E-Commerce, M-Commerce, and Emerging Technologies – CA Inter EIS Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
E-Commerce, M-Commerce, and Emerging Technologies – CA Inter EIS Question Bank
Question 1.
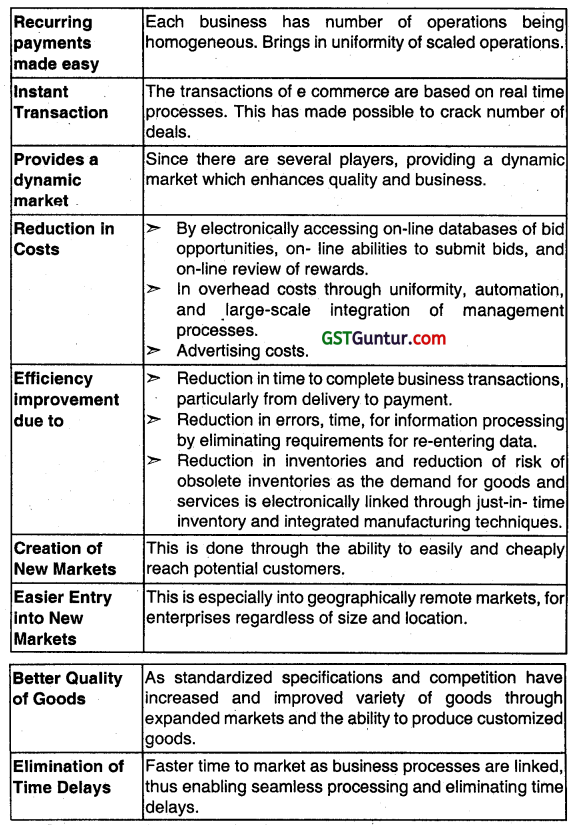
e-business benefits individuals, businesses, government and society at large. As a business seller, analyse the benefits that you would draw from e-business.
Answer:
Benefits of e-business to a Seller Increased Since the number of people getting online Is Increasing, Customer Base which are creating not only new customers but also retaining the old ones.
Question 2.
Describe the term ‘Digital Library’. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Digital Library:
A digital library is a special library with a focused collection of digital objects that can include text, visual material, audio material, video material, stored as electronic media formats (as opposed to print, microform, or other media), along with means for organizing, storing, and retrieving the files and media contained in the library collection. Digital libraries can vary immensely in size and scope and can be maintained by individuals, organizations, or affiliated with established physical library buildings or institutions, or with academic Institutions. The digital content may be stored locally, or assessed remotely via computer networks. An electronic library is a type of information retrieval system.
Question 3.
Write a short note on:
(i) Digital Library
(ii) Payment Gateway (Jan 2021, 4 marks)
Question 4.
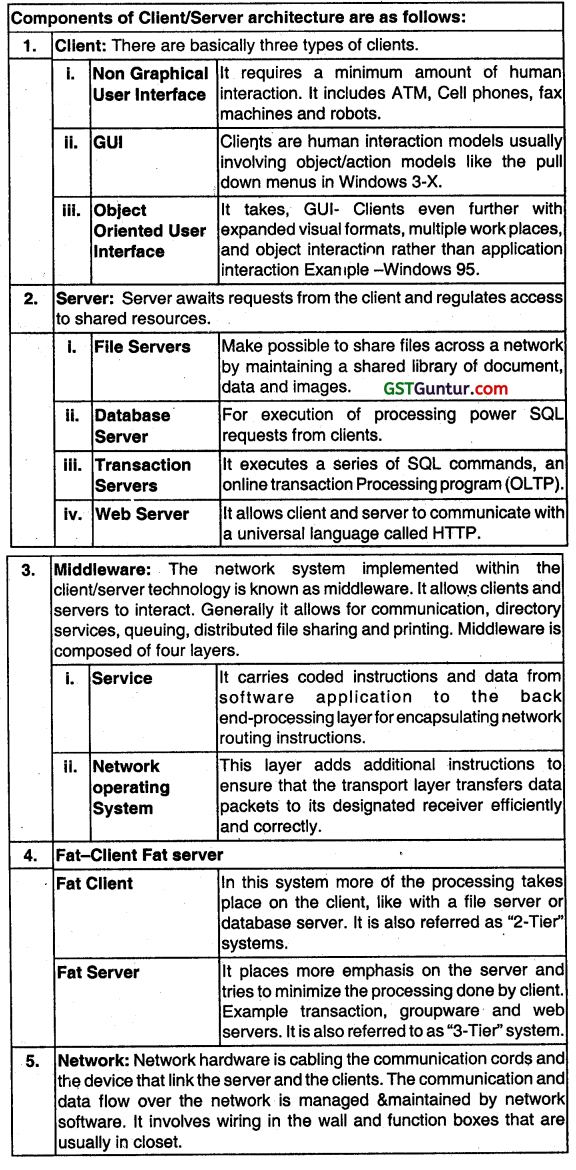
Describe in brief the various components of Client Server Architecture. (May 2009, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 4.
Write the important characteristics of the Client-Server technology. (Nov 2010, 8 marks)
OR
Mention briefly the prominent characteristics of a ‘Client-Server’ architecture. (Nov 2015, Nov 2016, 4 marks each)
Answer:
Client Server: Organization of individual computers on a network decides that how they will interact with other computers on the network. One of the ways of organising network of computers Is the client-server technology or strategy. In this kind of technology, one host computer handles the other connected computer (nodes) on the network. This host computer serves the storage needs and sometimes the processing needs of all the network nodes. This host computer Is also called the server and the connected nodes as clients. The most common type of dent server arrangement is a LAN composed of microcomputers connected to a network server which serves to all the clients (users) of the LAN.
A client program running on one of the microcomputers can request specific data from server. The server program retrieves data from its database and returns to the client. This way a LAN permits all the computers connected to it to share hardware, software, and data. Disk storage and printers are the most commonly shared devices.
Characteristics of Client/Server technology:
- Client/Server architecture consists of a client process and a server process that can be distinguished from each other.
- The client portion and the server portion can operate on separate computer platforms.
- Either the client platform or the server platform can be upgraded without having to upgrade the other platform.
- The server Is able to service multiple clients concurrently.
- In some client/server systems clIents can access multiple servers.
- The client-server system Includes some sort of networking capability.
- A vital portion of the application logic resides at the client end.
- The action is usually Initiated at the client end, not the server end.
- GUI (Graphical user Interface) generally resides at the client end.
- SQL (Structural Query Language) capability is characteristic of majority of the client/server systems.
