Preparation of Financial Statements from Incomplete Records – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Preparation of Financial Statements from Incomplete Records – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short note on the following:
Weaknesses of Single Entry System (June 2017, 5 marks)
Answer:
Weaknesses of single entry system:
- As principle of double entry is not followed, the trial balance cannot be prepared. As such, arithmetical accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
- Profit or loss can be found out only by estimates as Nominal Accounts are not maintained.
- It is not possible to make a balance sheet in absence of Real Accounts.
- It is very difficult to detect frauds or errors.
- The valuation of assets and liabilities is not proper.
- The external agencies like banks cannot use financial information. A bank cannot decide whether to lend money or not.
- It is quite likely that the business and personal transactions of the proprietor get mixed.
Question 2.
Write short note on the following:
Features of Single Entry System. (June 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Single Entry System has the following features:
(a) Maintenance of books by a sole trader or partnership firm: The books which are maintained according to this system can be kept only by a sole trader or by a partnership firm.
(b) Maintenance of cash book: In this system, it is very often to keep one cash book which mixes up business as well as private transactions.
(c) Only personal accounts are kept: In this system, it is very common to keep only personal accounts and to avoid real and nominal accounts. Therefore, sometimes, this is precisely defined as a system where only personal accounts are kept.
(d) Collection of information from original documents: For information one has to depend on original vouchers, example, in the case of credit sales, the proprietor may keep the invoice without recording it anywhere, and at the end of the year the total of the invoices gives an idea of total credit sales of the business.
(e) Lack of ‘uniformity: It lacks uniformity as it’s a mere adjustment of double entry system according to the convenience of the person.
(f) Difficulty in preparation of final accounts: It ¡s much difficult to prepare trading, profit and loss accounts, and balance sheets due to the absence of nominal and real accounts in the ledger.
Descriptive Questions
Question 3.
In the single-entry system, which two methods are used to ascertain profit or loss? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
- Statement of affairs method.
- Conversion method.
Practical Questions
Question 4.
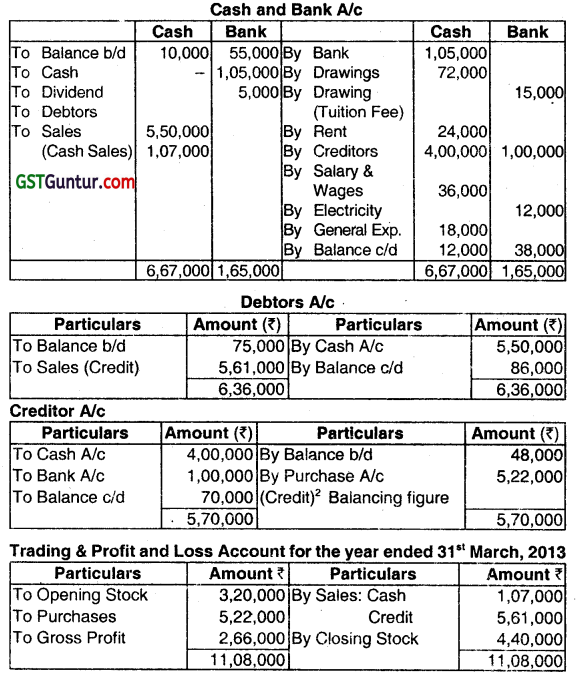
Mr. Dipankar a retail trader needs financial statements for the year ended 31.03.2013 for availing a bank loan. He gives you the following information regarding receipts and payments.
(i) Cash deposited into the bank account ₹ 1,05,000.
(ii) Dividend from companies deposited in bank account ₹ 5,000.
(iii) Tuition fees of doctor oaid by cheque ₹ 15,000.
(iv) Rent for the year paid by cash ₹ 24,000.
(v) Cash collections from debtors ₹ 5,50,000.
(vi) Amounts paid to creditor ₹ 4,00,000 in cash and ₹ 1,00,000 by cheque.
(vii) Salary and wages paid in cash ₹ 36,000.
(viii) Office electricity paid by cheque ₹ 12,000.
(ix) General expenses incurred in cash ₹ 18,000.
(x) Drawings every montt’ ₹ 6,000 by cash.
(xi)
| Particulars | 31 03.2012 | 31 .03.2013 |
| Stock | 3,20,000 | 4,40,000 |
| Bank | 55,000 | 38,000 |
| Cash | 10,000 | 12,000 |
| Debtors | 75,000 | 86,000 |
| Creditors | 48,000 | 70,000 |
Prepare his Trading & Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2013 and Balance Sheet as at
31.03.2013. (Dec 2013, 10 marks)
Answer:

₹ 4,12,000 + ₹ 1,81,000 – ₹ 72,000 ₹ 15,000
[Opening Capital + Net Profit – Drawings – Doctor Fees]
![]()
Question 5.
Answer the following question (give working):
Calculate the average collection period from the following details by adopting 360 days an year.
| Average Inventory – ₹ 10,80,000 Gross Profit Ratio – 10% |
| Debtors – ₹ 6,90,000 Credit sales to total sales – 20% |
| Inventory Turnover – 6 Times 1 year – 360 |
| ratio – days |
(June 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Inventory turnover ratio = \(\frac{\text { Cost of goods sold }}{\text { Average Inventory }} \)
6 = \(\frac{\text { COGS }}{10,80,000} \)
COGS = 64,80,000 .
GP ratio =10%
Hence, Sales = COGS × \(\frac{100}{90}\)
= 64,80,000 × \(\frac{100}{90}\) = 72,00,000
Credit sales = 72,00,000 × 20% = 14,40,000
Average collection Period = \(\frac{\text { Average Debtors }}{\text { Credit Sales }} \times 360 \)
= \(\frac{6,90,000}{14,40,000} \) × 360 = 172.5 days
Question 6.
