Preparation of Financial Statements of Commercial Organisations – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Preparation of Financial Statements of Commercial Organisations – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short note on the following:
Provision for Discount on Debtors (June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Provision for Discount on Debtors:
We know that cash discount is allowed by the suppliers to customers for prompt settlement of cash. Naturally a provision is created for this purpose. Thus, the provision which is created on Sundry Debtors for allowing discount on receipt of cash in that accounting period is called Provision for Discount on Debtors. It is needless to say that if the customer pays their debts before the due dates, they may claim discounts and that ¡s why discount is allowed to debtors for prompt settlement Is an usual practice.
Where goods are sold on credit, debtors accounts are debited but the amount may not be realized in this same accounting periods. Naturally, a possible aim is to allow discount whether cash is received. The same will happen in the next accounting period. Due to this reason a provision for discount on debtors is made on the basis of past experience at an estimate rate on Sundry Debtors. Care should be taken while calculating discounts. Discount should be calculated at a specified rate on of debtors (i.e. after discounting bad debts and provision for bad debts).
Descriptive Questions
Question 2.
Form presentation of financial statements is known as Horizontal” form or “Vertical” form. (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Horizontal form.
![]()
Practical Questions
Question 3.
On 1st April, 2013 the balance of provision for bad and doubtful debts was ₹ 13,000. The bad debts during the year 2013-14 were ₹ 9,500. The sundry debtors as on 31st March, 2014 stood at ₹ 3,25,000 out of these debtors of ₹ 2,500 are bad and cannot be realized. The provision for bad and doubtful debts is to be raised to 5% on sundry debtors.
(i) Pass necessary adjustment entries for bad debts and its provision on 31st March, 2014.
(ii) Prepare the necessary ledger accounts.
(iii) Show the relevant items in the profit and loss account and Balance Sheet. (June 2014, 3+3+2 = 8 marks)
Answer:
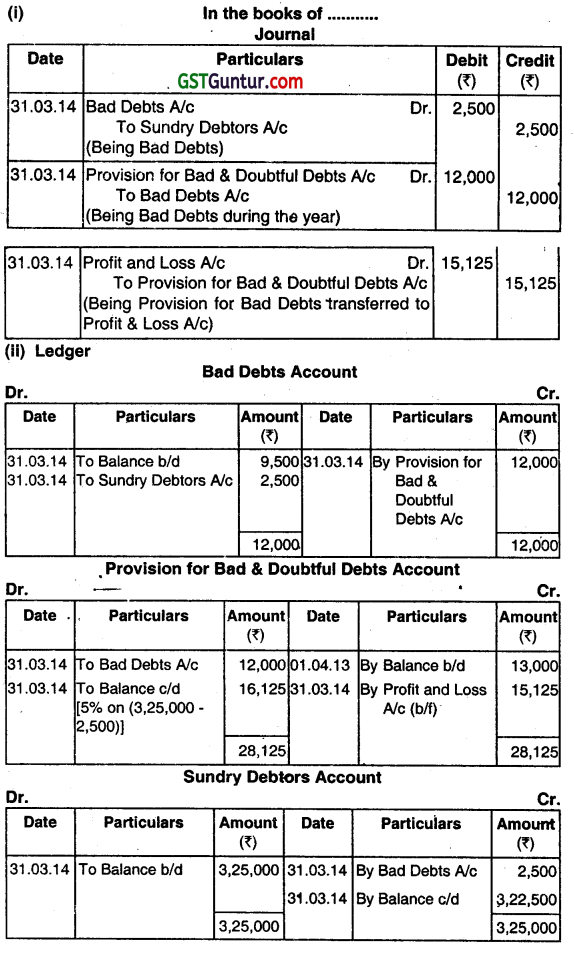

Question 4.
Answer the following question.
