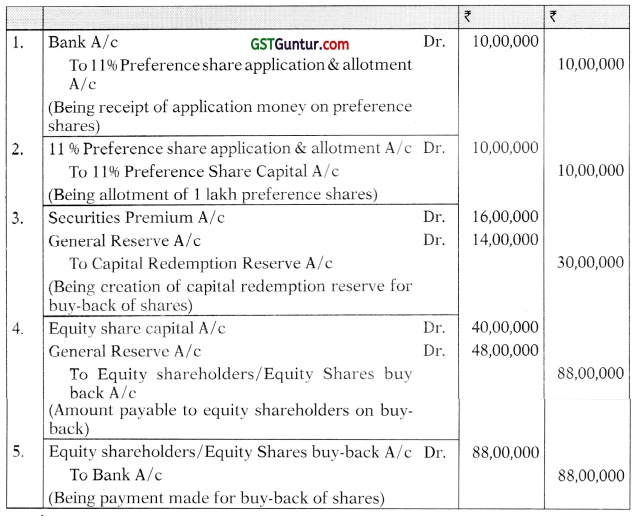
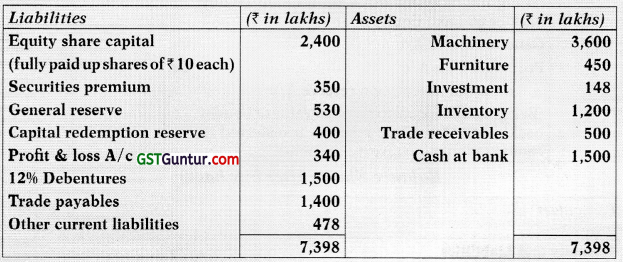
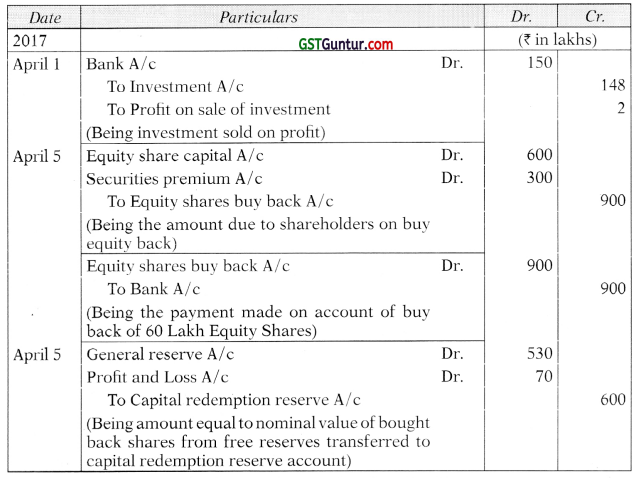
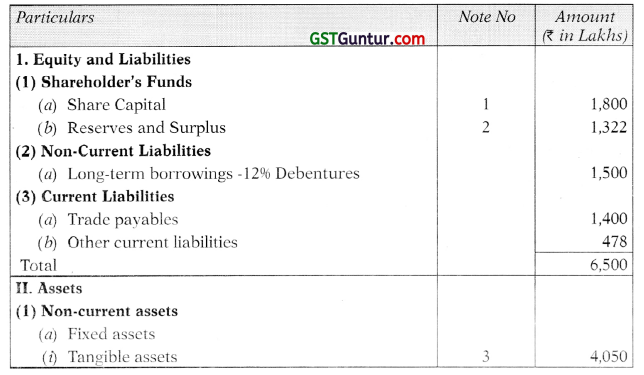
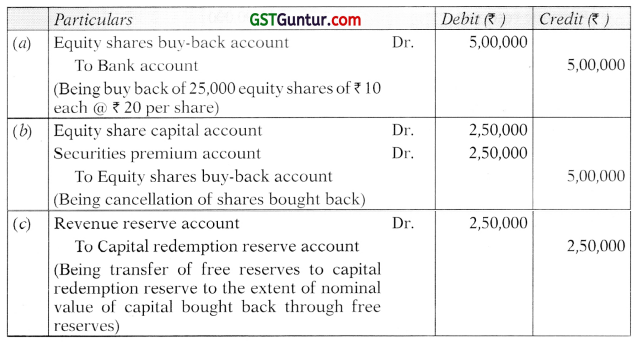
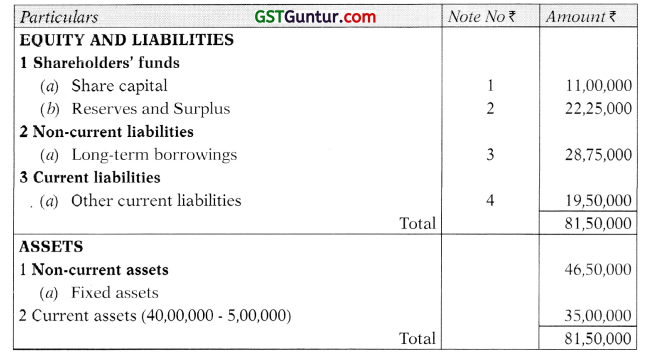
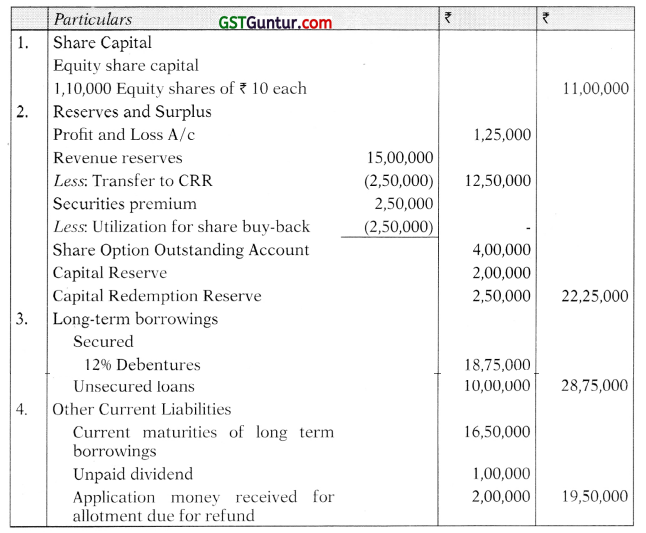
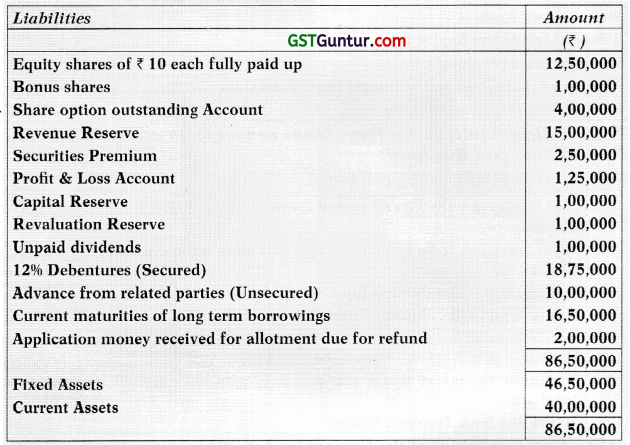
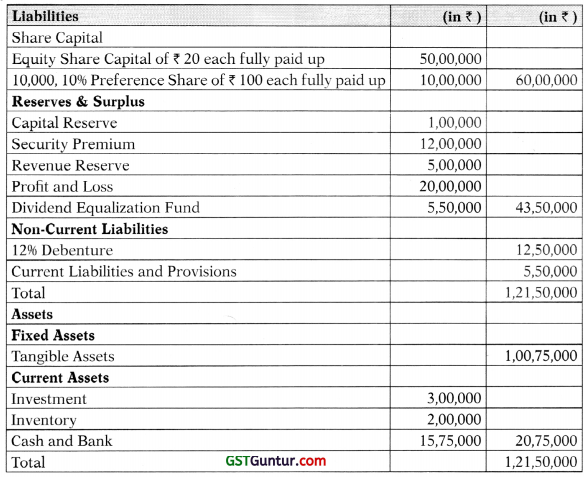
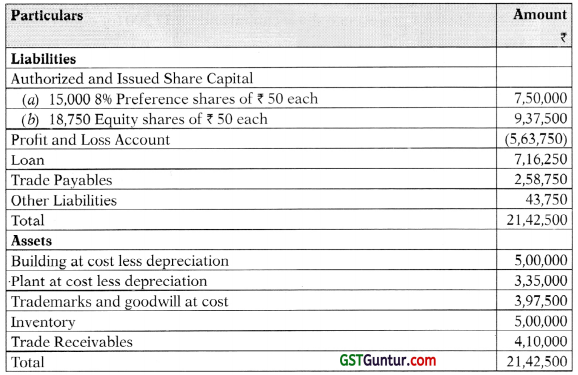
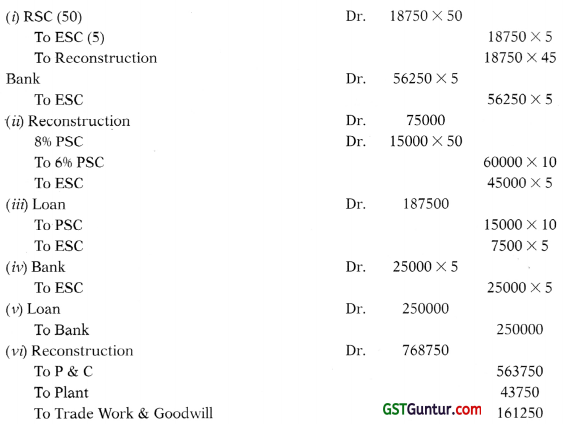
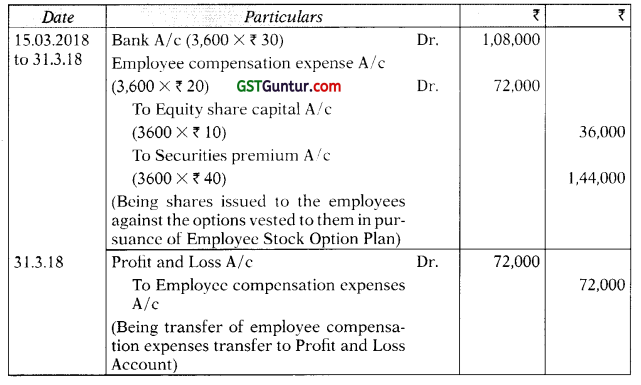
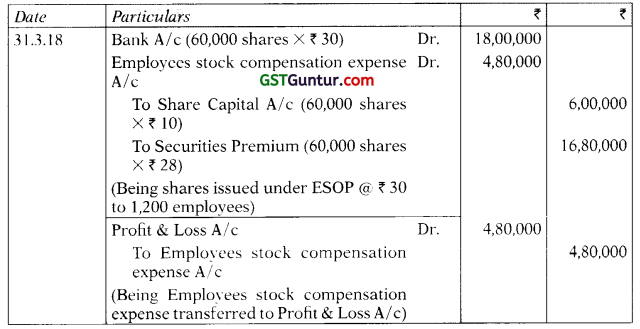
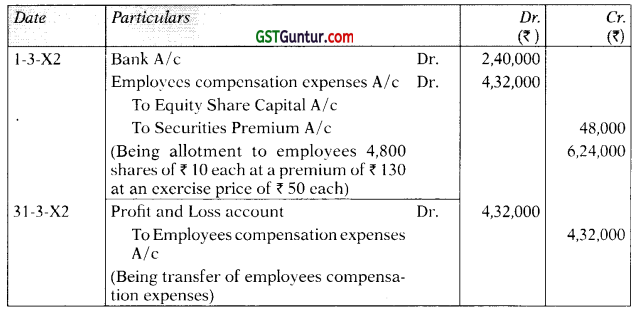
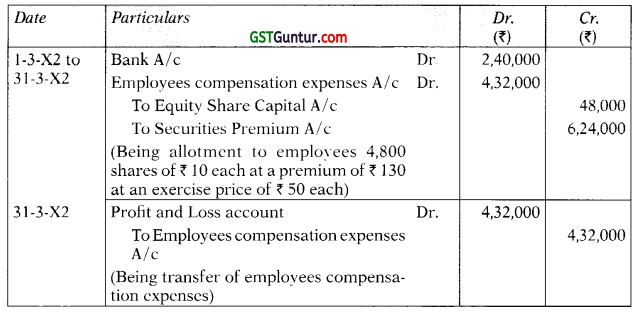
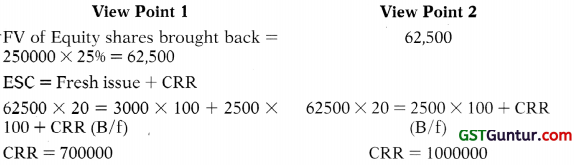Students should practice these The Company Audit – CA Inter Audit MCQ based on the latest syllabus.
The Company Audit – CA Inter Audit MCQ
Question 1.
Auditor appointed at AGM shall hold the office from the conclusion of that AGM till the conclusion of
(a) Sixth AGM
(b) Next AGM
(c) Fifth AGM
(d) Tenth AGM
Answer:
(a) Sixth AGM
Question 2.
An Individual auditor of a Listed company who has completed his term shall not be eligible for re-appointment as auditor in the same company for years from the conclusion of his term
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 10
Answer:
(c) 5
Question 3.
Which of the following company shall notappoint an audit firm as auditor for more than two terms of five consecutive years:
(a) Unlisted Public company having Turnover of ₹ 10 Cr. or more
(b) Unlisted Public company having Turnover of ₹ 2 0 Cr. or more
(c) Unlisted Public company having Paid up share capital of ₹ 10 Cr. or more
(d) Unlisted Public company having Paid up share Capital of ₹ 20 Cr. or more
Answer:
(c) Unlisted Public company having Paid up share capital of ₹ 10 Cr. or more

