Audit of Balance Sheet Items – CA Inter Audit Questions bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Audit of Balance Sheet Items – CA Inter Audit Question Bank
Question 1.
Discuss the following:
(a) Name the assertions for the following audit procedures:
(ii) Depreciation has been properly charged on all assets. (May 2018, 1 mark)
Answer:
Assertions for Depreciation has been properly charged on all assets Valuation assertion
Question 2.
Discuss the following:
(a) Name the assertions for the following audit procedure:
(i) Year-end inventory verification. (May 2018, 1 mark)
Answer:
Year and inventory verification
Existence Assertion
Question 3.
Discuss the following:
(a) Name the assertions for the following audit procedure:
(iii) The title deeds of the lands disclosed in the Balance Sheet are held In the name of the company. (May 2018,1 mark)
Answer:
The title deeds of the lands disclosed In the balance sheet are held in the name of the company.
Rights and Obligation Assertion
Question 4.
Discuss the following:
(a) Name the assertions for the following audit procedure:
(iv) All liabilities are properly recorded in the financial statements. (May 2018, 1 mark)
Answer:
All liabilities are properly recorded In the financial statements. Completeness Assertion.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the audit procedures to be performed as an auditor for valuation (assertion) of following:
(i) Loans and Advances and other current assets. (Nov 2018, 5 marks)
(ii) Finished goods and goods for resale. (Nov 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
(i) Audit Procedures to be performed while auditing of Loans and Advances and Other Current Assets.
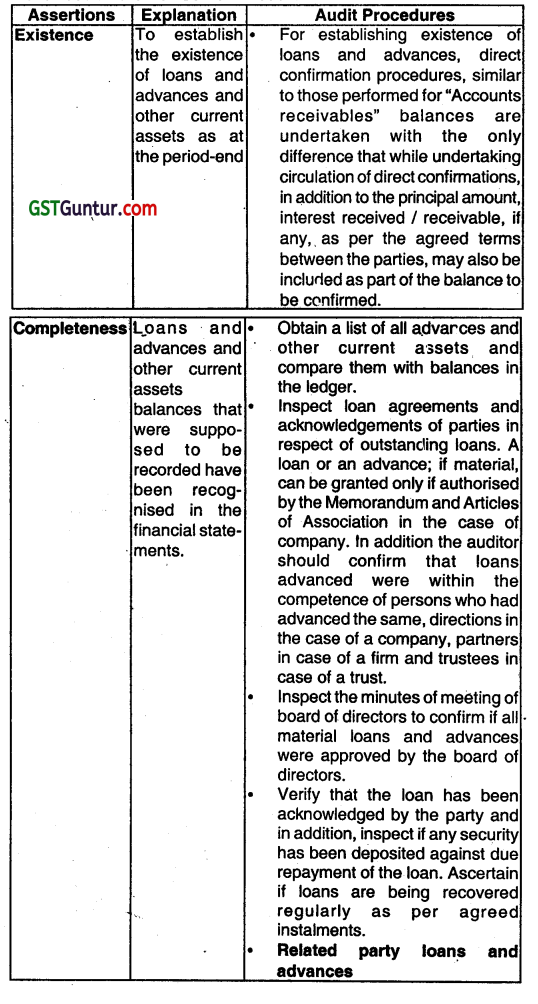
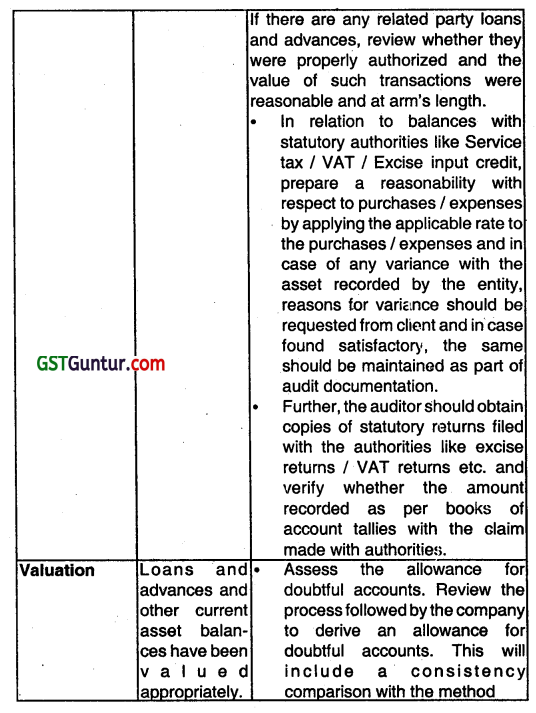

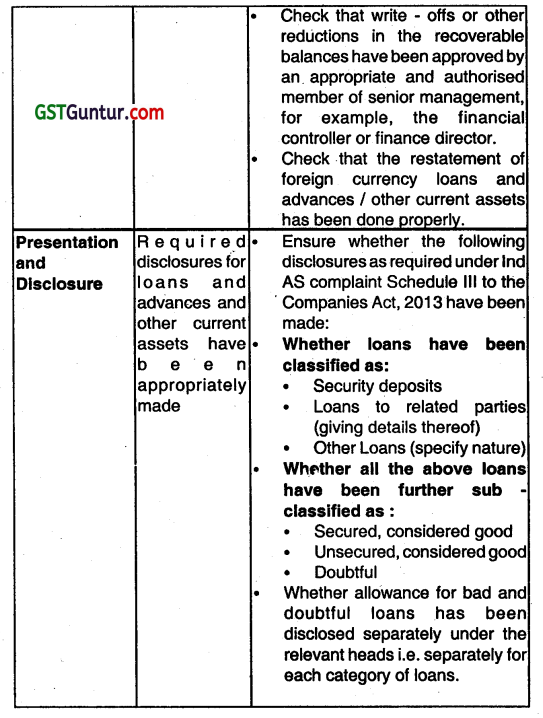
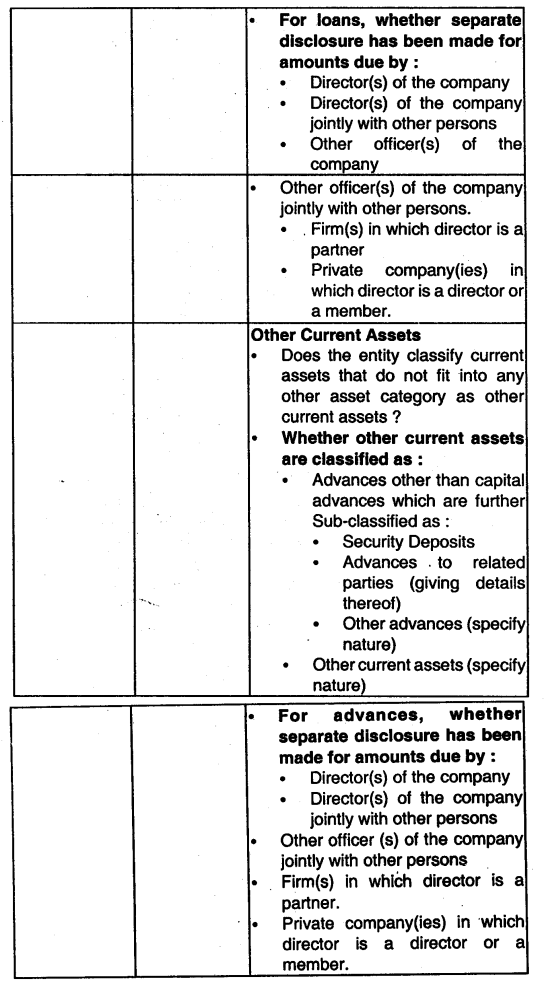
(ii) Finished goods and goods for resale:
Enquire into what costs are included, how these have been established and have been established and ensure that the overheads included have been determined based on normal costs and appear reasonable in relation to the information disclosed in the draft financial statements.
Ensure that inventories are valued at net realizable value if they are likely to fetch a value lower than their cost. For any such items, also verify If the relevant semi partly processed inventories (Work In Progress) and raw materials have also been written down.
Follow up for Items that are obsolete, damaged, slow-moving and ascertain the possible realizable value of such items. For the purpose, request the client to provide an Inventory aging split between less than 30 days, 30-60 days old, 60-90 days old. 90- 180 days old, 180- 365 days old, and more than 365 days old. Follow up any inventories which at time of observance of physical counting were noted as being damaged or obsolete.
