date of furnishing of return under section 39 for the month of September following financial year 2018-2019
III. Furnishing of the Annual return for financial year 2017-20 18
IV. Furnishing of the Annual return
for financial year 2018-2019
(a) Earlier of I & III
(b) Later of I & III
(c) Earlier of II & IV
(d) Later of II & IV
Answer:
(a) Earlier of I & III
Question 127.
Determine the amount of ITC admissible to XYZ Limited in respect of following:

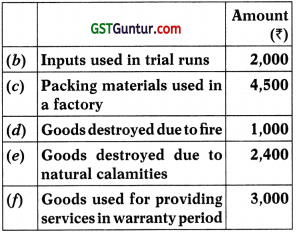
(a) 36,900
(b) 35,900
(c) 33,500
(a) 30,500
Answer:
(c) 33,500
Question 128.
Mr Kamal becomes liable to registration on 25th October, 2018. Accordingly, he has applied for GST registration
on 7th November, 2018. As per section 18(1)(a), Kamal shall be eligible for ITC on Inputs held in stock as on:
(a) 24th October
(b) 25th October
(c) 26th October
(d) 7th November
Answer:
(a) 24th October

Question 129.
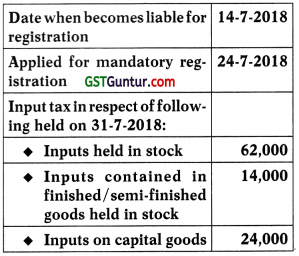
What is the amount of ITC available as per section 18(1)(a)?
(a) ₹ 1,00,000
(b) ₹ 76,000
(c) ₹ 38,000
(D) ₹ 86,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 76,000
Question 130.
KMB limited is a registered person engaged in supply of goods which are ex-empt from tax. On 22-6-2018, exemption notification was rescinded and the goods become liable for tax. Determine the eligible credit in respect of capital goods purchased on 4-12-2017 for ₹ 7,00,000 plus GST @ 12%. These capital goods have been exclusively used in supplying exempted goods. What is the amount of ITC available on capital goods?
(a) ₹ 84,000
(b) ₹ 71,400
(c) ₹ 12,600
(d) ₹ 7,00,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 71,400
Question 131.
When a person under regular scheme changes to composition scheme, he shall pay an amount by way of debit in the Electronic Credit Ledger or Electronic cash ledger, equivalent to credit of input tax in respect of inputs held in stock and inputs contained in semi-finished stock and on capital goods on the:
(a) Day preceding the date of exercising such option
(b) Date of exercising such option
(c) Day after the date of exercising such option
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Day preceding the date of exercising such option
Question 132.
Mr. A bought a machinery for ₹ 1,00,000 on which IGST was paid @ 18% (i.e. ₹ 18,000). After use of machine for 3 years, 7 months and 15 days. Mr. A decided to convert from normal to composition scheme. The amount to be reversed in this case is :
(a) ₹ 18,000
(b) ₹ 4,800
(c) ₹ 9,000
(d) ₹ 4,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 4,800
Question 133.
Mohan is registered under normal scheme in GST. He wants to shift from normal scheme to composition scheme. At the time of exercise of such option, the machine has already been used for 4 years, 8 months and 2 days. The ITC taken at the time of purchase of machine was ₹ 2,10,000. How much ITC needs to be reversed in respect of this machine (capital goods)?
(a) ₹ 2,10,000
(b) ₹ 1,05,000
(c) ₹ 21,000
(d) ₹ 10,500
Answer:
(d) ₹ 10,500
Question 134.
When a person under regular scheme changes to composition scheme, the ITC in respect of inputs held in stock, inputs contained in semi-finished and finished goods held in stock and capital goods (subject to deduction) is reversed. After reversing the ITC so calculated, the balance in the credit of Electronic Credit ledger will ………
(a) Be refunded
(b) Be adjusted for other business vertical
(c) Be lapsed
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Be lapsed
Question 135.
Dev Anand becomes liable to pay tax on 15-7-2019 and has applied for registration on 19-7-2019. He obtained registration on 24-7-2019. As per section 18(1 )(d), Dev is entitled to take credit of input tax paid in respect of inputs held in stock, inputs contained in finished and semi-finished goods held in stock on:
(a) 14-7-2019
(b) 15-7-2019
(c) 16-7-2019
(d) 24-7-2019
Answer:
(a) 14-7-2019

Question 136.