The following details are abstracted from the record of VENELA LTD. for the year ended March 31st, 2016.
| Net Working Capital | ₹ 35,00,000 |
| profit before Tax | ₹ 25,00,000 |
| The Current Ratio | 2.4:1 |
You are required to calculate the amount of Current Assets of Venela Ltd. for Ihe year ended March 31,2016. (June 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Net Working Capital
= Current Assets (C.A) – Current Liabilities (C.L) = 35,00,000
Or, C.A – C.L = ₹ 35,00,000 Equation (i)
Again Current Ratio = \(\frac{C.A}{C.L}=\frac{2.4}{1} \) = 2.4 C.L
Or, CA. – 2.4 C.L = 0 ……………………. Equation (ii)
After multiplying (i) with 2.4 we get
2.4 C.A -2.4 C.A = ₹ 84,00,000 ……………………… Equation (iii)
∴ [ (iii) – (ii) ] –

Hence, Current Assets of Venela Ltd. = ₹ 60,00,000
![]()
Question 5.
M/S ADHUNA & CO. had a provision for Bad Debts of ₹ 13,000 against their book debts on 15th April, 2015. During the year ended 31st March 2016, ₹ 8,500 proved irrecoverable and it was desired to maintain the provision for bad debts @5% on Debtors which stood at ₹ 3,90,000 before writing off Bad Debts. Prepare the provision for Bad Debt Account for the year ended March 31, 2016. (Dec 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
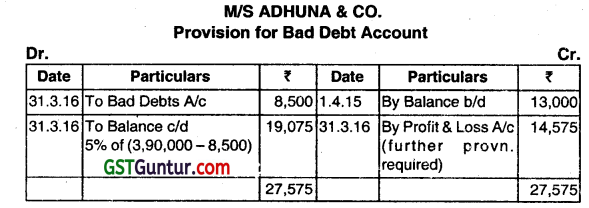
Question 6.
A company maintains its reserve for bad debts @ 5% and a reserve for discount on debtors @ 2%. You are given the following details:
| Particulars | 2016 | 2017 |
| Bad debts | 800 | 1,500 |
| Discount allowed | 1,200 | 500 |
| Sundry debtors (before providing all bad debts and discounts) | 60,000 | 42,000 |
On 01/01/2016, Reserve for bad debts and Reserve of discount on debtors had balances of ₹ 4,550 and ₹ 800 respectively. Show Reserve for Bad Debts and Reserve for Discount on Debtors Account for the years 2016 and 2017. (June 2018, 7 marks)
Answer:
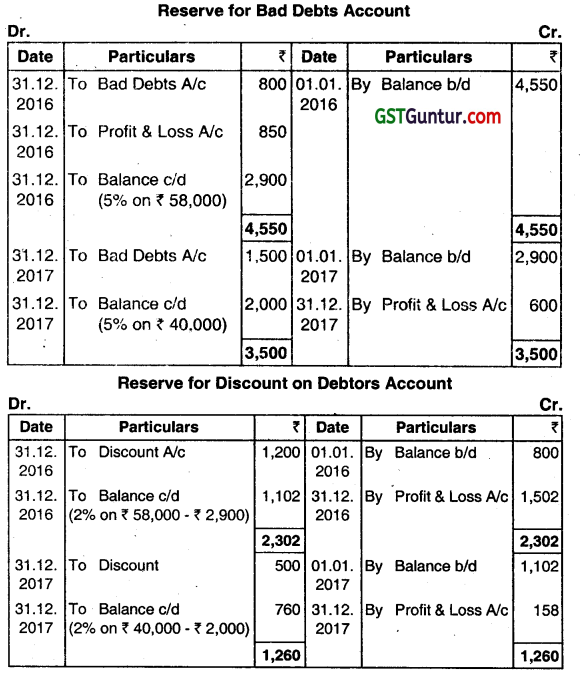
Question 7.