- The database server should provide protection and security.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe briefly any four features of Application Servers. (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Features of Application Servers
| 1. Component Management | Provides the managers with tools for handling all the components and runtime services like session management and synchronous/asynchronous client notifications as well as executing server business logic. |
| 2. Fault Tolerance | Ability of the application server with no single point of failure defining policies for recovery and trail – over recovery in case of failure of one object. |
| 3. Load Balancing | Capability to send the request to different servers depending on the load and availability of server. |
| 4. Management Console | Single-point graphical management console for remotely monitoring client and server clusters. |
Question 6.
What is Server? Briefly explain any four types of servers based on the nature of service they piovide. (May 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Meaning
A Server is a computer (hardware) or device on a network dedicated to run one or more Services (as a host), to serve the needs of the users of other Computers on a network.
Types of Server
| 1. File Server | This is a computer and storage device dedicated to storing files. Any user on the network can store files on the server. |
| 2. Print Sever | This is a computer that manages one or more printers. |
| 3. Network Server | This is a computer that manages network traffic. |
| 4. Database Server | This is a computer System that processes database queries. |
| 5. Application Server | This is a program that handles all application operations between users and an enterprise’s back-end business applications or databases. |
| 6. Web Server | Web Server is a computer that delivers web pages. Every web server has an IP address and possibly a domain name. |
| 7. Mail Server | Mail Server moves and stores mail over corporate networks. |
Question 7.
List the two advantages and two disadvantages of 3-tier architecture. (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
| Advantages of 3-Tier Architecture | |
| 1. Separation of user Interface control and data presentation from application logic | Through this separation, more clients are able to have access to wide variety of server application. |
| 2. Dynamic load balancing | If bottlenecks in terms of performance occur, the server process can be moved to other servers at runtime. |
| Disadvantages of 3-Tier Architecture | |
| 1. There is an increased need for network traffic management, server load balancing and fault tolerance. 2. Current Tools in 3-tier architecture are relatively immature and are more complex. |
|
Question 8.
Answer the following question in brief:
Briefly explain three tiers in three-tier architecture. (May 2015, 2 marks)
OR
Write a brief description of three-tier architecture of Application Software. (Nov 2019, 2 marks)
Answer:
Three-tier architecture is a client-server software architecture pattern in which the user interface (presentation), functional process logic (business rules), computer data storage, and data access are developed and maintained as Independent modules, most often on separate platforms.
A three-tier architecture s a client-server architecture in which the functional process logic, data access, computer data storage, and user interface are developed and maintained as Independent modules on separate platforms.
Three-tier architecture is a software design pattern and a well-established software architecture.
The Three Tiers In a three-tier architecture are –
| 1. Presentation Tier | Occupies the top level and displays information related to services available on a website. This tier communicates with other tiers by sending results to the browser and other tiers in the network. It is thus used for input and output of data or information. |
| 2. Application Tier | Also called the middle tier, logic tier, business logic or logic tier, this tier s pulled from the presentation tier. It controls application functionality by performing detailed processing. Application logics are used for processing data according to the business rules. |
| 3. Data Tier | It maintains data and provides data management service. Houses database servers where information is stored and retrieved. Data in this tier is kept independent of application servers or business logic. |
Question 9.
Write sho1 note on ‘Mobile Commerce’. (May 2011,2 marks)
OR
What is M-Commerce? Discuss The business areas affected by M-Commerce technology. (May 2013, 4 marks)
OR
Write short flotes on the following:
m-commerce (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Mobile Commerce
Meaning Mobile commerce or m-commerce Is about the explosion of application and service that are becoming accessible from internet enable mobile devices. It involves new technologies. Service and business models, It is quite different from traditional e-commerce. Mobile phones or PDAs impose very different constraints than desktop computers. But they also open the door to a new applications and services.
M-commerce (mobile commerce) is the buying and selling of goods and services through wireless handheld devices such as cellular telephone and personal digital assistants (PDAs) known as next-generation e-commerce m-commerce enables users to access the internet without needing to find a place to plug in. The emerging technology behind m-commerce, which is based on the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), has made strides in countries, where mobile devices equipped with web-ready micro-browsers are much more common.
Scope:
As content delivery over wireless devices are faster, more secure and scalable there Is wide speculation that M-commerce will surpass wireline e-commerce as the method of choice for digital commerce transactions.
The main payment methods used to enable M-commerce are:
- Premium rate calling numbers;
- Charging to the mobile telephone users bill; or
- Deducting from their calling credit, either directly or via reverse-changed SMS
The Industries affected by m-commerce include:
Financial Services, which includes mobile banking (when customers use their handheld devices to access their account and pay their bills) as well as brokerage services, in which stock quotes can be displayed and trading conducted from the same handheld device. Tele Communication in which service changes, bill payments, and account reviews can alt be conducted from the same handheld device.
Service/Retail, as consumers are given the ability to place and pay for orders on the fly. Information Services, which include the delivery of financial news, sports figures, and traffic updates to a single mobile device.
![]()
Question 10.
Draw a Workflow Diagram for e-commerce and describe various steps and corresponding activities involved in this diagram. (May 2018, 8 marks)
Answer:
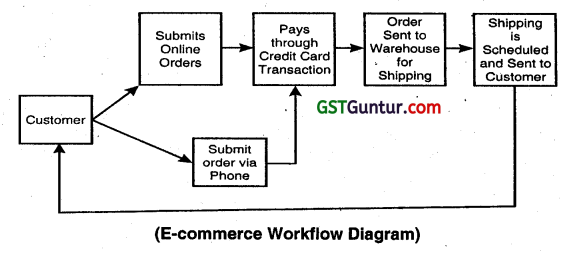
Various steps and corresponding activities Involved In above diagram
| Step | Activities |
| 1. Customers login | Few e-commerce merchants may allow same transactions to be done through phone, but the also Information flow is e-mode. |
| 2. Product/Service Selection | customer selects products/services from ‘available options. |
| 3. Customer places order | Order is placed for selected product/service customer. This step leads to next important activity PAYMENT GATEWAY. |
| 4. Payment Gateway | Here Customer makes a selection of the payment method. In case payment methods other than cash on delivery (COD), the merchant gets the update from payment gateway about payment realisation from customer. In case of COD, e-commerce vendor may do an additional check to validate customer. |
| 5. Dispatch and Shipping Process | This process may be executed at two different. First if product/service inventory managed by an e-commerce vendor, then dispatch shall be initiated at merchant warehouse. Second, many e-commerce merchants allow Third-party vendors to sale through merchant websites. For example: FLIPKART states that it has more than 1 lakh registered third parts vendors on its website. |
| 6. Delivery Tracking | Another key element denoting success of e-commerce business is timely delivery. Merchants keep a track of this. All Merchants’ have provided their delivery staff with hand-help devices, where the product/service delivery to customers are immediately updated. |
| 7. COD Tracking | In case products are sold on COD payment mode, merchants need to have additional checks on matching delivery with payments. |
Numerous services are of the nature which does not have a separate delivery need, for example booking a train ticket through IRCTC. Co. in. this case, there is no separate delivery of service, tickets booking updates are generated as soon as payments are received by IRCTC. Co. in payment gateways.
