Deductions, Rebate, and Reliefs – CMA Inter Direct Tax Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Deductions, Rebate, and Reliefs – CMA Inter Direct Tax Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short flotes on deduction under Section 😯 TTA in respect of interest from banks. (June 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
80TTA
Individual/HUF – Eligible Assessee
Interest on savings account with a Scheduled Bank, or a Co-operative Bank or Post Office Upto ₹ 10,000.
Section – 80 TTB
(Deduction in respect of Interest on Deposits in case of Senior Citizens) Deduction under section 8OTTB is available (from the assessment year 2019-20) if the following conditions are satisfied –
- The assessee is a senior citizen (i.e., a resident individual who is at least 60 years of age at any time during the previous year).
- His income includes interest on deposits with a bank/co-operative bank post office (it may be interest on fixed deposits, interest on savings account or any other interest).
Amount of deduction – If these conditions are satisfied, the assessee can claim deduction under section 8OTTB which is equal to ₹ 50,000 or the amount of aforesaid interest, whichever is lower.
Note: with effect from the A.Y. 2019-20, a senior citizen who can avail deduction u/s 8OTTB, shall not be eligible for the deduction u/s 80TTA.
Descriptive Question
Question 2.
What is the effect of contribution made by an individual to electoral trust on his taxable income? (June 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
The scope of Section 8OGGC has been widened so as to enable an individual to claim deduction from gross total income in respect of amount of contribution made by him to an electoral trust during the year.
Question 3.
Write a brief note on the deduction available under Section 8ODDB. (June 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
80TTA
Resident individual/ HUF – Eligible Assessee
Medical Treatment of Specified Disease of Self, Spouse, Parent, Children, Brother, Sister. Amount received from Insurance Company shall be deducted from ₹ 40,000 or ₹ 1,00,000 if incurred in respect of Senior Citizen or in respect of very senior citizen. The Assessee must furnish a certificate in form No. 10-l along with the return of Income.
![]()
Question 4.
Who are not ‘Regular Workmen, u/s 80 JJAA of the Income Tax Act, 1961? (June 2014, 3 marks)
Answer:
Following are not regular workmen u/s 80 JJAA –
- Casual workmen and workmen employed through contract labour.
- Other workmen if employed for less than 150 days during the previous year.
Practical Questions
Question 5.
Determine the eligibility and quantum of deduction under Chapter VI-A in the following cases:
(ii) Contribution to notified pension scheme (referred to Section 80 CCD) by the employer ₹ 40,000 for an employee whose basic salary plus dearness allowance was ₹ 3,00,000 for the year. (Dec 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
An assessee who is an individual employed by central Govt. (or any other employer) make any contribution to his account under a pension scheme notified (or as may be notified by Central Govt.) the assessee shall be allowed a deduction in computation of his total income, the deduction is subjected to amount of 10% of his salary in previous year. (Sec. 80CCD)
Contribution to Notified Pension Scheme
Amount of deduction u/s 80CCD(2)
(least of the following)
1. Actual Amount Paid – ₹ 40,000
2. 10% of Salary 3,00.000 x 10% – ₹ 30,000
Hence, Amount of Deduction is ₹ 30,000.
Question 6.
Answer the following sub-divisions briefly in the light of the provisions of the Income-tax Act, 1961:
A life insurance policy was taken in April, 2022 for a capital sum assured of ₹ 8 lakhs. The annual premium amounts to ₹ 1,10,000 for 10 years. How much is deductible under Section 80C? (Dec 2013, 1 mark)
Answer:
Only 10% of the premium on the capital sum assured is eligible for deduction. Amount Deductible u/s 80C = 8,00,000 × 10% = ₹ 80,000.
![]()
Question 7.
Compute the quantum of deduction under Section 80C for Mr. Niraj for the assessment year 2023-24.
| ₹ | |
| Life Insurance premium | |
| Own – Capital sum assured 2,00,000 (being the first premium paid) | 25,000 |
| Brother’s life – dependent on Niraj | 10,000 |
| Major son – doing business | 5,000 |
| Contribution to recognized provident fund | 15,000 |
| Repayment of bank loan for purchase of residential apartment-let out | 60,000 |
| Tuition fees for M.Com (part-time) pursued by wife | 12,000 |
(Dec 2013, 3 marks)
Answer:
Computation of deduction u/s 80c
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Life insurance premium | |
| Own- capital sum assured ₹ 2,00,000 (being the first premium paid) – limited to 10°/o i.e. ₹ 2,00,000 × 10% | 20,000 |
| Major son – doing business – allowed | 5,000 |
| Contribution to recognized provident fund – allowed | 15,000 |
| Repayment of loan for purchase of residential apartment -let out – allowed | 60,000 |
| Total amount eligible for deduction u/s 80 C | 1,00,000 |
Note: Brother’s Life – Dependent on Niraj & Tuition fees for M.Com (part-time) pursued by wife will not be allowed as Deduction u/s 80 C.