Question 4.
Subsequent auditor in case of Government Company shall be appointed within from the commencement of the financial year
(a) 30 days
(b) 90 days
(c) 120 days
(d) 180 days
Answer:
(d) 180 days
Question 5.
First auditor shall hold office till conclusion of
(a) First AGM
(b) Sixth AGM
(c) Next AGM
(d) Second AGM
Answer:
(a) First AGM
Question 6.
Casual vacancy in the office of an auditor, shall be filled by the Board of Directors within
(a) 30 days
(b) 60 days
(c) 90 days
(d) 120 days
Answer:
(a) 30 days
Question 7.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Casual Vacancy in case of resignation of auditor shall be filled by Board of Directors within 90 days
(b) Casual Vacancy in case of Government company shall be filled by Central Govt, within 90 days
(c) Casual Vacancy means a vacancy arises after com-pletion of the tenure
(d) None of the Above
Answer:
(d) None of the Above
Question 8.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Where at any AGM, no auditor is appointed or re-appointed, it amounts to casual vacancy and will be filled by Board of Directors
(b) Where at any AGM, no auditor is appointed or re-appointed, it amounts to casual vacancy and will be filled by Central Government
(c) Where at any AGM, no auditor is appointed or re-appointed, it amounts to casual vacancy and will be filled by members in EGM
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 9.
The Auditor appointed under section 139 of Companies Act, 2013 may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term by
(a) Ordinary Resolution
(b) Special Resolution
(c) Board Resolution
(d) None of the Above
Answer:
(b) Special Resolution
Question 10.
The application for removal of auditor before expiry of his term shall be made to Central Govt, within 30 days of
(a) Ordinary Resolution
(b) Special Resolution
(c) Board Resolution
(d) None of the Above
Answer:
(c) Board Resolution
Question 11.
In case of removal of auditor before expiry of his term, the company shall hold the within 60 days of receipt of approval of the Central Government for passing the
(a) General Meeting, Ordinary Resolution
(b) Board Meeting, Special Resolution
(c) General Meeting, Special Resolution
(d) Board Meeting, Board Resolution
Answer:
(c) General Meeting, Special Resolution
Question 12.
The auditor who has resigned from the company shall file within a period of from the date of resignation, a statement in the Form
(a) 30 days, ADT-1
(b) 30 Days, ADT-3
(c) 60 days, ADT-1
(d) 60 days, ADT-3
Answer:
(b) 30 Days, ADT-3

Question 13.
To appoint as auditor, a person other than a retiring auditor, who is eligible for reappointment, ______ is required
(a) Approval of Central Government
(b) Special Notice
(c) Approval of CAG
(d) Ordinary Resolution
Answer:
(b) Special Notice
Question 14.
Which of the following is qualified to be appointed as auditor of the company?
(a) A person whose relative is holding security of the company of face value exceeding ₹ 1 Lac
(b) A person whose relative is holding security of the company of market value exceeding ₹ 1 Lac
(c) A person whose relative is holding security of the company of face value not exceeding ₹ 1 Lac
(d) A person whose relative is holding security of the company of market value not exceeding ₹ 1 Lac
Answer:
(c) A person whose relative is holding security of the company of face value not exceeding ₹ 1 Lac
Question 15.
A person is disqualified to be appointed as auditor of the company if he himself or his relative or partner is indebted to the company for an amount exceeding ?
(a) One Lac
(b) Two Lacs
(c) Five Lacs
(d) Ten Lacs
Answer:
(c) Five Lacs
Question 16.
A person is disqualified to be appointed as auditor of the company if he himself or his relative or partner has given any guarantee in connection with the indebtedness of any third person to the company for an amount exceeding ?
(a) One Lac
(b) Two Lacs
(c) Five Lacs
(d) Ten Lacs
Answer:
(a) One Lac
Question 17.
A person is disqualified to be appointed as auditor of a company if he has been convicted by a court of an offence involving fraud and a period of ______ years has not elapsed from the date of such conviction
(a) 2 Years
(b) 5 Years
(c) 7 Years
(d) 10 Years
Answer:
(d) 10 Years
Question 18.
A person is disqualified to be appointed as auditor of a company if such person as at date of such appointment holding appointment of more than ______ companies
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 20
(d) 30
Answer:
(c) 20

Question 19.
The remuneration of first auditor appointed by members of the company shall be fixed by
(a) Company
(b) Board of Directors
(c) Central Government
(d) CAG
Answer:
(a) Company
Question 20.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) Remuneration of auditor shall in addition to the fees payable include expenses, if any incurred by the auditor in connection with the audit of the company
(b) Remuneration does not include any remuneration paid to auditor for any other service rendered by him at the request of the company
(c) Both of the Above
(d) None of the Above
Answer:
(c) Both of the Above
Question 21.
In addition to listed companies, which of the following companies are required to constitute audit committee:
(a) Public Companies with a paid-up capital of ₹ 10 Cr. or more
(b) Private Companies with a paid-up capital of ₹ 20 Cr. or more
(c) Both of the Above
(d) None of the Above
Answer:
(a) Public Companies with a paid-up capital of ₹ 10 Cr. or more
Question 22.
In which of the following cases, appointment of auditor shall be made after taking into account the recommendations of audit committee:
(a) Appointment of Subsequent Auditor
(b) Filling of Casual vacancies
(c) Re-Appointment of Retiring Auditor
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 23.
Every auditor of a company shall have a right of access at all times to of the company whether kept at the registered office of the company or at any other place
(a) Books and Account
(b) Books and Papers
(c) Books of Account and Vouchers
(d) Statutory registers
Answer:
(c) Books of Account and Vouchers
Question 24.
Auditor is required to inquire which of the following matters under Section 143(1):
(a) Sale of Shares and debentures at a price less than purchase amount by a banking company
(b) Sale of Shares and debentures at a price less than purchase amount by an investment company
(c) Sale of Fixed Assets and Inventory at a price less than purchase amount by a non-banking company
(d) Sale of Shares and debentures at a price less than purchase amount by a non-banking company
Answer:
(d) Sale of Shares and debentures at a price less than purchase amount by a non-banking company
Question 25.
Auditor is required to inquire which of the following matters under Section 143(1):
(a) Charging of personal expenses to revenue account
(b) Charging of capital expenses to revenue account
(c) Charging of Provisions to revenue account
(d) Charging of Depreciation to revenue account
Answer:
(a) Charging of personal expenses to revenue account

Question 26.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Reporting on propriety matters u/s 143(1) is required if the auditor finds answer to any of the matters in positive
(b) Reporting on propriety matters u/s 143(1) is required if the auditor finds answer to any of the matters in negative
(c) Reporting on propriety matters u/s 143(1) is required in every case irrespective of auditor’s observations
(d) Reporting on propriety matters u/s 143(1) is not the duty of auditor, it is the duty of management
Answer:
(b) Reporting on propriety matters u/s 143(1) is required if the auditor finds answer to any of the matters in negative
Question 27.
Under Section 143(2) auditor is required to make a report to the members of the company on the following:
(a) Accounts Examined by him
(b) Financial statement laid before the company in general Meeting
(c) Both of the above
(d) None of the Above
Answer:
(c) Both of the above
Question 28.
Under Section 143(3), auditor is required to report on following
1. Whether loans and advances made by the company have been shown as deposits
2. Whether transactions represented by book entries are prejudicial
3. Whether any director is disqualified from being appointed as director u/s 164(2)
4. Whether financial statements comply with the accounting Standards Correct answer is:
(a) 1 & 2
(b) 3 & 4
(c) 1 & 3
(d) 1,2, 3 & 4
Answer:
(d) 1,2, 3 & 4
Question 29.
CAG shall within from the date of receipt of the audit report have a right to conduct a supplementary audit
(a) 30 days
(b) 45 days
(c) 60 days
(d) 90 days
Answer:
(c) 60 days
Question 30.
As per Sec. 143(9) of Companies Act, 2013, every auditor shall comply with
(a) Accounting Standards
(b) Auditing Standards
(c) Engagement Standards
(d) Accounting and Auditing Standards
Answer:
(b) Auditing Standards

