Core Banking Systems – CA Inter EIS Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Core Banking Systems – CA Inter EIS Question Bank
Question 1.
Automation of business processes has introduced new types of risks in banking service. You being the Branch Manager of a CBS branch, list out some of the internal controls you think to be implemented In your branch. (May 2018, 6 marks)
Answer:
Automation of business processes has introduced new types of risks In banking services. As a Branch Manager of a CBS Branch, following are some of the internal controls to be implemented in the branch:
- Work of one staff member Is Invariably supervised/checked by another staff member, irrespective of the nature of work (Maker-checker process)
- A System of job rotation among stalls exists.
- Financial and administrative powers of each official position is fixed and communicated to all persons concerned.
- Branch Managers must send periodic confirmation to their controlling authority on compliance of the laid down systems and procedures.
- All books are to be balanced periodically. Balancing is to be confirmed by an authorized official.
- Details of lost Security forms are Immediately advised to controlling so that they can exercise caution.
- Fraud-prone items like currency, Valuables, draft forms, term deposit receipts, traveler’s cheques, and other such security forms are in the custody of at least two officials to the Branch.
Question 2.
Information Technology (IT) risks can be reduced by Implementing the right type and level of control in automated environment that is done by integrating controls into information technology. Being an IT consultant, suggest various steps of IT-related control to a branch manager of a bank. (May 2019, 6 marks)
Answer:
Information Technology (IT) risks can be reduced by implementing the right type and level ot control in automated environment that is done by integrating controls into information technology.
So being an IT consultant, following are the various stops of IT-related Control suggested to a Branch Manager of a bank.
- The system maintains a record of all log-ins and log-outs.
- If the transaction is sought to be posted to a dormant (or inoperative) account, the processing is halted and can be proceeded with only with a supervisory password.
- The system checks whether the amount to be withdrawn is within the drawing power.
- Access to the system Is available only between stipulated hours and specified days only.
- The system flashes a message it the balance in a hen account would fall below the lien amount after the processing of the transaction.
- Exception situations such as limit excess, reactivating dormant accounts, etc. can be handled only with a valid supervisory-level password.
- A user time-out is prescribed. This means that after a user long-in and there is no activity for a predetermined time, the user is automatically logged – Out of the system.
- Individual users can access only specified directories and files. Users should be given access only on a need-to-know basis based on their role in the bank. This is applicable for internal users of the bank and customers.
- Once, the end-of-the-day process is over, the ledgers cannot be opened without a supervisory-level password.
Question 3.
General controls are pervasive controls and app’y to all systems components, processes and data for a given enterprise or systems environment. As an IT consultant, discuss some of the controls covered under general controls which you would like to ensure for a given enterprise. (May 2019,6 marks)
Answer:
General controls are pervasive controls and apply to all systems components, processes and data toc a given enterprise oc systems environment.
General controls includes but are not limited to:
1. Information Security Policy
The security policy is approved by the senior management and encompasses all areas of operations of the bank and drives access to information across the enterprise and other stakeholders.
2. Administration, Access, and Authentication
It should be administered with appropriate policies and procedures clearly defining the levels, of access to information and authentication of users.
3. Separation of key IT functions
Secure deployment of IT requires the bank to have separate IT organization structure with key demarcation of duties for different personnel within IT department and to ensure that there are no SOD conflicts.
4. Management of Systems Acquisitions and Implementation
Software solutions for CBS are most developed acquired and implemented. Hence, process of acquisition and Implementation of systems should be properly controlled.
5. Change Management
IT solutions deployed and its various components must be changed in tune with changing needs as per changes in technology environment, business processes, regulatory and compliance requirements. These changes impact the live environment of banking services. Hence, change management process should be implemented to ensure smooth transition to new environments covering all key changes including hardware, Software, and business processes. All changes must be properly approved by the management, before implementation.
