Lease Accounting – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Lease Accounting – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short note:
Operating Lease and Finance Lease (Dec 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Operating Lease and Finance Lease
A lease is an agreement whereby the lessor conveys to the lessee in return for a payment or sones of payments the right to use an asset for an agreed period of time.
A finance lease is a lease that transfers substantially all the risks and rewards incidental to ownership of an asset. Title may or may not eventually be transferred.
An operating lease is a lease other than a finance lease. As per AS 19, a lease is classified as a finance lease if it transfers substantially all the risks and rewards incidental to ownership. A lease is classified as an operating lease if it does not transfer substantially all the risks and rewards incidental to ownership.
Question 2.
Write short note:
Finance Lease (June 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Finance Lease:
It is a lease, which transfers substantially all the risks and rewards incidental to ownership of an asset to the Lessee by the Lessor but not the legal ownership. In following situations, the lease transactions are called Finance Lease.
- The lessee will get the ownership of leased asset at the end of the lease term.
- The lessee has an option to buy the leased asset at the end of term at price, which is lower than its expected fair value at the date on which option will be exercised.
- The lease term covers the major part of the life of asset.
- At the beginning of lease term, present value of minimum lease rental covers substantially the initial fair value of the leased asset.
- The asset given on lease to lessee is of specialized nature and can only be used by the lessee without major modification.
Descriptive Questions
Question 3.
Answer the following:
State the types of lease to which AS-19 are not applicable. (June 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
The Accounting Standard AS-19 is not applicable to the following types of Lease:
- Lease agreement to explore natural resources such as oil, gas, timber, metal and other material rights;
- Licensing agreements for motion picture film, video recording, Plays, manuscripts, patents and other rights;
- Lease agreement to use land.
![]()
Practical Questions
Question 4.
Kovid Limited has taken a Machinery on Lease from Krishna Limited.
The following information are provided by Kovid Limited:
Lease Term 5 years
Fair value at inception of Lease ₹ 20 Lakhs
Lease Rent ₹ 5 Lakhs per annum payable at the end of the year
Expected Residual value ₹ 3 Lakhs
Guaranteed Residual value ₹ 2 Lakhs
Implicit Interest rate 15.5% per annum
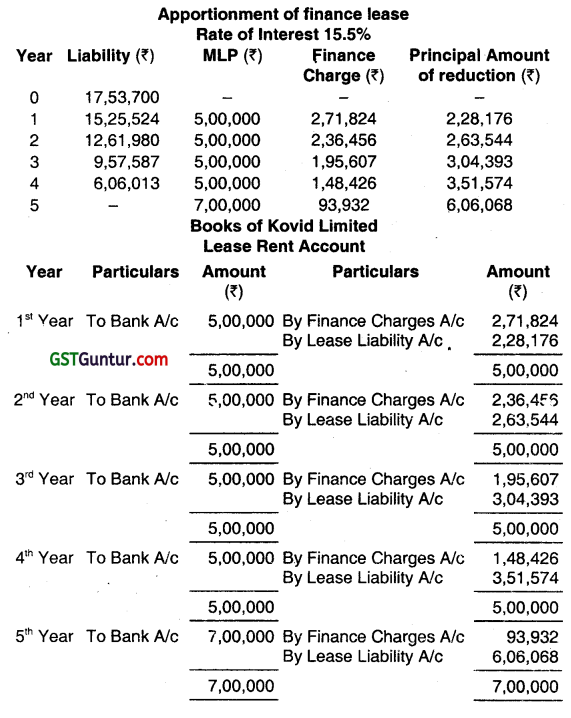
You are required to prepare Lease Rent Account and Lease Liability Account in the Books of Kovid Limited. (The present value of Re. 1 at Discount rate of 15.5% are 0.8658, 0.7496, 0.6490, 0.5619 and 0.4865 for year it year 5 respectively.) (Dec 2013, 8 marks)
Answer:
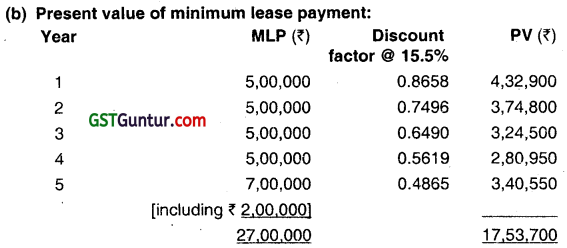
Present value of minimum lease payment (₹ 17,53,700) is less than fair value at the inception of lease ( ₹ 20,00,000) so the leased asset and liability should be recognized at ₹ 17,53,700.

Question 5.
Answer the question:
(a) Makkhu Limited leased a machine to Gunu Limited on the following terms:
(i) Fair value of the machine ₹ 72 lakhs
(ii) Lease term 5 years
(iii) Lease rental per annum ₹ 12 lakhs
(iv) Guaranteed residual value ₹ 2.40 lakhs
(v) Expected residual value ₹ 4.50 lakhs
(vi) Internairateot return 15%
Discounted rates at 15% for? 1, 1st year to 5th year are 0.8696, 0.7561, 0.6575, 0.5718 and 0.4972 respectively. Ascertain Unearned Finance Income. (June 2015, 8 marks)
Answer:
As per AS-19 on leases, unearned finance income is the difference between
(a) the gross investment in the lease and
(b) the present value of minimum lease payment under the finance lease from the standpoint of the lessor,
and any unguaranteed residual value accruing to the lessor, at the interest rate implicit in the lease.
where:
(a) Gross investments in the lease Is the aggregate of:
(i) minimum lease payments from the standpoint of the lessor and
(ii) any unguaranteed residual value accruing to the lessor.
