Information System and its Components – CA Inter EIS Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Information System and its Components – CA Inter EIS Question Bank
Question 1.
Write short notes on the Intranet. (Nov 2007, May 2010, Nov 2013, 2 marks each)
Answer:
Intranet: intranet is a type of information system that facilitates communication within the organization, among widely dispersed departments, division and regional location. Technology used for intranet is same as that of internet which uses Web Browsers, Web Server and Data Warehouses in a single view.
The same browser makes available all information applications and data. The main objective of such facility is to organize each individual’s desktop with nominal cost, time and effort to be more productive, cost efficient, timely and competitive.
Question 2.
Describe briefly the Cache memory (Nov 2008,1 mark)
Answer:
Cache Memory: It Is the high speed st9rage device used to Increase the processing speed by making available the current programs and data to the CPU at a faster rate. Processor incorporates their own Internal cache memory which acts as a temporary memory and boosts processing power significantly.
Cache memory acts as temporary memory and boosts processing power significantly. The cache that comes with the processor Is called level one (L1) cache. This cache runs at processors clock speed, and therefore is very fast. The L1 cache is divided into two sections-one for data and other for instructions.
Question 3.
Explain the Smart Card System (Nov 2008, 1 marks)
OR
Explain the Smart Cards (Nov 2011, 2 marks)
Answer:
Smart Card System: A Smart Card is a plastic card about the size of a credit card with an embedded micro chip that can be loaded with data used for telephone calling, electronic cash payment and other applications. A smart card is more secure than a magnetic stripe card and can be programmed to self-destruct it wrong password Is entered too many times. They contain a microprocessor chip and memory and include keypad.
Question 4.
Explain the basic functions of an Operating system. (Nov 2008, 5 marks)
OR
Describe any four basic functions of an operating system. (Nov 2010, May 2013, 4 marks each)
Answer:
Various functions performed by Operating Systems are listed below
| 1. Schedule Jobs | it determines the sequence in which the jobs are to be executed using priorities established by the organisation. |
| 2. Manage Hardware and Software resources | It first loads the application programs Into the primary storage and then causes various hardware units to perform the task as specified by the application. |
| 3. Maintain System Security | A password is created for every user to ensure that unauthorized persons are denied to access the data In the system. |
| 4. Enable Multiple User Resource sharing | It enables many users to share the programs at the same time with a feature called multi-programming. |
| 5. Handling Interrupts | it is a technique used by the operating system to temporarily suspend processing of the program and enable the other program to be executed. |
| 6. Maintain Usage Records | It can keep track of the amount of time used by each user for each system unit-the CPU. secondary storage, arid input and output devices. This information is used to charge departments using the organization computing resources. Few of operating systems known are Microsoft Disk operating system (MS-DOS), MS-WINDOWS, UNIX. OS/2, Window NT etc. |
Question 5.
Explain the Multitasking. (May 2010,1 marks)
Answer:
Multitasking: Multi-tasking refers to the ability of the Operating System’s to execute two or more of a single user’s tasks concurrently. Multiple tasks are executed by the CPU switching between them. This is accomplished through foreground/background processing. In this method, the CPU time is shared by different processes.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the difference between ‘Dynamic RAM’ and ‘Static RAM’. (Nov 2010, 2 marks)
Answer:
| Basis | Dynamic RAM | Static RAM |
| 1. Meaning | It is the most common type of main memory. It is dynamic because each memory cell loses its charge, so it must be refreshed hundreds of times each second to prevent data from being lost. | It is a lot faster, expensive and larger memory and commonly used in cache memory. Since it is static, it need not be continually refreshed. |
| 2. Data Storage | Data remains stored as long as the refreshing process is continued each second. | Data remains stored as long as the power is on. |
| 3. Power Consumption | Power consumption of dynamic RAM is less. | Power consumption of static RAM is more. |
| 4. Speed and Cost | Speed of dynamic RAM is slower than that of static RAM but cost wise it is cheaper as compared to static RAM. | Speed of static RAM is more than dynamic RAM but cost wise is expensive and larger as compared to dynamic RAM. |
Question 7.
Why a virtual memory in computer is required? (2011- May 2 marks)
Answer:
Need of Virtual Memory in Computer:
Virtual Memory is a technique that allows the execution of a process, even though the logical address space requirement of the process Is greater than the physically available main memory.
It extends primary memory by treating disk storage as a logical extension of the main memory, thus increasing the storage capacity. If a computer lacks RAM needed to run a program or operations, Windows uses virtual memory. Virtual memory combines RAM with temporary space on the hard disc. When RAM runs low virtual memory moves data from RAM to a space called paging file. This frees up the RAM to complete its work.
Question 8.
Explain the function of ‘Arithmetic Logic Unit’. (May 2011, 2 marks)
Answer:
Arithmetic Logic Unit:
An arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a digital circuit used to perform arithmetic and logic operations. it represents the fundamental building block of the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer. Data is transferred from the storage unit to ALU where It is worked upon and redirected to storage unit.
Functions of ALU
| 1. Arithmetic Operations | Additions, subtractions, multiplications and division etc are example of arithmetic operations. ALU is also responsible for the following conditions: Equal- to conditions, Less than condition and greater than condition. |
| 2. Logical Operations | Logical operations Include comparison between numbers, letter and or special characters. Operations like AND, OR, NOR, NOT etc. using logical circuitry are examples of logical operations. |
| 3. Data Manipulations | Operations such as flushing a register is an example of data manipulation. Shifting binary numbers are also example of data manipulation. |
Question 9.
What are the functions of a Control Unir? (May 2011, 2 marks)
Answer:
Functions of Control Unit:
1. The Control Unit (CU) controls and guides the interpretation, flow and manipulation of ail data and Information. The CU sends control signals until the required operations are done properly by ALU and memory.
2. CU helps in program execution that is, carrying out all the instructions stored in the program. The CU gets program instructions from memory and executes them one after the other. After getting the instructions from memory in CU, the instruction is decoded and interpreted that is, which operation is to be performed. Then the asked operation is carried out. After the work of this instruction, is completed, control unit sends signal to memory to send the next instruction in sequence to CU.
3. The control unit even controls the flow of data from Input devices to memory and from memory to output devices.
4. Acts as a Central Nervous System by maintaining the order and directing the flow of sequence of operation and data. within the computer,
5. It selects the program statement from the storage unit, interprets the statement and sends the appropriate electronic impulses to Arithmetic Logic and storage units which carries Out the required operation,
6. It is basic function Is to Instruct the input device, when to start and stop transferring data to output devices.
Question 10.
Differentiate volatile and non-volatile memory. (May 2012, 2 marks)
Answer:
| Volatile Memory | Non Volatile Memory |
| 1. Requires a power source to retain information. | Does not require a power source to retain Information. |
| 2. When power source is disconnected, information is lost or deleted, | When power source is disconnected, information is not lost or deleted. |
| 3. Often used for temporary retention of data, sub as with RAM, or for retention of sensitive data. | Often used for long-term retention of data, such as files and folders. |
| 4. Volatile memory is often used because it is faster, as well as because it is better suited to retaining sensitive information because shutting off a power source can quickly delete that Information. | Non-volatile memory Is used because It Is better suited to long-term retention of information. |
| 5. It is typically used for primary storage. Example: RAM, is a form of volatile memory. RAM is used to temporarily hold the data required to run programs and applications on an electronic device. | it is typically used for secondary, tertiary and offline storage. Example: ROM, computer hard- disk drive, which is used to hold data such as files and documents. |
![]()
Question 11.
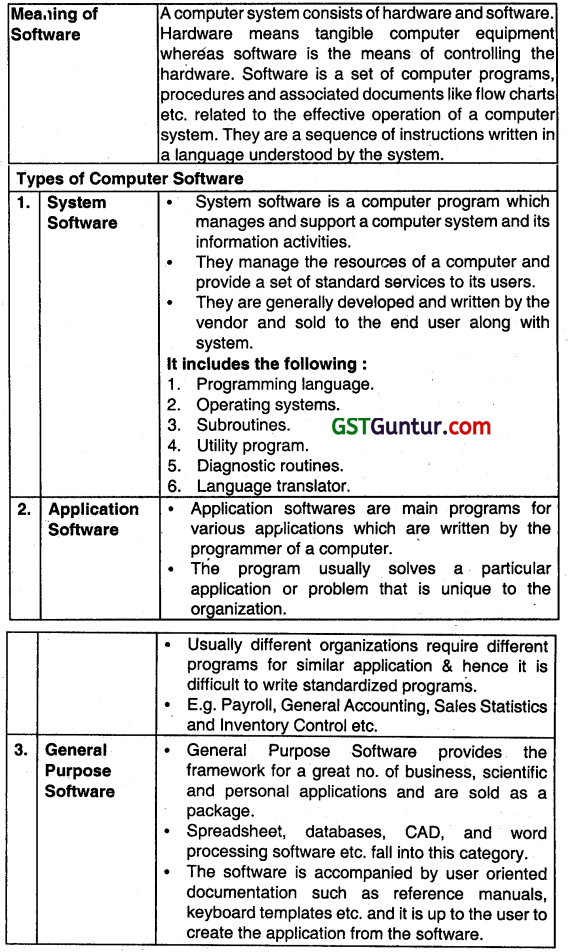
What is Software? Describe various types of software In brief. (Nov 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
Meaning of A computer system consists of hardware and software. Software Hardware means tangible computer equipment whereas software is the means of controlling the hardware. Software is a set of computer programs, procedures and associated documents like flow charts etc. related to the effective operation of a computer system. They are a sequence of instructions written in a language understood by the system.
Question 12.
Describe briefly the following terms with reference to Information Technology:
Virtual Memory (May 2013, 1 mark)
Answer:
Virtual Memory:
Virtual Memory is a technique that allows the execution of a process, even though the logical address space requirement is greater than the physical available memory. It is a primary storage that does not actually exist, It uses the hardware and the software feature which provide for automatic segmentation of a program and for moving the segment from secondary
storage to primary storage when needed.
Question 13.
Distinguish between ‘Cache Memory’ and ‘Virtual Memory’. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Difference between ‘Cache Memory’ and ‘Virtual Memory
Cache Memory:
Cache memory is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations so that Processor/Registers can access it more rapidly than main memory. It is the property of locaiity of reference, which allows Improving substantially the effective memory access time in a computer system.
Virtual Memory:
Virtual memory is in fact not a separate device but an imaginary memory area supported by some operating systems (for e.g. windows) in conjunction with the hardware. If a computer lacks the Random Access Memory (RAM) needed to run a program or operation, windows uses virtual memory to compensate. Virtual memory combines computer’s RAM with temporary space on the hard disk. When RAM runs low, virtual memory moves data from RAM to a space called a paging file. Moving data to and from the paging file frees up RAM to complete its work. Thus, virtual memory is an allocation il hard disk space to help RAM.
Question 14.
Mention briefly the different types of application software. (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Types of Application Software
| 1. Application Suite | it has multiple applications bundled together Related functions, features and user interfaces interact with each other e.g. MS Office 2010 which has MS Word, MS Excel, MS Access etc. |
| 2. Content Access Software | It is used to access contents and addresses a desire for published digital content and entertainment e.g. Media players, adobe digital etc. |
| 3. Educational Software | It holds contents adopted for use by students e.g. Examination test CDs. |
| 4. Enterprise Software | It addresses an enterprises needs and data flow in a huge distributed environment. E.g. ERP applications like SAP. |
| 5. Enterprise Infrastructure Software | It provides capabilities required to support enterprise software systems e.g. E-mail servers, security software. |
| 6. Information Worker Software | It addresses individual needs required to manage and create information for individual projects with in departments e.g. Spreadsheets, CAAT etc. |
| 7. Media Development Software | It addresses individual needs to generate and print electronic media for others to consume. E.g. Desktop publishing, video editing etc. |
Question 15.
Write short note on the Android (May 2015, 2 marks)
OR
What is Android? Discuss its significance. (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Android:
- Android is a Linux-based operating system designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers.
- It was built to enable developers to create compelling mobile applications that take full advantage of all a handset has to offer.
- It powers devices from some of the best handset and tablet manufacturers in the world, like Samsung, HTC, Motorola, Sony, Asus, and more. It provides access to a wide range of useful libraries and tools that can be used to build rich applications.
Question 16.
Write short flotes on Memory Management (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Memory Management:
Memory Management features of operating system allow controlling how memory is accessed and maximize available memory & storage operating system also provides virtual memory by carving an area of hard disk to supplement the functional memory capacity of RAM. In this way it augments memory by creating a virtual RAM.
![]()
Question 17.
Write short flotes Read Only Memory (May 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
| 1. Used for | ROM is used for storing microprograms and control instructions that allows special operations to be performed by the machine. |
| 2. Volatility | ROM is non-volatile or permanent memory. |
| 3. Users | Only machines use ROM. |
| 4. Things Stored | ROM does not allow data to be stored instead they are written by its manufacturer once for all. |
| 5. Reading and Re-writing | Instructions written on ROM can be read but cannot be re-written. |
| 6. Power Interruptions | Power interruptions do not destroy the contents of ROM. |
Question 18.
