Departmental Accounting – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Departmental Accounting – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Distinguish Between
Question 1.
Distinguish between Branch and Departmental Accounting. (June 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
The differences between Branch and Departmental are listed below:-
| Departmental | Branch |
| 1. Departmental always in Inland | 1. It is either Inland or Foreign. |
| 2. All departments of a Business remain generally under one roof. | 2. Branch of a concern is established at different place in the same town or at different town. |
| 3. Departments are made to increase the efficiency of the Business. | 3. Branch is opened to increase the Sale. |
Practical Questions
Question 2.
Surya Co. Ltd. has three departments. It made purchases during the financial year 2012-13 as below

Stock as on 01.04.2012
Dept. A = 240 units
Dept. B = 160 units
Dept. C = 304 units
Sales made were
Dept. A 2040 units at ₹ 20 each
Dept. B 3840 units at ₹ 22.50 each
Dept. C 4992 units at ₹ 25 each
The rate of gross profit is uniform for all the departments. Assume the unit price of opening stock and purchase unit cost are uniform. Prepare Departmental Trading Account. (June 2013, 7 marks)
Answer:
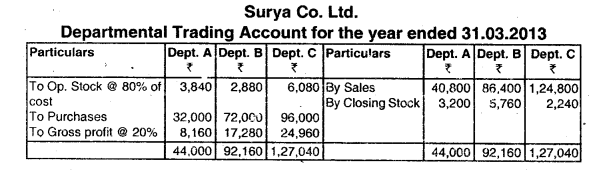
Working Notes:
1. Cost of each unit of the different departments. Since the rate of G.P. is uniform for all products. Assuming if all goods purchased was sold then the gross profit would be:
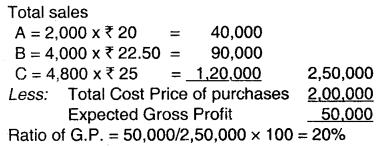
Cost Price Per Unit
A= 20 – 20 × 20% = 16
B = 22.50 – 22.50 × 20% = 18
C = 25 – 25 × 20% 20
Purchase Price Per Unit
A = 2,000 × 16 = 32,000
B = 4,000 × 18 = 72,000
C = 4,800 × 20 = 96,000
2. Opening Stock
A = 240 × 16 = 3,840
B = 160 × 18 = 2,880
C = 304 × 20 = 6,080
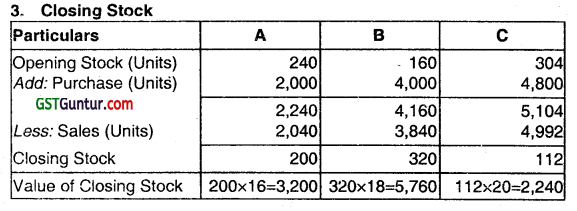
4. Sales:
A:2,040 × ₹ 20 = 40,800
8: 3,840 × ₹22.5O = 86,400
C: 4,992 × ₹ 25 = 1,24,800
![]()
Question 3.
The following details are available in respect of a business for a year.
| Department | Opening Stock | Purchase | Sales |
| X | 120 units | 1,000 units | 1,020 units at ₹ 20.00 each |
| Y | 80 units | 2,000 units | 1,920 units at ₹ 22.50 each |
| Z | 152 units | 2,400 units | 2,496 units at ₹ 25.00 each |
The total value of purchases is ₹ 1,00,000. It is observed that the rate of Gross Profit is the same in each department. Prepare Departmental Trading Account for the above year. (Dec 2017, 8 marks)
Answer:
1. Computation of Closing Stock Quantity (In units)
| Particulars | X | Y | Z |
| Opening Stock | 120 | 80 | 152 |
| Add: Purchase | 1,000 | 2000 | 2,400 |
| Less: Units Sold | (1,020) | (1,920) | (2,496) |
| Closing Stock | 100 | 160 | 56 |
2. Computation of Gross Profit Ratio:
We are informed that the GP Ratio is the same for all departments. Selling Price is given for each department’s products but the Sale Quantity is different from that of Purchase Quantity. To find the Uniform
GP Hate, the sale value of Purchase Quantity should be compared with the Total Cost of Purchase, as under.
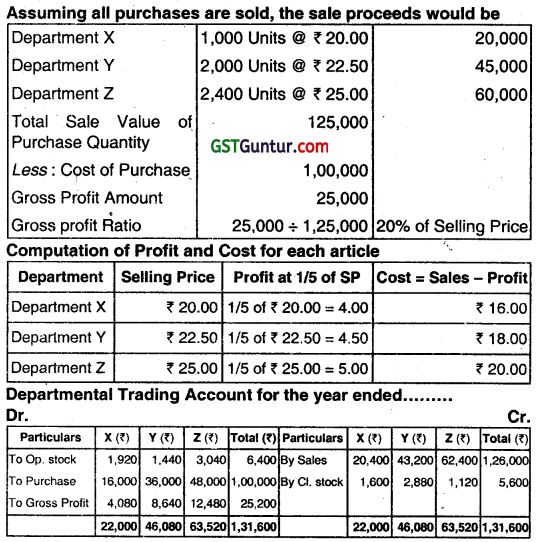
Opening and Closing Stocks are valued at Cost as indicated in WN 3 above. Sale Amount in the Trading Account is computed for the Sale Quantity only. Gross Profit is calculated at 20% of Sale Value.
Question 4.