Gross investment = Minimum Lease Payments + Unguaranteed Residual Value
= Total lease rent + Guaranteed Residual Value (GRV) + Unguaranteed Residual Value (URV)
= (12,00000 × 5) + 2,40,000 + 2,10,000
= 64,50,000 (a)
(b) Table showing present value of (1) Minimum Lease Payments (MLPs) and Unguaranteed Residual Value (URV):
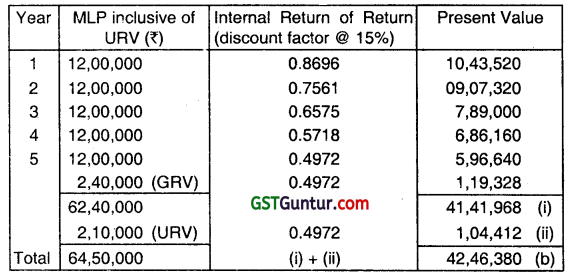
Unearned finance income = (a) – (b)
= 64,50,000 – 42,46,380
= 22,03,620
Question 6.
Answer the question:
Classify the following into either Operating or Financial Lease (briefly give you reasoning):
1. Lessee has option to purchase the asset at lower than fair value, at the end of lease term. It is certain that the lessee will exercise the option
2. Economic life of the asset is 7 years, lease term is 6 years, but asset is not acquired at the end of lease term.
3. Economic life of the asset is 6 years, lease term is 2 years, but the asset is of special nature and has been procured only for use of the lessee.
4. Present value of minimum lease payment = X. Fair value of the asset = Y. (Dec 2015, 8 marks)
Answer:
- Finance lease if it becomes certain at the inception of lease itself that the option will be exercised by the lease that also at a price which is lower than its expected fair value.
- Finance lease, since a substantial portion of the life of the asset is covered by lease term.
- Finance lease since the asset is procured only for the use of lessee.
- Finance lease since at the beginning of the lease term, present value of minimum lease rental covers substantially the initial fair value of the leased asset. Where X is minimum tease rental and Y is initial fair value.
Question 7.
X Ltd. has leased equipment over its useful life that costs ₹7,46,55,100 for a three year lease period. After the lease term the asset would revert to the Lessor. You are informed that:
(i) The estimated unguaranteed residual value would be? 1 lakh only.
(ii) The annual lease payments have been structured in such a way that the sum of their present values together with that of the residual value of the asset will equal the cost thereof.
(iii) Implicit interest rate is 10%.
You are required to ascertain the annual lease payment and the unearned finance income P.V. factor @ 10% for years 1 to 3 are 0.909, 0.826, and 0.751 respectively. (June 2016, 6 marks)
Answer: .
Calculation of lease rental:
Cost of Assets
= Present value of lease rental + Present value of residual valued
7,46,55,100 = 2.486x + .751 × 1,00,000
7,46,55,100 -75,100 = 2.486x
\(\frac{7,45,80,000}{2.486}\) = x
x = 3,00,00,000
Calculation of Unearned Financial Income:
Gross investment – Net investment
[(3,00,00,000 x 3) + 1,00,000] – 7,46,55,1 00
9,01,00,030 – 7,46,55,100
1,54,44,900
![]()
Question 8.
M Ltd. sold machinery having WDV of ₹ 200 Lakhs to N Ltd. for ₹ 250 Lakhs and the same machinery was leased back by N Ltd. to M Ltd. The leaseback is an operating lease. Comment on the accounting treatment as per AS 19 in the following circumstances:
(i) Fair value is ₹ 230 Lakhs and sale price is ₹ 250 Lakhs
(ii) Fair value is ₹ 175 Lakhs and sale price is ₹ 195 Lakhs (June 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) Profit of ₹ 30 Lakhs (230 Lakhs – 200 Lakhs) to be immediately recognised in its books and balance profit of ₹ 20 Lakhs (250 Lakhs – 230 Lakhs) is to be amortized/deferred over lease period.
(ii) Loss of ₹ 25 Lakhs (200 Lakhs – 175 Lakhs) to be immediately recognised by M Ltd. in its books and profit of ₹ 20 Lakhs (195 Lakhs – 175 Lakhs) should be amortised/deferred over lease period.
Question 9.
A Ltd. has taken the assets on lease from X Ltd. The following information is given below:
Lease Term = 3 years
Fair value at inception of lease = ₹ 14,00,000
Lease Rent = ₹ 6,00,000 p.a. at the end of each year
Guaranteed Residual Value = ₹ 44,000
Implicit Interest Rate 15% p.a.