Question 6.
Discuss the following
(a) Name the assertions for the following audit procedure:
(v) Related party transactions are shown properly. (May 2018, 1 Mark)
Answer:
Related petty transactions are shown properly.
Presentation and Disclosure Assertion
Question 7.
The securities premium account may only be applied by the company towards the issue of unissued shares of the company to the members of the company as fully paid bonus shares, Comment. (May 2019, 3 marks)
Answer:
The securities premium account may be applied by the company:
1. towards the issue of unissued shares of the company to the members of the company as fully paid bonus shares
2. in writing off the preliminary expenses of the company:
3. in writing off the expanses of, o the commission paid or discount allowed on, any issue of shares or debentures of the company:
4. if providing for the premium payable on the redemption of any redeemable preference shares or of any debentures of the company: or
5. for the purchase of Its own shares or other securities under Sec. 68. Thus, we cannot say that Securities Premium Account may only be applied by the company towards the issue of unissued shares of the company to the members of the company as fully paid bonus shares.
Question 8.
Validity and consequence of issue of shares at discount, check with respect to the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. (2019- Nov 4 marks)
Answer:
According to Section 53 of the Companies Act, 2013, a company shall not issue shares at a discount, except in the case of an issue of sweat equity shares given under Section 54 of the Companies Act, 2013. The auditor needs to verify that the sweat equity shares issued by the company at discount are of a class of shares already issued and following conditions have been complied with:
1. the issue Is authorised by a special resolution passed by the company
2. the resolution specifies the number of sharšs, the current market price, consideration, It any, and the class or classes of directors or employees to whom such equity shares are to be issued;
3. not less than one year has, at the date of such issue, elapsed since the date on which the company had commenced business; and
4. where the equity shares of the company are listed on a recognised stock exchange, the sweat equity shares are issued In accordance with the regulations made by the Securities and Exchange Board In this behalf and It they are not so listed, the sweat equity shares are Issued in accordance with such rules as may be prescribed.
Question 9.
Mr. X, a shareholder of the company pointed out that:
Premium received on issue ot shares prior to the date of balance sheet has been transferred to Profit and Loss account for arriving at the figure of commission payable to the managing director. (Nov 2009, 3 marks)
Answer:
Premium received on issue of shares is capital receipt and should not be credited to profit and loss account. According to the Companies Act, 2013 premium on issue of shares should not be considered In computation of net profit for the purpose of managerial remuneration. The auditor should have qualified the audit report and qualified the amount by which the profit stands inflated.
![]()
Question 10.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is True or False: The term fund’ and reserve’ can be used Inter change ably. (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
The word “fund in relation to any Reserves should be used only where such reserve is specifically represented by earmarked investments. The reserve is created out of the profits but It is not necessary the same amount is present in that reserve actually, but In case of fund the equal amount is appropriated to the fund.
Question 11.
As an Auditor how would you react to the following situations/ comments? In a company PPE have been revalued and there has been resulting surplus of ₹ 2,00,000, which is transferred to revaluation reserve. The Company has a Debit balance in Profit and Loss account ₹ 1,20,000 as accumulated brought forward losses. The company has adjusted this loss balance against Revaluation reserve. (Nov 2008, 8 marks)
Answer:
The above accounting treatment Is not correct because the debit balance of one lakh twenty thousand rupees In the statement profit and loss A/c is actual loss whereas two lakh rupees in Revaluation Reserve is unrealized gain and as per accounting policies, standards, statutes, conventions etc. actual losses cannot be set off against anticipated profits or gains in the reserves.
The revalued amounts of PPE are presented in financial statements either by restating both the gross book value and accumulated depredation so as to give a net book value equal to the net revalued amount or by restating the net book value by adding therein the net increase on account of revaluation.
An upward revaluation does not provide a basis for crediting to the profit and loss statement the accumulated depreciation existing at the date of revaluation. Further, an increase in net book value arising on revaluation of PPE is normally credited directly to owners interests under the heading of revaluation reserves and is regarded as not available for distribution.
A decrease in net book value arising on revaluation of PPE is charged to profit and loss statement except that, to the extent that such a decrease is considered to be related to a previous increase on revaluation that is included in revaluation reserve, it is sometimes charged against that earlier increase, It sometimes happens that an increase to be recorded is a reversal of a previous decrease arising on revaluation which has been charged to profit and loss statement in which case the increase Is credited to profit and loss statement to the extent that It offsets the previously recorded decrease.
On disposal of a previously revalued item of fixed asset (PPE), the difference between net disposal proceeds and the net book value is normally charged or credited to the profit and loss statement except that, to the extent such a loss is related to an Increase which was previously recorded as a credit to revaluation reserve and Which has not been subsequently reversed or utilized, it is charged directly to that account. The amount standing In revaluation reserve following the retirement or disposal of an asset which relates to that asset may be transferred to general reserve.
Question 12.
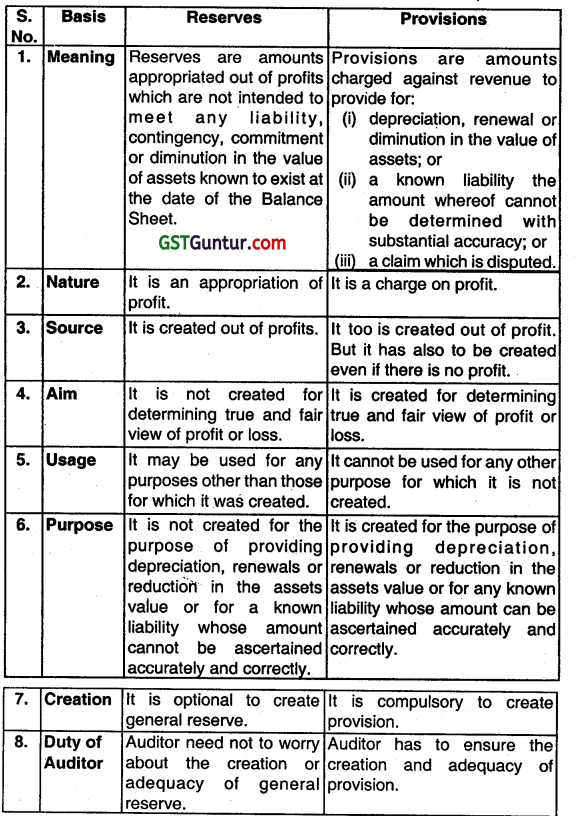
Distinguish between Reserves and Provisions. (May 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
Question 13.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
capital Reserve and Reserve Capital are the same. (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
Capital reserve means that part of profit reserved by the company for a particular purpose. Reserve capital means that part of the authorised capital that has not yet been called up by the company.
Question 14.
Explain the disclosure requirements of IND AS compliant Schedule III to Companies Act, 2013 toi’ each component of Other Equity. (Nov 2019,3 marks)
Answer.:
The following are the disclosure requirements of Ind As compliant Schedule Ill to the Companies Act, 2013 for each component of “Other Equity”.
Has the company sub-classified other equity into the following:
- Share application money pending allotment
- Equity component of compound financial instruments.
- Capital Reserve.
- Securities premium reserve.
- Other reserves (specify nature)
- Retained earnings
- Debt instruments through other comprehensive Income
- Equity instruments through other comprehensive income
- Effective portion of cash flow hedges.
- Revaluation surplus.
- Exchange difference of translation of financial statements of foreign operation.
- Other items of other comprehensive income (specify nature).
- Money received against share warrants
For each component of other equity, whether the company has disclosed the following(to the extent applicable):
(i) ‘Balance at the beginning of the reporting period.
(ii) Changes in accounting policy or prior period error.
(iii) Restated balance at the beginning of the reporting period.
(iv) Total Comprehensive Income for the year.
(v) Dividends
(vi) Transfer to retained earnings
(vii) Any other change (to be specified)
(viii) Balance at the end of the reporting period.
![]()
Question 15.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement Is True or False: ( 2008 – May, 2 marks)
Interest accrued but not due on “Secured loans” is required to be shown under appropriate sub-heads under the head “Secured loans.
Answer:
False:
Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013, prescribes the from of balance sheet and the requirements relating thereto. According to this, the interest accrued and due on Secured Loans should be Included under the appropriate sub-heads under the head “Secured Loans,” but the interest accrued but not due on secured loans is required lo be shown under Current Liabilities”.
