Partnership Accounting – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Partnership Accounting – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short note:
Guaranteed Partnership. (June 2013, 5 marks)
Answer:
In a partnership, there may be special agreement by virtue of which partner may get the guarantee of earning a minimum amount of profit. The guarantee may be given by one partner in particular or by the firm. It is given generally to encourage a junior partner or any sincere clerk of the business inducted to the benefits of partnership.
Guarantee given by the partner:
- The appropriation of profit should be made in the general course by applying the existing profit-sharing ratio.
- The minimum amount guaranteed is to be decided.
- In case the guaranteed amount (ii) is more, the excess should be deducted from the share of profit of the partner giving guarantee and calculated under (i) above. The same amount should be added with the original share of profit of the partner to whom the guarantee has been given.
Question 2.
Write short flotes on Designated Partner in a Limited Liability Partnership and what are their liabilities.
(Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Designated Partners:
As per Sec. 7 of the LLP Act, every limited liability partnership shall have at least two designated partners who are individuals and at least one of them shall be a resident in India.
Provided that in case of a limited liability partnership in which all the partners are bodies corporate or in which one or more partners are individuals and bodies corporate, at least two individuals who are partners of such limited liability partnership or nominees of such bodies corporate shall act as designated partners.
Explanation:
Subject to the purpose of this Section the term a resident in India means a person who has stayed in India for a period of not less 182 days during the immediately preceding one year. Subject to the provisions of sub-section (1).
1. If the incorporation document:
- Specifies who are to be designated partners, such persons shall be designated partners on incorporation; or
- States that each of the partners from time to time of limited liability partnership is to be designated partner, every such partner shall be a designated partner.
2. Any partner may become a designated partner by and in accordance with the limited liability partnership agreement and a partner may cease to be a designated partner in accordance with limited liability partnership agreement.
3. An individual shall not become a designated partner in any limited liability partnership unless he has given his prior consent to act as such to the limited liability partnership in such form and manner as may be prescribed.
4. Every limited liability participant shall file with the registrar the particulars of every individual who has given his consent to act as designated partner in such form and manner as may be prescribed within thirty days of his appointment.
5. An individual eligible to be a designated partner shall satisfy such conditions and requirements as may be prescribed.
Liabilities of Designated Partners:
As per Sec. 8 of LLP Act, unless expressly provided otherwise in this Act, a designated partner shall be:
- responsible for the doing of all acts, matters, and things as are required to be done by the LLP in respect of compliance of the provisions of this Act including filing of any document, return, statement and the like report pursuant to the provision of this act and as may be specified in the limited liability partnership agreement; and
- liable to all parties imposed on the limited liability partnership for any contravention of those provisions.
![]()
Question 3.
Write short notes on the following:
Criticism of the decision of Gamer vs. Murray. (Dec 2017, 5 Marks)
Answer:
Criticism of the decision of Garner vs. Murray
The following criticism may be advocated against the decisions laid down in Garner vs. Murray principle:
- If any solvent partner has a debit balance in capital account, he must not bear the deficiency of the insolvent partner;
- This principle does not apply it there are only two partners;
- In spite of having a credit balance in capital account the solvent partner must bring cash equal to the amount of loss on realization which is immaterial and useless; and
- If any solvent partner who possess more private asset but contributes less capital, he will naturally, as per Gamer vs. Murray’s decision, bear less amount of deficiency of the insolvent partner than the other solvent partner who possesses less private assets but contributes more capital to the firm. This is not justified.
Question 4.
Write short notes on extent of liability of LLP and its Partners. (May 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Under Sec. 27(3) of the LLP Act, 2008 an obligation of an LLP arising out of a contract or otherwise, shall be solely the obligation of the LLP. The limitations of liability Obtian LLP and Its partners are as follows:
The liabilities of an LLP shall be met out of the properties of an LLP:
- A partner is not personally liable, directly or indirectly (for an obligation of an LLP arising out of a contract or otherwise), solely by reason of being a partner in the LLP;
- An LLP is not bound by anything done by a partner in dealing with a person, if:
- The partner does not have the authority to act on behalf of the LLP in doing a particular acts, and
- The other person knows that the partner has no authority or does not know or believe him to be a partner in the LLP.
- The liability of the LLP and the partners perpetrating fraudulent dealings shall be unlimited for all or any of the debts or other liabilities of the LLP.
Question 5.
Write short note on the following:
(i) Applicability and Non-Applicability of Gamer vs. Murray Rule (Dec 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
In the case of dissolution of a partnership firm due to insolvency, Gamer vs Murray rule is applicable at the time of any partner becoming insolvent. It requires –
1. That the solvent partners should bear the loss arising due to insolvency of a partner in their capital ratio after making adjustments for past accumulated reserves, profits or losses, drawings, interest on drawings/capitals, remuneration to partners, etc., to the date of dissolution but before making adjustment for profit or loss on realization in case of fluctuating capital. In case of fixed capital no such adjustments are required.
2. That the solvent partners should bring in cash equal to their respective shares of the loss on realization.
Non-Applicability:
This rule is not applicable when:
- The solvent partner has a debit balance in the capital account.
- Only one partner is solvent.
- All partners are insolvent.
- The partnership deed provides for a specific method to be followed in case of insolvency of a partner, then the conditions given in the deed would prevail.
Question 6.
Write a short note on the following:
Maximum Possible Loss Method (June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Maximum Possible Loss Method:
Steps:
- Prepare a statement showing the distribution of cash
- Pay off the external Liabilities
- After all the payment is made for the external liabilities, the partners will be paid off. a

4. The maximum loss shall be shared amongst the partners in their profit-sharing ratio, as it, there will be no further realization.
5. If any of the partner capitals, after step (4) is negative, that partner shall be treated like an insolvent partner.
6. The deficiency of the in3olvent partner as per step (5) shall be shared by the other solvent partners (i.e. those partners who has positive capital balances) in their capital contribution ratio as per Gamer vs. Murray Rule.
7. Repeat the steps (3) to (6) till final realisation.
Question 7.
Write short flotes on the following:
Applicability of Section 37 of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Applicability of Section 37 of the Indian Partnership Act 1932:
In case of retirement, the retiring partner or in case of death, the executor of the deceased partner, if the duos are not settled, then such retired partner or the executor is entitled to the following:
Maximum of: Interest @ 6% p.a. on the amount due to them (i.e. if the amount is unsettled, like, rate of interest on loan to be allowed to the retired partner or the executor is not mentioned)
Or
The share of profit earned for the amount due to the partner Conditions:
- The surviving partners/continuing partners continue to carry on the business of the firm.
- The business is carried on without any final settlement of accounts between the continuing partners and the outgoing partners or his estate.
- There is no contract to the contrary of the options contained in Section 37 i.e. share in the profits or interest @ 6% p.a. on the unsettled capital.
Distinguish Between
Question 8.
Answer the following:
What are the distinction between an Ordinary Partnership Firm and a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)? (May 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Distinction between an Ordinary Partnership Firm and a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP):
| Basis of Difference | Partnership | LIP |
| 1. Applicable Law | Indian Partnership Act, 1932. | Limited Liability Partnerships Act, 2008. |
| 2. Formation | Formed by an Agreement. | Formed by Law. |
| 3. Registration | Optional. | Compulsory with ROC. |
| 4. Body Corporate | Not a body corporate. | A Body Corporate After registration with ROC, it becomes a body corporate. |
| 5. Separate Legal Identity | It has no separate legal identity. | All body corporate are said to have a separate legal Identity |
| 6. Perpetual Succession | No perpetual succession. | It has perpetual succession. |
| 7. Number of Partners | Minimum 2 and Maximum 100. | Minimum 2, but no maximum limit. |
| 8. Liability of Partners/ Members | Liability of the partners is unlimited. Partners are severally and jointly liable for actions of other partners and the firm and their liability extends to personal assets. | Liability of the partners is limited to the extent of their contribution towards LLP except in case of intentional fraud or wrongful act of omission or commission by a partner. |
| 9. Principal-Agent Relationship | Partners are the agents of the firm and of each other i.e. Mutual agency. | Partners are agents of the firm only and not of other partners. No Mutual agency. |
Descriptive Questions
Question 9.
Answer the following:
Under what circumstances, an LLP can be wound up by the Tribunal. (May 2015, 4 Marks each)
Answer:
Circumstances when an LLP can be wound up by the tribunal:
- The partnership shall be dissolved if mere is unlawful object of the firm.
- The partnership firm shall be dissolved when all the partners become insolvent.
- The partnership firm is dissolved by order of court.
- If there is any criminal law or case on the firm, the firm shall be dissolved.
- If partnership is under ‘oss on continuous basis then firm shall be dissolved by the tribunal.
- If partnership violates any rule of partnership Act then court may give order for dissolution.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the nature of Limited Liability Partnership. Who can be a designated partner in a Limited Liability Partnership? (Nov 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
1. Nature of LLP:
| Point | LLP |
| Governing law | The Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 |
| Registration | Registration with registrar of LLP mandatory. |
| Name | Name should contain limited liability partnership suffix. |
| Creation | Created by law |
| Separate entity | Separate legal entity under LLP Act, 2008. |
| Perpetual succession | LLP has perpetual succession, and partners may come and go. |
| Legal proceedings | A LLP is a legal entity can sue and be sued. |
| Annual filing of forms | Annual Statement of Accounts and Solvency & Annual return to be filed with registrar every year. |
| Digital signature for partners | As e-forms are filled electronically at least one designated partner should have digital signature. |
| Agency Relationship | Partners act as agents of LLP and not of the other partners. |
| Liability of Partners | Limited, to the extent their contribution towards LLP, except in case of intentional fraud or wrongful act of omission or commission by partner. |
2. Designated partners:
Sec. 7 of LLP Act deals with designed partners, and Sec. 8 deals with liabilities of Designated partners, given below:
- Every LLP shall at least 2 designated partners (DPs).