Shashi acquired a capital asset on 1-11-2017, at a cost of ₹ 4,00,000 plus GST @ 18%. He used this machinery
for production of exempt supplies only. On 15-5-2019, his supplies becomes taxable. As per section 18(1)(d) ………. will be available as ITC on capital goods.
(a) ₹ 72,000
(b) ₹ 25,200
(c) ₹ 46,800
(d) ₹ 36,000
Answer:
(c) ₹ 46,800
Question 137.
Radhey & Company registered sup-plier paying GST under regular scheme had made inter-State Taxable Supply of ₹ 8,00,000 and intra-State Taxable Supply of ₹ 6,00,000 chargeable under CGST, SGST, and IGST at the rates of 9%, 9% and 18% respectively. He is having available amount of ITC under CGST of ₹ 30,000 and under SGST of ₹ 20,000. Supplies made are exclusive of taxes. Amount of the total tax payable as CGST, SGST and IGST after availing the amount of ITC by Radhey & Company on such supplies shall be of ₹ ………
(a) 2,30,000
(b) 2,00,000
(c) 2,02,000
(d) 2,26,000
Answer:
(c) 2,02,000
Question 138.
Consider the following:
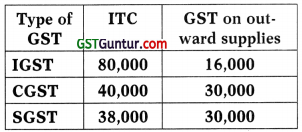
What would be the balance in ITC to be carried forward after utilisation as per sections 49, 49A, 49B and Rule 88A
(a) ₹ 64,000 (IGST), ₹ 10,000 (CGST) and ₹ 08,000 (SGST)
(b) ₹ 04,000 (IGST), ₹ 40,000 (CGST) and ₹ 38,000 (SGST)
(c) ₹ 34,000 (IGST), ₹ 40,000 (CGST) and ₹ 08,000 (SGST)
(d) ₹ 34,000 (IGST), ₹ 10,000 (CGST) and ₹ 38,000 (SGST)
Answer:
(b) ₹ 04,000 (IGST), ₹ 40,000 (CGST) and ₹ 38,000 (SGST)
Question 139.
Mr. Pankaj of Delhi supplied goods to Mr. Krishna of Delhi for ₹ 1 lakh, on which total GST was charged @ 12%. Mr. Krishna, after purchase of goods, added 20% margin of profit (on cost) and sold the entire goods to Mr. Ravi of Delhi. The total amount of tax payable after claiming input tax on such transaction by Mr. Krishna is :
(a) ₹ 12,000
(b) ₹ 14,400
(c) ₹ 2,400
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) ₹ 12,000
Question 140.
Consider the following:
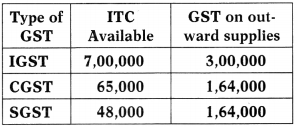
Considering the changes made vide the j Central GST (Amendment) Act, 2018, what would be the balance of IGST, CGST & SGST to be carried forward?
(a) ₹ 4,00,000 (IGST), ₹ Nil (CGST) and ₹ Nil (SGST)
(b) ₹ 2,36,000 (IGST), ₹ 65,000 (CGST) and ₹ Nil (SGST)
(c) ₹ 72,000 (IGST), ₹ 65,000 (CGST) and ₹ 48,000 (SGST)
(d) ₹ Nil (IGST), ₹ Nil (CGST) and ₹ Nil (SGST)
Answer:
(c) ₹ 72,000 (IGST), ₹ 65,000 (CGST) and ₹ 48,000 (SGST)
Question 141.
Consider the following:
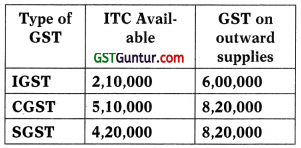
Considering the changes made vide the Central GST (Amendment) Act, 2018, what would be the amounts of IGST, CGST & SGST payable through Cash Ledger?
(a) ₹ 6,90,000 (IGST), ₹ 3,10,000 (CGST) and ₹ 4,00,000 (SGST)
(b) ₹ Nil (IGST), ₹ 4,30,000 (CGST) and ₹ 4,00,000 (SGST)
(c) ₹ Nil (IGST), ₹ 3,10,000 (CGST) and ₹ 7,90,000 (SGST)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) ₹ 6,90,000 (IGST), ₹ 3,10,000 (CGST) and ₹ 4,00,000 (SGST)

Question 142.