Question 31.
Under Section 143(12) of Companies Act, 2013, if an auditor of a company in the course of the performance of his duties as auditor, has reason to believe that an offence involving fraud is being or has been committed against the ______ he shall immediately report the matter to the
(a) company by officers or employees of the company; Registrar of Companies
(b) officers or employees of the company by directors; Central Government
(c) company by officers or employees of the company; Central Government
(d) officers or employees of the company by directors; Registrar of Companies
Answer:
(c) company by officers or employees of the company; Central Government
Question 32.
If the auditor does not report u/s 143(2) with respect to fraud, he shall be punishable with fine ranging from:
(a) ₹ 1 Lac to ₹ 10 Lacs
(b) ₹ 1 Lac to ₹ 25 Lacs
(c) ₹ 5 Lacs to ₹ 10 Lacs
(d) ₹ 5 Lacs to ₹ 25 Lacs
Answer:
(b) ₹ 1 Lac to ₹ 25 Lacs
Question 33.
Report u/s 143(12) with respect to fraud shall be sent to
(a) Registrar of Companies
(b) National Company Law Tribunal
(c) Secretary, Ministry of Home affairs
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 34.
The Audit Committee or the Board of Directors, are required to give their reply over the report of auditor in relation to fraud noticed by the auditor, within
(a) 15 days
(b) 30 days
(c) 45 days
(d) 60 days
Answer:
(c) 45 days
Question 35.
Report u/s 143(12) shall be in the form of a statement as specified in
(a) ADT-1
(b) ADT-2
(c) ADT-3
(d) ADT-4
Answer:
(d) ADT-4
Question 36.
An auditor appointed under Companies Act, 2013, shall provide only such other services as are approved by
(a) Board of Directors
(b) Central Government
(c) Board of Directors or the Audit Committee
(d) Registrar of Companies
Answer:
(c) Board of Directors or the Audit Committee
Question 37.
Auditor appointed under Companies Act, 2013 cannot render which of the following services:
(a) Actuarial Services
(b) Tax Audit
(c) Review of Interim Financial Statements
(d) Examination of Prospective Financial Statements
Answer:
(a) Actuarial Services
Question 38.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Communication relating to General meeting need not be forwarded to the auditor of the company
(b) Auditor has discretion to attend the general meeting
(c) Auditor shall have a right to be heard at general meeting
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Auditor shall have a right to be heard at general meeting

Question 39.
The auditor shall attend ______ any general meeting
(a) himself
(b) through his authorised representative
(c) either by himself or through his authorised representative
(d) at his discretion
Answer:
(c) either by himself or through his authorised representative
Question 40.
Right of Lien refers to
(a) Right for lawful possession of somebody’s else property
(b) Right of access to records of the company
(c) Right to obtain necessary information and explanation
(d) Right of access to records of subsidiary companies
Answer:
(a) Right for lawful possession of somebody’s else property
Question 41.
RightofIiencanbeexercisedfor
(a) Non-payment of statutory dues
(b) Non-payment of fees by the client
(c) Both of the above
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Non-payment of fees by the client
Question 42.
CA. X is a partner in M/s AB & Associates and M/s MN & Associates simultaneously. M/s AB & Associates has completed its tenure of 10 years as an auditor in XYZ Ltd. immediately preceding the current financial year, it may be noted that the provisions for applicability of rotation of auditors are applicable to XYZ Ltd. Now, the company wants to appoint M/s MN & Associates as auditor for 5 years.
(a) M/S MN & Associates cannot be appointed as auditor being not eligible u/s 141(3) of Companies Act, 2013
(b) M/S MN & Associates cannot be appointed as auditor being not eligible as per Rule 6 of Companies (Audit & Auditor’s) Rules, 2014
(c) M/S MN & Associates cannot be appointed as auditor being not eligible as per proviso to Sec. 139(2) of Companies Act, 2013
(d) M/S MN & Associates cannot be appointed as auditor being not eligible u/s 141(1) of Companies Act, 2013
Answer:
(c) M/S MN & Associates cannot be appointed as auditor being not eligible as per proviso to Sec. 139(2) of Companies Act, 2013
Question 43.
ABC Pvt. Ltd., a new company, incorporated on 01.07.2018 is engaged in the manufacturing business. On 30.07.2018, the Managing Director of ABC Pvt. Ltd. himself appointed CA Mohan, as the first auditor of the company.
(a) Appointment of Mr. Mohan is invalid as first auditor of a company can be appointed by members of the company as per Sec. 139(6) ofCompanies Act, 2013
(b) Appointment of Mr. Mohan is invalid as first auditor of a company canbe appointed by Board of Directors as per Sec. 139(6) of Companies Act, 2013
(c) Appointment of Mr. Mohan is invalid as first auditor of a company can be appointed by members of the company asperSec. 139(1) of Companies Act, 2013
(d) Appointment of Mr. Mohan is invalid as first auditor of a company can be appointed by Board of Directors as per Sec. 139(1) ofCompanies Act, 2013
Answer:
(b) Appointment of Mr. Mohan is invalid as first auditor of a company canbe appointed by Board of Directors as per Sec. 139(6) of Companies Act, 2013
Question 44.
KM Pvt. Ltd., engaged in the manufacturing business of Silk Shirts, is a newly incorporated company dated 01.09.2018. On 28.09.2018, the members of KM Pvt. Ltd. themselves appointed CA Raj, a renowned practitioner, as the first auditor of the company opposing that Board is not authorised to appoint the auditor.
(a) Appointment of CA. Raj is valid as first auditor of a company can be appointed by members of the company as per Sec. 139(6) ofCompanies Act, 2013
(b) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a company within 30 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by CAG as per Sec. 139(6) of Companies Act, 201.3
(c) Appointment of CA. Raj is valid as first auditor of a company can be appointed by members of the company as per Sec. 139(1) of Companies Act, 2013
(d) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a company within 30 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by Board of Directors as per Sec.-139(6) of Companies Act, 2013
Answer:
(d) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a company within 30 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by Board of Directors as per Sec.-139(6) of Companies Act, 2013
Question 45.
KM Ltd., a Government company is incorporated on 01.09.2018.0n 28.09.2018, the Board of Directors themselves appointed CA Raj, a renowned practitioner, as the first auditor of the company.
(a) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a government company within 30 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by Central Government as per Sec. 139(7) of Companies Act, 2013.
(b) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a government company within 60 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by Central Government as per Sec. 139(7) ofCompanies Act, 2013.
(c) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a government company within 3 0 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by CAG as per Sec. 139(7) ofCompanies Act, 2013.
(d) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a government company within 60 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by CAG as per Sec. 139(7) of Companies Act, 2013.
Answer:
(d) Appointment of CA. Raj is invalid as first auditor of a government company within 60 days of incorporation of company can be appointed by CAG as per Sec. 139(7) of Companies Act, 2013.

Question 46.
PQR Company Ltd. removed their first auditor by passing a resolution in the meeting of the Board of Directors for his removal without obtaining prior approval from the Central Government.
(a) Removal is valid as approval of Central Government is not required in case of first auditor.
(b) Removal is not valid as approval of Central Government is not obtained.
(c) Removal is not valid as first auditor of a company cannot be removed.
(d) Removal is not valid as first auditor can be removed by Audit Committee.
Answer:
(b) Removal is not valid as approval of Central Government is not obtained.
Question 47.
“Mr. A”, a practicing Chartered Accountant, is holding securities of “XYZ Ltd.” having face value of ₹ 90000. XYZ Ltd. wants to appoint Mr. B, partner of Mr. Aas itsauditor. Mr. B does not hold any securities in the company.
(a) Mr. B is not eligible for appointment as an Auditor of “XYZ Ltd” as his partner holds securities of the company.
(b) Mr. B is eligible for appointment as an Auditor of “XYZ Ltd” as the value of securities hold by his partner is less than ₹ 1 Lac.
(c) Mr. B is eligible for appointment as an Auditor of “XYZ Ltd” as he do not hold any securities of the company.
(d) Mr. B not eligible for appointment as an Auditor of “XYZ Ltd.” as his partner holds securities of the company exceeding ₹ 1,000.
Answer:
(a) Mr. B is not eligible for appointment as an Auditor of “XYZ Ltd” as his partner holds securities of the company.
Question 48.
Mr. B, a partner of Mr. A held shares of face value of ₹ 1,05,000 in DEF Ltd., the holding company of ABC Ltd. Mr. B has sold the securities after a period of 45 days from the date of appointment of Mr. A as an auditor of ABC Ltd.
(a) Appointment of Mr. Ain ABC Ltd. as auditor is valid as his partner Mr. B sold the securities within 60 days of appointment of Mr. A.
(b) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. as auditor is valid as shareholding of Mr. B in the holding company of ABC Ltd. is of no relevance.
(c) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. as auditor is invalid as his partner Mr. B hold shares in the holding company of ABC Ltd. at the time of appointment.
(d) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. as auditor is invalid as his partner Mr. B hold shares in the holding company of ABC Ltd. in excess of ₹ 1 Lac.
Answer:
(c) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. as auditor is invalid as his partner Mr. B hold shares in the holding company of ABC Ltd. at the time of appointment.
Question 49.
Mrs. A, wife of Mr. A had given a financial guarantee for the principal amount of a debt owed by Mr. X to ABC Ltd. for ₹ 6 lakhs. Mr. X has repaid ₹ 5 lakhs to ABC Ltd. 2 days before the date of appointment of Mr. A as an auditor of the company.
(a) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. is not valid as his wife has given guarantee to ABC Ltd. for an amount in excess of ₹ 1 Lac.
(b) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. is not valid as his wife has given guarantee to ABC Ltd. for an amount in excess of ₹ 5 Lac.
(c) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. is valid as the outstanding amount of guarantee given by his wife at the time of appointment does not exceed ₹ 1 Lac.
(d) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. is valid as guarantee given by the relative of the auditor is of no relevance.
Answer:
(c) Appointment of Mr. A in ABC Ltd. is valid as the outstanding amount of guarantee given by his wife at the time of appointment does not exceed ₹ 1 Lac.
Question 50.
As per Sec. 141 (3) (g) of the Companies Act, 2013, a person shall not be eligible for appointment as an auditor if he is in full time employment elsewhere or a person or a partner of a firm holding appointment as its auditor, if such persons or partner is at the date of such appointment or reappointment holding appointment as auditor of more than twenty (20) Companies, other than one-person company, dormant companies, small companies and private companies having paid up capital
(a) ₹ 100 Crores, which has not committed default in filing its financial statements under section 137 or annual return under section 92 of the Companies Act with the Registrar.
(b) less than ₹ 100 Crores, which has not committed default in filing its financial statements under section 137 or annual return under section 92 of the Companies Act with the Registrar.
(c) less than ₹ 100 Crores, which has not committed default in filing its financial statements under section 92 or annual return under section 137 of the Companies Act with the Registrar.
(d) ₹ 100 Crores, which has not committed default in filing its financial statements under section 92 or annual return under section 13 7 of the Companies Act with the Registrar.
Answer:
(b) less than ₹ 100 Crores, which has not committed default in filing its financial statements under section 137 or annual return under section 92 of the Companies Act with the Registrar.
Question 51.
Which of the following is true?
(a) Where at any AGM, no auditor is appointed or re-appointed, the existing auditor shall continue be the auditor of the company.
(b) If the auditor appointed at the AGM refuses to accept the same, the Company can appoint another person by holding General Meeting.
(c) If appointment of a person as an auditor is void-ab-initio, it should be treated as a casual vacancy.
(d) An auditor can be appointed as first auditor of a newly formed company simply because his name has been stated in the Articles of Association.
Answer:
(a) Where at any AGM, no auditor is appointed or re-appointed, the existing auditor shall continue be the auditor of the company
Question 52.
As per proviso to Sec. 140(5) of Companies Act, 2013, if the application is made by the Central Government and the Tribunal is satisfied that any change of the auditor is required, it shall within ______ of receipt of such application, make an order that he shall not function as an auditor and the ______ may appoint another auditor in his place.
(a) 15 days, Tribunal
(b) 15 days, Central Government
(c) 30 days, Tribunal
(d) 30 days, Central Government
Answer:
(b) 15 days, Central Government
Question 53.
As per proviso to Sec. 140(5) of Companies Act, 2013, an auditor, whether individual or firm, against whom final order has been passed by the Tribunal under this section shall not be eligible to be appointed as an auditor of ______ for a period
of from the date of passing of the order.
(a) any company, 5 years
(b) same company, 5 years
(c) any company, 10 years
(d) same company, 10 years
Answer:
(a) any company, 5 years