Answer the question:
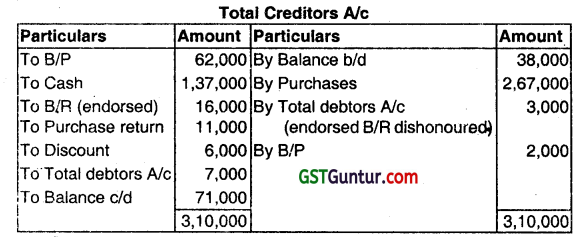
Prepare Total Creditors Account for the year ended on 31.03.2013 from the data given below:
| ₹ | |
| Creditors Balance on 01.04.2012 | 38,000 |
| Credit Purchases during the year | 2,67,000 |
| Bills payable accepted | 62,000 |
| Cash paid to Creditors | 1,37,000 |
| B/R endorsed to creditors | 16,000 |
| Endorsed B/R dishonoured. | 3,000 |
| B/P dishonoured | 2,000 |
| Purchase returns | 11,000 |
| Discount received | 6,000 |
| Transfer from Debtors’ ledger | 7,000 |
(Dec 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 7.
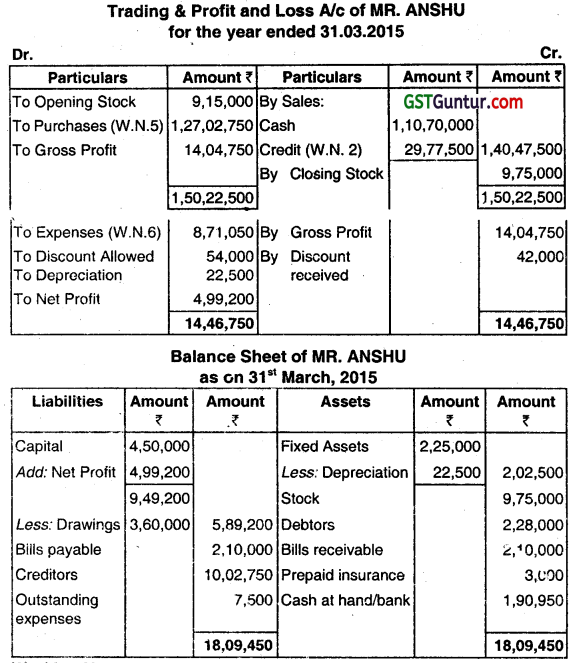
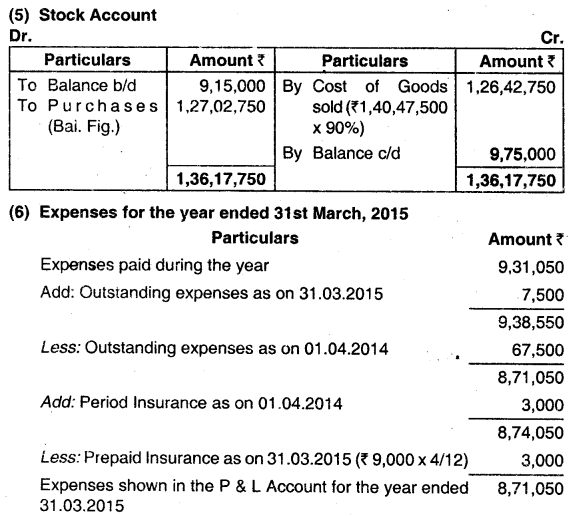
ANSHU keeps his books under a single-entry system. On 31st March, 2014 his Balance Sheet was as follows:
| Liabilities | ₹ | Assets | ₹ |
| Capital | 4,50,000 | Fixed Assets | 2,25,000 |
| Creditors | 8,70,000 | Stock | 9,15,000 |
| Bills Payable | 1,87,500 | Debtors | 2,22,000 |
| Expenses Outstanding | 67,500 | Bills Receivable | 90,000 |
| Prepaid Insurance | 3,000 | Cash/Bank Balance | 1,20,000 |
| 15,75,000 | 15,75,000 |
(i) Following is the summary of cash and bank transaction for the year ended 31st March, 2015:
Cash Sales ₹ 1,10,70,000;
Collection from Debtors ₹ 22,65,000;
Payments to Creditors ₹ 1,12,60,500;
Paid for Bills Payable ₹ 12,22,500;
Sundry Expenses Paid ₹ 9,31,050;
Drawings for Domestic expenses by Mr. Anshu ₹ 3,60,000;
Cash and Bank Balance as on 31 -03-2015 ₹ 1,90,950.
(ii) Following further details are furnished:
Gross Profit on Sales @ 10%;
Bills Receivable from Debtors during the year ₹ 6,52,500;
Discount Allowed to Debtors ₹ 54,000
Discount Received from Creditors ₹ 42,000;
Bills Receivable Endorsed to Creditors ₹ 22,500;
Annual Fire Insurance Premium paid (This is paid on 1st August every year) ₹ 9,000;
Depreciation on Fixed Assets @ 10%.
(iii) Balance as on 31-03-2015 are given below:
Stock in hand ₹ 9,75,000;
Debtors ₹2,28,000;
Bills Receivable ₹ 2,10,000;
Outstanding Expenses ₹ 7,500;
Bills payable ₹ 2,10,000.
You are required to prepare:
(1) Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended March 31, 2015; and
(2) Balance Sheet as on 31.03.201 5. (June 2015, 4 + 3 + 5 = 12 marks)
Answer:

Question 8.
