Go through this Bank Reconciliation Statement – CS Foundation Fundamentals of Accounting and Auditing Notes will help students in revising the entire subject quickly.
Bank Reconciliation Statement – CS Foundation Fundamentals of Accounting Notes
Introduction:
- Bank A/c is a personal A/c.
- An institution which deals with money is known as Bank.
- The main business of bank is to accept deposits and lend money.
Services of Banks:
- Accept deposits
- Give loans
- Discounts promissory notes, etc.
- Make payment of premium, etc. on behalf of client
- Allow overdrafts
- Issues letter of credits and many other functions
- Collects money and make Payment on behalf of clients.
Bank Account is a personal account of the clients.
Types of Personal Accounts:
- Current Account
- Savings Account
- Fixed Deposit Account
- Recurring Deposit Account
Current Account:
- These accounts are opened by business concerns.
- The deposits and withdrawals from the accounts can be done as many number of times as required and can be withdrawn without notice.
- Generally, they have very low interest rate on deposits.
- It provides overdraft facilities to its customers.
- Bank credits Client’s A/c when collection is made and debits when making payment.
Overdraft:
Overdraft is a facility where by a customer is allowed to draw more than the amount deposited in his account.
Saving Account:
- These accounts are opened by individuals who wish to save their income.
- It imposes restrictions on the amount and number of withdrawals that can be made.
- Not for business concern but for Individual or Institution which do not need withdrawals very often.
- Number of transactions are less as compared to current account.
- Bank allows a small rate of interest on such deposits.
Fixed Deposit Account:
- Here the money is to be deposited for a particular period of time before which it cannot be withdrawn.
- The bank pays the highest interest rate on such deposits.
- Fixed deposit is evidenced by a receipt called “Fixed Deposit Receipt”’issued by bank in the name of Depositor.
Recurring Deposit Account:
- Here, a fixed amount of money is deposited every month for a fixed period time.
- Bank pays interest on such deposits compounded quarterly at a fixed rate.
Bank Pass Book:
- Pass book is a copy of the clients account in the bank’s ledger.
- Pass book is issued to the client.
- It shows all the transactions entered between the client and the bank.
- The bank balance as per the bank ledger indicated in the bank pass book is called bank balance as per pass book.
Pass Book and Cash Book:
- Pass book is maintained by bank whereas cash book is maintained by customer.
- In pass book, transactions are recorded from the point of view of bank whereas in cash book they are recorded from point of view of client.
- Entries done in the cash book are exactly opposite to that posted in pass book.
Example:
- Mr. A deposited ₹ 4,000 in bank.
- Mr. A withdrew ₹ 2,000.
The above transaction will be shown in cash book and pass book as follows:
1. Debit balance of cash book = Credit balance of pass book
2. Credit balance of cash book = Debit balance of pass book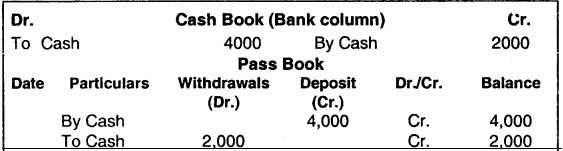
Generally, the above is always true but sometimes, there is a difference between them, to trace these differences between balances of pass book and cash book a Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared.
Bank Reconciliation Statement:
- A bank reconciliation statement is a statement which is prepared to reconcile the balance as per cash book with the balance as per pass book.
- It shows the causes of differences between the two.
- Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) is prepared at a particular date.
BRS:
- BRS is a statement.
- It is prepared on a particular date to reconcile the bank balance as per cash book with the balance as per pass book by showing the causes of difference between the two.
Causes of difference in Bank Balance of Cash Book and Pass Book:
| Reasons |
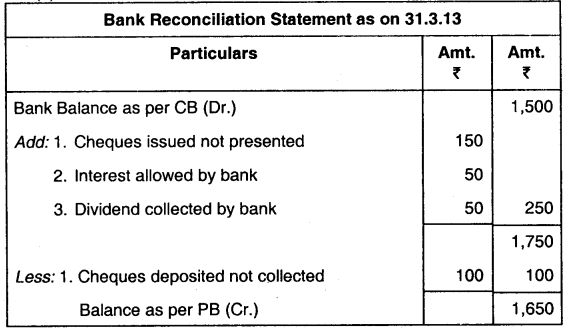
Effect on Cash Book / Pass Book |
| Cash Book |
Pass Book |
| 1. Cheque issued but not presented for payment |
lower than PB |
No effect |
| 2. Cheque Paid / Sent to bank for collection but not collected |
more than PB |
No effect |
| 3. Interest & Dividend received by Bank |
No effect |
More than CB |
| 4. Direct deposits made by customers |
No effect |
More than CB |
| 5. Direct payment made by bank |
No effect |
Less than CB |
| 6. Interest credited by bank on account |
No effect |
More than CB |
| 7. Interest Debited by bank on overdraft |
No effect |
Less than CB |
| 8. Bills collected by bank |
No effect |
More than CB |
| 9. Dishonour of bill discounted by bank |
No effect |
Less than CB |
| 10. Dishonour of a cheque deposited with bank |
More than PB |
No effect |
| 11. Any Error and omission |
Retrospective effect |
Retrospective |
Significance of BRS:
- Highlights causes of difference, necessary adjustment can therefore be carried out at early date.
