Strategy Implementation and Control – CA Inter SM Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Strategy Implementation and Control – CA Inter SM Question Bank
Question 1.
Briefly answer the following:
Difference between Strategy formulation and Strategy Implementation. (Nov 2008, 2 marks)
OR
(b) Distinguish between the following:
Strategy Formulation and Strategy imptemeniation. (May 2011, May 2015, May 2019, 4+4+3 =11 marks)
OR
Discuss any three differences between strategy formulation any strategy implementation. (Nov 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Strategy implementation is fundamentally different from strategy formulation.
Strategy formulation and implementation can be contrasted in following ways:
| Basis | Strategy Formulation | Strategy Implementation |
| Meaning | Strategy formulation is positioning forces before the action. | Strategy implementation is managing forces during action. |
| Focus | Strategy formulation focuses on effectiveness. | Strategy Implementation focuses on efficiency. |
| Nature | Strategy formulation is primarily an intellectual process. | Strategy Implementation is primarily an operational process. |
| Skill Required | Strategy formulation requires good incitive and analytical skills. | Strategy implementation requires motivation and leadership skills. |
| Co-ordination Vs Combination | Strategy formulation requires coordination among a few individuals. | Strategy implementation requires combination among many individuals. |
Question 2.
Elaborate the interrelationship between strategy formulation, and implementation. (May 2012, 3 marks)
Answer:
Strategic implementation is concerned with translating a decision into action, with presupposes that the decision itself (i.e., the strategic choice) was made with some thought being given to feasibility and acceptability.
A firm will definitely be successful only when the strategy formulation is sound and strategy implementation is excellent. Hence, organizational success s a function of a good strategy and proper implementation. This is represented by the following matrix:
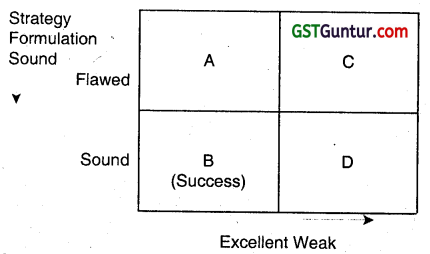
Strategy Implementation
| Square A | Is a situation where Strategy formulation Is flowed and strategy implementation is weak which results in difficulty in formulation. |
| Square B | Is a situation where Strategy formulation is sound and strategy implementation is excellent which results In success of a company. This is an ideal situation. Every firm wants to be at this square. |
| Square C | Is a situation where Strategy formulation is flawed & strategy implementation is weak which results In failure In fomulation and Implementation both. So a firm here has to redesign the complete strategic model. |
| Square D | Is a situation where Strategy formulation is Sound and strategy implementation is weak which results In failure in implementation. |
Question 3.
Describe the principal aspects of strategy-execution process, which are included In most situations. (May 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
In most situations, strategy – execution process Includes the following principal aspects:
- Developing budgets that steer ample resources into those activities is critical to strategic success.
- Staffing the organization with the needed skills and expertise, consciously building and strengthening strategy, supportive competencies and competitive capabilities, and organizing the work effort.
- Ensuring that policies and operating procedures facilitate rather than impede effective execution.
- Using the best-known practices to perform core business activities and pushing for continuous Improvement.
- installing information and operating systems that enable company personnel to better carry out their strategic roles day in and day Out.
- Motivating people to pursue the target objectives energetically.
- Creating a company culture and work climate conducive to successful strategy implementation and execution.
- Exerting the internal leadership needed to drive implementation forward and keep improving strategy execution.
- When the organization encounters stumbling blocks or weaknesses, management has to see that they are addressed and rectified quickly.
![]()
Question 4.
State with reasons which of the following statement is correct/incorrect:
Changes of any type are & always disquieting, sometimes they may be threatening. (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect: The toughest management task Is to talk about change. This is because of heavy anchor of deeply held values and habits – people cling emotionally to the old and familiar. However, favourable changes either in the external environment on internal environment are not threatening or disquieting.
Question 5.
State with reasons which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
There is both opportunity and challenge in Change. (Nov 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct: Business works in an climate of change. Change is what makes business dynamic as it poses both challenges and opportunity. Challenge to accept the change which necessitates appropriate action. Opportunity to face the future in a more determined way. It calls for innovative thinking to new potentials to be unfurled in future.
Question 6.
