E-Commerce, M-Commerce and Emerging Technologies – CA Inter EIS Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
E-Commerce, M-Commerce and Emerging Technologies – CA Inter EIS Study Material
Question 1.
What are the benefits of E-Commerce to the Customer? (MTP)
Answer:
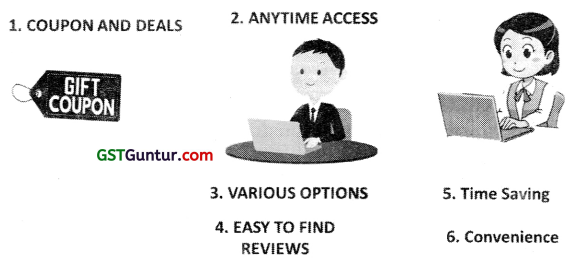
- Coupon and Deals: To promote Online transaction discount coupons and reward points are available.
- Anytime Access: 24 by 7 access to the e-commerce platforms is available, which helps the customer to avail products and services anytime.
- Various Options: These helps customers to compare various options given by various competitors in the market.
- Easy to find reviews: Reviews from previous customers helps to provide important feedback about the product.
- Time saving: Increase in number of operations both by the purchasers and sellers saves time.
- Convenience: Products are available at the tip of finger on internet.
![]()
Question 2.
What Are the benefits of E-Commerce to the Business? (RTP Nov. 2018)
Answer:
- RECURRING PAYMENTS MADE EASY: Similar kind of transactions made helps in bringing uniformity.
- INSTANT TRANSACTION: Since, the transactions of e commerce are based on online real time processes, number of deals can be solved easily.
- COST REDUCTION:
- For Buyers: From increased competition in procurement of essentials because more suppliers are able to compete electronically.
- For Suppliers: Electronically accessing online databases of bids, submitting bids online.
- In overhead costs through automation and uniformity.
- Advertisement costs.
- PROVIDES A DYNAMIC MARKET: This helps to improve quality and the business.
- INCREASED CUSTOMER BASE: Number of consumers online is getting increased, which are creating new customers and also retaining the old customers.
- EFFICIENCY IMPROVEMENT DUE TO:
- Reduction in errors, time, to process information through elimination of requirements to enter data again.
- Reduction in time to complete transactions related to business.
- Due to Just-in- time inventory and integrated manufacturing techniques; there is Reduction in inventories and reduction of risk of obsolete inventories.
- CREATION OF NEW MARKETS: With the help of internet, once can easily reach new customers.
- EASIER ENTRY INTO NEW MARKETS: Markets which are geographically remote can easily be entered.
- BETTER QUALITY OF GOODS: Due to standardized specifications, increased competition and improvement is goods.
- ELIMINATION OF TIME DELAYS: Since business processed are linked, there is fast processing and save time.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain in brief E-Commerce Business Model.
Answer:
- Business Model is
- organization of service, product and information flows,
- the sources of revenues and benefits for suppliers and customers.
- The adaptation of an organization’s business model to the internet economy is E-Business Model.
- To describe how an organization makes money on a sustainable basis and grows, Business Model is adopted by an organization. It is regarded as a Framework.
- E-business models helps to utilize the benefits of electronic communications of data.
- A business model helps firm to analyze environment more effectively, helps to understand its customers; and increases entry barriers for competitors.
Question 4.
Describe the term “Digital Library” (Nov. 18; 2 Marks)
Answer:
- Digital Library’s main focus in on collection of Digital objects.
- It is basically a special library.
- It basically includes video material, audio material, text stored as electronic media formats.
- Digital libraries are vast in size and its scope.
- They can be managed and maintained by individuals, organizations, or affiliated with established institutions.
- Digital content can be stored locally in the devices and can be accessed remotely via computer networks.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain in brief “Payment Gateway”.
Answer:
- It is basically a mode through which customers make payments.
- It represents the way e-commerce/m-commerce vendors collects their payments.
- This gives assurance to the seller of receipt of payment from buyer of goods/services from e-commerce vendors.
- Currently many methods of payments are being used such as: Credit/ Debit Card Payments, Online bank payments, Vendors own payment wallet, Third Party Payment wallets, like SBI BUDDY or PAYTM, Cash on Delivery (CoD) and Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
Question 6.
E-commerce runs through different network-connected systems that can have two architecture namely Two-Tier Architecture and Three-Tier Architecture. Determine the difference between both. (MTP)
OR
Write a brief description of three tier architecture of Application Software [Nov. 2019; 2 Marks]
Answer:
- In case of e-commerce, Architecture describes the manner in which network architectures are build.
- Architecture is basically a term used to define the style of design and method of construction.