- Reduce chances of fraud.
- Act as a moral check.
- Actual position of bank balance can be found.
Methods for BRS:
- Bank Reconciliation Statement without adjusting CB
- Bank Reconciliation Statement after adjusting CB
(i) Proforma of BRS without adjusting Cash Book : BRS (as on../…/….)
| Particulars |
Amount ₹ |
Balance as per Pass Book / Cash Book (Dr./Cr.)
Add:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Sub:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) |
……………………. |
|
Balance as per Cash Book / Pass Book (Cr./Dr.)
(ii) BRS with adjusted Cash Book : under this method we make two things:
1. Adjusted Cash book: In adjusted cash book we record only those transaction which have an impact over cash (i.e. increase or decrease) and are correct. Correctly recorded transaction have no need to be adjusted.
Adjusted Cash book neglect following transactions:
- Cheque issued but not presented
- Cheque sent to bank but not collected
- Any mistake by bank
2. BRS : Items which are not considered in adjusted cash book are considered in BRS.
Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement:
Step 1 : Start preparing BRS by taking any one balance (either of cash book or pass book).
Note :
There can be four types of balances :
- Debit balance of cash book (Favourable)
- Credit balance of cash book (Unfavourable)
- Debit balance of pass book (Unfavourable)
- Credit balance of pass book (Favourable)
Step 2 : Ascertaining and treating the causes of difference
Case – 1 : Starting with favourable balance of cash book (Dr. balance)
(i) Items of differences which have led to decreased cash book balance – Add them
Example : Cheque issued but not presented for payment. This amount would have been deducted from cash book and not from pass book hence it has led to decreased cash book balance. So it will be added.
(ii) Items of differences which have led to increased cash book balance. – Deduct them
Example: Cheques deposited but not collected. When cheque was deposited, entry would have been in cash book but since they are not collected no entry has been made in pass book. This has led to an increased cash book balance so it is deducted, in order to bring it equal to pass book.
Case – 2 : Starting with unfavourable balance or bank overdraft balance of cash book (credit balance)
(i) Items of differences which have led to increased overdraft Cash Book balance – Deduct them.
Example : Cheques issued but not presented for payment – Entry must have been done in cash book and due to this overdraft balance must have been increased. So, it is deducted.
(ii) Items of differences which have led to decreased overdraft cash book balance — Add them.
Example : Cheques deposited but not yet cleared. Entry has been done in cash book but not in pass book. This means credit balance of cash book would have been reduced, so this item is added.
Case – 3 : Starting with favourable balance of pass book (credit balance)
(i) Items of differences that have led to increased pass book balance – Deduct them
Example : Cheques issued but not presented for payment. Entry has been done in cash book so cash book is showing a reduced balance. No entry done in pass book so pass book is showing increased balance. In order to bring pass book balance equal to cash book, deduct this amount.
(ii) Items of differences that have led to reduced pass book balance – Add them
Example : Cheques deposited but not collected by bank. Entry is made in cash book so it shows an increased balance but no entry has been made in pass book, so pass book balance shows a reduced figure. So, add this item to the pass book credit balance.
Case – 4 : When unfavourable balance as per pass book is given (Debit balance)
(i) Items of differences that have led to increased overdraft (unfavourable) pass book balance – deduct them
Example : Interest charged. This entry would have been done by the bank. So, the overdraft balance of the pass book would have been increased but no entry of it has been done in the cash book so deduct this from pass book balance.
(ii) Items of differences that have led to decreased pass book overdraft balance – Add them
Example : Dividend collected by bank. This entry has been done in pass book so it has reduced overdraft balance. But no such entry is in cash book yet, so this item is added to the pass book balance to bring it equal to cash book balance.
Summary of Bank Reconciliation Statement:
1. Preparation of BRS when favourable balance is given:
| Transactions |
if starting with
bal. as per
Pass Book |
if starting
with bal. as
per Cash Book |
Cheque issued but not presented
Cheque deposited but not yet collected
Cheque received but not deposited
Dishonour of cheques (sent for collection)
Collection of interest, dividend, direct deposits, Bills
Bank charges, interest on overdraft charged
Dishonor of Bill discounted
Balance |
Deduct
Add
Add
Add
Deduct
Add
Add
Bank balance
as per Cash
book |
Add
Deduct
Deduct
Deduct
Add
Deduct
Deduct
Bank
balance as
per Pass book |
Note: In case of overdraft balance the treatment will be reverse.
Bank Reconciliation Statement MCQ Questions
1. A bank reconciliation statement is prepared to :
(a) Establish the causes of the difference between the balance shown by the bank columns of the cash book and that shown by the pass book.
(b) Ascertain the causes for the difference between the cash balance and the pass book balance.
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Establish the causes of the difference between the balance shown by the bank columns of the cash book and that shown by the pass book.
