Accounting Fundamentals – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Accounting Fundamentals – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short note:
(c) Accounting convention of consistency; (Dec 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
In order to enable the management to draw important conclusions regarding the working of a company over a number of years it is essential that accounting practices and methods remain unchanged from one accounting period to another. According to AS-1 consistency is a fundamental assumption and it is assumed that accounting policies are consistent from one period to another. Where this assumption is not followed, the fact should be disclosed with proper reasons.
Kohler has talked about three types of consistencies:
- Vertical consistency: Consistency maintained within the interrelated financial statements of the same date.
- Horizontal consistency: This enables the comparison of performance of the organization in one year with its performance of previous/next year.
- Third-dimensional consistency: Performance of one organization can be compared with that of another organization in the same industry.
Question 2.
Write short note on the following:
The Accrual Concept (June 2017, 5 marks)
Answer:
The Accrual Concept:
The accrual concept is based on recognition of both cash and credit transactions. In case of a cash transaction, owner’s equity is instantly affected as cash either is received or paid. In a credit transaction, however, a mere obligation towards or by the business is created. When credit transactions exist (which is generally the case), revenues are nt the same as cash receipts and expenses are not same as cash paid during the period.
When goods are sold on credit as per normally accepted trade practices, the business gets the legal right to claim the money from the customer. Acquiring such right to claim the consideration for sale of goods or services is called accrual of revenue. The actual collection of money from customers could be at a later date.
Similarly, when the business procures goods or services with the agreement that the payment will be made at a future date, it does not mean that the expense effect should not be recognized. Because an obligation to pay for goods or services is created upon the procurement thereof, the expense effect also must be recognized. Today’s accounting systems based on accrual concept are called as Accrual System or Mercantile System of Accounting.
![]()
Question 3.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Objectives of Accounting
(b) Methods! Criteria for the selection and application of Accounting policies (Dec 2017, 5 marks each)
Answer:
(a) Objectives of Accounting:
The main objective of Accounting is to provide financial information to stakeholders. This financial information is normally given via financial statements, which are prepared on the basis of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). There are various accounting standards developed by professional accounting bodies all over the world.
In India, these are governed by The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, (ICAI). In the US, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) is responsible to lay down the standards. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is the body that sets up the International Accounting Standards. These standards basically deal with accounting treatment of business transactions and disclosing the same in financial statements:
The following are the main objectives of accounting:
- To ascertain the amount of profit or loss made by the business i.e. to compare the income earned versus the expenses incurred and the net result thereof.
- To know the financial position of the business i.e. to assess what the business owns and what it owes.
- To provide a record for compliance with statutes and laws applicable.
- To enable in readers to assess progress made by the business over a period ot time.
- To disclose information needed by different stakeholders.
(b) The major considerations governing the selection and application of accounting policies are:
1. Prudence: Generally maker of financial statements has to face uncertainties a the time of preparation of financial statement, these uncertainties may be regarding collectability of recoverable, number of warranty claims that may occur. Prudence means making of estimates that are required under conditions of uncertainty.
2. Substance over form: It means that transactions should be accounted for in accordance with actual happening and economic reality of the transactions not by its legal form.
3. Materiality: financial statement should disclose all the items and facts which are sufficient enough to influence the decisions of reader or/user of financial statement.
Question 4.
Write short note on the following:
The Accrual concept (June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
The Accrual Concept:
The accrual concept is based on recognition of both cash and credit transactions. In case of a cash transaction, owner’s equity is instantly affected as cash either is received or paid. In a credit transaction, however, a mere obligation towards or by the business is created. When credit transactions exist (which is generally the case), revenues are nt the same as cash receipts and expenses are not same as cash paid during the period.
When goods are sold on credit as per normally accepted trade practices, the business gets the legal right to claim the money from the customer. Acquiring such right to claim the consideration for sale of goods or services is called accrual of revenue. The actual collection of money from customers could be at a later date.
Similarly, when the business procures goods or services with the agreement that the payment will be made at a future date, it does not mean that the expense effect should not be recognized. Because an obligation to pay for goods or services is created upon the procurement thereof, the expense effect also must be recognized. Today’s accounting systems based on accrual concept are called as Accrual System or Mercantile System of Accounting.
Question 5.
Write short notes on the following:
Users of Accounting Information (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Users of Accounting Information
Accounting provides information both to internal users as well as external users. The internal users are all the organizational participants, at all levels of management (i.e. top, middle, and lower). Generally top: level management requires information for planning. middle level management which requires information for controlling the operations. For internal use, the information is usually provided in the form of reports, for instance, Cash Budget Reports, Production Reports, Idle Time Reports, Feedback Reports, whether to retain or replace an equipment decision reports, project appraisal reports, and the like.
The external users (e.g. Banks, Creditors) do not have direct access to all the records of an enterprise, they have to rely on financial statements as the source of information. External users are basically, interested in the solvency and profitability of an enterprise.
Question 6.
Write short flotes on Source documents: (Dec 2021, 3 marks)
Answer:
Source documents:
Vouchers are the documentary evidence of the transactions so happened. Source documents at the basis on which transactions are recorded in subsidiary books, i.e source documents are the evidence and proof of transactions.
Question 7.
Write short notes on Errors of principle. (Dec 2021, 3 marks)
Answer:
An error of principle: Entering revenue expenses as capital expense or vice versa or entering revenue receipt as capital receipt or vice versa.
![]()
Question 8.
Write short notes:
(a) Advantages of Double Entry System.
(b) The main objective of the Depreciation Policy. (Dec 2022, 5 marks each)
Distinguish Between
Question 9.
