CA Inter Advanced Accounts Paper May 2019 – Advanced Accounts CA Inter Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
CA Inter Advanced Accounting Question Paper May 2019
Question 1.
(a)
(i) AP Ltd., a construction contractor, undertakes the construction of com-mercial complex for Kay Ltd. AP Ltd. submitted separate proposals for each of 3 units of commercial complex. A single agreement is entered into between the two parties. The agreement lays down the value of each of the 3 units, i.e. ₹ 50 Lakh, ₹ 60 Lakh and ₹ 75 Lakh respectively. Agreement also lays down the completion time for each unit. Comment, with reference to AS-7, whether AP Ltd., should treat it as a single contract or three separate contracts.
(ii) On 1st December, 2017, GR Construction Co. Ltd. undertook a contract to construct a building for ₹ 45 lakhs. On 31 st March, 2018, the company found that it had already spent ₹ 32.50 lakhs on the construction. Additional cost of completion is estimated at ₹ 15.10 lakhs. What amount should be charged to revenue in the final accounts for the year ended 31st March, 2018 as per provision of AS-7? [5 × 4 = 20 Marks]
Answer:
(i) As per AS 7, when a contract covers a number of assets, the construc-tion of each asset should be treated as a separate construction contract when:
(a) separate proposals have been submitted for each asset;
(b) each asset has been subject to separate negotiation and the con-tractor and customer have been able to accept or reject that part of the contract relating to each asset; and
(c) the costs and revenues of each asset can be identified.
Analysis:
- AP Ltd. submitted separate proposals for each of 3 units of commercial complex.
- Agreement also lays down the completion time for each unit.
- The agreement lays down the value of each of the 3 units, i.e. ₹ 50 Lakhs, ₹ 60 Lakhs and ₹ 75 Lakhs respectively
Conclusion:
Mr. AP Ltd. is required to treat construction of each unit as a separate con-struction contract as the above mentioned conditions of AS 7 are met.
(ii)
| ₹ in lakhs | |
| Cost of construction incurred till date | 32.50 |
| Add. Estimated future cost | 15.10 |
| Total estimated cost of construction | 47.60 |
Percentage of completion:
= \(\frac{32.50}{47.60}\) × 100
Revenue recognition for the year ended 31st March, 2018:
= Contract price × percentage of completion = ₹ 45 lakhs × 68.2896 = ₹ 30.73 lakhs.
| ₹ in lakhs | |
| Total cost of construction Less: Total contract price
Less: Total contract price Total foreseeable loss to be recognized as expense immediately |
47.60
(45.00) 2.60 |
Question 1.
(b) Given below are the following information of M/s. B.S. Ltd.
(i) Goods of ₹ 50,000 were sold on 18-03-2018 but at the request of the buyer these were delivered on 15-04-2018.
(ii) On 13-01-2018 goods of ₹ 1,25,000 were sent on consignment basis of which 2096 of the goods unsold are lying with the consignee as on 31 – 03-2018. ”
(iii) ₹ 1,00,000 worth of goods were sold on approval basis 01-12-2017. The period of approval was 3 months after which they were considered sold. Buyer sent approval for 7596 goods up to 31 -01 -2018 and no approval or disapproval received for the remaining goods till 31-03-2018.
You are required to advise the accountant of M/s. B.S. Ltd., with valid reasons, the amount to be recognized as revenue for the year ended 31st March, 2018 in above cases in the context of AS-9.
Answer:
As per AS 9 “Revenue Recognition”, in a transaction involving the sale of goods, performance should be regarded as being achieved when the following conditions are fulfilled:
(i) the seller of goods has transferred to the buyer the property in the goods for a price or all significant risks and rewards of ownership have been transferred to the buyer and the seller retains no effective control of the goods transferred to a degree usually associated with ownership; and
(ii) no significant uncertainty exists regarding the amount of the consider-ation that will be derived from the sale of the goods.
Analysis and conclusion:
Part (i)
The sale is complete but delivery has been postponed at buyer’s request.
B.S. Ltd. should recognize the entire sale of ₹ 50,000 for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Part (ii)
In case of consignment sale revenue should not be recognized until the goods are sold to a third party.
2096 goods lying unsold with consignee should be treated as closing inventory and sales should be recognized for ₹ 1,00,000 (80% of ₹ 1,25,000).
Part (iii)
Tn case of goods sold on approval basis, revenue should not be recognized until the goods have been formally accepted by the buyer or the buyer has done an act adopting the transaction or the time period for rejection has elapsed or where no time has been fixed, a reasonable time has elapsed.
Therefore, revenue should be recognized for the total sales amounting ₹ 1,00,000 as the time period for rejecting the goods had expired.
Overall conclusion:
Thus, total revenue amounting ₹ 2,50,000 (50,000 + 1,00,000 + 1,00,000) will be recognized for the year ended 31st March, 2018 in the books of B.S. Ltd.
![]()
Question 1.
(c) Jaya Ltd. took a machine on lease from Deluxe Ltd., the fair value being ₹ 11,50,000. Economic life of the machine as well as lease term is 4 years. At the end of each years, lessee pays ₹ 3,50,000 to lessor. Jaya Ltd. has guaranteed a residual value of ₹ 70,000 on expiry of the lease to Deluxe Ltd., however Deluxe Ltd. estimates that residual value will be only ₹ 25,000. The implicit rate of return is 10% p.a. and present value factors at 10% are: 0.909, 0.826, 0.751 and 0.683 at the end of 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th year respectively.
Calculate the value of machinery to be considered by Jaya Ltd. and the value of the lease liability as per AS-19.