Section 2(6) of the CGST/SGST jg Act, 2017 defines aggregate turnover H which is being computed on all India basis excluding the taxes charged under CGST Act, SGST Act, UTGST Act and IGST Act. Aggregate turnover shall include all supplies made by a taxable person comprising of:
I. Taxable supply
II. Exempt supply
III. Export of goods
IV. All Inter-State supply of persons having same PAN
V. Inward supply on which tax is levied on reverse charge basis
VI. Value of all inward supply
(a) I, III, IV and V
(b) I, III, IV and VI
(c) I, II, III and IV
(d) All the above (I to VI)
Answer:
(d) All the above (I to VI)
Question 143.
Consider the following information:
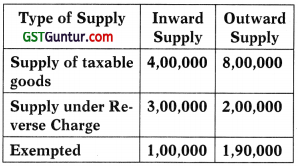
Find out the value of aggregate turnover as per Explanation I of section 22 of CGST Act, 2017?
(a) ₹ 1,90,000
(b) ₹ 8,00,000
(c) ₹ 9,90,000
(d) ₹ 12,90,000
Answer:
(a) ₹ 1,90,000
Question 144.
Section 24 of the CGST Act, 2017 lists categories of persons who are re-quired to take registration even if they are not covered under section 22 of the Act. Find out from the following categories of persons who are being required to take registration as per section 24 of the CGST Act, 2017:
I. Casual Taxable Person
II. Non-resident Taxable Person
III. Recipient of service under Reverse Charge
IV. Inter-State supplier
V. Input service distributor
(a) I, III and V
(b) I, II, IV and V
(c) I, III and V
(d) All the persons in I to V
Answer:
(d) All the persons in I to V
Question 145.
State which shall be taken as the effective date of registration as per CGST Act, 2017 where the aggregate turnover of Madhur company engaged in supply of taxable services in the State of Rajasthan exceeded ₹ 20 Lakh during the year on 25th September, 2017, the application for registration under GST was filed on 19th October, 2017 and the registration certificate was granted on 29th October, 2017 by the authority:
(a) 25-9-20 17
(b) 19-10-2017
(c) 24-10-2017
(d) 29-10-2017
Answer:
(a) 25-9-20 17
Question 146.
For CTP & NRTP, registration is required compulsorily at least …….. Prior to commencement of business.
(a) 5 days
(b) 9 days
(c) 1 days
(d) 14 days
Answer:
(a) 5 days
Question 147.
The GST system is based on electronic networking. Under GST, invoices may be issued:
(a) Manually
(b) Electronically
(c) Any of (a) or (b)
(d) Electronic issue of invoice is mandatory
Answer:
(c) Any of (a) or (b)

Question 148.
Debit Note is issued by the supplier of goods when:
(a) Tax charged in the invoice is excessive
(b) When the goods are returned by the recipient
(c) Tax charged is less than the tax payable
(d) When the goods supplied are deficient
Answer:
(c) Tax charged is less than the tax payable
Question 149.
Where at the time of receipt of advance, the rate of tax of supply is not determinable, then tax shall be paid at the rate of ………..