- Though Architecture is used normally for buildings, physical structures.
Networked systems normally have two types of architecture:
-
- Two tier, and
- Three tier.
1. Two Tier Client Server:
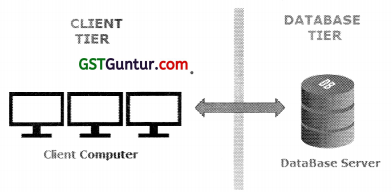
- Under this, client (user) sends request to Server
- Server will respond to the request by obtaining the data.
- The Two-tier architecture is divided into two tiers- Presentation Tier and Database Tier.
- Presentation Tier (Client Application/Client Tier):
- It basically is an interface which allows the user to interact with vendor.
- User has to log in into e-commerce vendor platform through this tier itself.
- It also connects to database tier and displays the various products/ prices to customers.
- Database Tier (Data Tier):
- Data with respect to Price, Product, Customer, etc. are kept here.
- User has no access to data/information in this case.
- But user can display all data/information stored here through application tier.
The Advantages of Two-Tier Systems are as follows:
- The performance of system will be high because Application Tier’s logic and Database are close physically.
- More users /clients will be able to interact with the system, because processing is shared between the client and server.
- It is quiet easy to setup and maintain the entire system comfortably.
The Disadvantages of Two-Tier Systems are as follows:
- If the number of users/clients increases, then the performance of the system goes down.
- Less Flexibility.
- Limited choice of DBMS because data language which is used in server is proprietary to each vendor.
![]()
2. Three Tier Client Server
- It is a Client Server architecture.
- It is basically a design pattern of a software and a software architecture.
- The Three Tiers are Presentation Tier, Application Tier and Data Tier.
- Under this Architecture:
- user interface,
- process logic,
- computer data storage.
are developed and managed as independent module.
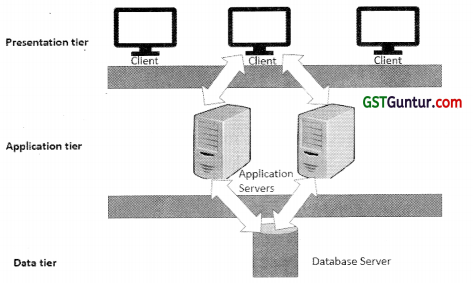
Brief Explanation of Three tiers are given as under:
- Presentation Tier:
- It basically Occupies the top level in Architecture.
- It displays information on the website with respect to products & services available.
- It also Communicates with other tiers in the form of sending results to the browser and other tiers.
- Application Tier/Middle Tier/Logic Tier/Business Logic:
- This tier is basically pulled from presentation tier.
- It helps to control application functionality by performing processing operations in detail.
- In computer software, business logic or domain logic is the part of the program that encodes the business rules.
- Database Tier:
- This tier basically arranges database servers.
- Under the database servers, information is stored and retrieved i.e. extracted.
- Data in this tier is normally kept independent of application servers i.e. no dependence on the application servers.
- The data tier includes database servers, file shares, etc.
- Data access layer should provide an Application Programming Interface (API) to the application tier.
Advantages of Three-Tier Systems are:
- Clear separation of user-interface-control and data presentation from application logic. Because of this, more clients can have access to a wide variety of server applications. There will be quicker development and a shorter test phase.
- Dynamic load balancing: If bottlenecks occurs in terms of performance then the server process can be moved to other servers quickly.
- Change management: It is very easy and quick to exchange or replace a component on the server instead of having new PCs and new Programs.
The Disadvantages of Three-Tier Systems are as follows:
- There is increment in the need for network traffic management, load balancing of servers, and fault tolerance.
- Current tools are immature and complex.
- Maintenance tools are inadequate with respect to maintaining server libraries. This is an obstacle to simplify the maintenance.
![]()
Question 7.
A Customer X intends to place an order for an electronic cooker on an online portal ABC.com. With the help of the diagram, determine the general workflow of the E-Commerce Transaction that will take place. (RTP May 2018)
Draw Workflow Diagram for e-commerce and describe various steps and corresponding activities involved in this diagram. [May 2018; 8 Marks]
Answer:
Description of various steps and corresponding activities in e-Commerce workflow are as follows:
Step 1: Customers login: Few e-commerce merchants may allow1 same transactions to be done through phone, but the basic information flow is e-mode.
Step 2: Product/Service Selection: From the available options, customer may select products/services as per the choice.
Step 3: Customer Places Order: Once customer place the order for product / service; ‘Payment Gateway” is opened.
Step 4: Payment Gateway: Customer will select a particular method of payment. If payment method of Cash on Delivery is selected, then e – commerce vendor wall do additional check to validate customer.