- OPs shall be individuals only.
(Note: !t all partners of LLP are bodies corporate, or one or more partners are individuals or bodies corporate, at least 2 individuals who are partners of such LLP or Nominees of such bodies corporate, shall act as designated partners).
- At least I DP should be resident in India. (Note: Resident means a person who has stayed in India ≥ 182 days during. The immediately preceding 1 year).
- An individual can become a DP in any LLP, only it he has given his consent to act as such, to the LLP.
Question 11.
Why is goodwill considered to be an intangible asset and not a fictitious asset? (Dec 2017, 1 mark)
Answer:
Goodwill is not a fictitious asset because it has a realisable value. It is an intangible asset because it cannot be seen and touched.
Question 12.
Answer the following:
Under what circumstances an LLP can be wound up by the tribunal? (Nov 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
An LLP may be wound up by the Tribunal in the following circumstances:
- If the LLP decides that it should be wound up by the Tribunal;
- If for a period of more than six months, the number of partners of the LLP is reduced below two;
- If the LLP is unable to pay its debts;
- If the LLP has acted against the interests of the integrity and sovereignty of India, the security of the state or public order;
- If the LLP has defaulted in the filing of the Statement of Account and Solvency with the Registrar for five consecutive financial years;
- If the Tribunal is of the opinion that it is just and equitable that the LLP be wound up.
Question 13.
Explain the nature of a Limited Liability Partnership. Who can be a designated partner in a Limited Liability Partnership and what are their liabilities? (May 2022, 5 marks)
Answer:
Nature of Limited Liability Partnership:
A limited liability partnership is a body corporate formed and incorporated under the LLP Act, 2008, and is a legal entity separate from that of its partners. A limited liability partnership shall have perpetual succession and any change in the partners of a limited liability partnership shall not affect the existence, rights or liabilities of the limited liability partnership.
Designated Partners:
Every limited liability partnership shall have at least two designated partners who are individuals and at least one of them shall be resident in India. In case of a limited liability partnership in which all the partners are bodies corporate or in which one or more partners are individuals and bodies corporate, at least two individuals who are partners of such limited liability partnership or nominees of such bodies corporate shall act as designated partners.
Liabilities of designated partners:
As per section 8 of the LLP Act, unless expressly provided otherwise in this Act, a designated partner should be:
- Responsible for the doing of all acts, matters, and things as are required to be done by the Iimged liability partnership in respect of the provisions of this Act including tiling of any document, return, statement.
- Lable to all penalties imposed on the limited liability partnership for any contravention of those provisions.
Practical Questions
Question 14.
Ashok & Bala who where in partnership sharing 7/12 and 5/12 respectively admitted Chand as a partner giving him 1/5th share from 01.042011. The new profit-sharing ratio is 7: 5:3. Chand brought ₹ 96,000 towards goodwill to be shared by Ashok & Bala In their sacrificing ratio. The amount so brought was however credited to Chand’s capital account by mistake:
The Trial Balance of the firm as on 31 March, 2012 is given below:
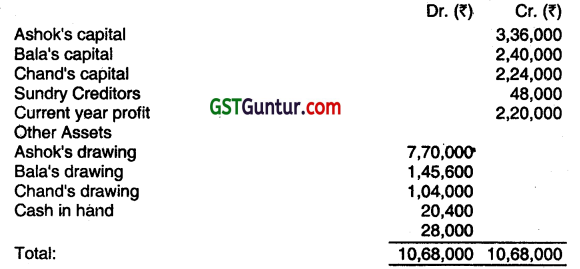
Interest on drawings is to be ignored but interest on capital is to be charged at 5% per annum which was not made so far. Prepare new Balance Sheet as at 31.03.2012 gMng effect to above adjustments/omissions. (Dec 2012, 8 marks)
Answer:
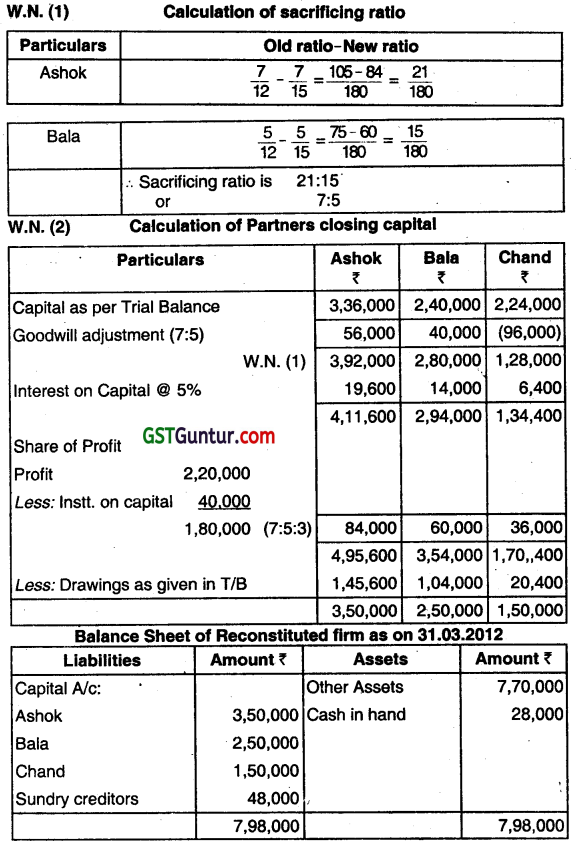
Question 15.
Sachin & Ganguly are partners of a firm SG & Co. From the following information calculate the value of goodwill by super profit method and capitalization method:
(i) Average capital employed in the business ₹ 5,00,000.
(ii) Net trading profit of the firm for the last three years ₹ 1,50,000; ₹ 1,70,000 and ₹ 1,90,000.
(iii) Rate of return expected from capital having regard to risk involved @ 15 % per annum.
(iv) Goodwill to be valued at 2 years’ purchase. (Dec 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
Calculation of Goodwill
(i) Super Profit Method
Goodwill = Super Profit x No. of years of purchase
= 95,000/- × 2 = 1.90,000/-
= Average Profit – Normal Profit
= 1,70,000 -(5,00,000 × 15%) = 95,000
Average Profit = \(\frac{1,50,000+1,70,000+1,90,000}{3}\) = 1,70,000
(ii) Capitalization Method
Goodwill = Value of Business – Avg. Capital Employed
= \(\left(\frac{1,70,000}{15 \%}\right)\) – 5,00,000
= 11,33,333 – 5,00,000 = 6,33,333/-
Question 16.
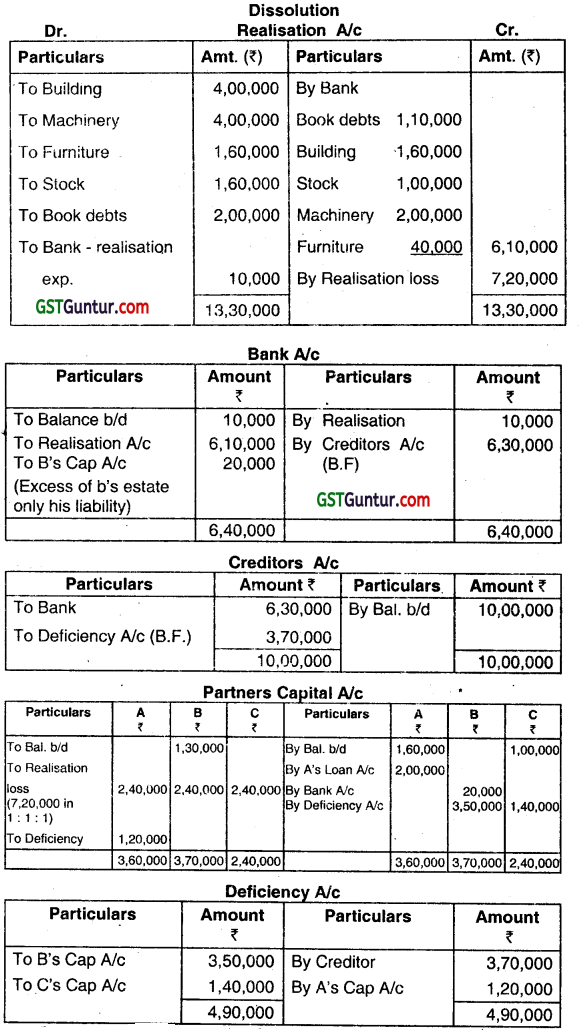
Ram, Rahim, and Robert are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the proportion of 3 : 3 : 2. Their Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2013 was as follows:
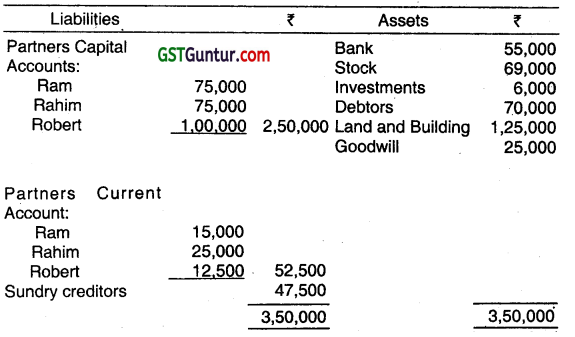
They decided to dissolve the firm on 01.04.2013. They report the result of realization as follows: .