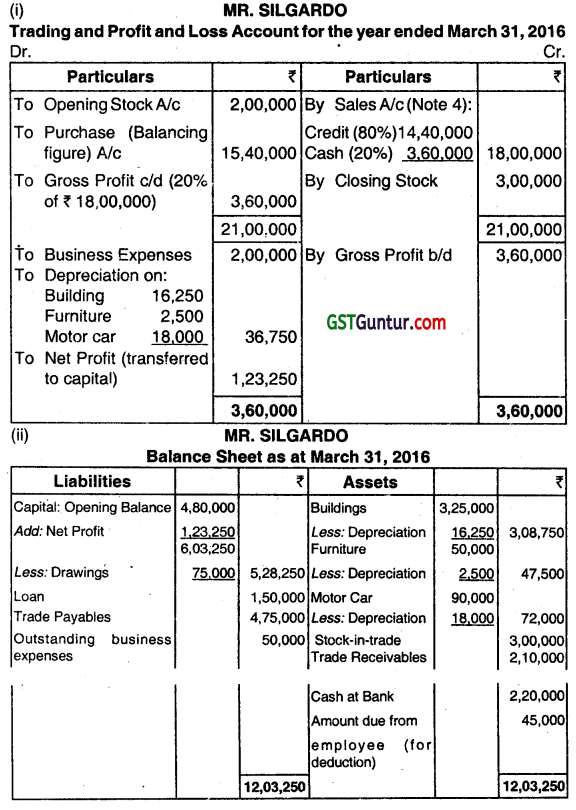
The following is the Balance Sheet of MR. SILGARDO as on March 31, 2015.
| Liabilities | ₹ | Assets | ₹ |
| Capital Account | 4,80,000 | Buildings | 3,25,000 |
| Loan | 1,50,000 | Furniture | 50000 |
| Trade Creditors | 3,10,000 | Motor car | 90,000 |
| Stock | 2,00,000 | ||
| Trade Debtors | 1,70,000 | ||
| Cash in hand | 20,000 | ||
| Cash at bank | 85,000 | ||
| 9,40,000 | 9,40,000 |
A fire occurred on the night of 31st March, 2016, in which all books and records were lost. The cashier had absconded with the available cash. MR. SILGARDO gives you the following information:
(a) His sales for the year ended March 31, 2016 were 20% higher than the previous years. He always sells his goods at cost plus 25%. 20% of the total sales for the year ended March 31, 2016 was for cash. There were no cash purchases.
(b) On April 1, 2015 the stock level was raised to ₹ 3,00,000 and the stock was maintained at this level throughout the year.
(c) Collection from Debtors amounted to ₹ 14 lakh of which ₹ 3.50 lakh was recewed in cash. Business expenses amounted to ₹ 2,00,000 of which ₹ 50,000 was outstanding on March 31, 2016 and ₹ 60,000 was paid by cheques.
(d) Analysis of the passbooks revealed on the following:
Payment to creditors ₹ 13.75 lakh, Personal drawings ₹ 75,000.
Cash deposited in bank ₹ 7.15 lakh.
Cash withdrawn from bank ₹ 1,20,000.
(e) Gross profit as per last year’s audited accounts was ₹ 3,00,000.
(f) Provide depreciation on buildings and furniture at 5% and on motor cars at 20%.
(g) The amount defalcated by the cashier may be treated as recoverable from him.
Required:
(i) Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended March 31,2016.
(ii) Prepare Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2016. (June 2016, 5 + 5 + (2 + 1 + 1 + 1) = 15 marks)
Answer:

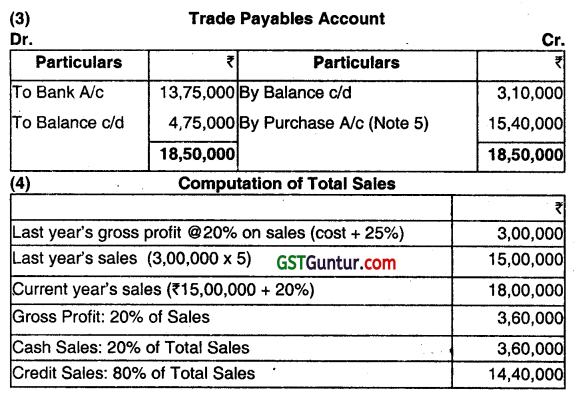
5. Calculation of Purchase:
(Sales + Closing Stock) – (Opening Stock + Gross Profit)
= (18,00,000 + 3,00,000) – (2,00,000 + 20% of 18,00,000)
= (21,00,000 – 5,60,000) = ₹ 15,40,000.
![]()
Question 9.
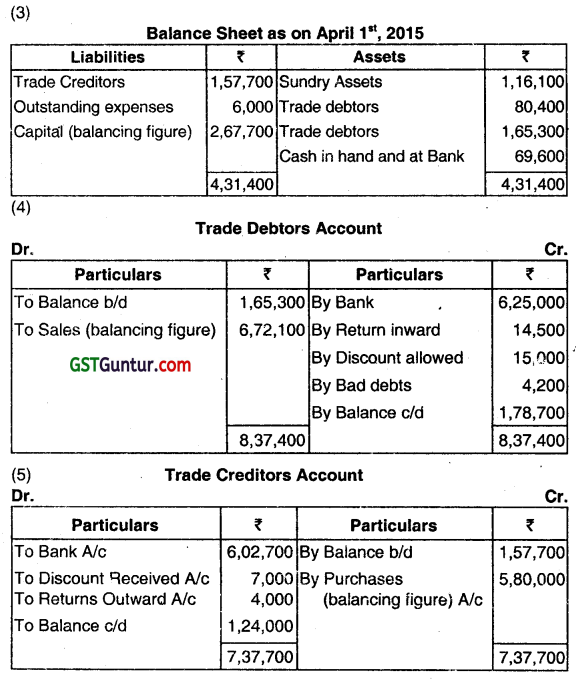
M/S SHOANI a trader who maintained books under Single Entry System, approaches you with the following details:
| 01.04.2015 | 31.03.2016 | |
| Assets and Liabilities: | ₹ | ₹ |
| Trade Creditors | 1,57,700 | 1,24,000 |
| Sundry Expenses Outstanding | 6,000 | 3,300 |
| Sundry Assets (Net) | 1,16,100 | 96,000 |
| Stock-in -Trade | 80,400 | 1,11,200 |
| Cash at Bank | 40,000 | 69,200 |
| Cash in hand | 29,600 | 12,000 |
| Trade Debtors | 1,65,300 | 1,78,700 |
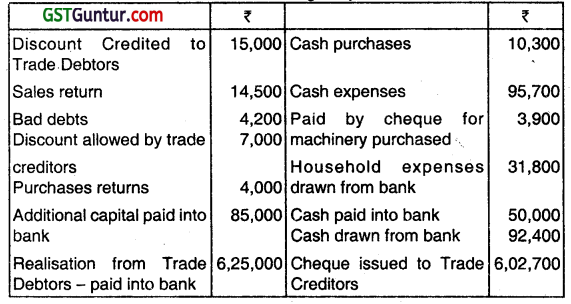
(1) Details relating to transactions during the year ended March 31, 2016.