If payment methods is other than Cash on Delivery (CoD), the merchant will received update from payment gateway about payment realization from customer.
Step 5: Dispatch and Shipping Process: In case product/service inventory is managed by e-commerce vendor themselves, than dispatch shall be initiated at merchant warehouse. But many e-commerce merchants also allows third party vendors to sale via websites of merchant.
Step 6: Delivery Tracking: It is the most important element to bring success in e-commerce business.
To have a track of delivery, merchants provide their delivery staff with hand held devices, where product/service delivery to customers are updated immediately.
Step 7: CoD Tracking: In this case merchants should do additional checking on matching delivery with payments.
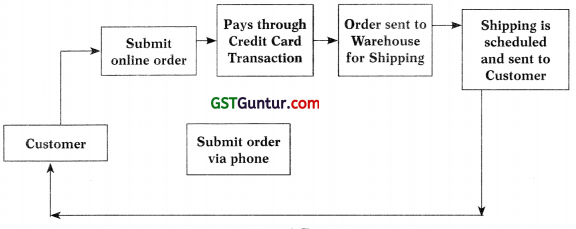
E-Commerce Workflow Diagram
![]()
Question 8.
In an e-business environment, controls are necessary for all persons in the chain. Describe in brief.
Answer:
- Users: Genuine user should use the c-commerce/m-commerce platform. If user accounts are hacked and hackers buy the products or services, there is a tremendous risk.
- Sellers/Buyers/Merchants: There need to be proper framework and controls in place to ensure success of business. These include controls on:
a. Product catalogues.
b. Product returns,
c. Price catalogues,
d. Discounts schemes,
e. Accounting for cash received through Cash on Delivery mode. - Government: Government have few critical concerns with respect to electronic transactions, namely:
- Tax accounting of all products/services sold.
- All products/services sold need to be legal.
- Network Service Providers: Proper availability and security of network should be ensured by Network Service Providers. Downtime of network can be harmful for business.
- Technology Service Providers: These include cloud computing back ends, applications back-ends, etc (Le. all other service provider other than network service provider). They are also prone to risk of security.
- Logistics Service Providers: They are finally responsible for timely product deliveries.
- Payment Gateways: Payment gateways need to be efficient, effective and complete.
![]()
Question 9.
As an IT consultant, advise some tips to an aspiring e-commerce vendor so that his business can be protected from intrusion. (RTP Nov. 2018)
OR
Explain the concept of E-Commerce briefly. How can you protect your E-Commerce business from intrusion? (Nov. 2019; 4 Marks)
Answer:
- Viruses: Virus attack may result in loss of critical and valuable data. Therefore, one should Check website daily for viruses.
- Hackers: With the help of Software packages, regular assessment of your website can be done to know how vulnerable our website is with respect to attack from hackers.
- Passwords: Password need to be change regularly. Also, passwords set by ex-employees need to be made non-operational.
- Regular software updates: Update the site with Latest versions of Security Software. Failing to do so, it leave your website vulnerable to attacks.
- Sensitive data: Encryption of Confidential Data and Financial information should be done with the help of Encryption software. By doing so, hackers will be unable to access encrypted data without a key.
- Details of your payment service provider contract should he known.
Question 10.
Explain various Control Objectives of E-commerce or M-commerce. (May 2018;4Marks)
Answer:
Not In Syllabus
![]()
Question 11.
Describe any six Commercial Laws each in brief, that are applicable to any E-Commerce or M-Commerce Transactions. (RTP May 2018)
Commercial Laws that are applicable to any E-Commerce or M-Commerce Transactions are as described below:
Answer:
1. Income-tax Act, 1961: Provisions regarding taxation of income in India are detailed in Income-tax Act. Deciding the place of origin for tax purpose is a critical issue in e-commerce/m-commerce transactions.
2. The Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 (GST): Each sales and purchase invoice shall be uploaded on one central IT infrastructure as required by this Act for each business as applicable including e-commerce/m-commerce. The Act also mandates reconciliations of transactions between business, generating tax credits on GST payments, simplifying filling of e-returns, etc.
3. Companies Act, 2013: Companies Act, 2013, regulates the Companies- business sector, defining the regulations applicable on the companies incorporated in India. Companies – both private and public, are the major merchants in e-commerce/m-commerce business.
4. Indian Contract Act, 1872: Essentials of a valid contact are define in this Act which are important in case of e-commerce/m-commerce business transactions.
5. Factories Act, 1948: This Act covers and regulates the working conditions of the workers along with place of storage and transportation; which are necessary for the merchants in e-commerce/m-commerce business to comply with.