Name any four activities executed by the Operating System. (Nov 2020, 2 marks)
Question 19.
What is virtual memory? How does it differ from secondary memory? (Jan 2021, 2 marks)
Question 20.
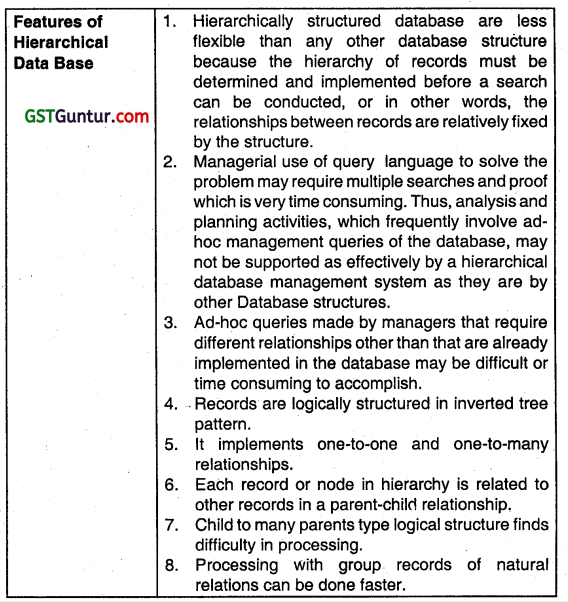
Describe salient features of Hierarchical Database structure. (Nov 2007, Nov 2012, 5,4 marks)
Answer:
Hierarchical Database
Meaning of Hierarchical Database Structure
In this type of structure, records are logically arranged into a hierarchy of relationships. Records are logically arranged in a tree pattern. Hierarchy structure Implements one to one and one-to-many relationships. All records in hierarchy are called nodes. Each node is related to other in a parent-child relationship as each parent record may have one or more child record but no child record may have more than one parent record. The top parent record in the hierarchy is called the root.
Question 21.
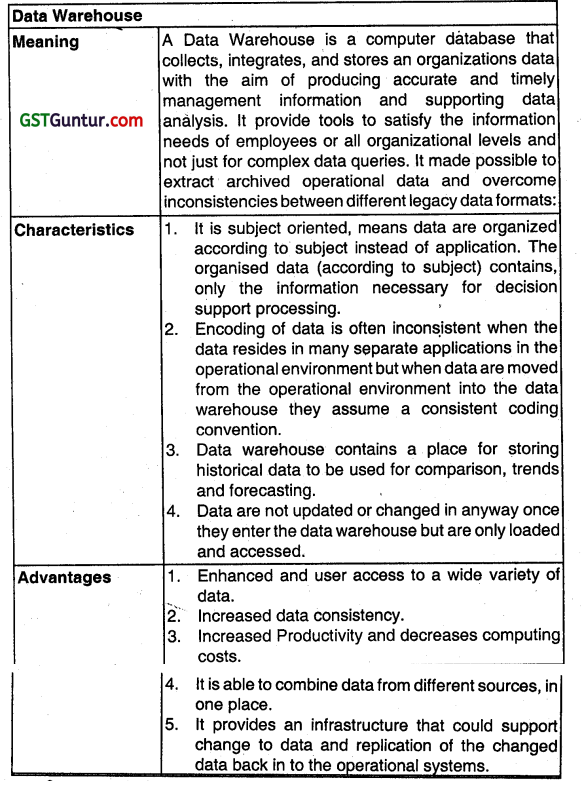
Write short note on the Data warehouse (May 2008, 5 marks)
Answer:
Question 22.
Explain the Data Warehouse (Nov 2008,1 mark)
Answer:
Data Warehouse: A Data Warehouse is a computer database that collects, integrates, and stores an organizations data with the aim of producing accurate and timely management Information and supporting data analysis It provides tools to satisfy the information needs of employees or all organizational levels and not just for complex data queries. It makes possible
to extract archived operational data and overcome inconsistencies between different legacy data formats.
Question 23.
Explain the Real-time data warehouse (May 2009, 1 mark)
Answer:
Real Time Data Warehouse: A data warehouse is a repository of an organisation’s electronically stored data. It is designed to facilitate reporting and supporting data analysis. Real-time Data warehouse is the stage where data warehouses are updated on a transaction or event basis, every time an operational system performs a transaction.
![]()
Question 24.
Write short note on the Stages of Data Mining (May 2010, 5 marks)
Answer:
Data Mining
Meaning Data mining is the extraction of implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful information from data. It searches for relationship and global patterns that exist in large databases but are hidden among the vast amount of data. These relationships represent valuable knowledge about database & objects in the database that can be put to use in the areas such as decision support, prediction, forecasting and estimation. In other words data mining is concerned with the analysis of data and the use of software techniques used for finding patterns and regularities in sets of data. It is the computer responsible for finding the patterns by Identifying the underlying rules and features in the data.
Stages In Data Mining
| 1. Selection | Selecting or segmenting the data according to some criteria so that subsets of the data can be determined. |
| 2. Pre-processing | This is the data cleansing stage where certain information is removed which is deemed unnecessary and may slow down queries. Also, the data is re-configured to ensure a consistent format as there is a possibility of Inconsistent formats because the data is drawn from several sources. |
| 3. Transformation | The data is not merely transferred across but transformed In that overlays may be added. For example, demographic overlays are commonly used in market research. The data is made usable and navigable. |
| 4. Data Mining | This stage is concerned with the extraction of patterns from the data. A pattern can be defined as a given set of facts (data) Fs, a language L, and some measures of certainty C. A pattern in a statement S in L that describe relationships among a subset F of F with a certainty C such that S is simpler In some sense than the enumeration of all the facts in Fs. |
| 5. Integration and Evaluation | The patterns identified by the systems are interpreted Into knowledge which can then be used to support human decision-making. For example, prediction and classification tasks, summarizing the contents of a database or explaining observed phenomena. |
Question 25.
What is importance of Address bus on a motherboard? (Nov 2010, 2 marks)
Answer:
Importance of Address Bus: The address bus is a set of wires on the motherboard similar to data bus that connects the CPU and RAM and carries the addresses of the memory locations where data can be retrieved or stored. It determines maximum number of memory and address. Number of parallel wires in the address bus determines the maximum number of
memory locations the CPU can address.
Question 26.
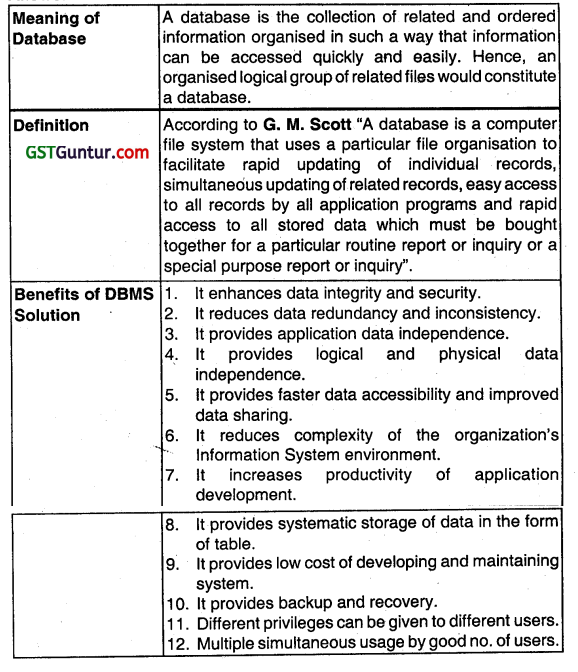
What is Database? What are the benefits of Database, Management Solution? (Nov 2011, 4 marks)
OR
Describe any four benefits of database management solutions for an organization. (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 27.
Write short note on the Data Mining (May 2014, Nov 2016, 2 marks each)
Answer:
Data mining is the extraction of implicit, previously unknown, and potentially useful information from data. It searches for relationships and global patterns that exist In large databases but are hidden among the vast amount of data.
These relationships represent valuable knowledge about databases & objects in the database that can be put to use in the areas such as decision support, prediction, forecasting, and estimation. In other words data mining is concerned with the analysis of data and the use of software techniques used for finding patterns and regularities in sets of data. It is the computer responsible for finding the patterns by identifying the underlying rules and features in the data.
Question 28.
What are the major advantages and disadvantages of DBMS? (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
OR
Explain any four advantages of using a Data Base Management System (DBMS). (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Advantages of DBMS
| 1. Permits Date Sharing | One of the principle advantages of a DBMS is that the same information can be made available to different users. |
| 2. Minimizes Data Redundancy | In a DBMS duplication of Information or redundancy is, if not eliminated, carefully controlled or reduced i.e. there is no need to repeat the same data over and over again. Minimizing redundancy can therefore significantly reduce the case of storing information on hard drives and other storage devices. |
| 3. Maintains Integrity | Data integrity Is maintained by having accurate, consistent, and up-to-date data. Updates and changes to the data only have to be made in one more place in DBMS ensuring integrity. The chances of making mistake increase it the same data needs to be changed at several different places than making the change in one place. |
| 4. Consistency of Program and File | Using a DBMS, file formats and programs are standardized. This makes the data files easier to maintain because the same rules and guidelines apply across all types of data. The level of consistency across files and programs also makes It easier to manage data when multiple programs or involved. |
| 5. User Friendly | DBMS makes the data access and manipulation easier for the user. DBMS also reduce the reliance of users on computer experts to meet their data needs. |
| 6. Achieving Data Independence | In a DBMS data does not reside in applications but data based programs & data are Independent of each other. |
| 7. Faster Application Development | In the case of deployment of DBMS, application development becomes fast. The data is already there in databases. Application developer has to think of only the logic required to retrieve the data in the way a user needs. |
| Disadvantages of DBMS: | |
| 1. Cost | Implementing a DBMS system can be expensive and time-consuming, especially in large enterprises. Training requirements alone can be quite costly. |
| 2. Security | Even with safeguards in place, it may be possible for some unauthorized users to access the database. if one gets access to a database then it could be an all-or-nothing proposition. |
Question 29.
Write short notes on the Object Oriented Data Base Model (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Object Oriented Data Base Model:
It is based on trie concept that the world can be modeled in term of objects and their interactions. Objects are entities covering some meaning for us and possess certain attributes to characterize them and interacting with each other. In these databases, the data is modeled and created as objects.
![]()
Question 30.
What an enterprise has to do to manage Its Information in an appropriate manner? Also, mention any tour operations that can be carried out with the help of Data Base Management System. (DBMS). (Nov 2017,4 marks)
Answer:
Database Management Systems (DBMS):
Every enterprise needs to manage its Information in an appropriate and desired manner. The enterprise has to do the following for this:
- Knowing its information needs.
- Acquiring that information.
- Organizing that information in a meaningful way.
- Assuring information quality, and
- Providing software tools so that users in the enterprise can access information they require.
- DBMS are software that aid in organizing, controlling and using the data needed by the application programme.
- Commercially available database management system are orade, my SQL, SQL services.
Data is given facts from which additional facts can be Inferred thus database is a collection of tacts.
Database – This is a collection of files.
- File – This is a collection of records
- Records – This is a collection of fields
- Field – This is a collection of characters.
- Characters – These are a collection of bits.
Hierarchical Database Model
Network Database Model
Relational Database Model, and
Object Oriented Database Model.
Question 31.
Data Warehouse extracts data from one or more of the organization’s databases and loads it into another database for storage and analysis purpose. As a Data Warehouse Manager, determine the design criteria, which should be met while designing Data Warehouse. (May 2018, 6 marks)
Answer:
Data Warehouse extracts data from one or more of the organization’s databases and loads it Into another database for storage and analysis purpose. As a data warehouse manager, following are the design criteria which should be met while designing Data Warehouse.
It uses non-operational data. This means that the data warehouse is using a copy of data from the active databases that the company uses in its day-to-day operations, so the data warehouse must pull data from the existing databases on a regular, scheduled basis.
The data is time-variant. This means that whenever data is loaded into the data warehouse, it receives a time stamp, which allows for comparisons between different time periods.
The data is standardized. Because the data in a data warehouse usually comes from several different sources, it is possible that the data doesn’t use the same definitions or units. For example, our Events table In our Student clubs database lists the event dates using the mm/dd/yyyy format (eg.01/10/2013). A table in another database might use the format yy/mm/ dd (eg.13 /01/10) for dates, For the data warehouse would have to be converted to use this standard format, This process is called Extraction – Transformation load (ETL).
Question 32.
Explain various types of Data Coding Errors. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Transcription Errors:
Meaning it is a special type of data entry error that is commonly made by human operators or by Optical Character Recognition (OCR) programs.
Types
1. Addition errors:
Addition errors occur when an extra digit or character is added to the code. For example,
inventory item number 83276 is recorded as 832766.
2. Truncation errors:
Truncation errors occur when a digit or character is removed from the end of a code. In this type of error, the inventory item above would be recorded as 8327.
3. Substitution errors:
Substitution errors are the replacement of one digit In a code with another. For example, code number 83276 is recorded as 83266.