ABC Ltd. plans to introduce changes in its structure, technology, and people. Explain how Kurt Lewin’s change process can help this firm. (May 2011, 3 marks)
Answer:
An early model of change developed by Kurt Lewin described change as a three-stage process. Kurt Lewin theorized a three-stage model of change that is known as the unfreezing-change-refreeze model that requires prior learning to be rejected and replaced. Lewin’s theory states behavior as “a dynamic balance of forces working in opposing directions. “For Lewin, the process of change entails creating the perception that a change is needed, then moving toward the new, desired level of behavior, and finally, solidifying that new behavior as the norm.
| 1st Stage | He called unfreezing”. It involved overcoming inter alía and dismantling the existing “mindset. Defense mechanisms have to be bypassed. |
| 2nd Stage | The change occurs. This is typically a period of confusion and transition. We are aware that the old ways are being challenged but we do not have a clear picture as to what we are replacing them with yet. |
| 3rd Stage | He called “freezing”. The new mindset is crystallizing and one’s comfort level is returning to previous levels. This is often misquoted as “refreezing”. So ABC Ltd. can change its structure, technology, and people as per Kurt Lewin’s change process. |
Question 7.
Write short note on the following:
Steps for initiating a strategic change. (Nov 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
Strategic change refers to organization-wide change which is a fundamental and radical reorientation of the way an organisation operates. It affects the entire organisation and often goes against the values held by members In the organisation. It may relate to change in goals and objectives, change in technology mergers, collaborations, acquisition. Basically, there are five stages of corporate strategy formulation implementation process.
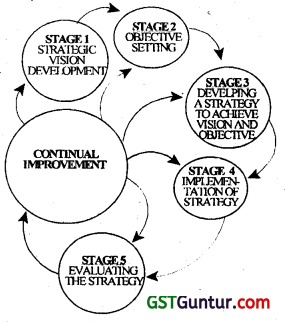
Stage 1
Developing a Strategic Vision
First a firm must determine what directional path the firm should take and what changes in the firm’s product-market-customer- technology-focus would improve its current market position and its future prospects. Top managements views and conclusions about the firm’s direction and the product- customer-market-technology focus constitute a strategic vision for the company.
Stage 2
Setting Objectives
Corporate objectives represent the quantum of growth the firm seeks to achieve In the given time frame. It provides the basis for the major decisions of the firm and the performance to be realized at each level. The purpose of setting objectives is to convert the strategic vision into specific performance targets i.e. results the management wants to achieve and then use these objectives as yardsticks for tracking the firm’s progress and performance.
Stage 3
Developing a Strategy to Achieve the Vision and Objective
The strategizing process generally has proceeded from the corporate level to the business level and then from the business level to the functional and operating levels. Mid-level and frontline managers cannot do good strategy-making without understanding the firm’s long-term direction and higher-level strategies. Good communication of strategic themes and guiding principles serves a valuable strategy-unifying purpose. Developing a strategic vision, setting objectives, and crafting a strategy are basic direction-setting tasks.
Stage 4
Implementation of Strategy
To convert strategic plans into actions and results, a manager must be able to direct organizational change, motivate people, build and strengthen company competencies and competitive capabilities, create a strategy-supportive work climate, and meet or beat performance targets.
Stage 5
Monitoring Developments, Evaluating Performance and making Corrective Adjustments
A firm’s vision, objectives, strategy, and approach to strategy execution are never final. Evaluating the firm’s progress, assessing the impact of new external deployments, and making corrective adjustments are continuous method. Whenever a firm encounters disruptive changes in its external environment, questions need to be raised about the appropriateness of its direction and strategy. It is to be expected that a company will modify its strategic vision direction objectives, and strategy over time.
![]()
Question 8.
Distinguish between:
Unfreezing the situation and Refreezing – the two stages of Kurt Lewin change process. (Nov 2014, 3 marks)
Answer:
The process of Unfreezing simply makes the individuals or organizations aware of the necessity for change and prepares them for such a change. Lewin proposes that the changes should not come as a surprise to the members of the organization. Sudden and unannounced change would be socially destructive and morale-lowering. Refreezing occurs when the new behaviour becomes a normal way of life.
The new behaviour must replace the former behaviour completely for successful and permanent change to take place. In order for the new behaviour to become permanent, it must be continuously reinforced so that this new acquired behaviour does not diminish or extinguished.
Question 9.
Write a short note on strategic change and explain the process, of strategic change. (Nov 2018, 7 marks)
Answer:
The changes in the environmental forces often require businesses to make modifications in their existing strategies and bring out new strategies. Strategic change is a complex process and it involves a corporate strategy focused on new markets, products, services, and new ways of doing business.