2. Difference in bank balance as per pass book and cash book may arise on account of:
(a) Cheque issued and presented
(b) Cheque issued but dishonoured
(c) Cheque deposited but not cleared
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
3. Pass book is the statement of the account of the customer maintained by the:
(a) Bank
(b) Debtors
(c) Creditors
(d) Any one of the above.
Answer:
(a) Bank
4. Debit balance in the cash book is :
(a) Debit balance as per pass book
(b) Credit balance as per pass book
(c) Debit balance as per cash book
(d) Credit balance as per cash book.
Answer:
(b) Credit balance as per pass book
5. Bank reconciliation statement is a part of:
(a) Cash book
(b) Ledger
(c) Financial statement
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
6. Started with cash book balance, interest charged on overdraft by bank is :
(a) Added
(b) Subtracted
(c) No effect
(d) Added twice.
Answer:
(b) Subtracted
7. An amount of ₹ 5,000 is debited twice in the bank column of cash book. When credit balance as per pass book is taken as starting point, what will be done?
(a) Add ₹ 5,000 to balance as per pass book
(b) Subtract ₹ 5,000 from balance as per pass book
(c) Add 10,000 to balance as per pass book
(d) Subtract ₹ 10,000 from balance as per pass book.
Answer:
(a) Add ₹ 5,000 to balance as per pass book
8. Overdraft bank balance as shown by the cash book is ₹ 6,000. A cheque for ₹ 10,400 was deposited to bank but omitted in the cash book. In the pass book the amount is wrongly entered in the withdrawal column. Overdraft balance as per pass book:
(a) 16,400
(b) 16,000
(c) 15,900
(d) 13,050.
Answer:
(a) 16,400
9. Unfavourable balance as per pass book means :
(a) Debit balance in pass book
(b) Credit balance in pass book
(c) Bank overdraft
(d) (a) and (c).
Answer:
(d) (a) and (c).
10. Cash at bank as shown by cash book ₹ 75,000. Cheque drawn but not presented ₹ 5,000. Cheque paid into bank but not yet credited, ₹ 1,900. Bank charges not yet entered in cash book ₹ 100 find balance as per pass book.
(a) 82,000
(b) 78,000
(c) 75,000
(d) 72,000
Answer:
(b) 78,000
11. When balance as per pass book is taken, interest allowed by bank is :
(a) Added
(b) Subtracted
(c) No Effect
(d) None.
Answer:
(b) Subtracted
12. Overdraft as per cash book means :
(a) Credit balance in the pass book
(b) Credit balance in the bank column of the cash book
(c) Debit balance as per pass book
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
13. The bank statement shows an overdraft balance of ₹ 4,000. A cheque for ₹ 1,000 drawn in favour of a creditor has not yet been presented for payment. When the creditor presents the cheque for payment, the bank balance will be :
(a) ₹ 3,000
(b) ₹ 5,000
(c) ₹ 3,000 (overdraft)
(d) ₹ 5,000 (overdraft)
Answer:
(d) ₹ 5,000 (overdraft)
14. Bank pass book is a :
(a) Copy of customer’s account in bank books
(b) Bank column of cash book
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Copy of customer’s account in bank books
15. The bank pass book showed ₹ 5,000 but the cash book shows a different balance. While analysing the cause of difference, it was noticed that total of debit side of cash book was carried forwarded to next page as ₹ 1,901 instead of 190. What would be the balance as per cash book:
(a) r 6,901
(b) ₹ 6,711
(c) ₹ 1,540
(d) ₹ 6,801
Answer:
(b) ₹ 6,711
16. Any wrong entry on debit side of the pass book :
(a) Will differ the balances of pass book and cash book.
(b) Will have no effect in the books
(c) Only cash book will be effected
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Will differ the balances of pass book and cash book.
17. Bank charges recorded twice in the cash book will be added to the overdraft of in the preparation of the bank reconciliation statement.
(a) Passbook
(b) Cash book
(c) Purchase book
(d) Sales book.
Answer:
(a) Passbook
18. If transaction of different months in the cash book are given, the transactions will appear in BRS.
(a) Common
(b) Uncommon
(c) All
(d) None.
Answer:
(a) Common
19. The cash book showed an overdraft of ₹ 1,500 as cash at bank, but the pass book made up to the same date showed that cheques of ₹ 100, ₹ 50 and ₹ 125 respectively had not been presented for payments; and the cheque of ₹ 400 paid in to account had not been cleared. The balance as per the cash book will be.
(a) ₹ 1,100
(b) ₹ 2,175
(c) ₹ 1,625
(d) ₹ 1,375.
Answer:
(c) ₹ 1,625
20. When drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement, if you start with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be:
(a) Added;
(b) Deducted;
(c) Not required to be adjusted
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Added;
21. A debit balance in the depositor’s cash book will be shown as :
(a) A debit balance in the bank statement
(b) A credit balance in the bank statement
(c) An overdraft balance in bank statement
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) A credit balance in the bank statement
22. The difference in the balances of both the cash-book and the pass – book can be because of:
(a) Errors in recording the entries either in the cash-book or pass-book.
(b) Same entry recorded in either of the book earlier and in the other book later.