Question 16.
How would you vouch/verify the following? Borrowing from Bank (May 2008, 5 marks)
Answer:
Borrowing from Banks can be verified as follows:
| Documents to be vouched | Aspects to be verified |
| 1. Reconciliation from Pass Book | Borrowings may be in the form of overdrafts or loans. Reconcile the balances of loan A/c with that of the Bank Pass Book. Also, confirm the balance stated at last by obtaining a certificate from Bank showing the accounts balances at the year-end. |
| 2. Securities Certificate and Records of Registrar | Obtain a securities certificate from the bank that shows the particulars of securities deposed with the bank as security for loan or charge created on an asset (s) of the business. Also ensure that these facts have been appropriately disclosed and duly registered with the Registrar of the companies and written down in the Register of charges. |
| 3. Purpose and Authority of Loan Incrementation | Determine the purpose for raising loan or overdraft and the mode of utilizing it and also that it has not caused any damage to the concern. Also, check the authority under which the loan or overdraft has been raised. In a company, only the Board of Directors can raise loan or borrow from banks. |
Question 17.
How would you vouch/verify the following:
Bank overdraft. (2009 – Nov 5 marks)
Answer:
Bank Overdraft:
| Documents to be vouched | Aspects to be verified |
| 1. Minute Book | The Auditor should ensure that the facility of overdraft is authorised by the Board of Directors. |
| 2. Agreement | (i) The Auditor should pursue the agreement Document with the bank and see whether the overdraft is clean or against hypothecation or pledge of company’s property. (ii) The Auditor should verify the rate of interest and other terms and conditions from the agreement. |
| 3. Certificate from Bank | The Auditor should if the overdraft is against hypothecation of assets like stocks, a certificate from the bank should be obtained. |
| 4. Financial Statement | (i) The Auditor should if the overdrafts is against hypothecation of assets or pledge of company’s property, see that overdraft is properly shown under ‘secured loans’ and nature of security has been properly disclosed. (ii) The Auditor should verily the amount of overdraft from the books of accounts and compare It with the passbook. |
| 5. Register of Charges | The Auditor should verify the register of charges and ensure that the charge has been registered with Registrar of Companies. |
Question 18.
Recovery of Bad debts written off. (Nov 2007, May 2014, May 2016, 5, 4, 4 marks)
Answer:
Bad Debts:
- Major amount of bad debts In the schedule be taken for scrutiny.
- The amount of bad debts should be traced to the schedule of bad debts written oft during the year.
- The bad debts should be property disclosed in P&L account according to its materiality.
- Check that the amount considered in write-off had been overdue for long and scrutinize the correspondence files.
- Check the authority for write oit and the level of authority is sufficient higher than the executive involved In collection.
- It provision had already been created for bad debts, see that to the extent of actual bad debts written ott, the provision is released.
Question 19.
Disclosure requirements of debtors in the financial statements. (Nov 2011, 5 marks)
Answer:
Disclosure: The audit or should satisfy himself that trade receivables, loans and advances have been disclosed prope,iy in the financial statements. Where the relevant statute lays down any disclosure requirements in this behalf, the auditor should examine whether the same have been complied with.
Note: 6(P) of Part I of Schedule Ill to be Companies Act, 2013 requires that company shall disclose lrade Receivables” in notes to accounts as follows:
(i) Aggregate amount of Trade Receivables outstanding for a period exceeding six months from the Date they are due for payment should be separately stated.
(ii) Trade receivables shall be sub-classified as:
- Secured, considered good;
- Unsecured considered good;
- Doubtful.
(iii) Allowance for bad and doubtful debts shall be disclosed under the relevant heads separately.
(iv) Debts due by directors or other officers of the company or any of them either severally or jointly with any other person or debts due by firms or private companies respectively in which any director is a partner or a director of a member should be separately stated.
Question 20.
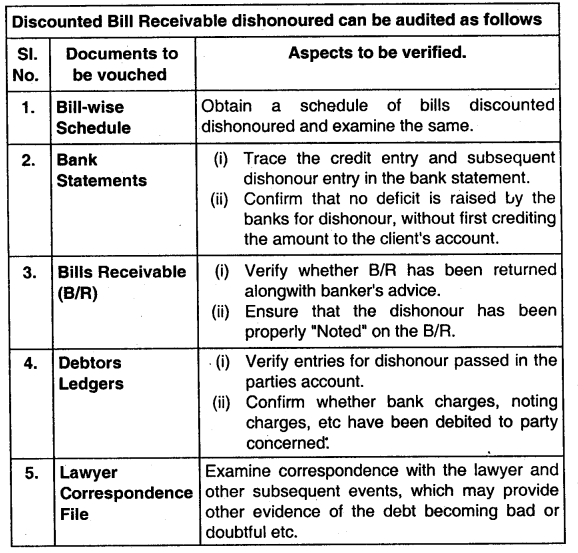
Write short note on Audit of discounted bills receivable dishonored. (Nov 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 21.
Discuss the following:
Disclosure requirement relating to Trade Receivables under Revised Schedule ill to the Companies Act. 2013. (Nov 2014, 5 marks)
Answer:
Disclosure requirement relating to Trade Receivables under Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013. The aggregate amount of Trade Receivables outstanding for a period exceeding 6 months from the date they are due for payment should be separately stated. Security-wise classification: Trade Receivables shall be separate and sub-classified as:
(a) Secured, considered good
(b) Unsecured, considered good
(c) Doubtful.
Bad Doubtful: Allowance for bad and doubtful loans and advances shall be disclosed under the relevant heads separately.
Directors etc: Debts due by directors or other officers of the company or any of them either severally or jointly with any other person or debts due by firms or Private Companies respectively in which any director is a partner or a director or a member should be separately stated.
![]()
Question 22.
While conducting the audit of Amrit Ltd. the auditor A of ABC and Associates, Chartered Accountants observes that there are a large number of trade receivables standing n the books of account as on 31st March. The auditor wanted to send confirmation request to a few large trade receivables but the management refused the auditor to send confirmation request. How would the auditor proceed? (Nov 2020, 4 marks)
Question 23.
M, Statutory Auditors of ABC Ltd. wants to verify cash on hand as on 31st March 2009. The Management informs Mr. M. that It is not possible to cooperate, as cashier has been hospitalized. Advise Mr. M., how to deal with the situation. (May 2009, 4 marks)
Answer:
The scope of audit may be limited for various reasons
(i) the entity may impose restrictions on scope of audit,
(ii) the limitation may be imposed by circumstances.
(a) When the audit is carried out under and as per statute, the auditor should not accept the assignment when his duties are curtailed by agreement unless required by any Law.
(b) When audit is carried out in accordance with the entity’s terms voluntarily, the auditor may indicate his scope In his audit report.
In some cases, the circumstances may impose restrictions on audit scope. e.g. when the auditor is appointed after the year end, how may not be able to participate in stock verification. Or sometimes, the records required may not be available so that the auditor may not be able to check details in the manner he likes. Such limitations in scope may warrant an auditor to express a disclaimer of opinion or qualified opinion in his audit report depending upon the circumstances. The non-cooperation of ABC Limited will amount to limitation on scope of auditors.
Question 24.