(a) 12%
(b) 18%
(c) 24%
(d) 28%
Answer:
(b) 18%
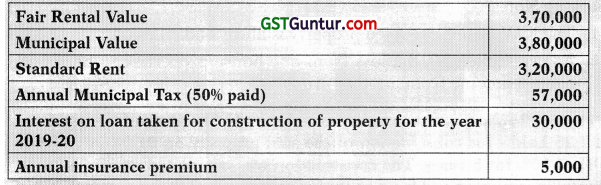
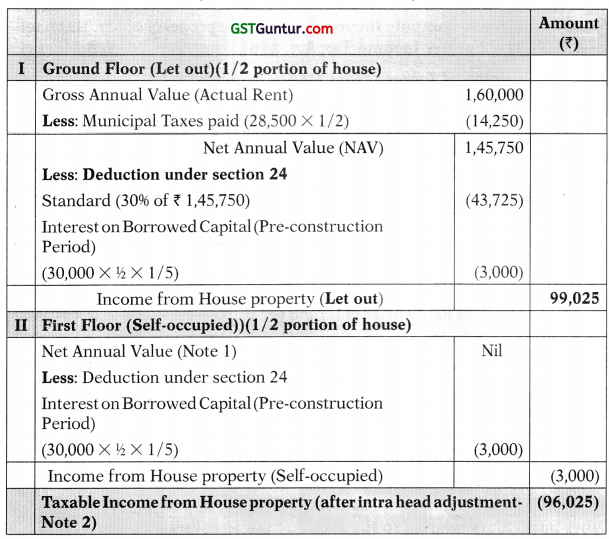
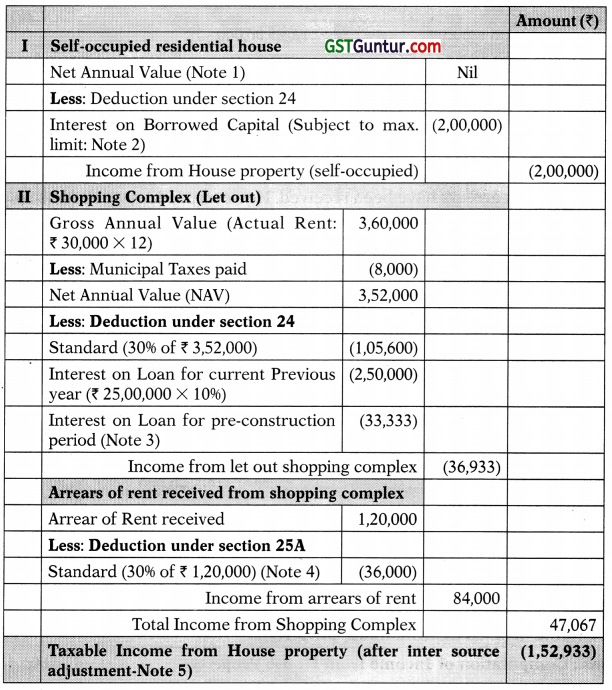
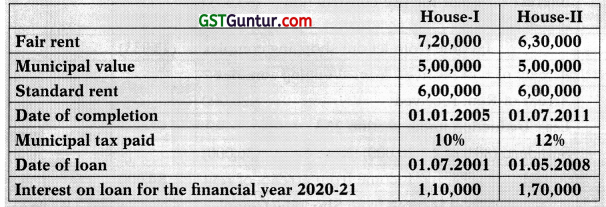
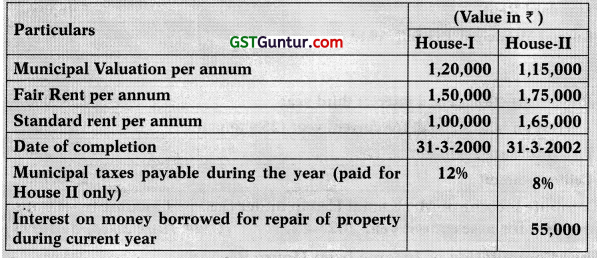
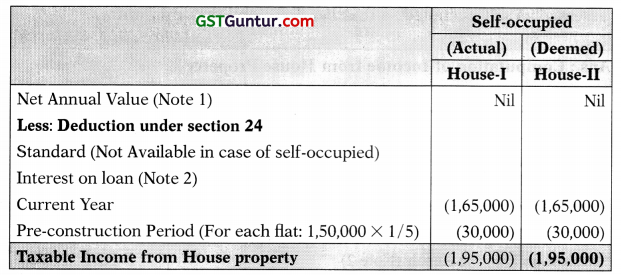
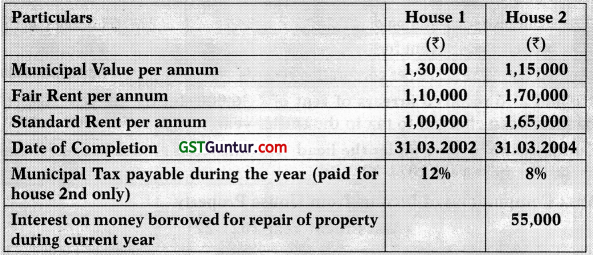