Land and Buildings 90,000 – realized in cash
Debtors 60,000 – realized in cash
Investments 5,500 – taken over by Ram
Stock 75,500 – taken over by Rahim
Goodwill 18,000 – taken over by Robert
The realization expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000. Close the Accounts of the firm. (June 2013, 5 marks)
Answer:
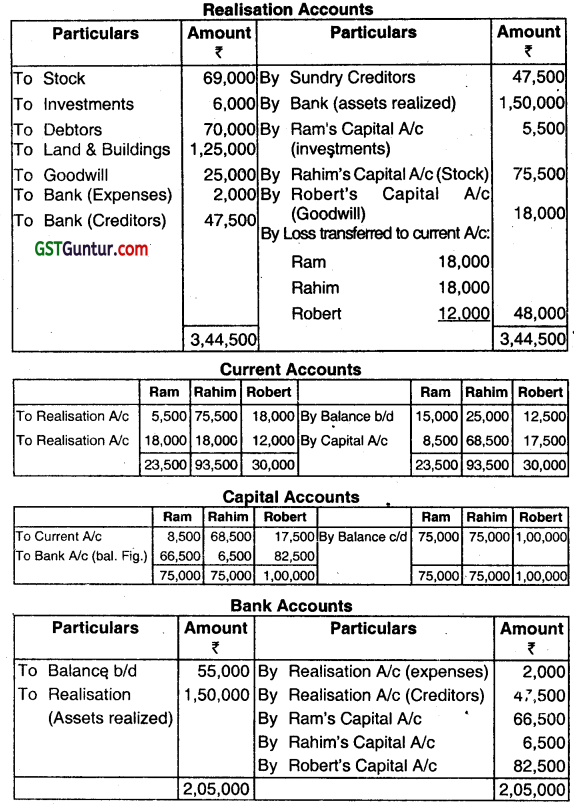
![]()
Question 17.
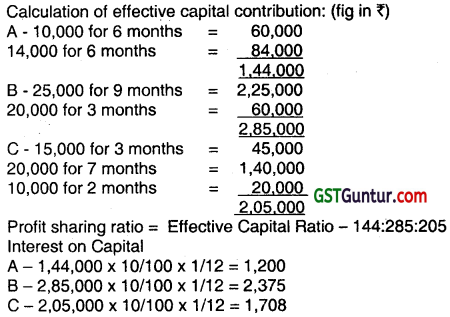
A, B, and C started a partnership firm on 1.1.2012. A introduced ₹ 10,000 on 1.1.2012 and further introduced ₹ 4,000 on 1.7.2012. B introduced ₹ 25,000 at first on 1.1 .2012 but withdrew ₹ 5,000 from the business on 31.9.2012. C introduced ₹ 15,000 at the beginning on 1.1.2012, increased it by ₹ 5,000 on 1.4.2012, and reduced it to ₹ 10,000 on 1.11.2012.
During the year 2012 they made a net profit of ₹ 75,500. The partners decided to provide interest on their capitals at 10% p.a. and to divide the balance of profit in their effective capital contribution ratio. Prepare the Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ended 31.12.2012. (June 2013, 5 marks)
Answer:

Question 18.
Answer the following question (give workings wherever required):
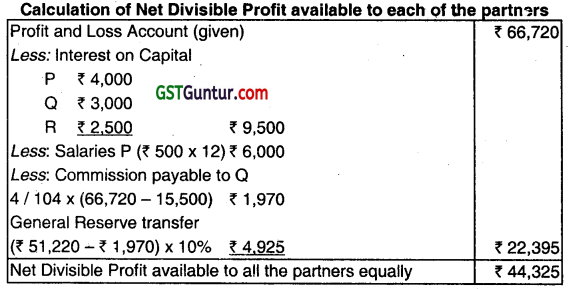
P, Q, and R are three partners sharing profit and loss equally. Their respective capitals as on 01.04.2012 were P- ₹ 80,000, Q – ₹ 60,000, and R- ₹ 50,000. They mutually agreed on the following points as per the partnership deed:
Interest on capital to be allowed @ 5%.
P to receive a salary of ₹ 500 per month.
Q to receive a commission @ 4% on net profit after charging such commission.
After charging all other items, 10% of the net profit to be transferred to General Reserve.
The firm made profit of ₹ 66,720 during the financial year 2012-13. What will be the Net Divisible Profit available to each partner? (Dec 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Net Divisible profit available to each of the partner will amount to = ₹ 44,325/3 = ₹ 14,775.
Question 19.
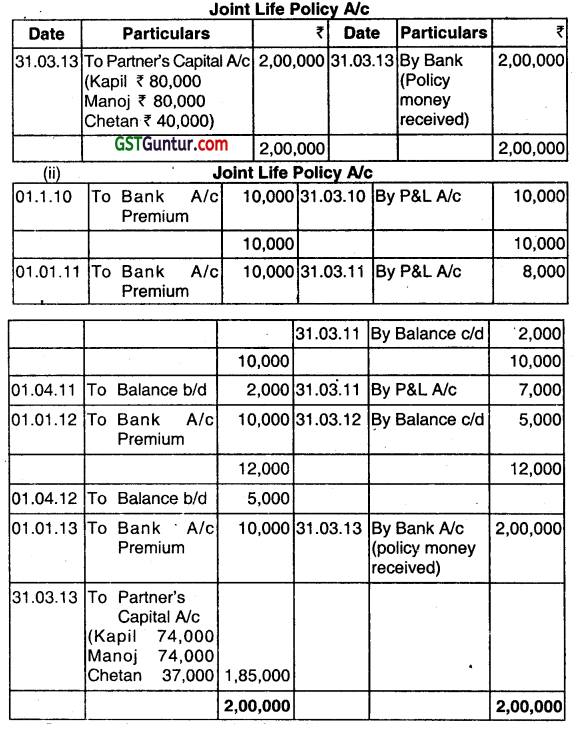
Kapil, Manoj and Chetan are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 2: 1. On 1st January 2010, they took out a loint life policy of ₹ 2,00,000. Annual premium of ₹ 10,000 was payable on 1st January each year. Last premium was paid on 1st January, 2013. Manoj died on 1st March, 2013, and policy money was received on 31st March, 2013. The surrender value of policy as on 31st March each year were as follows:
2010:Nil .
2011: ₹ 2,000
2012: ₹ 5,000
Show Joint Life Policy accounts as on 31 March each year assuming that:
(i) The premium is charged to profit and loss account every year.
(ii) The premium is debited to joint life policy account and the balance of the joint life policy account is adjusted every year to its surrender value. (Dec 2013, 6 marks)
Answer:
1. In this case, premium paid is charged to Profit & Loss account every year. So nothing will appear in the joint life policy account of 2010, 2011, and 2012. However, in 2013, the joint life po1icy account will appear as follows.
Question 20.
Answer the following question (give workings):
(A) Babbu and Dabbu are partners, sharing profit or loss in the ratio 3:2. They admit Kachari for \(\frac{1}{6}\) th share of profits in the firms of which she takes \(\frac{2}{3}\) rd from Babbu and \(\frac{1}{3}\) rd from Dabbu. Find the new profit-sharing ratio. (June 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Share surrendered by Babbu = \(\frac{1}{6} \times \frac{2}{3}=\frac{2}{18}\)
Share surrendered by Dabbu = \(\frac{1}{6} \times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{1}{18} \)
New Ratio:
Babbu = \(\frac{3}{5}-\frac{2}{18}=\frac{44}{90} \)
Dabbu = \(\frac{2}{5}-\frac{1}{18}=\frac{31}{90} \)
Kachari = \(\frac{1}{6} \times \frac{15}{15}=\frac{15}{90} \)
NPSR = 44:31:15
Question 21.
The Balance Sheet of A, B, and C who are sharing profits in proportion to their capital stood as follows on March 31st, 2012:
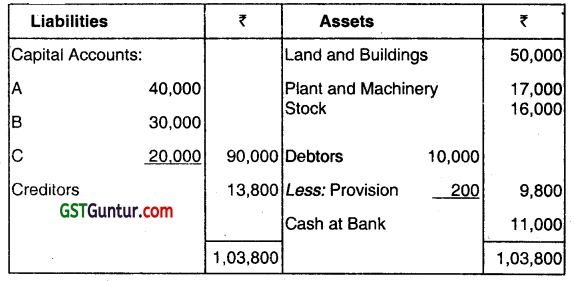
B retired on the above date and the following was agreed upon:
(i) The stock be depreciated by 6%.
(ii) That the provision for doubtful debts be brought up to 5% on Debtors.
(iii) That the Land and Buildings be appreciated by 20%.
(iv) That a provision for ₹ 1,540 be made in respect of outstanding legal charges.
(v) That the Goodwill of the entire firm be fixed at ₹ 21,600 and B’s share of it be adjusted into the accounts of A and C who are going to share future profits in the ratio of 5 : 3.
(vi) That the assets and liabilities (except Cash at Bank) were to appear in the Balance Sheet at their old figures.