(c) Debit balance of cash book is the credit balance of pass-book
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Errors in recording the entries either in the cash-book or pass-book.
23. Payment done by the account holder through issuing a cheque is entered in:
(a) The pass-book at the time of issuing the cheque
(b) The cash-book at the time of presenting the cheque to the bank for payment
(c) The pass-book at the time of presenting the cheque to the bank for payment
(d) The cash-book at the time of issuing the cheque
Answer:
(c) The pass-book at the time of presenting the cheque to the bank for payment
24. Direct payment to third party by the bank on behalf of the account holder is entered in:
(a) The cash – book when the amount is paid by the bank
(b) The cash – book when the entry is posted in the pass – book
(c) The pass – book when the amount is paid by the bank
(d) The pass – book when the entry is posted in the pass – book
(e) (a) and (d)
(f) (b) and (c).
Answer:
(f) (b) and (c).
25. When favourable balance as per cash book is the starting point, wrong debit given by the bank to the firm’s account will be ________.
(a) Added
(b) Deducted
(c) No effect
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Deducted
26. The credit balance of ₹ 1,000 in the bank column of the cash book was carried forward as its debit balance. When overdraft as per pass book is the starting point:-
(a) ₹ 1,000 will be deducted
(b) ₹ 1,000 will be added
(c) ₹ 2,000 will be deducted
(d) ₹ 2,000 will be added.
Answer:
(c) ₹ 2,000 will be deducted
27. When overdraft as per pass book is the starting point, bank charges of ₹ 100 recorded twice in cash book will be:
(a) Added by ₹ 100
(b) Added by ₹ 200
(c) Deducted ₹ 100
(d) Deducted by ₹ 200.
Answer:
(a) Added by ₹ 100
28. When the overdraft as per cash book is the starting point, a cheque of ₹ 500 deposited into bank but not recorded in cash book will be:
(a) Added by ₹ 500
(b) Deducted by ₹ 500
(c) Added by ₹ 1,000
(d) Deducted by ₹ 2,000.
Answer:
(b) Deducted by ₹ 500
29. Debit balance as per cash book is ₹ 2,000, cheques deposited but not cleared amounts to ₹ 100 and cheques issued but not presented of ₹ 150. The bank allowed interest amounting ₹ 50 and collected divided ₹ 50 balance as per pass book should be:
(a) ₹ 2,100
(b) ₹ 1,950
(c) ₹ 2,350
(d) ₹ 2,150.
Answer:
(d) ₹ 2,150.
30. The cash book showed an overdraft of ₹ 2,000 as cash at bank, but the pass book made up the same date showed that cheques of ₹ 150 and ₹ 125 respectively had not been presented for payment; and the cheque of ₹ 400 paid into account had not been cleared. The balance as per pass book will be:
(a) ₹ 1,600
(b) ₹ 2,675
(c) ₹ 2,125
(d) ₹ 1,875.
Answer:
(c) ₹ 2,125
31. The balance shown by bank column of cash book was ₹ 48,000 on 31.1.98. A Cheque issued worth ₹ 24,000 on 16th Jan was not cleared till 31st Jan. Cheque worth ₹ 10,000 received on 20th Jan. and deposited on 21s1 Jan. was cleared on 27-1 -98. The balance as per pass book as on 31st January (assuming opening balance of pass book and cash book are equal) is:
(a) ₹ 14,000
(b) ₹ 24,000
(c) ₹ 72,000
(d) ₹ 82,000.
Answer:
(c) ₹ 72,000
32. On 31st March, 2007 Ram Kumar Gupta’s pass book showed a credit balance of ₹ 10,300. A comparison of the entries with the cash book revealed that he had paid in cheques amounting to ₹ 1,200 on 27th March 2007, which were not credited in his account. He had issued a cheque amounting to ₹ 1,500 before 31s1 March 2007 which were not presented for payment during the month. There was a debit of ₹ 25 in the pass book in respect of bank charges and a credit of ₹ 35 for interest on current account. Prepare bank reconciliation statement (balance as per pass book) as on 31st March, 2007.
(a) ₹ 12,025
(b) ₹ 9,990
(c) ₹ 10,490
(d) ₹ 10,940.
Answer:
(b) ₹ 9,990
33. A bank statement at 31.01.2007 showed a balance of ₹ 1,000 (Dr.) The following did not appear on the statement:
(i) Cheques not presented for payment ₹ 230
(ii) A cheque for ₹ 400 banked on 31.1.2007
(iii) Bank charges of ₹ 200 had not been entered in the cash book What was the original balance in the cash book at 31.1.2007, before it was amended?
(a) ₹ 630 (Cr.)
(b) ₹ 630 (Dr.)
(c) ₹ 970 (Cr.)
(d) ₹ 970 (Dr.)
Answer:
(a) ₹ 630 (Cr.)