(2) Depreciation was provided 20% of WDV on Sundry Assets for the year.
You are requested to prepare:
(i) Trading and Profit & Loss Account for the year ended March 31, 2016 and
(ii) Balance Sheet as on that date. (Dec 2016, 5+3+1+1+1+1 = 12 marks)
Answer:
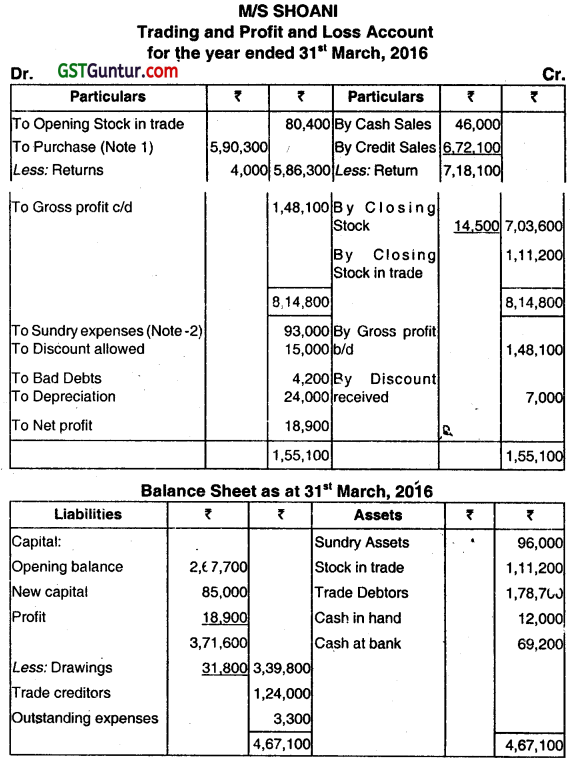
Working Notes.
1. Purchase = Credit 5,80,000+ Cash 10,300= ₹ 5,90,300.
2. Sundry expenses = paid in cash ₹ 95,700 pius outstanding on 31.03.2016, ₹ 3,300 outstanding on 01.04.2015 ₹ 6,000 = ₹ 93,000.

Question 10.
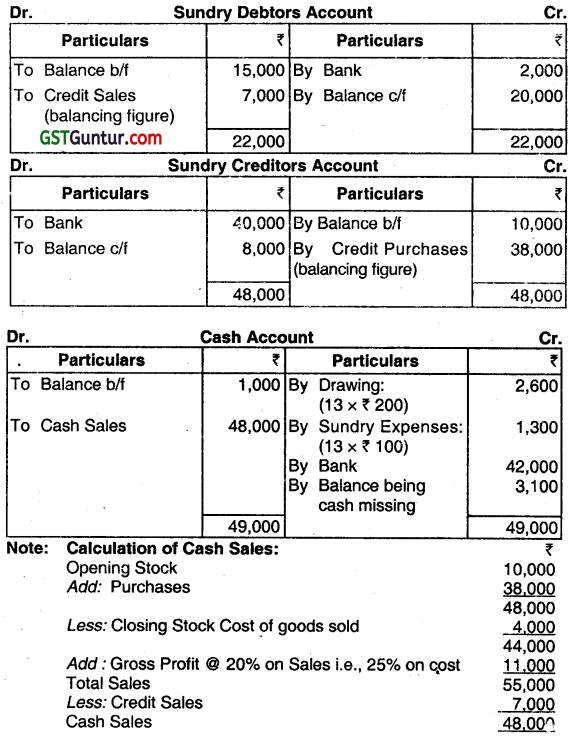
The statement of Affairs of Mr. M on Saturday, the 31st December 2015 was as follows:
| ₹ | ₹ | ||
| Capital | 50,000 | Fixed Assets | 30,000 |
| Sundry Creditors | 10,000 | Stock | 10,000 |
| Liability for Expenses | 1,000 | Debtors | 15,000 |
| Bank | 5,000 | ||
| Cash | 1,000 | ||
| 61,000 | 61,000 |
Mr. M did not maintain has books on the Double Entry System. But he carefully follows the following system:
(a) Every week he draws 200.
(b) After meeting his weekly sundry expenses ( 100 on average) and his drawings, the balance of weekly collection is banked at the commencement of the next week.
(c) No cash purchase is made and creditors are paid by cheques.
(d) Sales are at fixed price which includes 20% profit on sales.
(e) Credit sales are few and are noted in a diary. Payments are received in cheques only from such parties.
(f) Expenses other than sundries and other special drawings are made in cheques
(g) All unpaid bills are kept in a tile carefully.