To make the change lasting, Kurt Lewin proposed three phases of the change process for moving the organization from the present to the future. These stages are unfreezing, changing and refreezing.
(a) Unfreezing the Situation:
The process of uni freezing simply makes the individuals or organizations aware of the necessity for change and prepares them for such a change. Lewin proposes that the changes should not come as a surprise to the members of the organization. Sudden and unannounced change would be socially destructive and morale-lowering.
The management must pave the way for the change by first, unfreezing the situation, so that members would be willing and ready to accept the change. Unfreezing is the process of breaking down the old attitude and behaviors, customs, and traditions so that they start with a clean slate. This can be achieved by making announcements, holding meetings, and promoting the ideas throughout the organization.
(b) Changing to New Situation:
Once the unfreezing process has been completed and the members of the organization reorganize the need for change and have been fully prepared to accept such change, their, behaviour patterns need to be redefined. H.C. Keliman has proposed three methods for reassigning new patterns of behaviour. These are compliance, identification and internalization.
1. Compliance:
It is achieved by strictly enforcing the reward and punishment strategy for good or bad behaviour. Fear of punishment, actual punishment or actual reward seems to change behaviour for the better.
2. Identification:
Identification occurs when members are psychologically impressed upon to identify themselves with some given role models whose behaviour they would like to adopt and try to become like them.
3. Internalization:
Internalization involves some internal changing of the individual’s thought processes in order to adjust to a new environment. They have given freedom to learn and adopt new behaviour In order to succeed in the new set of circumstances.
(c) Refreezing:
Refreezing occurs when the new behaviour becomes a normal way of life. The mew behaviour must replace the former behaviour completely for successful and permanent change to take place. In order for the new behaviour to become permanent, it must be continuously reinforced so that this newly acquired behaviour does not diminish or extinguish.
Change process is not a one-time application but a continuous process due to dynamism and ever-changing environment. The process of unfreezing, changing and refreezing is a cyclical one and remains continuously in action.
Question 10.
Explain the concept and need of Strategy Audit. Why is it more difficult in present scenario? (May 2018, 7 marks)
Answer:
Strategy Audit:
Concept
Companies review their business plans and strategies on regular basis to identify weaknesses and shortcomings to enable a successful development plan. The strategy audit secures that all necessary information for the development of the company are included in the business plan and that the management supports it.
A strategy audit is an examination and evaluation of areas affected by the operation of a strategic management process within an organization.
A strategy audit provides an excellent platform for discussion with the top management regarding necessary corporate actions or changes in the existing business plan. It also identifies the need to adjust the existing business strategies and plans.
Need of Strategy Audit:
- A Strategy Audit Is needed under the following conditions.
- When the performance indicators reflect that a strategy is not working properly or is not producing desired outcomes.
- When the goals and objectives of the strategy are not being accomplished.
- When a major change takes place in the external environment of the organization.
When the Top Management Plans
(a) to fine-tune the existing strategies and introduce new strategies and.
(b) to ensure that a strategy that has worked in the past continues to be in tune with subtle internal and external changes that may have accrued since the formulation of strategies.
Reasons why Strategy Evaluation (audit) is more difficult in Present scenario Include the following trends A dramatic increase in the environment’s complexity.
- The increasing difficulty of predicting the future with accuracy.
- The Increasing number of variables in the environment.
- The rapid rate of obsolescence of even the best plans.
- The increase in the number of both domestic and world events affecting organizations.
- The dcreasing time span for which planning can be done with any degree of certainty.
Question 11.
Write a short note on requirements of strategy audit. What are the basic activities of strategic audit? (Nov 2020, 5 marks)
![]()
Question 12.
What is Strategy Audit? Explain briefly the criteria for strategy audit given by Richard Rumelts.
Answer:
A Strategy Audit is an examination and evaluation of areas affected by the operation of a strategic management process within an organization.
Richard Rumeit’s Criteria for Strategy Audit
(a) Consistency A Strategy should not present Inconsistent goals and policies. Organizational conflict and inter-departmental bickering are often symptoms of managerial disorder, but these problems may also be a sign of strategic inconsistency. Three guidelines help determine if organizational problems are due to inconsistencies in strategy:
If managerial problems continue despite changes in personnel and it they tend to be issue-based rather than people-based, then strategies may be inconsistent.
If success for one organizational department means or is interpreted to mean, failure for another department, then strategies may be in consistent.
If policy problems and issues continue to be brought to the top for resolution, then strategies may be inconsistent.
