Corporate Level Strategies – CA Inter SM Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Corporate Level Strategies – CA Inter SM Question Bank
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of following concepts:
Directional Strategies (May 2012, 1 mark)
OR
Explain the meaning of Directional Strategy. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
According to Glueck and Jouch, there are four Generic Strategic Alternatives:
They are:
(a) Stability Strategy
(b) Expansion Strategy
(c) Detriment Strátegy
(d) Combination Strategy
These are the business strategies to provide basic direction for strategic actions towards achieving long terms business objectives and hence known as directional strategies.
Question 2.
Discuss the broad areas In which Functional Strategies of a business organization is carried out. (Nov 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Once higher level corporate and business strategies are developed, management need to formulate and implement strategies for each functional area. For effective implementation, strategists have to provide direction to functional management depends critically on the manner in which strategies are implemented.
Functional area strategy such as marketing, financial, production and human resource are based on the functional capabilities of an organisation. For each functional area, first the major sub areas are Identified and then for each of these sub functional areas, contents of functional strategies, important factors, and their Importance In the process of strategy
implementation is identified.
In terms of the levels of strategy formulation, functional strategies operate below the SBL or business-level strategies, within functional strategies there might be several sub-functional areas. Functional strategies are made within the higher level-strategies and guidelines therein that are set at higher levels of an organisation. Functional managers need guidance from the business strategy in order to make decisions. Operationals plans tell the functional managers, what has to be done while policies state how the plans are to be implemented.
Question 3.
Briefly answer the following:
Grand Strategy Alternative during Recession (May 2010, 2 marks)
Answer:
Stability Strategy is a recommendable option for the organisations facing recession. During recession businesses face reduced demand for their products even at low prices. Funds capital become scarce, expenditure on expansion is stopped, profits decline and businesses try to minimise the costs. They work hard to maintain the existing market share, so that
company survives the recessionary period.
![]()
Question 4.
State with reason which of the following statements is correct or Incorrect. Stability strategy is not a do-nothing’ strategy. (May 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct:
Stability Strategy is not a ‘do-nothing’ strategy. Stability is important goal of business enterprise to safeguard its existing interests and strengths, to pursue well-established and tested objectives, to continue in the chosen business path, to maintain operational efficiency on sustained basis.
Question 5.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct/incorrect:
Acquisition is a strategy. (Nov 2007, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct:
Acquisitions provide a rapid means of gaining an established product/market position. Acquisitions may be a particularly attractive means of corporate development under certain strategic and financial conditions. In mature industries containing a number of established firms, entry through acquisition can avoid the competitive reaction that can accompany attempts to enter the industry by internal development: rather than intensifying the rivalry by adding a further player, the potential competition is purchased.
In other industries in which competitive advantage rests In assets built up over considerable periods of time acquisitions can Immediately achieve a market position that could be virtually impossible to develop internally. For example, Sony, the Japanese electronics.
Question 6.
Briefly answer the following:
That is meant by Concentric diversification? (Nov 2007, 2 marks)
Answer:
Concentric or Heisted Diversification:
When an organization takes up an activity related to its existing business definition or one or more of a firms businesses in terms of customer groups, customer functions or alternative technologies, it is called concentric diversification.
Concentric diversification occurs when a firm adds related products or markets. The goal of such diversification is to achieve strategic fit. Strategic fit allows an organization to achieve synergy. In essence, synergy is the ability of two or more parts of an organization to achieve greater total effectiveness together than would be experienced if the efforts of the independent parts were summed. Synergy may be achieved by combining firms with complementary marketing, financial, operating, or management efforts.
Question 7.
Differentiate clearly between forward and backward integration. (May 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
Forward and backward integration form a part of vertically integrated diversification. In this firms opt to engage In those businesses that are vertically related to the existing business of the firm. For increasing the business, firms engaged in those businesses that are linked forward or backward in the chain and make specific product process with the intention of making them into the new business for the firm.
Difference between Forward and Backward Integration
| Basis of Difference | Forward Integration | Backward Integration |
| Meaning | Forward integration is moving forward in the value chain and entering in the business that use existing products. Forward integration will also take place where organisations enter into business of distribution channels. | Backward integration is a step towards, creation of effective supply by entering into the existing business to expand profits and gain greater control over production. |
| Focus | When companies are looking forward they are usually looking to expand their distribution or improve the placement of their products, stated differently, forward integration focuses on the manner in which a company oversees its product distribution. | Backward movement usually involves internal steps to reduce overall dependency on things like suppliers and service providers. It thus concentrates on how a company regulates its goods and supplies. |
Question 8.