6. Custom Act, 1962: This act provides for levy of customs duty on the import/export of goods/’services from India. Being a signatory to WTO’s GATT – World Trade Organizations General Agreement on Trade and Tariff, customs duty can only be levied on GATT compliant transactions leaving it as one of the most debatable subject across globe.
7. Competition Act, 2002: It is a law that ensures that the merchants are not engaging in predatory practices that have adverse effect on competition in India.
8. Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA 1999): It is an Act which regulates the flow of foreign exchange in India by monitoring the foreign direct investments which has direct implications on e-commerce and m-commerce business activities. Foreign Investments in B2C e-commerce activities is regulated so as to undertake retail trading through e-commerce through:
- Selling of manufactured products through retail by a manufacturer.
- A physically present single brand entity operating stores, is permitted to undertake retail trading through e-commerce.
- Sells through e-commerce retail, an Indian manufacturer should be a company of brand who invests and manufactures at least 70% worth value and source’s through at least 30% from Indian manufacturers.
9. Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Act, 1992: An Act enhances foreign trade by easing imports into, increasing exports and incidental matters thereto. Amazon has given access to Indian buyers to its global stores for purchases.
10. Consumer Protection Act, 1986: This act enables to protect rights of consumers for transactions done through e-commerce and m-commerce through litigations.
![]()
Question 12.
Subsequent to demonetization, one of your elderly neighbour, who was using traditional digital methods of making payments like cards, net banking etc., asked for your help to know about the various new’ methods of Digital Payments. Identify and explain various new methods of Digital – Payments for him. (Nov. 2018; 6 Marks)
Answer:
NEW METHODS OF DIGITAL PAYMENT:
- Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD):
- Making payments through mobiles is an innovative idea where there is no need for a smart phone or internet. A basic phone is sufficient for making payments.
- A mobile banking based digital payment mode is USSD banking or 99# Banking.
- USSD banking is as easy as checking of mobile balance.
- User can use this service for many financial and non-financial operations, to name a few checking balance, sending money, changing Mobile Banking Personal Identification Number (MPIN)
- Mobile Wallets:
- Storing paYment card information on a mobile device is defined as virtual wallets.
- User can make-in-store payments through Mobile wallets, through merchants who are listed with such service providers.
- To name a few, Paytm, Freecharge, Buddy, MobiKwick etc. are some wallets which are either owned by banks or by private companies.
- Aadhaar Enabled Payment Service (AEPS):
- AEPS is an Aadhaar based digital payment mode which is being planned to launch soon by Government of India in near future. Once launched it can be used at Point of sale terminal also.
- Customer would need only his or her Aadhaar number to pay to any merchant and also allows bank to bank transactions.
- Customers will need to link their AADHAAR numbers to their bank accounts after which through AEPS money will get deducted from their account and will get credited to the payee’s account directly.
- Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) :
- It is an instant interbank electronic fund transfer service through mobile phones also now being extended covering other channels such as ATM, Internet Banking, etc.
- Mobile Apps:
- E-payments are now facilitated directly through all Indian banks using Unified Payment Interface. This is being done using a mobile App -BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money) developed by National payments Corporation of India (NPCI) which is based on UPI.
- It is built on the Immediate Payment Service infrastructure which allows the user to instantly transfer money between the bank accounts of any two parties.
- BHIM works on all mobile devices and enables users to send or receive money to other UPI payment addresses by scanning QR code or using account number with Indian Financial Systems Code (IFSC) code or MMID (Mobile Money Identifier Code for users who do not have a UPI-based bank account.
- UPI Apps:
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI) and retail payment banks are Changing the very face of banking in terms of moving most of banking to digital platforms using mobiles and apps.
- UPI is a system that powers multiple bank accounts (of participating banks), several banking services features like fund transfer, and merchant payments in a single mobile application.
- UPI or unified payment interface is a payment mode which is used to make fund transfers through the UPI mobile apps between two accounts.
- User must register for mobile banking to use UPI apps which is currently available only through android phones.
- User need to download a UPI app and create a VPA or UPI ID.
- There are too many good UPI apps available such as BHIM, SBI UPI app, HDFC UPI app, Mobile, PhonePe app etc.
![]()
Question 13.
What are the Drawbacks of Digital Payments?
Answer:
Every coin has two sides so as the digital payments. Despite many advantages, digital payments have a few drawbacks also.
- Difficult for a Non-technical person: As most of the digital payment modes are based on mobile phone, the internet and cards. These modes are somewhat difficult for non-technical persons such as farmers, workers etc.
- The risk of data theft: There is a big risk of data theft associated with the digital payment. Hackers can hack the servers of the bank or the E- Wallet a customer is using and easily get his/her personal information. They can j use this information to steal money from the customer’s account.