The distinction between Fundamental ‘accounting assumptions and Accounting policies. (Dec 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
| Basis of Discountion | Fundamental Accounting Assumptions | Accounting Policies |
| 1. Number | There are only three fundamental accounting assumptions viz. Going Concerned, Consistency, and Accrual. | There is no single list of accounting policies which are applied in all circumstances. As a result, there may be different accounting policies adopted by different enterprises. |
| 2. Disclosure if followed | No disclosure is required if all the fundamental assumptions have been followed. | Disclosure is required if a particular accounting policy has been followed |
| 3. Disclosure not ‘followed | In case the fundamental assumptions are not followed; the fact has to be disclosed in the financial statements together with the reasons. | In case, the policy is changed in subsequent year, the reasons for such change and the resulting financial consequences have to be disclosed. |
| 4. Choice | There is no choice. | The firm has a choice to select a particular policy. |
Descriptive Questions
Question 10.
Answer the following question (give workings wherever required):
State briefly the three fundamental accounting assumptions. (Dec 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
The three fundamental assumptions are (a) going concern; (b) consistency; and (c) accrual. Going Concerned: It is assumed that the concern would be continuing in operation for the foreseeable future. It is also assumed the enterprise has neither the intention nor the necessity of liquidation or of curtailing materially the scale of operations.
Consistency: The accounting policies followed are consistent from one accounting period to another.
Accrual: The revenues and expenses are accrued, that is recognized as they are earned or incurred, and recorded in the financial statements of the periods to which they relate.
Question 11.
What are the steps or phases of ‘Accounting Cycle’? (Dec 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Steps Phases of Accounting Cycle:
- Recording of Transaction: As soon as a transaction happens it is at first recorded in subsidiary book.
- Journal: The transactions are recorded in Journal chronologically.
- Ledger: All journals are posted into ledger chronologically and in a classified manner.
- Trial Balance: After taking all the ledger account’s closing balances, a Trial Balance is prepared at the end of the period for the preparations of financial statements.
- Adjustment Entries: All the adjustments entries are to be recorded properly and adjusted accordingly before preparing financial statements.
- Adjusted Trial Balance: An adjusted Trial Balance may also be prepared.
- Closing Entries: All the nominal accounts are to be closed by the transferring to Trading Account and Profit and Loss Account.
- Financial Statements: Financial statements can now be easily prepared which will exhibit the true financial position and operating results.
Question 12.
What is a depreciable cost? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Depreciable cost = Cost of asset- Scrap value.
Question 13.
Name the side on Which increase in capital is recorded. (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Credit side.
Question 14.
Under which accounting concept provision ¡s made for doubtful debts. (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Prudent concept.
Question 15.
Why is the capital of the owner shown on the liability side of the balance sheet? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Due to separate entity concept.
Question 16.
What type of account is a revaluation account? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Nominal account.
![]()
Question 17.
What is the traditional function of accounting? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Recording of financial transactions.
Question 18.
Should a transaction be first recorded in a journal or Ledger. Why? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Transactions are first recorded in a journal because it is a book of original entries.
Question 19.
On which basis of accounting outstanding expenses are not recorded? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Cash basis of accounting.
Question 20.
Name the error committed by violating the wies of accounting. (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Error of principle.
Question 21.
Define merchandise. (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Merchandise means goods for resale.
Question 22.
Which transactions will:
(i) Decrease the assets and decrease the capital.
(ii) Increase the assets and increase the liabilities.
(iii) Increase the assets and decrease other assets.
(iv) Decrease the assets and decrease the liabilities. (Dec 2021, 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) Drawing or expenses.
(ii) Purchase of an asset on credit.
(iii) Purchase or sale of an asset in cash.
(iv) Payment of liability.
Question 23.
When you proceed to reconcile the bank account starting with ‘credit’ cash book Balance, how is the following dealt with and why?
(i) Cheque issued but not presented for payment
(ii) Cheque deposited but not yet credited.
(iii) Bank charges charged by the bank not recorded in the cash book.
(iv) Interest allowed by the hank is not recorded in the cash book. (Dec 2021, 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) Cheques issued but not yet presented for payment are deducted because the bank shows lower overdrawn balance.
(ii) Cheques deposited but not deared are added because the bank shows a higher overdrawn balance.
(iii) Bank charges are added because the bank shows a higher overdrawn balance.
(iv) Interest allowed is deducted because the bank shows lower overdrawn balance.
Question 24.
Why is goodwill considered an “Intangible asset” but not a “fictitious assets? (Dec 2021, 2 marks)
Answer
Goodwill cannot be seen or touched. It can only be felt. Hence, it is treated an intangible asset. But it is not a fictitious asset because fictitious do not have a value. Whereas Goodwill has value and it can be purchased or sold with any other asset.
Practical Questions
Question 25.
Mr. X is owner of a Cinema Hall. He spent a heavy amount for complete renovation of the hail, for installation of air-conditioning machines and for sitting arrangement with cushion seats. As a result the revenue has been doubled. He also spent for few more doors for emergency exit. State your opinion about the treatment of the entire expenditure. (Dec 2012, 2 marks)
Answer:
If due to any expenditure, the future benefits from the assets increases beyond its previously assessed standard of performance. then it should be capitalized. The size of the expenditure is not Important for capitalizing the expenditure. In the present case, renovation expenses should be capitalized because it has enhanced the revenue-generating capacity of the hail but expenditure for making more emergency exit does not enhance the revenue-generating capacity of the hall, so it should be charged to revenue.
![]()
Question 26.