(vii) That the entire capital of the firm as newly constituted by fixed at ₹ 56,000 between A and C in the proportion of 5 : 3 (actual cash to be brought in as paid off, as the case may be). Show the Balance Sheet after B’s retirement. (June 2014, 10 marks)
Answer:
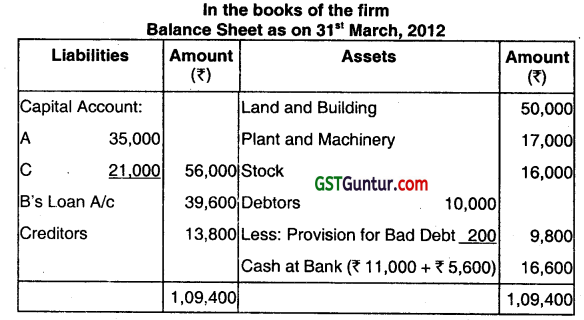
Note: Since assets and liabilities will appear in the Balance Sheet at their old figure Memorandum Revaluation Account should be opened.
Working Note:
Gaining Ratio
A = \( \frac{5}{8}-\frac{4}{9}=\frac{45-32}{72}=\frac{13}{72}\)
C = \(\frac{3}{8}-\frac{2}{9}-\frac{27-16}{72}=\frac{11}{72} \)
Hence, gaining ratio = 13:11
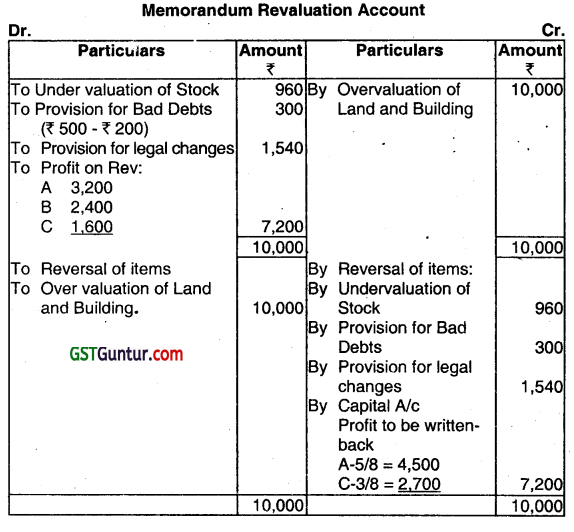
∴ B’s share of goodwill = ₹ 21,600 × 3/9 = ₹ 7,200
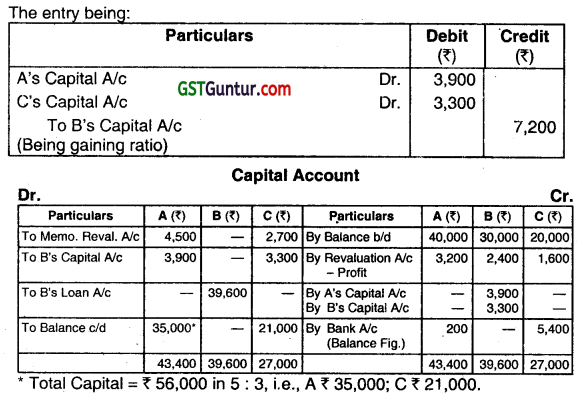
Question 22.
Answer the following question (Give workings):
Gunnu and Chinu are partners. They are entitled for 9% interest on their capital contributions. The firm allowed ₹ 54,000 towards interest on capital to partners. Calculate the capital contribution of each partner if interest on Gunnu’s capital is ₹ 13,500 more than the interest on Chinu’s capital. (Dec 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Let Chinu’s capital be x.
∴ Interest on Chinu’s capital = 0.09x
And interest on Gunnu’s capital = 0.09x + 13,500
0.09x + 0.09x + 13,500 = 54,000
0.18 x = 40,500
x = 2,25,000
Interest on Gunnu’s capital = (0.09 × 2,25,000) + 13,500 = 33,750
∴ Gunnu’s capital = 3,75,000
And Chinu’s captal (x) = 2,25,000
![]()
Question 23.
Answer the question:
Doll and Dolly are in partnership sharing profits and losses equally. They keep their books by Single Entry System. No ready figures are available for the total sales but they maintain a steady gross profit rate of 25% on sales. An abstract of their cash transactions for the year ended 30th June 2011 is given below:
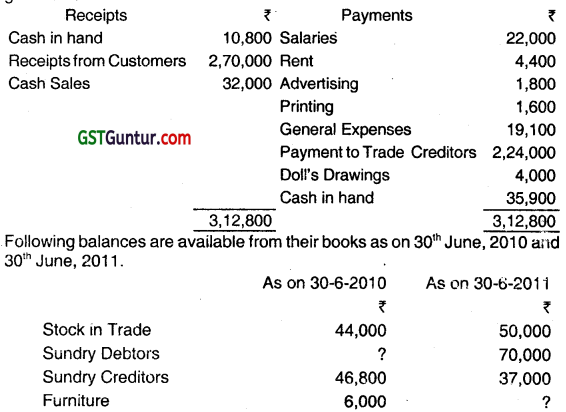
Other Information:
(i) Discount allowed, ₹ 2,800.
(ii) Discoun4 earned, ₹ 2400.
(iii) Outstanding Printing, ₹ 500.
(iv) Capital of Doll as on 30th June, 2010 was ₹ 4,000 more than Capital of Dolly.
(v) Provide depreciation of Furniture @ 10% p.a.
From the above, you are required to prepare in the books of Doll and Dolly:
(i) The Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 3oth June, 2011 and
(ii) The Balance Sheet as on the date. (Dec 2014, 12 marks)
Answer:
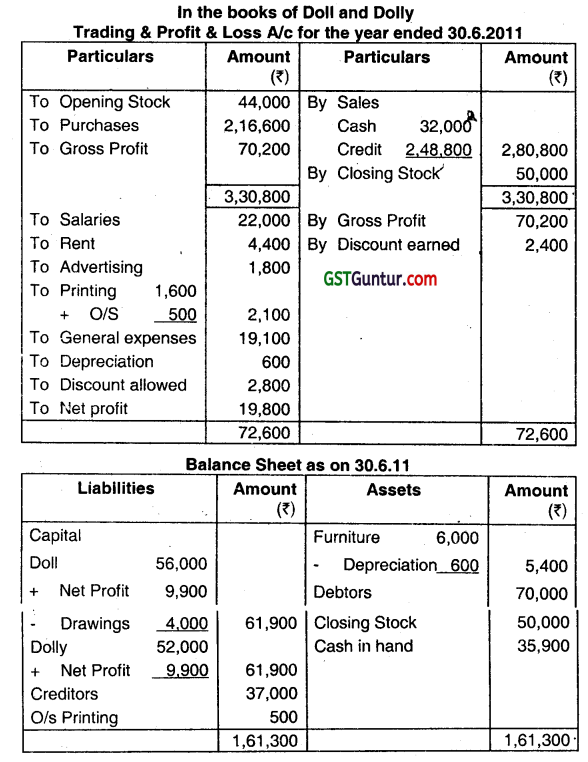

G.P. on sales = 25%
∴ G.P.on cost = 33.33%
Cost = Opening stock + Purchase – Closing stock = 2,10,600
G.P. = 70,200
Question 24.
Answer the question:
X, Y, and Z are partners in the ratio of 3 : 2: 1. W is admitted with 1/6th share in future profits. Z would retains his original shares. Find out the new profit-sharing ratios of the partners. (June 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
X’s New share = 3/6 – (1/6 x 3/5) = 12130
Y’s New share = 2/6 – (1/6 x 2/5) 1= 8/30
Z’sshare = 1/6
W’sshare = 1/6
Therefore, NPSR = X:Y:Z: W=12:8:5:5
Question 25.
A, B, and C were equal partners in a firm. Their Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2015 was as follows:
| Liabilities | Amount ₹ | Assets | Amount ₹ |
| A’s Capital’ | 1,60,000 | Building | 4,00,000 |
| C’s Capital | 1,00,000 | Machinery | 4,00,000 |
| A’s Loan | 2,00,000 | Furniture and Fixtures | 1,60,000 |
| Creditors | 10,00,000 | Stock | 1,60,000 |
| Book Debts | 2,00,000 | ||
| Cash at Bank | 10,000 | ||
| B’s Capital (Overdrawn) | 1,30,000 | ||
| 14,60,000 | 14,60,000 |
The firm was dissolved as all the partners were declared insolvent. The assets were realized as under:
Book debts: 45% less; Building: ₹ 1,60,000: Stock: ₹ 1,00,000; Machinery: ₹ 2,00,000; and Furnitures and fixtures; 40,000. Realization expenses were ₹ 10,000.
| Partner | Private Assets ₹ | Private Liabilities ₹ |
| A | 2,50,000 | 2,50,000 |
| B | 2,00,000 | 1,80,000 |
| C | 2,30,000 | 2,50,000 |
You are required to prepare:
(i) Realisation Account,
(ii) Bank Account,
(iii) Creditors Account,
(iv) Partner’s Capital Account, and
(v) Deficiency Account. (June 2015, 4 + 2 + 1 + 3 + 2 = 12 marks)
Answer:
![]()
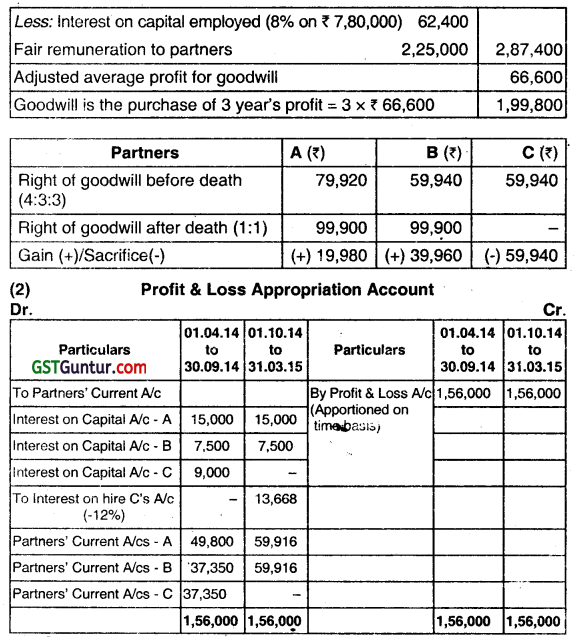
Question 26.