Question 54.
Sec. 143(3)(i) of Companies Act, 2013 requires the auditor to report, whether the company has adequate internal financial controls with reference to financial statements in place and the operating effectiveness of such controls. This reporting is not required in case of private companies:
(a) which is a one person company or a small company
(b) which has turnover less than ₹ 50 crores as perlatest audited financial statement or which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 25 Cr.
(c) which has turnover less than ₹ 25 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 50 Cr.
(d) which has turnover less than ₹ 100 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 50 Cr.
Answer:
(a) which is a one person company or a small company
Question 55.
Sec. 143(3)(i) of Companies Act, 2013 requires the auditor to report, whether the company has adequate internal financial controls with reference to financial statements in place and the operating effectiveness of such controls. This reporting is not required in case of private companies:
(a) which has turnover less than ₹ 50 crores as per latest audited financial statement or which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 25 Cr.
(.b) which has turnover less than ₹ 25 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 50 Cr.
(c) which has turnover less than ₹ 100 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 50 Cr,
(d) which has turnover less than ₹ 50 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 25 Cr.
Answer:
(d) which has turnover less than ₹ 50 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 25 Cr.
Question 56.
As per Sec. 143(6) of Companies Act, 2013, the Comptroller and Auditor General of India shall within ______ days from the date of receipt of the audit report have a right to, conduct a ______ of the ______ of the company by such person or persons as he may authorise in this behalf.
(a) 60 days, Supplementary Audit, books of account
(b) 60 days, Supplementary Audit, financial statements
(c) 60 days, Test Audit, books of accounts
(d) 90 days, Test Audit, financial statements
Answer:
(b) 60 days, Supplementary Audit, financial statements
Question 57.
As per Sec. 143(8) of Companies Act, 2013, where the branch office of a company is situated in a country outside India, the accounts of the branch office shall be audited
(a) only by the company’s auditor
(b) only by a person duly qualified to act as an auditor of the accounts of the branch office in accordance with the laws of that country
(c) either by the company’s auditor or by an accountant or by any other person duly qualified to act as an auditor of the accounts of the branch office in accordance with the laws of that country
(d) either by the company’s auditor or by a cost accountant or by any other person duly qualified to act as an auditor of the accounts of the branch office in accordance with the laws of that country
Answer:
(c) either by the company’s auditor or by an accountant or by any other person duly qualified to act as an auditor of the accounts of the branch office in accordance with the laws of that country
Question 58.
As per Sec. 143(12) of Companies Act, 2013, if an auditor of a company in the course of the performance of his duties as auditor, has reason to believe that an offence of fraud involving such amount or amounts as may be prescribed, is being or has been committed in the company by its officers or employees, the auditor shall report the matter to the Central Government within such time and in such manner as may be prescribed. The amount prescribed for purpose is
(a) Individually ₹ 1 Cr. or above
(b) Individually above ₹ 1 Cr.
(c) ₹ 1 Cr. or above in aggregate
(d) above ₹ 1 Cr. in aggregate
Answer:
(a) Individually ₹ 1 Cr. or above

Question 59.
Reporting of fraud to Central Government required under Section 143(12) of Companies Act, 2013 read with Rule 13 ofCompanies (Audit & Audi-tor’s) Rules, 2014 shall be in the form of a statement as specified in and sent to
(a) Form ADT-3; Secretary, Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
(b) FormADT-4; Secretary, Ministry of Corporate Affairs
(c) Form ADT-4; Secretary, Ministry of Law and Justice
(d) Form ADT-3; Secretary, Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs
Answer:
(b) FormADT-4; Secretary, Ministry of Corporate Affairs
Question 60.
As per Sec. 143(15) of Companies Act, 2013, if any auditor, cost accountant or company secretary in practice do not comply with the provisions of Sec. 143 (12), he shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than ______ but which may extend to ______
(a) ₹ 1 lac; ₹ 25 Lacs
(b) ₹ 5 lac; ₹ 25 Lacs
(c) ₹ 1 lac; ₹ 5 Lacs
(d) ₹ 1 lac; ₹ 10 Lacs
Answer:
(a) ₹ 1 lac; ₹ 25 Lacs
Question 61.
As per Section 144 of the Companies Act, 2013, auditor appointed under this Act cannot render certain services to the company. Which of the following service is not covered in the services prescribed u/s 144?
(a) Investment Banking Services
(b) Investment Advisory Services
(c) Design and implementation of any Operational information system
(d) rendering of outsourced financial services
Answer:
(c) Design and implementation of any Operational information system
Question 62.
As per Section 144 of the Companies Act, 2013, auditor appointed under this Act cannot render certain services to the company, whether such services are rendered directly or indirectly. For the purposes of this section, the term “directly or indirectly” shall include rendering of services by the auditor, in case of auditor being an individual, either himself or through
(a) his partner or any other person connected or associated with such individual or through any other entity, whatsoever, in which such individual has significant influence or control, or whose name or trade mark or brand is used by such individual
(b) his relative or any other person connected or associated with such individual or through any other entity, whatsoever, in which such individual has significant influence or control, or whose name or trade mark or brand is used by such individual
(c) his relative or any other person connected or associated with such individual or through any other entity whatsoever, in which such individual may or may not have significant influence or control, or whose name or trade mark or brand is used by such individual
(d) his relative or any other person connected or associated with such individual or through any other entity, whatsoever, in which such individual has significant influence or control, or whose name or trade mark or brand may or may not use by such individual
Answer:
(b) his relative or any other person connected or associated with such individual or through any other entity, whatsoever, in which such individual has significant influence or control, or whose name or trade mark or brand is used by such individual
Question 63.
AsperSection 144 of the Companies Act, 2013, auditor appointed under this Act cannot render certain services to the company or its
(a) holding company or subsidiary company
(b) holding company, subsidiary company or associate company
(c) holding company, subsidiary company, associate company or another subsidiary of holding company
(d) holding company, subsidiary company, associate company, another subsidiary of holding company or subsidiary of associate company
Answer:
(a) holding company or subsidiary company
Question 64.
As per Sec. 147 of the Companies Act, 2013, if any of the provisions of sections 139 to 146 (both inclusive) is contravened, the company shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than ______ but which may extend to ______
(a) ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs
(b) ₹ 10,000; ₹ 1 Lac
(c) ₹ 50,000; ₹ 25 Lacs
(d) ₹25,000; ₹ 1 Lac
Answer:
(a) ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs
Question 65.
As per Sec. 147 of the Companies Act, 2013, if any of the provisions of sections 139 to 146 (both inclusive) is contravened, every officer of the company who is in default shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to ______ or with fine which shall not be less than ______ but which may extend to ______ or with both
(a) 1 year; ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs
(b) 1 year; ₹ 10,000; ₹ 1 Lac
(c) 3 years; ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs
(d) 3 years; ₹ 10,000; ₹ 1 Lac
Answer:
(b) 1 year; ₹ 10,000; ₹ 1 Lac
Question 66.
As per Sec. 147 of the Companies Act, 2013, if an auditor of a company contravenes any of the provisions of Sec. 139, Sec. 143, Sec. 144 or Sec. 145, the auditor shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than but which may extend to
(a) ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs or five times the remuneration of auditor whichever is less
(b) ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs or five times the remuneration of auditor whichever is more
(c) ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs or four times the remuneration of auditor whichever is less
(d) ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs or four times the remuneration of auditor whichever is more
Answer:
(c) ₹ 25,000; ₹ 5 Lacs or four times the remuneration of auditor whichever is less