Consonance Consonance refers to the need for strategists to examine sets of trends, as well as individual trends, in auditing strategies. A strategy must represent an adaptive response to the external environment and to the critical changes occurring within it. One difficulty in matching a firm’s key internal and external factors in the formulation of strategy is that most trends are the result of interactions among other trends.
For example, the day-care school centre came about as a combined result of many trends that included a rise in the average level of education, need for different education pedagogy, increase In Income, inflation. and an increase In women in the workforce. Although single economic or demographic trends night appear steady for many years, there are waves of change going on at the interaction level.
(c) Feasibility:
A Strategy must neither overtax available resources nor create unsolvable sub-problems. The final broad test of strategy is its feasibility; that is, can the strategy be attempted within the physical, human, and financial resources of the enterprise? The financial resources of a business are the easiest to quantify and are normally the first limitation against which strategy is audited.
It is sometimes forgotten, however, that innovative approaches to financing are often possible. Devices, such as captive subsidiaries, sale-leaseback arrangements, and tying plant mortgages to long-term contracts, have all been used effectively to help win key positions in suddenly expanding industries. A less quantifiable, but actually more rigid, limitation on strategic choice is that Imposed by Individual and organizational capabilities. It is auditing a strategy, it is important to examine whether an organization has demonstrated in the past that it possesses the abilities, competencies, skills, and talents needed to carry out a given strategy.
(d) Advantage
A Strategy must provide for the creation and/or maintenance of a competitive advantage in a
selected area of activity. Competitive advantages normally are the result of superiority in one of three areas:
- resources,
- skills, or
- position.
The idea that the positioning of firm’s resources that enhance their combined effectiveness is familiar to military theorists and chess players. Position can also play a crucial role in an organization’s strategy. Once gained, a good position is defensible- meaning that it is so costly to capture that rivals are deterred from full-scale attacks.
Positional advantage tends to be self-sustaining as long as the key internal and environmental factors that underlie it remain stable. This is why entrenched firms can be almost impossible to unseat, even if their skill levels are only average. Although not all positional advantages are associated with size, it is true that larger organizations tend to operate in markets and use procedures that turn their size Into advantage, while smaller firms seek product/market positions that exploit other types of advantage.
The principal characteristic of good position is that it permits the firm to obtain advantage from policies that would not similarly benefit rivals without the same position. Therefore, In auditing strategy, organizations should examine he nature of positional advantages associated with a given strategy.
Question 12.
What is strategic control? Briefly explain the different types of strategic control. (May 2012, 1 +3 = 4 marks)
OR
What is strategic control? Explain the types of strategic controls. (Nov 2016, 7 marks)
OR
Explain different types of strategic control in brief. (May 2018, 3 marks)
Answer:
Strategic Control focuses on the dual questions of whether:
- the strategy is being implemented as planned; and
- the results produced by the strategy are those intended.
There are Four types of Strategic Control:
Premise Control
A Strategy is formed on the basis of certain assumptions or. premises about the environment. Premise control is a tool for systematic and continuous monitoring of the environment to verify the validity and accuracy of the premises on which the strategy has been built.
Strategic Surveillance
Strategic surveillance unfocussed. It involves general monitoring of various sources of information to uncover unanticipated information having a bearing on the organizational strategy.
Special Alert Control
At times unexpected events may force organizations to reconsider their strategy. Sudden changes in government, natural calamities, unexpected merger/acquisitions by competitors, industrial disasters, and other such events may trigger an immediate and intense review of strategy.
Implementation Control
Managers implement strategy by converting major plans into concrete, sequential actions that form incremental steps. Implementation control is directed towards assessing the need for changes In the overall strategy in light of unfolding events results.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the meaning of the following concepts:
Premise control. (Nov 2012, 1 mark)
Answer:
Premise Control is a tool for systematic and continuous monitoring of the environment to verify the validity and accuracy of the premises on which the strategy has been built. it primarily involves monitoring two types of factors:
(a) Environmental factors such as economic (Inflation, liquidity, interest rates), technology, sadat and regulatory.
(b) Industry factors such as competitors, suppliers, substitutes.
Question 14.
Distinguish between the following:
Operational Control and Management Control. (Nov 2013,Nov 2017, 3, 4 marks)
Answer: .
Difference between Operational Control and Management Control:
| Operational Control | Management Control |
| 1. Controls individual tasks or transactions thus narrow scope. | Controls the entire function of a department or organisation thus wides in scope. |
| 2. Basic purpose is to formulate a set of standards, plan or instructions for a task or transaction. | Basic purpose is to achieve the organisational goal. |
Question 15.
