Company Audit – CA Inter Audit Questions bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Company Audit – CA Inter Audit Question Bank
Question 1.
State with reasons (n short) whether the following statement Is True or False:
C.A. Mr. X is the Auditor of PQ Ltd. in wtiich one of his relative is having substantial interest, whether Mr. X is qualified to be an Auditor? (Nov 2008, 2 marks)
Answer: .
False:
CA Mr. X Is not qualified to be an auditor of PQ Ltd. according to Sec. 141(3) of Companies Act. 2013 and Rule 10 of companies (Audit and Auditor’s Rule, 2014).
Question 2.
State with reason (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect.
Rajat, an auditor recovers his fees on progressive basis is said to be indebted to company. (Nov 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
If an auditor recovers fees from the company on a progressive basis, even though the audit has not been completed, he cannot be said to be Indebted to the company and therefore, he shall not vacate the office of auditor held by him.
Question 3.
State with reason (in short) whether the toflowing statement is correct or
incorrect.
Mr. ‘R’, a practicing Chartered Accountant, is appointed as a “Tax Consuttanr of MN Ltd., in which his father Mr ‘C’ is the managing director. (Nov 2013, 2 marks)
OR
State with reasons ‘(In short) whether the following statement is correct or ircorrect:
Mr. Pawan, a practicing Chartered Accountant, is appointed as “Tax Consultant” of ABC Ltd., In which his father. Mr. Singh is the Managing Director. (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct: .
A Chartered Accountant appointed as an auditor of a company, should disclose his interest while making the audit report. It this disclosure is not made, it.would amount to rnisconducf’ under the Chartered Accountants Act. 1949 read with Guidance Note on Independence of Auditors. In this case, Mr. R is a Tax Consultanr and not a “Statutory Auditor” or “Tax Auditor” of MN Ltd., hence he is not liable to disclose his relationship with Managing Director of the company.
Question 4.
State with reasons (In shod) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
If an LLP (Limited Liability Partnership Firm) is appointed as an auddor of a company, every partner of a firm shall be authorized to act as an auditor. (May 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per Sec. 141(2) of the Companies Act, 2013, where a firm including a limited liability partnership (LLP) is appointed as an auditor of a company, only the partners who are Chartered Accountants shall be authorised to act and sign on behalf of the firm.
![]()
Question 5.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statements are correct or incorrect:
(i) AB & Co. Is an audit firm having partners Mr. A and Mr. B. Mr. C, the relative of Mr. B is holding securities having lace value of ₹ 2,00,000 In XYZ Ltd. AB & Co. is qualified for being appointed as an auditor of XYZ Ltd. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
(ix) A Chartered Accountant holding securities of S Ltd. having face value of ₹ 950 is qualified for appointment as an auditor of S Ltd. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
(x) Mr. N, a member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of England and Wales, is qualified to be appointed as auditor of Indian Companies. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer.
(i) Incorrect:
As per Sec. 141 (3) of the Company’s Act, 2013 and Rule 10 of Companies (Audit & Auditor’s Rule, 2014) a person is disqualified to be appointed as an auditor of a company if his relative ¡s holding any security of or interest in the company of tace value exceeding one lakh rupees.
Therefore, AB & Co. shall be disquahfied for being appointed as an auditor of XYZ Ltda as Mr. C, the relative of Mr. B who is partner in AB & Co., is holding securities In XYZ Ltd. having face value of ₹ 2 lakh i.e. exceeding ₹ 1 lakh.
(ix) Incorrect:
A who is hoLding any security of the company during the year is disqualified for being appointed as the auditor.
(x) Incorrect:
The auditor should be the member of institute of the Chartered Accountants o f India. So here, Mr. N is disqualified for being appointment of auditor of Indian companies.
Question 6.
Answer the question:
A person shall not be eligible for appointment as an auditor of a company where subsidiary or associate company or any other form of entity is engaged as on the date of appointment in consulting and specialized services as provided in Sec. 144. Explain. (Nov 2017,6 marks)
Answer:
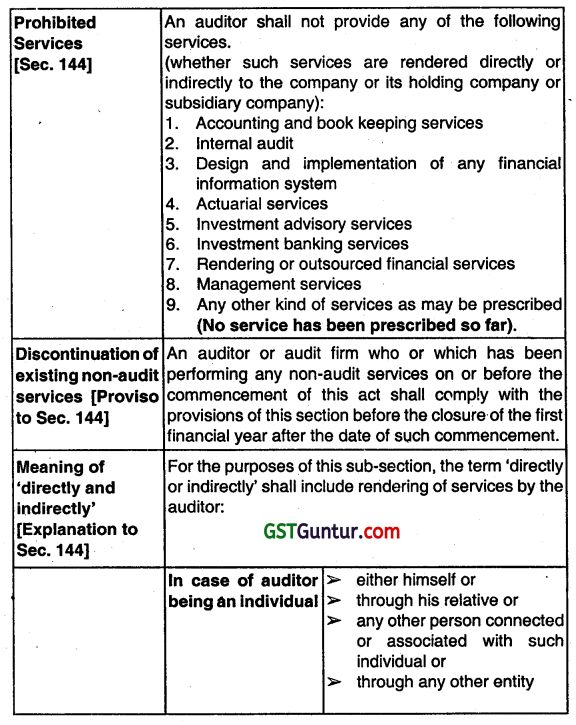
Sec. 144 of the Companies Act, 2013 is prescribes certain services not to be rendered by the auditor. An auditor appointed under this Act shall provide to the company only such other services as are approved by the Board of Directors or the audit committee, as the case may be, but which shall not include any of the following services, namely:
- Accounting and bookkeeping services;
- Internal audit;
- Design and implementation of any financial Information system;
- Actuarial services;
- Investment advisory services;
- Investment banking services;
- Rendering of outsourced fïnanaal services;
- Management services; and
- Any other kind of services as may be prescribed.
Question 7.
Examine with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
An Auditor is considered to lack Independence It the partner of the audit firm deals with shares and securities of the audited entity. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct:
As per Sec 141 (3)(d), a person shall not be eligible for appointment as an auditor of a company namely- a person, or his relative or partner is holding any security of or interest in the company or Its subsidiary, or of its holding or associate company or a subsidiary of such holding company. From the above it can be concluded that If the partner deals with shares and securities of the audited entity, he would be lacking independence, hence, disqualified to be appointed as an auditor.
Further, the Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants, prepared by the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) Identifies five types of threats and if partner of the firm deals with shares and securities of the audited firm then such threat Is known as the Advocacy Threats and auditor will be lacking independence.
Question 8.
Answer the following:
CA NM who is rendering management consultancy service to LA Ltd. wants to accept Otter letter for appointment as an auditor of the LA Ltd. for the next financial year, Discuss with reference to the provision of the Companies Act, 2013. (Nov 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Provision;
As per Sec. 144 of the Companies Act, 2013, an auditor appointed under this Act shall provide to the company only such services as approved by the board of directors or the audit committee, as the case may be. But such services shall not include management consultancy services. So that auditor is prohibited to serve management consultancy services to the company.
Present Case:
In this case, CA. NM is rendering management consultancy Services to LA Ltd. wants to accept offer letter for appointment as an auditor of LA Ltd. for the next financial year. So as per above provision LA Ltd. cannot appoint CANM as the auditor and it still appoints him it is invalid appointment of auditor as per the provisions of the Companies Act,2013.
Question 9.
Answer the following:
M/S. ABC & Co. ¡s an Audit firm, having partners CA. A, CA. B and CA. C. The firm has been offered the appointment as an Auditor of XYZ Ltd. for the Financial Year 2017-18. Mr. D, the relative of CA. A, is holding 25,000 shares (face value of lo each) in XYZ Ltd. having market value of ₹ 90,000. Are M/s. ABC & Co. qualified to be appointed as Auditors of XYZ Ltd.? (May 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Provision:
As per Sec. 141 (3) (d) (i), a person is disqualified to be appointed as an auditor it he or his relative or partners holding any security of or interest in the, company or its subsidiary, or of its holding or associate company or a subsidiary of such holding company, Further as per proviso to this section, the relative of the person may hold the securities or interest in the company of face value not exceeding one lakh rupees.
Present Case:
In the instant case, M/S ABC & Co. will be disqualified for appointment as an auditor of XYZ Ltd. For the Financial Year 2017-18 as the relative of CA A. (i.e. Partners of MIS ABC & Co.) Is holding securities in XYZ Ltd. of ₹ 2,50,000 (25,000 shares of ₹ 10 face value) which is exceeding the limit specified in provison to Sec. 141(3) (d) (i). The market value of shares for this section is irrelevant.
![]()
Question 10.
State with reason (In short) whether the following statement is True or False:
An auditor can be appointed as first auditor of a newly formed company simply because his name has been stated in the Articles of Association. (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
According to Sec 139 (6) of the Companies Act, 2013, the first auditor of a company can be appointed by the Board of Directors within thirty days of the date of registration of the company to hold office till the conclusion of first AGM.
Question 11.
State with reason (in short) whether the following statement es correct or incorrect.
The first auditor of PQR Ltd., a Government Company was appointed by the board of directors of company. (Nov 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
In respect of any Government Company, appointment of auditor is governed by the provisions of Sec, 139(5) and 139(7) of the Companies Act, 2013. As per this Sec. the auditor of a Government Company shall be appointed or re-appointed by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
Question 12.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The first Auditor is generally appointed by the company at a General Meeting. (Nov 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
incorrect:
The first auditor shall be appointed by board of directors in board meeting within thirty days from date of registration of the company.
Question 13.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The first auditor of a Government company was appointed by the Board in its meeting after 10 days from the date of registration. (May 2015,2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per Sec. 139(7), The appointment of first auditor of a government company shall be done by Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) within sixty days from the date of registration of the company. In case CAG does not appoint such an auditor within the said period, BOD of the company shall appoint such auditor within next thirty days.
Question 14.
State with reasons (wi short) whether the following statement Is correct or incorrect:
The managing director of A Ltd. himself appointed the first auditor of the company. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per Sec. 139(6) of the Companies Act, 2013, the first auditor of a company, other than a government company, shall be appointed by the Board of Directors within 30 days from the date of registration of the company.
Question 15.
State with reason (In short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
It the Board of directors fails to appoint the first auditor in case of a company other than a Government Company, then the Central Government shall appoint the auditor. (May 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per Sec. 139 of Companies Act, 2013, If the BOD fail to appoint first auditor the Board shall inform the members who shall then appoint the auditor n EOGM within ninety days.
Question 16.
Examine with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
K Ltd., a non-government company, was incorporated on 01-10-2017. Mr. B, Managing Director of K Ltd., himself appointed the first auditor of the company on 31-12-2017. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per Sec. 139 (6), of the Companies Act, 2013, first auditor of a company shall be appointed by the Board of Directors within 30 days from the registration of the company. So, Mr. B. Managing Director of K Ltd. alone cannot appoint the first auditor of the company.
![]()
Question 17.