Transposition Errors:
| Meaning | It is a simple error of data entry that occurs when two digits that are either individual or part of larger sequence of numbers are reversed (transpose) when posting a transaction. |
| Types | 1. Single transposition errors: It occurs when two adjacent digits are reversed. For instance, 12345 are recorded as 21345. 2. Multiple transposition errors: It occurs when non-adjacent digits are transposed. For example, 12345 are recorded as 32154. |
Question 33.
Write a short note on, Extraction-Transformaton-Load (ETL). (Jan 2021,3 marks)
Question 34.
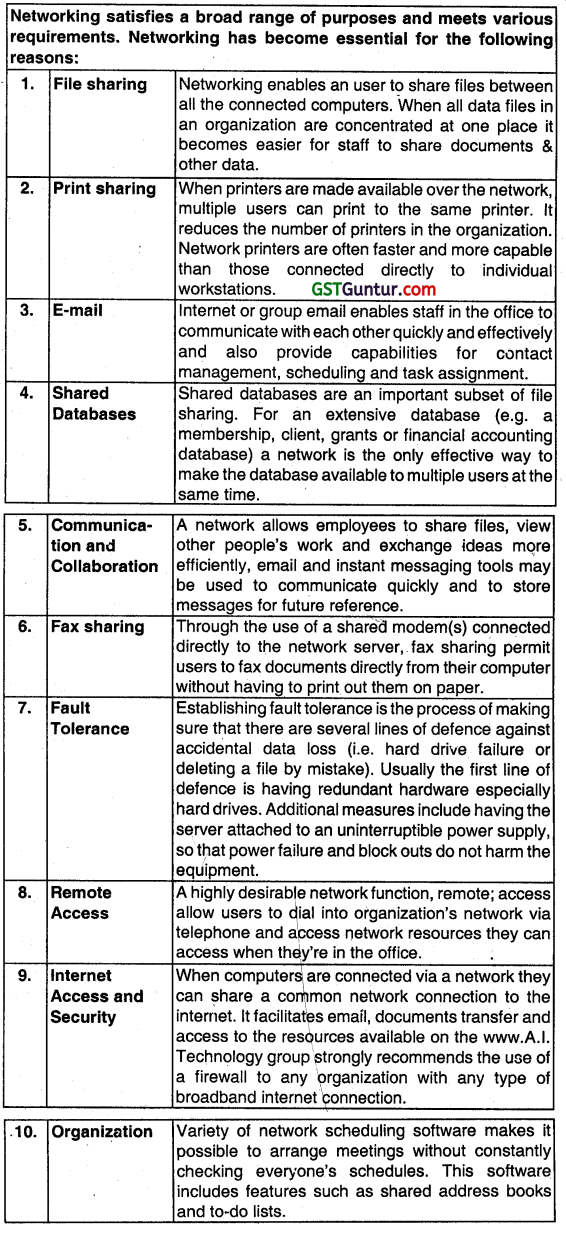
Describe the ways a computer network can help business. (May 2009, 7 marks)
Answer:
Question 35.
Describe any four limitations of the Computer system. (May 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:
The Limitations of Computer System are as follows:
| 1. GIGO | Garbage In Garbage Out i.e. computer does not have its own IQ and an incorrect input data would result in an incorrect output. The computer does what it is programmed to do and can do nothing else. |
| 2. Limitation of Software | To perform specialized functions, special-purpose softwares are required. The investment in software is much more than in hardware. |
| 3. Tampering of Data | Data handling through computers requires special protection routines. |
| 4. Limitations of Hardware | Smaller computers can perform relatively limited work at a slower speed. So more investment is required for higher speed computers. |
Question 36.
List any four features of computerized, networking in an organization. (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
| Features of Computerised Networking | Network computing and their clients provide a browser-based user interface. Network computers are microcomputers without floppy or hard disk drives that are designed as low-cost network computing devices. Application and database servers provide the operating system, application software, applets databases needed by the end users in the network. |
| File Sharing | Networking enables an user to share files between all the connected computers. When all data files in an organization are concentrated at one place it becomes easier for staff to share documents and other data. |
| Print Sharing | When printers are made available over the network, multiple users can print to the same printer. It reduces the number of printers in the organization. Network printers are often faster and more capable than those connected directly to individual workstations. |
| Remote Access | A highly desirable network function, remote access allow users to dial into organization’s network via telephone and access network resources they can access when they’re In the office. |
| Internet Access and Security | When computers are connected via a network they can share a common network connection to the internet. It facilitates email, documents transfer, and access to the resources available on the www.A.I. Technology group strongly recommends the use of a firewall to any organization with any type of broadband Internet connection. |
Question 37.
Describe briefly the Repeaters (Nov 2007, 1 mark)
OR
Describe briefly the following terms with reference to Information Technology:
Repeaters (May 2013, 1 mark)
Answer:
Repeaters: In digital communication systems, a repeater is a device that receives a digital signal on an electromagnetic or optical transmission medium and regenerates the signal along the next leg of the medium. In electromagnetic media, repeaters overcome the attenuation caused by free space electromagnetic-field divergence or cable loss. A repeater decreases distortion by amplifying or regenerating a signal so that it can be transmitted onwards in its original strength form. A series of repeaters make possible the extension of a signal over a distance.
![]()
Question 38.
Describe briefly the DNS Server (May 2008, 1 mark)
Answer:
DNS Server: DNS is an internet-wide distributed database system that documents and distributes network-specific information. The internet protocol recognises any computer by its IP number and Domain names are given for users’ convenience. Therefore it becomes necessary to translate the domain names to corresponding IP address or vice versa. This is done by DNS.
Question 39.
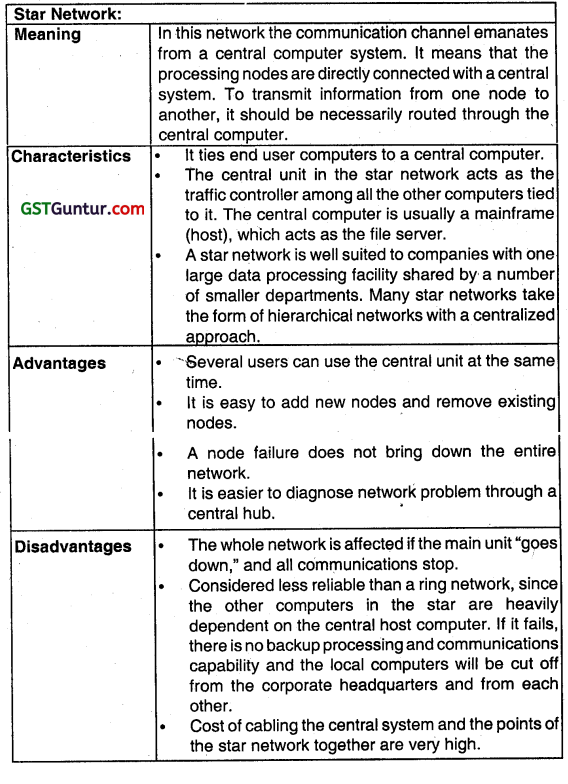
Write short note Star Network topology (Nov 2008, 5 marks)
OR
Explain Star Network Topology. Discuss its advantages and disadvantages. (Nov 2013, 4 marks)
OR
What are the characteristics of Star Network? Write any two advantages and two disadvantages of Star Network. (May 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 40.
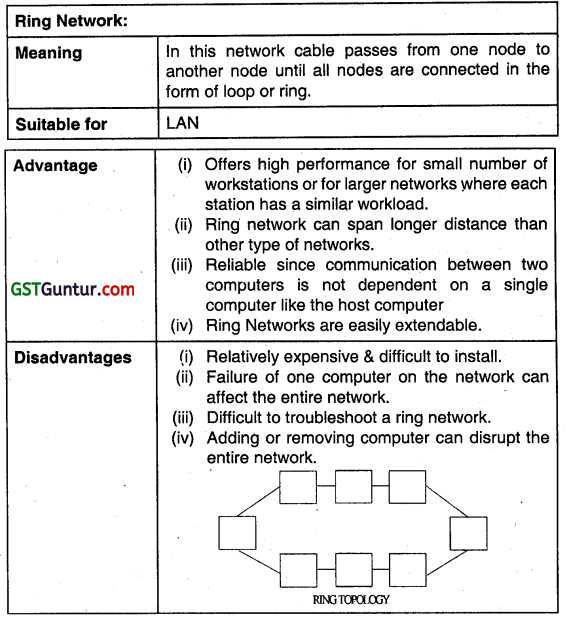
Describe the Ring Network. Discuss its advantages and disadvantages. (Nov 2009, 5 marks)
OR
Define Ring Topology. Discuss its advantages and disadvantages. (Nov 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 41.
Describe briefly the WiFi. (May 2010,1 mark)
OR
Answer the following question in brief:
What s WiFi? (May 2012, 2 marks)
Answer:
WIFI: WiFi means ‘Wireless Fidelity’ which describes the underlying technology of a wireless local area network based on IEEE 802.11 specifications. WiFi is used for mobile computing devices, Internet and VOIP phone access, gaming applications, consumer electronics, public transport, and mobile commerce, etc.
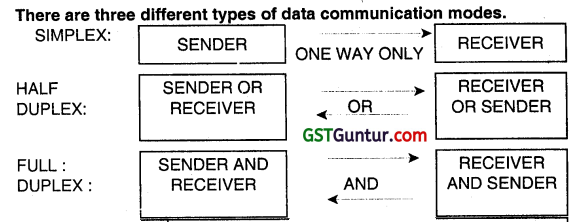
Question 42.
Discuss in brief various data transmission modes. (Nov 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:

Question 43.
Describe briefly Conventions or rules of a Protocol (May 2012, 2 marks)
Answer:
Communication Protocols are the set of rules for inter-computer communication that have been agreed upon and implemented by many vendors, user and standard bodies. Ideally, a Protocol standard allows heterogeneous computer to talk to each other.
Protocols are software that performs a variety of actions necessary for data transmission between computers. At the most basic level, protocols define the physical aspects of communication, such as how the system components will be interfaced and at what voltage levels will be transmitted.
Question 44.
Describe briefly, the following terms with reference to information Technology. Switch (Nov 2012, 1 mark)
Answer:
Switch: Switch ¡s a hardware device used to direct messages across a network. It creates temporary point-to-point links between two nodes on a network and sends all data along that link throughout the network.
Question 45.
Describe briefly terms:
(ii) Wireless LAN (Nov 2012, 2 marks)
Answer:
Wireless LAN: Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a flexible data communications system that does not require any physical media or cables for data transmission. Using Radio Frequency (RF) technology, Wireless LANs transmit and receive data over the air. Users can access shared information without any plug-in or without any physical connection. Wireless LAN configurations range from simple peer-to-peer topologies to complex networks offering distributed data connectivity, flexibility, and mobility.
![]()
Question 46.
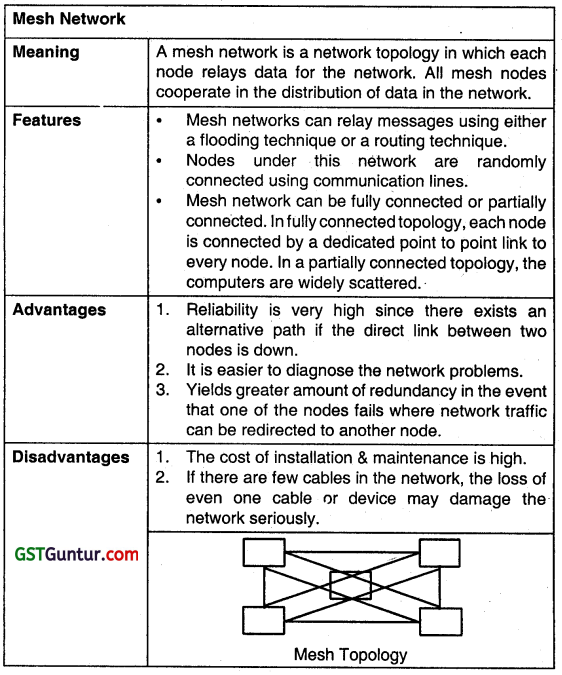
Describe Mesh Network Topology. Discuss its advantages. (May 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 47.
Describe briefly the following terms with reference to Information Technology.
(v) Hub (Nov 2013, 1 mark)
Answer:
Hub: Hub is a common connection point for devices in a network. Hubs are commonly used to connect segments of a LAN. It contains multiple ports. When a packet arrives at one port, it is copied to the other ports so that all segments of the LAN can see all packets. It works on half duplex mode.
Question 48.
Distinguish between the following:
(c) Half Duplex and Full Duplex Connection (Nov 2013, 3 marks)
Answer:
Difference between Half Duplex and Full Duplex
| Half Duplex | Full Duplex |
| It is a connection in which the data flows in one direction or the other but not both at the same time. E.g. Wireless systems. | Data can be transmitted in both the direction simultaneously. E.g. Telephone system, Internet chatting. |
| This type of connection makes It possible to have bidirectional communications using the full capacity of the line. | Since data can flow in both directions simultaneously, each end of the line can thus transmit and receive at the same time. |
Question 49.