Write short note on the following:
implementation Control (Nov 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
Implementation Control
Managers implement strategy by converting major plans into concrete, sequential actions that form incremental steps, Implementation control is directed towards assessing the need for changes In the overall strategy in light of unfolding events and results associated with incremental steps and actions. Strategic implementation control is not a replacement to operational control. Strategic implementation control, unlike operational controls, continuously monitors the basic direction of the strategy.
Basic Forms of Implementation Control
(i) Monitoring Strategic Trusts
Monitoring strategic trusts helps the managers to.
determine whether the overall strategy is progressing as desired or whether there is need for readjustment.
(ii) Milestone Reviews:
All key activities necessary to Implement strategy are segregated In terms of time, events or major resource allocation. It normally involves a complete reassessment of the strategy. It also assesses the need to continue or refocus the direction of an organization.
Question 16.
What is strategic control? Kindly explain the statement that premise control is a tool for systematic and continuous monitoring of the environment. (Nov 2020, 5 marks)
Question 17.
Sanya Private Limited is an automobile company. For the past few years, it has been observed that the progress of the company has become stagnant. When scrutinized, it was found that the planning department was performing fairly well but the plans could not be implemented due to improper use of resources, undesirable tendencies of workers and non-conformance to norms and standards. You are hired as a Strategic Manager. Suggest the elements of process of control to overcome the problem. (Jan 2021, 5 marks)
![]()
Question 18.
Define Business Process Re-engineering. Briefly outline the steps therein. (May 2009, 4 + 6 = 10 marks)
OR
Write short notes on Implementation steps in BPR
Answer:
Business Process Re-engineering
Concept of BPR
BPR is defined as the analysis and redesign of workflows and processes both within and between the organization and the external entities like suppliers, distributors, and service providers. BPR is an approach to bring improvement in operating effectiveness through the redesigning of critical business process and supporting business activities.
Features of BPR
Business process re-engineering Is an approach which seeks improvement in operating effectivity throug the re-designing of core business processes and other supporting systems. It intends at starting all over, starting from scratch. It begins with re-thinking with a totally tree state of mind without having any pre-notion or motive. It first determines what must be done and then decides how to do it.
Advantage of BPR
- It aims at taking advantage of Its operational excellence.
- it leads to process orientation which basically analyses what work is being done and how is it being done.
- It prepares to survive and tackle competition.
- It brings about fresh ideas and proceeds without being influenced by old ideas.
Steps of BPR:
1. Determining Objectives and Framework
It helps in building a comprehensive foundation for the re-engineering process. This will provide the required focus, direction, motivation etc., for redesign process.
2. Identify Customers and Determine \their needs
The designers have to understand the customer’s needs and wants, their profits, their steps in acquiring, using arid disposing a product and the purpose is to provide added value to the customer.
3. Study the Existing Process
This will provide an important base for the redesigners. The purpose of this is to understand the what” and ‘why of the targeted process.
4. Formulate a Redesign a Process Plan
The information gained through the earlier steps is translated into an ideal redesign process. in this step, alternative process are considered and the best is selected.
5. Implement the Redesign
It is easy to formulate new process but to implement them is hard. Implementation of the redesign process and application of other knowledge gained from the previous step is to achieve dramatic improvement.
Question 19.
Explain the meaning of the following concepts:
Business Process Re-engineering (May 2011, 1 mark)
Answer:
Concept of BPR:
BPR is defined as the analysis and redesign of workflows and processes both within and between the organization and external entities like suppliers, distributors and service providers. BPR is an approach to bring improvement in operating effectiveness through the redesigning of critical business process and supporting business activities.
![]()
Question 20.
Write short note on the following:
Role of IT In Business Process Re-engineering. (Nov 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:
BPR + Information Technology Tools = Business Engineering Today BPR and Information Technology term known as Business Engineering. Business Engineering combines the Innovations of Information Technology with BPR and focus on better business processes. The main trust of using information technology in BPR lie in far-reaching (best procedure-based) processes oriented solutions.
The Impact of IT on BPR can be identified as
- Drastic reduction in operational time,
- Defeating restrictions of geographical area,
- Provide timely, reliable, and accurate information, and
Information Technology increases Business Values in terms of
- Efficiency – by way of Increased productivity,
- Effectiveness – by way of better management,
- innovation – by way of improved products and services.
The Role played by IT in BPR can be summarised as
- It increases the efficiency by way of increased productivity.