Question 11.
Explain various Control Objectives of e-commerce or m-commerce. (May 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
Various Control Objectives of e-Commerce or m-Commerce are as follows:
| 1. Prevent organizational costs of data Loss | Data is a critical resource of an Organization for its present and future process and its ability to adapt and survive in a changing environment. |
| 2. Prevent loss from incorrect decision making | Management and operational controls taken by managers Involve detection, investigations and correction of out-of-control processes. These high-level decisions require accurate data to make quality decision rules. |
| 3. Prevent loss of Computer Hardware, Software and Personnel | These are critical resources of an organization which has a credible impact on its infrastructure and business competitiveness. |
| 4. Prevent from high costs of computer Error | in a computerized enterprise environment where many critical business processes are performed, a data error during entry or process would cause great damage. |
| 5. Safeguard assets from unauthorized access | The information system assets (hardware, software, data files etc.) must be protected by a system of internal controls from unauthorized access. |
| 6. Ensure data Integrity | The importance to maintain integrity of data of an organization depends on the value of information, the extent of access to the information, and the value of data to the business from the perspective of the decision-maker, competition, and the market environment. |
| 7. System Effectiveness Objectives | Effectiveness of a system is evaluated by auditing the characteristics and objective of the system to meet substantial user requirements. |
| 8. System Efficiency Objectives | To optimize the use of various Information system resources (machine time, peripherals, system software and Labour) along with the impact on its computing environment. |
Question 12.
Explain the concept of E-Commerce briefly. How can you protect your ECommerce business from intrusion? (Nov 2019, 4 marks)
OR
As an IT consultant, advise some tips to an aspiring e-commerce vendor so that his business can be protected from Intrusion.
Answer:
“E-commerce Is the Sale/Purchase of Goods! services through electronic mode is e-commerce,” This could include the use of technology in the form of computers, Desktops, Mobile Applications, etc.
E-commerce is the process of doing business electronically. It refers to the use of technology to enhance the processing of commercial transactions between a company, its customers, and its business partners. It involves the automation of a variety of Business-to-Business (B28) and Business-To- Consumer (B2C) transactions through reliable and secure connections.
Tips to protect any e-Commerce business from Intrusion are as follows:
| 1. Viruses | Check your website daily for viruses, the presence of which can result in the loss of valuable data. |
| 2. Hackers | Use software packages to carry out regular assessments of how vulnerable your website is to hackers. |
| 3. Passwords | Ensure employees change these regularly and that passwords set by former employees of your organization are defunct. |
| 4. Regular Software Updates | Your site should &ways be up to date with the newest versions of security software. If you fail to do this, you leave your website vulnerable to attack. |
| 5. Sensitive Data | Consider encrypting financial information and other confidential data (using encryption software). Hackers or third parties will not be able to access encrypted data without a key. This is particularly relevant for any e-Commerce sites that use a shopping cart system. Know the details of your payment service provider contract. |
Question 13.
Subsequent to demonetization, one of your elderly neighbours, who was using traditional digital methods of making payments like cards, net banking, etc., asked for your help to know about the various new methods of Digital payments. Identity and explain various new methods of Digital Payments for him. (Nov 2018, 6 marks)
Answer:
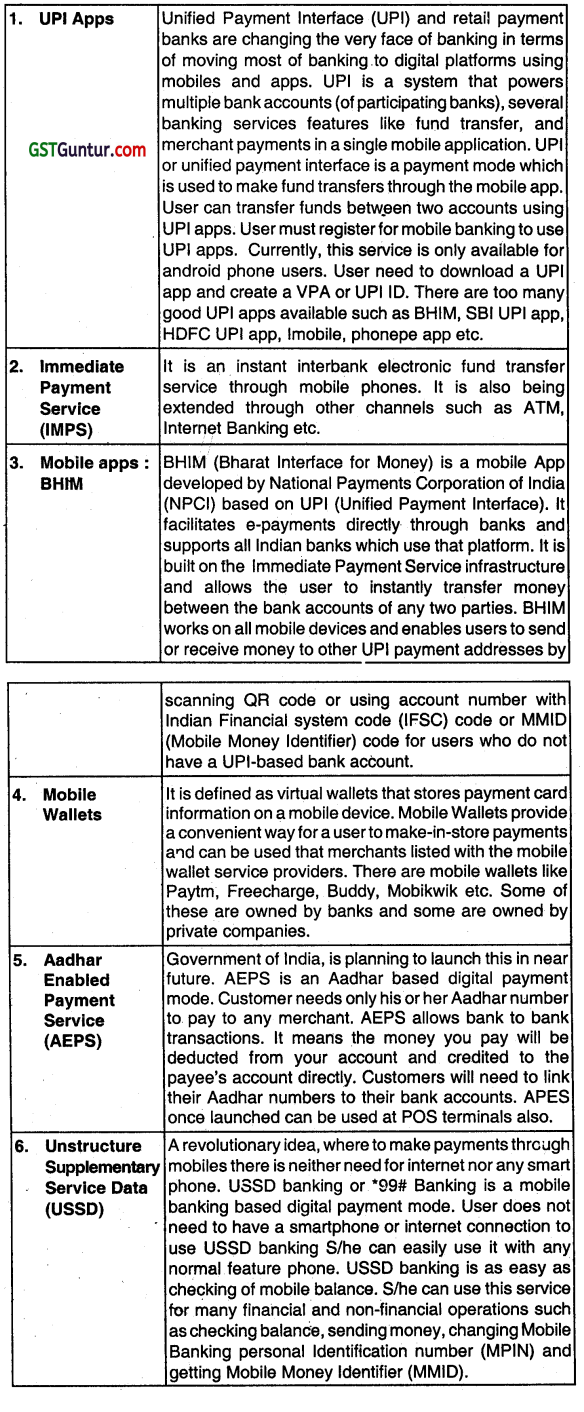
Question 14.
From traditional digital payment methods, India is moving towards newer methods of digital payments. In light of the above statement, briefly explain following new methods.
(i) BHIM
(ii) USSD (Jan 2021, 4 marks)
Question 15.
Write short note on the following:
Hardware Virtualization (Nov 2014, Nov 2017, 2 marks each)
Answer:
Hardware Virtualization:
Hardware Virtualization refers to the creation of a virtual machine that acts like a real computer with an operating system. Software executed on these virtual machines is separated from the underlying hardware resources. Hardware virtualization can give root access to a virtual machine.