Question 8.
Mr. Praveen Kumar (aged 59 years) having gross total income of ₹ 27,50,000 during previous year 2022-23 incurred expenditure of ₹ 1,30,000 during the said year on medical treatment of his dependant father (aged 80 years) who is suffering from chronic disease specified in Section 8ODDB of the Income-tax Act and also paid medical insurance premium of ₹ 26,000. Determine total income of Mr. Praveen Kumar for Assessment Year 2023-24. (Dec 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Computation of Total Income of Mr. Praveen Kumar for A.Y. 2023-24:
| Gross Total Income | 27,50,000 |
| Less: Deductions u/s 80 D | |
| For medical insurance premium for self under section 80D- | |
| maximum allowable is ₹ 25,000 | 25,000 |
| u/s 80 DDB | 1,00,000 |
| Total Income | 26,25,000 |
Note: Amendment to (Section-800DB)
Section 800DB has been amended (with effect from the assessment year 2020-21) so as to raise the above monetary limit of deduction to ₹ 1,00,000 for both senior citizens and super senior citizens.
Question 9.
Mr. Gangai Amaran (age 50) incurred following expenditures during the financial year 2022-23:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| (i) Medical expenditure on the treatment of his non-dependent father (age 82) | 30,000 |
| (ii) Medical expenditure on treatment of his non-dependent mother (age 73) | 25,000 |
| (iii) Medical expenditure for a surgery undergone by himself | 50,000 |
| (iv) Medical insurance premium for non-dependent mother (age 73) | 35,000 |
| (v) Medical insurance premium for self (paid by cheque) | 27,000 |
| (vi) Preventive medical health check-up paid in cash for himself. | 7,000 |
Computer the amount eligible for deduction under section 80-D for the financial year 2022-23. (Dec 2017, 7 marks)
Answer:
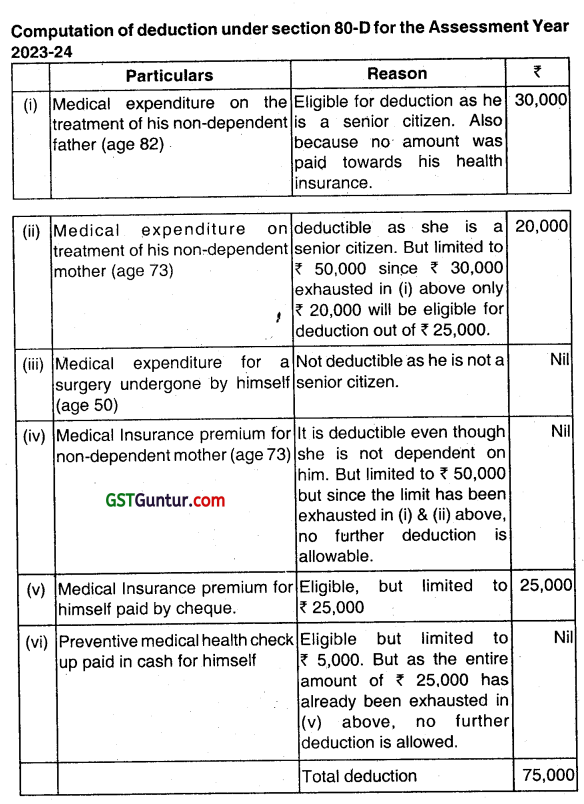
Note: Amendment to [Section – 80D]
The following amendments have been made to the scheme of section 80D with effect from the assessment year 20 19-20 as follows:
Section 80D, inter alla, provides that for medical insurance (or preventive health ‘of a senior citizen), deduction of ‘₹ 30,000
shall be allowed. Further, in the case of supersenior citizens, the said section also provides for a deduction of medical expenditure within the overall limits of ₹ 30,000.
The above monetary limits have been extended so as to provide that the deduction of ₹ 50,000 in aggregate shall be allowed to senior citizens in respect of medical insurance or preventive health check-ups or medical expenditures.
In case of single premium health insurance policies having cover of more than one year, deduction under section 80D shall be allowed on proportionate basis for the number of years for which health insurance cover is provided, subject to the specified monetary limit.
![]()
Question 10.
With brief reasons compute the quantum of eligible deduction in the following independent cases:
(i) Ranjit made tax saver deposit in SBI of ₹ 80,000 in his wife’s name and paid life insurance premium of 25,000 on a sum assured policy of ₹ 2,00,0O0 taken on 01.06.2019.