The following are his bank transactions for 13 weeks:
| ₹ | ₹ | ||
| Balance on Jan. 1 | 5,000 | Creditors paid | 40,000 |
| Cheques deposited | 2,000 | Rent paid | 600 |
| Cash deposited | 42,000 | Expenses (other than Sundry Expenses) | 3,000 |
| Balance on April 1 | 5,400 | ||
| 49,000 | 49,000 |
After 13 weeks on 1st April Monday, the entire cash was missing when it was to be deposited in the bank. The following further tacts are ascertained:
(a) Stock on that day was valued at ₹ 4,000;
(b) Sundry Debtors amounted to ₹ 20,000 as per diary;
(c) Sundry Creditors were ₹ 8,000 as per unpaid bills file. Find out the amount of cash missing. (June 2017, 15 marks)
Answer:
Question 11.
The following is the Balance Sheet of Chirag as on 31st March, 2015:
| Liabilities | ₹ | Assets | ₹ |
| Capital Account | 48,000 | Building | 32,500 |
| Loan | 15,000 | Furniture | 5,000 |
| Creditor | 31,000 | Motor Car | 9,000 |
| Stock | 20,000 | ||
| Debtors | 17,000 | ||
| Cash in hand | 2,000 | ||
| Cash at Bank | 8,500 | ||
| 94,000 | 94,000 |
A riot occurred on the night of 31st March, 2016 in which all books and records were lost. The cashier had absconded with the available cash. He gives you the following information:
(a) His sales for the year ended 31 March, 2016 were 20% higher than the previous year’s. He always sells his goods at cost plus 25%; 20% of the total sales for the year ended 31st March, 2016 were for cash. There were no cash purchases.
(b) On 1st April, 2015 the stock level was raised to ₹ 30,000 and stock was maintained at this new level all throughout the year.
(c) Collection from debtors amounted to ₹ 1,40,000 of which ₹ 35,000 was received in cash, Business expenses amounted to ₹ 20,000 of which ₹ 5,000 was outstanding on 31st March, 2016 and ₹ 6,000 was paid by cheques.
(d) Analysis of the Pass Book revealed the Payment to Creditors ₹ 1,37,500, Personal Drawing ₹ 7,500, Cash deposited in Bank ₹ 71,500, and Cash withdrawn from Bank ₹ 12,000.
(e) Gross Profit as per last year’s audited accounts was ₹ 30,000.
(f) Provide depreciation on Building and Furniture at 5% and Motor Cr at 20%.
(g) The amount dedicated by the cashier may be treated as recoverable from him.
You are required to prepare the Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2016 and Balance Sheet as on that date. (Dec 2017, 15 marks)
Answer:
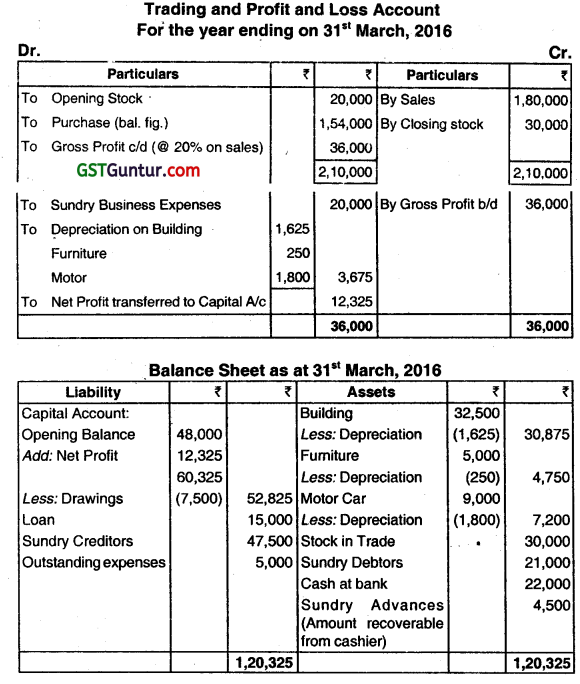

(iv) Last year’s Total Sales = Gross Profit x 100/20 = ₹ 30,000 x 100/20 = ₹ 1,50,000 ‘
(v) Current years Total Sales = ₹ 1,50,000 + 20% of ₹ 1,50,000 = ₹ 1,80,000
(vi) Current years Credit Sales = 1,80,000 80% = 1,44,000
(vii) Cost of Goods Sold = Sales – G.P. = ₹ 1,80,000 – ₹ 36,000 = ₹ 1,44,000
(viii) Purchases = Cost of Goods Sold + Closing Stock – Opening Stock
= ₹ 1,44,000 + ₹ 30,000 – ₹ 20,000
= ₹ 1,54,000.
![]()
Question 12.