Explain the meaning of the following strategies and also give suitable examples (on each):
(i) Forward Integration
(ii) Backward Integration
(iii) Horizontal Integration
(iv) Conglomerate Diversification
(v) Divestment
(vi) Liquidation
(vii) Concentric Diversification (Nov 2010, 7 marks)
Answer:
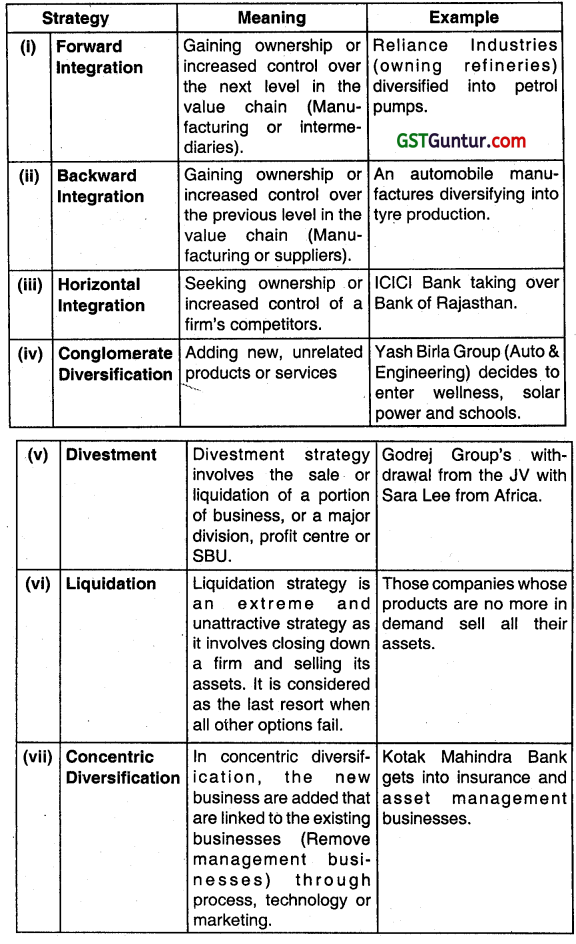
Question 9.
Distinguish between the following:
Concentric Diversification and Conglomerate Diversification. (Nov 2011, Nov 2013, May 2016, 3, 4 marks)
Answer:
| Basis of Difference | Concentric Diversification | Conglomerate Diversification |
| 1. Occurrence | Concentric diversification occurs when a firm adds related products or markets. | On the other hand conglomerate diversification occurs when a firm diversifies into areas that are unrelated to Its current line of business. |
| 2. Linkages | In centric diversification the new business is linked to the existing businesses through process, technology or marketing. | In conglomerate diversification, no such linkages exist; the new business/product Is disjointed from the existing businesses/ products. |
| 3. Reason | The most common reasons for pursuing a concentric diversification are that opportunities in a firm’s existing line of business are available. | Common reasons for pursuing a conglomerate growth strategy is that opportunities in a firm’s current line of business are limited or opportunities outside are highly lucrative. |
![]()
Question 10.
Distinguish between the following:
Vertically integrated- Diversification and Horizontally Integrated DiversIfication. (Nov 2012,3 marks)
Answer:
Vertically integrated Diversification
In vertically integrated diversification, firms opt to engage in businesses that are related to the existing business of the firm. The firm remains vertically within the same process.
Horizontally Integrated Diversification
Under horizontal Integrated Diversification, diversification takes place through the acquisition of one or more similar businesses operating at the same stage of production- marketing chain that is going into complementary product by product or taking over competitors’ products.
Question 11.
What is meant by backward integration? Name any two backward integration strategies that hospitals may pursue. (Nov 2014, 1 + 2 = 3 marks)
Answer:
‘Backward Integration
Backward integration is a form of vertical integration that involves the purchase of, or merger with, suppliers up the supply chain. Companies pursue backward integration when it is expected to result in improved efficiency and Cost savings. This type of integration might cut transportation costs, improve profit margins and make the firm more competitive.
Backward Integration Strategies Pursued by Hospitals
1. Health plans: It’s hard to imagine improving the medical marketplace until hospitals and health plans work together to build an efficient and effective delivery system. The potential benefits of provider-payer collaboration surely will come sooner if both parties contribute their unique and complementary. expertise according to the economic law of comparative advantage. With very few exceptions, hospitals don’t have the resources or skills to start their own insurance companies, nor are insurance companies generally competent to provide health services. They need each other to succeed in the new marketplace, but other partners must also be at the table to prevent harmful collusion.