The total of debit side of the Trial Balance of Lotus Stores as at 31.03.2012 is ₹ 3,65,000 and that of the credit side is ₹ 2,26,000. After checking, the following mistakes were discovered:
| Items of account | Correct figures (as it should be) (₹) | Figures as it appears in the Trial Balance (₹) |
| Opening stock | 15,000 | 10,000 |
| Rent and rates | 36,000 | 63,000 |
| Sundry creditors | 81,000 | 18,000 |
| Sundry debtors | 1,04,000 | 1,58,000 |
Ascertain the correct total of the Trial Balance. (Dec 2012, 5 Marks)
Answer:
In the books of Lotus Stores calculation of correct Total of Trial Balance
| Particulars | Dr. | Cr. |
| Total of Trial Balance as per on 31.03.12 | 3,65,000 | 2,26,000 |
| Add understatement of op. stock | 5,000 | – |
| Less: overstatement of Rent & Rates | 27,000 | – |
| Add: understatement of sundry creditors | – | 63,000 |
| Less: overstatement of sundry debtors | 54,000 | – |
| Correct Total | 2,89,000 | 2,89,000 |
Question 27.
State whether the following items are ¡n the nature of capital, Revenue and/or Deferred Revenue Expenditure:
(i) Expenditure on special advertising campaign ₹ 66,000; suppose the advantage will be received for six years.
(ii) An amount of ₹ 8000 spent as legal charges for abuse of trademark.
(iii) Legal charges of ₹ 15,000 incurred for raising loan.
(iv) Share issue expenses ₹ 5,000.
(v) Freight charges on a new machine ₹ 1,500 and erection charges ₹ 1,800 for that machine. (June 2013, 1 x 5 = 5 marks)
Answer:
(i) As per Para 56 of AS 26, the expenditure incurred on intangible items would have to expense off when they are incurred. So, the Advertisement Expenses is not carried forward to the next year, and the full amount is shown in the Profit & Loss A/c. So, ₹ 66,000
consider for revenue expenditure.
(ii) Revenue expenditure ₹ 8,000
(iii) Capital expenditure ₹ 15,000
(iv) Capital expenditure ₹ 5,000
(v) Capital expenditure = 1,500+ 1,800 = ₹ 3,300.
Question 28.
Answer the following questions (give workings wherever required):
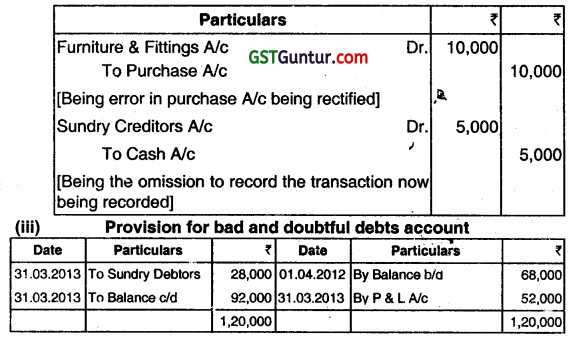
(i) A trader acquired furniture & fittings for ₹ 10,000 but included the same in purçhase account. He paid ₹ 5,000 to a supplier which was omitted to be recorded in the books. State the types of errors and pass journal entries t rectify the errors.
(iii) The company maintains 10% of debtors as provision towards bad debts. It has routed all bad debts through the provision account. The opening balance of provision as on 01.04.2012 was ₹ 68,000. The closing provision i.e. on 31st March, 2013 was ₹ 92,000. Bad debts written off debited to provision account was ₹ 28,000. How much should be debited to Profit & Loss Account towards provision for doubtful debts for the year ended 31st March, 2013? (Dec 2013, 2 marks each)
Answer:
(i) The first error is error of principle. The capital expenditure has been claimed as revenue expenditure. The second one is error of omission.
The Journal Entries are:
Question 29.
State with reason whether the followings are capital or revenue expenditure:
(i) Freight charges of ₹ 12,000 incurred foie machinery purchased for ₹ 2,00,000.
(ii) ₹ 90,000 being expenditure incurred for a well-equipped labour welfare centre.
(iii) Compensation of ₹ 1,50,000 each paid to three employees who were retrenched.
(iv) Purchase of TV set for ₹ 30,000 to be installed in the reception hall. (Dec 2013, 1 x 4 = 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) Expenditure incurred towards freight charges for bringing the machinery to the location and till regular production is capital expenditure. Hence, the freight charge is to be capitalized.
(ii) Labour welfare centre is a permanent addition and therefore a capital expenditure.
(iii) Compensation to retrenched employees will not bring any permanent benefit and hence is revenue expenditure.
(iv) Television set purchased is a capital expenditure unless the person acquiring the same is a dealer of television sets.
Question 30.
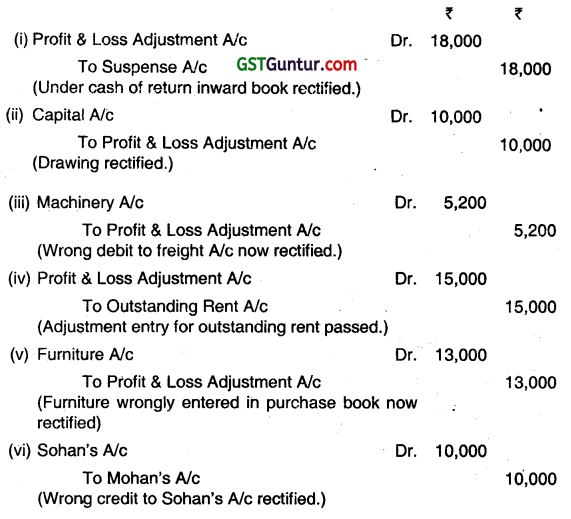
Answer the question:
(b) Pass necessary journal entries to rectify the following errors assuming’ that the errors were detected after the preparation of final accounts:
(i) Return inward book was undercast by ₹ 18,000.