Write short note on the following:
VOIP (May 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
VOIP: Voice Over Internet protocol Is a network layer protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables packets to be routed. Other terms commonly associated with VoIP are IP telephony, Internet telephony. Voice over Broadband (VoBB), broadband telephony and broadband phone. This allows delivery of voice communications over IP networks, for example, phone calls.
Question 50.
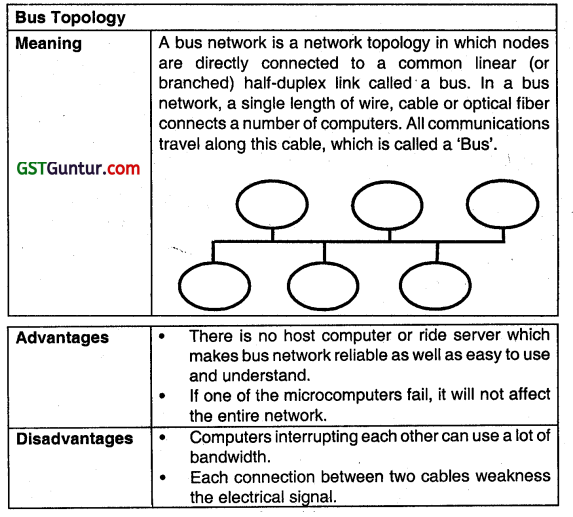
What is Bus Topology? List its two advantages and two disadvantages. (Nov 2014, 3 marks)
Answer:
Question 51.
Which network topology can be used in case of Military Installations with a very small number of nodes and why It should be used? List advantages and disadvantages of such network topology? (May 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Mesh Topology
| Meaning | A mesh network Is a network topology in which each node relays data for the network. All mesh nodes cooperates in the distribution of data in the network. Mesh networks can relay messages using either a flooding technique or a routine technique. In case of Military Installations Mesh Topology is used because it Is created for highly reliable and security-sensitive applications. |
| Advantages | Yields the greatest amount of redundancy in the event that if one of the nodes fails, the network traffic can be redirected to another node. Network problems are easier to diagnose. |
| Disadvantages | Installation and maintenance cost is very high as more cable is required in Mesh Topology. |
Question 52.
Answer the following questions In brief. In what way a Switch Is different from a Router in the computer networks? (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
| Switch | Router |
| 1. Switch is a communications processor that makes connections between telecommunications circuits In a network so that a telecommunications message can reach its intended destination. | Router is a communications processor that interconnects networks based on different rules or protocols, so that a telecommunications message can be routed to its destination. |
| 2. Switches connects telecommunications circuits In a network. | Router interconnects networks bases on rules or protocols. |
Question 53.
Answer the following questions In brief:
What do you understand by Transmission mode”? Name three types of transmission modes. (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Transmission Mode:
The transmission mode is used to define the direction of signal flow between two linked devices. There are three types ot transmission modes characterized according to the direction of the exchanges:
- Simplex
- Half- Duplex
- Full Duplex
Question 54.
Answer the following in brief;
Present two differences between Switch and Bridge In Telecommunication Network. (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Difference between Switch and Bridge:
| Basis of Difference | Switch | Bridge |
| 1. Meaning | Switch is a communicating processor that makes connections between telecommunication circuits in a network so that a tele- telecommunication message can reach its intended destination. | Bridge is a communication processor that connects number of Local Area Networks (LAN). It magnifies the data transmission signal. |
| 2. Mode of interconnection | By Hardware | Via Software |
| 3. No. of ports for inter-connection | Dozens of Ports (Hundreds) | Very few ports (2 – 16) |
| 4. Cost | Lower than Bridge | Higher than switch |
Question 55.
Describe the Wireless technologies that have evolved and widely used in modem day computerized environments. (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Wireless Media
| 1. Terrestrial Microwave | Terrestrial microwave media uses the atmosphere as the medium through which to transmit signals and is used extensively for high-volume as well as long-distance communication of both data and voice in the form of electromagnetic waves. |
| 2. Radio waves | Radio waves are an invisible form of electromagnetic radiation that varies in wavelength from around a millimeter to 1,00,000 km. making If one of the widest ranges in the electromagnetic spectrum. |
| 3. Microwaves | Microwaves are radio waves with wavelengths ranging from as long as one metor to as short as one millimeter or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHZ (0.3 Ghz) and 300 Ghz. |
| 4. Infrared waves | Infrared light is used In industrial scientific and medical applications. Night-vision devices using infrared illumination allow people or animal to be observed without the observer being detected. |
| 5. Communication Satellites | Communication Satellites use the atmosphere as the medium through which to transmit signals. They are used extensively for high-volume as well as long- distance communication of both data and voice. |
Question 56.
Write short note on Packet Switching”. (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Packet Switching:
Packet Switching refers to protocols In which messages are broken up into small transmission units called packets, before they are sent. Each packet is transmitted individually across the net. The packet may even follow different routes to the destination, Since there is no fixed path, different packets can follow different path and thus they may reach to destination out of order.
Question 57.
Distinguish between Star Network and Mesh Network.
Answer:
| Star Network | Mesh Network |
| The star network, a popular network configuration, involves a central unit that has a number of terminals tied Into it. The characteristics of a Star Network are; It ties end-user computers to a central computer The central unit in the star network acts as the traffic controller among all the other computers tied to it. The central computer is usually a mainframe (host), which acts as the tile server. A star network is well suited to companies with one large data processing facility shared by a number of smaller departments. |
In the structure, there is random connection of nodes using communication links. A mesh network may be fully connected or connected with only partial links. In fully interconnected topology, each node is connected by a dedicated point-to-point link to every node. The reliability is very high as there are always alternate paths available IT direct link between two nodes is down or dysfunctional. Fully connected networks are not very common because of the high cost. Only military installations, which need high degree of redundancy, may have such networks, that too with a small number of nodes. |
Question 58.
Write any 8 Information Systems Control procedures covering the access safeguards over computer programs. (May 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Information System Control Procedure:
A well-designed information system should have controls built in for all its sensitive or critical sections. Information system control procedure may include the following:
- Strategy and direction.
- General Organization and Management.
- Access to IT resources, including data and programs.
- System development methodologies and change control.
- Operation procedures system programming and technical support functions.
- Quality Assurance Procedures
- Physical Access Controls
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and Disaster Recovery Planning (DRP)
- Network and communication, Database Administration
- Protective and detective mechanisms against internal and external attacks.
Question 59.
Describe the Information Systems Management Controls usually performed by Top Management. (May 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
An Information System Control is defined as a system of collection, storage, and processing of financial and accounting data that Is used by decision-makers. An accounting information system is generally a computer-based method for tracking accounting activity in conjunction with information technology resources. The top-level management are in charge of the management of different Information system control.
![]()
Question 60.
Define any two information system controls based on objectives of controls. (Nov 2020, 2 marks)
Question 61.
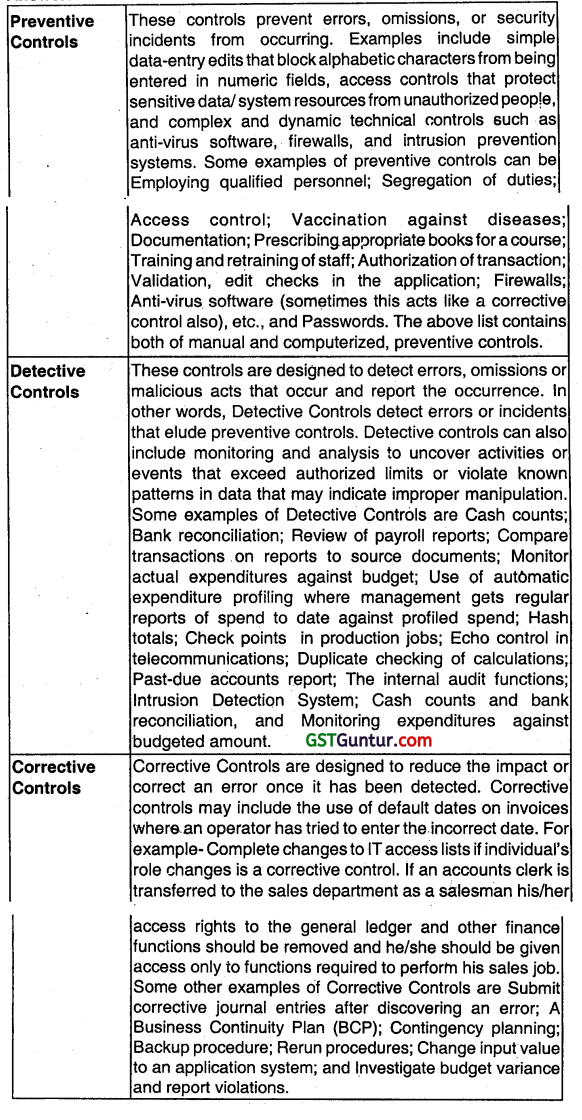
Determine the controls that are classified based on the time when they act, relative to a security incident.
Answer:
Question 62.
Explain the Firewalls (May 2008, May 2010,1 mark)
OR
Write short note on Firewall (May 2014, Nov 2015, 2 marks each)
Answer:
Fire Wall: Fire wail is a device that forms a barrier between a secure and an open environment when the latter environment Is unusually considered. Firewalls are systems which control the flow of traffic between the Internet and the firms internal LANs and systems. They are packaged as turnkey hardware/software packages arid are set up to enforce the specified security policies that are desired. A firewall is a personal and effective means of protecting the firms internal resources from unwanted intrusion.
Question 63.
Explain the Transaction log. (May 2008, Nov 2009, Nov 2013, 1 mark each)
Answer:
Transaction Log:
A Transaction log is a file that records database modifications. Database modifications Consist of inserts, updates, deletes, commits, rollbacks, and database schema changes. A transaction log is not required but is recommended. The database engine uses a transaction log to apply any changes made between the most recent checkpoint and the system failure.
The checkpoint ensures that all committed transactions are written to disk. During recovery, the database engine must find the log file at specified location. When the transaction log tile is not specifically identified then the database engine presumes that the log file is in the same directory as the database file.
Question 64.
Explain the Operating system (May 2009,1 mark)
Answer:
Operating System: Operating system is a master control program of a computer that manages its Internal functions, provides means to control the computer’s operations and file system. They are written by programmers and are different than those In a typical application program. The codes of the operating system of a computer are stored externally in a series of program files on the computer’s hard disk or external memory.
Question 65.
Discuss the various tools that are available for the protection of Information and system against compromise Intrusion or misuse. (May 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:
Several tools are available to protect Information and system against compromise, instruction or misuse:
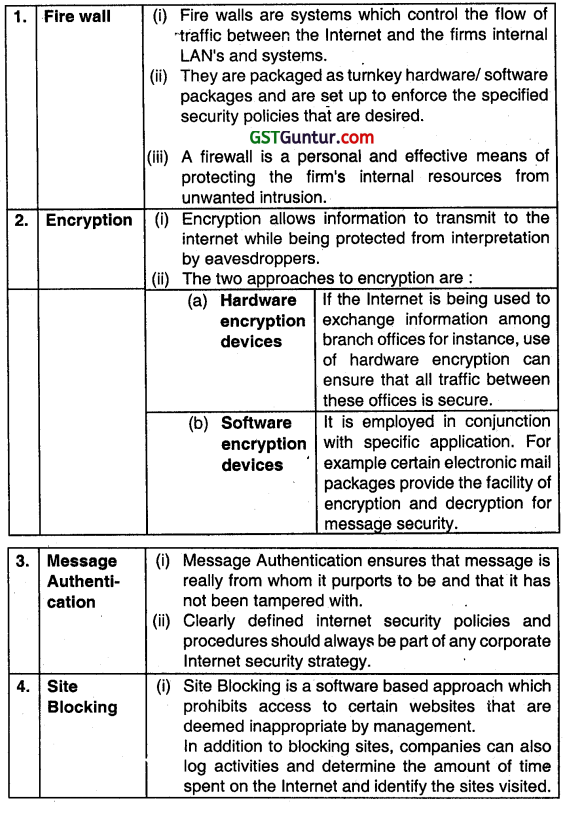
Question 66.
Briefly explain the two main approaches to establish access controls in Software Systems. (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
To ensure that all information that is generated from system is accurate, complete and reliable for decision making there is a requirement for proper controls.
| 1. Application controls | Application are the controls on the sequence Controls of processing events. These controls cover all phases of data right from data origination to its final disposal. Application controls cover transactions as they are recorded in each stage of processing into muster parameter and transaction files and include controls relating to transmission and distribution of output through display, electronic media or printed reports. |
| Internal Controls | SA-315 defines the system of Internal control as the plan of enterprise and all the methods and procedures adopted by the management of an entity to assist achieving management’s objective of ensuring as far as practicable the orderly and efficient conduct of its business including adherence to management policies, the safeguarding of assets, prevention and detection of fraud. |
Question 67.