Comment on the following:
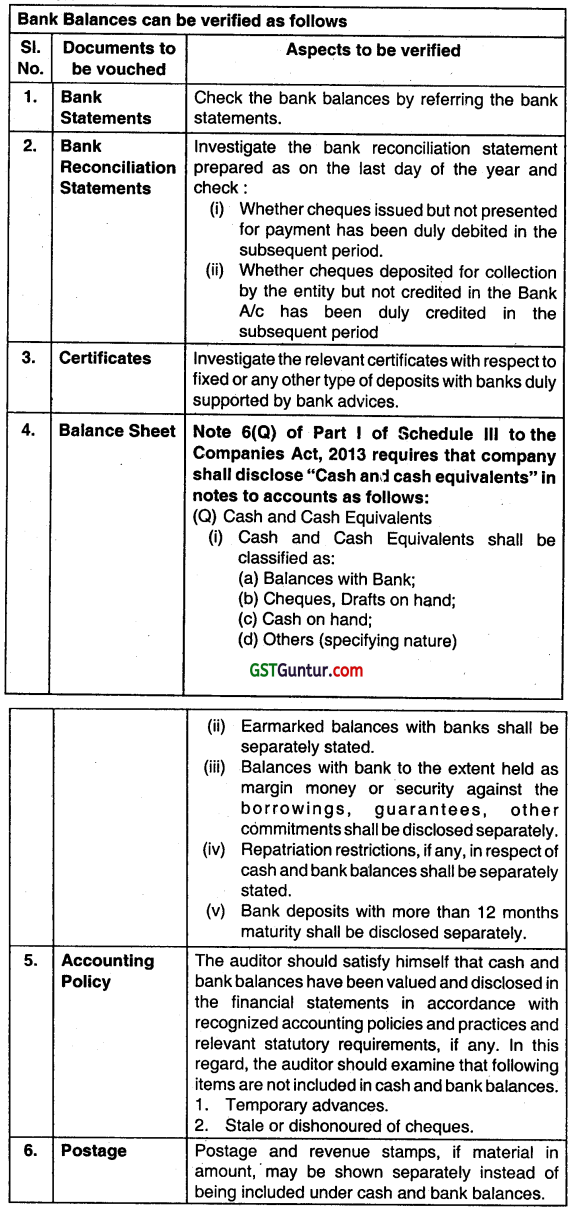
What procedure an auditor should adopt to test the authenticity of cash at bank. (Nov 2011, 5 marks)
Answer:
Question 25.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
Teeming and lading is one of the techniques of inflating cash payments. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer
Incorrect:
Teeming and lading is one of the techniques of suppressing cash receipts and not of inflating cash payments.
Question 26.
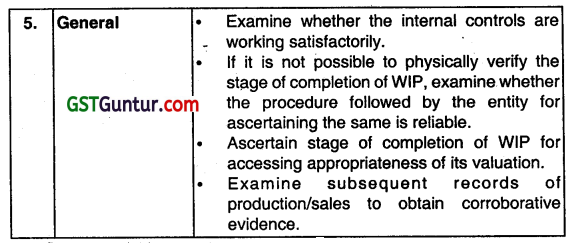
How would you vouch/verify the following? Work in progress. (2008- May, 2013 – May, 2015 May, 5, 4, 4 marks)
Answer:
Work-In-progress will be verified as follows:
| Documents to be vouched | Aspects to be verified |
| 1. Cost Sheets | The cost sheets of work-in-progress should be duly attested by the works engineer and works manager. |
| 2. Cost Records | The correctness of cost disclosed by the cost records should be property examined by verifying the cost and quantity of materials, wages and other charges included In the cost sheets with reference to the records maintained in respect of that. |
| 3. Cost Comparison | Mark comparison between the unit or job cost shown by the cost sheet and the ‘standard or estimated cost expected. |
| 4. Allocation of Expenses | The allocation of overhead expenses should be done on a rational basis. |
Question 27.
How would you vouch/verify the following? Goods lying with third party. (May 2009, 5 marks)
Answer:
If the goods are lying with Third Party, Auditor should:
- Check the materiality of the item under this caption included in stocks.
- Obtain confirmation of the amount of goods lying with them. The confirmation may be directly obtained by auditor or be produced by client depending upon the situation.
- Inquire into the necessity of subcontractor retaining the stock. Ho should ensure the process that they perform are related to the business requirement and there is no ground for suspicion on this score.
- The records, voucher/slips for the regulating the movement of stock Into and out of entity for sub-contracting work be reviewed by vouching for few transactions for ensuring existence and working of internal control system for them.
- The goods lying with them for very long period would merit auditors’ special attention for making provision.
- The excise gate pass, entry in such records, information in returns, be also cross-verified.
- The valuation of stocks should be correctly made for including material cost on appropriate stock valuation formulae and also for Inclusion of proportionate processing charges for the work in process with the contractors.
- The provision should be created for work done. billed for processing and also for incidence of any applicable levy like service tax payable.
Question 28.
Write short note on Physical attendance by auditor during inventory taking (May 2009, 5 marks)
Answer:
Physical Attendance at stocktaking by Auditor during Inventory Taking
1. The physical verification of stock is the responsibility of the management. The auditor may find It appropriate to attend the stock taking, if the inventory value is material in his opinion.
2. The extent of participation in inventory taking depends upon the internal control system prevailing, results of examination of inventory records and analytical review procedures.
3. When auditor attends inventory taking, he ensures that the instructions given for inventory taking are followed.
4. Auditor should test check few items by himself for their existence and quantum. He selects to test high-value items importantly.
5. The physical conditions of stock – like its age, deterioration, obsolescence etc., are looked into by auditor.
6. The auditor reviews stores records and notes down major discrepancies for reconciling them in a subsequent date.
7. The cutoff arrangement is also looked in to ensure that the entity accounts for stock for which liability had been booked and excludes stock Which has been sold.
![]()
Question 29.
Answer the question:
State the analytical review procedures normally carried out in the audit of inventories. (May 2017, 6 marks)
Answer:
Physical Attendance at stock-taking by Auditor during Inventory Taking
1. The physical verification of stock is the responsibility of the management. The auditor may find It appropriate to attend the stock taking if the inventory value is material in his opinion.
2. The extent of participation in inventory taking depends upon the internal control system prevailing, results of examination of inventory records and analytical review procedures.
3. When auditor attends inventory taking, he ensures that the instructions given for inventory taking are followed.
4. Auditor should test check few items by himself for their existence and quantum. He selects to test high-value items importantly.
5. The physical conditions of stock – like its age, deterioration, obsolescence etc., are looked into by auditor.
6. The auditor reviews stores records and notes down major discrepancies for reconciling them in a subsequent date.
7. The cut oft arrangement Is also looked in to ensure that the entity accounts for stock for which liability had been booked and excludes stock which has been sold.
Question 30.
Answer the question;
State the analytical review procedures normally carried out in the audit of inventories. ( May 2017, 6 marks)
Answer:
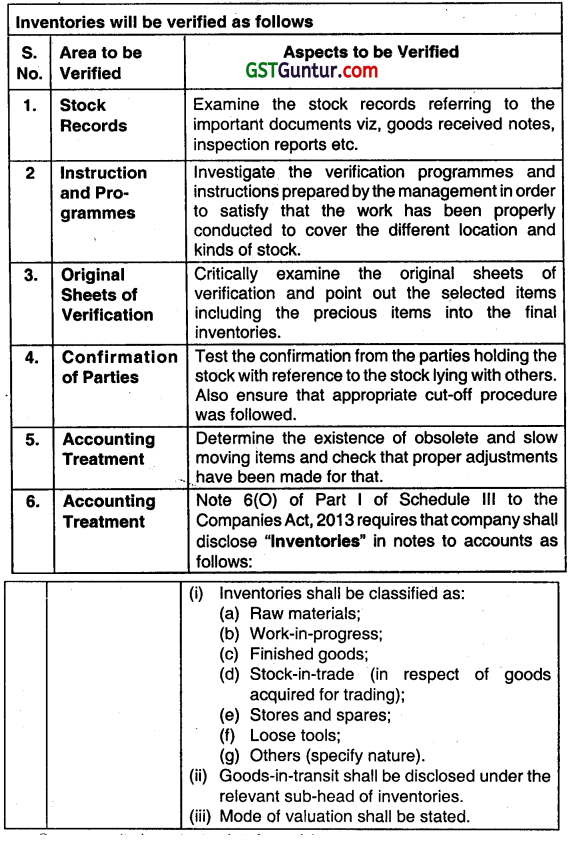
Question 31.
Briefly mention the matters that are relevant in planning attendance at physical inventory counting. (Nov 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Metters relevant In planning attendance at physical Inventory counting include, for example:
- Nature of inventory.
- Stages of completion of work in progress.
- The risks of material misstatement related to inventory.
- The nature of the internal control related to inventory.
- Whether adequate procedures are expected to be established and proper instructions issued for physical inventory counting.
- The timing of physical inventory counting.
- Whether the entity maintains a perpetual inventory system.
- The locations at which inventory is held, including the materiality of the inventory and the risks of material misstatement at different locations, In deciding at which locations attendance Is appropriate.
- Whether the assistance of an auditors expert is needed.
Question 32.