6. Backup, Recovery, and Business Continuity
Heavy dependence on IT and criticality makes it imperative that resilience of banking operations should be ensured by having appropriate business continuity including backup recovery and oil-site data center.
7. Proper Development and Implementation of Applications Software
Application software drives the business processes of the banks. These solutions in case developed and implemented must be properly controlled by using standard software development process.
8. Confidentiality, integrity and Availability of Software and data files
Security is implemented to ensure Confidentiality. Integrity and Availability (CIA) of information. Confidentiality refers to protection of critical information. Integrity refers to ensuring authenticity of information at all stages of processing. Availability refers to ensuring availability of information to users when required. IT operations refer to how IT is deployed, implemented and maintained within the bank. All IT operations need to be controlled by appropriate policies and procedures.
9. Incident response and management:
There may be various incidents created due to failure of IT. These Incidents need to be appropriately responsed and managed as per pre-defined policies and procedures.
Question 4.
Analyse new set of IT risks and challenges associated with the businesses and standards that the banks should consider?
Answer:
The business processes and standards adopted by Banks should consider these new set of IT risks and challenges:
1. Frequent Changes or Obsolescence of Technology
Technology keeps on evolving and changing constantly and becomes obsolete very quickly.
Hence, there is always a risk that the investment in technology solutions unless properly planned may result in loss to bank due to risk of obsolescence.
2. Multiplicity and Complexity of Systems
The core of banking services remains same but by using technology the way these banking products and services are provided changes drastically. The Technology architecture used for services could include multiple digital platforms and is quite complex. Hence, this requires the bank personnel to have personnel with requisite technology skills or the management of the bank’s technology could be outsourced to a company having the relevant skill set.
Question 5.
Explain the Internal controls In banks?
Answer:
Risks are mitigated by Implementing internal controls as appropriate to the business environment. These types of controls must be Integrated in the IT solution Implemented at the bank’s branches. Some examples of internal controls in bank branch are given here:
- Work of one staff member is invariably supervised. checked by another staff member, Irrespective of the nature of work (Maker-Checker process).
- A system of job rotation among staff exists.
- Financial and administrative powers of each official? position Is fixed and communicated to all persons concerned.
- Branch managers must send periodic confirmation to their controlling authority on compliance of the Laid down systems and procedures.
- All books are to be balanced periodically. Balancing is to be confirmed by an authorized official.
- Details of lost security forms are mediately advised to controlling so that they can exercise caution.
- Fraud-prone items like currency, valuables, draft forms, term deposit receipts, traveler’s cheques, and other such security forms are in the custody of at least two officials of the branch.
Question 6.
Write short note on Core Banking System (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
CORE stands for Centralized Online Real-time Environment. Core banking system may be defined as the set of basic software components that manage the services provided by a bank to its customers through its branches. In other words, the platform where communication technology and Information technology are managed to suit core needs of banking is known as core banking solutions. This technologies has cut down time, working at a same time as on dissimilar issue and escalating usefulness. Here, computer software is developed to perform core operations of banking like recording of transactions, passbook maintenance and interest calculation on loans and deposits, customer records, balance 0f payments
and withdrawal.
![]()
Question 7.
Write short note on the following:
Nucleus Finn One (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Nucleus FlnnOne:
The Nucleus FinnOne banking suite, made and marketed by India-based company Nucleus software, comes with a wide variety of integrated applications that cover different aspects of global web banking. These applications include a loan orientation system that automates and manages the processing of many types of loans, a credit card application system with strong credit and fraud detection tools, and a multilingual web-based collection service that organizes legal payouts.
FinnOne is a web-based global banking product designed to support banks and financial solution companies in dealing with assets, liabilities core financial accounting, and customer service. The solution is wholly focused on banking and financial services spanning across solutions in the areas of Retail and Corporate Banking, Cash Management, Relationship Banking, CRM, Credit Risk, EAI, Internet Banking, etc.
Question 8.