(ii) Goods purchased for proprietor’s use for ₹ 10,000 debited to purchase account.
(iii) ₹ 5,200 paid for freight on machinery was debited to freight account.
(iv) No adjustment entry was passed for an amount of ₹ 15,000 relating to outstanding rent. ‘
(v) Furniture of ₹ 13,000 purchased from Chandra Furniture House was entered in purchase book.
(vi) ₹ 10,000 received from Mohan has been credited to Sohan. (Dec 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 31.
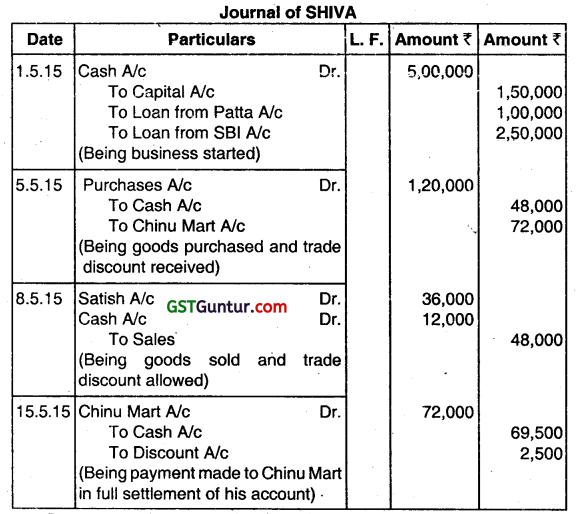
Answer the question:
(a) Journalise the following transactions in the books of SHIVA.
01.05.2015 – Started business with ₹ 5,00.000 of which 50% amount was borrowed from SB! and 20% amount was borrowed from his sister Patta.
05.05.2015 – Purchased goods from China Mart worth ₹ 1,60,000 at 25% trade discount and 40% amount paid in cash.
08.05.2015 – Sold goods to Satish ₹ 60,000 at 20% trade discount and received ¼ amount in cash.
15.05.2015 – Paid to Chinu Mart ₹ 69,500 in full settlement of A/c. (June 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 32.
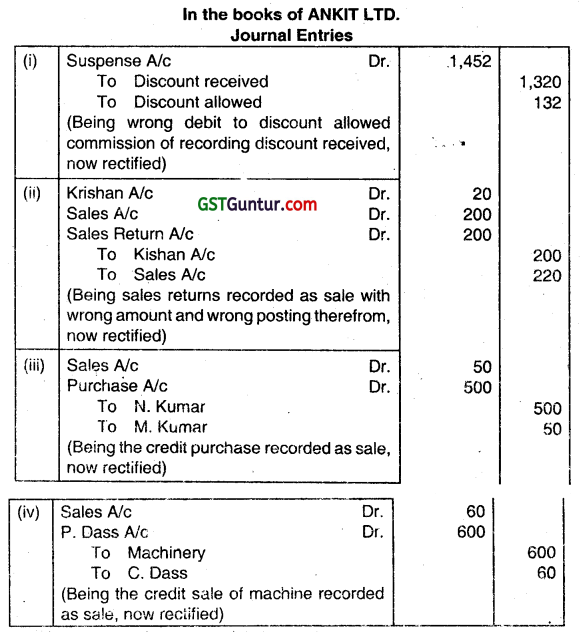
Answer the question.
(a) Trial Balance of ANKIT LTD. failed to agree and the difference was put into Suspense Account pending investigation which discovered the following:
(i) Discount received ₹ 1,320 had been debited to Discount allowed as ₹ 132.
(ii) Goods of the value of ₹ 200 returned by Kishan were entered in the Sales Day Book and posted therefrom to the credit of Krishan as ₹ 20.
(iii) A credit purchase of ₹ 500 from N. Kumar was recorded as sale to M. Kumar for ₹ 50.
(iv) A credit sale of machine of P. Dass for ₹ 600 recorded through Sales Day Book as sale to C. Dass for ₹ 60.
Required:
Pass the Rectifying Entries in the Book of Ankit Ltd. (Dec 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
![]()
Question 33.
Answer the question.
MILTON LTD. sold goods worth ₹ 1,00,000 to NARMADALTD. Narmada Ltd. asked for discount of ₹ 16,000 which was agreed by Mton Ltd. The sale was effected and Goods despatched. After receiving, Goods Worth ₹ 14,000 was found defective, which they returned immediately. They made the payment of ₹ 70,000 to Milton Ltd. The accountant of Milton Ltd. booked the Sales for ₹ 70,000. Discuss whether the accounting entry passed by the accountant of the company is correct? (Dec 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
The accounting entry passed by the accountant of the company is incorrect as it does not depict the original transaction. Sates should be shown at the gross amount and thereafter, entry of sales return should be passed. The goods returned cost 14,000 on which discount was availed which needs to be reversed.
Discount = \(\frac{14,000 \times 16,000}{1,00,000}\)
= 2,240
Question 34.