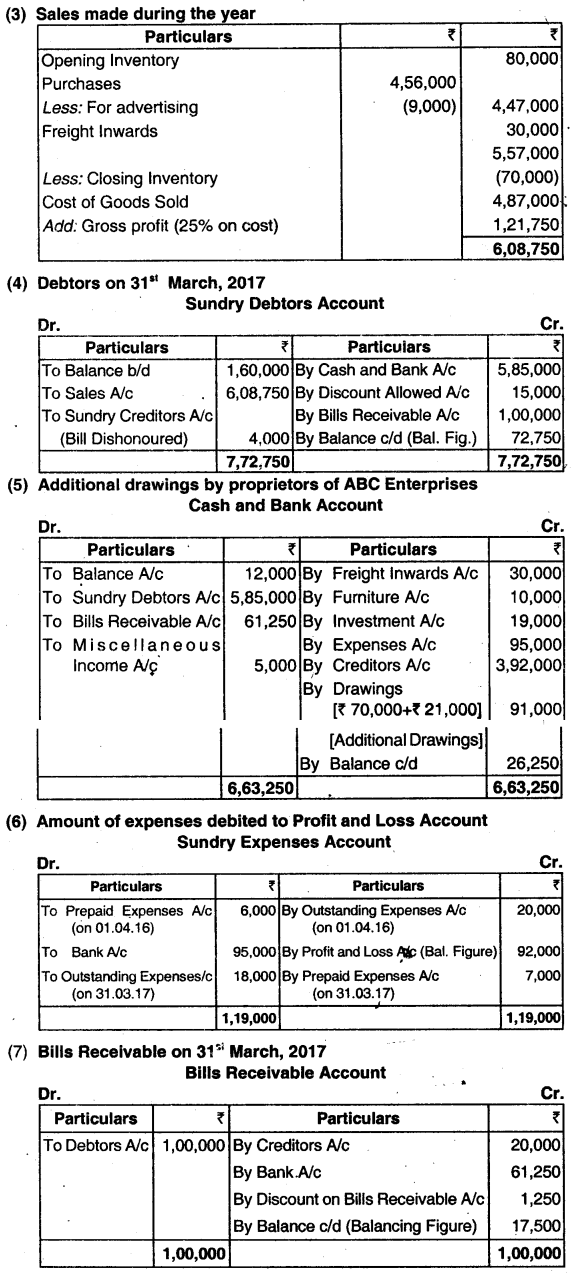
The following information relates to the business of ABC Enterprises, which requests you to prepare a Trading and Profit & Loss A/c for the year ended 31st’ March, 2017 and a Balance Sheet as on that date:
(a) Assets and Liabilities as on:
| 01.04.2016 ₹ | 31.03.2017 ₹ | |
| Furniture | 60,000 | 63,500 |
| Stock | 80,000 | 70,000 |
| Sundry Debtors | 1,60,000 | ? |
| Sundry Creditors | 1,10,000 | 1,50,000 |
| Prepaid Expenses | 6,000 | 7,000 |
| Outstanding Expenses | 20,000 | 18,000 |
| Cash in Hand & Bank Balance | 12,000 | 26,250 |
(b) Cash transactions during the year:
(i) Collection from Debtors, after allowing discount of ₹ 15,000 amounted to ₹ 5,85,000.
(ii) Collection on discounting of Bills of Exchange, after reduction of discount of ₹ 1,250 by bank, totaled to ₹ 61,250.
(iii) Creditors of ₹ 4,00,000 were paid ₹ 3,92,000 in full settlement of their dues.
(iv) Payment of Freight inward of ₹ 30,000.
(v) Mount withdrawn for personal use ₹ 70,000.
(vi) Payment for office furniture ₹ 10,000.
(vii) Investments carrying annual interest of 6% were purchased at ₹ 95 (200 shares, face value ₹ 100 each) on 1st’ October, 2016, and payment made there of.
(viii) Expenses including salaries paid ₹ 95,000.
(ix) Miscellaneous receipts of ₹ 5,000.
(c) Bills of exchange drawn on and accepted by customers during the year amounted to ₹ 1,00,000. of these, bills of exchange of ₹ 20000 were endorsed in favour of creditors. An endorsed bill of exchange of ₹ 4,000 was dishonored.
(d) Goods costing ₹ 9,000 were used as advertising material.
(e) Goods are invariably sold to show a gross profit of 20% on sales.
(f) Difference in cash book, if any, is to be treated as further drawing or introduction of capital by proprietor of ABC enterprises.
(g) Provide at 2% for doubtful debts on closing debtor. (June 2018, 15 marks)
Answer:


Question 13.
Ram Prakash keeps his books on Single Entry System. From the following information provided by him, prepare Trading and Profit & Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018 and Balance Sheet as at that date:
| Particulars | 31st March, 2017 (₹) | 31st March, 2018 (₹) |
| Furniture | 1,00,000 | 1,20,000 |
| Stock of Goods-in-Trade | 60,000 | 20,000 |
| Sundry Debtors | 1,20,000 | 1,40,000 |
| Prepaid Expenses | – | 4,000 |
| Sundry Creditors | 40,000 | ? |
| Unpaid Expenses | 12,000 | 20,000 |
| Cash | 22,000 | 6,000 |
Receipts and Payments during the year were as follows:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Receipts from Debtors | 4,20,000 |
| Paid to Creditors | 2,00,000 |
| Transportation | 40,000 |
| Drawings | 1,20,000 |
| Sundry Expenses | 1,40,000 |
| Furniture Purchased | 20,000 |
Other Information: There were a considerable amount of Cash Sales. Credit Purchases during the year amounted ₹ 2,30,000. Provide a provision for Doubtful Debts to the extent of 10% on Debtors. (Dec 2018, 8 marks)
Answer:

Question 14.
Mr. Kanan is running a business of readymade garments. He does not maintain his books of accounts under double-entry system. While assessing the income of Mr. Kanan for the financial year 2018-19, Income Tax Officer feels that he has not disclosed the full income earned by him from his business. He provides you the following information:
| On 31st March, 2018 | |
| Sundry Assets | ₹ 16,65,000 |
| Liabilities | ₹ 4,13,000 |
| On 31st March, 2019 | |
| Sundry Assets | ₹ 28,40,000 |
| Liabilities | ₹ 5,80,000 |
| Mr. Kanan’s drawings for the year 2018-19 | ₹ 32,000 per month |
| Income declared to the Income Tax Officer | ₹ 9,12,000 |
During the year 2018-19, one life insurance policy of Mr. Kanan was matured and amount received ₹ 50,000 was retained in the business. State whether the Income Tax Officer’s contention is correct. Explain by giving your working. (June 2019, 7 marks)
Answer:
Determination of Capital balance of Mr. Kanan on 31.3.2018 and on 31.3.2019
| 31.3.2018 ₹ | 31.3.2019 ₹ | |
| Assets | 16,65,000 | 28,40,000 |
| Less: Liabilities | 4,13,000 | 5,80,000 |
| Capital | 12,52,000 | 22,60,000 |
Determination of Profit by applying the method of the capital comparison.
| ₹ | |
| Capital Balance as on 31.3.2019 | 22,60,000 |
| Less: Fresh capital introduces(matured life insurance policy amount) (50,000) | 22,10,000 |
| Add: Drawings (₹ 32,000 x 12) | 3,64,000 |
| 25,94,000 | |
| Less: Capital Balance as on 1.4.2018 | (12,52,000) |
| Profit | 13,42,000 |
| Income declared | 9,12,000 |
| Suppressed Income | 4,30,000 |
The Income Tax Officers’ contention that Mr. Kanan has not declared his true income is correct. Mr. Kanan’s true income is in excess of the disclosed income by ₹ 4,30,000.