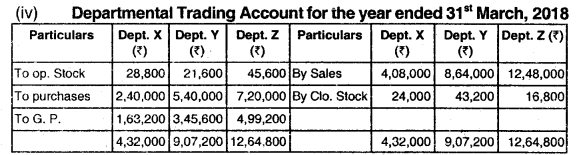
The following information provided by the Shobha Departmental Store for the year ended 31 March, 2018:
| Department | Purchase (units) | Sales | Closing Stock (units) |
| X | 2500 | 2550 units @ ₹ 160 per unit | 250 |
| Y | 5000 | 4800 units @ ₹ 180 per unit | 400 |
| Z | 6000 | 6240 units @ ₹ 200 per unit | 140 |
The total value of purchases is ₹ 15 Lakh. it is observed that the rate or gross profit is the same in each department.
You are required to prepare the Departmental Trading Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018. (Dec 2018, 9 marks)
Answer:
(i) Computation of Opening Stock Quantity (units):
| Particulars | Dept. X | Dept. Y | Dept. Z |
| Sales- units Add: Closing Stock- units |
2550 250 |
4800 400 |
6240 140 |
| Less: Purchases-units | 2800 2500 |
5200 5000 |
6380 6000 |
| Opening Stock- units | 300 | 200 | 380 |
(ii) Computation of Gross Profit Ratio:
| ₹ | |
| Sales value of Total purchase Quantity: | |
| Department – X = ₹ 160 x 2,500 | 4,00,000 |
| Department – Y = ₹ 180 x 5,000 | 9,00,000 |
| Department – Z = ₹ 200 x 6,000 | 12,00,000 |
| Sale value of total purchase Quantity | 25,00,000 |
| Less: total purchase price | 15,00,000 |
| Gross profit | 10,00,000 |
| Rate of gross profit = (₹10 lakh/25 lakh) x 100 = 40% |
(iii) Computation of Cost per unit for each Department
| Particulars | Dept. X (₹) | Dept. Y (₹) | Dept. Z (₹) |
| Selling Price per unit | 160 | 180 | 200 |
| Less: G. P. @ 40% | 64 | 72 | 80 |
| Cost per unit | 96 | 108 | 120 |
Question 5.
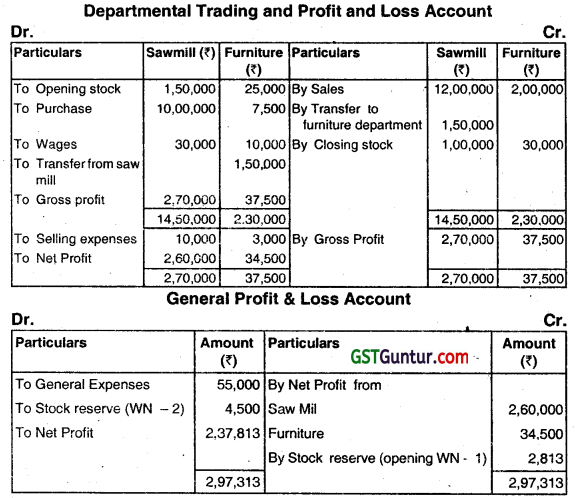
A firm has two departments-Sawmill and Furniture. Furniture is made with wood supplied by the Sawmill department at its usual selling price. From the following figures prepare Departmental Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year 2018:
| Sawmill (₹) | Furniture (₹) | |
| Opening Stock on 1 January, 2018 | 150,000 | 25,000 |
| Sales | 12,00,000 | 2,00,000 |
| Purchases | 10,00,000 | 7,500 |
| Supply to Furniture Department | 1,50,000 | – |
| Selling expenses | 10,000 | 3,000 |
| Wages | 30,000 | 10,000 |
| Closing Stock on 31st December, 2018 | 1,00,000 | 30,000 |
The value of stocks in the Furniture Department consist of 75% wood and 25% other expenses. The Sawmill Department earned Gross Profit at 15% on sales in 2017. General expenses of the business as a whole came to ₹ 55,000. The firm adopts FIFO method for assigning costs to inventories. (Dec 2019, 8 marks)
Answer:
Working Notes:
1. Calculation of Stock Reserve (opening)
25,000 × 75% wood × 15% = ₹ 2,813
2. Calculation of closing stock reserve
Gross profit Rate of Sawmill of 2018
2,70,000/ (12,00,000 + 1,50,000) × 100 =20%
30,000 × 75% × 20% = ₹ 4,500
Question 6.
X Ltd. has three rt,A, B and C from the particulars given below compute:
(i) The values of stock as on 31st December 2020, and
(ii) The departmental result showing the actual amount of gross profit.
| A ₹ |
B ₹ |
C ₹ |
|
| Stock (on 1.1.2020) | 24,000 | 30,000 | 12,000 |
| Purchases | 1,46,000 | 1,24,000 | 48,000 |
| Actual Sales | 1,72,500 | 1,59,400 | 74,600 |
| Gross Profit on normal selling price | 20% | 25% | 33\(\frac{1}{3}\) % |
During the year ended 31st December 2020, certain items were sold at discount, and these discounts were reflected in the value of sales shown above. The items sold at discount were:
| A ₹ |
B ₹ |
C ₹ |
|
| Sales at normal price | 10,000 | 3,000 | 1,000 |
| Sales at actual price | 7,500 | 2,400 | 600 |
(Dec 2021, 6 marks)
Answer:
| Calculation of Departmental Result Deptt. | A | B | C |
| Gross Profit | ₹ 32,500 | 39,400 | 24,600 |
| Value of Stock (31/12/2020) | ₹ 2,500 | 600 | 400 |
Departmental Accounting CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Departmental Accounts
Departmental Accounts helps in identifying the performance of each department. Each department is considered to be an Activity Centre. It is. a tool which helps management in decision-making.
![]()
Advantage
Departmentation offers the following advantages:
- Proper Allocation
- Control
- Proper absorption
Inter-Departmental Transfer
- Transfer made by one department to another may be recorded either:
- At Cost Price; and
- At Invoice Price i.e., Market Based Price.