34. Your firm’s bank statement on 31.10.2006 shows a balance of ₹ 13,400. You subsequently discover that the bank has dishonoured a customer’s cheque for ₹ 300 and has charged bank charges of ₹ 50, neither of which is recorded in your cash book. There are unpresented cheques totalling ₹ 1,400. You further discover that an automatic receipt from a customer of ₹ 195 has been recorded as credit in your cash book. Your cash book, prior to correcting the errors and omission was:
(a) ₹ 11,455
(b) ₹ 11,960
(c) ₹ 12,000
(d) ₹ 12,155.
Answer:
(b) ₹ 11,960
35. Who said this statement “All the money’s kind of sitting in a bank account”:
(a) Karl Pearson
(b) Alex Tew
(c) Luco Pacoli
(d) Philip Kotler
Answer:
(b) Alex Tew
36. ________ is a tool for such comparison and arriving at the causes and amount of difference between the two, if any.
(a) Fund flow statement
(b) Cash flow statement
(c) Bank reconciliation statement
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Bank reconciliation statement
37. Same pay-in-slips are filled for outstation cheques:
(a) True
(b) False
(c) True, in case of saving account
(d) True, in case of current account
Answer:
(b) False
38. When deposits are made, form is filled ________.
(a) Account opening form
(b) TDS forms
(c) Preparation of draft form
(d) Pay-in-slips
Answer:
(d) Pay-in-slips
39. A Bank Reconciliation statement is:
(a) A part of pass book
(b) A statement prepared by bank
(c) Cash book relating to cash column
(d) A statement prepared by customer
Answer:
(d) A statement prepared by customer
40. Which of these types of errors are not detected during Bank Reconciliation?
(a) Cash embezzlement by cashier
(b) Cheques deposited but not credited by bank
(c) Casting mistakes in bank column of cash book
(d) Interest or commission charged by the bank not accounted in cash book
Answer:
(a) Cash embezzlement by cashier
41. Balance as per cash book is ₹ 5,000. Cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹ 2,000 and cheques sent for collection but not collected ₹ 1,500. The Bank had wrongly debited the account of firm by ₹ 20. Balance as per pass book will be:
(a) ₹ 5,580
(b) ₹ 5,480
(c) ₹ 4,520
(d) ₹ 5,520
Answer:
(b) ₹ 5,480
42. Balance shown by:
Cash Book ₹ 10,000
Cheques issued but not Presented for payment ₹ 4,000
Cheques deposited but not yet collected ₹ 3,000
Balance as per Pass Book will be:
(a) ₹ 9,000
(b) ₹ 10,000
(c) ₹ 11,000
(d) None
Answer:
(c) ₹ 11,000
43. In arriving at adjusted cash balance which of the following is not taken into account?
(a) Amount deposited by our customer directly in our account
(b) Errors in the cash book
(c) Errors in the pass book
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Amount deposited by our customer directly in our account
44. If balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, then uncollected cheques are:
(a) Added in BRS
(b) Subtracted in BRS
(c) Ignored while preparing BRS
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Added in BRS
45. On 31.03.09, the balance of the cash book is ₹ 7,074 (credit) and Balance as per Bank statement is ₹ 3,159 (debit). On scrutiny, it was found that the difference was due to cheques issued but yet not presented for payment. The Bank Balance as on 31.03.09 to be shown in Balance Sheet is:
(a) As Bank overdraft ₹ 3,159
(b) As Cash at bank ₹ 7,074
(c) As Bank overdraft ₹ 7,074
(d) As Cash at bank ₹ 3,159
Answer:
(c) As Bank overdraft ₹ 7,074
46. A trader issued cheques worth ₹ 7,800 out of which cheques worth ₹ 6,500 only presented into Bank then, on reconciling the Cash Book with the Pass Book, the amount to be added will be:
(a) ₹ 1,300
(b) ₹ 7,800
(c) ₹ 6,500
(d) ₹ 14,300
Answer:
(a) ₹ 1,300
47. When money is withdrawn from bank, the bank:
(a) Credits customer’s a/c
(b) Debits customer’s a/c
(c) Credits and Debits customer’s a/c
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Debits customer’s a/c
48. Sunita, a customer of Digvijay deposited ₹ 1,000 directly in his Bank A/c. For this Sunita will debit the a/c of:
(a) Sunita
(b) Digvijay
(c) Cash
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
49. The account in which fixed amount is deposited every month is called:
(a) Current Account
(b) Savings Account
(c) Fixed Deposit Account
(d) Recurring Deposit
Answer:
(d) Recurring Deposit
50. The form used for depositing money in bank is called as:
(a) Pay in slip
(b) Deposit form
(c) Credit slip form
(d) Cash deposit papers
Answer:
(a) Pay in slip
51. If the balance as per cash book is ₹ 25,000 and cheques of ₹ 10,000 were issued but were not presented for payment then, the balance as per pass book will be:
(a) ₹ 25,000
(b) ₹ 35,000
(c) ₹ 15,000
(d) ₹ 50,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 35,000
52. If the cash book shows an overdraft of ₹ 12,000 and cheque of ₹ 2,000 were issued but not presented for payment and a cheque of ₹ 1,000 deposited in bank was not cleared then, the balance as per pass book will be:
(a) ₹ 10,000
(b) ₹ 9,000
(c) ₹ 14,000
(d) ₹ 11,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 11,000
53. If the overdraft as per cash book is ₹ 2,000 and the bank deducts bank charges of ₹ 100 and also credits ₹ 500 as bank interest, then the balance as per pass book will be:
(a) ₹ 2,600
(b) ₹ 1,400
(c) ₹ 1,900
(d) ₹ 1,600
Answer:
(d) ₹ 1,600
54. Unfavourable bank balance means:
(a) Credit balance in cash book
(b) Credit balance in pass book
(c) Debit balance in cash book