![]()
Question 16.
Write short note on the following:
Network Virtualization (May 2015, May 2017, 2 marks each)
Answer:
Network Virtualization:
Virtualization is known as the process of creating logical computing resources with the help of available physical resources.
The network virtualization is accomplished by using virtualization software.
Network virtualization allows a large physical network to be provisioned into multiple smaller logical networks.
Network virtualization allows better utilization of hardware resources between multiple users and group of users.
Question 17.
Write short note on the following:
Storage Virtualization (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Storage Virtualization:
Storage virtualization Is the apparent pooling of data from multiple storage devices, even different types of storage devices, into what appears to be a single device that is managed from, a central console. It helps the storage administrator perform the tasks of backup, archiving, and recovery more easily and In less time by disguising the actual complexity of a Storage Area Network (SAN). Administrators can Implement virtualization with software, applications or by using hardware and software hybrid appliances.
The servers connected to the storage system aren’t aware of where the data really is. Storage virtualization is sometimes described as abstracting the logical storage from physical storage.”
Question 18.
Explain the Concept of Virtualization. Enumerate any 2 major applications of virtualization. (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Virtualization refers to technologies designed to provide a layer of abstraction between computer hardware system and the software running on them.
Application of Virtualization:
| 1. Testing and Training | Virtualization can give root access to a virtual machine. This can be very useful such as in kernel development and operating system courses. |
| 2. Portable workspace | Recent technologies have used virtualization to create portable workspaces on devices like ipads and USB memory sticks. |
Question 19.
Discuss various application areas of Virtualization’. (Nov 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
Application Areas of Virtualization:
| 1. Server Consolidation | Virtual machines are used to consolidate many physical servers Into fewer servers, which in turn host virtual machines. Each physical server is reflected as a virtual machine “guest” residing on a virtual machine host system. This is also known as “Physical-to – virtual” or P2V transformation. |
| 2. Disaster Recovery | Virtual machines can be used as “hot standby environments for physical production servers. This changes the classical backup-and-restore” philosophy, by providing backup images that can “boot into live virtual machines, capable of taking over workload for a production server experiencing an outage. |
| 3. Testing and Training | Virtualization can give root access to a virtual machine. This can be very useful such as in kernel development and operating system courses. |
| 4. Portable Applications | Portable Applications are needed when running an application from a removable drive, without installing it on the system’s main disk drive. Virtualization can be used to encapsulate the application with a redirection layer that stores temporary tiles, windows registry entries and other state information in the application’s installations directory and not within the system’s permanent file system. |
| 5. Portable Workspaces | Recent technologies have used virtualization to create portable workspaces on devices like memory stick. |
Question 20.
Differentiate between Storage Virtualisation and Hardware Virtualisation.
Answer:
Storage Virtualization:
Storage virtualization is the apparent pooling of data from multiple storage devices, even different types of storage devices, into what appears to be a single device that is managed from a central console. Storage virtualization helps the storage administrator perform the tasks of backup, archiving, and recovery more easily and in less time by disguising the actual complexity of a Storage Area Network (SAN). Administrators can implement virtualization with software applications or by using hardware and software hybrid appliances. The servers connected to the storage system aren’t aware of where the data really is Storage virtualization is sometimes described as abstracting the logical storage from the physical storages.
Hardware Virtualization:
Hardware Virtualization or Platform Virtualization refers to the creation of a virtual machine that acts like a real computer with an operating system. Software executed on these virtual machines is separated from the underlying hardware resources. For example, a computer that is running Microsoft Windows may host a virtual machine that looks like a computer
with the Linux operating system-based software that can be run on the virtual machine. The basic idea of Hardware virtualization is to consolidate many small physical servers into one large physical server so that the processor can be used more effectively.
Question 21.
Briefly explain Grid Computing. What are possible reasons of using grid computing? (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:

Question 22.
Discuss the constraints that need to be taken into consideration while developing a secured Grid Architecture. (May 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Constraints that need to be taken Into account while developing a secured Grid Architecture:
| 1. Single Sign-on | A user should authenticate once and they should be able to acquire resources, use them, and release them and to communicate internally without any further authentication. |
| 2. Protection of Credentials | User passwords, private keys etc. should be protected. |
| 3. Interoperability with Local security situations | Access to local resources should have local security policy at a local level. Despite of modifying every local resource there Is an inter-domain security server for providing security to local resources. |
| 4. Exportability | The Code should be exportable i.e. they cannot use amount of encryption at a time. There should be a minimum communication at a time. |
| 5. Support for Secure group communication | In a communication, there are number of processes which coordinate their activities. This coordination must be secure and for this there is no such security policy. |
| 6. Support for Multiple implementations | There should be a security policy which should provide security to multiple sources based on public and private key cryptography. |
![]()
Question 23.
List out the application areas of Grid Computing. (Nov 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Application Areas of Grid Computing:
- Civil engineers collaborate to design, execute and analyze shake table experiments.
- An Insurance company mines data from partner hospitals for fraud detection.
- An Application service provider out loads excess load to a compute cycle provider.
- An Enterprise conf figures internal and external resources to support e-business workload.
- Large-scale science and engineering are done through the interaction of people, heterogeneous computing resources, information systems, and instruments all of which are geographically and organizationally dispersed.
Question 24.
Define any four constraints which are usually taken from the characteristics of grid environment and application in order to develop grid computing security architecture. (Nov 2020, 4 marks)
Question 25.
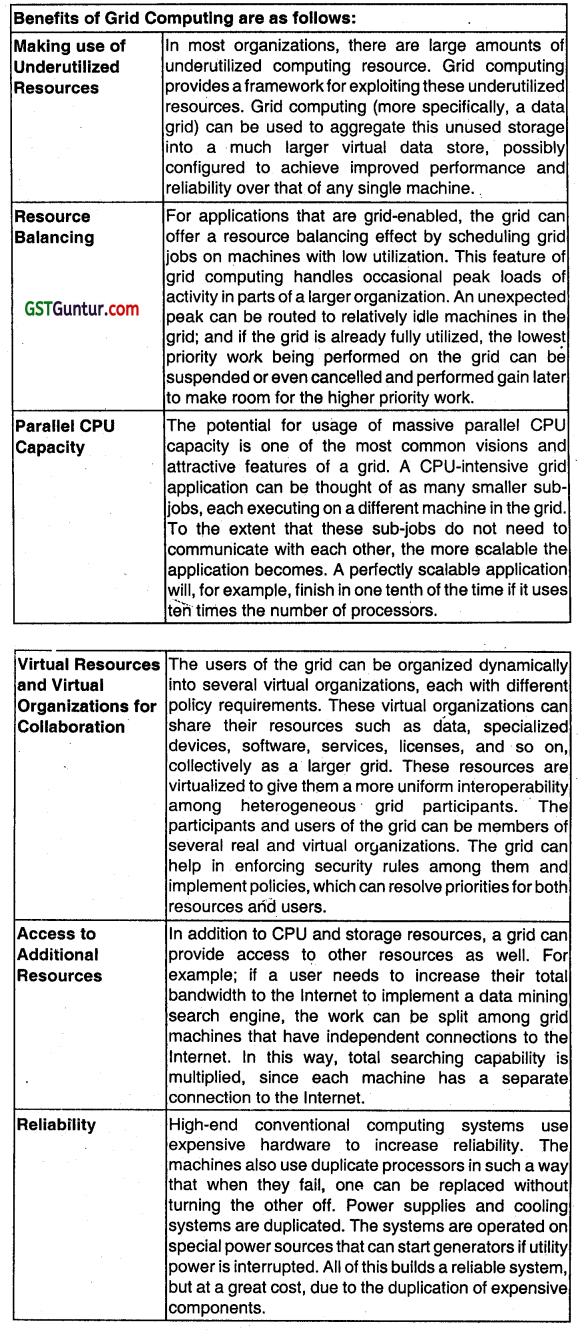
What are the benefits of Grid Computing?