A, B, and C have been in business partnership for some years, Sharing Profit in the proportions of 4:3:3. The balances in the books of the firm as on 31st March, 2015 subject to final Adjustment, were as under:
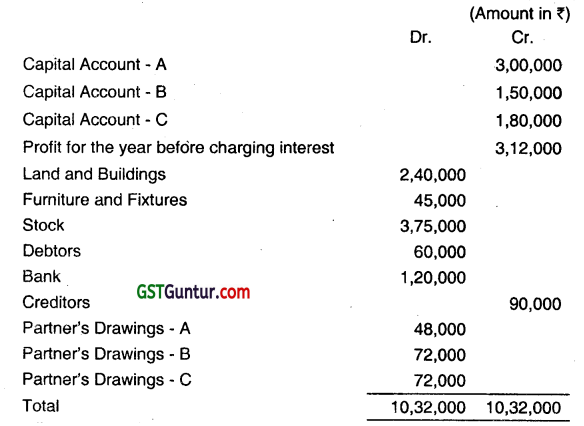
C died on 30.09.2014. The Partnership deed provided that:
(1) Interest was to be credited on Capital accounts of partners at 10% P.A. on the balance at the beginning of the year.
(2) On the death of a Partner
(i) Goodwill was to be valued at three years’ purchase of average Annual Profits of three years up to the date of death, after deducting interest on Capital Employed at 8% P.A. and a fair remuneration for each of the partners;
(ii) Fixed Assets were to be vali’d by an independent valuer and all other assets and liabilities to be taken at Book Value.
(3) Wherever necessary, profit or loss should be apportioned on a time basis.
(4) The amount due to the deceased partner’s Sole Heir was to receive interest @ 12% RA. from the date of death until paid.
It was ascertained that:
(a) Profits for three years, before charging partners’ interest were: 2011-1 2 – ₹ 3,36,000, 2012-13 – ₹3,78,000 and 2013-14 – ₹ 3,60,000 respectively.
(b) The independent valuation at the date of death revealed: Land and Buildings – ₹ 3,00,000 and Furniture and Fixtures – ₹30,000.
(c) A fair remuneration for each of the Partners would be ₹ 75,000 P.A. and that the Capital employed in business to be taken as ₹ 7,80,000 throughout.
It was agreed among the Partners that:
(i) Goodwill was not to be shown as an asset of the firm as on 31.03.2015. Therefore, adjustment for goodwill was to be made in Capital Accounts.
(ii) A and B would share equally from the date of death of C.
(iii) Depreciation on revised value of assets would be Ignored.
You are required to prepare:
(i) Revaluation Account
(ii) Partners’ Capftal Accounts
(iii) Partners’ Current Accounts
(iv) C’s Heir Account
(v) Balance Sheet as on 31 .03.2015 (Dec 2015, 1+2+1+1+4+3 = 12 marks)
Answer:


Question 27.
Answer the following question.
(i) S and N are partners sharing Profit /(Loss) in the ratio of 5:3. They admit J into partnership for \(\frac{3}{10}\) th in the Profit /(Loss) in which J acquired \(\frac{1}{5}\)th share from S and \(\frac{1}{10} \) th share from N respectively. Calculate the new Profit/Loss sharing ratios of the partners. (June 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Ss new share = \(\left(\frac{5}{8}-\frac{1}{5}\right)=\frac{25-8}{40}=\frac{17}{40}\)
N’s new share = \(\left(\frac{3}{8}-\frac{1}{10}\right)=\frac{15-4}{40}=\frac{11}{40} \)
J’s share = \(\frac{3}{10}=\frac{12}{40} \)
Hence New profit/loss sharing ratios of the partners = 17:11:12
Question 28.
A, B, and C are in partnership sharing Profits and Losses in the ratio 3:2:1 respectively. The Balance Sheet of the Partnership firm as on 31st March, 2016 is as under:
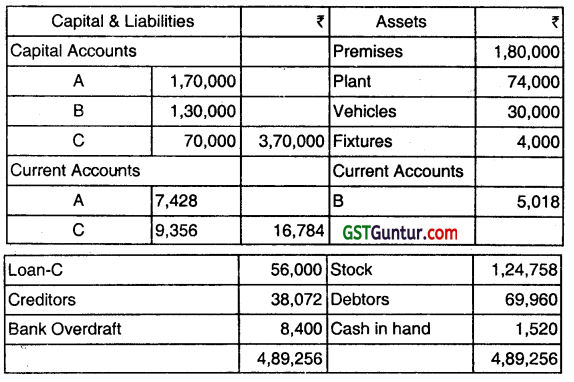
C decides to retire from the business as on the above date and D is admitted as a partner on that date. The following matters agreed:
(i) Assets revalued as: Premises – ₹ 2,40,000, Plant- ₹ 70,000 Stock – ₹1,08,358.
(ii) A provision of ₹ 6,000 is created against debtors.
(iii) Goodwill is to be recorded in the books on the day C retires at 84,000.
The partners in the new firm do not wish to maintain a Goodwill Account so that amount is to be written off against the New Partners Capital Accounts.
(iv) A and B are to share profit in the same ratio as before, and D is to have the same share of profits as B.
(v) C is to take a car at its book value of ₹ 7,800 in part payment, and the balance of all he is owed by the firm in cash except ₹ 40,000 which he is willing to leave as a Loan Account.
(vi) The partners in the new firm are to start on an equal footing so far as Capital and Current Accounts are concerned. D is to contribute cash to bring his Capital and Current Accounts to the same amount as the original partner from the old firm who has the lower investment in the business. The original partner in the old firm who has the higher investment will draw out cash so that his capital and current account balances equal those of his new partners.
(vii) Revaluation profit or loss is to be adjusted in the Partners’ Current Account.
You are required to prepare:
(a) Revaluation Account
(b) Partners’ Capital Accounts
(C) Partners’ Current Accounts
(d) C’s Loan Account.
(e) Bank Account.
(f) Balance Sheet of the New Firm as at 01.04.2016. (June 2016, 3+2+2+1+2+5 = 15 marks)
Answer:


Question 29.
Answer the following question (Give workings):
P and R are currently partners in a firm sharing Profit/Loss in the ratio of 4:3. A new partner D ¡s admitted and after his admission new Profit/Loss sharing ratio between P, R, and D becomes 5:3:2. What will be the sacrifice ratio of P and R after admission of D? (Dec 2016, 2 marks)
Answer: .
Calculation of sacrificing ratio of P&R after D’s admission:
Partners P R D
Old Ratio 4: 3: –
‘New Ratio 5: 3: 2
P = \(\frac{4}{7}-\frac{5}{10}=\frac{(40-35)}{70}=\frac{5}{70} \)
R = \(\frac{4}{7}-\frac{5}{10}=\frac{(40-35)}{70}=\frac{5}{70}\)
Sacrificing ratio or P&R = 5:9.
Question 30.
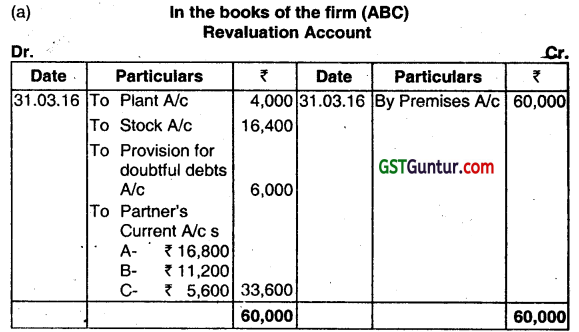
P, Q, R, and T have been carrying on business in partnership sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4: 1: 2 : 3. The following is their Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2016:

It has been agreed to dissolve the partnership on 1st April, 2016, on basis of following points agreed upon:
(i) P is to take over Trade Debtors at 80% of Book Value (₹ 3,50,000);
(ii) T is to take over the stock in Trade at 95% of the value; and
(iii) R is to discharge Trade Creditors.
(iv) The realisation is: Premises ₹ 2,75,000 and Furnitures ₹ 25,000.
(y) The expenses of realisation come to ₹ 30,000.
(vi) Q is found insolvent and ₹ 21,900 is realised from his estate.
Note: The loss arising out of capital deficiency may be distributed following decision in Garner vs. Murray.
You are required to Prepare:
(a) Realisation Account
(b) Bank/Cash Account
(c) Capital Accounts of the Partners. (Dec 2016, 5+4+5+1 = 15 marks)
Answer:

Question 31.