- It enhances the effectiveness through better management.
- It brings about Innovation by developing improved products and services.
- It leads to compression of time.
- It helps In overcoming geographic restrictions.
- It re-structures relationship.
Question 21.
Being a strategic professional, analyze and redesign the workforce in the context of business process re-engineering. (May 2012, 3 marks)
Answer:
Business Process Re-engineering:
Business Process Re-engineering is an approach which seeks improvement in operating effectivity through the re-designing of core business processes and other supporting systems. It intends at starting all over,” starting from scratch. It begins with re-thinking with a totally free state of mind without having any pre-notion or motive. It first determines what must be done and then decides how to do it.
Redesigning the workforce In the context of BPR:
- The workflows are to be studied, appraised, and improved in terms of time, cost, output, quality, and responsiveness to customers.
- The re-design effort aims to simplify and streamline a process by eliminating all extra avoidable steps, activities, and transactions.
- With the help of re-designing workflows, organizations can drastically reduce the number of stages of work, and improve their performance. Thus increasing the efficiency.
Question 22.
What is the rationale behind Business Process Re-engineering (BPR)? What steps would you recommend to implement BPR in an organization? (May 2014, 7 marks)
Answer:
Rationale behind BPR:
1. To obtain in the performance of the process in terms of time, and quantum cost. output, quality, and responsiveness to gains customers;
2.’ To simplify and Streamline the process by
- eliminating all redundant and non-value-adding steps, activities, and transactions,
- reducing drastically me number of stages or transfer points of work, and
- speeding up the workflow through the use of info-tech systems.
3. To obtain dramatic improvement
In operational effectiveness. by re-designing core business processes and supporting business systems.
Steps of BPR:
1. Determining Objectives and Framework
It helps in building a comprehensive foundation for the re-engineering process. This will provide the required focus, direction, motivation etc., for redesign process.
2. Identify Customers, and Determine their needs
The designers have to understand the customer’s needs and wants, their profits, their steps in acquiring, using, and disposing a product and the purpose is to provide added value to the customer.
3. Study the Existing Process
This will provide an important base for the redesigners. The purpose of this is to understand the “wtiar and “Why of the targeted process.
4. Formulate a Redesign a Process Plan
The information gained through the earlier steps is translated into an ideal redesign process. In this step, alternative processes are considered and the best is selected.
5. Implement the Redesign
It is easy to formulate new process but to implement them is hard. Implementation of the redesign process and application of other knowledge gained from the previous step is to achieve dramatic Improvement.
Question 23.
State with reason which of. the following statement is correct or incorrect:
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) means partial modification or marginal improvement in the existing work processes. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect: Business Process Reengineering refers to the full change in business process from starting to the end and improvement in the work processes. Business process re-engineering is an approach which seeks improvement in operating effectivity through the re-designing of core business processes and other supporting systems.
It intends at starting all over, starting from scratch. It begins with re-thinking with a totally free state of mind without having any pre-notion or motive. It first determines what must be done and then decides how to do it.
Question 24.
Identify three aspects of impact of IT Systems on Business Process Reengineering and list three areas where it provides business value. (Nov 2018, 3 marks)
Answer:
Impact of IT – Systems on BusIness process Re-engIneering are identified as:
- Compression of time
- Overcoming restrictions of geography and/or distance
- Restructuring of relationships
- IT initiatives provide business values In three distinct areas:
- Efficiency – by way of Increased productivity,
- Effectiveness – by way of better management.
- Innovation – by way of Improved products and services.
Question 25.
Explain concept and nature of BPR. (Nov 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Concept and nature of BPR:
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) refers to the analysis and redesign of workflows and processes both within and between the organizations. The orientation of the redesign effort is radical; i.e., it is a total deconstruction and rethinking of a business process in its entirely unconstrained by Its existing structure and pattern. Its objective is to obtain quantum gains in the performance of the process in terms of time, cost, output, quality, and responsiveness to customers. The redesign effort aims at simplifying and streamlining a process by eliminating all redundant and non-value adding steps, activities aid transactions, reducing drastically the number of stages or transfer points of work, and speeding up the workflow through the use of IT systems.
BPR is an approach to unusual improvement in operating effectiveness through the redesigning of critical business processes and suppotting business systems. It Is revolutionary redesign of key business processes that involves examianation of the basic process itself, It looks at the minute details of the process, such as why the work Is done, who does It, where it ¡s done and when it is done. BPR focuses on the process or producing the output and output of an organization is the result of its process.