Calculate the value of the asset to be considered by A Ltd. and the interest (finance charges) in each year. Present value of ₹ 1.00 at 15% is given below.
| Year | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| PVIF (15%) | 0.869 | 0.756 | 0.657 |
(June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Calculation of Present value of Minimum Lease Payments:
| Year (end) | MLP (₹) | PVIF at 15% | Present Value (₹) |
| 1 | 6,00,000 | 0.869 | 5,21,400 |
| 2 | 6,00,000 | 0.756 | 4,53,600 |
| 3 | 6,44,000(6,00.000+44,000) | 0.657 | 4,23,108 |
| 13,98,108 |
Value of the asset will be the lower of fair value at the inception of lease and present value of MLP plus residual value. Therefore, the value of the asset will be ₹ 13,98,108.
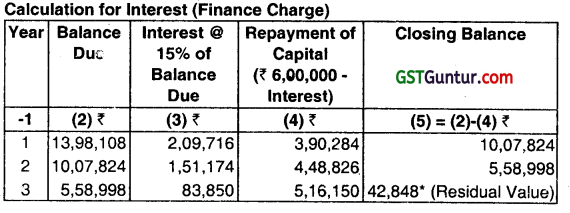
(Alternative Calculation)
| Year | Liability (₹) | MLP (₹) | Finance Charge (₹) | Principle Amt. of reduction (₹) |
| 1 | 13,98,108 | – | – | – |
| 2 | 10,07,824 | 6,00,000 | 2,09,716 | 3,90,284 |
| 3 | 5,58,998 | 6,00,000 | 1,51,174 | 4,48,826 |
| 4 | – | 6,44,000 | 83,850 | 5,60,150 |
Note: The difference between this figure and the guaranteed residual value (as per the problem) is due to approximation.
Question 10.
L Ltd. leased a machine to T Ltd. on the following terms:
| Particulars | (₹ In Lakhs) |
| (i) Fair Value of the machine | 72 |
| (ii) Lease Term | 5 Years |
| (iii) Lease rental per annum | 12 |
| (iv) Guaranteed residual value | 2.4 |
| (v) Expected residual value | 4.5 |
| (vi) Internal Rate of return | 15% |
Discounted rates @ 15% for 1 year to 5th year are 0.8696, 0.7561, 0.6575, 0.5718 and 0.4972 respectively.
From the above calculate
(i) Gross investment in the lease
(ii) Unearned Finance Income. (Dec 2021, 6 marks)
Answer:
As per AS-19 on leases, unearned finance income is the difference between
(a) the gross investment in the lease and
(b) the present value of minimum lease payment under the finance lease from the standpoint of the lessor,
and any unguaranteed residual value accruing to the lessor, at the interest rate implicit in the lease.
where:
(a) Gross investments in the lease Is the aggregate of:
(i) minimum lease payments from the standpoint of the lessor and
(ii) any unguaranteed residual value accruing to the lessor.
Gross investment = Minimum Lease Payments + Unguaranteed Residual Value
= Total lease rent + Guaranteed Residual Value (GRV) + Unguaranteed Residual Value (URV)
= (12,00000 × 5) + 2,40,000 + 2,10,000
= 64,50,000 (a)
(b) Table showing present value of (1) Minimum Lease Payments (MLPs) and Unguaranteed Residual Value (URV):

Unearned finance income = (a) – (b)
= 64,50,000 – 42,46,380
= 22,03,620
Lease Accounting CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Lease
A lease is an agreement whereby the lessor conveys to the lessee in return for a payment or series of payments the right to use an asset for an agreed period of time.
Finance Lease
A finance lease is a lease that transfers substantially all the risks and rewards incident to ownership of an asset.
Operating Lease
An operating lease is a lease other than a finance lease.
Fair Value
Fair value is the amount for which an asset could be exchanged or a liability settled between knowledgeable, willing parties in an arm’s length transaction.
Economic Life
Economic life is either: (a) the period over which an asset is expected to be economically usable by one or more users; or (b) the number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the asset by one or more users.
Useful Life
Useful life of a leased asset is either: (a) the period over which the leased asset is expected to be used by the lessee; or (b) the number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the use of the asset by the lessee.
![]()
Residual value
Residual value of a leased asset is the estimated fair value of the asset at the end of the lease term.
Gross Investment In the Lease
Gross investment in the lease is the aggregate of the minimum lease payments under a finance lease from the standpoint of the lessor and any unguaranteed residual value accruing to the lessor.
Net Investment
Net investment in the lease is the gross investment in the lease less unearned finance income.
Contingent Rent
Contingent rent is that portion of the lease payments that is not fixed in amount but is based on a factor other than just the passage of time (e.g., percentage of sales, amount of usage, price indices, market rates of
interest).
Leases are classified into two types:
Finance Lease
A lease is classified as a finance lease if it transfers substantially all the risks and rewards incident to ownership. Title may or may not eventually be transferred.
Operating Lease
A lease is classified as an operating lease if it does not transfer substantially all the risks and rewards incident to ownership.
Sale and Leaseback Transactions
A sale and leaseback transaction involves the sale of an asset by the vendor and the leasing of the same asset back to the vendor. The lease payments and the sale price are usually interdependent as they are negotiated as a package.