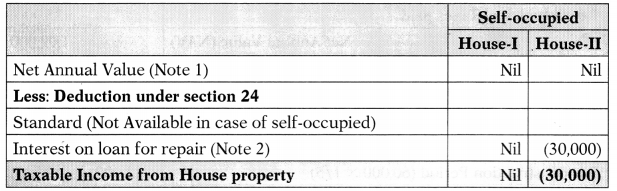
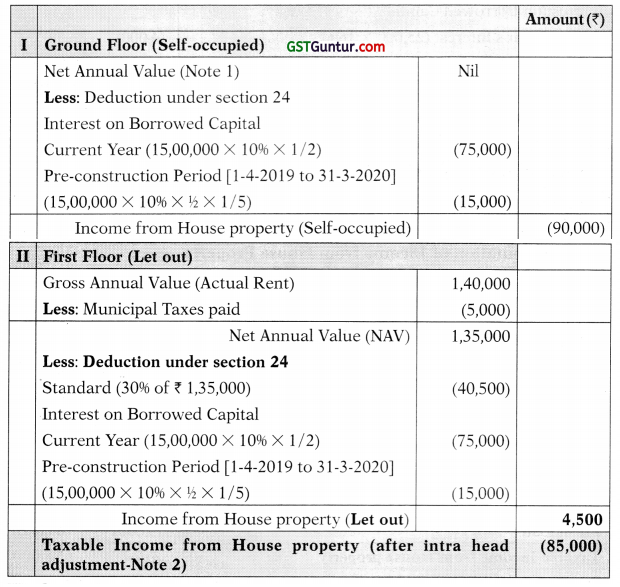
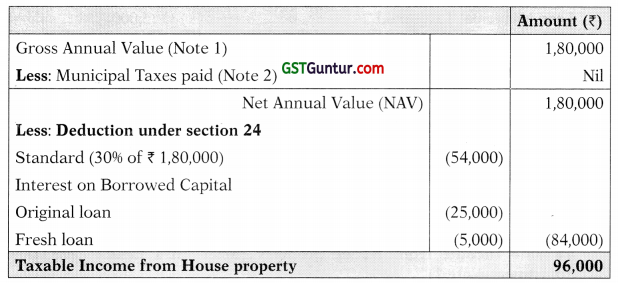
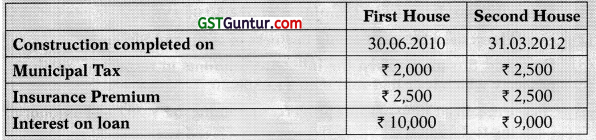
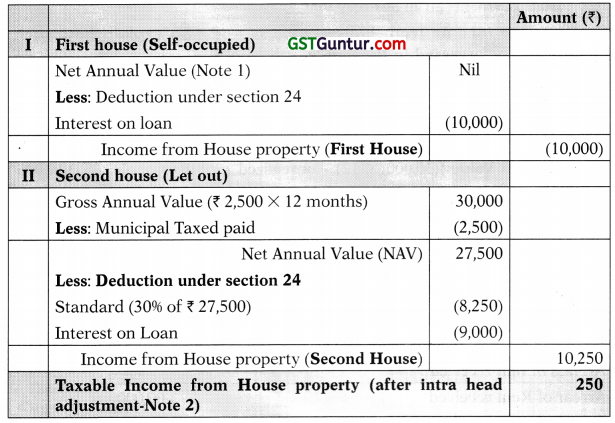
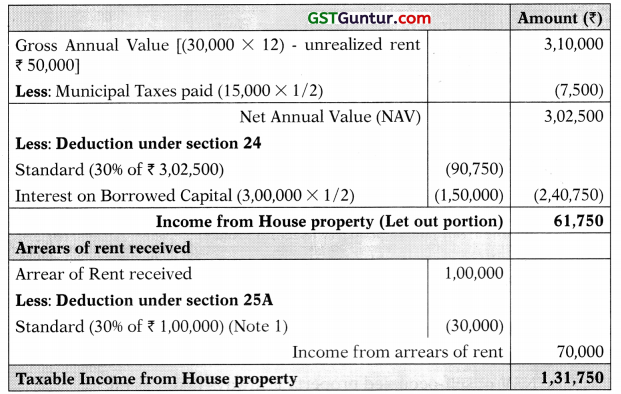
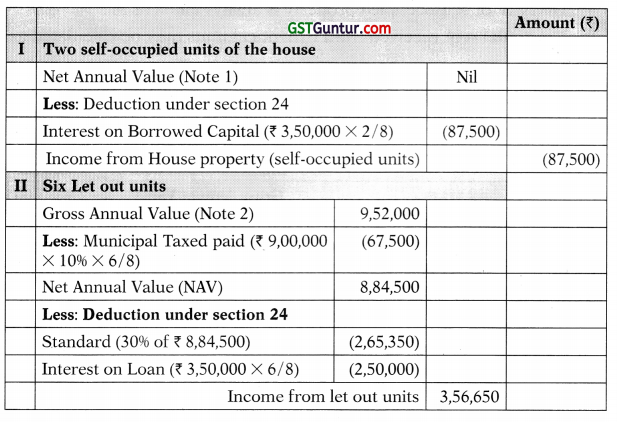