Following is the Trial Balance as on 31 March, 2019 of Bajrang Traders:
| Particulars | Debit (₹) | Credit (₹) |
| Stock on 01 .04.2018 | 1,35,000 | |
| Purchases and Sales | 28,50,000 | 46,25,000 |
| Returns | 35,000 | 22,500 |
| Carriage Inwards | 24,000 | |
| Carriage Outwards | 33,000 | |
| Wages | 1,25,000 | |
| Salaries | 3,52,000 | |
| Printing and Stationery | 6,500 | |
| Insurance Premium | 15,000 | |
| Repairs | 11,000 |
| Discounts Allowed | 30,500 | |
| Discounts Received | 15,500 | |
| Bad Debts | 28,000 | |
| Provision for Bad Debts | 35,000 | |
| Advertisement | 38,000 | |
| Interest on Investment | 42,000 | |
| Drawings | 2,10,000 | |
| Investment | 8,00,000 | |
| Furniture and Fixtures | 3,50,000 | |
| Office Equipments | 2,45,000 | |
| Land and Building | 15,00,000 | |
| Sundry Debtors and Creditors | 6,90,000 | 4,55,000 |
| Establishment Expenses | 35,000 | |
| Capital | 31,05,000 | |
| Cash at Bank | 7,24,000 | |
| Cash in Hand | 63,000 | |
| Total | 83,00,000 | 83,00,000 |
Additional Information:
(i) Closing Stock of goods amounted to ₹ 1,85,000 and of stationery amounted to ₹ 1,500.
(ii) Depreciation to be charged on Land and Building @ 10%; On Office Equipments @ 15%; and On Furniture and Fixtures @ 10%.
(iii) Insurance Premium paid on 1st July 2018 for one year.
(iv) Write off further as bad debts ₹ 5,000 and maintain a provision for bad debts of 5% on debtors.
(v) Provision made for discount on debtors @ 2%.
(vi) Goods costing ₹ 12,500 used for given free samples to customers.
(vii) Goods costing ₹ 25,000 were sent on approval basis to a customer for ₹ 40,000 on 26th March, 2019. This was recorded as actual sales but approval did not received till 31st March, 2019.
(viii) Outstanding salaries were for one month.
(ix) Investment made at 7.50% per annum on 1st May, 2018.
You are required to prepare Trading Account and Profit & Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2019 and a Balance Sheet as on that date. (June 2019, 15 marks)
Answer:
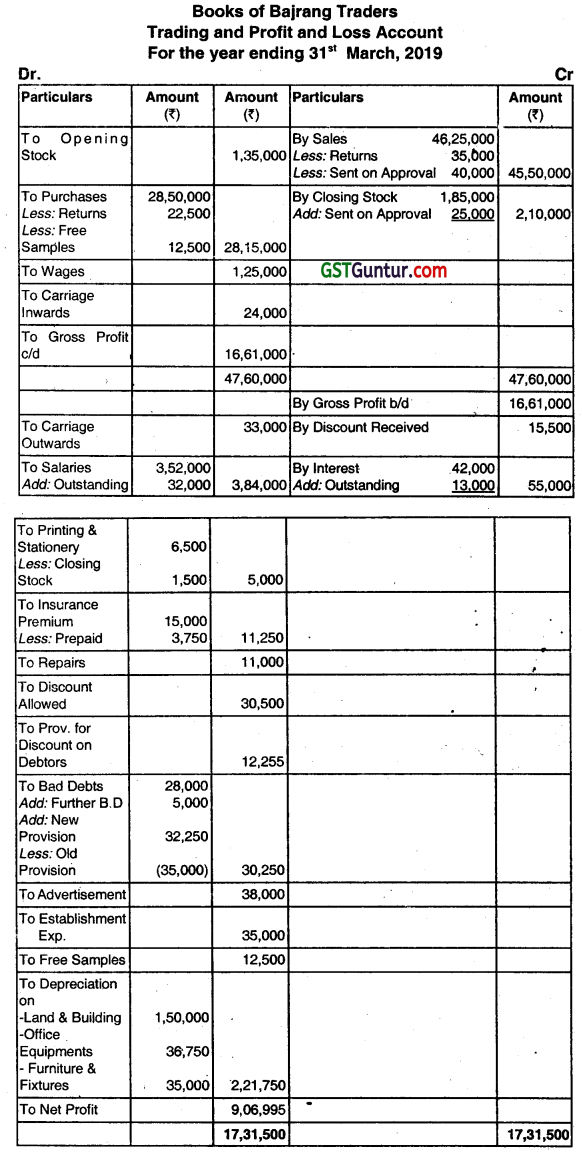

Working Notes:
(i) Prepaid Insurance Premium from 1.4.19 to 30.6.19= ₹ 15,000 × 3/12 = ₹ 3,750.