Explain various key aspects in-built into the architecture of a Core Banking System. (Nov 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
Some key aspects inbuilt into architecture of a core Banking System are as follows:
| 1. Information flow | Facilitates information flow within the bank and improves No speed and accuracy of decision-making. It deploys systems that streamline integration and unite corporate Information to create a comprehensive analytical infrastructure. |
| 2. Customer-centric | Through a holistic core banking architecture, enable banks to target customers with the right offers at the right time with the right channel to Increase profitability. |
| 3. Regulatory compliance | Compliance in case of banks Is complex and expensive. CBS has a built-in and regularly updated regulatory platform which will ensure compliance. |
| 4. Resource optimization | Optimizes utilization of information and resources o banks and lowers costs through improved asset reusability, faster turnaround times, faster processing an increased accuracy. |
Question 9.
What do you understand by the term EF Describe in brief, the different EFT systems in operations. (May 2009, 5 marks)
OR
Describe briefly
Electronic Fund Transfer (Nov 2011, 2 marks)
Answer:
Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT)
Meaning
Electronic fund transfer (EFT) represents the way the business can receive direct deposits of all payments from the financial institution to the company bank account. Once the user signs up, money comes to him directly. It is fast, safe and means that the money will be confirmed in user’s bank account quicker that he had to wait for the mail, deposit the cheque, and wait for the funds to become available.
Following are some examples of EFT systems in operation:
| 1. Automated | These machines are used with a debit or EFT Teller Machines card and a code, which is often called a personal (ATM.) identification number or PIN. |
| 2. Point of sale (POS) Transactions | Some debit or EFT cards (referred to as check cards) can be used when shopping, to allow the transfer of funds from the consumer’s A/c to the merchant’s. |
| 3. Pre-authorized Transfer | Under this method, funds are automatically deposited or withdrawn from an individual’s account, when the account holder authorizes the bank or a third party to do so. |
| 4. Telephone Transfers | Funds can be transferred from one account to another from saving to checking e.g. can order payments of specific bills by phone. |
Question 10.
Define ‘Proxy Server. (Nov 2018, 2 Marks)
Answer:
Proxy Server:
A proxy server is a computer that offers a computer network service to allow clients to make indirect network connections to other network services. A client connects to the proxy server and then requests a connection, file or other resource available on a different server. The proxy provides the resource either by connecting to the specified server or by serving it from a cache. In some cases, the proxy may alter the client’s request or the server’s response for various purposes.
Question 11.
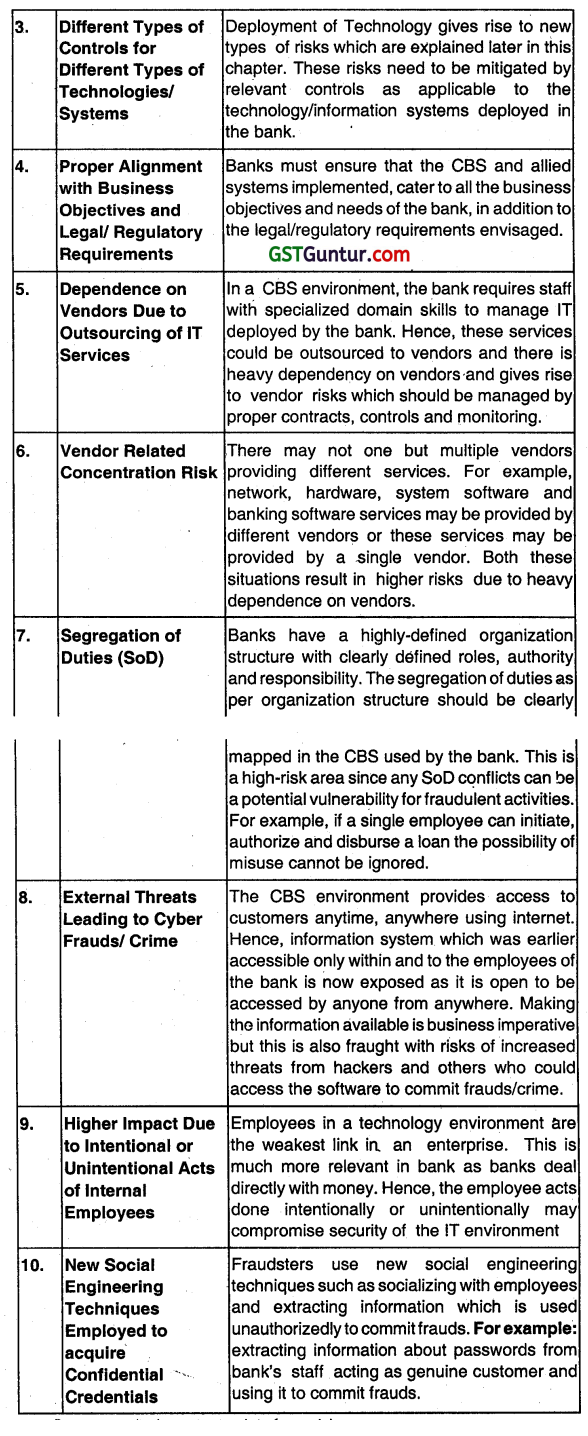