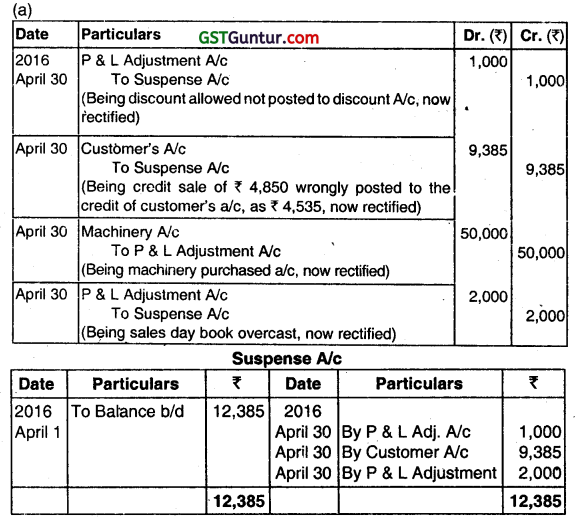
(a) The trial balance of M/s SEWADA & CO., on 31st March 2016 did not agree. In order lo close the books, the accountant placed the difference of ₹ 12,385 (Dr.) to Supens Account for necessary adjustments In the next period. On 30th April, 2016 the following errors, arising in 2015-16 were detected:
(i) ₹ 1,000 allowed as cash discount to a trade debtor was not debited to the discount account.
(ii) Credit sale of ₹ 4,850 was posted to the credit of the customer’s account as ₹ 4,535.
(iii) Machinery purchased for ₹ 50,000 in cash was posted to the Purchases Account in the ledger.
(iv) Sales Book was overcast by ₹ 2,000 in February 2016.
Required:
(a) Pass the necessary Journal Entries to rectify these errors.
(b) Prepare suspense account in the book of SEWADA & CO. (June 2016, 5 +2 =7 marks)
Answer:
Question 35.
The Trial Balance of a concern has agreed but the following mistakes were discovered after the preparation of Final Accounts.
(i) No adjustment entry was passed for an amount of ₹ 2,000 relating to outstanding rent.
(ii) Purchase book was overcast by ₹ 1,000.
(iii) ₹ 4,000 depreciation of Machinery has been omitted to be recorded in the book.
(iv) ₹ 600 paid for purchase of stationary has been debited to Purchase A/c.
(v) Sales books was overcast by ₹ 1,000.
(vi) ₹ 5,000 received, in respect of Book Debt had been credited to Sales A/c.
Show the effect of the above errors in Profit and Loss Account and balance Sheet. (June 2017, 6 marks)
Answer: .
Effects of the errors in Profit and Loss A/c and Balance Sheet
| Profit and Loss A/c | Balance Sheet |
| (a) Profit was overstated by ₹ 2,000 | (a) Capital was also overstated by ₹ 2,000 and outstanding Liability was understated by ₹ 2,000. |
| (b) Gross profit was understated by ₹ 1,000 and also the Net Profit. | (b) Capital was understated by ₹ 1,000. |
| (c) Net Profit was overstated by ₹ 4,000. | (c) Machinery was overstated by 4,000 and so the Capital A/c was also overstated by ₹ 4,000. |
| (d) No effect on Net Profit. | (d) No effect in Balance Sheet. |
| (e) Gross Profit & Net Profit were overstated by ₹ 1,000. | (e) Capital was overstated by ₹ 1,000. |
| (f) Gross Profit & Net Profit were overstated by ₹ 5,000. | (f) Capital & Sundry Debtors were overstated by ₹ 5,000. |
Question 36.
(a) Khetan Ltd. has received two lakh subscriptions during the current year under its new scheme whereby customers are required to pay a sum of ₹ 4,500 for which they will be entitled to receive a magazine for a period of 3 years. Khetan wants to treat the entire amount as revenue for current year. Comment. (June 2017, 3 marks)
(b) Alex. Ltd. intends to set up a solar plant. Alex Ltd. has acquired a dilapidated factory, having an area of 7500 acres at a cost of ₹ 70,000 per acre. Alex Ltd. has incurred ₹ 50,00,000 on demolishing the old factory building thereon. A sum of ₹ 43,57,500 (including 5% Sales Tax) was realized from sale of material salvaged from the site. Alex Ltd. also incurred Stamp Duty and Registration Charges of 5% of Land Value, paid Legal and Consultancy Charges ₹ 5,00,000 for land acquisition, and incurred ₹ 2,00,000 on Title Guarantee Insurance. Compute the value of land acquired. (June 2017, 6 marks)
Answer: .
(a) As illustrated in AS 9 ‘Revenue Recognition’, revenue received or billed should be deferred and recognized either on a straight line basis over time or, where the items delivered vary ¡n value from period to period, revenue should be based on the sales value of the item delivered in relation to the total sales value of all items covered by the subscription.
Accordingly, in the given case the accounting treatment adopted by Khetan Ltd. to treat the entire amount as revenue for the current year is not in accordance with AS 9. The revenue should be recognized on a straight-line basis over the period of 3 years.

Question 37.
The Trial Balance of a concern Fas agreed but the following mistakes were discovered after the preparation of final Accounts.
(i) No adjustment entry was passed for an amount of ₹ 2000 relating to outstanding rent.
(ii) Purchase book was overcast by ₹ 1,000.
(iii) ₹ 4,000 depreciation of Machinery has been omitted to be recorded in the book.
(iv) ₹ 600 paid for purchase of stationary has been debited to Purchase A/c.
(v) Sales books was overcast by ₹ 1,000.
(vi) ₹ 5000 received in respect of Book Debt had been credited to Sales A/c.