Under what circumstances the retiring Auditor cannot be re-appointed? (Nov 2008, Nov 2013, 5, 6 marks)
Answer:
Re-appointment of Retiring Auditor
As per Sec. 139(2) of Companies Act, 2013, no listed company or a company belonging to such class or classes of companies as is prescribed. shall appoint or re-appoint:
- an individual as auditor for more than one term of five consecutive years; and
- an audit firm as auditor for more than two terms of five consecutive years:
Provided that:
1. an individual auditor who has completed his term under clause (a) shall not be eligible for re-appointment as auditor in the same company for five years from the completion of his term;
2. an audit firm which has completed its term under clause (b), shall not be eligible for re-appointment as auditor n the same company for five years from the completion of such term:
Provided further that as on the date of appointment no audit firm having a common partner or partners to the other audit firm, whose tenure has expired in a company immediately preceding the financial year, shall be appointed as auditor of the same company for a period of five years.
Further Sec. 139(9) provides that
Subject to the provisions of sub-section (1) and the rules made thereunder a retiring auditor may be re-appointed at an annual general meeting, if;
- he is not disqualified for re-appointment;
- he has not given the company a notice in writing of his unwillingness to be re-appointed; and
- a special resolution has not been passed at that meeting appointing some other auditor or providing expressly that he shall not be re-appointed.
Question 18.
State with reason (in short) whether the following statement is True or False:
The auditor should study the Memorandum and Artides of Association to see the validity of his appointment. (May 2010, Nov 2015, 2, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
MOA lays down the object to be carried on and AOA reflects the regulations of the company to govern its internal management and to regulate the rights of the members. Auditor should ascertain whether the company has complied with provisions of Sec. 139.
Question 19.
Write short note on the following:
Provisions regarding the re-appointment of a retiring auditor at the Annual General Meeting for a company not covered under auditor rotation provisions. (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Sec. 139(1) of the Companies (Amendment) Act, 2017 whIch Is applicable to all companies, irrespective of size, provides that an auditor shall be appointed who shall hold office from the conclusion of that meeting till the conclusion of its sixth annual general meeting and thereafter till the conclusion of every sixth meeting.
Sub-section (2) of the Sec. 139 requires mandatory rotation of auditors for certain classes of companies only. For a company fall which outside the purview of Sec. 139(2) of the Act, the mandatory rotation will not be applicable.
However, this does not mean that Sec. 139(1), which is applicable to all companies, shall not apply to such companies. Hence, the tenure of auditors appointed by the said companies would have to be for a continuous period of five years.
Question 20.
CA Raj an auditor was removed by PQR Ltd. before the expiry of his term. Discuss the procedure to be taken by PQR Ltd. to appoint an auditor other than retiring auditor U/Sec. 140(4) of the Companies Act, 2013. (Jan 2021, 4 marks)
Question 21.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is True or False:
If appointment of a person as an auditor is void-ab-initio, it should be treated as a casual vacancy. (Nov 2007, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
Casual vacancy arises due to accidental or fortuitous circumstances. Thus if appointment of a person as an auditor is void-ab-into, It cannot be treated as casual vacancy.
Question 22.
Comment on the following situation:
P, the first auditor of XYZ Ltd. resigned as auditors of the Co. Board of Director appointed Mr. Q as statutory auditors in their place. (May 2009, 6 marks)
OR
At the AGM of HDB Pvt. Ltd., Mr. R was appointed as the statutory auditor. He, however, resigned after 3 months since he wanted to pursue his career in banking sector. The Board of Director has appointed Mr. L as the statutory auditor in board meeting within 30 days. Comment on the matter with reference to the provisions of Companies Act, 2013. (May 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Casual Vacancy on Account of Resignation:
As per Sec. 139(8) of Companies Act, 2013, any casual vacancy in the office of an auditor shall:
In the case of a company other than a company whose accounts are subject to audit by an auditor appointed by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India, be tilled by the Board of Directors within thirty days.
If such casual vacancy is as a result of the resignation of an auditor, such appointment shall also be approved by the company at a general meeting convened within three months of the recommendation of the Board and he shall hold the office till the conclusion of the next annual general meeting;
Analysis and Conclusion: The casual vacancy created on account of registration by Mr. P, cannot be filled in by the Board of Directors itself, such appointment shall also be approved by the company at a general meeting convened within three months of the recommendation of the board.
![]()
Question 23.
Discuss on the following:
Filling of a casual vacancy of auditor in respect of a company audit. (Nov 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
Filling of a Casual Vacancy
As per Sec. 139(8) of Companies Act, 2013, any casual vacancy in the office of an auditor shall:
(i) In the care of a company other than a company whose accounts are subject to audit by an auditor appointed by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of india, be filled by the Board of Directors within thirty days.
If such casual vacancy is as a result of the resignation of an auditor, such appointment shall also be approved by the company at a general meeting convened within three months of the recommendation of the Board and he shall hold the office till the conclusion of the next annual general meeting;
(ii) In the case of a company whose accounts are subject to audit by an auditor appointed by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India, be filled by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India within thirty days:
In case the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India does not fill the vacancy within the said period the Board of Directors shall fill the vacancy within next thirty days.
Question 24.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect.
The Board of Directors can fill the casual vacancy caused by the resignation of an auditor, who shall hold office until the conclusion of the next annual general meeting. ( May 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
Casual vacancy caused by the resignation of an auditor shaH only be tilled by the company in general meetings.
Question 25.
Examine with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
PQR & Co., Chartered Accountants, resigned from the audit of a Government Company and filed the resignation with the company and the registrar within 30 days. Comment, whether PQR & Co. has complied with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. (May 2018,2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per Sec. 140 (2) of the Companies Act, 2013, the auditor who has resigned from the Government company shall within 30 days from the date of resignation, require to file a statement with the company and the Registrar, and the auditor shall also require to file such statement with the comptroller and Auditor General of India.
In this case, PQR & Co has not complied with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. As it has filed a statement with the company and the Registrar within 30 days but not with the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
Question 26.
Examine with reason (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The Board of Directors of ABC Ltd., a listed company at Bombay Stock Exchange, is required to fill the casual vacancy of an auditor only after taking into account the recommendations of the audit committee. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct:
As per Sec. 139(11). where a company is required to constitute an audit committee under Sec. 177. all appointments including the filing of a casual vacancy of an auditor under this Section shall be made after taking into account the recommendations of such committee.
Question 27.
Examine with reasons whether the following statement is correct or incorrect.
(e) CA. K has resigned as auditor, after 2 months from appointment of a NML Ltd. He needs to file ADT-3 with the Registrar within 60 days from the date of resignation. (Nov 2019,2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per section 140(2) of the Companies Act, 2013, the auditor who has resigned from the company shall file within a period of 30 days from the date of resignation, a statement in the prescribed From ADT-3 (as per Rule 8 of CAAR) with the company and the Registrar.
Question 28.
Explain whether the following statements are correct or incorrect, with reasons/explanations examples:
As per Section 139(8) of the Companies Act, 2013, any casual vacancy in the office of an auditor shall In case of a company other than a company whose accounts are subject to audit by an auditor appointed by Comptroller and Auditor General of India, be filled by the Shareholders at an Annual General Meeting within 60 days (Jan 2021, 2 marks)
Question 29.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct o incorrect:
The manner of rotation of auditor will not be applicable to company A. which is having paid-up share capital of ₹ 15 crores and having public borrowing from nationalized bank of ₹ 50 crore because It is a Private Limited Company. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
According to Sec. 139(2) of the Companies Act, 2013 and Companies (Audit and Auditors) (Amendment) Rules. 2017, the provisions related to rotation of auditor are applicable to all private limited companies having paid-up share capital of fifty crore rupees or more; and all companies having paid-up share capital of below the threshold limit mentioned above, but having public borrowing from financial institutions, banks or public deposits of fifty crore rupees or more.
Question 30.
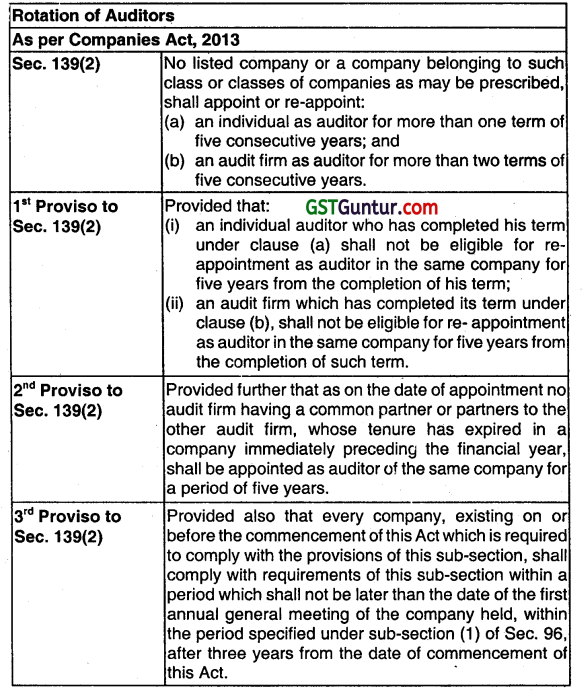
State the manner of rotation of auditors on expiry of their term. (May 2015, 4 marks)
OR
What are the provisions regarding appointment of auditors by rotation, after expiry of the term of the current auditor, that a company should consider? (May 2017, 5 marks)
Answer:

Question 31.
Specify the class of companies to whom rotation of auditor applies, under the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Class of Companies to whom Rotation of Auditor’s Applies [(Rule 5 of Company (Audit and Auditors) (Amendment) Ruled, 2017]-
- All listed Companies.
- All unlisted PubliC Companies having paid-up share capital of ten crore rupees or more.
- All Private Limited Companies having paid-up share capital of fifty crore rupees or more.
- All companies having paid up capital below the above-specified limits but having Public Borrowing from Financial Institutions, Banks or Public Deposits of fifty crore rupees or more.
Question 32.
Clue Ltd. is a Public unlisted company having paid-up share capital of ₹ 9 crores and public borrowings from the financial institutionS of ₹ 51 crores. They appointed MIs Pray and Co., A Chartered Accountant firm as the statutory auditor in its annual general meeting for 11 years.
(i) Is the manner of rotation of auditor applicable in case of Clue Ltd.?
(ii) Whether the appointment of M/s Pray and Co. is valid? (Nov 2020, 4 marks)
![]()
Question 33.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is True or False:
The first auditor appointed by the board of directors can be removed by the board at its subsequent meeting. (Nov 2007, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
According to Sec. 140 of the Companies Act, 2013 an auditor may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term by the company in general meeting after obtaining prior approval of the Central Government in that behalf.
Question 34.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement Is True or False:
An Auditor may be removed from Office before the expiry of his term, by the company In General Meeting. (Nov 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
True:
Sec. 140(1) of the Companies Act, 2013 provides that first auditor appointed by the BOD can be removed by the company at a general meeting before the expiry of his term by passing special resolution. The other auditors of the company can be removed at the general meeting after obtaining prior approval of Central Government.
Question 35.