ABC Limited has a closing balance of work in progress of inventories aggregating ₹ 850 lakhs in their balance sheet as at March 31st, 2020. As Statutory Auditor of ABC Limited, explain various audit procedures which needs to be performed to confirm Work-in-progress of inventories have been valued appropriately and as per generally accepted accounting policies and practices. (Jan 2021, 3 marks)
Question 33.
How would you vouch/verify the following? Trade Marks and Copyrights. (Nov 2008, 5 marks)
Answer:
Trademarks and Copyright may be verified as follows:
| Document to be Vouched | Aspects to be verified |
| 1. Schedule of Trademark and Copyright | Get the schedules of trademarks and copyright duly signed and scrutinized by the responsible authority and also confirm that these are shown in the B/S. |
| 2. Written Agreement and assigning deed | Examine the written agreement for the copyright and for transfer Assignment of trademark and also ensure that trademark and copyright are duly registered. |
| 3. Contract | Verify the existence of copyright referring to the contract between the author and the entity and note down the payment terms of royalty. |
| 4. Value and Cost | Check that the value has been properly determined and cost incurred for obtaining the trademarks and copyright is capitalised. |
| 5. Legal life and Payment | Make certain that the legal life of the trademark and copyright has not expired and also ensure that the payment for them is property amortised with regards to appropriate legal and commercial considerations. |
Question 34.
Write a short note on impairment of Assets”. (2008- Nov, 2013 – May 5, 4 marks)
Answer:
Impairment of asset : An asset s impaired if its carrying amount exceeds the amount to be recovered through use or sale of the asset and in the given situation the standard requires the enterprise to recognize an impairment loss i.e. the amount by which the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its recoverable amount.
Impairment loss = Carrying amount- Recoverable Amount.
Impairment loss is a normal expense and thus will have impact on distributable profit and other provisions of the Companies Act 2013 and applicable enactment (Acceptance of Deposit Rules).
AS-28 requires recoverable amount to be measured as the higher of net obtainable selling price and value in use (present value of estimated future cash flows expected to arise from continuing use and on disposal).
After the recognition of Impairment loss the depreciation/amortization charge for the asset should be adjusted in future periods, to allocate the assets revised carrying amount less residual value on a systematic basis over its remaining useful life.
Impairment of assets does not apply to inventories, construction contract assets, deferred tax assets, investments covered by AS-13 and financial Instruments because other AS provides for recognizing and measuring these assets.
Assessment for impairment of assets needs to be made at The B/S date as to any Indication in this context based on external or Internal sources of information.
![]()
Question 35.
Mr. X. a shareholder of the company pointed out that:
The goodwill in the Balance Sheet of the company has appeared on same figure during the past three years. (Nov 2009, 3 marks)
Answer:
Facts: According to provisions of AS 26 “Intangible Assets, an intangible asset should be carried in the books at cost less accumulated amortization and accumulated impairment losses. The depreciable amount of an intangible asset should be allocated on a systematic basis over the best estimate of its useful life. There is a reputable presumption that the useful life of an Intangible asset will not exceed ten years from the date when the asset is available for use according to Para 63 of AS 26.
Analysis and Conclusion;
In the given question, the company has not amortized any value ol goodwill since past three years. The auditor should have indicated this fact in his report that no amount of goodwill has been written off during the past three years.
Question 36.
How would you vouch/verify the following? Leasehold property. (Nov 2009,5 marks)
OR
Write short note on the following:
Verification of assets acquired on lease. (Nov 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:
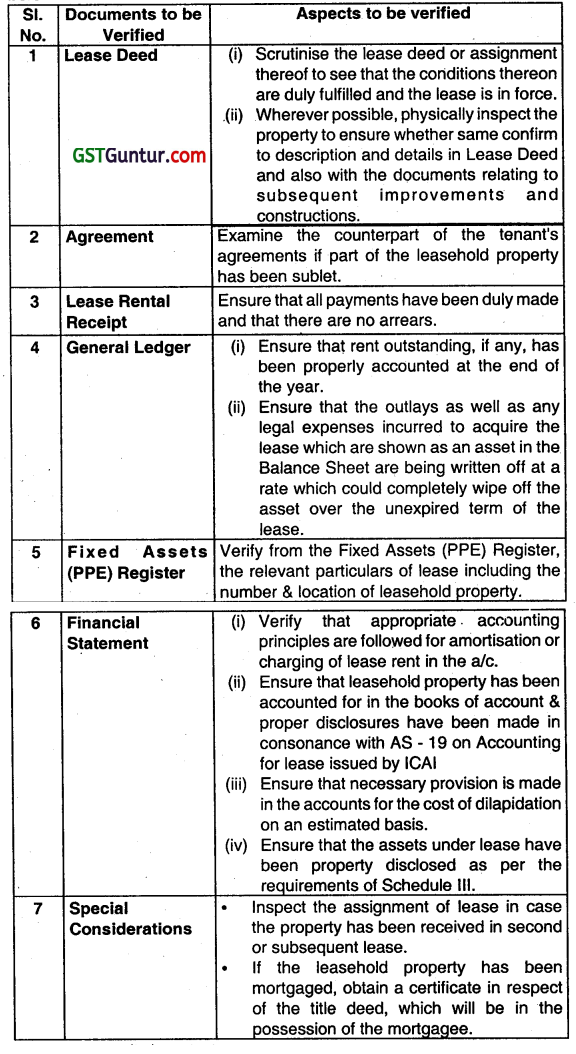
Question 37.
Write short note on the following:
Physical verification of fixed assets (PPE) at reasonable intervals”.(Nov 2010, 4 marks)
Answer:
Reasonable Intervals for verification of fixed assets (PPE):
- Reasonable Intervals” depends upon the circumstances of each case.
- The factors to be considered regarding this are number of assets, nature of assets, relative value of assets, difficulty in verifications, situation and spread of the assets etc.
- The management may decide about the periodicity of physical verification of fixed assets (PPE) considering the above factors while an annually verification may be reasonable.
- It may be impracticable to carry out the same in some cases. Even in such cases the verification program should be such that all assets are verified at east once In every three years where verification of all assets is not macle during the year.
- It will be necessary for the auditor to report the fact, but it he is satisfied regarding the frequency of verification, he should also make a suitable comment on this regard.
- The auditor is required to comment, it any material discrepancies were noticed on verification and, if so, whether the same have been properly dealt with in the books of account.
It would be appropriate foc the auditor to obtain a management representation letter confirming that the fixed assets (PPE) are physically verified by the company in accordance with the policy of the company. - The management representation letter should also mention the periodicity el the physical verification of fixed assets (PPE).
- The letter should also include the details of the material discrepancies noticed during the physical verification of the fixed assets (PPE).
- If no discrepancies were noticed during the physical verification, the management representation letter should also mention this fact clearly.
Question 38.
A partnership firm revalued its PPE like land and building. The firm adequately disclosed the revalued amounts in the Balance Sheet. Do you, as an auditor, approve the disclosure given by the partnership firm? (Nov 2010, 4 marks)
Answer:
Disclosure of revalued PPE of a partnership firm:
Facts: According to AS 10 “Property, Plant and Equipment”, revalued amounts substituted for historical costs of PPE, method adopted to compute the revalued amounts, nature of indices used, year of any appraisal made, and whether an external valuer was involved, in case where PPE are Stated at revalued amounts, the fact should be disclosed in the financial statements.
Analysis: In the given case, the partnership firm revalued its PPE like building and land and adequately disclosed the revalued amounts in the Balance sheet. The firm did not disclose the method adopted by it for arriving at the revalued figures.
Inference: The firm had disclosed the revalued amounts in the balance sheet but the method and nature of Indices used etc. are not disclosed. So, this act of the firm is In contravention with the AS 10 for “Property, Plant and Equipment”. Therefore, the auditor cannot approve the disclosure given by the partnership firm and shall have to quality the report.
Question 39.
Comment on the following:
Computer software which is the integral part of the related hardware can be treated as intangible assets or fixed assets (PPE). (May 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Intangible assets are those assets which do not have physical Identity but are used by the enterprise for production or supply purposes. As such computer software which Is an Integral part of related hardware has to be treated as a fixed asset (PPE).
Question 40.
How Will You vouch/verify the followings? Patterns dies, loose tools etc. (May 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Patterns, dies, loose tools etc.