2. Medical groups:
Physician relations are surely a close No.2 on the list of threats to providers’ viability. Hospitals can’t exist without a medical staff, but many physicians can be successful without a hospital. However, hospitals have much boiler access to capital and can create the technological infrastructure needed to support 21st-century health care. In return, physician leaders need to help steer hospitals away form their focus on inpatient care Physician-hospital integration should be structured to build a better health system.
Question 12.
Write short note on the following:
Expansion through acquisitions and mergers. (Nov 2014, 3 marks)
Answer:
Expansion Strategies are used to expand firms’ operations by adding markets, products, services, or stages of production to the existing business. The purpose of diversification is to allow the company to enter tines of business that are different from current operations. When the new venture is strategically related to the existing lines of business, it is called co-centric diversification. Conglomerate diversification occurs when there is no common thread of strategic fit or relationship between the new and old lines of business; the new and old businesses are unrelated.
External diversification occurs when a firm looks outside of its current operations and buys access to new products or markets. Mergers are one common form of external diversification. Mergers occur when two or more firms combine operations to form one corporation, perhaps with a new name.
These firms are usually of similar size. One goal of a merger is to achieve management synergy by creating a stronger management team. This can be achieved In a merger by combining the management teams from the merged firms.
Acquisitions, a second form of external growth, occur when the purchased corporation loses Its identity. The acquiring company absorbs It. The acquired company and its assets may be absorbed Into an existing business unit or remain intact as an Independent subsidiary within the parent company. Acquisitions usually occur when a larger firm purchases a smaller company. Acquisitions are called friendly if the firm being purchased is receptive to the acquisition. (Mergers are usually “friendly”.) Unfriendly mergers or hostile takeovers occur when the management of the firm targeted for acquisition resists being purchased.
Question 13.
Write short note en the following:
Conglomerate Merger. (May 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
Conglomerate Merger:
Mergers occur when two or more firms combine operations to form one corporation, perhaps with a new name. These firms are usually of similar size. One goal of a merger is to achieve management synergy by creating a stronger management team. This can be achieved in a merger by combining the management teams from the merged firms.
Conglomerate Mergers are the combination of Firms that are unrelated to each other. There are no linkages with respect to customer groups, customer functions, and technologies being used.
There are no important common factors between the organizations in production, marketing, research and development, and technology. In practice, however, there Is some degree of overlap in one or more of these factors.
![]()
Question 14.
A Bakery starts producing pastries and other similar products. What type of diversification strategy ¡s being followed by it and why? (Nov 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
A diversification strategy should be pursued only after a careful study of buyers’ needs and preferences to determine the feasibility of incorporating one or more differentiating features into a unique product that features the desired attributes. A successful differentiation strategy allows a firm to charge a higher price for Its product and to gain customer loyalty because consumer may become strongly attracted to differentiation features.
Here a backery starts producing pastries and similar products then first it should study the buyers needs and preferences that what the buyers like to eat and what kind of products the buyers like.
The backery should also take into the consideration that they should make their product unique than the other seller. This is because the consumer attracts the unique feature of Backery’s products and allows the firm to charge the prices of the products. It should follow concentric diversification strategy because of above reasons.
Question 15.
Identify with reasons the type of growth strategies followed in the following cases:
(i) A leading producer of confectionery products advertising the new uses of its product ‘Chokoo Mix’ aggressively.
(ii) A company in publishing industry deciding to revise college textbooks.
(iii) A renowned company in textile industry starting to manufacture PFY and PSF. critical raw materials for textiles,
(iv) A business giant in auto manufacturing enters into edible oils, hotels, financial services, and dairy businesses. (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) The Producer Is Following Market PenetratIon Growth Strategy.
- Market Penetration is growth strategy where business focuses on selling existing products In the existing market. It is achieved by making more sales to present customers without changing products in any major way. It is done by more advertisement.
- Here, the producer of confectionary products advertising the new uses of its existing product in existing market. So, the product and market are same as previously so producer is following market penetration growth strategy.
(ii) The company here follows product Development Growth Strategy:
- Product development refers to a growth strategy where business aims to introduce new product in market.
- Here the company In publishing industry decides to revise product text books in market. So it is following product development growth strategy.
(iii) The company has adopted Backward Integration Growth Strategy under vertically integrated diversification. Since it has started with manufacture of critical raw materials it will ensure uninterrupted supply of critical raw materials and also ensure that company retains the margins in dealing with raw materials which otherwise would have gone to its suppliers.