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Credit balance in cash book
55. Overdraft as per cash book means:
(a) Debit balance in cash book
(b) Credit balance in pass book
(c) Credit balance in cash book
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Credit balance in cash book
56. Bank Reconciliation Statement is:
(a) Prepared by customers
(b) Prepared by Bank
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(a) Prepared by customers
57. A Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared to know the causes for difference between:
(a) Balance as per cash column of cash book & pass book
(b) Balance as per bank column of cash book and pass book
(c) Balance as per cash column and bank column of cash book
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Balance as per bank column of cash book and pass book
58. Bank Balance shown in Trial Balance is:
(a) Balance as per pass book
(b) Balance as per cash book
(c) Balance as per sales book
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) Balance as per cash book
59. When money is withdrawn from bank, then the bank will:
(a) Credit customers A/c
(b) Debit customers A/c
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Debit customers A/c
60. When the balance as per pass book is the starting point, direct payment made by the bank will be:
(a) Added in bank reconciliation statement
(b) Subtracted in bank reconciliation statement
(c) No adjustment is required
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Added in bank reconciliation statement
61. When balance as per cash book is the starting point, cheques uncollected by the bank will be:
(a) Added in bank reconciliation statement
(b) Subtracted in bank reconciliation statement
(c) No adjustment will be made
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Subtracted in bank reconciliation statement
62. If the balance as per cash book is ₹ 50,000 and it is undercasted by ₹ 12,000. Also cheques of ₹ 20,000 deposited in bank were dishonoured, then the balance as per pass book will be:
(a) ₹ 32,000
(b) ₹ 58,000
(c) ₹ 82,000
(d) ₹ 42,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 42,000
63. If the balance as per cash book is 20,000 and cheques of ₹ 3,000 deposited in bank are not yet collected and cheques issued of ₹ 2,000 were not presented for payment then, the balance as per pass book will be:
(a) ₹ 19,000
(b) ₹ 21,000
(c) ₹ 25,000
(d) ₹ 15,000
Answer:
(a) ₹ 19,000
64. Who prepares Bank Reconciliation Statement?
(a) Bank employee
(b) Customer of bank or his representative or his accountant
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Customer of bank or his representative or his accountant
Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared by businessman or customer of bank or his representative or his accountant. Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement prepared as on a particular date to reconcile. The bank balance as per cash book with balance as per pass book by showing all causes of difference between the two.
65. For the purpose of bank reconciliation statement, only the column of the cash book is to be considered.
(a) Cash
(b) Bank
(c) Cash and Bank
(d) Discount
Answer:
(b) Bank
Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement prepared as on a particular date to reconcile the bank balance as per cash book with balance as per pass book. Thus, for the purpose of bank reconciliation statement, only the bank column of the cash book is to be considered.
66. Bank balance as per cash book of ABC Enterprises as on 31st March, 2013 is ₹ 1,500. Cheques deposited with bank but not cleared amount to ₹ 100 and cheque issued.but not presented for payment amount to ₹ 150. The bank allowed interest amounting to ₹ 50 and collected dividend ₹ 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per pass book should be:
(a) ₹ 1,600
(b) ₹ 1,450
(c) ₹ 1,850
(d) ₹ 1,650
Answer:
(d) ₹ 1,650

67. Which of the following is true about bank reconciliation statement ________.
(a) Bank reconciliation statement need not to be prepared where the balance of cash book and pass book matches
(b) Bank reconciliation statement is to be prepared necessarily as per the Income tax Act, 1961
(c) Bank reconciliation statement is prepared on yearly basis
(d) Bank reconciliation statement is to be prepared and supplied by bank.
Answer:
(a) Bank reconciliation statement need not to be prepared where the balance of cash book and pass book matches.
On a particular date when businessman find that bank balance of cash book and bank balance as per pass-book do not tally, he makes efforts for their reconciliation. The reconciliation is prepared and presented in the form of a statement generally known as Bank Reconciliation Statement. Where the balance of cash book and pass book matches, Bank Reconciliation Statement need not to be prepared.
68. Cash book shows Dr. balance ₹ 10,000, cheque issued ₹ 4,000 and cheques presented ₹ 3,000. Calculate the balance as per pass book.
(a) 13,000
(b) 7,000
(c) 6,000
(d) 10,000.
Answer:
(b) 7,000
| Balance as per cash book |
10,000 |
| Less : Cheque issued |
(4,000) |
| Add : Cheque issued but not presented |
1,000 |
| Balance as per pass book |
7,000 |
69. If the cheque is not presented for the payment upto the date of the preparation of the Bank Reconciliation Statement then the balance as per pass book will be:
(a) Higher than the balance shown by the cash book by the amount of unpresented cheque.