A, B & C Company Ltd. removed its first Auditor before the expiry of his term without obtaining approval of the Central Government. (Nov 2009,6 marks)
OR
PQR Company Ltd. removed their first auditor by passing a resolution In the meeting of the Board of Directors for his removal without obtaining prior approval from the Central Government. Offer your comments in this regard. (Nov 2010, 4 marks)
OR
Comment on the following:
Removal of auditor before expiry of term. (Nov 2011, 5 marks)
OR
Discuss about the provisions for removal of auditor before expiry of term. (Nov 2015, 6 marks)
Answer:
Removal of First Auditor before expiry of term:
As per Sec. 140(1), of the Companies Act, 2013 the auditor appointed under Sec. 139 may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term only by a special resolution of the company, after obtaining the previous approval of the Central Government (Power now delegated to Regional Director vide Notification No. SO. 4090(E) dt. 19.12.2016 w.e.f. 19.12.2016.) in that behalf in the manner prescribed under Rule 7 of Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules 2014. Provided that before taking any action under this sub-section, the auditor concerned shall be given a reasonable opportunity of being heard.
As per Rule 7 prescribed under Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014:
1. The application to the Central Government for removal of auditor shall be made in Form ADT – 2 and shall be accompanied with fees as provided for this purpose under the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014.
2. The application shall be made to the Central Government within thirty days of the resolution passed by the Board.
3. The company shall hold the general meeting within sbcty days of receipt of approval of the Central Government foi passing the special resolution.
Analysis and Conclusion:
The first auditor appointed by the Board of Directors was removed by a resolution in the meeting of the Board of Directors. In spite of the special resolution of the Company as per the requirement of Sec. 140 (1) was not obtained the prior approval of the Central Government in that behalf. Due to contravention of the provision of sub-Sec. (1) Sec. 140, the removal of auditor is not justified.
Question 36.
Board of Directors of XYZ Ltd. found the auditors of the Company acted in a fraudulent manner, and decided to remove the auditors in board’s meeting. Comment on the action of Board of Directors and describe correct procedure to be followed for removal of auditors before expiry of their term. (May 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Provision
According to Sec. 140(1) of the Companies Act, 2013, the auditor appointed under Sec. 139 may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term only by a special resolution of the company, after obtaining the previous approval of the Central Government in that behalf as per Rule 7 of CAAR, 2014
The following procedures shall b. followed for remov& of auditor:
1. The application to the Central Government for removal of auditor shall be made in Form ADT -2 and shall be accompanied with fees as provided for the purpose under the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014
2. The application to the Central Government shall be made within 30 days of receipt of approval of the Central Government for passing the special resolution.
It is important to note that before taking any action for removal of auditor before expiry of his terms, the auditor concerned shall be given a reasonable opportunity of being heard.
Present Case:
In this case, the contention of Board of Director of XYZ Ltd. for removal of auditor by way of passing resolution in Board meeting is not valid in law. XYZ Ltd. shall require to follow the above procedures for the removal of auditor before expiry of his term.
Question 37.
Discuss on the following:
Ceiling on number of audits in a company to be accepted by an auditor.(Nov 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
Ceiling on Number of Audits:
The provision related to ceiling on number of audits Is laid down Sec. 141 (3)(g) of the Companies Act, 2013. Sec. 141(3)(g) of the Companies Act, 2013 prescribes that a person who is in full-time employment elsewhere or a person or a partner of a firm holding appointment as its auditor, If such person or partner is at the date of such appointment or reappointment holding appointment as auditor of more than twenty companies;
As per Rule 7 prescribed under Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014:
- The application to the Central Government for removal of auditor shall be made in Form ADT – 2 and shall be accompanied with fees as provided for this purpose under the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014.
- The application shall be made to the Central Government within thirty days of the resolution passed by the Board.
- The company shall hold the general meeting within sixty days of receipt of approval of the Central Government foi passing the special resolution.
Analysis and Conclusion:
The first auditor appointed by the Board of Directors was removed by a resolution in the meeting of the Board of Directors. In spite of the special resolution of the Company as per the requirement of Sec. 140 (1) was not obtained the prior approval of the Central Government in that behalf. Due to contravention of the provision of sub-Sec. (1) Sec. 140. the removal of auditor is not justified.
Question 38.
Board of Directors of XYZ Ltd. found the auditors of the Company acted in a fraudulent manner, and decided to remove the auditors in board’s meeting. Comment on the action of Board of Directors and describe correct procedure to be followed for removal of auditors before explry of their term. (May 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Provision
According to Sec. 140(1) of the Companies Act, 2013, the auditor appointed under Sec. 139 may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term only by a special resolution of the company, after obtaining the previous approval of the Central Government In that behalf as per Rule 7 of CAAR, 2014
The following procedures shall be followed for removal of auditor:
1. The application to the Central Government for removal of auditor shall be made in Form ADT -2 and shall be accompanied with fees as provided for the purpose under the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014
2. The application to the Central Government shall be made within 30 days of receipt of approval of the Central Government for passing the special resolution.
It is important to note that before taking any action for removal of auditor before expiry of his terms, the auditor concerned shall be given a reasonable opportunity of being heard.
Present Case:
In this case, contention of Board of Director of XYZ Ltd. for removal of auditor by way of passing resolution in Board meeting is not valid in law. XYZ Ltd. shall require to follow the above procedures for the removal of auditor before expiry of his term.
![]()
Question 39.
Discuss on the following:
Ceiling on number of audits ¡ri a company to be accepted by an auditor. (Nov 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
Ceiling on Number of Audits:
The provision related to the ceiling on number of audits Is laid down In Sec.141 (3)(g) of the Companies Act, 2013. Sec. 141(3)(g) of the Companies Act, 2013 prescribes that a person who is in full-time employment elsewhere or a person or a partner of a firm holding appointment as its auditor if such person or partner is at the date of such appointment or reappointment holding appointment as auditor of more than twenty companies;
In the case of e firm of auditors: It has been further provided that ‘specified number of companies’ shall,be construed as the number of companies specified for every partner of the firm who is not in full-time employment elsewhere.
This limit 0f 20 company audits Is per person: In the case of an audit firm having 4 partners, the overall ceiling will be 4×20=80 company audits. Sometimes, a Chartered Accountant is a partner in a number of auditing firms. In such a case, all the firms In which he is partner or proprietor will be together entitled to 20 company audits on his account. Subject to the overall ceiling of company audits, how they allocate the 20 audits between themselves is their affairs.
In the case of a firm of Chartered Accountants in practice: The specified number of audit assignments shall be construed as the specified number of audit assignments for every partner of the firm.
Where any partner of the firm of Chartered Accountants in practice is also a partner of any other firm or firms of chartered accountants in practice: The number of audit assignments which may be taken for all the firms together in relation to such partner shall not exceed the specified number of audit assignments In the aggregate.
Where any partner of a firm or firms of Chartered Accountants in practice accepts one or more audit assignments In his individual capacity: Or in the name of his proprietary firm, the total number of such assignments which may be accepted by all firms in relation to such Chartered Accountant and by him shall not exceed the specified number of audit
assignments in the aggregate.
In computing the specified number of audit assignments.
- the number of such assignments, which he or any partner of his firm has accepted whether singly or in combination with any other Chartered Accountant in practice or firm of such Chartered Accountants, shall be taken into account.
- the number of partners of a firm on the date of acceptance of audit assignment shall be taken into account.
- a Chartered Accountant In lull time employment elsewhere shall not be taken into account.
Question 40.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The auditor of a Ltd. The company wanted to refer to the minute books during audit but board of directors refused to show the minute books to the auditors. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
The client or directors should provide such information which the auditor required from them. So here, directors should provide minute books to auditors during the course of audit.
Question 41.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement ¡s correct or incorrect:
The auditor of a Ltd. Company wanted to refer to the minute books during audit but board of directors refused to show the minute books to the auditors. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
The Client or directors should provide such information which the auditor required from them. So here, directors should provide minute books to auditors during the course of audit.
Question 42.
Auditors have right to attend only those general meetings at which the accounts audited by them are to be discussed. Comment. (May 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
As per Sec. 146, of the Companies Act, 2013, all the notices of, any other communications relating to, any general meeting shall be forwarded to the auditor of the company, and the auditor shall, Unless otherwise exempted by the company, attend either by himself or through his authorized representative, who shall also be qualified to be an auditor, any general meeting and shall have right to be heard at such meeting on any part of the business which concerns him as the auditor.
The auditor of a company have right to receive the notices. The auditors of a company are entitled to attend any general meeting of the company as this right Is not restricted to those at which the accounts audited by them are to be discussed. The auditor shall also to receive all the notices and other communications relating to the general meetings, which
members are entitled to receive and to be heard at any general meeting in any part of the business of the meeting which concerns them as auditors.
Thus, it is right of the auditor to receive notices and other communications relating to any general meeting and to be heard at such meetings, relating to the matter of his concern, however, it is duty of the auditor to attend the same oc through his authorised representative unless otherwise exempted.
Question 43.
Though legally auditor may exercise right of a Lien in case of companies, it is mostly impracticable for legal and practicable constraints. Do you agree? (May 2019, 3 marks)
Answer:
The statement provided Is correct and can be agreed upon. Right of Lien means any person having the lawful possession of somebody else’s property, on which he has worked, may retain the property for non-payment of his dues on account of the work done on the property.
On this premise, auditor can exercise lien on books any documents placed at his possession by the client for non-payment of fees, for work done on the books and documents. Sec. 128 of the Companies Act, 2013. ordinarily, make it impracticable for the auditor to have possession of the books and documents. The company provides reasonable facility to auditors for inspection of the books of account by directors and others authorized to inspect under this Act.
Taking an overall view of the matter, It seems that though legally, auditor may exercise right of lien in cases of companies, It is mostly Impracticable for legal and practicable constraints.
![]()
Question 44.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is True or False:
The Auditor of a Company is entitled to attend any General Meeting of the company as his duty. (Nov 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
True:
According to Sec. 146 of Act, 2013, unless otherwise exempted by the company the auditor shall attend either by himself or through, his authorized representative (who shall also be qualified to be an auditor), any general meeting of the company.
Question 45.
State with reasons (in shot) whether the following statement is True or False:
It is no part of subsequent auditors duty to verify opening balances of Ledger accounts of current years, on the basis of Balance Sheet audited by Previous Auditor. (May 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
According to SA-510 “Initial Audit Engagement-Opening Balances” it is the duty of the auditor to verify and obtain appropriate evidence in respect of opening balances brought forward from the preceding period.
Question 46.
State with reason (In short) whether the following statement Is true or false.
Mr. X, a Chartered Accountant, is an employee of M/s M & N Co. a firm of Chartered Accountants of India. The firm is the auditor of ABC & Co. Ltd. After auditing the accounts of the Company the audit firm allowed Mr. X, their employee, to sign the audit report; which he did. (Nov 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
An employee Chartered Accountant cannot sign the auditor’s report on behalf of the listing firm. Only a partner in the firm can sign the audit report in compliance with the provisions of Sec. 145 of the Companies Act, 2013.
Question 47.