(ii) Vikas having basic pay and DA (forming part of retirement benefits) of ₹ 4,50,000 contributed ₹ 50,000 to a pension scheme notified under section 80 CCD and repaid education loan of SBI of ₹ 60,000 for son’s education outside India. The education loan was taken in the financial year 2017-18.
(iii) Ms. Madhuri engaged in manufacturing activity paid ₹ 30,000 to National Urban Poverty Eradication Fund on 31.12.2023. She also paid rent for residential premises @ ₹ 25,000 per month. She does not own any house property. Her gross total income (computer) is ₹ 6,50,000. She has not claimed any other deduction under Chapter VI-A. (Dec 2019, 2 x 3= 6 marks)
Answer:
Quantum of eligible deduction
(i) Deduction under Section 80C
Tax Saver Deposit in the name of wife is not eligible for deduction under section 80C.

(ii) Deduction u/s 80CCD
Amount of deduction = Lower of following:
1. employee contribution (50,000)
2. 10% of Salary (45,000)
Deduction = 45,000
Deduction u/s 80E
deduction in respect of interest on loan for higher education in India or abroad
Amount of Deduction = ₹ 60,000
(iii) Deduction u/s 8OGG = Rent paid of House property
Amount of deduction:
Lower of following
- ₹ 5,000 1 month [5 x 12,000] 60,000
- 25% of 6,50,000 1,62,500
- Rent paid 10% of GTI = (3,00,000 – 65,000) 2,35,000
- Amount of deduction = ₹ 60,000
Question 11.
Determine the quantum of deduction under the applicable provisions of Chapter VI-A for the assessment year 2023-24 in the following cases:
(i) Rahul engaged in manufacture of household utensils applied for housing loan for the first house property for self-residential use. The loan was sanctioned in June, 2022 of ₹ 40 lakhs and the balance ₹ 8 lakhs was met from his own source. Interest on loan for the year ended 31.03.2023 amounts to ₹ 2,40,000.
(ii) Prarnod employed in a listed company availed loan from SBI for the purpose of purchase of electric car. The cost of electric car was ₹ 15,00,000 for which he borrowed loan of ₹ 12 lakhs. Interest payable on loan for the financial year 2022-23 amounts to ₹ 1,70,000.
(iii) Priti (P) Ltd. contributed ₹ 5 lakhs to an electoral trust and incurred ₹ 90,000 on advertisement in a brochure of a recognized political party.
(iv) The gross total income of Everest (P) Ltd. includes profits and gains of ₹ 11 lakhs from the collecting and processing of bio-degradable waste for producing biogas. The company began the business in the financial year 2019-20. (Dec 2022, 8 marks)
Descriptive Question
Question 12.
Briefly explain marginal relief allowable while computing tax payable by certain assessee. (June 2010, 3 marks)
Answer:
Marginal Relief: In case of Surcharge
A.
- In case of individual and HUE, where total income exceeds ₹ 50 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 1 crore, the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shall be restricted to. (Tax on ₹ 50 lakhs) + (Total Income – ₹ 50 lakhs)
- In case of individual and HUF, where total income exceeds ₹ 1 crore but does not exceed ₹ 2 crore, the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shall be restricted to: (Tax on ₹ 1 crore with surcharge of 10%) + (Total Income – ₹ 1 crore)
- In case of individual and HUE, where total income exceeds ₹ 2 crore but does not exceed ₹ 5 crore, the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shalt be restricted to: (Tax on ₹ 2 crore with surcharge of 15%) + (Total Income – ₹ 2 crore)
- In case of individual and HUF, where total income exceeds ₹ 5 crore, the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shall be restricted to: (Tax on ₹ 5 crore with surcharge of 25%) + (Total Income – ₹ 5 crore)
B. In case of Local authority and Firm, where the total income exceeds ₹ 1 crore, then the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shalt be restricted to: (Tax on ₹ 1 crore) + (Total Income – ₹ 1 crore)
C. In case of domestic/Foreign company, where the total income exceeds ₹ 1 crore but does not exceed? 10 crores, then the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shall be restricted to: (Tax on ₹ 1 crore) + (Total Income – ₹ 1 crore)
D. In case of domestic company, where the total income exceeds ₹ 10 crore, then the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shall be restricted to: (Tax on ₹ 10 crore with surcharge of 7%) + (Total Income – ₹ 10 Crore)
![]()
E. In case of foreign company. where the total income exceeds ₹ 10 crore, then the aggregate of income tax and surcharge shall be restricted to: (Tax on ₹ 10 crore with surcharge of 2%) + (Total Income – ₹ 10 Crore).