Answer:

Question 26.
What is cloud computing? Describe any three types of douds in cloud computing environment. (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Cloud computing
Cloud is the use of various services such Computing as software development platforms, servers, storage and software over the internet often referred to as the cloud.
The cloud computing environment can consist of multiple types ot clouds based on their deployment and usage:
| Public Clouds | The public cloud is made available to the general public or a large industry group. They are administrated by third parties or vendors over the Internet and services are offered on pay-per-use basis. it is widely used In the development, deployment, and management of enterprise. |
| Private/Internal Clouds | This cloud computing environment resides within the boundaries of an organisation and is used exclusively for the organizations benefits. They are built primarily by IT departments within enterprises who seek to optimize utilization of infrastructure resources within the enterprise by provisioning the infrastructure with applications using the concepts of grid-arid virtualization. The private cloud enables and enterprise to manage the infrastructure and have more control. |
| Hybrid Clouds | It is a composition of two or more clouds (Private, Community or Public) and is maintained by both Internal and external providers. Though they maintain their unique identity, they are bound together by standardized data and application portability. With a hybrid cloud, organizations might run non-core applications in a public cloud. |
Question 27.
Write short note on the following:
Software as a Service (SAAS) (Nov 2014, 2 marks)
Answer
Software as a Service (SAAS): It includes a complete software offering on the cloud. Users can access a software application hosted by the cloud vendor on a pay-per-use basis. SAAS is a model of software deployment where an application ¡s hosted as a service provided to customers across the internet by removing the need to install and run an application on a user’s own computer.
Question 28.
Discuss any four key characteristics of Cloud Computing. (May 2015, 4 marks)
OR
Explain any four characteristics of cloud computing. (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
| 1. On-demand self-service | A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider. |
| 2. Broad network access | Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops and workstations. |
| 3. Resource pooling | The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand. There is a sense of location independence in that the customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact location of the provided resources but may be able to specify location at a higher level of abstraction e.g… country, state or data center. |
| 4. Rapid elasticity | Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released, in some cases automatically, to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time. |
| 5. Measured service | Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for the provider and consumer. |
Question 29.
Discuss any four advantages of Cloud Computing. (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Cloud Computing
Meaning
it is a network technique Which helps organizations to share resources using internet. Cloud Computing is the use of various services sud as software development platforms, servers, storage, and software over the internet often referred to as the Cloud. A cloud is collection of servers, applications, databases, documents, agreements, spreadsheets, storage capacity, etc. which allows organizations to share these resources from anywhere.
Cloud services allow Individuals and business to use software and hardware that are managed by third parties. Examples of cloud services include online file storage, social networking sites, webmail, and online business applications. Cloud computing provides a shared pool of resources, including data storage space, networks, computer processing power, and specialized corporate and user applications. A cloud is normally set up by a big information technology company such as Google, Microsoft, Oracle, IBM, Amazon, etc. for providing cloud-based services to their users.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
1. With cloud computing an organization can use any scale of information technology capacity immediately without Investing in new hardware Infrastructure or buying new software licenses. Cloud computing is highly beneficial to business organizations who do not want to set up expensive data centers but they want to use services of dedicated data centers from anywhere.
2. The consumer or user no longer has to be at a PC i.e. user can use any device for using applications.
3. The consumer does not purchase a specific version of software which is required to be configured for Smartphones, PDAs etc. The consumer can download the required version from cloud.
4. The consumer can access multiple servers from anywhere on the globe without knowing where they are located.
Question 30.
Define the term ‘Cloud Computing Architecture’. Explain the two parts of Cloud Computing Architecture. (May 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Cloud Computing Architecture
Meaning
Cloud Computing Architectural refers to the components and subcomponents that typically consist of a front-end platform (fat client, thin client, mobile device), back-end platforms (servers, storage), a cloud-based delivery, and a network (Internet, Intranet, Intercloud). Combined these components make up cloud computing architecture. it typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other over a tight or loose coupling of cloud resources, services, middleware, and software components.
Types of Cloud Computing Architecture:
1. Front End
The front end of the cloud computing system comprises of the client’s devices (or it may be a computer network) and some applications that are needed for accessing the cloud computing system. All the cloud computing systems do not give the same interface to users.
For e.g. Web services like electronic mail programs use some existing web browsers such as Firefox, Microsoft’s Internet Explorer or Apples safari. Other types of systems have some unique applications which provide network access to its clients.
2. Back End refers to some physical peripherals. In cloud computing, the back end is cloud itself which may encompass various computer machines, data storage systems, and servers. Groups of these clouds make a whole cloud computing system. Theoretically, a cloud computing system can include practically any type of web application program such as video games to applications for data processing, software development, and entertainment residing on its individual dedicated server for services. There are some set of rules, generally called as protocols which are followed by this server and It uses a special type of software known termed as middleware that allows computers that are connected to networks to communicate with each other.
If any cloud computing service provider has many customers, then there’s likely to be very high demand for huge storage space. Many companies that are service providers need hundreds of storage devices.
![]()
Question 31.
State two Features of Infrastructure as a Service (laaS) model of Cloud Computing. (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Features of lasS Model of Cloud Computing:
It provides clients with access to serve hardware, storage, bandwidth, and other fundamental computing resources. It provides access to shared resources on a need basis without revealing details like location and hardware to clients.
Question 32.