Comment on the following situation:
C Ltd. declared dividend amounting to ₹ 5 lacs out of Profits 13r the year ended 31.3.2009. Subsequently, it was noticed that company had failed to make provisions for Outstanding expenses of ₹ 7.80 lacs and Closing stock was also overvalued, which was not reported by auditors of the company. Management of C Ltd. held auditors responsible for this situation. (May 2010,8 marks)
Answer:
Failure to detect untrue and Incorrect financial position of a company:
In the given question, profit of the company has been inflated by the non-provisioning of outstanding expenses of 7.80 lacs and by the overvaluation of dosing stock and based on such inflated profit the company has declared and paid dividend of ₹ 5.00 lacs.
Therefore it can be said that dividend has been paid out “inflated profit” and not out of real profit”. If there is insufficient profit after above adjustment of outstanding expenses and correction of stock valuation and there is rio past reserve, it would amount to payment of dividend out of capital.
The auditors duty is to ascertain whether the Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss AIc of the company show a true and fair view of the financial position and revenue earning capacity.
For this purpose he has to exercise proper audit procedure of substantive test (i.e. vouching and verification) and valuation of various items of Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss a/c.
The auditor should have checked whether all the outstanding expenses have been provided or not and whether dosing stock has been properly valued as per AS-2. If he was not satisfied, he should have issued a qualified report or adverse report.
In this case auditor has failed to do so, he will be guilty of gross negligence in the performance of his duty. In the given questions, the facts are similar to the established judgment on The Leeds Estate Building & Investment Co. Ltd vs Shepherd (1887), where, it was held, that it was an auditor’s duty to ascertain that the accounts, he certifies, are correct and that it he fails in his duty, he is liable for damages for dividends wrongly paid by the company out of capital.
Question 48.
What are the general considerations about the duties of an auditor that can be summarized on the basis of legal decisions taken by Tribunal so far’ (Nov 2013, 5 marks)
Answer:
Duties of a Company AudItor on the basis of legal decisions of the Tribunal of law from time to time.
1. To examine the truthfulness and justification of the Balance Sheet [Leeds Estate Building and Investment Society Ltd. Vs Shephard]
2. To give clear-cut information with honesty [London and General Bank]
3. To perform the work tactfully, cautiously, and carefully. [Kingston Cotton Mill Co. Ltd.]
4. Auditor is a watchdog and not a blood wound (Kingston Cotton Mill Co. Ltd.
5. To advise the company Is not a duty of the auditor [London arid General Bank Ltd.
6. Duties regarding verification [Davar & Son Ltd. Vs M.S. Krishnaswami]
7. Intensive check of doubtful situation [London oil storage Co. Ltd. Vs Sear Has Luck & Co.]
8. Report regarding non-compliance of Company Act [ICAI vs K.R. Sharma]
Question 49.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The auditor has to report to Central Govt. within 90 days of his knowledge of an offense involving fraud. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
The auditor should report to Government within 60 days of his knowledge of offence involving fraud and not 90 days.
Question 50.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The members of XYZ Ltd. preferred a complaint against the auditor stating that he has failed to send the auditor’s report to them. (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
It is duty of board of directors to supply a copy of financial statement to the member. The auditors report shall require to be sent to first board of director and not to members.
![]()
Question 51.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The members of XYZ Ltd. preferred a complaint against the auditor stating that he has tailed to send the auditor’s repot to them. (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
It is duty of board of directors to supply a copy of financial statement to the member. The auditor’s report shall require to be sent to first board of directors and not to members.
Question 52.
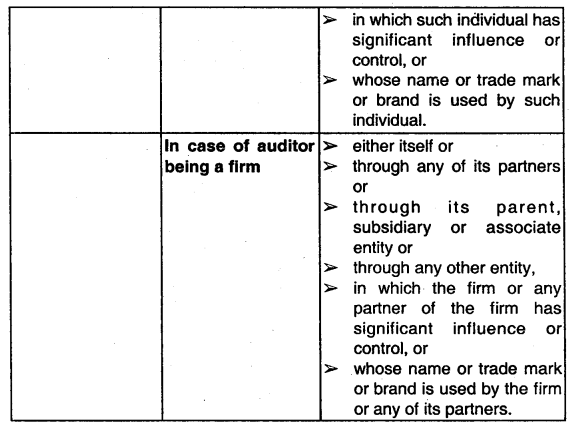
State the services which are not to be rendered by an auditor as per the provisions of Companies Act. 2013. (Nov 2016, 6 marks)
Answer:
Auditor not to render certain services:
Services to be An auditor shall provide to the company approved [Sec. Only such other services as are approved by:
144]
1. the Board of Directors or
2. the Audit Committee, as the case may be.
Question 53.
Discuss which class of companies are specifically exempt from the applicability of CARO-2020. (Nov 2016, 6 marks)
Answer:
Non-Applicability of CARO 2020:
It shall apply to every company including a foreign company as defined in Clause (42) of Sec. 2 of the Companies Act, 2013 (18012013) There in after referred to as the Companies Act.
Except:
- a banking company as defined in Clause (C) of Sec. 5 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (10 of 1949);
- an insurance company as defined under the Insurance Act, 1938 (4 of 1938);
- a company licensed to operate under Sec. 8 of the Companies Act;
- a One Person Company as defined under clause (62) of Sec. 20f the Companies Act and a small company as defined under Clause (85) of Sec. 2 of the Companies Act; and
- a private limited company, not being a subsidiary or holding company of a public company, having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus not more than rupees one crore as on the balance sheet date and which does not have total borrowings exceeding rupees one crore from any bank or financial institution at any point of time during the financial year and which does not have a total revenue as disclosed In Scheduled III to the Companies Act, 2013 (Including revenue from discontinuing operations) exceeding rupees ten crore during the financial year as per the financial statements.
Question 54.
State the matters to be included in the auditor’s report as per CARO 2020, regarding:
(i) Private Placement of Preferential issues.
(ii) Utilisation of IPO and further public otter. (May 2018, 2 marks each)
Answer:
(i) Private Placement of Preferential Issues:
The Auditor Is required to report as per Clause xb of Para 3 of CARO 2020 as to:
Whether the company has made any preferential allotment or private placement of shares or convertible debentures (fully, partially or “optionally convertible) during the year and if so, whether the requirements of section 42 and section 62 of Companies Act, 2013 have been complied with and the funds raised have been used for the purposes for which the funds were raised. if not, provide details in respect of amount Involved and nature of non-compliance;
(ii) Utilisation of IPO and further public offer:
The Auditor is required to report as per Clause xa of Pare 3 of CARO 2020 as to:
Whether moneys raised by way of Initial public offer or further public offer (Including debt instruments) during the year were applied for the purposes for which those are raised, If not, the details together with delays or default and subsequent rectification, if any, as may be applicable, be reported.
Question 55.
The company has raised funds by issuing fully convertible debentures. These funds were raised for the expansion and diversification of the business. However, the company utilized these funds for repayment of long term loans and advances.” Advise the auditor regarding reporting requirements under CARO, 2020. (Nov 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
Provisions:
As per Clause (xb) of Paragraph 3 of CARO, 2020, whether the company has made any preferential allotment or private placement of shares or convertible debentures (fully, partially or optionally convertible) during the year and if so, whether the requirements of section 42 and section 62 of Companies Act, 2013 have been complied with and the funds raised have been used for the purposes for which the funds were raised, if not, provide details In respect of amount invoived and nature of non-compliance;
Present Case:
In this case, the company has raised funds by issuing fully convertible debentures. These funds were raised for the expansion and diversification of the business. However, the company utilized these funds for repayment of long term loans and advances. So, here the reporting required as per para. 3 (xiv) of CARO, 2020. The auditor shall require to disclose wi his audit report details of amount involved along with nature and reason for non-compliance with condition.
Question 56.
Explain the Reporting requirements the auditor should ensure under CARO 2020 related to Property, Plant and Equipment. [Modified] (May 2019, 3 marks)
Answer:
As per clause (I) of Paragraph 3 0f CARO, 2020, the auditor shall require to report on following requirements relating to Fixed Assets
(a)
(A) whether the company is maintaining proper records showing full particulars, including quantitative details, and situation of Property, Plant, and Equipment;
(B) whether the company is maintaining proper records showing full particulars of intangible assets;
(b) whether these Property, Plant, and Equipment have been physically verified by the management at reasonable intervals; whether any material discrepancies were noticed on such verification and it so. whether the same have been properly dealt with in the books of account;
(c) whether the title deeds of all the immovable properties (other than properties where the company is the lessee and the lease agreements are duly executed In favor of the lessee) disclosed in the financial statements are held in the name of the company, if not, provide the details thereof in the format below:

(d) whether the company has revalued its Property, Plant, and Equipment (including Right of Use assets) or Intangible assets Or both during the year and, if so, whether the revaluation is based on the valuation by a Registered Valuer; specify the amount of change, if change Is 10% or more in the aggregate of the net carrying value of each class of Property. Plant and Equipment or intangible assets;
(e) whether any proceedings have been initiated or are pending against the company for holding any benami property under the Benami Transactions (Prohibition) Act, 1988 (45 of 1988) and rules made there under, so, whether the company has appropriately disclosed the details in its financial statements.
![]()
Question 57.
Examine with reasons whether the following statement is correct or incorrect.
(d) Provision of CARO, 2020 is not applicable to ABC Pvt. Ltd., a subsidiary of XYZ Ltd. (a public company) having fully paid Capital and Reserves & Surplus of ₹ 50 lakhs, Secured loan from bank of ₹ 90 Lakhs and Turnover of ₹ 5 Crore, for the financial year 201 8-19. (Nov 2019, 2 marks)
Answer:
This statement is Incorrect.
Provision of CARO, 2016 is not applicable to the ABC Pvt. Ltd. only when it is nol a subsidiary or holding company of a public company and is having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus not more than ₹ 1 Cr. as on the balance sheet date and which does not have total borrowings exceeding ₹ 1 cr. and revenue of exceeding ₹ 10 Cr. In this case, ABC Pvt. Ltd. is a subsidiary of XYZ Ltd., a holding company. So CARO, 2016 is applicable to ABC Pvt. Ltd.
Question 58.