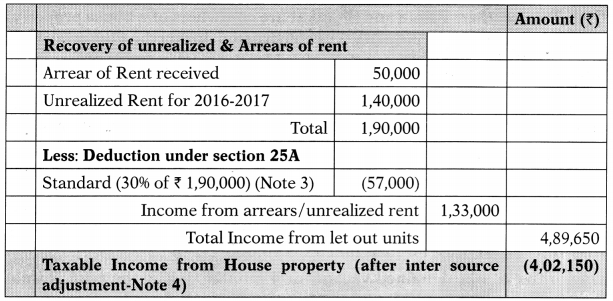
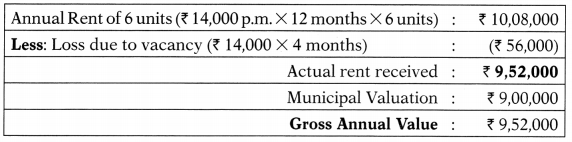
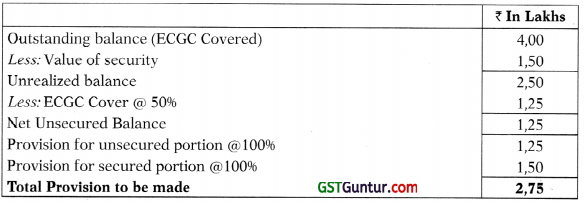
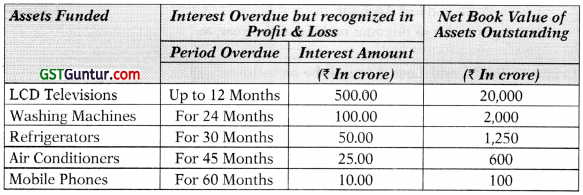
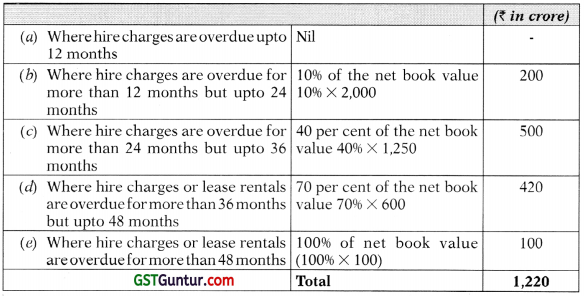
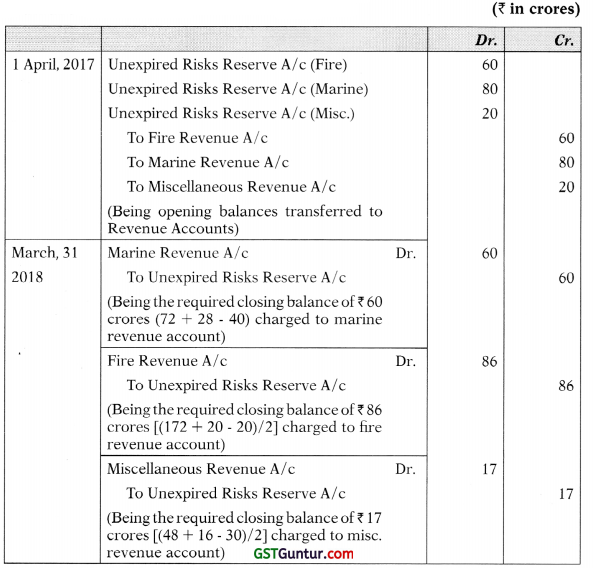
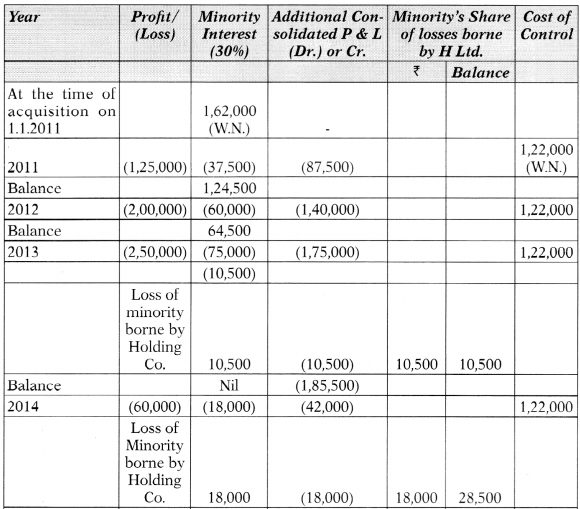
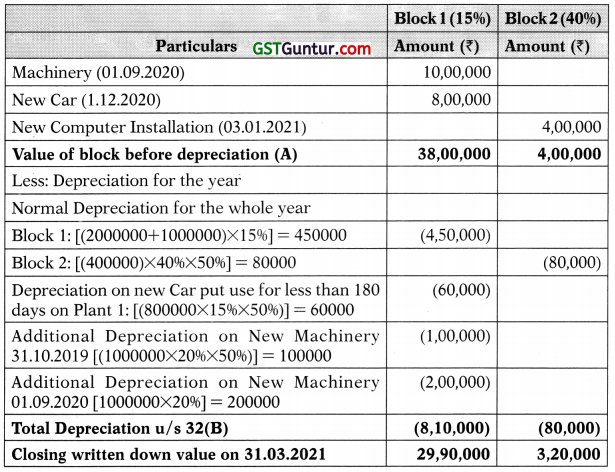