Answer:
According to para 11 of AS 19 “Leases”, the lessee should recognize the lease as an asset and a liability at an amount equal to the fair value of the leased asset at the inception of the finance lease. However, if the fair value of the leased asset exceeds the present value of the minimum lease payments from the standpoint of the lessee, the amount recorded as an asset and a lia-bility should be the present value of the minimum lease payments from the standpoint of the lessee.
Computation of Present value of MLP:
| Year | Minimum Lease Payment ₹ | Discount rate @10% | Present value ₹ |
| 1 | 3,50,000 | 0.909 | 3,18,150 |
| 2 | 3,50,000 | 0.826 | 2,89,100 |
| 3 | 3,50,000 | 0.751 | 2,62,850 |
| 4 | 4,20,000 | 0.683 | 2,86,860 |
| Total | 14,70,000 | 11,56,960 |
Conclusion:
The lease liability and machinery should be recognized in the books at ₹ 11,50,000. i.e. Lower of Present value of minimum lease payments ₹ 11,56,960 and fair value ₹ 11,50,000.
![]()
Question 1.
(d) Identify the related parties in the following cases as per AS-18
(i) Maya Ltd. holds 61% shares of Sheetal Ltd.
Sheetal Ltd. holds 51% shares of Fair Ltd.
Care Ltd. holds 49% shares of Fair Ltd.
(Give your answer Reporting Entity wise for Maya Ltd., Sheetal Ltd., Care Ltd. and Fair Ltd.)
(ii) Mr. Subhash Kumar is Managing Director of A Ltd. and also holds 72% capital of B Ltd. (B Ltd. is subsidiary of A Ltd.)
Answer:
(i)
(a) Reporting entity- Maya Ltd.
- Sheetal Ltd. (subsidiary) is a related party
- Fair Ltd. (subsidiary) is a related party
(b) Reporting entity- Sheetal Ltd.
- Maya Ltd. (holding company) is a related party
- Fair Ltd. (subsidiary) is a related party
(c) Reporting entity- Fair Ltd.
- Maya Ltd. (holding company) is a related party
- Sheetal Ltd. (holding company) is a related party
- Care Ltd. (investor/investing party) is a related party
(d) Reporting entity- Care Ltd.
- Fair Ltd. (associate) is a related party
(ii) Mr. Subhash Kumar is Key management personnel (KMP) as he has the authority for planning, directing and controlling the activities of A Ltd. He also holds substantial interest in B Ltd. as he holds 72% capital of B Ltd. Thus, Mr. Subhash is related party for both A Ltd. and B Ltd. Moreover, as per the definition of related party relationship described in para 3 of AS 18, enterprises over which Subhash is able to exercise significant influence are also related parties. Thus, a Ltd. and B Ltd. will also be construed as related to each other.
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Following is the summarized Balance Sheet of Super Ltd. as on 31st March, 2018.
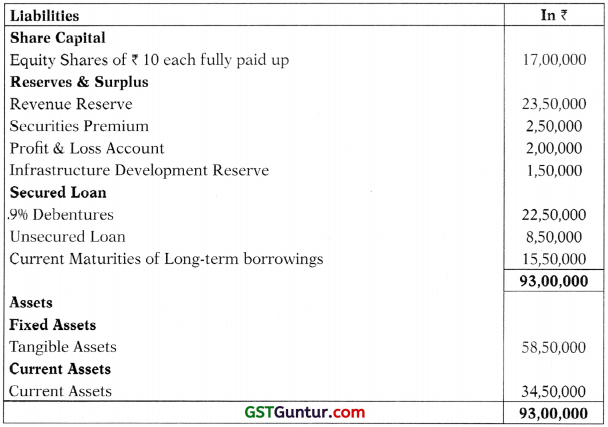
Super Limited wants to buy back 35,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each fully paid up on 1st April, 2018 at ₹ 30 per share.
Buy back of shares is fully authorized by its articles and necessary resolutions have been passed by the company towards this. The payment for buy back of shares will be made by the company out of sufficient bank balance available as part of the Current Assets.
Comment with calculations, whether the Buy Back of shares by the company is within the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. [10 Marks]
Answer:
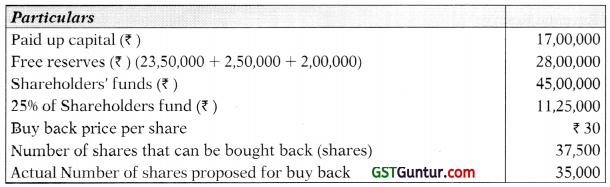
Shares Outstanding Test
Computation of maximum no. of shares that can be bought back as per the Companies Act, 2013
1.
| Particulars | (Shares) |
| Number of shares outstanding | 1,70,000 |
| 25% of the shares outstanding | 42,500 |
2. Resources Test:
Maximum permitted limit
25% of Equity paid up capital + Free Reserves
3. Debt Equity Ratio Test:
Loans cannot be in excess of twice the Equity Shareholder’s Funds post buy back
| Particulars | ₹ | |
| (A) | Loan funds (₹) (22,50,000+8,50,000+15,50,000) | 46,50,000 |
| (B) | Minimum equity to be maintained after buy back in the ratio of 2:1 (₹) (A/2) ‘ | 23,25,000 |
| (C) | Present equity/shareholders fund (₹) | 45,00,000 |
| (D) | Future equity/shareholders fund (₹) (see Working Note) (45,00,000 – 5,43,750) | 39,56,250 |
| (E) | Maximum permitted buy back of Equity (₹) [(D) – (B)] | 16,31,250 |
| (F) | Maximum number of shares that can be bought back @ ₹ 30 per share | 54,375 shares |
| (G) | Actual Buy Back Proposed | 35,000 shares |
Statement showing computation of maximum number of shares which can be bought back
| Particulars | Number of shares |
| Shares Outstanding Test (1) | 42,500 |
| Resources Test (2) | 37,500 |
| Debt Equity Ratio Test (3) | 54,375 |
| Maximum number of shares that can be bought back [least of 1,2 and 3] | 37,500 |
Since the company wants to buy-back only 35,000 equity shares @ ₹ 30. Therefore, buy-back of 35,000 shares, as desired by the company is within the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
Working Note:
Amount transferred to CRR and maximum equity to be bought back will be calculated by simultaneous equation method.