M Ltd. has given certain loans to related parties and also has accepted certain deposits. As an auditor, how you include the above Items In paragraph 3 of CARO, 2020? (Nov 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Paragraph 3 of the CARO. 2020 requires the auditor to include a statement in the auditor’s report regarding the matters of loans to related parties and acceptance of certain deposits as per following:
(iii) whether during the year the company has made Investments in. provided any guarantee or security or granted any loans or advances in the nature of loans, secured or unsecured, to companies, firms, Limited Liability Partnerships or any other parties, if so:
(a) whether during the year the company has provided loans or provided advances in the nature of loans, or stood guarantee. or provided security to any other entity (float applicable to companies whose principal business is to give loans), if so, indicate –
(A) the aggregate amount during the year, and balance outstanding at the balance sheet date with respect to such loans or advances and guarantees or security to subsidiaries, joint ventures, and associates;
(B) the aggregate amount during the year, and balance outstanding at the balance sheet date with respect to such loans or advances and guarantees or security to parties other than subsidiaries, joint ventures, and associates;
(b) whether the investments made, guarantees provided, security given and the terms and conditions of the grant of all loans and advances in the nature of loans and guarantees provided are not prejudicial to the company’s interest;
(c) in respect of loans and advances in the nature of loans, whether the schedule of repayment of principal and payment of interest has been stipulated, and whether the repayments or receipts are
(d) if the amount Is overdue, state the total amount overdue for more than ninety days, and whether reasonable steps have been taken by the company for recovery of the principal and interest;
(e) whether any loan or advance W the nature of loan granted which has fallen due during the year. has been renewed or extended or fresh loans granted to settle the overdue of existing loans given to the same parties, if so, specify the aggregate amount of such dues renewed or extended or settled by fresh loans and the percentage of the aggregate to the total loans or advances in the nature of loans granted during the year (not applicable to companies whose principal business is to give loans);
(f) whether the company has granted any loans or advances in the nature of loans either repayable on demand or without specifying any terms or period of repayment, if so, specify the aggregate amount, percentage thereof to the total loans granted, aggregate amount of loans granted to Promoters, related parties as defined in clause (76) of section 2 of the Companies Act, 2013;
(iv) In respect of such loans whether the provisions of Section 185 and Section 186 of the Companies Act, 2013 have been complied with. if not, provide details thereof.
(v) For the purpose of acceptance of deposits where. Whether the directives issued by the Reserve Bank of India and the provisions of Sections 73 to 76 or any other relevant provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 and the rules framed there under, where
applicable, have been complied with? If not, the nature of such contraventions be stated. If an order has been passed by Company Law Board o National Company Law Tribunal or Reserve Bank of India or any Court or any other Tribunal, whether the same has been complied with or not?
(vi) The loan is with related Parties so deck whether they are in compliance with Section 177 and Section 188 of the Companies Act, 2013. where applicable and the details have been disclosed In the Financial Statements etc., as required by the applicable accounting Standards.
Question 59.
The auditor’s requirement to report under clause (X) of paragraph 3 of the Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2016 is restricted to frauds noticed or reported during the year. Explain what auditors may consider for reporting under this clause? (Nov 2020, 3 marks)
Question 60.
State with reason (in short) whether the following statement is True or False:
All the joint auditors are jointly and severally responsible for the work, which is not divided and carried on jointly by all the joint auditors. (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
True:
As per SA – 299 i.e. ResponsIbility of Joint Auditors, In respect of the audit work divided among the joint auditors, each jont auditor is responsible only for the work allocated to such joint auditors including proper execution of the audit procedures.
On the other hand, all the joint auditors are jointly and severally responsible all the joint auditors shall be jointly and severally responsible for
(a) The audit work which is not divided among the joint auditors and is carried out by all Joint auditors;
(b) Decisions taken by all the joint auditors under audit planning in respect of common audit areas concerning the nature, timing, and extent of the audit procedures to be performed by each of the joint auditors.
(c) Matters which are brought to the notice of the joint auditors by any one of them and on which there is an agreement among the joint auditors;
(d) Examining that the financial statements of the entity comply with the requirements of the relevant statutes;
(e) Presentation and disclosure of the financial statements as required by the applicable financial reporting framework
(f) Ensuring that the audit report complies with the requirements of the relevant statutes, the applicable Standards on Auditing, and the other relevant pronouncements issued by ICAI.
In respect of decisions taken by all the joint auditors concerning the nature, timing or extent of the audit procedures to be performed any of the joint auditors.
In respect of matters which are bought to the notice of joint auditors by any one of them and on which there is an agreement among joint auditors
For examining the financial statements of the entity comply with disclosure requirements of the relevant statute. For ensuring that the audit report complies with the requirements of relevant statue.
Question 61.
Write short note on the following: Joint Audit. (Nov 2008, May 2009, 5 marks each)
OR
Explain the concept of Joint Audit. Discuss its advantages and disadvantages (May 2011, 8 marks)
OR
Discuss the following:
Advantages and disadvantages of Joint Audit. (Nov 2014, 5 marks)
Answer:
Joint Audit:
As per SA 299, (Revised) Joint Audit, a joint audit is an audit of the financial statements of an entity by two or more auditors appointed with the objective of issuing the audit report. Such auditors are described as joint auditors.
Audit Plan by Joint Auditors
Prior to the commencement of the audit, the joint auditors shall discuss and develop a joint audit plan. In developing the joint audit plan, the joint auditors shall:
(a) Identity division of audit areas and common audit areas amongst the joint auditors that define the scope of the work of each joint auditor;
(b) Ascertain the reporting objectives of the engagement to plan the timing of the audit and the nature of the communications required;
(c) Consider and communicate among all joint auditors the factors that, in their professional judgment, are significant In directing the engagement team’s efforts;
(d) Consider the results of preliminary engagement activities and, where applicable, whether knowledge gained on other or similar engagements performed earlier by the respective engagement partner(s) for the entity is relevant.
(e) Ascertain the nature, timing, and extent of resources necessary to perform the engagement.
Advantages:
- Pooling and sharing of expertise.
- Advantage of mutual consultation.
- Lower workload.
- Better quality of work performance.
- Improved service to the client.
- Displacement of the auditor of the company ri a take-over often obviated.
- In respect of multinational companies, the work can be spread using the expertise if the local firms which are in a better position to deal with detailed work and the local laws and regulations.
- Lower staff development costs.
- Lower costs to carry Out the work.
- A sense of healthy competition towards a better performance.
Disadvantages:
- The fees being shared.
- Psychological problems where firms of different standing are associated in the joint audit.
- General superiority or inferiority complexes of some auditors.
- Problems of coordination of the work.
- Areas of work of common concern being neglected.
Question 62.
A Joint Auditor is not bound by the views of the majority of the joint auditors regarding matters to be covered in the report.’ Justify this statement in the light of responsibilities of Joint Auditors under AAS 12. (May 2010, 5 marks)
OR
Discuss on the following:
In Joint Audit, each Joint Auditor is responsible only for the work allocated to him”.(May 2012, 5 marks)
OR
Mention the points/areas in which all the joint auditors are jointly and severally responsible. (Nov 2015, 6 marks)
OR
Write short notes on the following:
(c) Responsibility of Joint Auditors (Nov 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
In respect of audit work divided among the joint auditors, each joint auditor shall be responsible only for the work allocated to such joint auditor including proper execution of the audit procedures.
All the joint auditors shall be jointly and severally responsible for;
1. the audit work which is not divided among the joint auditors and is carried out by all joint auditors;
2. decisions taken by all the joint auditors under audit planning in respect of common audit areas concerning the nature, timing, and extent of the audit procedures to be performed by each of the joint auditors.
3. matters which are brought to the notice of the joint auditors by any one of them and on which there is an agreement among the joint auditors;
4. examine that the financial statements of the entity comply with the requirements of the relevant statutes;
5. present after in and disclosure of the financial statements as required by the applicable financial reporting framework;
6. ensuring that the audit report complies with the requirements of the relevant statutes, the applicable Standards on Auditing, and the other relevant pronouncements issued by ICAI.
![]()
Question 63.
Examine with reasons whether ‘the following statements are correct or incorrect:
Joint auditor is ways bound by the views of majority of the joint auditors regarding matters to be covered in report. (May 2019, 2 marks)
Answer:
This statement is Incorrect
A joint auditor is not bound by the views of the majority of the joint auditors regarding matters to be covered in the report and should express his opinion in a separate report in case of a disagreement.
Question 64.
“Before the commencement of audit, the joint auditors should discuss and develop a joint audit plan”. Discuss the points to be considered. in developing the joint audit plan by the joint auditors. (2019- Nov 4 marks)
Answer:
Before the commencement of the audit, the auditor shall discuss and develop a joint audit plan. In developing the joint audit plan, the joint auditors shall consider:
- Identify division of audit areas and common audit areas amongst the joint auditors that define the scope of the work of each joint auditors;
- Ascertain the reporting objectives of the engagement to plan the timing of the audit and the nature of the communications required;
- Consider and communicate among all joint auditors the factors that, in their professional judgement, are significant in directing the engagement team’s efforts;
- Consider the results of preliminary engagement activities and where applicable, whether knowledge gained on other or similar engagements performed earlier by the respective engagement partner(s) for the entity is relevant.
- Ascertain the nature, timing, and extent of resources necessary to perform the engagement.
Question 65.
As one of the Joint auditors of X Ltd. for the immediately preceding three financial years, you have been considered for ratification by the members in the AGM as the sole auditor, while the said Joint auditors are not reappointed. Comment. (Nov 2016,6 marks)
Answer:
When one of the joint auditors of the previous years is considered for ratification by the members as the sole auditor for the next year, it is similar to the non-reappointment of one of the retiring joint auditors. As per Sec. 140(4) of the Companies Act, 2013, special notice shall be required for a resolution at an annual general meeting appointing as auditor a person other than retiring auditor or providing expressly that a retiring auditor shall not be reappointed, except where the retiring auditor has completed a consecutive tenure of five years or, as the case may be, ten years as provided under subsection (2) of Sec. 139 of the said Act.
Accordingly, provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 to be compiled with are as under:
1. Ascertain that special notice under Sec. 140(4) of the Companies Act, 2013 was received by the company from such number of members holding not less than one percent of total voting power or holding shares on which an aggregate sum of not less than live lakh rupees has been paid up on the date of the notice not earlier than three months but at least 14 days before the AGM date as per Sec. 115 of the Companies Act, 2013 read with Rule 23(1) and 23(2) of the Companies (Management and Administration) Rules, 2014.
2. Check whether the said notice has been sent to all the members at least 7 days before the date of the AGM as per Sec. 115 of the Companies Act, 2013 read with Rule 23(3) of the Companies (Management and Administration) Rules, 2014.
3. Verify the notice contains an express Intention of a member for proposing the resolution for appointing a sole auditor in place of both the joint auditors who retire at the meeting but are eligible for reappointment.
4. The notice is also sent to the retiring auditor as per Sec. 1 40(4)(ii) of the Companies Act, 2013.
5. Verify whether any representation, received from the retiring auditor was sent to the members of the company.
6. Verity from the minutes book whether the representation received from the retiring joint auditor was considered at the AGM.
Question 66.
Comment on the following:
ABC Ltd. having a turnover of ₹ 100 crores during financial year 2011-12, need not get its branch audited whose turnover is ₹ 1.5 crores during the same year. (May 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Branch Audit:
As per Sec. 143 (8) of the Companies Act, 2013 If a company has a branch office, the accounts of that office shall be audited either by the auditor appointed for the company (here in referred to as the company’s auditor) under this Act oc by any other person qualified for appointment as an auditor of the company under this Act arid appointed as such under Sec. 139, or where the branch office is situated in a country outside India, the accounts of the branch office shall be audited either by the company’s auditor or by an accountant or by any other person duly qualified to act as an auditor of the accounts of the branch office in accordance with the laws of that country. Therefore, ABC Ltd. has to get its branch audited.