Write short note on the following:
Cloud vs. Grid Computing (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
| Basis of Difference | Grid Computing | Cloud Computing |
| 1. Meaning | Grid Computing is the provisioning of IT resources through a Control Server, to multiple locations, using web services. | Cloud Computing refers to the provisioning of IT resources as a service through the Internet. |
| 2. Structure | This uses Software to divide and carve out pieces of program, as a large system image, to many computer nodes. | Resources are maintained in the Cloud/Internet for easy access, without installation of Software in the User Device. |
| 3. Device Use | Generally, access to Grid Computing is through one type of device Only, e.g. only Desktop PCs, or only Laptops, etc. | Access to Cloud applications can be from a variety of devices – Desktop, Laptop, Smartphones, etc. |
| 4. Point of Failure | Sometimes, it one part of the Software in a Node tails, the application in other Nodes relying on such Node/Software, also fail. However, this can be avoided using certain Passover technologies. | Data is stored in the Cloud/Internet, which can be retrieved as per Users’ requirements. Failure of one Node, will not affect other Nodes. |
| 5. Data Storage | Suitable only for large volumes of data. Not economical if the data size is small. | Suitable for any size of data storage starting from 1 Byte to several Terabytes. |
| 6. Cost | Higher Cost of investment and Operating Expenses, due to need for large system images, and associated hardware to operate and maintain them. | Comparatively lower Investment and operating expenses, in areas of Hardware, Software, Training, Data Storage, etc. |
| 7. Focus | A Computational Grid focuses mainly on computationally intensive operations. | Cloud Computing offers two types of service levels/ instances – Standard and High-CPU. |
Question 33.
Write short note on the following Community Cloud (2017- May 4 marks)
Answer
Community Cloud:
Meaning
it is a Cloud infrastructure for the exclusive use by a specific community of Consumers from Organizations that have shared concerns (e.g. Mission, Security Requirements, Policy, and Compliance Considerations).
Owned and Managed by
- One or more of the organizations In the community,
- a third party, or
- some combination of them, and it may exist on or off-premises.
Features:
- Collaborative and Distributive: No single Company has full control over the whole cloud. This is usually distributive and hence better cooperation provides better results.
- Partially Secure: Only a few organizations share the Cloud, so there is a possibility that the data can be leaked from one organization to another, however, it is safe from the external world.
- Cost Effective: Community Cloud becomes cost-effective since it is shared by many organizations.
Question 34.
Public cloud is the cloud infrastructure that is provisioned for open use by the general public. Explain any four characteristics of public cloud. (Nov 2020, 4 marks)
Question 35.
Cloud-based applications are now taking over Installed applications, What are the major differences between Cloud based Applications and Installed Applications? Explain any four. (Jan 2021, 4 marks)
Question 36.
Differentiate between Pilvate Clouds and Community Clouds.
Answer:
Private Clouds: This cloud computing environment resides within the boundaries of an organization and Is used exclusively for the organization’s benefits. These are also called internal clouds. They are built primarily by IT departments within enterprises who seek to optimize utilization of infrastructure resources within the enterprise by provisioning the
infrastructure with applications using the concepts of grid and virtualization.
The benefit of a Private Cloud is that it enables an enterprise to manage the infrastructure and have more control, but these conies at the cost of IT department creating a secure and scalable cloud.
Community Clouds: This is the sharing of computing infrastructure in between organizations of the same community. For example, all Government organizations within India may share computing infrastructure on the cloud to manage data. The risk is that data may be stored with the data of competitors.
Question 37.
What is mobile computing? What are the three major concerns related to mobile computing? (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Mobile Computing
| Meaning | Mobile computing is the use of portable computing devices (such as laptop and handheld computers) In conjunction with mobile communication technologies to enable users to access the internet and data on their home or work computers from anywhere in the world. Mobile computing is enabled by use of mobile devices (portable and handheld computing devices) such as PPA, laptops, mobile phones. MP3 players, digital cameras, tablet PC, and palmtops on a wireless network. |
| Mobile computing involves mobile communication. Mobile hardware and Mobile software which are discussed as follows: | |
| Mobile Communication | Mobile communication refers to the infrastructure put In place to ensure that seamless and reliable communication goes on. These would include devices such as Protocols, Services, Bandwidth and Portals necessary to facilitate and support the stated services. The data format is also defined at this stage. |
| Mobile Hardware | Mobile hardware includes mobile devices or device components that receive or access the service of mobility. They would range from portable laptops, smartphones, tablet PC’s to Personal Digital Assistants. These devices will have receptors that are capable of sensing and receiving signals. These devices are configured to operate in full duplex where by they are capable of sending and receiving signals at the same time. |
| Mobile Software | Mobile software is the actual program that runs on the mobile hardware. It deals with the characteristics and requirements of mobile applications. This is the engine of that mobile device. In other terms, it is the operating system of that appliance. It is the essential component that makes the mobile device operates. |
Question 38.
Describe the various benefits of Mobile Computing. (May 2016, 6 marks)
Answer:
Mobile Computing Benefits:
- It provides mobile workforce with remote access to work order details, such as work order location contact information, required completion date asset history relevant warranties.
- It enables mobile sales personnel to update work order status In real-time, facilitating excellent communication.
- It provides access to corporate services and Information at any time.
- It provides remote access to corporate knowledge base at the job location.
- It enables to improve management effectiveness by enhancing Information quality. Information flow and ability to control a mobile workforce.
Question 39.
Answer the following in brief:
Major concerns relating to Mobile Computing. (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Mobile Computing:
Mobile computing is the use of portable computing devices (such as laptop) in conjunction with mobile communication technologies to enable user to access the Internet and data on their home or work computers from anywhere in the world. Mobile computing is enabled by use of mobile devices (portable and handheld computing devices) such as PDA, Laptops, Mobile Phones, MP3 Players, Digital Cameras, Tablet PC, and Palmtops on a wireless network.
Major Concerns Relating to Mobile Computing are given as follows:
- Mobile computing has its fair share of security concerns as any other technology.
- Dangers of misrepresentation – another problem playing mobile computing are credential verification.
- Power consumption – when a power outlet or portable generator is not available, mobile computers must rely entirely on battery power.
- Potential health hazards.
Question 40.
Mobile computing Is an important and rapidly evolving technology that allows users to transmit data from remote locations to other locations in mobility conditions. Being a communication expert, identify the limitations current scenario that impede or hesitate users to use this technology frequently. (May 2019, 8 marks)
Answer:
Mobile computing is an important and rapidly evolving technology that allows users to transmit data from remote locations to other locations in mobility conditions.