Suppose amount transferred to CRR account is ‘X’ and maximum permitted buy-back of equity is ‘Y’.
We can create the following equations:
(45,00,000 – X) – 23,25,000 = Y Equation (1)
(\(\frac{y}{30}\) × 10) = X or 3X = Y Equation (2)
Solving both the above equations, we get the values of:
X = ₹ 7 5,43,750
Y = ₹ 7 16,31,250
Question 2.
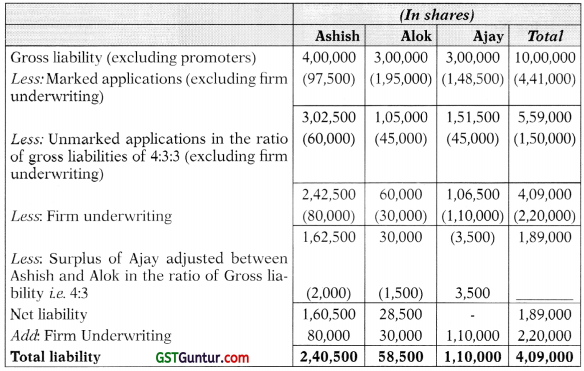
(b) Arohi Ltd. made a public issue of 11,00,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each at a premium of ₹ 10, the amounts payable on application were ₹ 4 long with the full amount of premium and ₹ 6 at allotment. Out of the above 1,00,000 equity shares were issued to promoters and the balance was offered to the public which was underwritten by three underwriters Ashish, Alok and Ajay as follows:
Ashish – 4,00,000 shares including firm underwriting 80,000 shares
Alok – 3,00,000 shares including firm underwriting 30,000 shares
Ajay- 3,00,000 shares including firm underwriting 1,10,000 shares
Total subscriptions received by Aarohi Ltd. were 1,50,000 shares (excluding firm underwriting and marked applications)
The marked applications (excluding firm underwriting) were,
Ashish-97,500 shares,
Alok-1,95,000 shares and
Ajay-1,48,500 shares.
Underwriters are entitled to maximum commission permissible by law on the issue price of shares. The underwriting contract provides that benefit of firm underwriting is to be give to individual underwriters.
You are required to:
(i) Determine the liability of each underwriter in number of shares;
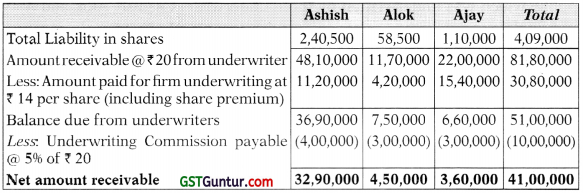
(ii) Compute the amounts payable or due from underwriters; and
(iii) Pass Journal Entries in the books of the company relating to underwriting.
Answer:
(i) Statement showing computation of total liability of underwriters:
(ii) Computation of amount payable to or due from underwriters:
(iii) Journal Entries in the books of the company:
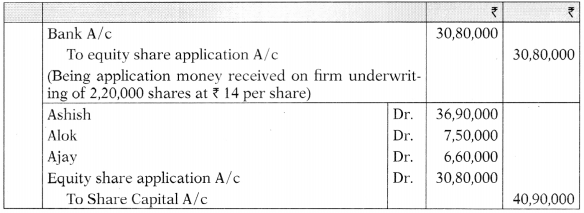
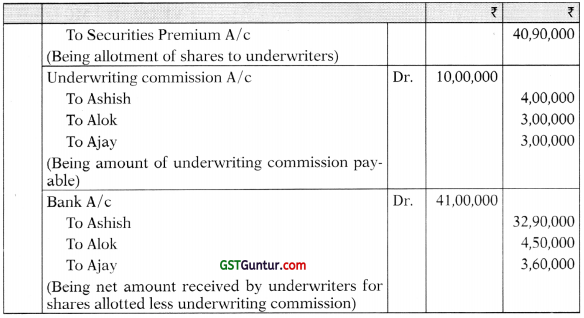
![]()
Question 3.
(a) The following are the summarized Balance Sheet of VT Ltd. and MG Ltd. as on 31st March, 2018:
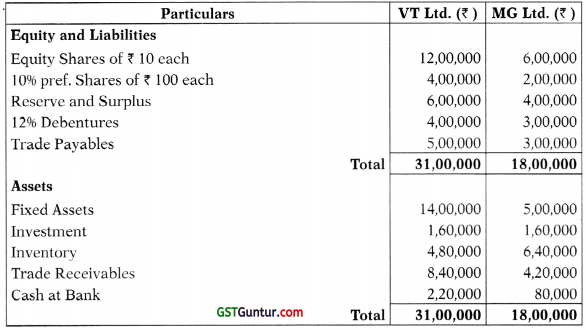
Details of Trade receivables and trade payables are as under:


- Fixed Assets of both the companies are to be revalued at 15% above book value.