Mention the two categories of encryption/decryption methods. What are two basic approaches to encryption? (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Two Categories of Encryption/Decryption Methods:
| 1. The Secret Key Method | In secret key encryption/decryption method, the same key is used by both sender and the receiver. The sender uses this key and an encryption algorithm to encrypt data; the receiver uses the same key and the corresponding decryption algorithm to decrypt the data, In this, the algorithm used for decryption is the inverse of the algorithm used for encryption. |
| 2. Public Key | In public key encryption, there are two keys: a private Method key and a public key. The private key is kept by the receiver and the public key is announced to the public. |
Two Basic Approaches to Encryption:
| 1. Hardware encryption: | Hardware devices are available at a Encryption reasonable cost, and can support high-speed traffic. If the internet is being used to exchange information among branch offices or development collaborators, for instance, use of such devices can ensure that all traffic between these offices is secure |
| 2. Software encryption: | Software is typically employed in Encryption conjunction with specific applications. Certain electronic mail packages, for e.g. provide encryption and decryption for message’s security. |
Question 68.
Data that is waiting to be transmitted are liable to unauthorized access called Asynchronous Attacks. Explain various types of Asynchronous attacks on data. (Nov 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
Types of Asynchronous attacks on data:
| 1. Data Leakage | This involves leaking Information out of the computer by means of dumping tiles to paper or stealing computer reports and tape |
| 2. Subversive Attacks | These can provide intruders with important information about messages being transmitted and the intruder may attempt to violate the integrity of some components in the sub-system. |
| 3. Wire-tapping | This involves spying on information being transmitted over Communication network. |
| 4. Piggybacking | This is the acts of following an authorized person through a secured door or electronically attaching to an authorized telecommunication link that intercepts and alters transmissions. This involves intercepting communication between the operating system and the user and modifying them or substituting new messages. |
Question 69.
An operating system allows users and their applications to share and access common computer resources and execute a variety of activities. Hence, protecting operating system access is extremely crucial. Identify various steps through which protection of operating system access can be achieved. (Nov 2018, 8 marks)
Answer:
An operating system allows users and their applications to share and access common computer resources and execute a variety of activities. Hence, protecting operating system access is extremely crucial and can be achieved using following steps:
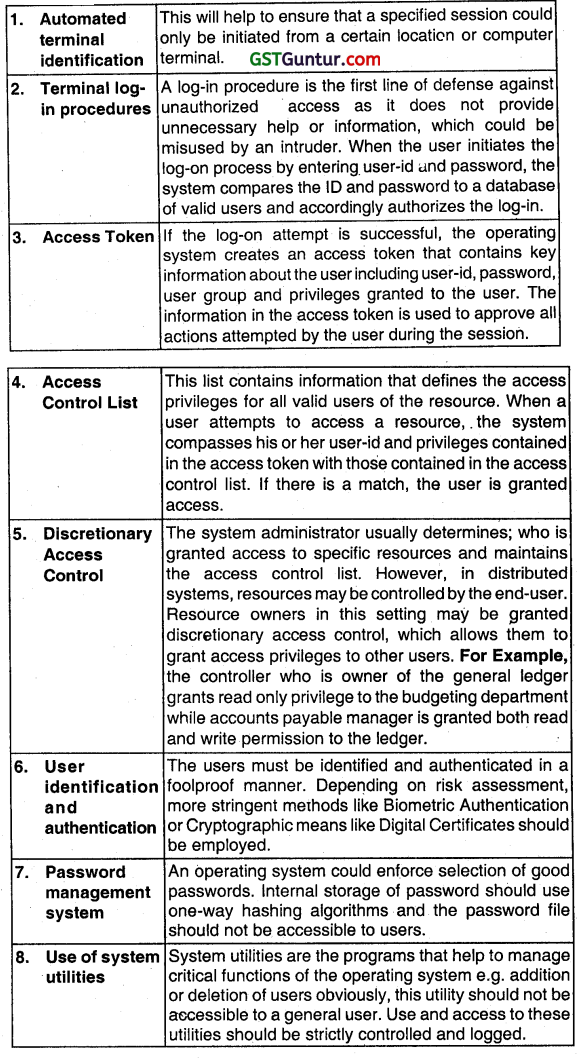
Question 70.
An internet connection exposes an organization to the harmful elements of the outside world. As a network administrator, which Network Access controls will you implement in the organization to protect from such harmful elements? (Nov 2019, 6 marks)
Answer:
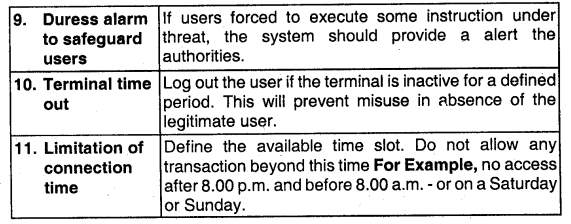
An internet connection exposes an organization to the harmful elements of the outside world. As a network administrator, following Network Access Control will be implemented in the organization to protect from such harmful elements.
![]()
Question 71.
Recognize the activities that deal with the System Development Controls in an IT Setup.
Answer:
The activities that deal with system development controls in IT setup are a follows:
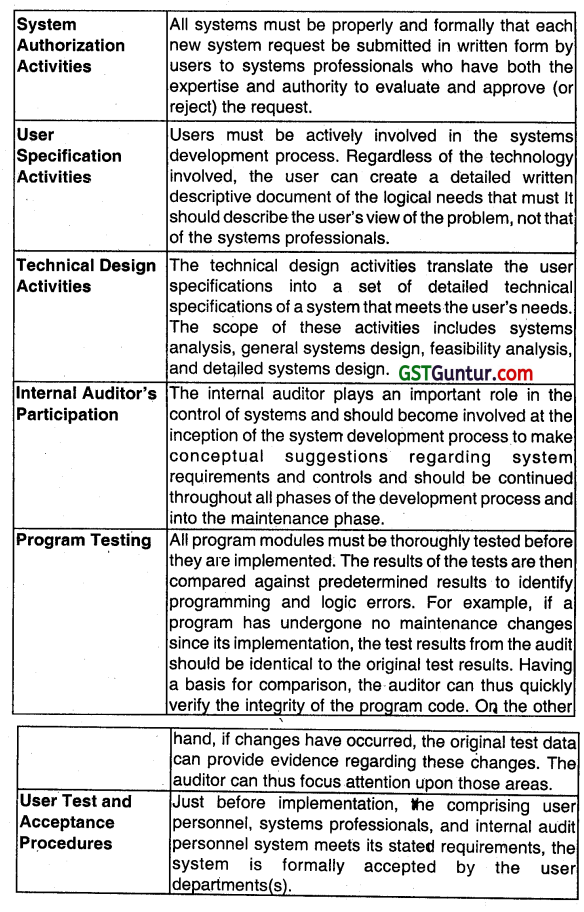
Question 72.
Describe the factors which have contributed to the growth of Local Area Network. (2007- Nov6 marks)
Answer:
Few Reasons for Growth of Local Area Network ere mentioned as under:
| 1. Security | Locking of servers by software and hardware security for programs and data files can be achieved. Diskless node also otter security by not allowing users to download important data on floppies or upload unwanted software or viruses. |
| 2. Expanded PC usage through Inexpensive workstation | In a LAN already set up, cost to automate additional employees through diskless PCs is less. |
| 3. Distributed Processing | Many companies operate as if they had distributed system in place. If numerous PCs are Installed around the office, these machines represent the basic platform for a LAN with inter-user communication and information exchange. |
| 4. Electronic Mail and Message Broadcasting | Electronic mail allows users to communicate more easily among themselves. This can be done by providing each user with a mailbox on the server. |
| 5. Organisational benefits | Benefits of LAN’s are numerous. These include reduced costs in computer hardware, software and peripherals, and a drastic reduction in the time and cost of training or re-training manpower to use the systems. Communication is easier and faster. Information flow between departments also becomes smoother.’ |
| 6. Data Management benefits | Data located on the central server hence much easier to manage and back it up. No file is transferred to use through floppies. |
| 7. Software cost and up-gradation | Since a single server is used hence the software is to be purchased only once instead of buying multiple copies, hence, resulting in reduced cost of software for every machine in organisation. Also up gradation is much easier. |
Question 73.
Explain the following “Multiplexer”. (May 2008, 1 mark)
OR
Describe briefly “Multiplexer”. (Nov 2011, Nov 2013, 2, 1 marks)
Answer:
Multiplexer: A multiplexer is a device that selects one of several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input Into a single line. Multiplexer enables various devices to share one communication line. It scans each device to collect and transmit data on a single line to CPU. It receives input signals from several low-speed lines, converts them Into one
line and transmits it to high-speed transmission channel.
Question 74.
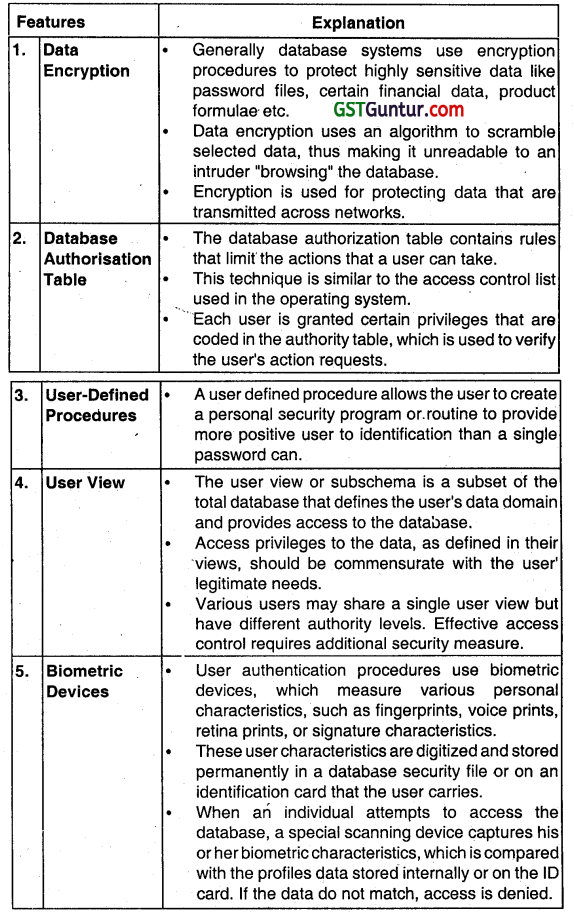
Briefly discuss any live database control features. (May 2008, 5 marks)
Answer:
Data Base Control Features:
Question 75.
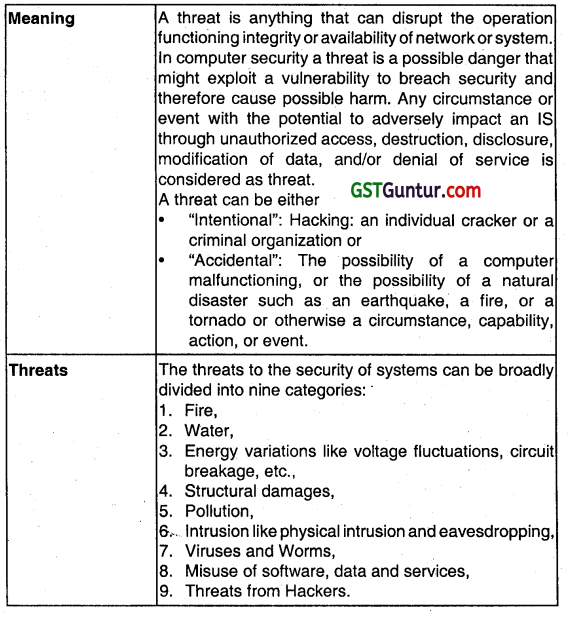
What are the Network Threats and Vulnerabilities? (May 2008, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 76.
Describe briefly the following terms MODEM’. (Nov 2008, Nov 2012, 1 mark each)
Answer:
MODEM: It stands for Modulator/Demodulator. It is a device that converts the digital computer signal to analog telephone signal and vice-versa. Modems are required to telecommunicate computer data with ordinary telephone lines because computer data is in digital form but telephone lines are analog. Modems are built with different range of transmission speed.
![]()
Question 77.
Why documentation‘s required? List any 4 types of documentation required to be prepared prior to delivery of customized software to a customer. (May 2009, 2 + 4 = 6 marks)
Answer:
Need for documentation
It provides a method to understand the various issues related with software development.
It provides means to access details related to system study, system development, system testing, system operational details.
It also provides details associated with the modification of software
Types
- Strategic and application plans.
- Application Systems and Program Documentation.
- System Software and Utility program documentation.
- Database documentation, Operation manual, User Manual, Standard Manual, Backup Manual and other.
Question 78.