(b) Same as shown by the cash book
(c) Twice the balance shown by the cash book
(d) Lower than the balance shown by the cash book by the amount of unpresented cheque
Answer:
(a) Higher than the balance shown by the cash book by the amount of unpresented cheque.
When a cheque is drawn or issued in favour of a third party, it is immediately recorded in the cash book by debiting the party and crediting the bank and this has the effect of reducing the bank balance in the cash book. But the bank will not debit client’s account until that cheque is presented for payment and honoured.
So long as it is not presented, the balance shown in the pass book is more than the balance shown by the cash book. So, the option (a) is correct. The balance as per pass book will be higher than the balance shown by the cash book by the amount of unpresented cheque.
70. The pass book shows an overdraft of ₹ 2,000. It was discovered that cheques of ₹ 200, ₹ 40 and ₹ 37 respectively has not been presented for payments and a cheque of ₹ 100 paid into account had not been cleared. The balance as per the cash book will be:
(a) ₹ 2,177 (Cr.)
(b) ₹ 1,977 (Cr.)
(c) ₹ 1,977 (Dr.)
(d) ₹ 2,177 (Dr.)
Answer:
(d) ₹ 2,177 (Dr.)

71. Bank Balance as per cash book of ABC Enterprises as on 31st March, 2013 is ₹ 1,500 cheques deposited with bank but not cleared amount to ₹ 100 and cheques issued but not presented for payment amount to ₹ 150. The bank allowed interest amounting ₹ 50 and collected dividend ₹ 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per pass book should be:
(a) ₹ 1,600
(b) ₹ 1,850
(c) ₹ 1,450
(d) ₹ 1,650
Answer:
(d) ₹ 1,650
|
(₹) |
| Dr. Bal as per cash book |
1,500 |
| Cheque deposit but not cleared |
-100 |
| Cheque issued but not presented |
+150 |
| interest allowed by bank |
+ 50 |
| Dividend collected by bank |
+ 50 |
|
1,650 |
72. A credit balance in the bank statement indicates:
(a) Cash at bank
(b) Cash in hand
(c) Bank overdraft
(d) Over payment to creditors.
Answer:
(a) Cash at bank
Credit balance in bank statement indicates positive balance which means cash balance in account.
73. If cash book balance (Dr.) is given then dividend collected by bank is:
(a) Added on Dr. side of cash book
(b) Added on Cr. side of cash book
(c) Subtracted in cash book
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Added on Dr. side of cash book
A banker may receive amounts due to the customer by way of dividends, rent, interest etc. directly from the persons concerned on account of standing instruction of the customers to such person. The bank credit the account of customer and same will be added in the Dr. side of cash book.
74. Cash Book (Dr.) Balance is ₹ 54,000. If cheque ₹ 5,000 issue but not presented for payment. What will be the effect in cash book:
(a) Added
(b) Subtracted
(c) Add ₹ 5,000
(d) Subtracted ₹ 5,000
Answer:
(d) Subtracted ₹ 5,000
When a cheque is drawn or issued in favour of a third party, it is immediately recorded in the cash book by debiting the party and crediting the bank and this has effect of reducing the bank balance in the cash book. The cash book balance will be substracted by 5,000.
75. Dr. Balance of cash book ₹ 20,000, cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 5,000, cheques collected but not yet credited ₹ 4,000. What is the balance as per pass book:
(a) ₹ 21,000
(b) ₹ 15,000
(c) ₹ 25,000
(d) ₹ 5,000
Answer:
(a) ₹ 21,000
| Dr. Balance as per cash book |
20,000 |
| (i) Cheque issued but not presented for payment |
+ 5,000 |
| (ii) Cheque collected but not yet presented |
– 4,000 |
| Cr. Balance as per pass book |
21.000 |
Thus, the option (a) i.e. ₹ 21,000 is the answer.
76. Dr. Balance as per Cash Book ₹ 20,000. Cheque collected of ₹ 5,000 but credited only ₹ 4,000. Balance of pass book:
(a) ₹ 13,000
(b) ₹ 17,000
(c) ₹ 19,000
(d) ₹ 10,000
Answer:
| Dr. Balance as per cash book |
20,000 |
| Cheque collected of ₹ 5,000 but credited |
|
| only ₹ 4,000, Pass book will reduce by |
-1,000 |
| Cr. Balance as per pass book |
19,000 |
Thus, the option (c) is correct.
77. The differences arising between bank statement and cash book is reconciled by the preparation of:
(a) Bank Reconciliation Statement
(b) Cash Flow Statement
(c) Funds Flow Statement
(d) Working Capital Statement.
Answer:
(a) Bank Reconciliation Statement
The differences arising between bank statement and cash book is reconciled by the preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement by showing all causes of difference between the two.
78. A cash book shows an overdraft of ₹ 2,000 as cash at bank but the pass book made upto the same date shows the cheque of ₹ 200, ₹ 40 and ₹ 37 respectively had not been presented for payment and a cheque of ₹ 100 paid into account had not been cleared. The balance as per the Pass Book will be:
(a) ₹ 1,823 debit
(b) ₹ 1,223 debit
(c) ₹ 1,523 debit
(d) ₹ 1,623 debit
Answer:
(a) ₹ 1,823 debit
Balance as per cash book (Cr.)