(ii) Outstanding Interest on Investment:
Total Interest (1.5.18 to 31.3.19) = ₹ 8,00,000 × 7.50% x 11/12 = ₹ 55,000
Outstanding = ₹ 55,000 – ₹ 42,000 = ₹ 13,000.
![]()
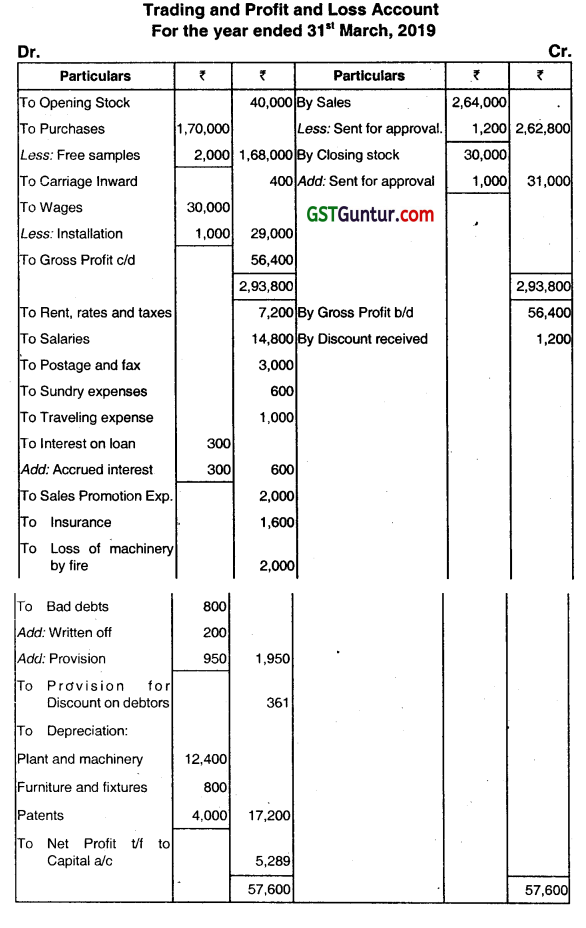
Question 8.
From the following Trial Balance of Bharat Tushar as on 31st March, 2019, you are required to prepare a Trading and Profit & Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2019 and Balance Sheet as on that date, after making the necessary adjustment as mentioned here under:
| Particulars | Debit Balance (₹) | Credit Balance (₹) |
| Capital and Drawings | 24,000 | 1,60,000 |
| Furniture and Fixtures | 8,000 | – |
| Plant and Machinery | 60,000 | – |
| Patents (ten years from 01.04.2018) | 40,000 | – |
| Opening Stock | 40,000 | – |
| Purchases and Sales | 1,70,000 | 2,64,000 |
| Salaries | 14,800 | – |
| Wages | 30,000 | – |
| Sundry Debtors and Creditors | 20,400 | 24,000 |
| Land | 28,350 | – |
| Loan from Shyam (at 6% from 01.10.2018) | – | 20,000 |
| Postage and Fax | 3,000 | – |
| Rent, Rates and Taxes | 7,200 | – |
| Bad Debts | 800 | – |
| Discount | – | 1,200 |
| Carriage Inward | 400 | – |
| Interest on loan | 300 | – |
| Insurance | 1,600 | – |
| Traveling expenses | 1,000 | – |
| Sundry expenses | 600 | – |
| Cash and Bank | 33,750 | – |
| Bank Overdraft | 15,000 | – |
| Total | 4,84,200 | 4,84,200 |
Adjustments:
(a) Closing Stock is valued at 30,000.