The following are the limitations In current scenario that impede or hesitate users to use this technology frequently.
| 1. Insufficient Bandwidth | Mobile Internet access s generally slower than direct cable connections using technologies such as General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and Enhanced Data for GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) Evolution (EDGE), and more recently 3G networks. These networks are usually available within range of commercial cell phone towers. Higher-speed wireless LANs are inexpensive but have very limited range. |
| 2. Security Standards | When working mobile, one is dependent on public networks, requiring careful use of Virtual Private Network (VPN). Security is a major concern while concerning the mobile computing standards on the fleet. One can easily attack the VPN through a huge number of networks interconnected through the line. |
| 3. Power consumption | When a power outlet or portable generator is not available, mobile computers must rely entirely on battery power. Combined with the compact size of many mobile devices, this often means unusually expensive batteries must be used to obtain the necessary battery life. Mobile Computing should also look into Greener IT in such a way that it saves the power or leases the battery life. |
| 4. Transmission Interferences | Weather, terrain, and the range from the nearest signal point can all interfere with signal reception. Reception in tunnels, some buildings, and rural areas is often poor. |
| 5. Potential health hazards | People who use mobile devices while driving is often distracted from driving and are thus assumed more likely to be involved in traffic accidents. Cell phones may interfere with sensitive medical devices. There are allegations that cell phone signals may cause health problems. |
| 6. Human Interface with device | Screens and keyboards tend to be small, Which may make them hard to use. Alternate input methods such as speech or handwriting recognition require training. |
![]()
Question 41.
Write short note on the following:
Best practices of Green IT. (May 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Best Practices of Green IT:
Green IT refers to the study and practice of establishing/using computers and IT resources In a more efficient, environmentally friendly and responsible way. Computer consumes lots of raw materials and natural resources, power to run them, raw materials to manufacture them and problem of disposing them at the end of their life cycle. It is the study and practice of designing.
manufacturing, using, and disposing of computers, servers, associated subsystems etc. in efficient and effective manner to mitigate negative effects on environment. The goals are to reduce hazardous materials, maximize energy efficiency during product’s lifetime and promote recyclability of defunct product and factory waste.
Question 42.
Explain the concept of green computing. How will you develop a sustainable green computing plan? (Jan 2021, 6 marks)
Question 43.
Write short note on the following:
(e) Advantages of BYOD (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Advantages of BYOD:
- It provides flexible workspaces.
- It leads to increased employees satisfaction.
- It reduces the desktop cost.
- It reduces maintenance cost and updation activity cost.
Question 44.
Every business decision is accompanied with a set of threats and so is BYOD program. Explain briefly the areas in which the risks associated with BYOD programs can be classified. (Nov 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Every business decision is accompanied with a set of threats arid so is BYOD program. The areas in which the risks associated with BYOD program are classified as follows:
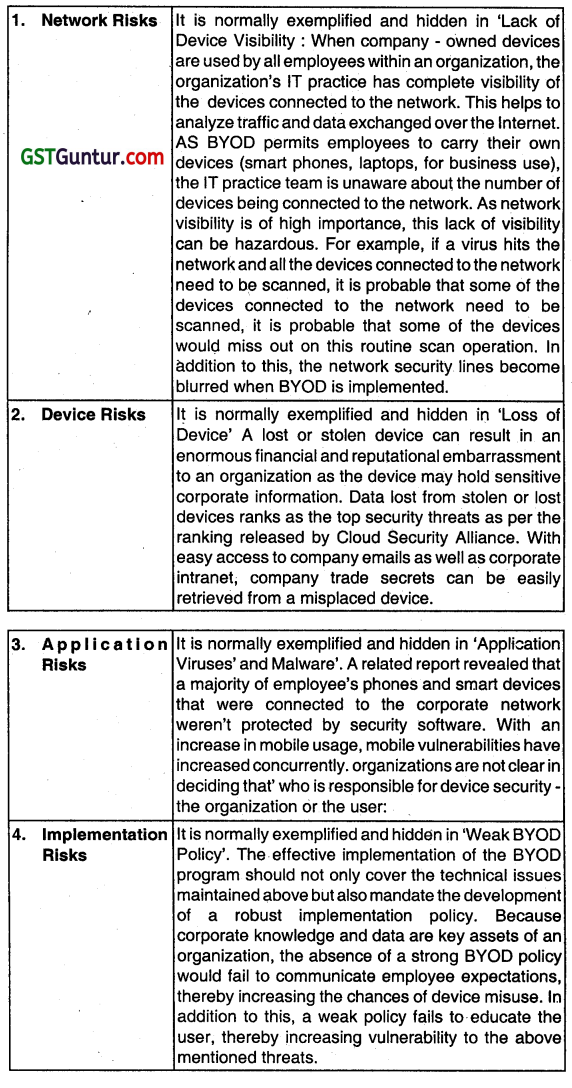
Question 45.
Explain the following in brief:
Internet of Things (loT) (May 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
Internet of Things (loT):
The Internet of Things (loT) is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction for example:
(i) Washing machines with WIFI networking capabilities can connect themselves to home Wi-Fi Once these machines are so connected, they can be controlled through machine manufacturer’s mobile APP from anywhere in the World.
(ii) India’s living ledged of cricket appearing In an Advertisement for water purifier informs that, the water purifier Is WiFi enabled. When the purifying agents deplete in the machine, it connects to home WiFi and informs the Service agents of the company. This examples are from products being sold in India.
Question 46.
Write any two application areas of Internet of Things (lOT). (May 2019,2 marks)
Answer:
Application areas of Internet of Things (LOT):
1. All home appliances to be connected and that shall create a virtual home.
- Homeowners can keep track of all activities in-house through their handheld devices.
- Home Security CCTV is also monitored through handheld devices.
2. Office machines shall be connected through Internet.
Human resource managers shall be able to see inter how many people have had a cup of coffee from vending machines and how many are present. How many printouts are being generated through office printers?
Question 47.
Write short note on the following:
(C) Major Components of WEB 3.0 (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Major Components of WEB 3.0
| 1. Semantic Web | This provides the web user a common framework that could be used to share and reuse the data across various applications, enterprises and community boundaries. This allows the data and information to be readily intercepted by machines, so that the machines are able to take contextual decisions on their own by finding, combining and acting upon relevant information on the web. |
| 2. Web Services | It is a software system that supports computer-to-computer interaction over the internet. For example: the popular photo-sharing website Flickr provides a web service that could be utilized and the developers to programmatically interface with Flickr In order to search for images. |
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
E-Commerce is the:
(a) Process of doing business electronically
(b) Electronic transaction between Buyer and Seller
(c) Electronic and exchange of goods between manufacturer and buyer
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Process of doing business electronically
Question 2.
Customer interaction under E-Commerce is.
(a) Face-to-Face
(b) Screen-to-Face
(c) Mobile-to-Face
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Screen-to-Face
![]()
Question 3.
Under E-Commerce Resource focus on
(a) Supply side
(b) Demand side
(c) Both Demand and Supply side
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Demand side
Question 4.