Business process as reengineering means starting all over, starting from scratch Reengineering, In other words, means putting aside much of the age-old practices and procedures of doing a thing. It implies for getting how work has been done so for, and deciding how it can best be done now.
![]()
Question 26.
Which of the following statement is correct and which is incorrect? Give reasons in brief for your answer. There is no distinction between benchmarking and Business Process Reengineering. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
Benchmarking relates to setting goals and measuring productivity based on best industry practices. The idea is to learn from the practices of competitors and others to improve the firm’s performance. On the other hand, business process re-engineering relates to analysis and redesign of work flows and processes both within and between organizations.
Question 27.
What is Benchmarking? Explain the various steps in Benchmarking process. (May 2019, 7 marks)
Answer:
Meaning
Benchmarking is an approach of setting goals and measuring productivity of firms based on best Industry practices or against the products, services and practices of its competitors or other acknowledged leaders In the industry. It developed out of need to have Information against which performance can be measured. Benchmarking helps businesses in improving performance by Learning from the best practices and the processes by which they are achieved. Thus, benchmarking is a process of continuous improvement in search for competitive advantage. Firms can use benchmarking practices to achieve improvements In diverse range of management functions like product development, customer services, human resources management, etc.
Steps Involved In Benchmarking Process
- Identifying the need for benchmarking: This step will define the objectives of the benchmarking exercise It will also involve selecting the type of benchmarking. Organizations identify realistic opportunities for improvements.
- Clearly understanding existing decisions processes: The step will involve compiling information and data on performance,
- Identify best processes: Within the selected framework best processes are identified. These may be within the same organization or external to them,
- Comparison of own process and performance with that of others:
The benchmarking process also Involves comparison of performance of the organization with performance of other organizations. Any deviation between the two Is analysed to make further improvements. - Prepare a report and implement the steps necessary to close the performance gap: A report on benchmarking initiatives containing recommendations is prepared. Such a report also contains the action plans for implementation.
- Evaluation: Business organizations evaluate the results of the benchmarking process in terms of improvements vis-a-vis objectives and also the other criteria set for the purpose. It periodically evaluates arid roset benchmarks in the light of changes in conditions that impact the performance.
Question 28.
Swift Ltd. and Quick Ltd. are two companies that are in the business of light industrial machines. While Swift is the market leader the sales of Quick has been falling. In the year 2017-18, the market share of the two companies was forty percent and five percent respectively. During the last five years the market share of quick reduced from third to sixth position. As an immediate corrective measure top management of Quick decided to emulate the successful standards of Swift Ltd. and set them as their own yardsticks. With the help of standards, they intended to compare, measure and judge their performance. What is the strategic tool Quick Ltd. is adopting? How is it implemented?
Answer:
The Top Management of Quick Ltd. is doing benchmarking. The benchmarking helps an organization to get ahead of competition. A benchmark may be defined as a standard or a point of reference against which things may be compared and by which something can be measured and judged. In simple words, benchmarking is an approach of setting goals and measuring productivity based on best Industry practices. In recent years, different commercial and non-commercial organizations are discovering the value of benchmarking and are applying it to improve their processes and systems. Benchmarking processes used by different organizations lack standardization. However, common elements are as follows:
I. Identifying the need for benchmarking: This step will define the objectives of the benchmarking exercise. It will also involve selecting the type of benchmarking. Organizations identify realistic opportunities for improvements.
II. Clearly understanding existing business processes: This step will involve compiling information and data on performance. This will include mapping processes.
III. Identify best processes: Within the selected framework, best processes are identified. These may be within the same organization or external to it.
IV. Compare own processes and performance with that of others: White comparing gaps in performance between the organization and better performers is identified. Further, gaps in performance are analysed to seek explanations. Feasibility of making the improvements is also examined.
V. Prepare a report and Implement the steps necessary to close the performance gap: A report on the Benchmarking initiatives containing recommendations is prepared. Such a report includes the action plan(s) for implementation.
VI. Evaluation: A business organization must evaluate the results of the benchmarking process in terms of improvements vis-a-vis objectives and other criteria set for the purpose. It should also periodically evaluate and reset the benchmarks In the light of changes in the conditions that impact its performance.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In which concept managerial exercise of putting a freshly chosen strategy into action?
(a) Strategy allocation
(b) Strategy Implementation
(c) Strategy formulation
(d) Functional Implementation
Answer:
(b) Strategy Implementation
Question 2.
success of a company depends when:
(a) Strategy formulation is sound
(b) Strategy implementation is excelled
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
![]()
Question 3.