- Inventory in Trade and Debtors are taken over 5% lesser than their book value.
- Both the companies are to pay 10% equity dividend, Preference divided having been already paid.
After the above transactions are given effect to, VT Ltd. will absorb MG Ltd. on the following terms:
- VT Ltd. will issue 16 Equity Shares of ₹ 10 each at par against 12 Shares of MG Ltd.
- 10% Preference Shareholders of MG Ltd. will be paid at 10% discount by issue of 10% Preference Shares of ₹ 100 each at par in VT Ltd.
- 12% Debenture holders of MG Ltd. are to be paid at 8% premium by 12% Debentures in VT Ltd. issued at a discount of 10%.
- ₹ 60,000 is to be paid by VT Ltd. to MG Ltd. for Liquidation expenses.
- Sundry Debtors of MG Ltd. includes ₹ 20,000 due from VT Ltd.
You are required to prepare:
(1) Journal entries in the books of VT Ltd.
(2) Statement of consideration payable by VT Ltd. [10 Marks]
Answer:
(i) Journal Entries in the Books of VT Ltd.
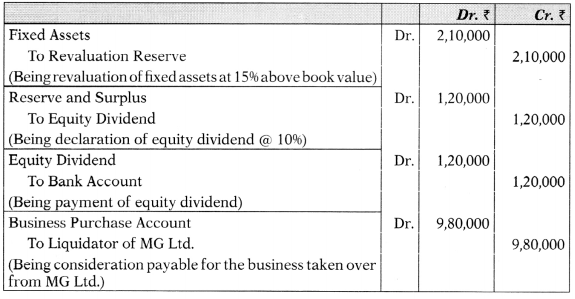
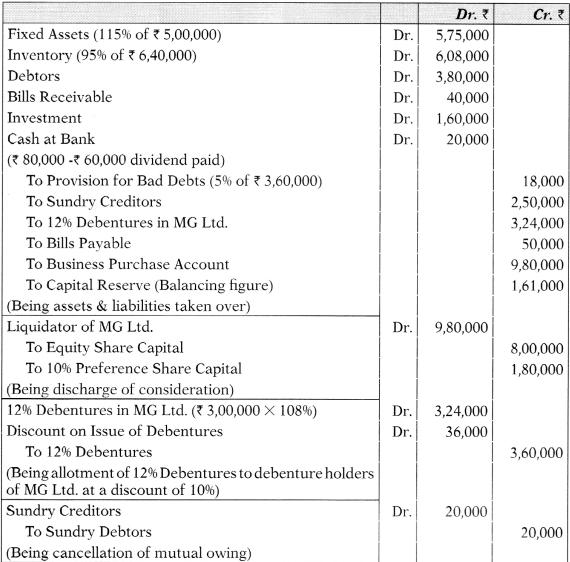

![]()
(ii) Statement of Consideration payable by VT Ltd. (Net payment method)
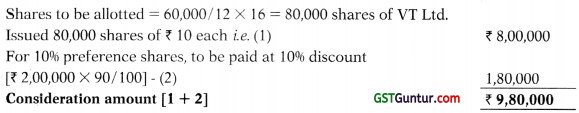
Question 3.
(b) BT Ltd. went into Voluntary Liquidation on 31st March, 2018, when their detailed Balance Sheet read as follows:
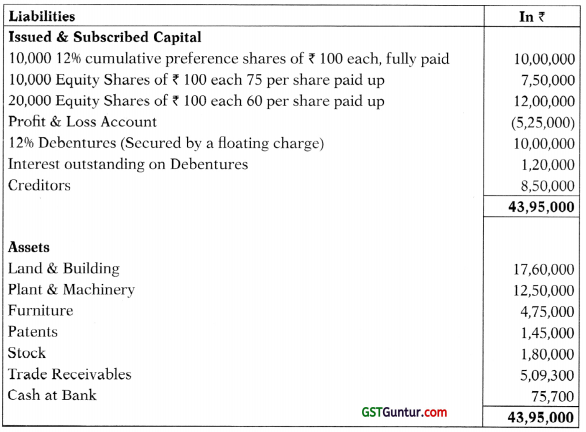
Preference dividends were in arrear for 1 year. Creditors include preferential creditors of ₹ 75,000. Balance creditors are discharged subject to 5% discount.
Assets are realized as under:—

- Expenses of liquidation amounted to ₹ 45,000.
- The liquidator is entitled to a remuneration of 3% on all assets realized (except cash at bank).
- All payments were made on 30th June, 2018.
You are required to prepare the Liquidator’s Final Statement of Account as on 30th June, 2018. Working Notes should form part of the answer. [10 Marks]
Answer:
BT Limited
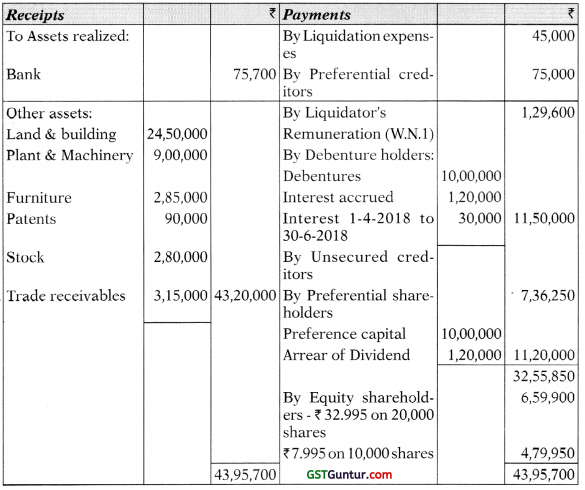
Working Notes:
Working Note 1:
Liquidator’s remuneration 43,20,000 × 3/100 = ₹ 1,29,600
Working Note 2:
As the company is solvent, interest on the debentures will have to be paid for the period 1-4-2018 to 30-6-2018
10,00,000 X 12% × 3/12 = ₹ 30,000
Working Note 3:

Loss to be borne by 30,000 equity shares:
Loss per share ₹ 27.005
Hence, Refund for share on ₹ 60 paid share (60 – 27.005) ₹ 32.995
Refund for share on ₹ 75 paid (75 – 27.005) ₹ 47.995
![]()
Question 4.