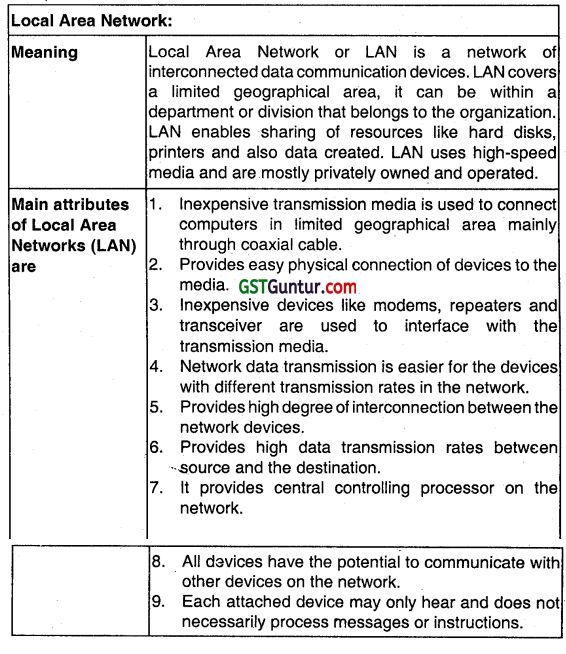
Discuss the various attributes of Local Area Network (LAN). (May 2010, 5 marks)
OR
What are the characteristics of Local Area Networks? (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 79.
What are the requirements of LAN? (May 2012, 4 marks)
Answer
Local Area Network or LAN ¡s a network of interconnected data communication devices. LAN covers a limited geographical area, It can be within a department or division that belongs to the organization. LAN enables sharing ot resources like hard disks, printers and also data created. LAN uses high-speed media and are mostly privately owned and operated.
A LAN should have the following requisite features:
| 1. Compatibility | A layer of compatibility at the software level must be provided by local area network system so that software can be easily written and widely distributed A LAN operating system must be flexible to support -large variety of hardware e.g. Novell Netware. |
| 2. Internet working | Bridging of different LANs together is one of the most important requirement of any LAN. Resources should be accessible from all workstations on the bridge network in a transparent way with no special commands requirement for crossing the bridge. Network operating system must be hardware Independent providing the same user interface irrespective of the hardware. |
| 3. Growth Path and Modularity | One more essential feature of LAN is its modularity. It means a set of PCs should get easily converted into a LAN which can grow in size simply by adding additional workstations. For additional storage requirements, another hard disk should be easily added to another server. |
| 4. System Reliability and Maintenance | All computers are prone to system lockups, power failures and catastrophes. In case of centralized processing, if central processor goes down, all users connected to it are left without a machine to work on. Such a situation can even arise in distributed or local area networks. Hence, a LAN operating system should be powerful enough to withstand accidents. |
Question 80.
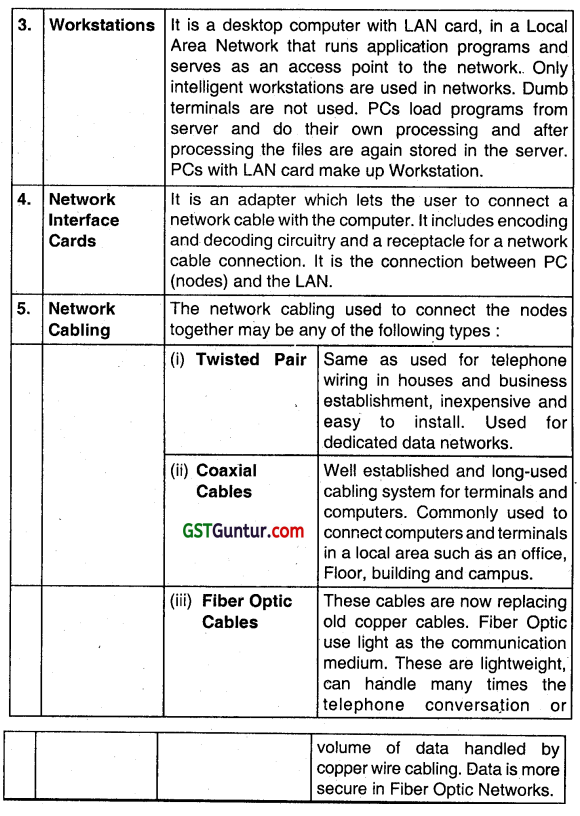
Explain briefly any four components of Local Area Network (LAN). (May 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Components of LAN are as follows:
1. File Servers
File servers are computers used for the purpose of managing file systems, servicing the network printers, handling network communications and other functions. It can be a dedicated or non-dedicated one.
2. The Network
it is a system software of LAN that integrates the Operating network’s hardware components. It establishes and System maintains the connection between the workstations and the file server. It contains two parts:
- File servers and
- Workstation software.
Question 81.
Answer the following question briefly:
What is the difference between backup and recovery? (May 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Difference between Backup and Recovery
- Backup and recovery systems are used for the protection and retention of data.
- Backup is used to keep copies of data for data protection purpose, while recovery is used for salvaging data that is already lost.
- In other words, backup can be considered a precautionary method (making and keeping copies of data in case they get lost), while recovery is a cure for already lost data.
- Even though precaution is always better than cure, there are many occasions when recovery is needed simply because some users do not take enough time/effort for backing up their data on a regular basis.
- One advantage of backing up Is that there is a guarantee that the data is secure, while ¡t is difficult to vouch that the recovery will always work.
- Using backed-up data in case of a data loss can be considered easier and quicker than recovering a lost file (which could be quite tedious depending on the situation).
- However, recovery could be the only solution in extreme cases like when both the original and backed-up data is lost.
![]()
Question 82.
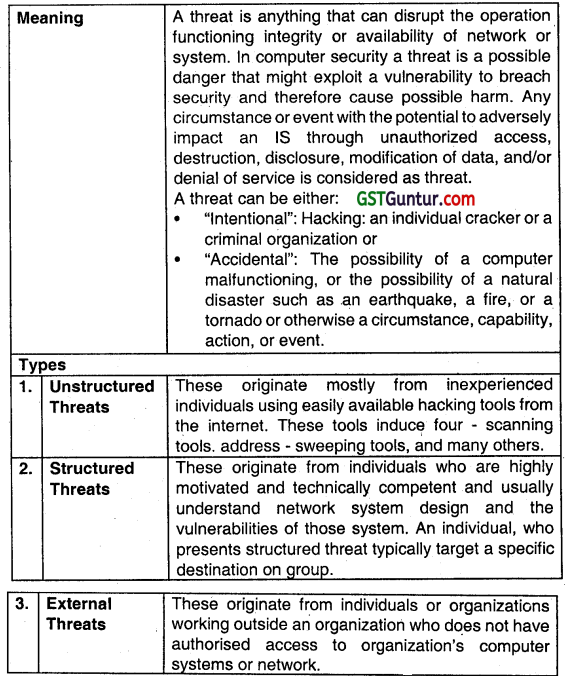
What is a ‘Threat’? Explain any three types of Network Security threat? (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 83.
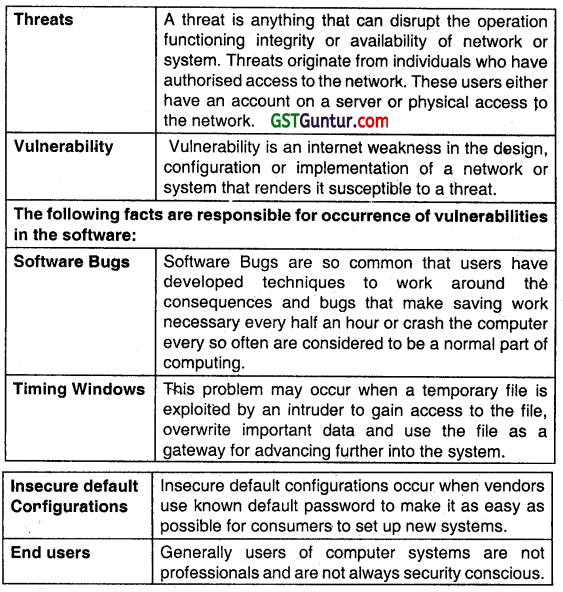
What do you mean by threat and vulnerability? Explain any three facts responsible for occurrence of vulnerabilities in me software. (Nov 2014, 5 marks)
Answer:
Question 84.
What are the major process controls, which should be enforced through front end application system, to have consistency in the control process? (May 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
The Process Controls that should be enforced through the front-end application system, to have consistency In the control process are as follows:
| Run-to-Run Totals | These help in verifying data that is subject to process through different stages. A specific record can be used to maintain the control total. |
| Reasonableness Verification | Two or more fields can be compared and cross verified to ensure their correctness. |
| Edit Checks | Edit checks similar to the data validation controls can also be used at the processing stage to verify accuracy and completeness of data. |
| Field initialization | Data overflow can occur, if records are constantly added to a table or if fields are added to a record without initializing it. |
| Exception Reports | Exception reports are generated to identify errors in data processed. |
| Existence/Recovery Controls | The check-point restart logs facility is a short-term backup and recovery control that enables a system to be recovered ¡f failure is temporary and localized. |
Question 85.
Answer the following questions in brief:
Explain Cryptographic Controls. (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Cryptographic Controls:
Cryptographic controls are designed to protect the privacy of data and to prevent unauthorized modifications of data. Cryptography achieves this goal by scrambling data into codes (cryptograms) so that it is meaningless to anyone who does not possess the authentication to access the respective system resource or file. Examples are encryption, digital signature etc.
Question 86.
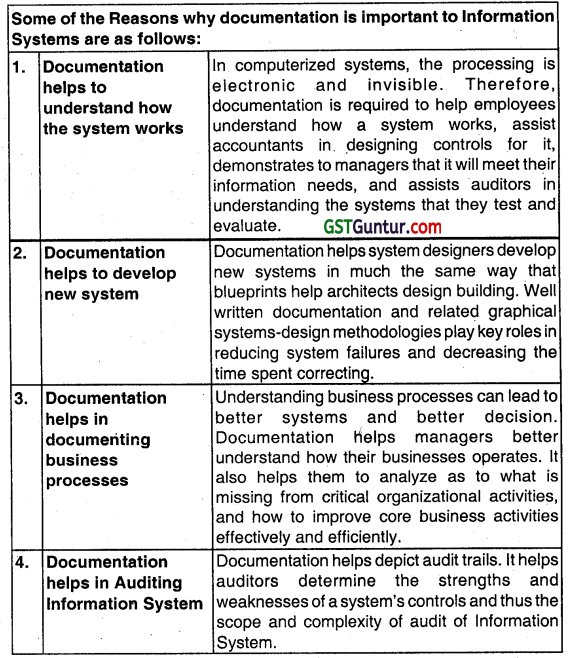
Describe any four reasons why documentation is important to Information Systems. (May 2016, 4 marks)
Answer;
Information System is defined as the processed data for decision-making. The information system shall be used to derive data for the organization. Documentation includes the flowcharts, narratives and other written communications that describe the inputs, processing and outputs of an Accounting Information System, It describes the logical flow of data within a computer system arid the procedures that employees must follow to accomplish application Tasks.
Question 87.
Describe any four output Controls that have to be enforced both in a batch-processing environment as well as in an online environment. (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Types of output controls can be described as follows:
| 1. Logging of Output Programme Execution | When. programms used for output of data, are executed, they should be logged and monitored. In the absence of control over such output programme executions, confidentially of data could be compromised. |
| 2. Controls over Printing | It should be ensured that unauthorised disclosure of information printed is prevented. Users must be trained to select the correct print and access restriction may be placed on the workstations that can be used for printing. |
| 3. Retention Controls | Retention controls consider the duration for which outputs should be retained before being destroyed. Consideration should be given to the type of medium on which the output is stored. |
| 4. Existence/ Recovery Controls | These controls are needed to recover output in the event that if it is lost or destroyed on in case that if the output is written to a spool of files or report files which stands untraceable. |
Question 88.
What are the advantages of Fiber-optic transmission? (May 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Advantages of Fibre Optic Transmission:
- Can carry digital as well as analog signals.
- High speed and greater carrying capacity than coaxial cable transmission and twisted pair lines.
- Lower error rate.
- Not susceptible to electronic noise.
- Not affected by electromagnetic radiation.
- Flexible and can be used undersea also.
Question 89.
Explain the following in brief:
Line Error Control (May 2o18, 2 marks)
Answer:
Line Error Control:
Whenever data is transmitted over a communication line, recall that it can be received in error because of attenuation distortion, or noise that occurs on the line. These errors must be detected arid corrected.
(i) Error Detection:
The error can be detected by either using a loop (echo) check or building some form of redundancy into the message transmitted.
(ii) Error Correction:
When line errors have been detected, they must then be corrected using either forward error correcting codes or backward error collecting codes.
![]()
Question 90.
Explain the term Cryptography’. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Cryptography:
It deals with programs for transforming data into cipher text that are meaningless to anyone, who does not possess the authentication to access the respective system resource or file. A cryptographic technique encrypts data (clear text) into cryptograms, (cipher text) and Its strength depends on the time and cost to decipher the cipher text by a cryptanalyst. Three
techniques of cryptography are transposition (permute the order of characters within a set of data), substitution (replace text with a key text) and product cipher (combination of transposition and substitution).
Question 91.
Protecting the integrity of a database when application software acts as an interface to interact between the user and the database are called update controls and report controls. Discuss any three update controls and three report controls. (Nov 2020, 6 marks)
Question 92.