Benefit/Profit Impact under E-Commerce:
(a) Increases the profit margin of manufacturers
(b) Above (a) allow manufacturers to give discounts to customers
(c) Customers get better price
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 5.
Effective Supply Chain Management needs to ensure:
(a) They have enough and right goods suppliers
(b) Suppliers are financially and operational safe
(c) Suppliers re able to provide real-time stock inventory and delivery time is very short
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 6.
UPI stands for ………………….. .
(a) Universal Payment Interface
(b) Unified Proximity Interface
(c) Unified Payment Interface
(d) Unified Payment Interaction
Answer:
(c) Unified Payment Interface
Question 7.
BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money) is an example of
(a) Mobile Hardware
(b) Mobile App
(c) Mobile Operating System
(d) Mobile Wallet
Answer:
(b) Mobile App
Question 8.
E-Commerce runs through.
(a) Computers
(b) Computers and Mobiles
(c) Network-connected system
(d) Satelite system
Answer:
(c) Network-connected system
Question 9.
E-Commerce runs through network-connected system. Networked systems can have ………………….. architecture.
(a) Two tier
(b) Three tier
(c) Multi-tier
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
![]()
Question 10.
Advantages of Two-tier systems is/are
(a) By having simple structure, it is easy to set up and maintain entire system smooth
(b) The system performance is higher because business logic and database are physically close
(c) Processing is shared between the client and server, more users could interact with system.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 11.
Three-tier software architecture does not consist:
(a) Presentation Tier
(b) System Tier
(c) Application Tier
(d) Database Tier
Answer:
(b) System Tier
Question 12.
In which buying and selling of goods and services through wireless handheld devices such as cellular telephones and personal digital assistants.
(a) E-Commerce
(b) M-Commerce
(C) B2 to B Business
(d) B2 to C Business
Answer:
(b) M-Commerce
Question 13.
Risk associated with e-commerce transactions except:
(a) Privacy and Security
(b) Quality Issue
(c) Discount to the customer
(d) Delay in goods and Hidden Costs.
Answer:
(c) Discount to the customer
Question 14.
In an e-commerce environment controls are necessary for Seller/Buyers/Merchants except on
(a) Product Catalogues
(b) Discounts and Promotional Schemes
(c) Tax accounting for all products/services sold
(d) Accounting for cash received through Cash on Delivery mode of Sales.
Answer:
(c) Tax accounting for all products/services sold
Question 15.
Commercial Laws Governing E-Commerce except
(a) The Competition Act, 2002
(b) The Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017
(c) Hindu Marriage Act, 1955
(d) Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
Answer:
(c) Hindu Marriage Act, 1955
Question 16.
E-Commerce ar covered under few other Law as these transactions are done electronically
(a) Information Technology Act, 2000 (As amended 2008)
(b) Reserve Bank of India, Act 1932
(c) Only (a)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 17.
BHIM Stands for ……………………… .
(a) Bharat Interface for Money
(b) Bharat Interpayment for Money
(c) Bbarat Interaction for Money
(d) Bharat interpersonal transaction for Money
Answer:
(a) Bharat Interface for Money
Question 18.
National Payments Corporation of India (MPCI) developes Mobile App based on UPI.
(a) Paytrn
(b) BHIM
(c) Phonepay
(d) Mobikwick
Answer:
(b) BHIM
Question 19.
IMPS stands for:
(a) Interpersonal Payment System
(b) Immediate Payment System
(c) Immediate payment Service
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Immediate payment Service
![]()
Question 20.
An instant interbank electronic fund transfer service through mobile phones, and is also being extended through other channels such as ATM Internet Banking, etc. Is known as
(a) UPI
(b) BHIM
(c) IMPS
(d) Internet banking
Answer:
(c) IMPS
Question 21.
BHIM works on all mobile devices and enable users to send or receive money to other UPI payment addresses by:
(a) ScannìngQCode
(b) Using account number with IFSC
(c) Using MMID (Mobile Money Identifier Code)
(d) Any one of the above mode
Answer:
(d) Any one of the above mode
Question 22.
USSD Stands for ……………………………………… .
(a) Unified Structure Service Data
(b) Unstructured SystematicService Data
(c) Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
(d) Unified Supplementary Service Data
Answer:
(c) Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
Question 23.
…………….. means to create a virtual version of a device or resource, such as a server, storage device, network o even an operating system where the framework divides the resource into one or more execution environments.
(a) Visualisation
(b) Virtualisation
(c) Virtualisation
(d) Verification
Answer:
Question 24.
The concept of virtualization relies in partitioning which divides a single physical server into ………………….. logical servers.
(a) Two
(b) Four
(c) Eight
(d) Multiple
Answer:
(d) Multiple
Question 25.
Virtualization refers to the creation of a virtual machine that acts like a real computer with an operating system is called …………………. .
(a) Software Virtualisation
(b) Hardware Virtualisation
(c) Platform Virtualisation
(d) Either (b) or (c)
Answer:
(d) Either (b) or (c)
Question 26.
………………………. is a computer network in which each computer’s resources are shared with every other computer in the system.
(a) Grid Computing
(b) Cloud Computing
(c) Hybrid Computing
(d) Mobile Computing
Answer:
(a) Grid Computing
Question 27.
Combination of both at least one private (internal) and at least one public (external) cloud computing environment – usually, consisting of infrastructure, platforms, and applications, is known as.
(a) Central Cloud
(b) Hybrid Cloud
(c) Community Cloud
(d) Comblnation of Cloud
Answer:
(b) Hybrid Cloud
![]()
Question 28.
The technology that allows transmission of data via a computer without having to be connected to a fixed physical link, is called …………………. .
(a) Grid computing
(b) Cloud computing
(c) Hybrid computing
(d) Mobile computing
Answer:
(d) Mobile computing
Question 29.
GSM Stands for …………………… .
(a) Global Service for Mobile Communication
(b) Global System for Mobile Communication
(c) Global System for Mobile Code
(d) Global Semantics for Mobile Communication
Answer:
(b) Global System for Mobile Communication
Question 30.
Green Computing is also known as …………………. .
(a) Green Accounting
(b) Green Evaluation
(c) Green Financing
(d) Green IT
Answer:
(d) Green IT
Question 31.
Study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT, s known as …………….. .
(a) Grid Computing
(b) Mobile Computing
(c) Green Computing
(d) Cloud Computing
Answer:
(c) Green Computing
Question 32.
Machine Learning is a type ‘of ………………. that provides computers with the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed and focuses on the development of computer programs that can change when exposed to new data.
(a) Mental Ability
(b) Computer Ability
(c) Artificial Intelligence
(d) Software Intelligence
Answer:
(c) Artificial Intelligence