Question 67.
State with reason (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect.
Branch auditor of a company should give photocopies of his working papers n demand by Company Auditor. (Nov 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per SA 230 on “Audit Documentation”, audit documentation is the property of the auditor. He may at his discretion, make portions of, or extracts from, audit documentation available to clients, provided such disclosure does not undermine the validity of the work performed, or, in the case of assurance engagements, the independence of the auditor or of his personnel.
Main auditor does not have right of access to the working papers of the branch auditor. In the case of a company, the main auditor has to consider the report of the branch auditor and has a right to seek clarification and to visit the branch but cannot ask for the copy of working papers and therefore, the branch auditor is under no compulsion to give photocopies of his working papers to the principal auditor of the Company.
Question 68.
State with reasons (In short) whether the following statement Is correct or incorrect:
The Managing Director of a company has shifted company’s books of accounts from Registered office (Mumbai) to Corporate Office (New Delhi). (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
Shifting of Books of Account:
As per Sec. 128(1) of the Companies Act, 2013, every company shall keep at its registered office proper books of accounts. It Is permissible, for all or any of the books of accounts to be kept at such place In India as the Board of Directors may decide but. when a decision in this regard is taken, the company must file within 7 days of such decision with the registrar of companies a notice In writing giving full address of the other place.
Question 69.
Examine with reasons (in short) whether the following statement Is correct or incorrect:
(j) Mr. A Is a statutory auditor of ABC Ltd. The branch of ABC Ltd. is audited by Mr. B, another Chartered Accountant. Mr. A requests for the photocopies of the audit documentation of Mr. B pertaining to the branch audit. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per SA 230, Audit Documentation and SQCI, Standard on Quality Control, working papers are the property of the auditor, he should not disclose such working papers of his client to other person without permission of the client or as required by law. So, Mr. A, Statutory auditor of ABC Ltd. cannot request for the photocopies of the audit documentation of Mr. B, the branch auditor pertaining to branch audit.
![]()
Question 70.
RJ Limited is in the business of trading, of cycles having Head Office at Delhi and brarch at Mumbai. Statutory audit of Head Office was to be done by CA D and statutory audit of branch at Mumbai was to be done by CA M. During the ceurse of audit by CA D at head office, CA D wanted to visit branch at Mumbai and verify the inventory records at Mumbai. The management of RJ Limited did not allow CA D to visit Mumbai office and verify the inventory records as the branch audit of Mumbal was already being undertaken by another CA M. In the above situation, discuss the rights available with CA D In terms of the Companies Act, 2013. (Nov 2020, 3 marks)
Question 71.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct Or incorrect:
Casual vacancy of a Cost Auditor of a company is filled by shareholders in general meeting within one month. (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
Any casual vacancy In the office of a Cost Auditor, whether due to resignation, death or removal, shall be tilled by the Board of Directors within 30 days of occurrence of such vacancy and the company shall Inform the Central Government in form CRA-2 within 30 days of such appointment of Cost Auditor.
Question 72.
“Mr. A is offered by ABC Ltd. for appointment as cost auditor and asked to certify certain requirements before such appointment.” Discuss those requirements with reference to the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. (Nov 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Rule 6 of the Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rules, 2014, requires the companies prescribed under the said rule to appoint an auditor within 180 days of the commencement of every financial year. However, before such appointment is made, the written consent of the cost auditor to such appointment and a certificate from him or it shall be obtained.
The certificate to be obtained from Mr. A shall certify that the:
- The individual or the firm, as th9 case may be, is eligible for appointment and is not disqualified for appointment under the Companies Act. 2013, the cost and Works Accountants Act, 1959 and the rules or regulations made thereunder;
- The individual or the firm, as the case may be, satisfies the criteria provided in Sec. 141 of the Companies Act, 2013 so far as may be applicable;
- The proposed appointment ¡s within limits laid down by or under the authority of the Companies Act. 2013: and
- The list of proceedings against the cost auditor or audit firm or any partner of the audit firm pending with respect to professional matters of conduct, as disclosed in the certificate, is true and correct.
Question 73.
Examine with reasons whether the following statements are correct or incorrect:
Rule 3 of the Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rule. 2014 provides the classes of companies, engaged in the production of goods or providing services, having an overall turnover of ₹ 25 crore or more during the immediately preceding financial year, required to InClude cost records in their books of account. (May 2019, 2 marks)
Answer:
This Statement is Incorrect
Rule 3 of the Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rules, 2014 provides the classes of companies, engaged In the production of goods or providing services, having an overall turnover from all its products and services of ₹ 35 crore or more during the immediately preceding financial year, required to include cost records in their books of account.
Question 74.
Comment as an auditor on the following situation:
(a) Mr. X, a oartner in X & Co., a firm of a Chartered Accountants, died on 31-3-2010 after completing routine audit work of XYZ Company Ltd.. Mr. Y another partner of the firm of Chartered Accountants signed the financial statements of XYZ Company Ltd., without reviewing the finalization work done by the assistants. (Nov 2010, 5 marks)
Answer:
Provisions of SA – 200: The following principles are Paid down:
1. When he auditor delegates work to assistants or uses work performed by other auditor and experts, he will continue to be responsible for forming and expressing his opinion on the financial statements.
2. He will be entitled to rely on the work, provided he exercises adequate skill and is not aware of any reason to believe that he should not have so relied.
3. He should carefully direct, supervise and review the work delegated to assistants. Aspect review: Following aspects should be reviewed:
- Audit programme
- Documentation
- Audit quarter
- Audit procedures
- Audit opinion
Analysis and Conclusion: In the present case, whether Mr. X, the deceased partner had reviewed the work performed by assistants or not, is not clearly stated. Hence, It shall be the duty of Mr. Y., to review the work performed by the assistants before expressing an opinion, Mr. Y. should review the working papers carefully, carry test checks and scrutinize the audit file thoroughly.
Question 75.
What are the prohibited services for auditor as per Companies Act, 2013? (Jan 2021, 3 marks)
Multiple Choice Question
Question 1.
The provisions relating to eligibility, qualifications and disqualifications of an auditor are governed by ………………….. of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) Sec 139
(b) Sec 140
(c) Sec 141
(d) Sec 148
Answer:
(c) Sec 141
Question 2.
A person shall be eligible for appointment as an auditor of a company only it he/she is a
(a) Cost Accountant
(b) Chartered Accountant
(c) Internal Accountant
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(b) Chartered Accountant
Question 3.
When a firm Induding LLP Is appointed as an auditor of a company,
(a) every member of the firm is eligible for signing on behalf of the firm
(b) Only partners shall be authorized.
(c) Only manager of the firm shall be authorised to act and sign on behalf of the firm
(d) Only the partners who are Chartered Accountants shall be authorised to act and sign on behalf of the firm.
Answer:
(d) Only the partners who are Chartered Accountants shall be authorised to act and sign on behalf of the firm.
Question 4.
Disqualification for appointment as an auditor of a company is defines under
(a) Section 141 of the Companies Act, 2013
(b) Rule 10 of the Section 141 of the Companies Act, 2013
(c) Subsection (5) of Section 142 of the Companies Act, 2013
(d) Subsection (3) of Section 141 of the Companies Act, along with Rule lo of CAAR -2014.
Answer:
(d) Subsection (3) of Section 141 of the Companies Act, along with Rule lo of CAAR -2014.
![]()
Question 5.
Under Companies Act. 2013, the term ‘releline’ for appointment of an auditor, excludes
(a) Father or Mother (including step)
(b) Father/Mother in law
(c) Son’s wife
(d) Daughter’s husband.
Answer:
(b) Father/Mother in law
Question 6.
Can a person appointed as an auditor if his relative is a Director or is in the employment of the company as a director or key Managerial personnel.
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) May or May not depending upon the situation
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) No
Question 7.
Accounting and bookkeeping services or internal audit conducted by an auditor is prohibited under ……………………. of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) Section 141
(b) Section 143
(c) Section 144
(d) Section 146
Answer:
(c) Section 144
Question 8.
First auditor of a company, other than a Government Company, shall be appointed by the
(a) Central Government
(b) Board of Directors
(c) Previous Auditor
(d) NCLT
Answer:
(b) Board of Directors
Question 9.
Appointment of first auditor, other than a Government Company is governed under …………………….. of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) Section 139(1)
(b) Section 139 (5)
(c) Section 139 (6)
(d) Section 139 (7)
Answer:
(c) Section 139 (6)
Question 10.
First auditor other than a Government Company shall be appointed by the Board of Director ……………………. from the date of registration of the company.
(a) within 3 days
(b) within 30 days
(c) within 90 days
(d) within 120 days
Answer:
(b) within 30 days
Question 11.
In the case of failure of the Board to appoint the first auditor, then it shall be inform to
(a) TCWG
(b) BOD
(c) Members of the company
(d) Central Government
Answer:
(c) Members of the company
![]()
Question 12.
in case of failure of the board to appoint the first auditor, then member of the company shall appoint auditor within ………………… .
(a) 30 days
(b) 60 days
(c) 90 days
(d) 120 days
Answer:
(c) 90 day
Question 13.
In case of failure of the board to appoint the first auditor, then member of the company shall appoint auditor at an
(a) board meeting
(b) general meeting
(c) annual general meeting
(d) extraordinary general meeting.
Answer:
(d) extraordinary general meeting.
Question 14.
First auditor hold his office till the
(a) extraordinary general meeting held
(b) annual general meeting
(c) conclusion to the first annual general meeting
(d) conclusion of ‘the first extraordinary general meeting
Answer:
(c) conclusion to the first annual general meeting
Question 15.
A ‘Government Company is a company in which not less than 51% of the paid-up share capital Is held by the
(a) Central Government
(b) State Government
(c) Partly by the Central Government and partly by one or more State Governments.
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(d) All the above.
Question 16.
First appointment of the first auditor, in case of Government company is governed under …………………. of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) Section 139 (1)
(b) Section 139 (5)
(c) Section 139 (6)
(d) Section 139 (7)
Answer:
(d) Section 139 (7)
Question 17.
Appointment of first auditor in case of Government Company mode by ………………. .
(a) TCWG
(b) Board of Directors
(c) Members of the company
(d) C & AG
Answer:
(d) C & AG
Question 18.
If C & AG fail to appoint first auditor in case of Government Company with in stipulated time penod then
(a) Central Government shall appoint such auditor within next 60 days
(b) Central Government shall appoint such auditor within next 30 days
(c) Board of Directors of the company shall appoint such auditor within 30 days
(d) Members of the company shall appoint such auditor with In 60 days.
Answer:
(c) Board of Directors of the company shall appoint such auditor within 30 days
Question 19.
If C & AG and BOD fail to appoint first auditor In case of Government Company within their stipulated time period then
(a) Central Government shall appoint such auditor within next 30 days
(b) State Government shall appoint such auditor within next 30 days
(c) Members of the company shall appoint within 30 days at a annual general meeting,
(d) Members of the company shall appoint within 60 days at an extraordinary general meeting.