Show the effect of the above errors in Profit and Loss Account and balance Sheet. (Dec 2017, 6 marks)
Answer:
| Profit and Loss A/c | Balance Sheet |
| (a) Profit was overstated by ₹ 2,000 | (a) Capital was also overstated by ₹ 2,000 and outstanding Liability was understated by ₹ 2,000. |
| (b) Gross profit was understated by ₹ 1,000 and also the Net Profit. | (b) Capital was understated by ₹ 1,000. |
| (c) Net Profit was overstated by ₹ 4,000. | (c) Machinery was overstated by 4,000 and so the Capital A/c was also overstated by ₹ 4,000. |
| (d) No effect on Net Profit. | (d) No effect in Balance Sheet. |
| (e) Gross Profit & Net Profit were overstated by ₹ 1,000. | (e) Capital was overstated by ₹ 1,000. |
| (f) Gross Profit & Net Profit were overstated by ₹ 5,000. | (f) Capital & Sundry Debtors were overstated by ₹ 5,000. |
Question 38.
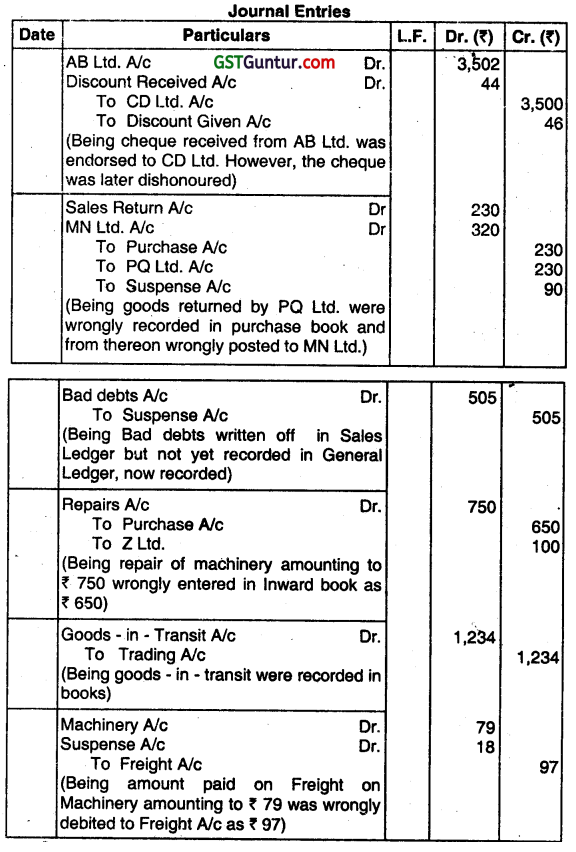
(a) The Trial Balance oIS Ltd. as on 31/03/2018 showed the credit in excess by ₹ 415 which was been carried to Suspense Account. On a closed scrutiny of the books, the following errors were revealed:
(i) A cheque of ₹ 3456 received from AB Ltd. after allowing it a discount of ₹ 46 was endorsed to CD Ltd. in full settlement for ₹ 3,500. The cheque was finally dishonoured but no entries are passed in the books of account.
(ii) Goods of the value of ₹ 230 returned by PQ Ltd. were entered in Purchase Day book and posted therefrom to MN Ltd. as ₹ 320.
(iii) Bad debts aggregating ₹ 505 written off during the year in Sales Ledger but were not recorded In Genéral Ledger.
(iv) Bill for ₹ 750 received from Z Ltd. for repairs to Machinery was entered in the Inward Invoice Book as ₹ 650.
(v) Goods worth ₹ 1,234 purchased from Y Ltd. on 28/03/2018 had not been entered in Day book and credited to Y Ltd. but Goods were not delivered till 5th April, 2018. The title of Goods was however passed on 28/03/2018 and was taken into stock on 31 -03-2018.
(vi) ₹ 79 paid for Freight on Machinery was debited to Freight account as ₹ 97. Pass the necessary Journal Entries to rectify the above-mentioned errors. (June 2018, 8 marks)
Answer:
![]()
Question 39.
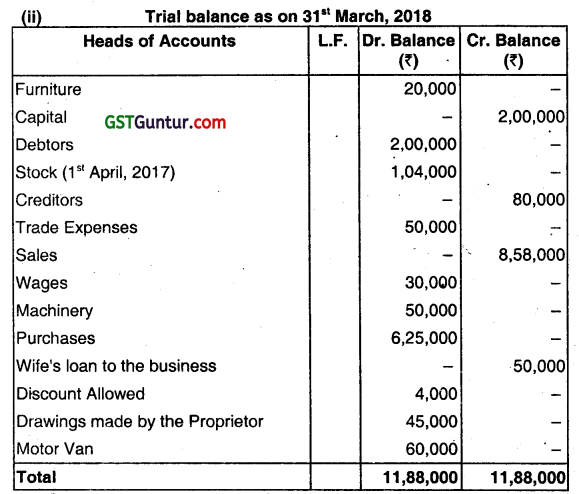
(a) A bookkeeper extracted the following Thai Balance as on 31st March 2018:
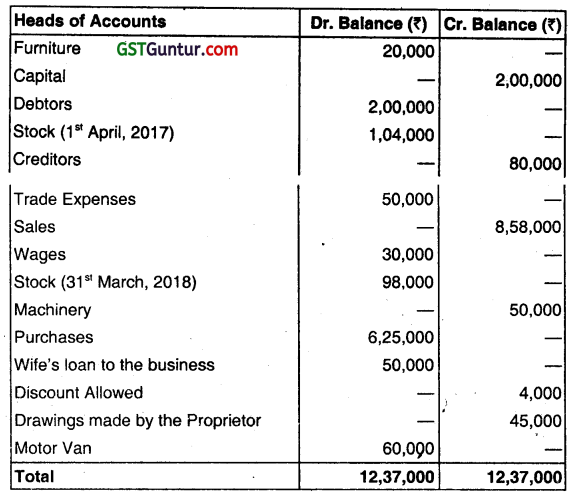
You are required to:
(i) State the errors giving reasons,
(ii) Redraft the Trial Balance correctly. (Dec 2018, 7 marks)
Answer:
(i) (I) Stock on 31st March 2018, will not appear in the Trial balance because it represents a part of the goods purchased but not yet sold. As the total purchases have been included in the Trial balance, there is no need of including the Closing Stock again.