Less: Cheque issued but not presented [200+40+37]
Add: Cheque deposited not collected |
2,000
277
100 |
| Balance as per Pass book (Dr.) |
1,823 |
79. In which of the following type of accounts, money is generally deposited periodically at a regular interval?
(a) Recurring Deposit Account
(b) Saving Bank Account
(c) Fixed Deposit Account
(d) Current Account
Answer:
(a) Recurring Deposit Account
In the Recurring Deposit Account, A certain fixed sum of money is deposited affixed or regular interval of time in the account.
80. Credit balance as per Cash Book ₹ 10,000, Bank charged Interest of ₹ 150, cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹ 2,500. Overdraft as per Pass Book will be:
(a) ₹ 12,650
(b) ₹ 12,350
(c) ₹ 12,500
(d) ₹ 7,650
Answer:
(d) ₹ 7,650

81. Some of the transaction that is dependent on bank statement are ________.
(a) Collection charges
(b) Dividend received
(c) Rent received
(d) All of above
Answer:
(d) All of above
A Bank Statement or Account Statement is a summary of financial transactions which have occurred over a given period on a bank account held by a person or business with a financial institution. Thus collection charges, dividend received, rent received are all transactions under the bank statement.
82. Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared by ________.
(a) Accountant of business
(b) Manager of business
(c) Controller of bank
(d) Accountant of the bank.
Answer:
(a) Accountant of business
Bank Reconciliation Statement is generally prepared by the company accountant or the bookkeeper with the purpose to compare the bank’s records with your own company records. It is done on monthly basis whenever bank statement arrives.
This statement is required to find out dmissions and mistakes if any and helps in identifying frauds and embezzlements in company funds. A detailed year-end bank reconciliation statement should be retained so that they are readily accessible when needed during the company annual audit. Thus option A is correct.
83. Balance as per cash book (adjusted) = 1000 unpresented cheques = 2000 uncredited cheques = 500. Compute the balance as per bank statement:
(a) 2,000
(b) Zero
(c) 3,000
(d) 2,500
Answer:
(d) 2,500
| Balance as per cash book |
1,000 |
| + Unpresented cheques |
2,000 |
|
3,000 |
| – Uncredited cheques |
500 |
| Balance as per bank statement |
2,500 |
84. Bank Balance as per Cash book of ABC Enterprises as on 31st March, 2016 is ₹ 1500. Cheques deposited with bank but not cleared amount to ₹ 100 and cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹ 150. The Bank allowed interest amounts to ₹ 50 and collect dividend of ₹ 50 on behalf of ABC enterprise Balance as per Pass Book is:
(a) 1850
(b) 1650
(c) 1600
(d) 1450
Answer:
(b) 1650
| Bank Balance as per Cash Book |
1,500 |
| Add: Cheques issued but not presented |
150 |
| Less: Cheques deposited but not cleared |
(100) |
| Add: Bank Interest collected |
50 |
| Add: Dividend collected |
50 |
| Total |
1,650 |
85. If you start with a debit balance as per the Cash Book, cheques that have been issued by a company but have not been shown in pass book are while preparing bank reconciliation statement.
(a) Not to be adjusted
(b) Added twice
(c) Subtracted
(d) Added
Answer:
(d) Added
Cheque issued but not presented are added while preparing Bank Reconciliation statement as per cash book.
86. Bank balance as per cash book at ABC Enterprises as on 31st March, 2013 is ₹ 1,500 Cheques deposited with bank but not cleared amount to ₹ 100 and cheque issued but not presented for payment amount to ₹ 150. The bank allowed interest amounting to ₹ 50 and collected divided ₹ 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per pass book should be:
(a) ₹ 1.600
(b) ₹ 1,450
(c) ₹ 1,850
(d) ₹ 1,650
Answer:
(d) ₹ 1,650
87. Cheque issued but not presented for payment are in passbook.
(a) Less
(b) Add
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Cheque issued but not presented treatment as per passbook: When a cheque is drawn for third party, it indicates that the bank a/c will be credited in cashbook and debited in passbook. If it is not presented for payment in then it has no effect in passbook and add in cashbook (as such amount is not deducted from bank). Hence, option (d) is correct.
88. Which of the following is true about bank reconciliation statement:
(a) Bank reconciliation statement need to be prepared where the balance of cash book and pass book does not match
(b) Bank reconciliation statement is to be prepared necessarily as per the income-tax Act, 1961
(c) Bank reconciliation Statement is prepared on yearly basis
(d) Bank reconciliation statement is to be prepared and supplied by bank
Answer:
(a) Bank reconciliation statement need to be prepared where the balance of cash book and pass book does not match.
Bank reconciliation statement is a statement which is prepared as on a particular date to reconcile the bank balance as per Cash Book with the balance as per pass book by showing all causes of differences between the two.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()