Answer:
(d) Members of the company shall appoint within 60 days at an extraordinary general meeting.
Question 20.
…………………. of the Companies Act. 2013 provides that every company shall, at the first annual general meeting appoint an individual or a firm as an auditor.
(a) Section 139 (1)
(b) Section 139 (5)
(c) Section 139 (6)
(d) Section 139 (7)
Answer:
(a) Section 139 (1)
![]()
Question 21.
Auditor- appointed at first AGM shall hold office till the conclusion of its
(a) next annual general meeting
(b) third annual general meeting
(c) sixth annual general meeting
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) sixth annual general meeting
Question 22.
In case of First Auditor, the company shall inform the auditor concerned of his or its appointment, and also file a notice of such appointment with the Registrar within ……………………. of the meeting in which the auditor is appointed.
(a) 7 days
(b) 15 days
(c) 30 days
(d) 60 days
Answer:
(b) 15 days
Question 23.
Appointment of Subsequent Auditor o? a Government Company defines under
(a) Section 139 (1)
(b) Section 139 (5)
(c) Section 139 (6)
(d) Section 139 (7)
Answer:
(b) Section 139 (5)
Question 24.
Subsequent Auditor in case of Government Company appointed by C & AG ……………. .
(a) within 30 days from the date of registration
(b) within 90 days from the commencement of the year
(c) within 120 days from the commencement of the financial year
(d) within 180 days from the commencement of the financial year
Answer:
(d) within 180 days from the commencement of the financial year
Question 25.
Subsequent Auditor appointed by C & AG in case of Government Company hold the office till
(a) the next financial year
(b) the next commencement of the annual general meeting
(c) the next conclusion of the annual general meeting
(d) the next conclusion of the extraordinary general meeting
Answer:
(c) the next conclusion of the annual general meeting
Question 26.
Filling of casual vacancy is governed under ………………….. of the companies Act 2013.
(a) Section 139 (5)
(b) Section 139 (6)
(c) Section 139 (7)
(d) Section 139 (8)
Answer:
(d) Section 139 (8)
Question 27.
Any casual vacancy in case of a company other than a company whose accounts are subject to audit by an auditor appointed by the C & AG of India, shall be tilled by the ……………………. .
(a) Central Government within 30 days
(b) State Government within 60 days
(c) Board of Directors within 30 days
(d) C & AG within 30 days
Answer:
(c) Board of Directors within 30 days
Question 28.
Any casual vacancy in case of a company whose accounts are subject to audit by the auditor appointed by the C & AG of India, shall be filled by the ……………….. .
(a) Central Government within 30 days
(b) State Government within 60 days
(c) Board or Directors within 30 days
(d) C & AG within 30 days
Answer:
(d) C & AG within 30 days
Question 29.
When an auditor resigned from the company he shall tile within a period of ………………………. from the date of resignation, and file a statement in the prescribed form ……………………… Indicating the reason of such resignation.
(a) 15 days, ATO -3 with company
(b) 30 days, AST -4 with Registrar
(c) 45 days, ADT-3 with C & AG
(d) 30 days, ADT- 3 with the company and Registrar
Answer:
(d) 30 days, ADT- 3 with the company and Registrar
Question 30.
When an auditor resigned from an the Government Company (u/s 139(5)], auditor shall file ADT-3 (As per Rule 8 of CAAR) with the fails of resignation to ………………… .
(a) Central Govemment
(b) Board of Directors
(c) C & AG of India
(d) Registrar of the Companies
Answer:
(c) C & AG of India
![]()
Question 31.
In the case of resignation of an auditor from the company fail to file ADT – 3 (as per Rule 8 of CAAR) with tho company and the Registrar within stipulated period, then auditor shall be punishable with fine which shall be ………………….. .
(a) Fifty thousand rupees
(b) Less than fifty thousand rupees
(c) Five Lakh rupees
(d) Not less than fifty thousand and it may extend to five lakh rupees.
Answer:
(d) Not less than fifty thousand and it may extend to five lakh rupees.
Question 32.
Can an auditor be re-appointed as auditor in annual general meeting
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) Partly yes
(d) None of them.
Answer:
(a) Yes
Question 33.
A retiring auditor may be re-appointed at an AGM, if:
(a) he is not disqualified for re-appointment
(b) he has not given the company a notice In writing of his unwillingness to be re-appointed.
(c) a special resolution has not been passed at that meeting appointing some other auditor or providing expressly that he shall not be reappointed.
(d) All of them
Answer:
(d) All of them
Question 34.
If at any AGM. no auditor is appointed or re-appointed them
(a) Central Government can appoint an auditor
(b) C & AG can appoint an auditor the next AGM
(c) BOD can appoint an auditor at extraordinary general meetings,
(d) The existing auditor shall continue to be the auditor of the company.
Answer:
(d) The existing auditor shall continue to be the auditor of the company.
Question 35.
Constitution of Audit committee of a company required under Section ………………… of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) 139 (2)
(b) 141 (3)
(c) 177
(d) 178
Answer:
(c) 177
Question 36.
In addition to listed companies following class of company shall not constitute an Audit Committee:
(a) all public companies with a paid-up capital of ten crore rupees or more
(b) all public companies having a turnover of on hundred crore rupees or more
(c) all public companies, having in aggregate, outstanding loans or borrowings or debentures or deposits less than fifty crore rupees or more
(d) All of above
Answer:
(c) all public companies, having in aggregate, outstanding loan or borrowings or debentures or deposits less than fifty crore rupees or more.
Question 37.
Manner and procedure of selection and appointment of an auditor is governed under
(a) Rule 1 of CAAR 2014
(b) Rule 2 of CAAR 2014
(c) Rule 3 of CAAR 2014
(d) Rule 5 of CAAR 2014
Answer:
(c) Rule 3 of CAAR 2014
Question 38.
Appointmen1 of an auditor as per Rule 30f CAAR 2014, shall be subject to ratification in every annual general meeting tile the sixth such meeting by way of passing of an ………………. .
(a) resolution
(b) ordinary resolution
(c) extraordinary resolution
(d) special resolution
Answer:
(b) ordinary resolution
Question 39.
The remuneration of an auditor describe under Section …………………. of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) 135
(b) 141
(c) 142
(d) 177
Answer:
(c) 142
Question 40.
Can Board of Directors of a company fix remuneration of the first auditor appointed by them.
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) May or May not
(d) Absolutely No.
Answer:
(a) Yes
![]()
Question 41.
Is auditor’s remuneration Includes the expenses, it any, Incurred by the auditor in connection with the audit and any facility extended to him.
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) It depends upon the situation
(d) If Central Government permits
Answer:
(a) Yes
Question 42.
Remuneration paid to him for any other service rendered by him at the request of the company,
(a) Included In the auditor’s
(b) Does not remuneration, include with the auditor’s remuneration u/s 142 of the Act.
(c) May be included in auditor’s remuneration if BoD approves
(d) May be included In the auditor’s remuneration if Central Government approves.
Answer:
(b) Does not remuneration, include with the auditor’s remuneration u/s 142 of the Act.
Question 43.
Auditor appointed under Section 139 may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term, u/s described under Section.
(a) 139 (5)(i)
(b) 140 (1)
(c) 140 (5)
(d) 140 (2)
Answer:
(b) 140 (1)
Question 44.
Auditor can be removed from his office before the expiry of his term only by …………………….. of the company.
(a) resolution
(b) simple resolution
(c) special resolution
(d) specific resolution
Answer:
(c) special resolution
Question 45.
Auditor can be removed from his office before the expiry of his term Only by a special resolution of the company, after obtaining …………………. .
(a) the management resolution
(b) the previous approval of BoD.
(c) the approval of the Central Government
(d) the previous approval of the Central Government
Answer:
(d) the previous approval of the Central Government
Question 46.
Application to the Central Government for removal of auditor shall be made in …………………. .
(a) Form ADT – 1
(b) Form ADT – 2
(c) Form ADT – 2
(d) Form ATD – 3
Answer:
(b) Form ADT – 2
Question 47.
Application to the Central Government for removal of auditor shall made in appropriate form and shalt be accompanied with fees as provided for this purpose under the
(a) CAAR -2014
(b) Companies Act 2013
(c) Companies (Fees and Penalty) Rules 2014
(d) Companies (Registration offices and Fees) Rules, 2014.
Answer:
(d) Companies (Registration offices and Fees) Rules, 2014.
Question 48.
Application to the Central Government for removal of auditòr shall be made to the Central Government of the resolution passed by the Board.
(a) Within 15 days
(b) Within 30 days
(c) Within 45 days
(d) Within 60 days
Answer:
(b) Within 30 days
Question 49.
Removal of an auditor from his office before the expiry of his term, company shall hold the general meeting within ……………. of receipt of approval of the Central Government for passing the special resolution
(a) Within 15 days
(b) Within 30 days
(c) Within 45 days
(d) Within 60 days
Answer:
(d) Within 60 days
Question 50.
Before taking any action for removal otan auditor before expiry of terms …………… .
(a) a notice from BoO should be served to concerned auditor
(b) a notice from the Central Government should be served to concerned auditor
(c) The auditor concerned shall be given a reasonable opportunity of being heared.
(d) None of than.
Answer:
(c) The auditor concerned shall be given a reasonable opportunity of being heared.
![]()
Question 51.
Ceiling on number of audits per auditor.
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 15
(d) 20.
Answer:
(d) 20.
Question 52.
Audit firm having five partners, In such case the ceiling will be ………………… company
(a) 20
(b) 50
(c) 80
(d) 100
Answer:
(d) 100
Question 53.
If any partner of the firm of Chartered Accountants in practice is also a partner of any other firm of Chartered Accountants in practice the number of audit assignments by the member will be ………………. .
(a) 20
(b) 40
(c) 60
(d) 80
Answer:
(b) 40
Question 54.
The specified number of tax audit assignments that an auditor, as an individual or as a partner of a firm, can accept is
(a) 20
(b) 40
(c) 60
(d) 80
Answer:
(c) 60
Question 55.
Statutory auditor has a right of assessing the books of accounts under section …………….. .
(a) 142 (1)
(b) 142 (2)
(c) 143 (1)
(d) 144 (1)
Answer:
(c) 143 (1)
Question 56.
Section 143(1) of the Companies Act, provides that the auditor of a company, at all times, shall have a right of assess to
(a) Books of accounts
(b) Vouchers of the company
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b) both
Answer:
(d) (a) and (b) both
Question 57.
Under Section 143(1) auditor of a company has a right to assess the books of accounts
(a) Kept at the registered óffìoe
(b) Kept at any other place
(c) Only (a) not (b)
(d) (a) and (b) both places
Answer:
(d) (a) and (b) both places
Question 58.
Books of Accounts includes all books which have
(a) any bearing
(b) likely to have any bearing on the accounts
(c) the statutory or statistical books
(d) any one of them.
Answer:
(d) any one of them.
Question 59.
Company Auditor cannot audit the branch’s records, is it
(a) Correct
(b) Wrong
(c) Partially correct
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Wrong
Question 60.