Question 67.
For the purposes of Section 148(1) of the Companies Act, 2013, the specified class of companies, including foreign companies, engaged in the production of the goods or providing services, having an overall turnover from all its products and services of ______ , shall include cost records for such products or services in their books of account
(a) ₹ 35 Cr. or more during the immediately preceding financial year
(b) ₹ 35 Cr. or more during the financial year
(c) More than ₹ 3 5 Cr. during the immediately preceding financial year
(d) More than ₹ 35 Cr. during the financial year
Answer:
(a) ₹ 35 Cr. or more during the immediately preceding financial year
Question 68.
Sec. 143 (1) of Companies Act, 2013 requires the auditor to inquire into certain matters of propriety matters. Which ofthe following matter is not covered in Sec. 143(1)?
(a) Whether loans and advances made by the company on the basis of security have been properly secured and whether the terms on which they have been made are prejudicial to the interests of the company or its members.
(b) Whether loans and advances made by the company have been shown as deposits.
(c) Whether the company has granted any loans, secured or unsecured to companies, firms, LLPs or other parties covered in the register maintained under section 189 of the Act. If so, whether the schedule of repayment of principal and payment of interest has been stipulated and whether the repayments or receipts are regular.
(d) Where it is stated in the books and documents of the company that any shares have been allotted for cash, whether cash has actually been received in respect of such allotment.
Answer:
(c) Whether the company has granted any loans, secured or unsecured to companies, firms, LLPs or other parties covered in the register maintained under section 189 of the Act. If so, whether the schedule of repayment of principal and payment of interest has been stipulated and whether the repayments or receipts are regular.
Question 69.
As per Sec. 143(3) of Companies Act, 2013, the auditor report shall also state certain matters. Which of the following is not covered in reporting u/s 143(3)?
(a) whether any director is disqualified from being appointed as a director under sub-section (2) of section 164.
(b) whether maintenance of cost records has been specified by the Central Government u/s 148(1) of the Companies Act, 2013 and whether such accounts and records have been so made and maintained.
(c) whether the company’s balance sheet and profit and loss account dealt with in the report are in agreement with the books of account and returns.
(d) whether the company has adequate internal financial controls with reference to financial statements in place and the operating effectiveness of such controls.
Answer:
(b) whether maintenance of cost records has been specified by the Central Government u/s 148(1) of the Companies Act, 2013 and whether such accounts and records have been so made and maintained.
Question 70.
As per Rule 11 of Companies (Audit & Auditor’s) Rules, 2014, the auditor’s report shall also include auditor’s views and comments on certain matters. Which of the following is covered in Rule 11?
(a) Whether moneys raised by way of initial public offer or further public offer (including debt instruments) and term loans were applied for the purposes for which those are raised
(b) Whether any fraud by the company or any fraud on the Company by its officers/employees has been noticed or reported during the year; If yes, the nature and the amount involved is to be indicated
(c) Whether the company has entered into any non-cash transactions with directors or persons connected with him and if so, whether provisions of Section 192 of Companies Act, 2013 have been complied with
(d) Whether there has been any delay in transferring amounts, required to be transferred, to the Investor Education and Protection Fund by the company
Answer:
(d) Whether there has been any delay in transferring amounts, required to be transferred, to the Investor Education and Protection Fund by the company
Question 71.
ABC & Co. is a firm of Chartered Accountants has three partners, A, B & C. The firm is holding audit of 55 companies which include 10 small companies, 5 government public companies, 5 listed companies, 5 OPC, 15 public companies and 15 private companies having paid up capital more than ₹ 100 crores. Firm has been offered the appointment as auditors of 30 companies. Of the 30 companies, 5 are private companies having paid up capital of each company is below ₹ 100 crores and the remaining 25 companies are public companies.
(a) Firm can accept audit of all 30 companies.
(b) Firm can accept audit of 25 companies including 5 private companies.
(c) Firm can accept audit of 20 companies including 5 private companies.
(d) Firm can accept audit of 15 companies including 5 private companies.
Answer:
(b) Firm can accept audit of 25 companies including 5 private companies.

Question 72.
As per Sec. 143(3)(i) of Companies Act, 2013, auditor’s report shall also state “the observations or comments of the auditors on financial transactions or matters which have any adverse effect on the functioning of the company”. The word “observations or comments” as used in the clause (i) refers to:
(a) EOM Paragraphs and the situations leading to modification in the auditor’s report.
(b) Key Audit matters communicated in the audit report.
(c) Matters covered under Sec. 143(1) relating to propriety aspects.
(d) Material uncertainty as to going concern which requires a separate section in the audit report titled “Material uncertainty relating to Going concern”.
Answer:
(a) EOM Paragraphs and the situations leading to modification in the auditor’s report.
Question 73.
If the auditor has contravenes provisions of Sec. 139,143,144 or 145, knowingly or wilfully with the intention to deceive the company or its shareholders or creditors or tax authorities, the auditor shall be punishable with imprisonment which may extend to and with fine ranging from
(a) one years; ₹ 25,000 – ₹ 5,00,000
(b) five years; ₹ 1,00,000 to lower of ₹ 25,00,000 or 8 times of remuneration
(c) one years; ₹ 50,000 to lower of ₹ 25,00,000 or 8 times of remuneration
(d) five years; ₹ 50,000 – ₹ 25,00,000
Answer:
(a) five years; ₹ 1,00,000 to lower of ₹ 25,00,000 or 8 times of remuneration
Question 74.
The auditor who has resigned from the company shall file within a period of 30 days from the date of resignation, a statement in the Form ADT-3 with the company and the Registrar. If the auditor does not comply with requirement of Sec. 140(2), he or it shall be punishable with fine of
(a) ₹ 50,000 or the remuneration ofthe auditor, whichever is less, but it may extend to ₹ 5 Lacs
(b) ₹ 50,000 or the remuneration ofthe auditor, whichever is higher, but it may extend to ₹ 5 Lacs
(c) ₹ 50,000 or two times of the remuneration of the auditor, whichever is less, but it may extend to ₹ 5 Lacs
(d) ₹ 50,000 or two times of the remuneration of the auditor, whichever is higher, but it may extend to ₹ 5 Lacs
Answer:
(a) ₹ 50,000 or the remuneration ofthe auditor, whichever is less, but it may extend to ₹ 5 Lacs
Question 75.
As per Sec. 143(12) of Companies Act, 2013, if an auditor of a company in the course of the performance of his duties as auditor, has reason to believe that an offence of fraud involving such amount or amounts as may be prescribed, is being or has been committed in the company by its officers or employees, the auditor shall report the matterto the Central Government within such time and in such manner as may be prescribed. The amount so prescribed is
(a) ₹ 1 Cr. or above, individually as per Rule 13 of Companies (Audit and Auditor’s) Rules, 2014
(b) ₹ 1 Cr. or above, in aggregate as per Rule 13 of Companies (Audit and Auditor’s) Rules, 2014
(c) ₹ 1 Cr. or above, individually as per Rule 13 of Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014
(d) ₹ 1 Cr. or above, in aggregate as per Rule 13 of Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014
Answer:
(a) ₹ 1 Cr. or above, individually as per Rule 13 of Companies (Audit and Auditor’s) Rules, 2014
Question 76.
As per Sec. 146 of Companies Act, 2013, ______ mentioned in the auditor’s report shall be read before the company in general meeting and shall be open to inspection by any member of the company
(a) the qualifications, observations or comments on financial transactions or matters, which have any adverse effect on the functioning of the company
(b) any qualification, reservation or adverse remark relating to the maintenance of accounts and other matters connected therewith
(c) any operating effectiveness of internal financial controls with reference to financial statements
(d) director’s disqualifications u/s 164(2) ofCompanies Act, 2013
Answer:
(a) the qualifications, observations or comments on financial transactions or matters, which have any adverse effect on the functioning of the company
Question 77.
The turnover criteria for applicability of Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rules, 2014 is
(a) at the end of immediately preceding financial year
(b) at the end of the financial year
(c) average of 3 preceding financial year
(d) when the company achieves the turnover during the current financial year
Answer:
(a) at the end of immediately preceding financial year

Question 78.
A cost auditor submits his report to
(a) Government
(b) Shareholders
(c) Statutory Auditor
(d) Board of Directors
Answer:
(d) Board of Directors
Question 79.
CA Mr. X was indebted to ABC Ltd. for a sum of ₹ 5,.10,000 as on 01.04.2018. However, Mr. X having come to knowr that he might be appointed as auditor of the company, he squared up the amount on 10.7.2018. Later on, he was appointed as an auditor of the company for the year ended 31.3.2019 at the Annual General Meeting held on 16.07.2018. Subsequently, one of the shareholders complains that the appointment of Mr. X as an auditor is invalid because he incurred disqualification under section 141 of the Companies Act, 2013
(a) Appointment of Mr. X is not valid as he is disqualified u/s 141(3) as at the beginning of the year for which he was appointed as auditor
(b) Appointment ofMr.X is not valid as he is disqualified u/s 143(3) of Companies Act, 2013
(c) Appointment of Mr. X is valid as he settles his in-debtedness before the appointment
(d) Appointment of Mr. X will be treated as valid only when special resolution was passed in this regard
Answer:
(c) Appointment of Mr. X is valid as he settles his in-debtedness before the appointment
Question 80.
Clause (i) of Sec. 143(3) shall not apply to a private company:
(a) which has turnover less than ₹ 50 crores as per latest audited financial statement or which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 25 Cr
(b) which has turnover less than ₹ 25 crores as per latest audited financial statement or which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 50 Cr
(c) which has turnover less than ₹ 50 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial 1 institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 25 Cr
(d) which has turnover less than ₹ 25 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 50 Cr
Answer:
(c) which has turnover less than ₹ 50 crores as per latest audited financial statement and which has aggregate borrowings from banks or financial 1 institutions or any body corporate at any point of time during the financial year less than ₹ 25 Cr
Question 81.
In which of the following companies, auditor is not required to report on matters specified under CARO, 2020:
(a) private limited company, which is a subsidiary company of a public company having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus not more than rupees one crore as on the balance sheet date
(b) private limited company, which is a holding company of a public company, which does not have total borrowings exceeding rupees one crore from any bank or financial institution at any point of time during the financial year
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 82.
In which of the following companies, auditor is required to report on matters specified under CARO, 2020:
(a) Foreign company
(b) Small Company
(c) One Person company
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Foreign company
Question 83.
A private limited company, in order to be covered under CARO, 2020, must satisfy which of the following conditions:
(a) total borrowings exceeding rupees ten crores from any bank or financial institution at any point of time during the financial year.
(b) total borrowings exceeding rupees one crore from any bank or financial institution as on the balance sheet date.
(c) total borrowings exceeding rupees ten crores from any bank or financial institution as on balance sheet date.
(d) total borrowings exceeding rupees one crore from any bank or financial institution at any point of time during the financial year.
Answer:
(d) total borrowings exceeding rupees one crore from any bank or financial institution at any point of time during the financial year.