Several entities have large investments in such assets which have a relatively short useful life and low unit cost, their treatment in the books of account differs from entities to entities. So, the auditor has to see what accounting treatment has been followed by the auditor enterprise. The auditor should consider the following points:
1. Production Accounts:
- Ensure that small tools and other similar items are charged oft to the production A/c.
- A proper record of issues and receipts of tools has also been maintained.
- Obtain list of those items which are not usable / in damaged or depleted condition.
- Ensure that sum total of opening balance plus purchase minus value of closing stock of these assets is charged oft to Production Account.
2. Cost: The auditor should find out
- The method of valuation adopted by the management
- The cost of purchase on the basis of date of acquisition and the market price either from the latest purchase or from market quotations, Examine copy of invoice for purchased items and costing records for internally manufactured items.
3. Valuation method: Verify whether the method of valuation is adopted consistently.
The following are the methods for different items:
| Items | Method of valuation |
| Purchased Items | Cost of purchase reduced by the amount of depreciation. |
| Manufactured Items | On the basis of Standard Cost with necessary adjustment for material variances reduced by the amount of depreciation decided by the management considering the life of the tools. |
| Obsolete Items | Valued on Net Realizable scrap value. |
| Defective/Damaged Items | Relevant adjustments in valuation shall be made after evaluating the conditions. |
Any change in the methods of valuation shall be disclosed along with its effect on the financial results of the company.
![]()
Question 41.
How will you vouch and verity the following? Assets acquired on hire purchase. (Nov 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Asset acquired on Hire Purchase
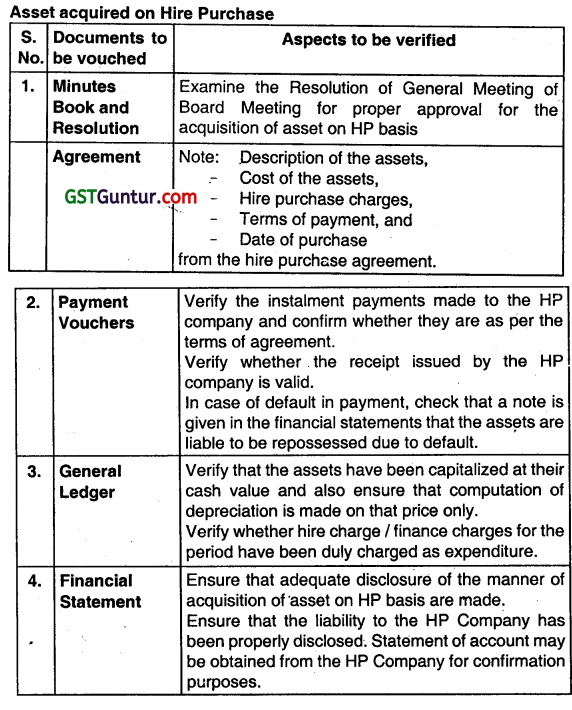
Question 42.
How will you vouch/verify the following? Building (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
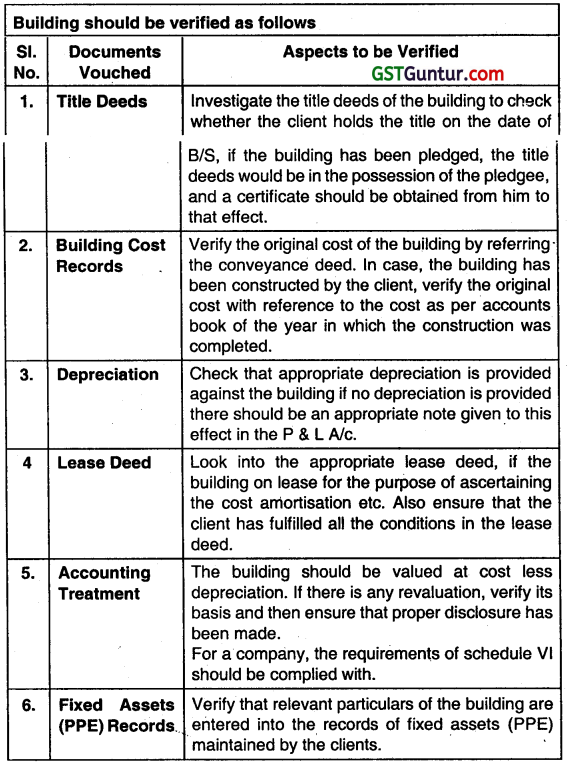
Question 43.
How will you vouch/verify the following: Intangible Assets. (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Intangible Assets:
An intangible asset is that asset which does not have a physical identity but which is used by the enterprise to production or supply of goods for retails to 0th or or for administrative purpose. Examine the list of intangible assets owned by client as on balance sheet date.
Verify the existence and ownership by examining certificates and letters. Examine due dates for renewal fees for assets. The auditor should take schedule of intangible assets and agreements made with other parties.
The auditor should ensure that valuation has been made on a fair and reasonable basis. The auditor should check amortization made in P&L a/c and balance of assets as on the balance sheet date. The auditor ensures that the treatment of intangible assets have been made as per the AS-26 – Intangible Assets. Note 6(I) of Part I of Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013 requires that company shall disclose “Tangible Assets” In notes to accounts as follows:
(i) Tangible Assets
(i) Classification shall be given as:
- Land
- Buildings
- Plant and Equipment
- Furniture and Fixtures
- Vehicles
- Office Equipment
- Others (specifying nature).
(ii) Assets under lease shall be separately specified under each class of asset.
(iii) A reconciliation of the gross and net carrying amounts of each class of assets at the beginning and end of the reporting period showing additions, disposals, acquisitions through business combinations, and other adjustments and the related depreciation and impairment losses/reversals shall be disclosed separately.
(iv) Where sums have been written-off on a reduction of capital or revaluation of assets or where sums have been added on revaluation of assets, every balance sheet subsequent to date of such write – off, or addition shall show the reduced or increased figures as applicable and shall by way of a note also show the amount of the reduction or Increase as applicable together with the date thereof for the first five years subsequent to the date of such reduction or increase.
Question 44.
Write short notes on Payment for Acquisition of Assets. (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Payment for AcquisitIon of Assets:
The asset if acquired for the business, then payment made shall be In the capital nature expenditure and it should be included in the cost of fixed assets (PPE) of the company. Such payment shall be either on the agreed term or quotation term or the market term. Such, payment shall be made in cash or through Bank. In this case, auditor should ensure that such payments are actually made and should also check the entry in seller books. He should also check the amount and validity of the payment.
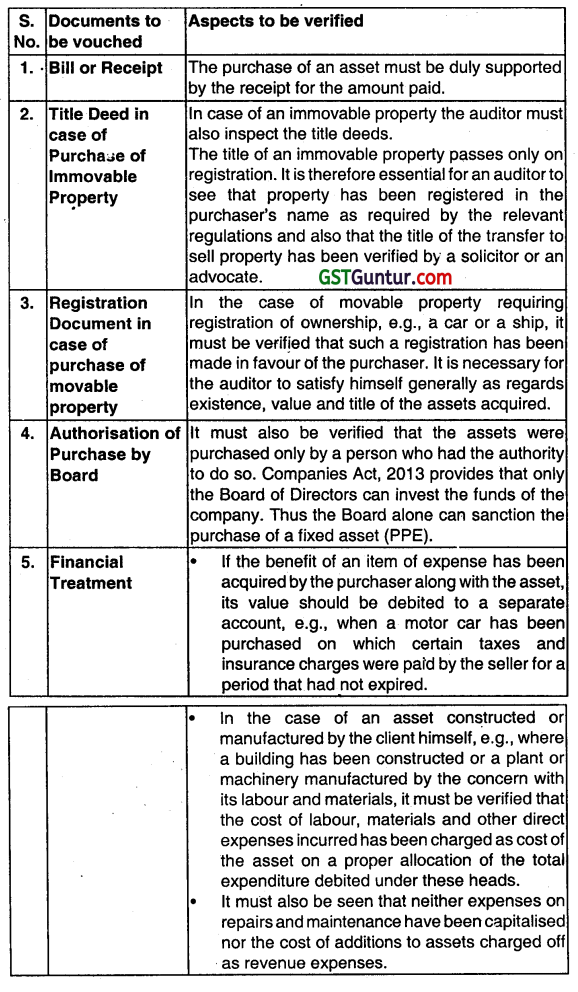
Question 45.