- Overspending: One keeps limited cash in his/her physical wallet and hence thinks twice before buying anything. But if digital payment modes are used, one has an access to all his/her money that can result in overspending.
Question 14.
Explain in brief Virtualization.
Answer:
- Core concept of Virtualization is Partitioning, in which single physical server is divided into multiple logical servers.
- Example of Virtualization – Partitioning of a hard drive because one drive is partitioned to create many hard drives.
- Virtualization basically means creating virtual version of a device such as a server, storage device, network.
- Technologies are designed to provide a layer of abstraction between hardware systems and the software.
- Virtualization allows users to run various operating systems at the same time on a single machine i.e computer/server.
- After that, each logical server can run an operating system and applications on their own.
![]()
Question 15.
Discuss various application areas of ‘Virtualization’. (Nov. 18; 4 Marks)
Answer:
1. Server Consolidation: Many physical servers are consolidated into Few Servers by using Virtual Machines. This in turn host virtual machines. Each physical server is imitated as a virtual machine “guest”. This is correspondingly known as “Physical-to-Virtual” or ‘P2V’ transformation.
2. Disaster Recovery: Virtual machines may be used as “hot standby” environments for physical servers. This deviates from the classical “backup-and-restore” philosophy, with the help of providing backup images.
3. Testing and Training: Root access to the virtual machine is given by way of virtualization making it as useful just like in operating system courses and kernel development.
4. Portable Applications: Running of an application can be done through Portable applications from a removable drive, without installing it on the system’s main disk drive. Summarizing the application can be done through Virtualization and not within the system’s permanent file system, it not only stores temporary files with a redirection layer but also windows registry entries and other state information in the application’s installation directory.
5. Portable Workspaces: Portable workspaces have been created on devices like ipods and USB memory sticks using virtualization.
Question 16.
What are the Common Types of Virtualization?
Answer:
Hardware Virtualization:
- Hardware Virtualization separates the Software executed on these virtual machines from the underlying hardware resources.
- Virtual machines acts like a real computer with an operating system, this is created by Virtualization or Platform Virtualization.
- For- example A computer with the Linux operating system-based software can be hosted and run on the virtual machine by a computer that is running Microsoft Windows.
- The processor can be used more effectively through hardware virtualization as it consolidates many small physical servers into one large physical server.
- Creation of a virtual machine on the host hardware is done by a soft ware called hypervisor or Virtual Machine manager.
- The hypervisor allows several different operating systems to run on the same machine without the need for a source code and controls the processor, no more and other components.
![]()
Network Virtualization:
I. Administrators are able to improve Network traffic control, enterprise and security due to such behavior of network virtualization. Platform virtualization is often combined with resource virtualization in network virtualization.
2. Network virtualization splits up the available bandwidth into channels to combine the available resources in the network. Each such channel is independent from the others, and can be assigned (or reassigned) in real time to a particular server or device.
3. Reliability, flexibility, scalability, security and optimized network speed is the core purpose of network virtualization.
4. Combination of any of following for network virtualization is offered by various equipment’s and software vendors
- Networks such as virtual LANs (VLANs);
- Network storage devices;
- Network hardware such as switches and network interface cards (NICs);
- Network elements such as firewalls and load balancers;
- Network machine-to-machine elements such as telecommunications devices;
- Network mobile elements such as laptop computers, tablet computers, smart phones.
Storage Virtualization:
- Pooling of data from multiple and different types of storage devices into an apparent single device that is managed from central console is done through storage virtualization.
- The tasks of backup, archiving, and recovery more easily – and in less time is performed by the storage administrator with the help of storage virtualization, by disguising the actual complexity of a Storage Area Network (SAN)
- Virtualization can be implemented with software applications or by using hardware and software hybrid appliances; by the administrators.
- “Abstracting the logical storage from the physical storage is what Storage virtualization is every so often described as.
- Where the data really is; is not known by the servers connected to the storage system.
![]()
Question 17.
Describe the Application Areas of Grid Computing.
Answer:
- Service provider offloads the excess load to another provider.
- Large-scale science and engineering are done with the help of interaction of people, heterogeneous computing resources and information systems.
- Insurance company mines data from partner hospitals which helps to detect fraud.
- Civil engineers collaborate among themselves to design, execute shake table experiments.
- Enterprise configures resources to support the workload of E-businesses.
Question 18.
Explain Grid Computing Security.
OR
Prepare a list of constraints that are required to develop Grid Computing Security.
Answer:
A list of constraints that are required to develop Grid Computing Security are:
- Single Sign-on: Firstly, a user need to authenticate and then the users should be able to acquire resources, use resources, and release the resources after completion of the work.
- Protection of Credentials: i.e. Protection of passwords and private- keys.