Question 84.
Astha Pvt. Ltd. which is a subsidiary company of Kiran Pvt. Ltd., has fully paid capital of ₹ 40 lakh. During the year, the company had borrowed ₹ 55 lakh each from a bank and a financial institution independently. It has the turnover of ₹ 175 lakhs.
(a) CARO is not applicable as Astha Pvt. Ltd. is a Small Company.
(b) CARO is applicable as total borrowings exceeds ₹ 1 Cr.
(c) CARO is not applicable as Astha Pvt. Ltd. is a sub-sidiary company of another Pvt. Ltd
(d) CARO is applicable as turnover exceeds ₹ 1 Cr.
Answer:
(b) CARO is applicable as total borrowings exceeds ₹ 1 Cr.
Question 85.
CARO, 2020 is applicable over a private limited company, having paid up capital and reserves and surplus is ₹ 1 crore or more as on the balance sheet date. For this purpose,
(a) Paid-up share capital would include equity share capital only
(b) Amount of calls unpaid should be added to the figure of paid-up capital
(c) Amount originally paid-up on forfeited shares should be added to the figure of paid-up capital
(d) Share application money received should be considered as part of the paid-up capital
Answer:
(c) Amount originally paid-up on forfeited shares should be added to the figure of paid-up capital
Question 86.
Para 3 (vi) of CARO, 2020 requires the auditor to report whether maintenance of cost records has been specified by the C.G. u/s 148(1) of the Companies Act, 2013 and whether such accounts and records have been so madeand maintained. For thispurpose, auditor should:
(a) a detailed examination of such records
(b) conduct a general review of the cost records
(c) rely only on written representation received from the management stating that cost records are being made and maintained
(d) any of the above
Answer:
(b) conduct a general review of the cost records
Question 87.
Para 3(xi) of CARO, 2020 requires the auditor to report on various fraud noticed or reported during the year. Which of the following frauds are covered in Para 3(xi)
(a) fraud on the company by its officers/employees (h) fraud on the company by its vendors/suppliers
(c) fraud on the company by its associate companies
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 88.
When reporting under CARO, 2020, auditor is required to state in case of Nidhi Companies, whether the Nidhi company has complied with:
(a) Net Owned funds to total debts in the ratio of 1:20
(b) Net Owned funds to deposits in the ratio of 1:20
(c) Net Owned funds to total debts in the ratio of 1:10
(d) Net Owned funds to deposits in the ratio of 1:10
Answer:
(b) Net Owned funds to deposits in the ratio of 1:20
Question 89.
Auditor’s report under CARO, 2020 in terms of Para 3(xvi) shall incorporate:
(a) Registration number of company under Companies Act, 2013
(b) Registration number of company allotted by RBI
(c) Both of the above
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 90.
As per Clause (0(a) of Paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020, the auditor is required to report on:
(a) whether the title deeds of immovable properties are held in the name of the company. If not, provide the details thereof.
(b) whether physical verification of inventory has been conducted at reasonable intervals by the manage-ment; and whether any material discrepancies were noticed on physical verification and if so, whether the same have been properly dealt with in the books of account.
(c) whether any fraud by the company or any fraud on the Company by its officers or employees has been noticed or reported during the year; If yes, the nature and the amount involved is to be indicated.
(d) whether the company is maintaining proper records showing full particulars, including quantitative details and situation of property, plant and equipment.
Answer:
(d) whether the company is maintaining proper records showing full particulars, including quantitative details and situation of property, plant and equipment.
Question 91.
Which of the following dues are required to be reported under Clause (vii) of Paragraph 3 of CARO, 2016:
(a) amount payable to creditors for purchase of goods
(b) annual performance bonus payable to employees
(c) state government taxes
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) state government taxes
Question 92.
If a company is not regular in deposit of statutory dues to the appropriate authorities, auditor need to report on arrears of outstanding dues as at the last day of the financial year concerned for a period of:
(a) more than 90 days from the date they became payable
(b) more than 6 months from the date they became payable
(c) more than 90 days from the reporting date
(d) more than 6 months from the reporting date
Answer:
(b) more than 6 months from the date they became payable

Question 93.
A company has not deposited the employees provident fund with the authorities due to existence of some dispute. Dispute is pending in Court of Law. Non-payment of employees provident fund due to dispute is required to be reported by the auditor:
(a) under Clause (vii)(a) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
(b) under Clause (vii)(b) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
(c) under Clause (viii) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) under Clause (vii)(b) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
Question 94.
Acompany has defaulted in repayment of loansor borrowings to a NBFC. Auditor is required to report the period and amount of the default:
(a) under Clause (vii)(a) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
(b) under Clause (vii)(b) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
(c) under Clause (ix) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
(d) no reporting required, as default of dues of NBFC are not covered in CARO, 2020
Answer:
(c) under Clause (ix) of Para 3 of CARO, 2020
Question 95.
Under Clause (x) of Paragraph 3 of CARO, 2020, auditor is required to report the application of money raised through for the purposes for which those are raised
(a) Initial Public Offer or Further Public Offer (excluding debt instruments) only
(b) Initial Public Offer or Further Public Offer (including debt instruments) and term loans
(c) Initial Public Offer or Further Public Offer (excluding debt instruments) and term loans
(d) Initial Public Offer or Further Public Offer (including debt instruments) and working capital loans
Answer:
(b) Initial Public Offer or Further Public Offer (including debt instruments) and term loans
Question 96.
While reporting under Clause (xi) of Para 3 of CARO, 2016, with respect to fraud, auditor is required to report on:
(a) fraud noticed and reported u/s 143(12) of Companies Act, 2013
(b) fraud suspected and reported u/s 143(12) of Companies Act, 2013
(c) fraud committed on the company by the vendors | of the company
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(a) fraud noticed and reported u/s 143(12) of Companies Act, 2013
Question 97.
As per Clause (xiii) of Paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020, the auditor is required to report on:
(a) Whether all transactions with the related parties are in compliance with Sections 177 and 188 of Companies Act, 2013 where applicable
(b) Whether the company has made any preferential allotment or private placement of shares or fully or partly convertible debentures during the year under review
(c) Whether the company has entered in to any non-cash ( transactions with directors or persons connected with him and if so, whether provisions of Section 192 of Companies Act, 2013 have been complied with
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Whether all transactions with the related parties are in compliance with Sections 177 and 188 of Companies Act, 2013 where applicable
Question 98.
As per Clause (x) of Paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020, the auditor is required to report on:
(a) Whether all transactions with the related parties are in compliance with Sections 177 and 188 of g Companies Act, 2013 where applicable.
(b) Whether the company has made any preferential allotment or private placement of shares or fully or partly convertible debentures during the year under review and if so, as to whether the requirement of Sec. 42 of the Companies Act, 2013 have been complied.
(c) Whether the company has entered into any non-cash transactions with directors or persons connected with him and if so, whether provisions of Section 192 of Companies Act, 2013 have been complied with.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Whether the company has made any preferential allotment or private placement of shares or fully or partly convertible debentures during the year under review and if so, as to whether the requirement of Sec. 42 of the Companies Act, 2013 have been complied.
Question 99.
Which clause of CARO, 2020 requires the auditor to report whether the company is required to be registered under section 45-IA of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. If so, whether the registration has been obtained
(a) Under Clause (xi) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
(b) Under Clause (xvi) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
(c) Under Clause (xv) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
(d) Under Clause (xiv) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
Answer:
(b) Under Clause (xvi) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
Question 100.
While carrying out audit of ABC ltd, auditor observed that a term loan was obtained by the company from a bank for ? 75 lakhs for acquiring R&D equipment, out of which ? 12 lakhs were used to buy a car for use of the concerned director, who was overlooking the R&D activities. Auditor is required to report the matter:
(a) Under Clause(vii)of paragraph 3 of the CARO,2020.
(b) Under Clause (viii) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
(c) Under Clause(ix)ofparagraph3 of the CARO,2020.
(d) No reporting required under the requirements of CARO, 2020.
Answer:
(c) Under Clause(ix)ofparagraph3 of the CARO,2020.
Question 101.
While carrying out audit of ABC Ltd, auditor observed that the company has taken a term loan from a nationalized bank in 2016 for ? 200 lakhs repayable in five equal instalments off 40 lakhs from 31st March, 2017 onwards. It had repaid the loans ® due in 2017 & 2018, but defaulted in 2019, 2020 & 2021. Auditor is required to report the matter:
(a) UnderClause(vii)of paragraph 3 of the CARO,2020.
(b) Under Clause (viii) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
(c) Under Clause (ix) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
(d) Both (b) and (c).
Answer:
(c) Under Clause (ix) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.

Question 102.
Big and Small Ltd. received a show cause notice from central excise department intending to levy a demand of f 25 lakhs in December, 2020. The company replied to the above notice in January, 2021 contending that it is not liable for the levy. No further action was initiated by the central excise department upto the finalization of the audit for the ! year ended on 31st March, 2 021. Auditor is required to report the matter:
(a) Under Clause (vi) of paragraph 3 ofthe CARO, 2020.
(b) Under Clause(vii)of paragraph3 of the CARO,2020.
(c) Under Clause (viii) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020.
(d) No reporting required under the requirements of CARO, 2020.
Answer:
(b) Under Clause(vii)of paragraph3 of the CARO,2020.
Question 103.
Reporting under CARO, 2020 will be required in case of which companies:
(a) X Pvt. Ltd. which is a subsidiary of ABC Ltd. a listed company
(b) X Pvt. Ltd. which is a One-person company, having paid up capital off 105 Lacs
(c) X Pvt. Ltd. which is a Small Company, having out-standing borrowings from banks in excess of ₹ 1 Cr
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) X Pvt. Ltd. which is a subsidiary of ABC Ltd. a listed company
Question 104.
In which of the following companies, auditor is required to report on matters specified under CARO, 2020:
(a) private limited company, which is a holding company of a public company having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus not more than rupees one crore as on the balance sheet date
(b) private limited company, which is a subsidiary company of a public company, which does not have total borrowings exceeding rupees one crore from any bank or financial institution at any point of time during the financial year
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 105.
Which clause of CARO, 2020 requires the auditor to report whether managerial remuneration has been paid or provided in accordance with the requisite approvals mandated by the provisions of Sec. 197 read with schedule V to the Companies Act?
(a) Clause (xi) of Para 3
(b) Clause (xii) of Para 3
(c) Clause (xv) of Para 3
(d) NO Reporting required under CARO
Answer:
(d) NO Reporting required under CARO
Question 106.
UnderClause (x) of Paragraph 3 of CARO, 2020, auditor is required to report the application of money raised through Initial Public Offer or Further Public Offer (including debt instruments) and term loans for the purposes for which those are raised. Term loans for this purpose includes:
(a) Term loans obtained from banks and financial institutions
(b) Term loans obtained from entities/person other than banks and financial institutions
(c) Term loans obtained from Scheduled banks only
(d) Term loans obtained from banks and financial institutions as well as from entities/person other than banks and financial institutions
Answer:
(d) Term loans obtained from banks and financial institutions as well as from entities/person other than banks and financial institutions