Once the complete business of a bank is captured by technology and processes are automated In Core Banking System (CBS), the data of the bank, customer, management and staff are completely dependent on the Data Centre. From a risk assessment point of view, it is critical to ensure that the bank can Impart training to its staff in the core areas of technology for efficient risk management. Explain any six common IT risks related to CBS. (Nov 2020, 6 marks)
![]()
Question 12.
Briefly explain any two types of Mortgage loans in a Banking system. (Nov 2020, 2 marks)
Question 13.
Define the Mortgage Loan. Briefly explain the types of Mortgage loans. (Jan 2021, 4 marks)
Question 14.
Briefly describe the four stages of processing Credit Card transactions. (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Stages of Processing Credit Card Transactions
| 1. Authorisation | A cardholder requests a purchase from the merchant the request is submitted to acquirer. The acquirer sends a request to the issuer to authorize a transaction. An authorization code is sent to the acquirer. The acquirer authorizes the transaction the cardholder receives product. |
| 2. Batching | The merchant stores alt the day authorised sales in a batch the merchant sends the batch to the acquirer at the end of the day to receive payment. |
| 3. Clearing | The batch is sent through the card network to request payment from the issuer. The card network distributes each transaction to the appropriate issuer. The issuer subtracts its interchange fees, which are shared with the card network, and transfers the amount. The card network routes the amount to the acquirer. |
| 4. Funding | The acquirer subtracts its discount rate and pays the merchant the remainder. The cardholder is billed. |
Question 15.
Now-a-days. Credit Cards are extensively being used for payment purposes. As a consultant to credit card section of a bank, advise the risks involved in the credit card process. (May 2018, 4 marks)
Answer
FoIowing are the risks involved In the Credit Card process:
- Credit Line setup Is unauthorized and not In line with the bank’s policy.
- Masters defined for the customer are not in accordance with the Pre-Disbursement Certificate
- Credit line setup can be breached.
- inaccurate Interest/charge being calculated In the Credit Card System.
- inaccurate reconciliation performed.
Question 16.
Discuss any four dimensions of e-commerce Security. (May 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Different dimensions of e-Commerce security are:
| 1. Integrity | The ability to ensure that Information being displayed on a website or transmitted or received over the internet has not been altered in any way in unauthorized party. |
| 2. Non-repudiation | The ability to ensure that e-commerce participants do not deny (i.e. repudiate) their online actions. |
| 3. Authenticity | The ability to identify the identity of a person or entity with whom we are dealing in the internet. |
| 4. Confidentiality | The ability to ensure that messages and data are available only to those who are authorized to view them. |
| 5. Privacy | The ability to control the use of information about oneself. |
| 6. Availability | The ability to ensure that an e-commerce site continues to function as intended. |
Question 17.