(a)
(i) The following is an extract of Trial Balance of SM Bank, an overseas bank as on 31st March, 2018.
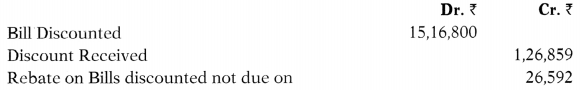
31st March, 2017
An analysis of bill discounted is as follows:
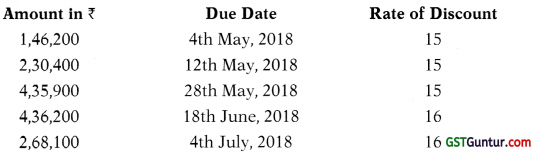
You are required to calculate Rebate on Bills Discounted as on 31st March,
2018 and show necessary Journal Entries.
(ii) The following informations are also given for SM Bank:

Additional Information:
- Standard Assets includes ₹ 15,00 Lakhs Advances to Commercial Real Estate (CRE).
- Out of ₹ 60,00 Lakhs of Sub-Standard Asset ₹ 20,00 Lakhs are unsecured. Unsecured includes ₹ 5,00 Lakhs in respect of Infrastructure Loan Accounts with ESCROW safeguard.
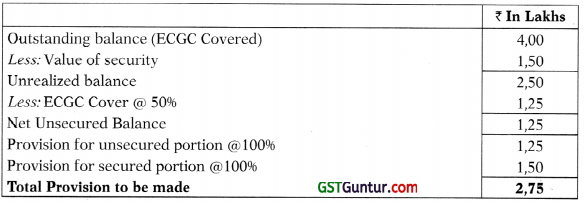
- Doubtful Asset for more than 3 Years includes ₹ 4,00 Lakhs, which is covered by 5096 ECGC, value of security of which is ₹ 150 Lakhs.
You are required to find out the amount of provision to be shown in the Profit & Loss Account of SM Bank. [10 Marks]
Answer:
(i) Statement showing computation of rebate on bills discounted:
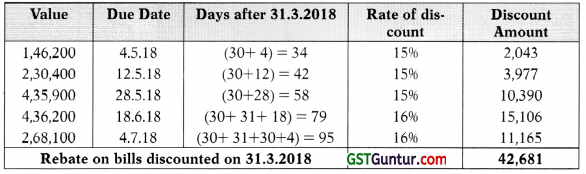
In the books of SM Bank Ltd.
Journal Entries
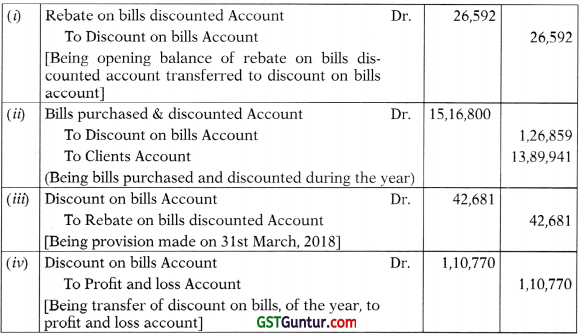
Credit to Profit and Loss A/c will be as follows:
= ₹ (1,26,859 + 26,592 – 42,681) = ₹ 1,10,770
![]()
(ii) Statement showing provisions on Assets:
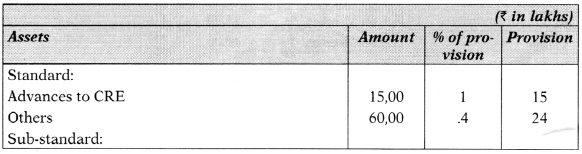
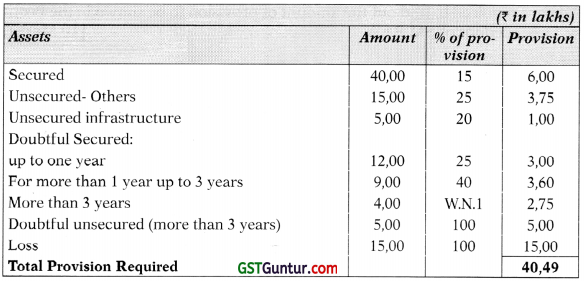
Working Note:
Provision required for assets covered by ECGC cover:
Question 4.
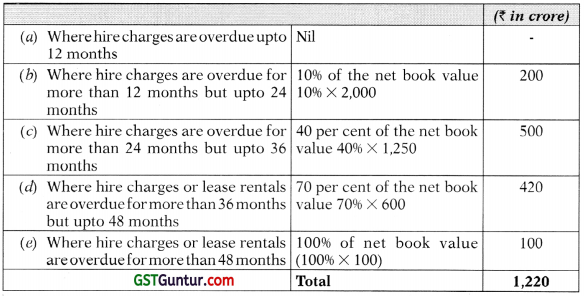
(b) Babu Bhai Financiers Ltd. is an NBFC providing Hire Purchase Solutions for acquiring consumer durables. The following information is extracted from its books for the year ended 31st March, 2018:
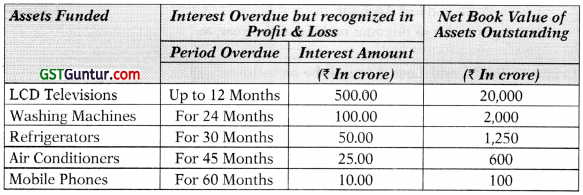
You are required to calculate the amount of provision to be made.