(b) A new machine was installed on 1st April, 2018 for ₹ 3000. No entry in this respect was passed in the books. Wages’of ₹ 1,000 paid for installing the machine were debited to Wages Account.
(c) Of the Sundry Debtors,₹ 200 are bad and are to be written off. You are required to maintain a Provision for Doubtful Debts @ 5% on Debtors and Provision for Discount on Debtors @ 2%.
(d) Goods costing ₹ 2,000 were given away as free samples for publicity.
(e) Depreciate Plant and Machinery at 20% per annum and Furniture and Fixture at 10% per annum.
(f) On 01.04.2018 Machinery of the value of ₹ 10,000 was destroyed by fire and the insurance claim settled at ₹ 8,000 was credited to Machinery Account.
(g) Goods for ₹ 1,200 were sent to a customer at a profit of 20% on cost on 30th March, 2018 on sale or return basis. This was recorded as actual sales. (Dec 2019, 15 marks)
Answer:

Preparation of Financial Statements of Commercial Organisations CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Profitability Statement
This statement is related to a complete accounting period. It shows the outcome of business activities during that period in a summarized form.
![]()
Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet shows the list of resources and the funding of the resources e. assets and Iiabihties (towards owners and outsiders).
Trading Account.
It is an account which is prepared by a merchandising concern which purchases goods and sells the same during a particular period. The purpose of it to find out the gross profit or gross loss which is an important indicator of business efficiency.
Direct expenses
It means all those expenses which are incurred from the time of purchases to making the goods in suitable condition.
Capital
This indicates the initial amount the owner or owners of the business contributed.
Reserves and Surplus
The business is a going concern and will keep making profit or loss year by year. The accumulation of these profit or loss figures (called as surpluses) will keep on increasing or decreasing owners’ equity.
Long-Term or Non-Current Liabilities
These are obligations which are to be settled over a longer period of time say 5-10 years.
Short-Term or Current Liabilities
A liability shall be classified as Current when it satisfies any of the following:
- It is expected to be settled in the organization’s normal Operating Cycle,
- It is held primarily for the purpose of being traded,
- It is due to be settled within 12 months after the Reporting Date.
Fixed Assets
These represent the facilities or resources owned by the business for a longer period of time. The basic purpose of these resources is not to buy and sell them but to use for future earnings. The benefit from use of these assets is spread over a very long period.
Investments
These are funds invested outside the business on a temporary basis.
Current Assets
An asset shall be classified as Current when it satisfies any of the following:
- It is expected to be realized in, or is intended for sale or consumption in the organization’s nórmal Operating Cycle,
- It is held primarily for the purpose of being traded,
- It is due to be realised within 12 months after the Reporting Date, or
- It is Cash or Cash Equivalent unless it is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a Liability for at least 12 months after the Reporting Date.
Stocks
This includes stork ot raw material, semi-finished goods or WIP, and finished goods.
Debtors
They represent customer balances which are not paid. The bad debts or a provision for bad debt is reduced from debtors and net figure is shown in balance sheet.
Bills receivables
Credit to customers may be given based on a bill to be signed by them payable to the business at an agreed date in future.
Cash in Hand
This represents cash actually held by the business on the balance sheet date.
Cash at Bank
Dealing through banks is quite common. Funds held as balances with bank are also treated as current asset, as it is to be applied for paying to suppliers.
Prepaid Expenses
They represent payments made against which services are expected to be received in a very short period.
Advances to suppliers
When amounts are paid to suppliers In advance and goods or services are not received till the balance sheet date, they are to be shown as current assets.
![]()
Bad Debts
Bad debts are uncollectible or irrecoverable debt or debts which are impossible to collect is called Bad Debts.
Doubtful Debts
The debts which will be receivable or cannot be ascertainable at the date of preparing the final accounts (i.e., the debts which are doubtful to realize) is known as doubtful debts.
Good Debts
The debts which are not bad Le., there is neither any possibility of bad debts nor any doubts about its realization, is called good debts. As such, no provision is necessary for it.