Question 107.
Para 3 (xi) of CARO, 2020, required the auditor to report the nature and amount of fraud in relation to:
(a) any fraud by the company and any fraud on the Company by its officers/employees suspected and reported during the year
(b) any fraud by the company and any fraud on the Company by its officers/employees noticed or reported during the year
(c) any fraud on the company and any fraud by the Company suspected and reported during the year
(d) any fraud on the company and any fraud by the Company noticed or reported during the year
Answer:
(d) any fraud on the company and any fraud by the Company noticed or reported during the year
Question 108.
While carrying out audit of ABC Ltd, auditor observed that the company had obtained a term loan of? 300 lakhs from a bank for the construction of a factory. Since there was a delay in the construction activities, the said funds were temporarily invested in short term deposits. Auditor is required to report the matter:
(a) Under clause (vii) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
(b) Under clause (viii) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
(c) Under clause (ix) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
(d) No reporting required under the requirements of CARO, 2020
Answer:
(c) Under clause (ix) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
Question 109.
Company auditor is required to report “Whether the Nidhi Company has complied with the Net Owned Fund to Deposits in the ratio of 1:20 to meet out the liability and whether the Nidhi Company is maintaining 10% unencumbered term deposits as specified in the Nidhi Rules, 2014 to meet out the liability”. This reporting requirement is prescribed by:
(a) Sec. 143(1) of Companies Act, 2013
(b) Para 3 of NBFC Auditor’s Report (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2016
(c) Para 3 (xii) of Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2020
(d) Para 3 (xvii) of Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2020
Answer:
(c) Para 3 (xii) of Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2020
Question 110.
H Ltd, granted unsecured loan of ₹ 1 crore @ 15% p.a. to two of its subsidiaries during the Financial Year 2020-21. Before the year end both the companies repaid the loan. The management of H Ltd. is of the opinion that since no balance is outstanding as on 31st March 2021, these loans are not required to be reported in CARO 2020. Auditor is required to report the matter:
(a) Under clause (iii) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
(b) Under clause (iv) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
(c) Under clause (vi) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
(d) No reporting required under the requirements of CARO, 2020
Answer:
(a) Under clause (iii) of paragraph 3 of the CARO, 2020
Question 111.
Which of the following is not an objective of SA 299?
(a) To lay down broad principles for the joint auditors in conducting the joint audit
(b) To mandate the requirement of joint audit in case of listed entities
(c) To identify the distinct areas of work and coverage thereof by each joint auditor
(d) To identify individual responsibility and joint responsibility of the joint auditors in relation to audit
Answer:
(b) To mandate the requirement of joint audit in case of listed entities
Question 112.
KRP Ltd., at its annual general meeting, appointed Mr. X, Mr. Y and Mr. Z as joint auditors to conduct auditing for the financial year 2017-18. For the valuation of gratuity scheme of the company, Mr. X, Mr. Y and Mr. Z wanted to refer their own known Actuaries. Due to difference of opinion, all the joint auditors consulted their respective Actuaries. Subsequently, major difference was found in the actuary reports. However, Mr. X agreed to Mr, Y’s actuary report, though, Mr. Z did not. Mr. X contends that Mr. Y’sactuary reportshali be considered in auditreport due to majority of votes. Now, Mr. Z is in dilemma
(a) Contention of Mr. X is correct as SA 299 requires a single report based on majority
(b) Contention of Mr. X may be considered as SA 299 does not provide any provision in relation to such situations
(c) Contention of Mr. X is not acceptable as SA 299 requires separate reports in a situation where opinion of joint auditors differs
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Contention of Mr. X is not acceptable as SA 299 requires separate reports in a situation where opinion of joint auditors differs

Question 113.
Which ofthe following is correct?
(a) All the joint auditors are responsible in respect of the appropriateness of the decisions concerning the nature, timing and extent of the audit procedures agreed upon among them and their proper execution
(b) Appropriateness of the decisions concerning the nature, timing and extent of the audit procedures agreed among joint auditors and proper execution of these audit procedures is the individual responsibility of the concerned joint auditor
(c) All the joint auditors are responsible only in respect of the appropriateness of the decisions concerning the nature, timing and extent of the audit procedures agreed upon among them, proper execution of these audit procedures is the individual responsibility of the joint auditor concerned
(d) Appropriateness of the decisions concerning the nature, timing and extent of the audit procedures agreed among joint auditors is the individual responsibility of the concerned joint auditor whereas, proper execution of these audit procedures is the joint responsibility of all the joint auditors
Answer:
(c) All the joint auditors are responsible only in respect of the appropriateness of the decisions concerning the nature, timing and extent of the audit procedures agreed upon among them, proper execution of these audit procedures is the individual responsibility of the joint auditor concerned
Question 114.
ABC & Co. and DEF & Co. Chartered Accountant firms were appointed as joint auditors of Good Health Care Ltd. for 2017-18. An investigation was conducted under Companies Act, 2013 during March 2019 and observed gross understatement of Revenue. The revenue aspects were looked after by DEF & Co, but there was no documentation for the division of work between the joint auditors
(a) Liability for negligence will arise only on DEF & Co
(b) Liability for negligence will arise only ABC & Co
(c) Both Joint auditors are jointly and severally responsible
(d) No liability arises on joint auditors as company was liable to maintain documentation for the division of the work between the joint auditors
Answer:
(c) Both Joint auditors are jointly and severally responsible
Question 115.
The jointauditorsare required to issuecommon audit report, however, where the joint auditors are in disagreement with regard to the opinion or any matters to be covered by the audit report, they shall express their opinion in a separate audit report. In such cases, separate audit report issued by the joint auditor shall make reference to the audit report issued by other joint auditors under the heading
(a) “Other Matter Paragraph” as per SA 706
(b) “Key Audit Matters” as per SA 701
(c) “Other Information” as per SA 720
(d) “Emphasis of Matter Paragraph” as per SA 706
Answer:
(a) “Other Matter Paragraph” as per SA 706
Question 116.
SA 600 deals with:
(a) Situations where an auditor reporting on the financial information of an entity, uses the work of another auditor with respect to the financial information of one or more components included in the financial information of the entity.
(b) Situations where two or more auditors are appointed as joint auditors.
(c) The auditor’s relationship with a predecessor auditor.
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(a) Situations where an auditor reporting on the financial information of an entity, uses the work of another auditor with respect to the financial information of one or more components included in the financial information of the entity.
Question 117.
The principal auditor, if decides to use the work of auditor of component in relation to audit of consolidated financial statements, he should comply with requirements of:
(a) SA 600 “Using the work of Another Auditor”
(b) SA 299 “joint Audit of Financial Statements”
(c) SA 720 “The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Other Information”
(d) SRS 4410 “Compilation Engagements”
Answer:
(a) SA 600 “Using the work of Another Auditor”
Question 118.
If auditor of parent company is also the auditor of all of the components, this association requires the auditor:
(a) to apply the procedures of SA 600 while auditing the consolidated financial statements.
(b) to report whether principles and procedures for preparation and presentation of consolidated F.S. as laid down in the relevant AS(s) have been followed.
(c) to incorporate emphasis of matter paragraph in the audit report to state his association with the component.
(d) both (a) and (b) above.
Answer:
(b) to report whether principles and procedures for preparation and presentation of consolidated F.S. as laid down in the relevant AS(s) have been followed.

Question 119.
If auditor of parent company is not the auditor of the components, the auditor of parent company while auditing the consolidated financial statements is required to:
(a) apply the procedures of SA 600 while auditing the consolidated financial statements.
(b) to incorporate Emphasis of Matter Paragraph in the audit report as per requirement of SA 706.
(c) to incorporate Other Matter Paragraph in the audit report as per requirement of SA 706.
(d) both (a) and (c) above.
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (c) above.
Question 120.
When planning to use the work of another auditor, the principal auditor need not to consider the professional competence of the other auditor in the context of specific assignment if the other auditor is:
(a) a member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India.
(b) not a member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India.
(c) a member of foreign professional accounting body.
(d) a state certified auditor.
Answer:
(a) a member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India.
Question 121.
In case of a company that is required to constitute an Audit Committee under section 177, the committee, and, in cases where such a committee is not required to be constituted, ______ , shall take into consideration the qualifications and experience of the individual or the firm proposed to be considered for appointment as auditor and whether such qualifications and experience are commensurate with the size and requirements of the company.
(a) the Board
(b) any Director
(c) Managing Director
(d) Whole time director
Answer:
(a) the Board
Question 122.
Under sub-section (3) of section 141 along with Rule 10 ofthe Companies (Auditand Auditors) Rules, 2014 (hereinafter referred as CAAR), the following persons shall not be eligible for appointment as an auditor of a company, namely
(i) a limited liability partnership registered under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008;
(ii) an officer or employee of the company;
(iii) a person who is a partner, or who is in the employment, of an officer or employee of the company;
(iv) a person who, or his relative or partner is holding any security of or interest in the company or its subsidiary, or of its holding or associate company or a subsidiary of such holding company. It may be noted that the relative may hold security or interest in the company of face value not exceeding ₹ 1,00,000.
Which of the above is incorrect?
(a) All statements are incorrect.
(b) (i)and(ii)
(c) (i) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer:
(c) (i) only
Question 123.
Which ofthe following is notan advantage of Joint Audit?
(a) Sharing of expertise.
(b) General superiority complexes of some auditors.
(c) Lower workload.
(d) Displacement of the auditor of the company taken over in a take over often obviated.
Answer:
(b) General superiority complexes of some auditors.
Question 124.
Which of the following is correct as per section 143(10) of the Companies Act, 2013?
(a) IFAC may prescribe the standards of auditing as recommended by the Institute of Chartered Ac-countants of India, in consultation with and after examination of the recommendations made by the National Financial Reporting Authority.
(b) the International Auditing Standards Board may prescribe the standards of auditing as recommended by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, in consultation with and after examination of the recommendations made by the National Financial Reporting Authority.
(c) the MCA may prescribe the standards of auditing as recommended by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, in consultation with and after examination of the recommendations made by the National Financial Reporting Authority.
(d) the Central Government may prescribe the standards of auditing as recommended by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, in consultation with and after examination of the recommendations made by the National Financial Reporting Authority.
Answer:
(d) the Central Government may prescribe the standards of auditing as recommended by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, in consultation with and after examination of the recommendations made by the National Financial Reporting Authority.