(II) Machinery is an asset and thus will appear in the debit column.
(III) Wife’s loan to the business is a liability. It will appear in the credit column.
(IV) Discount allowed, being an expense, will appear in the debit column.
(V) Drawings made by the proprietor is a decrease of capital (i.e., decrease of proprietor’s claim from the business). It will appear In the debit column.
Question 40.
(a) Rectify the following errors:
(i) A Credit Sale of goods to X ₹ 3,000 posted as ₹ 30,000.
(ii) A Cash Sale of goods to Y ₹ 3,000 posted as ₹ 30,000.
(iii) A Credit Sale of furniture to ₹ 3,000 posted as ₹30,000.
(iv) A Credit Sale of goods of ₹ 3,000 to Krishan entered in the purchases book as ₹ 30,000 and posted therefrom to the credit of Kishan as ₹ 3,000.
(v) A Cash Sale of goods of ₹ 3,000 to Krishan posted to the credited of Kishan as ₹ 30,000.
(vi) A Credit Purchase of old machinery from Sohan for ₹ 17,000 was entered in the Purchases Book as purchase from Mohan for ₹ 71,000. ₹ 3,000 paid as Repair Charges of this Machinery debited to General Expenses Account.
(vii) A Bill drawn on Meenu for ₹ 30,000 was passed through bills payable book with ₹ 3,000 and posted therefrom to the credit of Meena as ₹ 300.
(viiii) Sales included a sale of furniture having a book of value of ₹ 900 for ₹ 850 on 31st March 2018. , (June 2019, 8 marks)
Answer:
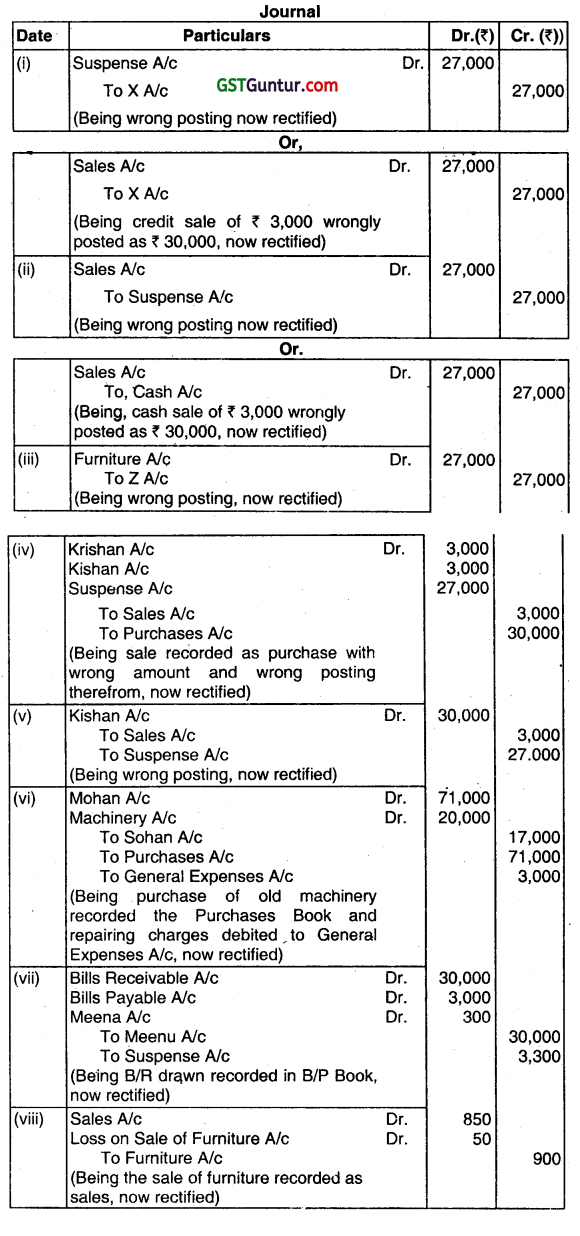
Question 41.
From the following particulars calculate operating profit.
Net profit. ₹ 1,00,000
Rent received. ₹ 10,000
Gain on the sale of machines. ₹ 15,000
Interest on loan paid. ₹ 18,000
Donation paid. ₹ 4,000 (Dec 2021, 2 marks)
Answer:
Operating Profit = 1,00,000 – 10,000 – 15,000 + 18,000 + 4,000 = 97,000
∵ Operating Profit = 97,000
Question 42.
Ruma Ltd. purchased a plant on 1st April 2015 for ₹ 2,40,000 it bought another plant on 1st July, 2016 for ₹ 1,60,000. On 1st January 2018 Plant bought on 1st April 2015 was sold for ₹ 1,60,000 and a fresh plant was purchased on the same date. Payment of this plant will be made as under.
1st January 2018 ₹ 40,000.
1st January 2019 ₹ 48,000.
1st January 2020 ₹ 44,000.
Payments made in 2019 and 2020 include interest of ₹ 8,000 and ₹ 4,000, respectively. Depreciation is charged at 10% P.a. on the diminishing balance method.