Answer the following question briefly:
What is the difference between integrity and Authenticity with reference to E-Commerce? ( May 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
integrity: The ability to ensure that information being displayed on website or transmitted or received over the internet has not been altered in any way by an unauthorized party.
Authenticity: The ability to identify the identity of a person or entity with whom we are dealing in the Internet.
Question 18.
Explain step-by-step online transaction processing In an e-commerce environment. (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
| 1. Order Placed | Customer places order through secure connection on website or merchant-managed keys in transaction. |
| 2. Authorization Request | Payment gateway receives the transaction through the secure internet connection, encrypts it, and submits an authorization to the credit card issuing bank. |
| 3. Authorization Response | Credit card issuing bank either approves or declines the request and sends a response back through the payment gateway to the website. |
| 4. Order Fulfilled | Once approved the merchant processes and ships the customer’s order. |
| 5. Settlement Request | The payment gateway sends a settlement request to the merchant account provider each day that transactions are processed. |
| 6. Settlement Deposited | The merchant account provider deposits the amount for each settlement into the merchant’s bank account. Usually, it takes 24-48 hours. |
Question 19.
In line with the suggestions of RBI, M/s. ABC Bank is planning to obtain Iso 27001: 2013 certification for its Information Security Management System. As an IS Auditor, you are required to prepare a sample list of Risks w.r.t. Information Security for the Bank. (Nov 2018, 6 marks)
Answer:
A Sample List of Risks w.r.t. information SecurIty for the Bank:
- Significant information resources may be modified inappropriately. disclosed without authorization, and/or unavailable when needed. (e.g., they may be deleted without authorization).
- Lack of management direction and commitment to protect information assets.
- Potential Loss of Confidentiality, availability, and integrity of data and system.
- User accountability is not established.
- It is easier for unauthorized users to guess the password of an authorized user and assess the system and/or data. This may result in loss of confidentiality, availability and integrity of data and system.
- Unauthorized viewing, modification or copying of data and/or unauthorized use, modification or denial of service in the system.
- Security breaches may go undetected.
- Inadequate preventive measures for key server and IT systems in case of environmental threats like heat, humidity, fire, flood etc.
- Unauthorized system or data access, loss, and modification due to views, worms, and Trojans.
Question 20.
Answer the following question in brief:
What is the difference between electronic cheque and paper cheque? (Nov 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Difference between Electronic Cheque and Paper Cheque
|
Electronic Cheque |
Paper Cheque |
| 1. Electronic cheque is in electronic form | Paper cheque is in paper form. |
| 2. Electronic cheque includes credit card, debit card, etc. | Paper cheque Includes crossed cheque, bearer cheque, etc. |
| 3. Electronic cheque functions as a message to the sender’s bank to transfer funds. | Paper cheque message is given initially to the receiver who In turn endorses the cheque and presents it to the bank to obtain funds. |
Question 21.
Describe any three key functions of RBI. (Nov 2019, 3 marks)
Answer:
Key functions of RBI
| 1. Monetary Authority | Formulates implements and monitors the monetary policy with the objective of maintaining price stability and ensuring adequate flow of credit to productive sectors. |
| 2. Regulator and supervisor of the financial system | Prescribes broad parameters of banking operations within which the country’s banking and financial system functions with the objective of maintaining public confidence in the system, protect depositors’ Interests, and provide cost-effective banking services to the public. |
| 3. Issuer of currency | Issues and exchanges or destroys currency and coins, not it for circulation with the objective to give the public adequate quantity of supplies of currency notes and coins and In good quality. |
Question 22.
Banks face the challenge of addressing the threat of money laundering on multiple fronts as banks can be used as primary means for transfer of money across geographies. In light of the above statement, discuss the Money Laundering process and Its different stages. (Nov 2019, 6 marks)
Answer:
Money Laundering process:
Money Laundering is the process b which the proceeds of the crime and the true ownership of those proceeds are concealed or made opaque so that the proceeds appear to come from a legitimate source. The objective In money laundering is to conceal the existence, illegal source, or illegal application of income to make it appear legitimate. Money Laundering Is commonly used by criminals to make “dirty” money appear clean” or the profits of criminal activities are made to appear legitimate.