Strategy implementation is primarily an operational process where as strategy formulation is …………………. .
(a) organisational process
(b) implementation process
(c) designing process
(d) intellectual process.
Answer:
(d) intellectual process.
Question 4.
Strategy formulation focuses on effectiveness whereas strategy implementation focuses on ………………….. .
(a) efficiency
(b) objectives
(c) diversification
(d) None
Answer:
(a) efficiency
Question 5.
Strategy formulation requires coordination among the executives at the ………………… .
(a) Lower Level
(b) Middle Level
(c) Top Level
(d) Middle and lower levels.
Answer:
(c) Top Level
Question 6.
Strategy implementation requires ………………… .
(a) Conceptual intuitive and analytical skills
(b) motivation skills
(c) Leadership skills
(d) Motivational and leadership skills
Answer:
(d) Motivational and leadership skills
Question 7.
Project Implementation, procedural implementation. Resource allocation followed by ……………….. are the sequential Issues in strategy implementation.
(a) Structural implementation
(b) Functional implementation
(c) Behavioural implementation
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 8.
Strategic change is a …………….. that involves a corporate strategy focused on new markets, products, services arid new ways of doing business.
(a) Simple process
(b) Complex process
(c) Managerial process
(d) Controlling process.
Answer:
(b) Complex process
Question 9.
Which is/are the important phase(s) in Kurt Lewin’s Model of change?
(a) Unfreezing the situation
(b) Changing to the new situation
(c) Refreezing
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
![]()
Question 10.
Which is not a type of organisational control
(a) Operational control
(b) Management control
(c) Strategic Control
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
Question 11.
…………….. is the process of evaluating strategy as it is formulated and implemented.
(a) Operational control
(b) Management control
(c) Strategic control
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Strategic control
Question 12.
Which are the major types of strategic control except?
(a) Premise control
(b) Strategic surveillance
(c) Operational control
(d) Implementation control
Answer:
(c) Operational control
Question 13.
Core of the Strategy Audit lies on
(a) How well is the current strategy Working and how ¡t is working in future?
(b) How can this be evaluated in present and future?
(c) How urgent is there a need to change the strategy?
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 14.
Strategy Audit includes basic activities except:
(a) Examining the underlying bases of a firm’s strategy
(b) Comparing expected results with actual results.
(c) Examining the factors not directly affecting the organisation
(d) Taking corrective actions to ensure that performance conforms to plans.
Answer:
(c) Examining the factors not directly affecting the organisation
Question 15.
Which is the reason that strategic evaluation is more difficult today?
(a) The rapid rate of obsolescence of even the best plans.
(b) A dramatic increase in the environments complexity
(c) The decreasing time span for which planning can be done with any degree of certainty
(d) Any of the above.
Answer:
(d) Any of the above.
Question 16.
What is a business process?
(a) A process is a set of logically related tasks or activities oriented towards achieving a specified outcome.
(b) Business process Is a collection of activities which creates an output of value to the customer and often transcends departmental or functional boundaries
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 17.
The core process of a company may change over a period of time according to the shifting requirements of its ………………. .
(a) need
(b) effectiveness
(c) competitiveness
(d) demand and supply position.
Answer:
(c) competitiveness
Question 18.
Process refers to the analysis and redesign of workflows and processes both within and between the organization, is known as
(a) Strategic Business Process
(b) Business Process Engineering
(c) Functional Process Re-engineering
(d) Functional Process Re-engineering
Answer:
(c) Functional Process Re-engineering
![]()
Question 19.
Which is not an element of a Business Process Reengineering?
(a) Re-engineering begins with a fundamental rethinking
(b) Re-engineering involves radical redesigning of process
(c) Re-engineering aims at achieving dramatic improvement in performance
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
Question 20.
The generic business processes of a firm needing redesign may be clarified In various categories except:
(a) Processes Comprising management activities
(b) Process involving interface(s) with customers
(c) Process pertaining to development and delivery of product(s) and/or services
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
Question 21.
Which Is not a step In Benchmarking Process?
(a) Identifying the need for benchmarking –
(b) Clearly understanding existing decision processes and identify best processes
(c) Prepare a report and implement the steps necessary to close the preformation gap and evaluation
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
Question 22.
Benchmarking is a process of continuous improvement in search for ……………… .
(a) growth of the firm
(b) facing the competition
(c) competitive advantage
(d) product development.
Answer:
(c) competitive advantage