Write short note on Cryptography. (Nov 2020, 2 marks)
Question 93.
A company XYZ Is implementing the software by using the program development life cycle methodology and applying control phases In parallel to the development phases to monitor the progress against plan. Being an IT developer, design the various phases and their controls for program development life cycle. (May 2019, 6 marks)
Answer:
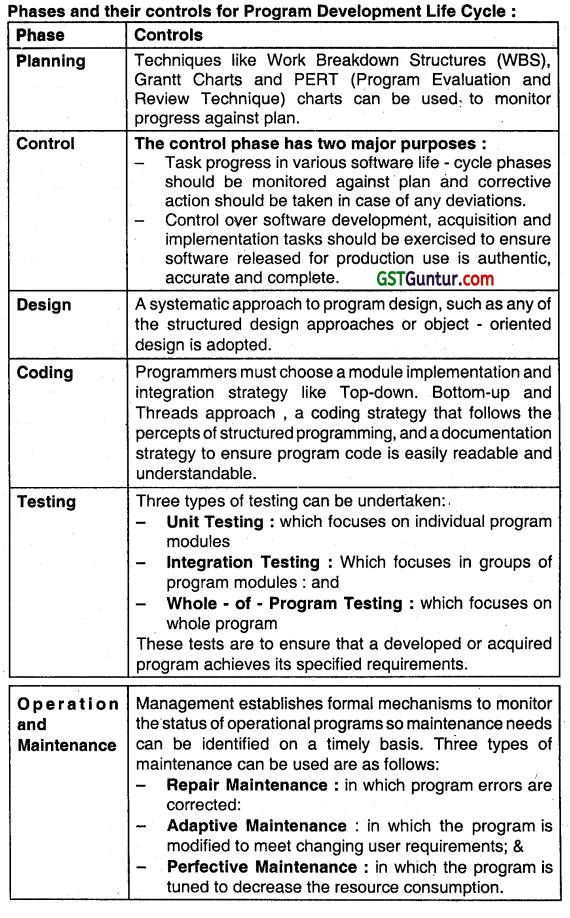
Question 94.
Answer the following In brief:
What kind of awareness is required by an auditor for auditing In an IT environment? (2017 May,2 marks)
Answer:
Auditing in a computerized environment would involves the process of evaluating and reporting the adequacy of system controls, efficiency, economy, effectiveness, and security practices. The auditor should make sure that assets and information resources are safeguarded, data integrity is protected, and the system complies with applicable policies,
procedures, standards, rules, laws, and regulations.
The Auditor has to look at both the manual and automated parts of the system, because of their interfacing nature.
The Increased risks and changes In the traditional control functions has caused to a shift the Auditor’s scope of work In IS Environment. The key concerns of auditor are:
- Develop and apply new criteria in evaluating control weaknesses In Computerized Information Systems (CIS),
- Tailor-testing techniques to the CIS understudy, and
- Use computers to perform some portions of audit examination.
Question 95.
Explain briefly the objectives of Information System’s Auditing. (May 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
Objectives of Information System’s Auditing
| 1. Asset Safeguarding Objectives | The information system assets (hardware, software, data information, etc.) must be protected by a system of Internal controls from unauthorized access. |
| 2. Data Integrity Objectives | It is a fundamental attribute of IS Auditing. The importance to maintain integrity of data of an organization requires all the time. It is also important from the business perspective to the decision-maker, competition, and the market environment. |
| 3. System Effectiveness Objectives | Effectiveness of a system is evaluated by auditing the characteristic and objectives of the system to meet business and user requirements. |
| 4. System Efficiency Objectives | To optimize the use various Information system resources (machine time, peripherals, system software and labour) along with the impact on its computing environment. |
Question 96.
Describe some of the advantages of continuous audit techniques. (May 2010, 5 marks)
Answer:
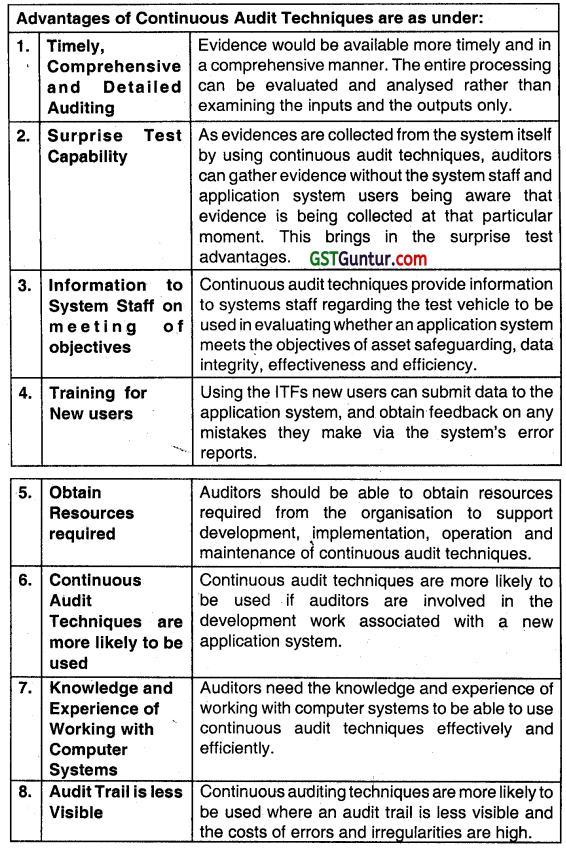
Question 97.
As an IS Auditor, explain the types of information collected for auditing by using System Control Audit Review File (SCARF) technique. (May 2011, 4 marks)
OR
As an IS auditor of a company, you want to use SCARF technique for collecting some information, which you want to utilize for discharging some of your functions. Briefly describe the type of information that can be collected through the use of SCARF technique. (May 2016, 6 marks)
Answer:
An IS Auditor might use SCARF to collect the following types of Information:
| 1. System Exception | SCARF can be used to monitor different types of application system exceptions. |
| 2. Snapshots and Extended Records | Snapshots and extended records can be written into the SCARF tile and printed when required. |
| 3. Performance Measurement | Auditors can use embedded routines to collect data that is useful for measuring or improving the performance of an application system. |
| 4. Application System Errors | SCARF audit routines provide an Independent check on the quality of system processing, whether there are any design and programming errors as well as errors that could creep into the system when it is modified and maintained. |
| 5. Statistical Sample | Some embedded audit routines might be statistical sampling routines, SCARF provides a convenient way of collecting all the sample information together on one file and use analytical review tools thereon. |
| 6. Policy and Procedural Variances | Organizations have to adhere to the policies, procedures and standards of the organization and the industry to which they belong. SCARF audit routines can be used to check when variations from these policies, procedures, and standards have occurred. |
| 7. Profiling Data | Auditor can use embedded audit routines to collect data to build profiles of system users. Deviations from these profiles indicate that there may be some errors or irregularities. |
Question 98.
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of Continuous Auditing Techniques In brief. (Nov 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:
Advantages of Continuous Auditing Techniques:
Objectives of Information System’s Auditing
| 1. Asset Safeguarding Objectives | The information system assets (hardware, software, data information etc.) must be protected by a system of Internal controls from unauthorized access. |
| 2. Data Integrity Objectives | It is a fundamental attribute of IS Auditing. The importance to maintain integrity of data of an organization requires all the time. It is also important from the business perspective to the decision-maker, competition, and the market environment. |
| 3. System Effectiveness Objectives | Effectiveness of a system is evaluated by auditing the characteristic and objectives of the system to meet business and user requirements. |
| 4. System Efficiency Objectives | To optimize the use various Information system resources (machine time, peripherals, system software and labour) along with the impact on its computing environment. |
Disadvantages
The following are some of the disadvantages and limitations of the continuous Audit System:
1. Auditors should be able to obtain resources required from the organization to support development, implementation, operation, and maintenance of continuous audit techniques.
2. Continuous audit techniques are more likely to be used it auditors are involved in the development work associated with a new application system.
3. Auditors need the knowledge and experience of working with computer systems to be able to use continuous audit techniques effectively and efficiently. Continuous auditing techniques are more likely to be used where the audit trail is less visible and the costs of errors and irregularities are high.
4. Continuous audit techniques are unlikely to be effective unless they are implemented in an application system that is relatively stable.
![]()
Question 99.
What do you mean by System Control Audit Review File’ (SCARF)? What types of information can be collected by Auditor using SCARF. (May 2013, 6 marks)
Answer:
- System Control Audit Review file uses embedded audit modules to continuously monitor transaction activity and collect data on transactions with special audit significance.
- The data are recorded in a SCARF or audit log.
- Transactions that might be recorded ¡n a SCARF include those exceeding a specified rupee limit, involving inactive accounts, deviating from company policy, or containing write-downs of asset values.
- Periodically, the auditor receives a printout of the SCARF file, examines the information to identify any questionable transactions and performs any necessary follow-up investigation.
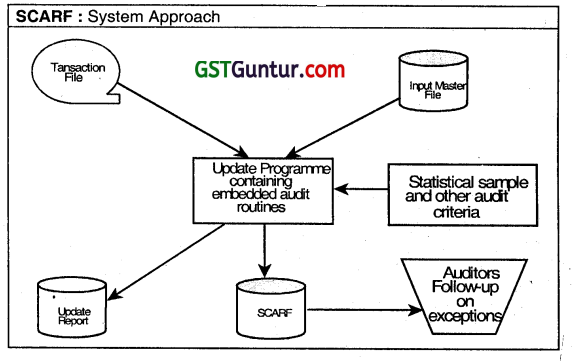
Question 100.
Write short note on the following:
Continuous and Intermittent Simulation (CIS) (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
CIS:
This is a variation of the SCARF continuous audit technique. This technique can be used to trap exceptions whenever the application system uses a database management system. During application system processing CIS executes in the following way:
- The database management system reads an application system transaction. It is passed to CIS. CIS then determines whether it wants to examine the transaction further. If yes, the next steps are performed or otherwise t waits to receive further data from the DBMS. :
- CIS replicates or simulates the application system processing.
- Every update to the database that arises from processing the selected transactions will be checked by CIS to determine whether discrepancies exist between the results it produces and those the application system produces.
- Exceptions identified by CIS are written to a exception log file.
- The advantage of CIS is that it does not require modifications to the application system and yet provides an online auditing capability.
Question 101.
Differentiate between Concurrent Audit and General Audit.
Answer: :
Concurrent Audit: In this, Auditors are members of the systems development team. They assist the team in improving the quality of systems development for the specific system they are building and implementing.
General Audit: In this, Auditors evaluate systems development controls overall. They seek to determine whether they can reduce the extent of substantive testing needed to form an audit opinion about management’s assertions relating to the financial statements in systems effectiveness and efficiency.
Question 102.
The management of ABC Ltd. wants to design a detective control mechanism for achieving security policy objectives in a computerized environment. As an auditor explain, how audit trails can be used to support security objectives. (May 2010, 10 marks)
Answer:
Audit trails can be used to support security objectives in three ways:
1. Detecting unauthorized access to the system,
2. Facilitating the reconstruction of events, and
3. Promoting personal accountability.
Each of these is described below:
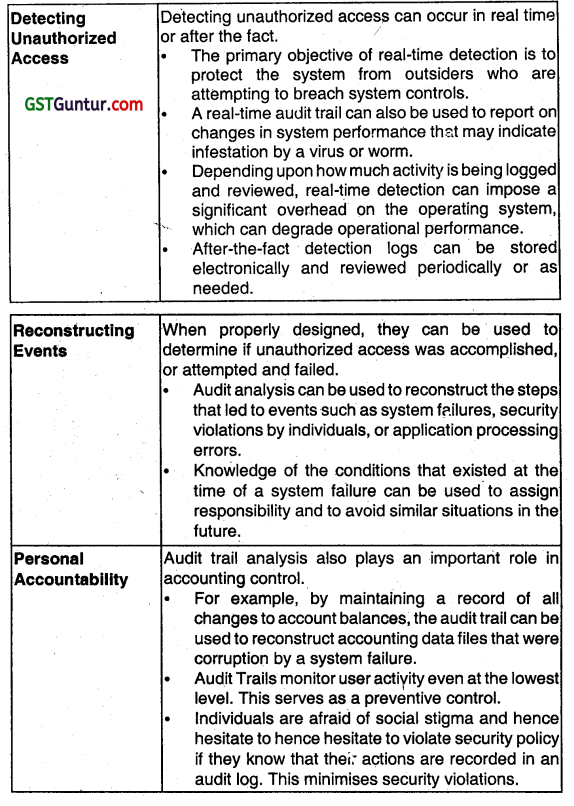
Question 103.