Auditor has a right to receive notices and other communications relating to any general meeting and to be heard at such meeting, relating to the matter of his concern discusses under Section ……………………… of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) 141
(b) 143
(c) 143 (1)
(d) 146
Answer:
(d) 146
![]()
Question 61.
It is duty of the auditor to attend the general meeting of the company personally statement is
(a) True
(b) Wrong
(c) Partially True
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Wrong
Question 62.
Unless otherwise exempted it is duty of an auditor to attend any general meeting of the company or through his
(a) Personal secretary
(b) Colleague
(c) Representative
(d) Authorised representative
Answer:
(d) Authorised representative
Question 63.
Books of accounts of the company must be kept at the office for audit, describe under Section …………………. of the Companies Act. 2013.
(a) 128
(b) 132
(c) 142
(d) 148
Answer:
(a) 128
Question 64.
Auditor has a right to retain such documents which are connected with the work on which
(a) work have not be done
(b) some dispute arises
(c) fees have not been paid
(d) none of them.
Answer:
(c) fees have not been paid
Question 65.
…………………. of the Companies Act, 2013 specifies the duties of an auditor of a company in a comprehensive manner.
(a) SectIon 140
(b) Section 141
(c) Section 142
(d) Section 143
Answer:
(d) Section 143
Question 66.
It is the duty al an auditor to inquire into the matter especially when
(a) Loan and advances made by the company have been shown as deposits.
(b) Personal expenses have been charged lo revenue account.
(c) Transactions of the company which are represented neatly by book entries are prejudicial to the interests of the company.
(d) Any of the above cases.
Answer:
(d) Any of the above cases.
Question 67.
Auditor of the company shall sign the auditor’s report or sign or certify any other document of the company in accordance with the provisions of ………………… .
(a) Section 141 (1)
(b) Section 141 (2)
(c) Section 141 (3)
(d) Section 141 (5)
Answer:
(b) Section 141 (2)
Question 68.
Section 141(2) of the Companies Act. 2013 states that where a ……………… is appointed as an auditor of a compary. only the partners who are Chartered Accountants shall be authoriseci to act and sign on behalf of them.
(a) Company
(b) Partnership firm
(c) Limited Liability Partnership Firm
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 69.
According to ………………… of the Companies Act. 2013, every auditor shall comply with the auditing standards.
(a) Section 142 (1)
(b) Section 143 (6)
(c) Section 143 (8)
(d) Section 143 (9)
Answer:
(d) Section 143 (9)
Question 70.
According to …………………. of the Companies Act, 2013) empower the Central Government to prescribe if needed, the standard of auditing as recommended by the ICAI, in consultation with and after examination of the recommendations made by the National Financial Reporting Authority.
(a) Section 143 (9)
(b) Section 143 (10)
(c) Section 143 (11)
(d) Section 143 (12)
Answer:
(b) Section 143 (10)
![]()
Question 71.
It an auditor of a company In the course of the performance of his duties as auditor, has reason to believe that an offence of fraud, which Involves or is expected to involve individually an amount of ₹ 1 crore oc above, is being or has been committed in the company by its officers or employees, the auditor shall report the matter to the Central Government according to.
(a) Section 143 (11) of the Companies Act. 2013
(b) Section 143 (12) of the Companies Act. 2013
(c) Rule 13 of the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules 2014,
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 72.
As per ………….. of the Companies Act, 2013 where any of the matters required to be included in the audit report is answered in the negative or with a qualification, the report shall state the reasons therefor.
(a) Section 143 (1)
(b) Section 143 (2)
(c) Section 143 (3)
(d) Section 143 (4)
Answer:
(d) Section 143 (4)
Question 73.
The CARO 2020, is an additional reporting requirement order, applies to every company including a …………….. as defined In clause (42) of Section 2 of the Companies Act, 2013.
(a) Private Limited Company
(b) Limited Liability Partnership
(c) Foreign Company
(d) Dormant Company
Answer:
(c) Foreign Company
Question 74.
Exempted class of Companies for reporting under CARO 2020 except.
(a) Banking Company
(b) Foreign Company
(c) Insurance Company
(d) One Person Company
Answer:
(b) Foreign Company
Question 75.
Unfavorable or Qualified Reporting under CARO 2020 requires
(a) to state the reason
(b) no reason to be stated
(c) explanation authentic proof is to be required
(d) none of them
Answer:
(a) to state the reason
Question 76.
Under which circumstances auditor should qualify his report.
(a) Accounts have not been preparing on accrual basis
(b) Proper disclosures regarding change in accounting policies have not been made
(c) Fundamental accounting assumption of going concern has not been followed and this fact has not been disclosed In the financial statements
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(d) Any of the above
Question 77.
In making a qualification disclosure in the audit report, the auditor should consider the ………………….. .
(a) Volume of such transaction
(b) Character of the transaction
(c) Materiality of the relevant transaction
(d) Any one of the above
Answer:
(c) Materiality of the relevant transaction
Question 78.
Advantages of Joint Auditor except
(a) Sharing of expertise & lowing workload
(b) Better quality of performance through mutual consultation
(c) A sense of healthy competition towards a better performance
(d) Fees being shared among the joint auditors
Answer:
(d) Fees being shared among the joint auditors
Question 79.
General disadvantages of joint audit except
(a) Displacement of the auditor of the company taken over in a take over other obviated.
(b) General superiority complexes of some auditors.
(c) Uncertainty about the liability for the work done.
(d) Problems of coordination of the work.
Answer:
(a) Displacement of the auditor of the company taken over in a take over other obviated.
Question 80.
Responsibilities of Joint – Auditors are governed by
(a) SA – 220
(b) SA- 235
(c) SA – 240
(d) SA -299
Answer:
(d) SA -299
![]()
Question 81.
“All the joint auditors are jointly and severally responsible in respect of the audit work which ¡s not divided among the joint auditors and is carried out by all of them. Statement is
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Partially True
(d) None
Answer:
(a) True
Question 82.
……………… of Section 143 of the Companies Act, 2013, prescribes the duties and powers of the company’s auditor with reference to the audit of the branch and branch auditor.
(a) Sub Sections (2)
(b) Sub-Section (4)
(c) Sub-Section (7)
(d) Sub-Section (8)
Answer:
(d) Sub-Section (8)
Question 83.
Branch auditor shaH submits his report to the company’s auditor and reporting of fraud by the auditor shall also extend to such branch auditor to the extent it relates to the concerned branch, according to.
(a) Section 143 Sub Section (7) of the Companies Act, 2013
(b) Section 143 Sub Section (8) of the Companies Act, 2013
(c) Rule 10 of the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014,
(d) Rule 12 of the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014,
Answer:
(d) Rule 12 of the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014,
Question 84.
Cost audit is an audit process for ……………… the cost of manufacture or production of any article.
(a) Verifying
(b) Valuation of
(c) Accounting
(d) Auditing
Answer:
(a) Verifying
Question 85.
Cost Audit is covered by Section 148 of the Companies Act, 2013. The Audit conducted under this section shall be in addition to the audit conducted under ………………. .
(a) Section 141
(b) Section 142
(c) Section 143
(d) Section 145
Answer:
(c) Section 143
Question 86.
The Central Government has notified the ……………. which prescribes the classes of companies required to include cost records in their book of account, applicability of cost audit, mamtenance of records etc.
(a) Companies Cost Audit Rules 2014
(b) Companies (Cost Audit Record) Rules 2014
(c) Companies (Cost Audit and Investigation) Rules 2014
(d) Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rules 2014
Answer:
(d) Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rules 2014
Question 87.
Every company under Rule 5 of CAAR 2014, all units and branches there of shall, in respect of each of its tinanctal year. Is required to maintain cost records in …………….. .
(a) Form CAR-1
(b) Form CRA – 1
(c) Form CAR – 2
(d) Form CRA – 2.
Answer:
(b) Form CRA – 1
Question 88.
No person appointed under ……………… of the Companies Act, 2013, as an a auditor of the company shall be appointed for conducting the audit of cost records.
(a) Section 139
(b) Section 141
(c) Section 142
(d) Section 146
Answer:
(a) Section 139
Question 89.
Rule 6 of the CAAR -2014 requires the companies prescribed under the said Rules to appoint an Auditor within ……………….. of the commencement of every financial year.
(a) 60 days
(b) 90 days
(c) 120 days
(d) 180 days
Answer:
(d) 180 days
Question 90.
The Cost Auditor appointed as such shall continue in such capacity till the expiry of 180 days from the dosure of the financial year or for the financial year for which he has been appointed.
(a) Till the end of next financial year
(b) Till the submits the cost audit reports
(c) Till the expiry of 240 days
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Till the submits the cost audit reports
![]()
Question 91.
The cost auditor may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term, through a after giving a reasonable opportunity of being heard to the cost auditor and recording the reasons for such removal in writing.
(a) Simple resolution
(b) Special resolution
(c) Board resolution
(d) Central Govt’s order
Answer:
(c) Board resolution
Question 92.
For the appointment of another cost auditor after the removal of existing cost auditor, intimating sucf appointment to the Central Government In form of.
(a) Form CRA – 1
(b) Form CAR – 1
(c) Form CRA -2
(d) Form CRA-4
Answer:
(c) Form CRA -2
Question 93.
Any casual vacancy in the of Cost Auditor, whether due to res1gnation, death or removal, shall be filled …………………… within ……………. days of occurrence of such vacancy.
(a) Board of Directors, 30
(b) Board of Directors, 60
(c) Central Govom ment, 15
(d) Central Government, 30
Answer:
(a) Board of Directors, 30
Question 94.
Submission of Cost Audit Report to the Board of Directors of the company in ………….. .
(a) Form CRA – 1
(b) Form CRA – 2
(c) Form CRA – 3
(d) Form CRA – 4
Answer:
(c) Form CRA – 3
Question 95.
Submission of Cost Audit Report to the Central Government in ……………….. .
(a) Form CRA- 1
(b) Form CRA -2
(c) Form CRA -3
(d) Form CRA -4
Answer:
(d) Form CRA -4
Question 96.
The provisions of Section 143(12) of the Companies Act, 2013 and the relevant rules on duty to report on fraud during the performance of audit functions under Section …………………… of the Act and these rules.
(a) 143(8)
(b) 143(15)
(c) 147
(d) 148
Answer:
(d) 148
Question 97.
Cost Audit Rules shall not be applicable to a company which is covered under Rule 3, and
(a) Which is operating from a special economic zone.
(b) Which es engaged,generation of electricity for captive consumption through Captive Generating plant.
(c) Whose revenue from exports, in foreign exchange, exceeds 75% of its total revenue
(d) Any of above
Answer:
(d) Any of above
![]()
Question 98.
If any of the provisions of Sections 139 to 146 is contravened the company shall be punishable with fine which shall
(a) not be less than ₹ 25,000 but may extend to ₹ 5,00,000
(b) not be less than ₹ 50,000
(c) not be less than ₹ 1,00,000
(d) not be less than ₹ 50,000 but not more than ₹ 5,00,000.
Answer:
(a) not be less than ₹ 25,000 but may extend to ₹ 5,00,000