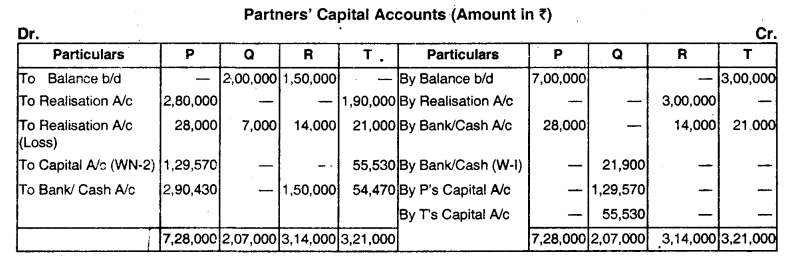
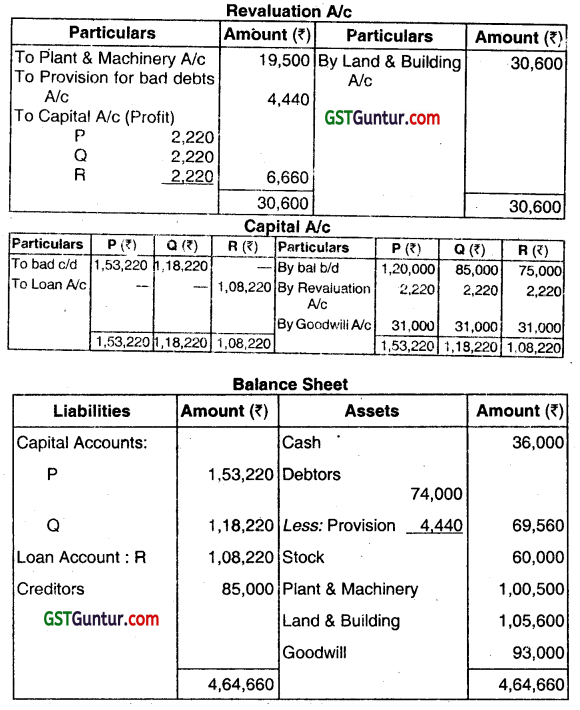
P, Q and R sharing profits and losses equally, had been trading for many years. R decided to retire on 31.3.2017 on which date Balance Sheet of the firm is as follows.
| ₹ | ₹ | ||
| Capital accounts: | Cash | 36,000 | |
| P | 1,20,000 | Debtors | 74,000 |
| Q | 85,000 | Stock | 60,000 |
| R | 75,000 | Plant and Machinery | 1,20,000 |
| Creditors | 85,000 | Land and Building | 75,000 |
| 3,65,000 | 3,65,000 |
Value of goodwill was agreed as ₹ 93,000. Land and building increased in value, it being agreed at ₹ 1,05,600, plant and machinery was revalued at ₹ 1,00,500 and it was agreed to provide 6% in respect of debtors. Prepare revaluation account, capital accounts and balance sheet. (June 2017, 5 +5+5 = 15 marks)
Answer:
![]()
Question 32.
(ii) The Balance Sheet of a Partnership Firm had an Investment Fluctuation Reserve of ₹ 10,000. A new partner ¡s admitted. Value of Investment is ₹ 60,000 against its book value of ₹ 70,000. What amount of, the investment Fluctuation Reserve will be distributed among partners?
(iii) When does the Capital Account of a partner not show a debit balance in spite of regular losses incurred by the firm?
(iv) At the time of dissolution of Partnership Firm realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 3,000 paid by Nisha, a partner who was to bear these expenses. What entry is required in the Books of the firm? (Dec 2017, 1 mark each)
Answer:
(ii) Nil. There is no excess amount in the Investment Fluctuation Reserve Account as the fall in the value of the investment is equal to the reserve.
(iii) When partners maintain Fixed Capital Account, all adjustments including share of profit or loss is shown in their Current Account. Hence, the Capital Account of the partners will not be disturbed and this will not show a debit balance in spite of regular losses.
(iv) No entry is required as the expenses are to be borne by the partners.
Question 33.
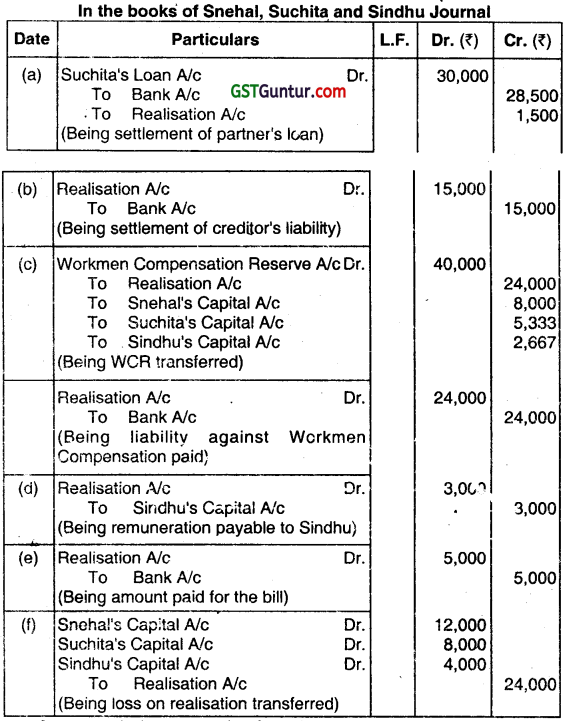
Snehal, Suchita and Sindhu were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2:1. The firm was dissolved on 31.03.2015. After transfer of assets and liabilities to Realisation A/c, the following transactions
took place.
Give journal entries in the books on dissolution of the firm.
(i) Suchita’s Loan to the firm ₹ 30,000 was settled at ₹ 28,500.
(ii) A creditor for ₹ 50,000, took over Machinery of Book value ₹ 40,000 at ₹ 35,000.
The balance was settled in Cash.
(iii) Workmen Compensation Reserve – ₹ 40,000. A liability equal to 60% of the Reserve was settled
(iv) Sindhu was to receive 5% of the value of assets realised as remuneration for completing the dissolution work and was to bear realization expenses. Realization expenses were ₹ 5,500 that was paid by Sindhu. Assets realised ₹ 60,000.
(v) The Balance Sheet disclosed a footnote, contingent liability for ₹ 5,000 in respect of a bill discounted. The bill was received from Megha. On the date of dissolution, Megha was declared insolvent and was not able to pay the amount due. The bill had to be met by the firm.
(vi) Loss on realization amounted to ₹ 24,000. (Dec 2017, 7 marks)
Answer:
Question 34.
A and O were partners of a firm sharing profits and losses in the rabo 2: 1. The Balance Sheet of the firm as at 31st March, 2017 was as under:
| Liabilities | Amount ₹ | Assets | Amount ₹ |
| Capital Accounts: | Plant and Machinery | 5,00,000 | |
| A | 8,00,000 | Building | 9,00,000 |
| B | 4,00,000 | Sundry Debtors | 2,50,000 |
| Reserves | 5,25,000 | Stock | 3,00,000 |
| Sundry Creditors | 2,75,000 | Cash | 1,50,000 |
| Bills Payable | 1,00,000 | ||
| 21,00,000 | 21,00,000 |
They agreed to admit P and Q into the partnership on the following terms:
(i) The firm’s goodwill to be valued at 2 years’ purchase of the weighted average of the pr1 its’ of tho last 3 years. The relevant figures are:
Year ended 31.03.2014 – Profit ₹ 37,000
Year ended 31.032015- Profit ₹ 40,000
Year ended 31.03.2016 – Profit ₹ 45.000
(ii) The value of the stock and Plant and machinery were to be reduced by 10%.
(iii) The building was to be valued at ₹ 10,11,000.
(iv) There was an unrecorded liability of ₹ 10,000.
(v) A, B. P & Q agreed to share profits and losses in the ratio 3 : 2: 1: 1.
(vi) The value of reserve, the values of liabilities, and the values of assets other than cash were not to be altered.
(vii) P and Q were to bring capitals equal to their shares of Profit considering B’s capita’ as base after all adjustments.