Describe the components of Intrusion Detection Systems. (May 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
The Components of intrusion Detection System are as follows:
| 1. Sensors | These are deployed In a network or on a device to collect data. They take input from various resources, Including network packets, log files, and system call traces. Input is collected, organized and then forwarded to one more analyzers. |
| 2. Analyzers | Analyzers in IDS collect data forwarded by sensors and then determine if an intrusion has actually occurred. Output from analyzers should include evidence supporting the intrusion report. The analyzers may also provide recommendations and guidance on mitigation steps. |
| 3. User interface | The user interface of the los provides the end users a view and way to interact with the system. Through the interface, the user can control and configure the system. Many user interfaces can generate reports as well. |
| 4. Honeypot | In fully deployed IDS, some administrators may choose to Install a Honey pots”, essentially a system components set up as bait or decoy for intruders. Honey pots can be used as early warning systems on an attack, decoys from critical systems, and data collection sources for attack analysis. |
Question 104.
Discuss the key activities, which require special attention for auditing the user access provisioning. (May 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Auditing the user access provisioning process requires attention to several key activities, including:
| 1. Access request processes | The IS auditor should identify all user access request processes and determine it these processes are used consistently throughout the organization. |
| 2. Access approvals | The IS auditor needs to determine how requests are approved and by what authority they are approved. The auditor should determine if system or data owners approve access requests, or if any accesses are ever denied. |
| 3. New employee provisioning | The IS auditor should examine the new employee provisioning process to see how a new employee’s user accounts are initially set up. The auditor should determine if new employee’s managers are aware of the access requests that their employees are given and if they are excessive. |
| 4. Segregation of Duties (SoD) | The IS auditor should determine if the organization makes any effort to identify segregation of duties. This may include whether there are any SoD matrices in existence and if they are actively used to make user access request decisions. |
| 5. Access reviews | The IS auditor should determine if there are any periodic access reviews and what aspects of user accounts are reviewed: this may include termination reviews, internal transfer reviews, SoD reviews, and dormant account reviews. |
Question 105.
Information systems have set high hopes for companies for their growth as it reduces processing speed and helps ¡n cutting cost. Being an auditor of ABC manufacturing company, discuss the key areas that should pay attention to while evaluating Managerial controls by top management. (Jan 2021, 4 marks)
Question 107.
Explain value-added services being offered by a Data Centre. (Nov 2007, 5 marks)
OR
Describe various value-added services offered by a Data Centre. (Nov 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Some of the value-added services that data centres provide are:
| 1. Database Monitoring | This is done via a database agent, which enables the high availability of the database through comprehensive automated management. |
| 2. Web Monitoring | It accesses and monitors website performance, availability, response, and integrity, from a visitor’s perspective. it reports on HTTP, FTP service status, monitors URL availability, verify web content accuracy and changes. |
| 3. Back up and Restore | it provides centralized multi-system management capabilities and a comprehensive integral management solution to data storage using backup agent for the operating systems, database, and applications. |
| 4. Storage on Demand | it provides back-end infrastructure as well as Expertise best practices and processes to give a robust and cost-effective storage strategy. It also provides security, reliability, and availability of data to meet company’s demand. |
| 5. Intrusion Detection System | It detects malicious activity on the host-based ID systems and network-based ID systems. |
Question 106.
What are the challenges faced by the management of a data centre? (May 2009, 3 marks)
Answer:
Data Centre
A Data Center is a centralized repository for the storage, management, and dissemination of data & information. Data center is a facility used for housing a large amount of electronic equipment, typically computers and communication equipments. The purpose of a data center is to provide space and bandwidth connectivity for server in a reliable, secure, and scalable environment.
It also provides facilities like housing websites, providing data serving and other services for companies. Such type of data center may contain a network operations center (NOC) which is restricted access area containing automated system that constantly monitors server activity, web traffic, network performance and reports even slight irregularities to engineers so that they can stop potential problems before they occur.
Challenges
| 1. Maintaining Infrastructure | A data center needs to set up an infrastructure comprising of a member of electronic equipment, typically computers and bandwidth connectivity for server in a reliable secure and scalable environment. |
| 2. Skilled Human Resources | A data center needs skilled staff experts at network management having software and hardware operating skill. |
| 3. Selection of Technology | A data center also faces the challenge of proper selection of technology crucial to the operation of the data center. |
| 4. Maintaining System Performance | A data centre has to maintain maximum uptime and system performance while establishing sufficient redundancy and maintaining security. |
![]()
Question 107.
Describe briefly salient features of Data Centres. (Nov 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:
Features of Data Centers
1. Data Centers are characterized by the size of their operations and require a minimum area of around 5,000 to 30,000 square meters. A. financially viable data center could comprise of a hundred to several thousand servers.
2. It should ensure maximum data security and availability. Data centers have to be protected against Intruders by controlling access to the facility and by video surveillance. They should be able to withstand natural disasters and calamities, like fire the power failures. Recovery sites must be well maintained.
3. The goal of a Data Center is to maximize the availability of data, and to minimize potential downtime. To do this, redundancy has to be built into all the mission-critical infrastructure of the data center, such as connectivity, electrical supply, security and surveillance, air conditioning, and fire suppression.
4. A Data Center should provide the highest power availability with uninterrupted power systems (UPS).
5. Physical Security and Systems Security are critical to operations. Thus, it should provide both types of security measures to ensure the security of equipments and data placed at the data center.
Question 108.
What are the various views taken into account, while designing the architecture of a Database? Which view is user dependent and which one user independent? Which view is storage device oriented? (May 2009, 3+2+1 = 6 marks)
Answer:
While designing the architecture of a database, the following views are taken into account.
| 1. External View | it is also known as user view As name suggests, it includes only those application programs which are user concerned. It is described by users/ programmers by means of external schema. |
| 2. Conceptual View | It is also known as global view. It represents the entire database and includes all database entities. It is defined by conceptual scheme and describes all records, relationships, constraints, or boundaries. |
| 3. Internal View | It is also known as physical view. It describes the data structure and the access methods. It is defined by internal schema and indicates how data will be stored. |
Out of the above three External View is user dependent and the rest two are user independent. Also, internal view is user Independent.
Question 109.
Explain any four examples of segregation of duties (SOD) controls. (Nov 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Examples of Segregation of duties (SoD) controls
| 1. Transaction Authorization | Information systems can be programmed or configured to require two (or more) persons to approve certain transactions. Many of us see this in retail establishments where a manager is required to approve a large transaction or a refund. In IT applications, transactions meeting certain criteria (for example, .exceeding normally accepted limits or conditions) may require a manager’s approval to be able to proceed. |
| 2. Split custody of high-value assets | Assets of high importance or value can be protected using various means of split custody. For example, a password to an encryption key that protects a highly-valued asset can be split in two halves, one half assigned to two persons, and the other half assigned to two persons so that no single individual knows the entire password. Banks do this for central vaults, where a vault combination is split into two or more pieces so that two or more are required to open it. |
| 3. Workflow | Applications that are workflow-enabled can use a second (or third) level of approval before certain high-value or high-sensitivity activities can take place. For example, a workflow application that is used to provision user accounts can include extra management approval steps in requests for administrative privileges. |
| 4. Periodic reviews | It or internal audit personnel can periodically review user access rights to identify whether any segregation of duties issues exists. The access privileges for each worker can be compared against segregation of duties control matrix. |
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A group of mutually related, cooperating elements with a defined boundary; working on reaching a common goal by taking inputs and producing outputs in organised transformation process, is called:
(a) Data
(b) Information
(c) Feedback
(d) System
Answer:
(d) System
Question 2.
Information System (IS) refers to the interaction between
(a) data and information
(b) data and processes
(c) processes and technology
(d) processes and controls
Answer:
(c) processes and technology
Question 3.
Any specific Information System aims to support
(a) operations
(b) management
(c) decision making
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
![]()
Question 4.
The main aim and purpose of each Information System is to convert the ………………. which is useful and meaningful.
(a) data into information
(b) information into information
(c) data into system
(d) information in process
Answer:
(a) data into information
Question 5.
An Information System comprise of ………………….. .
(a) people
(b) software and hardware
(c) data and network
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 6.
…………………… is in fact not a separate device but an imaginary memory area supported by some operating system in conjunction with the hardware.
(a) Cache memory
(b) Primary memory
(c) Secondary memory
(d) Virtual memory
Answer:
(d) Virtual memory
Question 7.
A set of instructions that tell the hardware, what to do, is known as:
(a) Operating System
(b) Software
(c) Logic Access
(d) RAM
Answer:
(b) Software
Question 8.
…………………. is a set of computer programs that manages computer hardware resources and acts as an interface with computer application programs.
(a) Operating System
(b) Application Software
(c) Operating Software
(d) Virtual Memory
Answer:
(a) Operating System
Question 9.
The process of analysing data to find previously unknown trends, patterns, and associations to make decisions, is known as:
(a) Big Data
(b) Data Warehouse
(c) Data Analysis
(d) Data Mining
Answer:
(d) Data Mining
Question 10.
…………………….. is a technology that takes an Internet Signal and convert into ratio waves.
(a) Packet Switching
(b) Wi-Fi
(c) Vo Ip
(d) DNS
Answer:
(b) Wi-Fi
Question 11.
A growing class of data being transferred over the Internet is Voice Data. A protocall enables sounds to be converted to a digital format for transmission over the Internet and then recreated at the other end is known as.
(a) Domain Name System (DNS)
(b) Wi-Fi
(c) Packet Switching
(d) Voice over IP (VolP)
Answer:
(d) Voice over IP (VolP)
![]()
Question 12.
Basic Purpose of Information System Controls in an organisation is to ensure that the basic objectives are achieved and undesired risk events is/are ……………… .
(a) prevented
(b) detected
(c) corrected
(d) all of the above.
Answer:
(d) all of the above.
Question 13.
An information syslems auditing includes
(a) Reviewing the implemented system
(b) Providing consultation
(c) Evaluating the reliability of operational effectiveness of controls.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 14.
Control objectives in Information System serve for the purpose of
(a) Outline the policies of the organisation as laid down by the management
(b) A benchmark for evaluating whether control objectives are met.
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 15.
Objective of controls In Information System
(a) Preventive
(b) Detective and Corrective
(c) Compensatory
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 16.
Classification on the basis of nature of Information System Resources are
(a) Environmental and Physical Access Control
(b) Environmental and Logical Access Control
(c) Environmental, Physical Access and Logical Access Controls
(d) Physical Access and Logical Access Controls
Answer:
(c) Environmental, Physical Access and Logical Access Controls
Question 17.
Quality Assurance (QA) personnel perform a monitoring role for management to ensure that:
(a) Quality goals are established and understood clearly by stakeholders
(b) Compliance occurs with the standards that are in place to attain quality Information system
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 18.
Wide Area Network Topologies have the characteristics:
(a) They span large geographIc, areas
(b) They often encompass components that are owned by other parties
(c) They provide relatively low-speed communication among nodes
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
![]()
Question 19.
Which of the following Is not a component of information Systems?
(a) People
(b) Data
(c) Network
(d) Transaction Processing System
Answer:
(d) Transaction Processing System
Question 20.
Which of the following is not a functional unit of Control Processing Unit?
(a) Control Unit
(b) Input Devices
(c) Registers
(d) Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Answer:
(b) Input Devices
Question 21.
Which of the following Is not a Corrective Control?
(a) Backup Procedure
(b) Hash Totals
(c) Rerun Procedure
(d) Contingency Planning
Answer:
(b) Hash Totals
Question 22.
Which of the following term is not used in Relational Database Models?
(a) Objects
(b) Relations
(c) Attributes
(d) Tables
Answer:
(a) Objects
Question 23.
SCARF stands for ………………….. .
(a) System Control Audit Review File
(b) System Control Audit Report File
(c) System Control Audit Review Format
(d) Simulation Control Audit Review File
Answer:
(a) System Control Audit Review File
![]()
Question 24.
…………………… Technical involves embedding audit software modules within a host application. system to provide continuous monitoring of the system’s transactions.
(a) Audit hooks
(b) SCARF
(c) Integrated Test Facility (ITF)
(d) Continuous and Intermittent Simulation (CIS)
Answer:
(b) SCARF
Question 25.
Audit trails can be used to support security objectives in the way of:
(a) Detecting Unauthorised Access
(b) Reconstructing Events
(c) Personal Accountability
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 26.
Accounting Audit Trail applies in
(a) Resource usage from log-onto log-out time
(b) Log of Resource Consumption
(c) Log-in and Log-out of Human Resource
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 27.
CISO stands for:
(a) Chief Information Security Office
(b) Chief Information Security Officer
(c) Central Infomiation Sécurity Office
(d) Central Informative Services Office
Answer:
(b) Chief Information Security Officer
Question 28.
Data Management Comprises the function of:
(a) Database Architect
(b) Database Administrator
(c) Database Analyst
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 29.
Segregation of Duties (SOD) also known as:
(a) Distribution of Duties
(b) Separation of Duties
(c) Classification Duties
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Separation of Duties
Question 30.
…………………. is the conversion of data into a secret code for storage in database.
(a) Cipher Text
(b) Encryption
(c) Decryption
(d) Logging
Answer:
(b) Encryption
![]()
Question 31.
In computer network …………………… refers to the ability of a network to recover from any kind of error like connection failure, loss of data, etc.
(a) Routine
(b) Connection
(c) Resilience
(d) Bandwidth
Answer:
(c) Resilience