Answer:
Computation of additional provision:
Question 4.
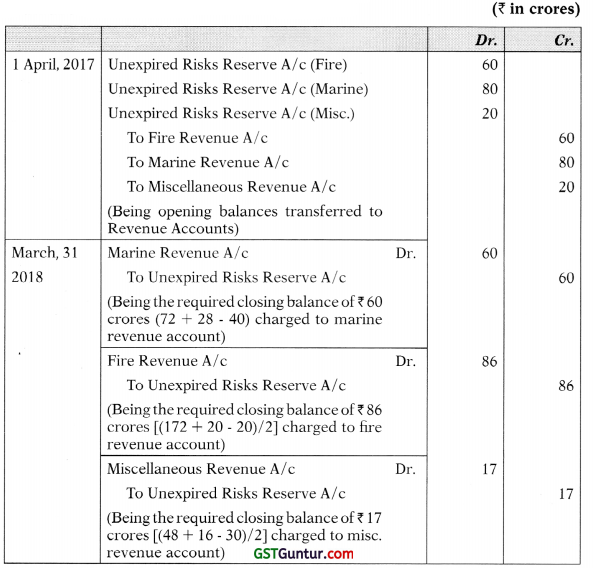
(c) From the following information given by M/s. Short Live Insurance Co. Ltd., you are required to pass necessary Journal Entries relating to Unexpired Risk Reserve.
(i) On 31.03.2017, it has reserve for unexpired risks amounting to ₹ 160 crores. Its composition was as under—
(a) ₹ 60 crores in respect of Marine Insurance Business
(b) ₹ 80 crores in respect of Fire Insurance Business
(c) ₹ 20 crores in respect of Misc. Insurance Business
(ii) M/s. Short Live Insurance Co. Ltd. reserves 100°6 of net premium income in respect of Marine Insurance Business and 50% of net premium income in respect of Fire and Misc. income policies.
(iii) During 2017-18, the following business was conducted:
| ₹ In crores | |||
| Premium Collected From: | Marine | Fire | Misc. |
| Insured in respect of Policies issued | 72 | 172 | 48 |
| Other Insurance Companies in respect of Risks undertaken | 28 | 20 | 16 |
| Premium paid/payable to other insurance Companies on business ceded | 40 | 20 | 30 |
[5 Marks]
Answer:
Journal of M/s. Short Live Insurance Co. Ltd.
![]()
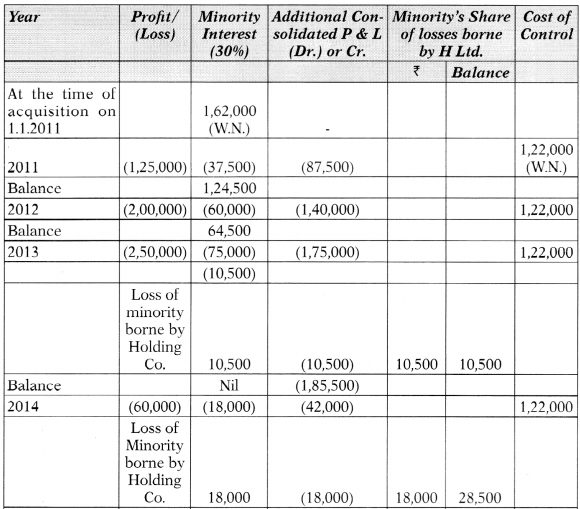
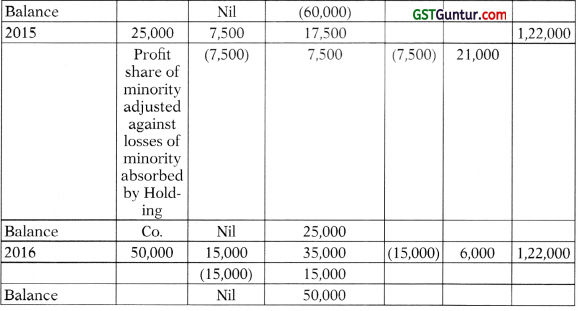
Question 5.
(a) H Ltd. acquire 70% of equity share of S Ltd. as on 1st January, 2011 at a cost of ₹ 5,00,000 when S Ltd. had an equity share capital of ₹ 5,00,000 and reserve and surplus of ₹ 40,000.
Both the companies follow calendar year as the accounting year.
In the four consecutive years, S Ltd. fared badly and suffered losses of ₹ 1,25,000, ₹ 2,00,000, ₹ 2,50,000 and ₹ 60,000 respectively.
Thereafter in 2015, S Ltd. experienced turnaround and registered an annual profit of ₹ 25,000. In the next two years i.e. 2016 and 2017, S Ltd. recorded annual profits of ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 75,000 respectively.