You are required to prepare:
(1) Memorandum Revaluation Account,
(2 Partner’s Capital Accounts and
(3) The Balance Sheet of the newly constructed firm. (June 2018, 15 marks)
Answer:
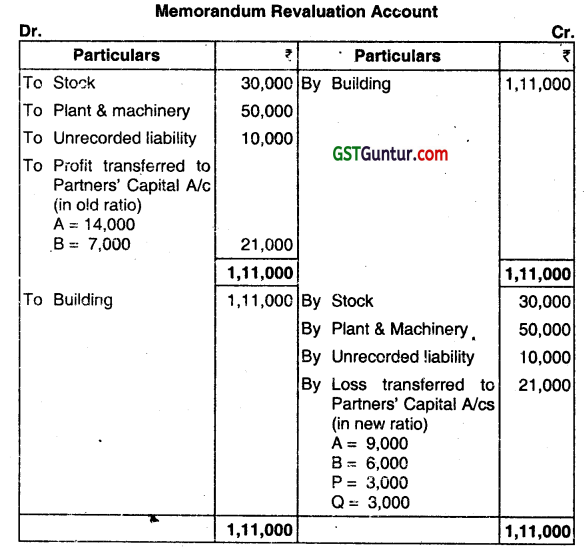

1. Calculation of Goodwill
Weighted Average Profit:
Weighted Average Profit = ₹ 2,52,000/6 = 42,000
Goodwill is valued at 2 year’s purchase
Value of Goodwill: ₹ 42000 x 2 = ₹ 84,000
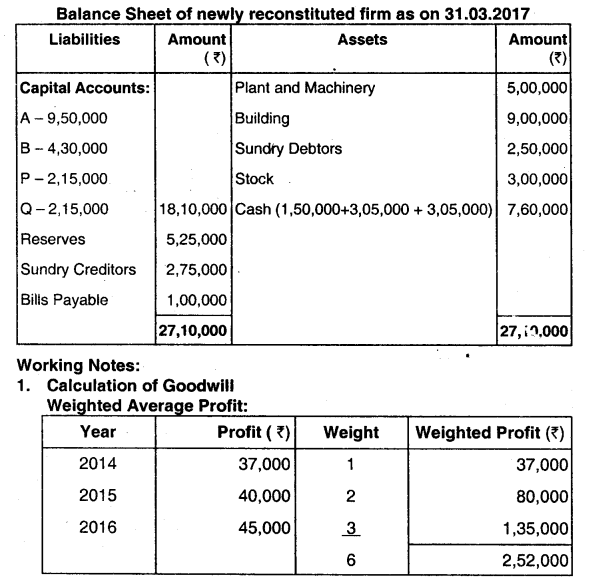

3. Calculation of closing capitals of P and O B’s capital is taken as base. Closing capital of B after all adjustments is ₹ 4,30,000. Total capital of firm will be = 4,30,000 x 7/2 = ₹ 15,05,000
Hence, P’s and O’s closing capital should be ₹ 2,15,000 (15,05,000 x 1/7) each i.e. at par with B (as per new profit and loss sharing ratio)
Question 35.
A, B, and C are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses as 3 : 2: 1. Their Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2018 was as follows:
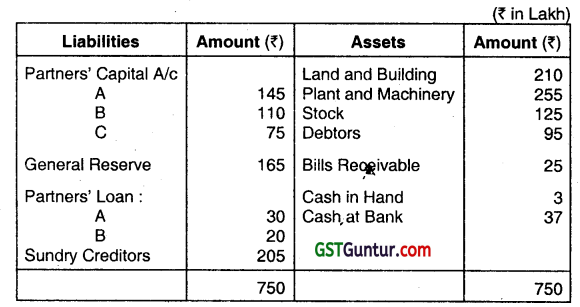
B died on 1st August, 2018. His account is to be settled under the following terms:
(i) Goodwill will be valued at 3 years purchase of last four accounting years average profit. Profits were :2014-15 ₹ 135 Lakh, 2015-16 ₹ 145 Lakh, 2016-17 ₹ 131 Lakh and 2017-18 ₹ 165 Lakh.
(ii) Land and Building will be valued at ₹ 250 Lakh and Plant and Machinery will be valued at ₹ 240 Lakh.
(iii) For the purpose of calculating B’s share in the profits of 01.04.2018 to 31.07.2018, the profits for the year 2017-18 will be taken as base.
(iv) Interest on Partners’ Loan will be calculated @ 6% per annum.
(v) A sum of ₹ 50 Lakh to be paid immediately to B’s Executor and the balance to be paid on 1st December 2018 together with interest @ 10% per annum.
You are required to pass necessary journal entries to record the above transactions and amount payable to B’s Executor’s Account. (Dec 2018, 15 marks)
Answer:
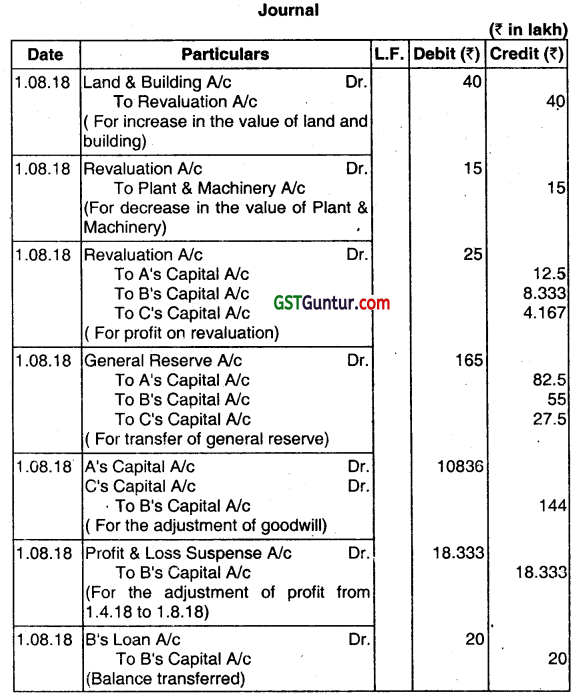

Working Notes:
(1) Calculation of Share of B in GoodwilL
Average of past tour years profits = (₹ 135 Lakh + ₹ 145 Lakh + ₹ 131 Lakh + ₹ 165 Lakh)/4 = ₹ 44 Lakh
Value of Firm’s Goodwill = ₹ 144 Lakh x 3 = ₹ 432 Lakh
B’s Share in Goodwill = ₹ 432 Lakh x 216 = ₹ 144 Lakh,
which will be credited to B’s Capita A/c and Debited to A’s Capital A/c & C’s Capital A/c in the ratio of 3:1
(2) B’s Share in profit f’om 01.04.18 to 1.8.18 = ( ₹165 x 4/12) x 216 = ₹ 18.333 Lakh
(3) Interest on B’s Loan from 01.04.18 to 1.8.18 = ₹ 20 Lakh x 6% x 4/1 = ₹ 40,000
(4) Interest to B’s Executor from 1.08.18 to 1.12.18 = ₹ 356.066 Lakh – ₹ 50 Lakh = ₹ 306.066 x 10% x 4/12 = ₹ 10.2022 Lakh
Question 36.
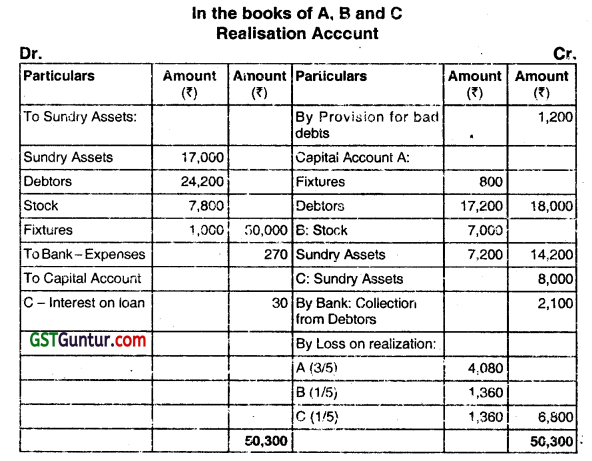
A, B, and C were partners in a firm sharing profits & losses in the ratio of 3:1: 1 agreed upon dissolution of there partnership. They each decide to take over certain assets and liabilities and continue business separately.
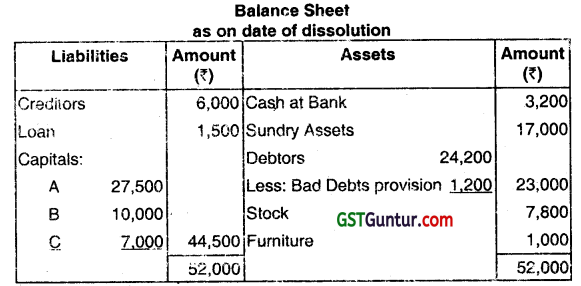
It is agreed as follows:
(i) Goodwill is to be ignored.
(ii) A is to take over all the Fixtures at ₹ 800; Debtors amounting to ₹ 20,000 at ₹ 17,200. The creditors of ₹ 6,000 to be assumed by A at that figure.
(iii) B is to take over all the stocks at ₹ 7,000 and certain of the sundry assets at ₹ 7,200 (being book value less 10%).
(iv) C takes over the remaining sundry assets at 90% of book values less ₹ 100 allowances and assumes responsibility for the discharge ot the loan, together with accruing interest of ₹ 30 which has not been recorded in the books of the firm.
(v) The expenses of dissolution were ₹ 270. The remaining debtors were sold to a debt-collecting agency for 50% of book values. Prepare Realisation Account, partners’ Capital Accounts, and Bank Account. (June 2019, 15 marks)
Answer:


![]()
Question 37.
The Balance Sheet of X and Y who shares profits and losses in the ratio of 3: 2, at 31 March, 2019 was as follows:
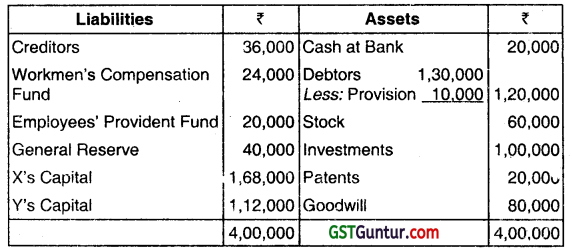
They decided to admit Z on that date for 1/4th share on the followng terms:
(a) New Profit sharing ratio will be 6 : 9: 5. Z is to bring in capita equal to 1/4th of the total capital of the new firm.
(b) Goodwill of the firm is to be valued at 4 years, purchase of the average super profits of the last three years. Average profits of the last three years are ₹ 70,000 while the normal profits that can be earned with the
capital employed are 30000. No Goodwill is to appear in the books. Z brings in ₹ 24,000 cash out of his share of Goodwill.