Note:
Closing capital is increased due to fresh capital introduction, so it is deducted.
Closing capital was reduced due to withdrawal by proprietor; so it is added back.
![]()
Question 15.
A retail trader had not kept proper books of account. From the details given below, you are required to prepare the Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2018.
| 1st April, 2017 (₹) | 31st March, 2018 (₹) | |
| Stock-in-Trade | 16,700 | 18,100 |
| Sundry Creditors | 15,400 | 19,200 |
| Sundry Debtors | 11,200 | 10,600 |
| Cash in Hand | 250 | 1,400 |
| Bank Overdraft | 19,200 | Nil |
| Bills Receivable | 16,000 | 5,000 |
| Fixtures and Fittings | 1,500 | 1,500 |
| Motor Van | 1,900 | Nil |
| Bank Balance | Nil | 2,900 |
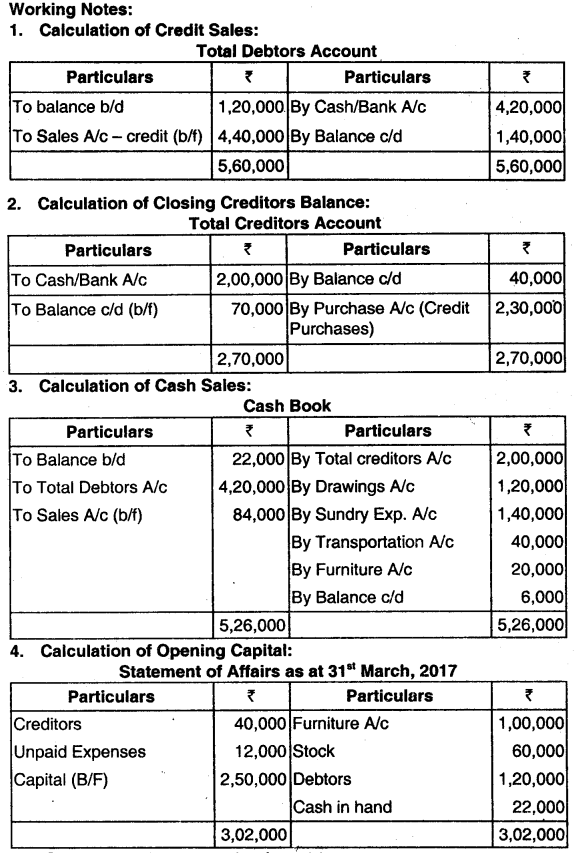
Drawings during the year amounted to ₹ 2,400. Depreciate Fixtures and Fittings by 10%. ₹ 600 is irrecoverable from Debtors. Provide 5% for Doubtful Debts and ₹ 200 in respect of Bills Receivable. (Dec 2019, 8 marks)
Answer:
Question 16.
Calculate:
(i) Gross profit.
(ii) Cost of goods sold and
(iii) Closing stock from the
following particulars.
Opening stock ₹ 20,000
Cash sales ₹ 60,000
Credit sales ₹40,000
Purchase ₹ 70,000
Rate of gross profit on cost 33\(\frac{1}{3} \) % (Dec 2021, 4 marks)
Answer:
Gross Profit = ₹ 25,000
Cost of Goods Sold = ₹ 75,000
Closing Stock = ₹ 15,000
Total Sales = 60,000 + 40,000 = 1,00,000
Sales – COGS =GP
Also COGS x 33.33% = GP
Sales – COGS = COGS x 33.33%
Sales = COGS + 0.33 COGS
Sales = 1.33 COGS.
COGS = \(\frac{\text { Sales }}{1.33}=\frac{1,00,000}{1.333}\) = 75000
GP = 1,00,000 – 75,000 = 25,000
Op. St + Purchase – Closing Stock = COGS
20,000 + 70,000 – CI Stock = 75,000
CI Stock = 15,000
Question 17.