Show the Minority Interests and Cost of Control at the end of each year for the purpose of consolidation. [10 Marks]
Answer:
Computation of MI and COC:
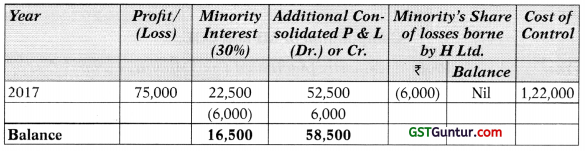
Working Note:
Computation of Minority interest and Cost of control on 1.1.2011
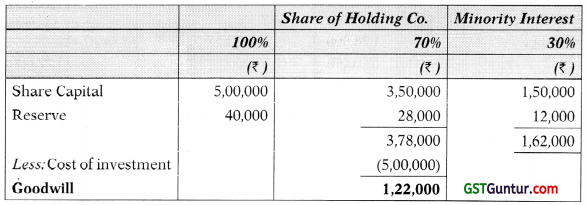
![]()
Question 5.
(b) The summarized Balance Sheet of T Ltd. for the year ended on 31st March, 2016, 2017 and 2018 are as follows:
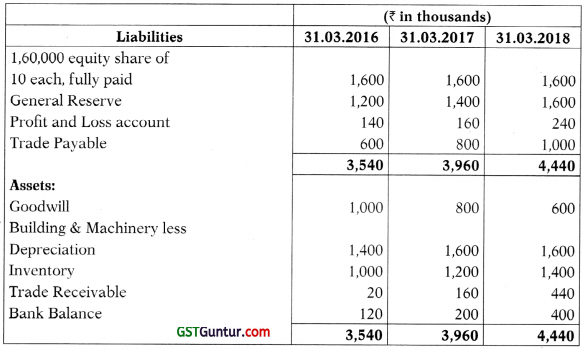
Additional Information:
(i) Actual Valuations were as under:
| Building & Machinery less depreciation | 1,800 | 2,000 | 2,200 |
| Inventory | 1,200 | 1,400 | 1,600 |
| Net Profit (including opening balance after writing off depreciation, goodwill, tax provision and transferred to general reserve | 420 | 620 | 820 |
(ii) Capital employed in the business at market value at the beginning of 2015-16 was ₹ 36,60,000 which included the cost of goodwill. The normal annual return on average capital employed in the line of business engaged by T Ltd. is 12.596.
(iii) The balance in the general reserve on 1st April, 2015 was ₹ 10 lakhs.
(iv) The goodwill shown on 31.03.2016 was purchases on 1.4.2015 for 110 lakhs on which date the balance in the Profit & Loss account was ₹ 1,20,000. You are required to find out the average capital employed in each year. Also, compute Goodwill, to be valued at 5 year’s purchase of Super profit (Simple average method). [10 Marks]
Answer:
Computation of Capital Employed at the end of each year:
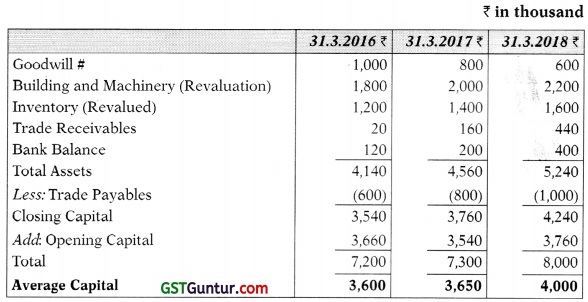
# Since the goodwill has been purchased, it is taken as a part of Capital employed. Alternatively, it may be excluded and a note to that affect given in the exam.
Valuation of Goodwill:
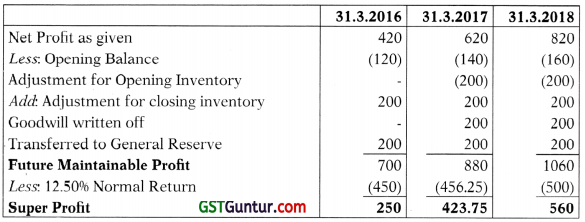
Average Super Profit — ₹ (250+423.75+560) ÷ 3 = ₹ 411.25 (thousand).
Thus,
Value of Goodwill at five years’ purchase= ₹ 411.25 × 5 = ₹ 2056.25 (thousand).
![]()
Question 6.
Answer any four of the following :
(a) Distinguish between Amalgamation, Absorption and External Reconstruc-tion of Company. [5 Marks]
Answer:
| Particulars | Amalgamation | Absorption | External |
| Meaning | Two or more companies are wound up and a new company is formed to takeover their business. | In this case, an existing company takes over the business of one or more existing companies. | In this Case, a newly formed company takes over the business of an existing company. |
| Minimum number of Companies involved | At least three companies are involved. | At least two companies are involved. | Only two companies are involved. |
| Number of new resultant companies | Only one resultant company is formed. Two companies are wound up to form a single resultant company. | No new resultant company is formed. | Only one resultant company is formed.
Under this case a newly formed company takes over the business of an existing company. |
| Objective | Amalgamation is done to cut competition and reap the economies in large scale. | Absorption is done to cut competition and reap the economies in large scale. | External reconstruction is done to reorganize the financial structure of the company. |
| Example | A Ltd. and B Ltd. amalgamate to form C Ltd. | A Ltd. takes over the business of another existing company B Ltd. | B Ltd. is formed to take over the business of an existing company A Ltd. |
![]()
Question 6.
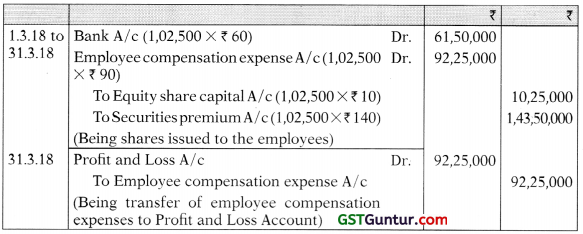
(b) Bee Co. Ltd. has its share capital divided into Equity Shares of ₹ 10 each. On 1st April, 2017, the company offered 250 shares to each of its 520 employees at ₹ 60 per share, when the market price was ₹ 150 per share. The options were to be exercised between 01-03-2018 to 31-03-2018.