- Interoperability with local security solutions: To access the local resources there should be local security policy. This local security policy is present at local level. There is an inter-domain security server which provides security to local resource.
- Exportability: They cannot use large amount of encryption at a time. And there must be minimum communication at a particular point of time.
- Support for secure group communication: There are number of processes which coordinate the activities in a communication. This coordination among the processes must be secure.
- Support for multiple implementations: A security policy must give security to multiple sources. This security policy is based on public and private key cryptography.
![]()
Question 19.
Ms. Y is using Google Apps through which she can access any application, service and data storage facilities on the Internet and pay as-per usage. Analyze which computing model is providing her these facilities. Also, determine the model’s key characteristics. (MTP)
OR
What are the Characteristics of Cloud Computing?
Answer:
Cloud computing model is the model which provides the facility to access any application, service and data storage facilities on the Internet and on pay as-per-usage.
Thus, we can say that Ms. Y is using the Cloud Computing model.
The following is a list of characteristics of a cloud-computing environment:
- On-demand:
- We use cloud services only when required. Therefore, they are not permanent parts of the infrastructure of Information technology.
- Under this, there is no need to have dedicated resources which are waiting to be used.
- Multi-Tenancy:
- Within the similar kind of infrastructure, Service Providers can host the cloud services for multiple users.
- Server and storage isolation can be physical or virtual.
- Elasticity and Scalability:
- Cloud computing provides ability to increase and reduce resources according to the requirement of the services.
- Example: we sometimes need large number of server resources to perform a specific tasks. After the completion of the task, we can then release these server resources.
- Workload Movement:
- In this, cloud-computing providers can migrate workloads across the servers (inside data centers and outside data centers)
- This migration can be necessitated:
- by cost
- efficiency considerations
- regulatory considerations
- Pay-per-Use:
Payment for cloud services as per the usage which can be for short term or for long term. - Resiliency:
This can completely isolate the failure of server and storage resources from cloud users.
With or without user awareness; Work can be migrated to a different physical resource within cloud.
![]()
Question 20.
What is Private cloud?
Answer:
- Alternative name of Private clouds are Internal Clouds or Corporate Clouds.
- Private clouds are built by IT departments within enterprises.
- It basically resides within the boundaries of an organization
- IT Department generally strive to optimize utilization of infrastructure resources within the enterprise.
- It is used primarily for the organization’s benefits.
- Private Clouds can either be:
- managed by the single organization (On-Premise Private Cloud) or
- can be managed by third party (Outsourced Private Cloud)
![]()
Question 21.
What do you understand by Public cloud?
Answer:
- They are basically used by the general public.
- Alternative name of Public clouds are Provider Clouds.
- They are basically owned, managed, and operated by a business house, academic institutions, or government and its organizations.
- They are basically administrated and managed by third parties or vendors with the help of Internet.
- Offering of services is on pay per use basis.
- Public cloud consists of users from all over the world under which user can simply purchase resources on pay per usage basis.
Question 22.
Write a short note on Hybrid Cloud.
Answer:
- This is a combination of both at least one private (interna!) and at least one public (external) cloud computing environments – usually, consisting of infrastructure, platforms and applications.
- The usual method of using the hybrid cloud is to have a private cloud initially, and then for additional resources, the public cloud is used.
- The hybrid cloud can be regarded as a private cloud extended to the public cloud and aims at utilizing the power of the public cloud by retaining the properties of the private cloud.
- It is typically offered in either of two ways:
(a) A vendor has a private cloud and forms a partnership with a public cloud provider or
(b) a public cloud provider forms a partnership/franchise with a vendor that provides private cloud platforms.
![]()
Question 23.
What is Community Cloud?
Answer:
- The community cloud is the cloud infrastructure that is provisioned for exclusive use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns (e.g. mission security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations).
- It may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises.
- In this, a private cloud is shared between several organizations.
- This model is suitable for organizations that cannot afford a private cloud and cannot rely on the public cloud either.
Question 24.
The Prime Minister Office of a country X plans to establish specific infrastructure setup with its access shared amongst members of the group constituting of some selected high-profiled dignitaries and officers from different ministries. The objective of the group is to carry out certain 1 assignments related to nation’s security and integrity. Which is the most suitable choice of the cloud under Cloud Computing? Discuss its advantages and limitations as well. (RTP Nov. 2019)
Answer:
- Community Cloud is the cloud infrastructure which is specifically most suitable for organisations having shared concerns binding them into exclusive community of consumers.
- To name a few mission security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations. Thus community cloud is the most suitable choice given the above mentioned situation.
- It is a cloud which exists both on or off premises and any one or more organizations in the community, a third party or a mixture of them can own, manage and operate the same.