State with reasons (in short) whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
All intangible assets are not required to be amortized. (Nov 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
As per AS-26, the depreciable amount of an Intangible asset should be allocated on a systematic basis over the best estimate of its useful life. The useful life of an intangible asset may be very long but it is always finite.
Question 46.
Mention the purposes for Which capital expenditure is incurred. (Nov 2016, 6 marks)
Answer:
Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditures are those expenditures which are non-recurring in nature and whose benefit is accrued over a long period of time i.e. more than one accounting period.
Purposes for which Capital Expenditure is Incurred:
- Acquiring of fixed asset (PPE).
- Acquiring of intangible asset.
- Repairing an existing asset so as to improve its useful lite.
- Upgrading an existing asset if it results in a superior fixture.
- Preparing an asset to be used in business.
- Restoring property or adapting ¡t to a new use.
- Starting or acquiring a new business.
Question 47.
You are an auditor of PQR Ltd. which has spent ₹ 10 lakhs on Research activities of the product during period under audit. Board of Directors want to recognize it as an internally generated intangible assets. Advise and discuss the conditions necessary to be fulfilled to recognize the intangible assets In the financial statements. (May 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
Provision
As per AS 26, Intangible Assets’ the recognition of on Item as an intangible asset requires an enterprise to demonstrate that the item meets the definition of an intangible asset and recognition criteria set out as below:
(a) It is probable that the future economic benefit that are attributable to the asset will flow to the enterprise. An enterprise uses judgment to assess the degree of certainly attached to the flow of future economic benefits that are attributable to the use of the asset on the basis of the evidence available at the time of initial recognition, giving greater weight to external evidence and
(b) The Cost of the asset can be measured reliably.
When assessing the probability of expected future economic benefits, reasonable and supportable assumptions should be used. representing management’s best estimate of the set of economic conditions that will be exist over the useful life of asset.
Further, AS 26 provides that no intangible asset arising from research or from the research phase should be recognised. Expenditure on research or on the research phase Should be recognised as an expense when it is incurred.
Present Case:
So, POR Ltd. can not recognised ₹ 10 lakhs as Incurred in the research phase/activities as intangible asset.
![]()
Question 48.
How would you vouch/verify the following? Trade Creditors. (Nov 2007, 5 marks)
Answer:
Trade Creditors:
- Check the adequacy of cut-off procedure to ensure that transactions of next period are not accounted and all transactions of year-end are accounted.
- Check positing in the bought ledger from books of prime entry.
- Compare the balances with the schedule of creditors with balances in bought ledger.
- Compare the balances with the confirmation or statement of account received from trade creditors.
- Pay special attention to long outstanding items and enquire about the reason there of.
- Verify subsequent payments and reversal entries In the bought ledger of year-end entries.
- See that trade creditors are classified and shown in the balance sheet as per requirement of Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013.
Question 49.
How would you vouctvvenfy the followng? Advances to suppliers. (Nov 2007, 5 marks)
Answer:
Advance given to Suppliers
| Document to be vouched | Aspects to be verified |
| 1. Schedules and Ledgers | Get the debit balance schedule in the account of creditors and give particular attention to the age of the balances. Also examine in detail Bought Ledger. |
| 2. Accounting Treatment | Investigate the unadjusted outstanding and check if any of them require provisioning. Also examine that according to Sec. 143(1) of the Companies Act, 2013, the advances have not been shown as deposits in the B/S. |
| 3. Final Documents | Obtain the confirmation of balances and ensure that any discrepancies or differences have been properly reconciled. |
Question 50.
Explain whether the following statements are correct or incorrect, with reasons/explanations! examples:
If the purpose of an audit procedure s to test for understatement in the existence or valuation of accounts payable then testing the recorded accounts payable may be relevant audit procedure. (Jan 2021, 2 marks)
Question 51.
State with reason (In short) whether the following statement is True or False:
Contingent liabilities are provided for in the accounts it they crystallize between the end of the accounting year and the date of signing the audit report. (May 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
False:
Contingent liabilities existing on the balance sheet date are disclosed by way of note and not provided for even if it had crystallized subsequently.
Question 52.
You are the auditor and examining the book debts of a company. Give some indications which leads to doubt about recovery as uncollectible debts from debtors and advances. (May 2012, 8 marks)
Answer:
Indications of doubtful and uncollectable debts, loans and advances:
- The terms of credit have been repeatedly ignored.
- There is stagnation or lack of healthy turnover in the account.
- Payments are being received but the balance is continuously increasing.
- Payments though being received regularly, are quite small in relation to the total outstanding balance.
- An old bill has been partly paid (or not paid), while later bills have been fully settled.
- The cheques received from the debtors have been repeatedly dishonoured.
- 7. The debt is under litigation, arbitration, or dispute.
- 8. The auditor becomes aware of unwillingness or inability of the debtor to pay the dues, e.g., a debtor has either become insolvent, or has dosed down his business, or is not traceable.
- Amounts due from employees, which have not been repaid on termination 0f employment.
- Collection is barred by statute of limitation.
Question 53.
How you will vouch/verify the following? Provision for income tax. (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Provision for Income Tax:
- General consideration as provision has been provided in the P&L A/c.
- Check whether such provision ¡s created every year for tax liability because it is current provision.
- Check whether it has been properly stated in P&L A/c and In Balance Sheet in liability side.
- Check whether tax paid has been properly deducted from provision for taxation.
- Provision has been created and written off every year.
Question 54.
Discuss the recognition principles of contingent liability. (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
As per AS – 29 (Revised) on Provisions, Contingent Liabilities, and Contingent Assets, an enterprise should not recognise a contingent liability. A contingent liability is disclosed, as required by paragraph 68 unless the possibility of an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits is remote.
As per Para 68, Unless the possibility of any outflow in settlement is remote, an enterprise should disclose for each class of contingent liability a’ the balance sheet date a brief description of the nature of the contingent liability and, where practicable:
(a) an estimate of Its financial effect, measured under paragraphs 35-45;
(b) an indication of the uncertainties relating to any outflow; and
(c) the possibility of any reimbursement.
Further, Where an enterprise Is jointly and severally liable for an obligation, the part of the obligation that is expected to be met by other parties is treated as a contingent liability. The enterprise recognises a provision for the part of the obligation for which an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits is probable, except in the extremely rare circumstances where no reliable estimate can be made.
Contingent liabilities may develop In a way not initially expected. Therefore, they are assessed continually to determine whether an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits has become probable. If it becomes probable that an outflow of future economic benefits will be required for an item previously dealt with as a contingent liability, a provision is recognized in accordance with paragraph 14 In the financial statements of the period in which the change in probability occurs (except in the extremely rare circumstances where no reliable estimate can be made).
![]()
Question 55.
How would you vouch/Verify the following? Receipt of Capital subsidy. (May 2010,Nov 2016, 5,4 marks)
Answer:
The receipt of Capital subsidy can be verified as follows:
| Document to be vouched | Aspects to be verified |
| 1. Application for subsidy | Examine the application made by the entity towards claim of subsidy to ascertain the purpose and the scheme under which the subsidy has been made available. |
| 2. Subsidy file correspondence | (i) Examine the correspondence and other documents for the grant of subsidy and note the conditions relating to its use. (ii) Verify whether the conditions under which subsidy is granted have been fulfilled. e.g. (a) Purchase of a specific asset. (b) Setting up a factory at a specific location. |
| 3. General Ledger | (i) Vouch the relevant entries for the receipt of capital subsidy, tracing the same into the cash book & the general book. (ii) Examine whether subsidy receivable, if any, has been properly accounted for. |
| 4. Financial Statements | Ensure compliance with requirements of AS-12 on Accounting for Government grants,. i.e. whether it relates to specific amounts or in the form of promoters contribution and also compliance with the disclosure requirements. |
Question 56.
How you will vouch/verify the following? investment in the shares and debentures of subsidiary. (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
- Investments in the shares and debentures of subsidiary:
- See that the unquoted shares held are investments by the company are properly accounted for in the investment register.
- Ensure that the shares are valued at cost.
- Ascertain from previous annual reports the trend of such investments.
- If the shares held is more than 50%, It has been properly disclosed in Balance Sheet.
Question 57.