410 employees accepted the offer and paid ₹ 60 per share purchased and the remaining options lapsed.
The company closes its books on 31st March every year.
You are required to show Journal Entries (with narrations) as would appear in the books of Bee Co. Ltd. for the year ended 31st March, 2018 with regard to employee stock options. [5 Marks]
Answer:
Journal Entries
[In the books of Bee Ltd.]
Question 6.
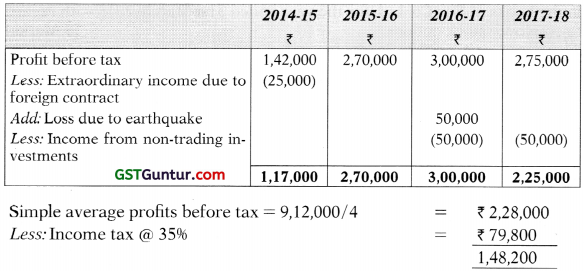
(c) Zest Ltd. gives the following information about its past profits:
| Year | Profit before Tax (₹ in ‘000′ |
| 2014-15 | 1,42 |
| 2015-16 | 2,70 |
| 2016-17 | 3,00 |
| 2017-18 | 2,75 |
Additional informations are given as below:
- In Year 2014-15, Zest Ltd. earned an extraordinary income of ₹ 25,000 due to a foreign contract.
- In September 2016, there was an earthquake, due to which the company lost ₹ 50,000 property and it was not covered by any Insurance Policy.
- There is a 1096 Non-trading Investment of ₹ 5,00,000 which was purchased at par by the company on 1st April, 2016.
- Income tax rate is 35%
- Capital Employed as on 31st March, 2018 is ₹ 6,00,000.
- Normal rate of return for the industry in which the company is engaged is 20%. ”
You are required to calculate the value of Goodwill at three years purchase of super profits. Consider simple average profits for calculation of Goodwill. [5 Marks]
Answer:
Computation of FMP:
Valuation of Goodwill
(Based on Super Profit Method)
| ₹ | |
| Future maintainable profits | 1,48,200 |
| Less: Normal profits (2096 of ₹ 6,00,000) | (1,20,000) |
| Super profit | 28,200 |
Goodwill at 3 years’ purchase of super profits = 3 × 1,28,200 = ₹ 84,600.
![]()
Question 6.
(d) A Mutual Fund purchased 20,000 debentures of a company on June 1, 2017 for ₹ 21.40 lakh and further 10,000 debentures on 1st November, 2017 for ₹ 10.90. lakh. The debentures carry fixed annual coupon of 12%, payable on every 31st March and 30th September. On Feb. 28, 2018 the fund sold 12,000 of these debentures for ₹ 13.56 lakh. Nominal value per debenture is ₹ 100.
Show Investment in Debenture A/c in books of the Mutual Fund. [5 Marks]
Answer:
Investment in Debentures A/c
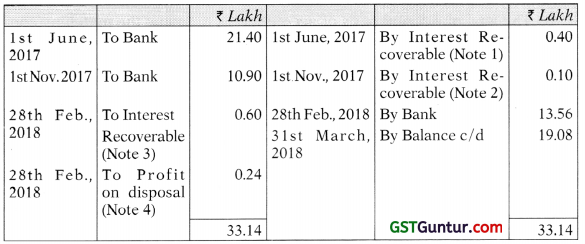
Working Notes:
Note 1:
20,000 × 100 × 12/100 × 2/12 = ₹ 0.40 Lakh
Note 2:
10,000 × 100 × 12/100 × 1/12 = ₹ 0.10 Lakh
Note 3:
12,000 × 100 × 12/100 × 5/12 = ₹ 0.60 Lakh
Note 4:
Cost of investments (per unit)
= [(21,40,000 – 40,000) +(10,90,000 – 10,000)]/30,000 units = [21,00,000 + 10,80,000]/30,000 = ₹ 106
Cost of investments sold = ₹ 106 × 12,000 = ₹ 12,72,000
Sale proceeds = ₹ 13,56,000 – ₹ 60,000 (interest) = ₹ 12,96,000
Profit = ₹ 12,96,000 – ₹ 12,72,000 = ₹ 24,000
Question 6.
(e) What do you mean by ‘Accrual’ in reference to AS-1? Also, specify any three reasons for ‘Accrual Basis of Accounting’. [5 Marks]
Answer:
The term “Accrual” has been explained in the AS-1, as under:
“Revenues and costs are accrued, that is, recognized as they are earned or incurred (and not as money is received or paid) and recorded in the financial statements of the periods to which they relate”.
Reasons for Accrual Basis of Accounting
- Accrual basis of accounting, attempts to record the financial effects of the transactions, events, and circumstances of an enterprise in the period in which they occur rather than recording them in the period(s) in which cash is received or paid by the enterprise.
- Receipts and payments of the period will not coincide with the buying, producing or selling events and other economic events that affect entity performance.
- The goal of Accrual basis of accounting is to follow the matching concept of income and expenditure so that reported net income measures an enterprise’s performance during a period instead of merely listing its cash receipts and payments.
- Accrual basis of accounting recognizes assets, liabilities or components of revenues and expenses for amounts received or paid in cash in past, and amounts expected to be received or paid in cash in the future.