Question 125.
Which of the following is not a duty of auditor to report under section 143(1)?
(a) whether loans and advances made by the company on the basis of security have been properly secured and whether the terms on which they have been made are prejudicial to the interests ofthe company or its members;
(d) whether transactions of the company which are represented merely by book entries are prejudicial to the interests ofthe company;
(c) where the company not being an investment com-pany or a banking company, whether so much of the assets of the company as consist of shares, debentures and other securities have been sold at a price less than that at which they were purchased by the company;
(d) whether the report on the accounts of any branch office of the company audited under sub-section (8) by a person other than the company’s auditors has been sent to him under the proviso to that sub-section and the manner in which he has dealt with it in preparing his report;
Answer:
(d) whether the report on the accounts of any branch office of the company audited under sub-section (8) by a person other than the company’s auditors has been sent to him under the proviso to that sub-section and the manner in which he has dealt with it in preparing his report;
Question 126.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) Under section 128 of the Act, books of account of a company must be kept at the registered office.
(b) Under section 128 of the Act, books of account of a company must be kept at the corporate office.
(c) Under section 128 of the Act, books of account of a company must be kept at the Head office of the company.
(d) Under section 128 of the Act, books of account of a company must be kept at the usual place of business.
Answer:
(a) Under section 128 of the Act, books of account of a company must be kept at the registered office.
Question 127.
Section 139(7) provides that in the case of a ® Government company or any other company owned or controlled, directly or indirectly, by the Central Government, or by any State Government, or Governments, or partly by the Central Government and | partly by one or more State Governments, the first auditor shall be appointed by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India ______ from the date of registration of the company.
(a) within 60 days
(b) within 30 days
(c) within 90 days
(d) within 45 days
Answer:
(a) within 60 days
Question 128.
As per Section 139(8), any casual vacancy in the ) office of an auditor shall in the case of a company other than a company whose accounts are subject to audit by an auditor appointed by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India,
(a) be filled by the Audit committee within 60 days.
(b) be filled by the Audit committee within 30 days.
(c) be filled by the Board of Directors within 60 days,
(d) be filled by the Board of Directors within 30 days.
Answer:
(d) be filled by the Board of Directors within 30 days.
Question 129.
As per section 140(2) the auditor who has resigned from the company shall
(a) file within a period of 60 days from the date of resignation, a statement in the prescribed Form ADT-3 (as per Rule 8 of CAAR) with the company and the Registrar
(b) file within a period of 30 days from the date of resignation, a statement in the prescribed Form ADT-3 (as per Rule 8 of CAAR) with the company and the Registrar
(c) file within a period of 30 days from the date of resignation, a statement in the prescribed Form ADT-3 (as per Rule 8 of CAAR) with the company.
(d) file within a period of 60 days from the date of resignation, a statement in the prescribed Form ADT-3 (as per Rule 8 of CAAR) with the company.
Answer:
(b) file within a period of 30 days from the date of resignation, a statement in the prescribed Form ADT-3 (as per Rule 8 of CAAR) with the company and the Registrar

Question 130.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) As per section 142 of the Act, the remuneration of the auditor of a company shall be fixed in its general meeting or in such manner as may be determined therein.
(b) As per section 142 of the Act, the remuneration of the auditor of a company shall be fixed in its general meeting.
(c) As per section 142 of the Act, the remuneration of the auditor of a company shall be fixed in its extra-ordinary general meeting.
(d) As per section 142 of the Act, the remuneration of the auditor of a company shall be fixed in its Board meeting or in such manner as may be determined therein.
Answer:
(a) As per section 142 of the Act, the remuneration of the auditor of a company shall be fixed in its general meeting or in such manner as may be determined therein.
Question 131.
In case of a fraud involving less than ₹ 1 crore, the auditor shall
(a) report the matter to the audit committee constituted under section 177 or to the Board in other cases within such time and in such manner as prescribed.
(b) report the matter to the audit committee constituted under section 177 within such time and in such manner as prescribed.
(c) report the matter to the Board within such time and in such manner as prescribed.
(d) report the matter to the audit committee constituted under section 177 and also to the Board within such time and in such manner as prescribed.
Answer:
(a) report the matter to the audit committee constituted under section 177 or to the Board in other cases within such time and in such manner as prescribed.
Question 132.
Which of the following is incorrect?
(a) According to Section 140(1),theauditorappointed under section 139 may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term only by a special resolution of the company, after obtaining the previous approval of the Central Government in that behalf as per Rule 7 of CAAR, 2014.
(b) The application to the Central Government for removal of auditor shall be made in Form ADT-2 and shall be accompanied with fees as provided for this purpose under the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014.
(c) The application shall be made to the Central Government within 30 days of the resolution passed by the Board.
(d) The company shall hold the general meeting within 30 days of receipt of approval of the Central Government for passing the special resolution.
Answer:
(d) The company shall hold the general meeting within 30 days of receipt of approval of the Central Government for passing the special resolution.
Question 133.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) A firm whereof all the partners practising anywhere are qualified for appointment may be appointed by its firm name to be auditor of a company.
(b) A firm whereof majority of partners practising anywhere are qualified for appointment may be appointed by its firm name to be auditor of a company.
(c) A firm whereof all the partners practising in India are qualified for appointment may be appointed by its firm name to be auditor of a company.
(d) A firm whereof majority of partners practising in India are qualified for appointment may be appointed by its firm name to be auditor of a company.
Answer:
(d) A firm whereof majority of partners practising in India are qualified for appointment may be appointed by its firm name to be auditor of a company.
Question 134.
As per Section 139(6), the first auditor of a company, other than a Government company, shall be appointed
(a) by the Board of Directors within 30 days from the date of registration of the company.
(b) by the audit committee within 30 days from the date of registration of the company.
(c) by the Managing Director within 30 days from the date of registration of the company.
(d) by the shareholders within 30 days from the date of registration of the company.
Answer:
(a) by the Board of Directors within 30 days from the date of registration of the company.
Question 135.
Where a company is required to constitute an Audit Committee under section 177,
(a) all appointments, including the filling of a casual vacancy of an auditor under this section shall be made after taking into account the recommendations of such committee.
(b) all appointments, excluding the filling of a casual vacancy of an auditor under this section shall be made after taking into account the recommendations of such committee.
(c) appointment of first auditors shall be made after taking into account the recommendations of such committee.
(d) appointment of subsequent auditors shall be made after taking into account the recommendations of j such committee.
Answer:
(a) all appointments, including the filling of a casual vacancy of an auditor under this section shall be made after taking into account the recommendations of such committee.
Question 136.
Which of the following is incorrect?
(a) In terms of the general principles of law, any person having the lawful possession of somebody else’s property, on which he has worked, may retain the property for non-payment of his dues on account of the work done on the property
(b) Under section 128 of the Act, books of account of a company must be kept at the registered office. These provisions ordinarily make it impracticable for the auditor to have possession of the books and documents.
(c) The company provides reasonable facility to auditor for inspection of the books of account by directors and others authorised to inspect under the Act.
(d) Working papers not being his own property auditor can exercise lien on working papers.
Answer:
(d) Working papers not being his own property auditor can exercise lien on working papers.

Question 137.
Springfield Hospital located in the rural area of Lonawala region is a government hospital run by the local doctors who are appointed by the government. The hospital was registered on 1st October 2018. Which of the following is correct in respect of the appointment of the first auditor for Springfield Hospital?
(a) The Board of Directors of the hospital have appointed the first auditor on 5th November 2018.
(b) The Comptroller Auditor-General of India appointed the first auditor on 15th December 2018.
(c) Since the Comptroller Auditor-General of India did not appoint the first auditor, the Board of Director appointed the first auditor on 15th December 2018.
(d) Since the Comptroller Auditor-General of India did not appoint the first auditor, the Board of Director appointed the first auditor on 10th November 2018.
Answer:
(c) Since the Comptroller Auditor-General of India did not appoint the first auditor, the Board of Director appointed the first auditor on 15th December 2018.
Question 138.
Eeyore Pvt. Ltd. is incorporated on 1st July, 2017. During the Financial Year ending on 31st March, 2018, the company did not opt for any borrowing at any point of time and have a total revenue of ₹ 60 Lakh. At the year end, it provides the following information regarding its paid-up capital and reserve & surplus
| Particulars |
Amount (in ₹) |
| Paid-up Capital |
|
| – Consideration received in cash for equity shares (including unpaid calls of ₹ 5,00,000) |
40,00,000 |
| – Consideration received in cash for preference shares |
25,00,000 |
| – Bonus shares allotted |
7,00,000 |
| – Share application money received pending allotment |
10,00,000 |
| Sub-Total |
82,00,000 |
| Reserve & Surplus |
|
| – Balance in Statement of Profit and Loss |
15,00,000 |
| – Capital Reserves |
10,00,000 |
| Sub-Total |
25,00,000 |
| GRAND TOTAL |
1,07,00,000 |
You are provided with the provisions regarding applicability of Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, @ 2020, (CARO, 2020) issued under section 143(11) of the Companies Act, 2013 to a private limited company that it specifically exempts a private limited company having a paid up capital and reserves and surplus not more than ₹ 1 crore as on the Balance Sheet date and which does not have total borrowings exceeding ₹ 1 crore from any bank at any point of time during the financial year and which does not have a total revenue as disclosed in Scheduled III to the Companies Act, 2013 exceeding ₹ 10 crore during the financial year.
Considering the information given above, which of the following shall be considered as a reason regard- ingapplicability or non-applicability ofCARO, 2020?
(a) Reporting under CARO, 2020 shall be applicable as the company is having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus of ₹ 1.07 crore i.e. more than ₹ 1 crore as on the Balance Sheet date.
(d) Reporting under CARO, 2020 shall be applicable as the company is having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus of ₹ 1.02 crore i.e. more than ₹ 1 crore as on the Balance Sheet date.
(c) Reporting under CARO, 2020 shall not be applicable as the company is having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus of ₹ 0.92 crore i.e. not more than ₹ 1 crore as on the Balance Sheet date.
(d) Reporting under CARO, 2020 shall not be applicable as the company is having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus of ₹ 0.82 crore i.e. not more than ₹ 1 crore as on the Balance Sheet date.
Answer:
(c) Reporting under CARO, 2020 shall not be applicable as the company is having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus of ₹ 0.92 crore i.e. not more than ₹ 1 crore as on the Balance Sheet date.
Question 139.
CA. Daffy is the auditor of x Bose Ltd. for the previous 2 years. However, due to certain unavoidable circumstances, no Annual General Meeting (AGM) was held for the current Financial Year ending on 31st March, 2018 within every possible time limit and thus, the ratification procedure for her appointment in the AGM could not be performed. Whether she may continue to hold the office of the auditor?
(a) CA. Daffy may continue to hold the office of the auditor for the current Financial Year only and thereafter shall resign herself as the ratification procedure could not be completed.
(b) CA. Daffy shall continue to hold the office of the auditor and ask the Board to re-appoint her in a private meeting.
(c) CA. Daffy shall continue to hold the office of the auditor as no such ratification provisions for ap-pointment by members at every AGM exist.
(d) CA. Daffy shall not continue to hold office of the auditor as the ratification procedure could not be completed as per proviso to section 139(1) of the Companies Act, 2013.
Answer:
(c) CA. Daffy shall continue to hold the office of the auditor as no such ratification provisions for ap-pointment by members at every AGM exist.
Question 140.
With respect to the forms specified by Companies (Cost Records & Audit) Rule 2014, which of the following is incorrect combination:
(a) Form CRA 1 – Maintenance of cost records by the Company.
(b) Form CRA 2 – Intimation of appointment of another cost auditor to Central Government.
(c) Form CRA 3 – Submission of Cost Audit Report to the Board of Directors of the company.
(d) Form CRA 4 – Submission of Cost Audit Report by the company to the Registrar.
Answer:
(d) Form CRA 4 – Submission of Cost Audit Report by the company to the Registrar.

Question 141.
Statement I: A firm whereof majority of partners practising in India are qualified for appointment may be appointed by its firm name to be auditor of a company.
Statement II: Where a firm including a limited liability partnership is appointed as an auditor of a company, all the partners shall be authorised to act and sign on behalf of the firm.
(a) Only Statement I is correct (,b) Only Statement II is correct
(c) Both statements are correct
(d) Both Statements are incorrect
Answer:
(a) Only Statement I is correct (,b) Only Statement II is correct
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()