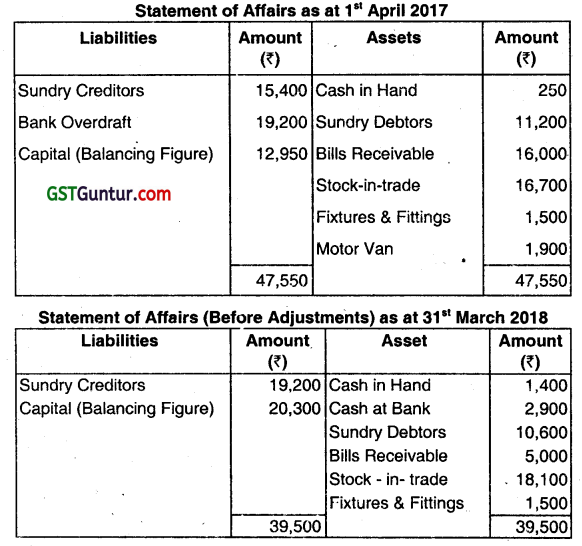
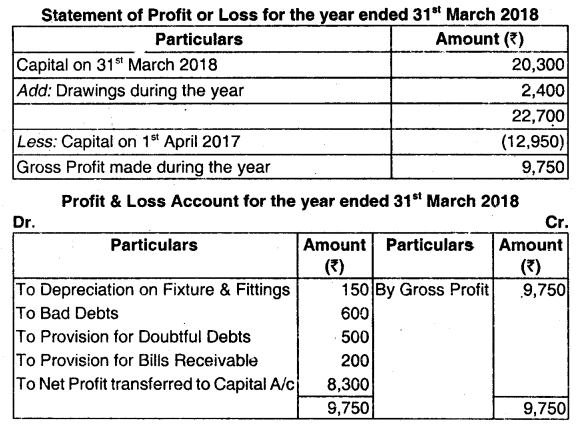
Alpana enterprises maintain their books of accounts under a single entry system. The balance sheet on 31st March, 2018 was a follows:
| Liabilities | Amount (₹) | Assets | Amount (₹) |
| Capital A/C | 6,75,000 | Furnitures and fixtures | 1,50,000 |
| Trade creditors | 7,57,500 | Stock | 9,15,000 |
| Outstanding expenses | 67,500 | Trade debtor | 3,12,000 |
| Prepaid insurance | 3,000 | ||
| Cash in hand and at the Bank | 1,20,000 | ||
| = 15,00,000 | = 15,00,000 |
The following was a summary of cash and bank book for the year ended 31st March, 2019
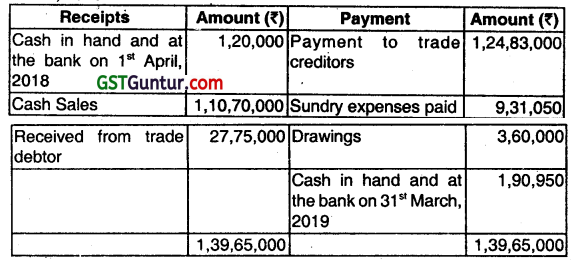
Additional information:
(a) Discounts allowed to trade debtors and received from trade creditors amounted to ₹ 54,000 and ₹ 42,500 respectively (For the years ended 31st March, 2019)
(b) Annual fire insurance premium ₹ 9,000 was paid every year on 1st August for the renewal of the policy.
(c) Furniture and fixture were subject to depredation @ 15% P.a. on diminishing balance method.
(d) The following are the balances as on 31st March, 2019.
Stock: ₹ 9,75,000
Trade Debtors ₹ 3,43,000
Outstanding expenses. ₹55,200
(e) Gross profit ratio of 10% on sales is maintained throughout the year. From the above particulars. Find out.
(i) Amount of credit sales. (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
(ii) Amount of credit purchase. (Dec 2021, 2 marks)
(iii) Amount of closing balance of creditors as on 31 -03-19(Dec 2021, 2 marks)
(iv) Amount of gross profit for the year ended 31-03-19 (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
(v) Amount of Sundry expenses to be charged to the profit and loss account for the year ended 31-03-19 (Dec 2021, 4 marks)
(vi) Amount of net profit for the year ended 31-03-19 (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
(vii) Amount of dosing capital as on 31-03-19. (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
(i) Credit Sale – ₹ 28,60,000
(ii) Credit Purchase – ₹ 1,25,97,000
(iii) Closing balance of Creditors – ₹ 8,29,000
(iv) Gross Profit – ₹13,93,000
(v) Sundry Expenses – ₹ 9,18,750
(vi) Net Profit – ₹ 4,40,250
(vii) Closing Capital (31-03-19) – ₹ 7,55,250
Question 18.
Following is the incomplete information of Jyotishikha Traders:
The following balances are available as on 31.03.2018 and 31.03.2019.
| Balances | 31.03.2018 | 31.03.2019 |
| Land and Building | 5,00,000 | 5,00,000 |
| Plant and Machinery | 2,20,000 | 3,30,000 |
| Office equipment | 1,05,000 | 85,000 |
| Debtors (before charging for Bad debts) | ? | 95,000 |
| Creditors for purchases | 2,25,000 | ? |
| Creditors for office expenses | 20,000 | 15,000 |
| Stock | ? | 65,000 |
| Long term loan from SBI @ 12% | 1,60,000 | 1,00,000 |
| Bank | 25,000 | ? |
| Other Information | In ₹ |
| Collection from debtors | 9,25,000 |
| Payment to creditors for purchases | 5,25,000 |
| Payment of office expenses (excluding interest on loan) | 42,000 |
| Salary paid | 32,000 |
| Selling expenses | 15,000 |
| Cash sates | 2,50,000 |
| Credit sales (80% of total sales) | |
| Credit purchases | 5,40,000 |
| Cash purchases (40% of total purchases) | |
| GP Margin at cost plus 25% | |
| Discount Allowed | 5,500 |
| Discount Received | 4,500 |
| Bad debts (2% of closing debtors) | |
| Depreciation to be provided as follows: | |
| Land and Building | 5% |
| Plant and Machinery | 10% |
| Office Equipment | 15% |
Other adjustments:
(i) On 01.10.18 they sold machine having Book Value 40,000 (as on 31.03.2018) at a loss of ? 15,000. New machine was purchased on 01.01.2019.
(ii) Office equipment was sold at its Book Value on 01.04.2018.
(iii) Loan was partly repaid on 31.03.19 together with Interest for the year.
You are required to prepare Trading, Profit & Loss Account, and Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2019. (Dec 2022, 15 marks)
![]()
Preparation of Financial Statements from Incomplete Records CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Preparation of Financial Statements From Incomplete Records
Many times small business organizations do not maintain a comprehensive accounting system which is based on the double entry principle. The businessman is usually happy with the minimum information like the balances of cash and bank accounts and whether he has made a profit or loss. These people maintain rough or sketchy records that serve a limited purpose. Because the principle of double entry is not followed, it is often referred to as a ‘single entry system.
Features of Single Entry System:
- Maintenance of books by a sole trader or partnership firm
- Maintenance of cash book
- Only personal accounts are kept.
- Collection of information from original documents
- Lack of uniformity
- Difficulty in preparation of final accounts