- In Community cloud typically a private cloud is shared amongst the several organization.
- Since community clouds arc shared amongst the organization it is the best choice for the organizations who are not willing to spend on private clouds and are reluctant to use public cloud.
Advantages of Community Cloud as mentioned below:
- Let’s create the organisation a low-cost private cloud.
- Facilitates collaborative work amongst the cloud users
- Responsibilities are shared among the organizations.
- In terms of security it is better than the public cloud.
Every cloud has its limitations too and therefore so has Community Cloud. Major limitation being that the independence of the organisation is compromised and the security features to are not as promising as private cloud. Therefore it is unsuitable for the organisations who are not willing to associate or collaborate.
![]()
Question 25.
ABC university wants to conduct online exams for its different I courses for which a contract is given to vendor XYZ. The vendor provides computing resources such as processing power, memory, storage, and networks to ABC university users to run their online exam application on-demand. Identify the Service Model of Cloud Computing that vendor XYZ is providing to ABC university and also describe its characteristics. (RTP May 2020)
Answer:
Service Model of Cloud Computing that vendor XYZ is providing to ABC university is Infrastructure as a Service.
Characteristics of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) of Cloud Computing are:
- Shared infrastructure: One to many delivery model is being followed by IaaS. It permits many IT users to share same infrastructure. By doing this, there is increased utilization of resources.
- Metered Services: The users need not buy the computing resources, and the computing resources can be taken on rent. Services consumed are measured, and users are charged accordingly on the basis of usage.
- Web access to the resources: Infrastructure resources can be accessed on internet, but the IT user may not get physical access to the servers.
- Centralized Management: Management console controls the computing resources which are distributed across. This ensures effective utilization and management of resources.
- Elasticity and Dynamic Scaling: According to the requirements, the usage of resources can be expand or reduced.
Question 26.
Discuss the Components of Mobile Computing.
Answer:
The three vital components of Mobile Computing are as follows:
- Mobile Communication:
- An uninterrupted and consistent communication is ensured in mobile computing infrastructure.
- Communication properties, protocols, data formats and concrete technologies are included.
- Mobile Hardware:
- Mobile devices or device machineries that receive or admits the service i of mobility are included in Mobile hardware ranging from Portable j laptops, Smart Phones, Tablet PCs, and Personal Digital Assistants ! (PDA) which uses the prevailing recognized network to work on.
- The communication between the internet and intranet infrastructure through handheld device is possible through backend servers like Application Servers, Database Servers and Servers with wireless support, WAP gateway, a Communications Server and/or MCSS (Mobile Communications Server Switch) or a wireless gateway embedded in wireless carrier’s network.
- The features of mobile computing hardware are defined by the size and form factor, weight, microprocessor, primary storage, secondary storage, screen size and type, means of input, means of output, battery life, communications capabilities, expandability and durability of the device.
- Mobile Software:
- The mobile hardware runs on Mobile Software which deals with the features and necessities of mobile applications.
- The most crucial component that operates the mobile device is the operating system of that appliance.
- For customers use organizations are developing mobile applications commonly called Apps. However, these apps could denote risk of flow of data, personal identification risks, introduction of malware and access to personal information.
![]()
Question 27.
Mobile computing is an important and rapidly evolving technology | that allows users to transit data from remote location to other locations ) in mobility condition.
Being a communication expert, identify the limitations in current scenario | that impede or hesitate users to use this technology frequently. (May 2019; 8 Marks)
Answer:
- TRANSMISSION INTERFERENCES:
- The signal reception can be interfered with nearest signal point due to weather, landscape and so on.
- Also the reception is poor in certain tunnels, buildings, and rural areas.
- INSUFFICIENT BANDWIDTH:
- Mobile Internet access is generally not as fast as direct cable connections using technologies such as General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and Enhanced Data for GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) Evolution (EDGE), and more recently 3G networks.
- These networks are usually available within range of viable cell phone towers. Higher speed wireless LANs are low-priced but have very restricted range.
- SECURITY STANDARDS:
- When working mobile, one is at the mercy of on public networks, requiring cautious use of Virtual Private Network (VPN).
- Safety and security is a key apprehension while concerning the mobile computing standards. One can effortlessly attack the VPN through a huge number of networks interconnected through the line.
- POWER CONSUMPTION:
- When a power outlet or portable generator is not available, mobile computers required to depend completely on battery power.
- Combined with the compact size of many mobile devices, this often means unusually costly batteries must be used to attain the required battery life. Mobile computing should also look into Greener IT in such a way that it saves the power or increases the battery life.