Mention the disclosure requirement of current investments as per Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013. (May 2016, 6 marks)
Answer:
Note 6 (N) of Part Q) of Revised Schedule (III) requires that company shall disclose Current Investments in notes to accounts as follows:
Current investments shall be classified as:
- Investments in Equity Instruments;
- Investments in Preference Shares
- Investments in government or trust securities;
- Investments in debentures or bonds;
- Investments in Mutual Funds;
- Investments in partnership firms
- Other investments (specify nature).
(i) Under each classification, details shall be given of names of the bodies corporate (indicating separately whether such bodies are
- subsidiaries,
- associates,
- joint ventures, or
- controlled special purpose entities) in whom Investments have been made and the nature and extent of the investment so made in each such body corporate (showing separately investments which are partly paid).
In regard to investments in the capital of partnership firms, the names of the firms (with the name of all their partners, total capital, and the shares of each partner) shall be given.
(ii) The following shall also be disclosed:
- The basis of valuation of individual Investments
- Aggregate amount of quoted investments and market value thereof;
- Aggregate amount of unquoted Investments;
- Aggregate provision made for diminution in value of investments.
Multiple Choice Question
Question 1.
All transactions that were supposed to be recorded have been recognized in the financial statements and further, transactions have been recognized in the correct accounting period, it is known as:
(a) Occurrence
(b) Completeness
(c) Measurement
(d) Existence
Answer:
(b) Completeness
Question 2.
” Transactions have been recorded accurately at their appropriate amounts and further, transactions have been classified and presented fairly in the financial statements is acknowledged as:
(a) Occurrence
(b) Completeness
(c) Measurement
(d) Existence
Answer:
(c) Measurement
Question 3.
The term Existence means
(a) Assets. Liabilities and equity, balances exist as at the period end
(b) Assets, Liabilities, and equity balances have been valued appropriately
(c) All Assets and Liabilities and equity balances that are supposed to be recorded have been recognized In the financial statement.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Assets. Liabilities and equity, balances exist as at the period end
![]()
Question 4.
Under ………………. entity has the right to ownership or use of the recognised assets, and the liabilities recognised in the financial statements represent the obligations of the entity.
(a) Existence
(b) Completeness
(c) Valuation
(d) Rights and Obligations.
Answer:
(d) Rights and Obligations.
Question 5.
All related parties; related party transactions and balances that should have been disclosed in the note forming part of financial statements, is represents its ………………… .
(a) Occurrence and Existence
(b) Completeness
(c) Measure
Answer:
(b) Completeness
Question 6.
As per Section 2(8) of the Companies Act, 2013. ‘Capital as is authorised by the memorandum of a company to be the maximum amount of share capital of the company. is called …………………. .
(a) Authorised Capital
(b) Nominal Capital
(c) Issued Capital
(d) Authorised Capital or Nominal Capital
Answer:
(d) Authorised Capital or Nominal Capital
Question 7.
Part of the authorised Capital which is offered by the company for subscription and includes the share allotted for consideration other than cash called.
(a) Nominal Capital u/s 2(8) of the Companies Act. 2013
(b) Authorised capital u/s 2(10) of the Companies Act, 2013
(c) Issued capital u/s 2(50) of the Companies Act, 2013
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Issued capital u/s 2(50) of the Companies Act, 2013
Question 8.
When there was increase in authorised share capital, auditor should verify whether the:
(a) The company has accurately calculated the fee.
(b) Stamp duty and Fees are duly paid to MCA and copy of such receipt are to be obtained.
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 9.
In case there is any change, auditor should:
(a) Obtains the certified copies of relevant resolutions passed at the meetings of Board of Directors.
(b) Obtain whether the shareholders are authorising the Increase of decrease in Authorised Capital.
(c) Obtain and verify copies of forms filed with MCA and filed it with RBI.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 10.
Verifying reduction of capital, the auditor should undertake the procedure except:
(a) Verify that the meeting of the shareholder held to pass the special resolution was properly convened and the proposal was circulated in advance among all the shareholders.
(b) Verify that the Memorandum of Association authorises reduction of capital.
(c) Examine the order of the Tribunal confirming the reduction and verify that a copy of the order and the minutes have been registered and filed with the Registrar of Companies.
(d) Confirm whether the revaluation of assets has been properly disclosed in the Balance Sheet.
Answer:
(b) Verify that the Memorandum of Association authorises reduction of capital.
Question 11.
According to md AS, Provision are the amounts charged against revenue to provide for:
(a) Renewal or diminution in the value of assets.
(b) A known liability, the amount whether of could only be estimated and cannot be determined with accuracy.
(c) A claim which is disputed,
(d) Any one of the above
Answer:
(d) Any one of the above
Question 12.
At the time of examination of the Balance Sheet, at a given time, and deduct the total liabilities to outside trade payables from the value of assets, the difference between the two figures will represent the ………………… .
(a) Equity Capital.
(b) Reserve and Surplus
(c) Net worth of the company based on the intrinsic value,
(d) Net worth of the company based on the book value of assets as on the date.
Answer:
(d) Net worth of the company based on the book value of assets as on the date.
Question 13.
Capital Reserve, generally, can be utilised for
(a) Writing down fictitious assets
(b) Writing oft the losses
(c) Issuing bonus shares It is realised
(d) Any one of the above
Answer:
(d) Any one of the above
![]()
Question 14.
In case of Borrowings,” auditor should adopts general audit procedure except:
(a) Review board minutes for approval of new lending agreement.
(b) Make sure that any new loan agreements or bond issuances are duly authorized.
(c) Ensure that significant debt commitments should not be approved by the board of directors,
(d) Gain an understanding of the business rationale for such significant unusual transaction
Answer:
(c) Ensure that significant debt commitments should not be approved by the board of directors
Question 15.
Audit procedure required for the presentation and disclosure for the trade receivable except.
(a) Cheek that therestatement of foreign currency trade receivables has been done properly.
(b) Verity that the split between more than 6 months and less than 6 months has been done horn the due date instead of sales invoice date.
(c) Check classification of amount due ¡s properly disclosed as:
Secured, Considered good
Unsecured, Considered good
Doubtful
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 16.
Audit procedures required for the disclosures requirement regarding cash and cash equivalent according to Ind AS, except:
(a) Cash and cash equivalents shall be classified as:
(i) Balance with Bank
(ii) Cheques, drafts on hand,
(iii) Cash in hand,
(iv) Others (Specify nature)
(b) Earmarked balances with banks (e.g. for unpaid dividends) shall be separately stated.
(c) Bank deposits with more than 3 months maturity shall be disclosed separately.
(d) Repatriation restrictions, if any, In respect of cash and bank balances shall be separately stated.
Answer:
(c) Bank deposits with more than 3 months maturity shall be disclosed separately.
Question 17.
Inventory is valued at lower of cost and net realisable value, according to AS-2 and nd AS -2 except:
(a) Raw Material
(b) Finished Goods
(c) Semi Finished Goods
(d) Working progress arising under construction contracts.
Answer:
(d) Working progress arising under construction contracts.
![]()
Question 18.
Steps of audit procedure adopted by an audit regarding presentation and Disclosure except:
(a) Examine whether mode of valuation has been stated separately.
(b) Examine whether goods. in-transit have been disclosed separately under each sub-head of inventory.
(c) Examine whether inventory has been classified as:
Raw Materials
Work-in-progress
Finished goods
Stores and spares
Loose tooLs etc.
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 19.
Property, Plant, and Equipment have valued appropriately and as per generally accepted accounting policies and practices, auditor should follow the following audit procedures except:
(a) Examine that the entity has charged depreciation on all Items of PPE unless any item of PPE is non- depreciating ike freehold and.
(b) Verify that the depreciation method used reflects the pattern in which the asset’s future economic benefits are expected to be consumed by the entity.
(c) Verify If management has undertaken an impairment assessment to determine whether an item of property, plant and equipment is impaired.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
Question 20.
Audit procedure should not be followed by an auditor regarding completeness of disclosures of loan and advances and other current assets.
(a) Examine a list of all advances and other current assets and compare then with balances in the ledger.
(b) Inspect the minutes of meeting of Board of directors to confirm if all material loans and advances were approved by the BOD,
(c) If there are any related party loans and advances, review whether they where properly authorised and the value of such transactions were reasonable and at arm’s length.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
Question 21.
Contingent Liabilities shown in Balance sheet under the classification ot
(a) Claim against the company not acknowledged as debts.
(b) Other money for which the entity is contingently liab’e.
(c) Guarantees
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.