From the above particulars, Find out.
(i) Cost of plant bought on January 1st’, 2018.
(ii) Loss on sale of plants.
(iii) Closing balance of plant 2 and plant 3 as on 31-3-2018 (Dec 2021, 6 marks)
Answer:
(i) Cost of Plant:
40,000 + 48,000 – 8,000 + 44,000 – 4,000 = 1,20,000
(ii) Loss on sale of Plant:
WDV on 1.1.2018 2,40,000-24,000 – 21,600 – 14,580 = 179,820
Loss = 1,79,820 – 1,60,000 = 19,820
(iii) Closing balance of Plant:
Plant 2
1,60,000 – \(\left(1,60,000 \times \frac{10}{100} \times \frac{9}{12}\right) \) -14,800 = 1,33,200
Plant 3
1,20,000 – 1,20,000 × \(\frac{10}{100} \times \frac{3}{12}\)
= 1,17,000
![]()
Question 43.
ABC Ltd. has entered into a binding agreement with XYZ Ltd. to buy a custom-made machine amounting to ₹ 4,00,000. As on 31st March, 2021 before delivery of the machine, ABC Ltd. had to change its method of production. The new method will not require the machine ordered and so it shall be scrapped after delivery. The expected scrap value is NIL. Show the treatment of machine in the books of ABC Ltd. (Dec 2022, 5 marks)
| Repeatedly Asked Questions | |
| Question | Frequency |
| 1. Write short note on the following: The Accrual Concept 17-June, 19 June |
2 Times |
Accounting Fundamentals – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Accounting Concepts
Accounting Concepts refer to the assumptions and conditions that define the parameters and constraints within which the accounting operates. They lay down the foundation for accounting principles, and ensure recording of financal facts on sound bases and logical considerations.
Accounting Conventions
Accounting Conventions are customs and methods. procedures or guidelines associated with the practical application of accounting principles.
Capital Expenditure
Capital Expenditure refers to that expenditure, benefit from which can be enjoyed by an entity over a number of accounting periods. This type of expenditure happens to be non-recurring in nature. A capital expenditure takes place when an asset or service is acquired or improvement of a fixed asset is affected.
Revenue Expenditure
Revenue Expenditure refers to that expenditure, benefit from which can be enjoyed by an entity ¡n the current accounting period. This type of expenditure happens to be recurring in nature. Revenue expenditures are incurred to carry on the regular course of operations by an organisation.
Capital Receipts
Capital Receipts refer to the receipts which are obtained by an entity from operations other than the regular operations f the entity. Capital receipts do not have any effect on the operating result during the course of a year.
Revenue Receipts
Revenue Receipts refer to the receipts which are obtained by an entity from its regular course of operations. Receipts of money in the revenue nature increase the profits or decrease the losses of a business and must be set against the revenue expenses in order to ascertain the profit for the period.
Capital Profit
Capital Profit refers to a profit which anses out of the non-operating activities of an entity. It is non-recumng in nature. Generally, capital profits arise out of the sale of assets other than inventory, or in connection with the raising of capital or at the time of purchasing an existing business.
Revenue Profit
Revenue Profit refers to a profit which arises out of the regular operating activities of an entity. It is recurring in nature.
![]()
Capital Loss
Capital Loss refers to a loss which does not arise to an entity in the regular course of its operations.
Revenue Loss
Revenue Loss arises to an entity from the normal course of business.
Charts of Accounts
A Chart of Accounts (COA) is a listing of all accounts in the general ledger, each account accompanied by a reference number.
Double Entry System
Double Entry System of Bookkeeping is an accounting system which recognizes the fact that every transaction has two aspects and both aspects of the transaction are recorded in the books of accounts.
Journal
Journals the book of original entry in which financial transactions are firstly recorded after their occurrence in chronological order. It is in this book of accounts where the transactions are recorded in the first place.
Ledger
The book of account in which transactions are recorded in respective account after they have been entered in the journal is called the Ledger. It is the book of account in which the transactions are recorded in a classified and permanent manner. It is the final destination of all the accounts, and hence, it is also called the Book of Final Entry. The process of recording the entry in the ledger is technically known as posting.
Cash Book
The book of account that records all cash receipts and cash payments of an organization is referred to as cash book. The receipts ar entered on the debit side, while the payments are recorded in the credit side of the cash book.
Bank Book
Deviating from the traditional method of keeping an additional column for bank transactions in a double and triple-column cash book, today organizations keep a separate subsidiary book similar to cash book to record all receipts and payments made through the bank. This is known as Bank Book or Bank Journal.
Bank Reconciliation Statement
At any point of time, the balances as per cash book (bank column) and pass book should be equal in amount. But, in reality, it rarely happens due to certain specific reasons. To reconcile the balances as reflected by these two related books a statement is prepared, which ¡s referred to as the Bank Reconciliation Statement.
Trial Balance
The Trial Balance is a statement drawn up using the ledger balances to test of the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger account. The primary purpose of drafting a Trial Balance is to ensure that there are no arithmetical errors.
Depreciation
The gradual decline in the value of a tangible asset is termed as Depreciation. Thus, in ears be stated that depreciation is a part of cost of tangible fixed asset which has expired because of its usage, lapse of time, etc.
![]()
Amortization
Amortization is a gradual and systematic writing of of intangible asset over its estimated useful life. For example, patents, purchased goodwill, and copyrights are amortized over their useful life being intangible assets.
Depletion
Depletion is the value of wasting assets extracted from quarry, mine, etc. Extraction reduces the available quantity of material.