- POTENTIAL HEALTH HAZARDS:
- People who use mobile devices while driving are habitually unfocused from driving are thus supposed to be more likely involved in traffic accidents.
- Cell phones may interfere with sensitive medical devices. There are claims that cell phone signals may cause health problems.
- HUMAN INTERFACE WITH DEVICE: Screens and keyboards tend to be small, which may make them tough to use. Another input methods such as speech or handwriting recognition require training.
![]()
Question 28.
Write a short note on green it/Green computing.
Answer:
- The study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT is referred to as Green Computing or Green IT.
- In other words, it is the study and practice of creating/using computers and IT resources in a more effective and ecologically friendly and accountable way.
- Computers consume a lot of natural resources from raw materials to power in manufacturing and using them along with the difficulties of disposing them at the end of their life cycle.
- It includes “designing, manufacturing, using, and disposing of computers, servers, and associated subsystems such as monitors, printers, storage devices, and networking and communications systems – efficiently and effectively with minimal or no impact on the environment’.
- The objective of Green computing is:
- to diminish the use of dangerous materials,
- maximize energy productivity during the products period, and
- promote the recyclability or biodegradability of non-operational products and factory leftover.
Question 29.
Every business decision is accompanied with a set of threats and so is BYOD program. Explain briefly the areas in which the risks associated with BYOD program can be classified. (Nov. 2019; 4 Marks)
Answer:
Every business decision is accompanied with a set of threats and so is BYOD program too; it is not immune from them. As outlined in the Gartner survey, a BYOD program that allows access to corporate network, emails, client data etc. is one of the top security concerns for enterprises. Overall, these risks can be classified into four areas as outlined below:
- Device Risks:
- It is illustrated and hidden in ‘Loss of Devices’.
- There can be massive monetary and reputational embarrassment to the entity due to lost device because such devices may be holding critical and sensitive corporate information.
- It is ranked as the top security threats by Cloud Security Alliance.
- With easy access to company emails as well as corporate intranet, company trade secrets can be easily retrieved from a misplaced device.
- Application Risks:
- It is illustrated and hidden in ‘Application Viruses and Malware’.
- It is noticed that many of phones and smart devices of personnel which are connected to the corporate network are not protected by an appropriate security software.
- With enormous rise in mobile usage, there is rise in mobile vulnerabilities.
- Network Risks:
- It is illustrated and hidden in ‘Lack of Device Visibility’.
- In case of company-owned devices are used by personnel within organization, the organization’s IT Team has broad visibility of the devices connected to the network.
- But the problem comes, as BYOD permits employees to carry their own devices; the IT Team is not aware about the number of devices being connected to the network.
- And if a virus hits the network and all devices which are connected to the network need to be scanned, there might be some devices which may miss out on this routine scan operation.
- Implementation Risks:
- It is illustrated and hidden in ‘Weak BYOD Policy’.
- If there is no strong BYOD policy, the employee’s expectations will not be communicated appropriately.
- BYOD program should cover the technical issues and also mandate the development of a robust implementation policy.
- Also, weak policy fails to educate the user which leads to increase in vulnerability.
![]()
Question 30.
Recognize the application areas where the concept of Internet of Things (IoT) has been implemented.
OR
Write any two Application Area of Internet of Things (IoT). (May 2019; 2 Marks)
Answer:
- Home Appliances like CCTV can be managed and regulated through hand help devices.
Owners may keep the track with the help of hand held smart devices of all activities of home. - OFFICE MACHINES can be interconnected through internet.
(a) Managers will be able to see how many consume cup of coffee from vending machine.
(b) Number of printouts being generated through office printer? - GOVERNMENTS may keep a track of resource utilizations.
Under SWACHH BHARAT mission government can tag all dustbins with IOT sensors. Once dustbins get full, they generate a message which will inform the cleaning supervisor of Municipality and the Bin j can be emptied.
Question 31.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Answer:
- Intelligence is defined as ability to use
- understanding, knowledge, memory, reasoning,
- experience, imagination and judgment
- It is used basically to solve the problems and take decisions accordingly.
- Above abilities when revealed by machines is called as Artificial intelligence (AI).
- It is an intelligence which is exhibited by machines.
- For example:
- Used in autonomous vehicles, Google cars.
- Apple online assistant SIRI is a good example.
![]()
Question 32.
What is Machine Learning?
Answer:
- In machine Learning, Computers gets the ability to learn without being programmed.
- It is a type of Artificial Intelligence.
- It basically focus on the development of computer programs which may change when it is exposed to new data.
- Process of Data mining and Machine Learning are similar.
- For example:
- Machine learning is being used for videos, images, and text recognition. Apple SIRI is a good example for Machine Learning.
- This technology is also used in autonomous vehicles, the google cars.