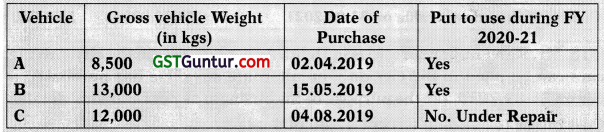
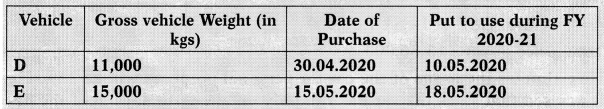
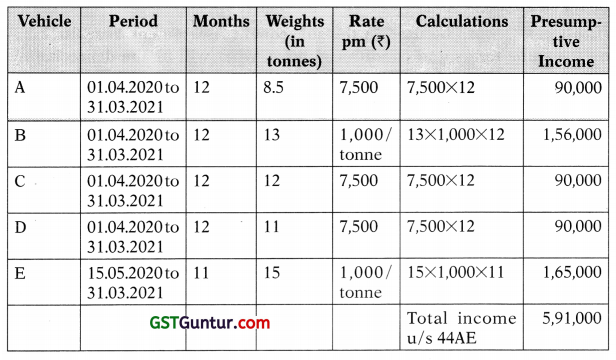
![]()
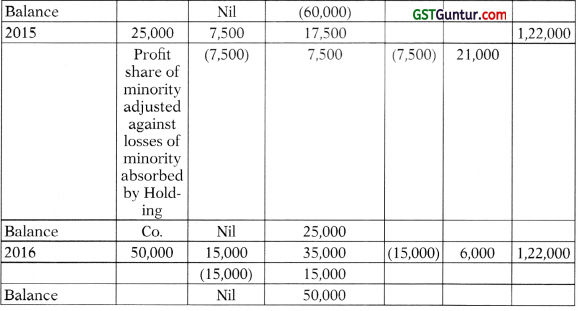
![]()
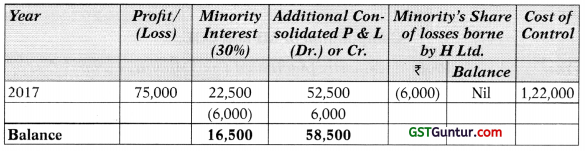
![]()
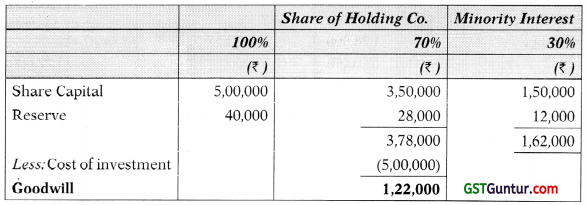
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()