(c) Patents to be written down to ₹ 3,000 and Stock is undervalued by ₹ 2,000. 20% of General Reserve to be transferred to Provision for Doubtful Debts. ₹ 9,000 included ¡n Sundry Creditors be written back as
no longer payable.
(d) Out of the amount of insurance which was debited entirely to P & L A/c, ₹10,000 be carried forward as an Unexpired Insurance. Unaccounted Accrued Income of ₹ 2,000 to be provided for. A debtor whose dues of
₹ 10,000 were written off as Bad Debts paid 80% ¡n full settlement. A claim of ₹ 6,000 on account of workmen’s compensation to be provided for.
(e) The market value of investments was ₹ 90,000. Half of the investments were to be taken over by old partners in their old profit-sharing ratio. Prepare Revaluation Account, Capital Accounts of the Partners and the
Balance Sheet of new firm. (Dec 2019, 15 marks)
Answer:
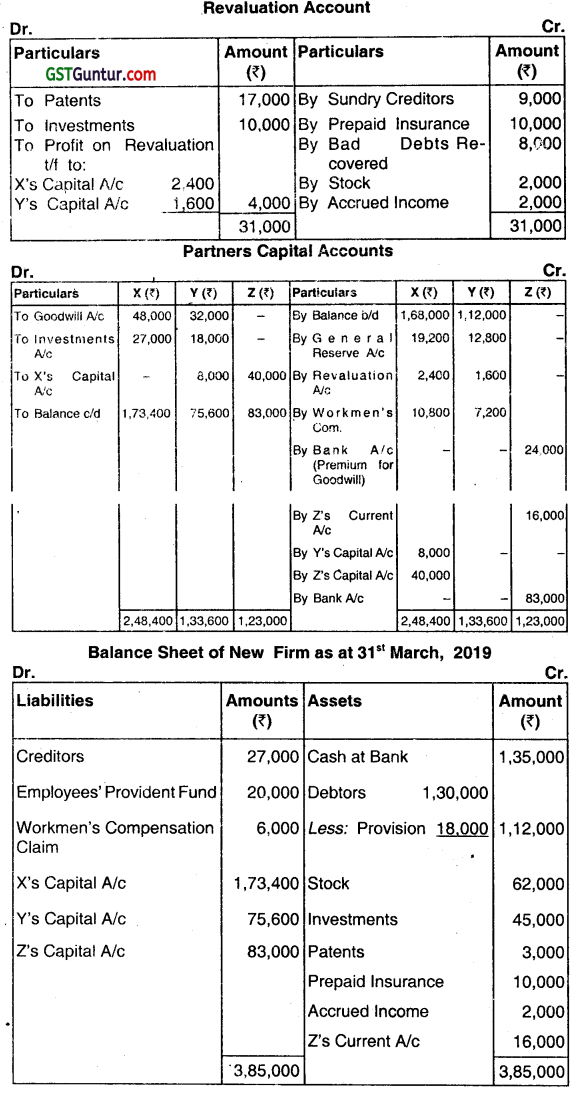
Working Notes
1. X’s sacrifice = 3/5 – 6/20 = 6/20, Y’s gain = 2/5 – 9/20 = (1/20)
2. Firm’s Goodwill = Super Profits × 4 = (₹ 70,000 – ₹ 30,000) × 4 = ₹ 1,60,000
3. Z’s Share of Goodwill = ₹ 1,60,000 x 1/4 = ₹ 40,000
4. Ys Share of Goodwill = ₹ 1 ,60,000 x 1/20 = ₹ 8,000
5. Z’s New Capital (₹ 1,73,400+ ₹ 7600)x 1/3 = ₹ 83,000
Question 38.
X and Y were Partners sharing profit/losses as 3:2. They admit Z as a new partner, giving him 1/5th share of future profits. What should be the new profit-sharing ratio? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
12:8:5
Question 39.
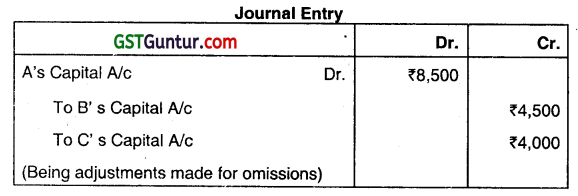
The partners of a firm distributed the profits for the year ended 31/3/2021 ₹ 90,000 in the ratio of 3:2:1 without providing for the following adjustments.
(i) A and B were entitled to a salary of ₹ 1,500 each per annum.
(ii) B was entitled to a Commission of ₹ 4,500.
(iii) B&C had guaranteed a minimum profit of ₹ 35,000 P.a to A.
(iv) Profits were to be shared in the ratio of 3:3:2
Pass the necessary journal entries for the above adjustments in the Books of the Firm. (Dec 2021, 6 marks)
Answer:
Question 40.
X & Y are partners. They decided to dissolve their firm. Pass necessary entries assuming that various assets and external liabilities have been transferred to the Realisation account.
(i) X’s loan(partner) was appearing on the liability side of the balance sheet at ₹ 30,000. He accepted an unrecorded asset of ₹ 50,000 in full settlement of his account.
(ii) Runa, a creditor, to whom ‘ ₹ 30,000 were due to be paid, accepted an unrecorded computer of ₹ 20,000 at a discount of 10%, and the balance was paid to him in cash.
(iii) Suman, an unrecorded creditor of ₹ 45,000, accepted an unrecorded motor car of ₹ 30,000 at 35,000, and the balance was paid to him in cash.
(iv) There was a contingent liability in respect of bills discounted but not matured ₹ 30,000.
(v) Furniture of ₹ 15,000 and goodwill of ₹ 20,000 were appearing in the balance sheet but no other information was provided regarding these two items. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
(i) Debit X’s loan account and credit realisation account by ₹ 30,000
(ii) Debit realisation account and credit bank account by ₹ 12,000
(iii) Debit realisation account and credit bank account by ₹ 10,000
(iv) No entry.
(v) No entry.
Question 41.
P, Q, R, and S are sharing profits and losses in the ratio 3 : 3 : 2: 1. Frauds committed by R during the year were found out and it was decided to dissolve the partnership on 31st March, 2019 when their Balance Sheet was asunder:
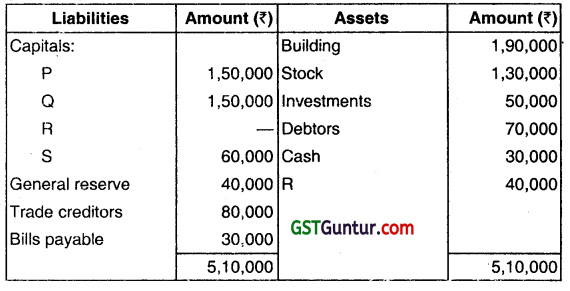
Following information is given to you:
(i) A cheque for ₹ 7,000 received from debtor was not recorded in the books and was misappropriated by R.
(ii) Investments costing ₹ 8,000 were sold by R at ₹ 11,000 and the funds transferred to his personal account. This sale was omitted from the firm’s books.
(iii) A creditor agreed to take over investments of the book value of ₹ 9,000 at ₹ 13,000. The rest of the creditors were paid off at a discount of 5%.
(iv) The other assets realized as follows:
Building:110% of book value
Stock: ₹ 1,20,000
Investments: The rest of investments were sold at a profit of ₹ 7,000
Debtors: The rest of the debtors were realized at a discount of 10%.
(v) The bills payable were settled at a discount of ₹ 500.
(vi) The expenses of dissolution amounted to ₹ 8,000.
(vii) It was found out that realization from Rs private assets would only be ₹ 7,000.
Prepare Realization Account, Cash Account and Partner’s Capital Accounts. All workings should part of your answer. (Dec 2022, 15 marks)
Partnership Accounting CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Admission of Partner
Partners of a continuing business may, by common consent, decide to admit a new partner for additional capital, technical skill or managerial efficiency.
Valuation of Inherent or Non-Purchased Goodwill
- Average Profits Methods
- Super Profits Method
- Capitalization of Profits Methods
- Annuity Method
Retirement of Partner
A Partner may leave the firm by taking retirement., Normally the retirement takes place by consent of all the partners and! or by other mode of communication by the intended Partner to all other partners.
Death of Partner
If a partner dies, the partnership is usually dissolved. But if the surviving partners desire so, they may purchase the share of the deceased partner and carry on the business. In that case, they have to decide (1) the total amount payable to the legal representative or executor of the deceased partner and (2) the mode of such payment.
Dissolution of a Partnership Firm
Whenever a reconstitution takes place within a Partnership in the form of admission, retirement or death of a Partner, the existing partnership is dissolved. The Partnership firm, may, however, continue, if the remaining partners desire so. But if the partnership firm is discontinued for any reason, that is called Dissolution of the firm.
![]()
Insolvency of a Partner
If a partner becomes insolvent and fails to pay his debit balance of Capital A/c either wholly or in part, the unrecoverable portion is a loss to be borne by the solvent partners.
The decision in Garner vs. Murray Case
Unless otherwise agreed, the decision in Gamer vs. Murray requires:
- That the solvent partners should bring in cash equal to their respective shares of the loss on realization;
- That the solvent partners should bear the loss arising due to the insolvency of a partner in the ratio of their Last Agreed Capitals.