Sec. 3 of PML Act, 2002 defines ‘money laundering’ as “Who so ever directly or indirectly attempts to indulge or knowingly assists or knowingly is a party or is actually involved in any process or actMty connected with the proceeds of crime and projecting it as untainted property shall be guilty of the offence of money laundering.”
Three Stages of Money Laundering
1. Placement The first stage Involves the placement of proceeds derived from illegal activities – the movement of proceeds, frequently currency, from the scene of the crime to a place, or Into a form, less suspicious and more convenient for the criminal.
2. Layering
Layering involves the separation of proceeds from IlLegal source using complex transactions designed to obscure the audit trail and hide the proceeds. The criminals frequently use shell corporations, obscure banks or countries with loose regulation and secrecy laws for this purpose. Layering Involves sending the money through various financial transactions to change its form and make it difficult to follow. Layering may consist of several banks to bank transfers or wire transfers between different accounts in different names In different countries making deposits and withdrawals to continually vary the amount of money in the accounts changing the moneys currency purchasing high-value items (boats, house cars, diamonds) to change the form of money – making it hard to trace.
3. Integration
Integration involves conversion illegal proceeds into apparently legitimate business earnings through normal financial or commercial, operations. Integration creates the illusion of a legitimate source for criminally derived funds and involves techniques as numerous and creative as those used by legitimate business. For e.g. false invcices for goods exported. domestic loan against a foreign deposit, purchasing of property and commingling of money in banks accounts.
![]()
Question 23.
What do you understand by Regulatory Compliance? (Nov 2019, 2 marks)
Answer:
Regulatory Compliance describes the goal that organizations aspire to achieve in their efforts to ensure that they are aware of and take steps to comply with relevant laws, policies, and regulations. Due to the increasing number of regulations and need for operational transparency, organizations are increasingly adopting the use of consolidated and harmonized sets of compliance controls. This approach is used to ensure that all necessary governance requirements can be met without the unnecessary duplication of efforts and activity from resources.
Regulatory compliance Is an organization’s adherence to laws, regulations, guidelines, and specifications relevant to its business. Violations of regulatory compliance regulations often result in legal punishment, Including interest, penalty and prosecution In some cases.
Question 24.
Explain the stages of Money Laundering. (Jan 2021, 6 marks)
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
………………… is a technology which allows machines to read and process cheques enabling thousands of cheque transactions in a short-time.
(a) IFSC
(b) MICR
(c) ECS
(d) SIP
Answer:
(b) MICR
Question 2.
MICR stands for …………………… .
(a) Magnetic Ink Character Record
(b) Magnetic Ink Character Register
(c) Magnetic Ink Character Recognition
(d) Magnetic Inter Clearing Route
Answer:
(c) Magnetic Ink Character Recognition
Question 3.
ECS stands for ………………. .
(a) Electronic Clearing Service
(b) Electric Clearing Service
(c) Electric Clearing System
(d) Easy Clearing System
Answer:
(a) Electronic Clearing Service
Question 4.
The dependence on technology In banking tot most of the key banking services and processes has led to various challenges except:
(a) Frequent changes or obsolescence of technology
(b) Multiplicity and complexity of systems
(c) Facilitate ECS
(d) Dependence on vendors due to outsourcing of IT services
Answer:
(c) Facilitate ECS
![]()
Question 5.
…………………….. refers to a common IT solution wherein a central shared database supports the entire banking application.
(a) MICR
(b) ECS
(c) CBC
(d) CIF
Answer:
(c) CBC
Question 6.
Popular CBS Software except
(a) Buys Bee
(b) Finele
(c) Finn One
(d) Bank Mate
Answer:
(a) Buys Bee
Question 7.
State the feature(s) of Core Banking Solution:
(a) On-line real-time processing
(b) All databases updated simultaneously
(c) Anytime, anywhere access to customers and vendors
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 8.
Which of the following is not a core banking services?
(a) Advance
(b) Letters of Credit
(c) Reporting
(d) Deposits
Answer:
(c) Reporting
Question 9.
Which of the following is an application control?
(a) Configuring system software
(b) Transaction Logging
(c) Setting parameters In masters
(d) Back up of data
Answer:
(b) Transaction Logging
Question 10.
Which of the following ¡s a General Control?
(a) Setting Database Security
(b) Edit Checks
(c) Completeness Check
(d) For
Answer:
(a) Setting Database Security
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following in one of the primary objectives of implementing controls?
(a) Frauds are detecting pro-actively
(b) All computer errors are prevented
(c) Undesired events are prevented or detected and corrected
(d) Revenue targets are achieved
Answer:
(c) Undesired events are prevented or detected and corrected
Question 12.
Which of the following best defines a risk?
(a) Undesired events are prevented
(b) Threat exploits vulnerability
(c) Physical threats are documented
(d) Inherent vulnerabilities are identified
Answer:
(b) Threat exploits vulnerability
Question 13.
Which is not a Mortgage Loan?
(a) Home Loan
(b) Personal Loan
(c) Top-Up Loan
(d) Loans for Under Construction Property
Answer:
(b) Personal Loan
Question 14.
IBAS Stands for?
(a) Internet Banking Application Server
(b) Internet Banking Application System
(c) Inter-Banking Adjustment System
(d) International Banking Adjustment System
Answer:
(a) Internet Banking Application Server
Question 15.
Risk associated with Core Banking System (CBS) except.
(a) Several Software interfaces across diverse network
(b) Authorisation and Authentication process
(c) On-Line real-time processing
(d) User Identity Management
Answer:
(c) On-Line real-time processing
Question 16.
…………………….. is a comprehensive set of reform measures, developed by the Basal Committee on Banking Supervision, to strengthen the regulation, supervision and risk management of the Banking Sector.
(a) Basel I
(b) Basel II
(c) Basel III
(d) Basel IV
Answer:
(c) Basel III
Question 17.
Artificial neural network logic Is also known as.
(a) Artificial Network
(b) Artificial Intelligence
(c) Algorithms Intelligence
(d) Application Intelligence
Answer:
(b) Artificial Intelligence
![]()
Question 18.
All Banking firms including Cooperative Banks ¡n India are regulated by the legislation:
(a) Banking Regulation Act, 1949
(b) Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002
(c) Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Banking Regulation Act, 1949
Question 19.
Which of the following is not computer-related offence as per in IT Act, 2000?
(a) Identity theft
(b) Stealing computer resource
(c) Violation ot privacy
(d) Stealing of mobile.
Answer:
(d) Stealing of mobile.
Question 20.
Which of the following best defines Money Laundering?
(a) Gifting Immoveabie property to relatives
(b) Converting proceeds of crime and projecting it as untainted property
(c) Tax Planning as per provision of IT Act
(d) Transferring fixed deposit to employees
Answer:
(b) Converting proceeds of crime and projecting it as untainted property
Question 21.
Which is the primary objective of SPDI?
(a) Protecting Computer Software
(b) Securing Critical Information
(c) Securing Personal Information
(d) Identifying Sensitive Information
Answer:
(c) Securing Personal Information
Question 22.
Which of the following is a cybercrime?
(a) Physical theft at branch
(b) Breaking into ATM
(c) Altering name in cheque
(d) Software piracy
Answer:
(d) Software piracy
![]()
Question 23.
The Information Technology Act was passed in 2000 and amended In 2008. But the Information Technology Act Rules were passed in
(a) 2009
(b) 2010
(c) 2011
(d) 2012
Answer:
(c) 2011