(iv) Here the company Is following the DIversifIcation Growth Strategy.
- Diversification growth strategy refers to the strategy where a business markets produces new products in new markets.
- Here a business grant in auto manufacturing enters into edible oils hotels, financing and dairy services so It produces new products and serves totally new customers.
Question 16.
What is expansion strategy? State and discuss briefly in few lines each the two types of expansion strategies followed by firms. (Nov 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Meaning of Strategy
The term strategy is derived from the Greek word strategos’ which means generalship – the actual direction of military force.
Expansion Strategy
Every organization plans to expand. An organization that is not expanding is said to be falling behind. Expansion strategy is followed when an organization broadens the scope of one or more of its businesses in order to improve Its overall performance.
Reasons for Adoption:
- Growth Is often a cherished cultural value.
- In face of changing environment growth is necessary for survival.
- Increasing size may lead to more control over the market.
- Advantage from the experience curve may accrue.
Variants of Expansion Strategy:
- Intensive growth strategy.
- Diversification Strategy.
A. Horizontal diversification:
- Concentric diversification.
- Conglometric diversification
B. Vertical diversification:
- Forward Integration
- Backward integration
Intensive Growth Strategy: Consists of increasing the sales revenue profit and market share of existing product line.
Diversification Strategy:
It is a strategy in which the growth objective or expansion objective is achieved by adding new products or services to the existing product line.
Horizontal Diversification:
It consists of adding parallel new products or services to the existing product or service line.
Question 17.
Distinguish between the following:
Co-generic Merger and Conglomerate Merger (May 2017, 3 marks)
Answer:
Co-generic Merger and Conglomerate Merger
In Co-generic Merger two or more merging organizations are associated in some way orthe other related to the production processes, business markets or basic required technologies. Such mergers Include the extension of the product line or acquiring components that are required in the daily operations. It offers great opportunities to businesses to diversify around a common set of resources and strategic requirements. For example, organization In the white goods categories such as refrigerators can diversify by merging with another organization having business In kitchen appliances.
Conglomerate Mergers are the combination of organizations that are unrelated to each other. There are no linkage with respect to customer groups, customer functions and technologies being used. There are no important common factors between the organizations in production, marketing, research and development and technology. In practice, however,
there is some degree of overlap in one or more of these factors.
Question 18.
State with reasons which of the following statement Is correct or incorrect:
Expansion strategy is a highly versatile strategy. (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct:
Strategy is a highly versatile strategy: ¡t offers several permutations and combinations for growth. A firm opting for the expansion strategy can generate many alternatives within the strategy by altering its propositions regarding products, markets, and functions and picking the one that suits it most.
![]()
Question 19.
State with reasons which of the following statements is correct or incorrect:
Forward and backward integration forms part of horizontally integrated diversification. (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
Forward and backward integration forms are part of horizontally integrated diversification is incorrect. Its vertically integrated diversification. In vertically integration diversification firms opt to engage in businesses that are vertically related to the existing business of the firm.
The firm remains vertically within the same process. While diversifying firms opt to engage in businesses that are linked forward or backward in the chain and enter specific product/process steps with the intention of making them into new businesses for the firm.
Question 20.
Describe the term ‘Co-generic merger. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Co- Generic Merger:
In a Co-generic merger, two or more merging organizations are associated in some way or the other related to the production processes, business markets, or basic required technologies. Such mergers include the extension of the product line or acquiring components that are required in the daily operations. It offers great opportunities for businesses to diversify around a common set of resources and strategic requirements. for example, an organization In the white goods category such as refrigerators can diversify by merging with another organization having business In kitchen appliances.
Question 21.
List the advantages of Strategic Alliances. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Advantages of Strategic Alliance are:
- Organizational: Learn skins and obtain capabilities from strategic partners.
- Economic: Sharing of costs and risks by members of alliance.
- Strategic: Rivals can join together to cooperate rather than compete.
- Political: Alliance with partners with political influence improve overall power position of the organisation.
Question 22.
Which of the following statements are correct and which are incorrect? Give reasons In brief for your answer.
(d) Acquiring of ambulance services by a hospital is an example of forward Integration strategy. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
(e) There is no such thing as backward integration. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
(d) incorrect:
Acquiring of ambulance services by a hospital is an example of backward integration strategy.
(e) Incorrect:
Backward integration is a step towards, creation of effective supply by entering business of input providers. For example, a large supermarket chain considers to purchase a number of farms that would provide it a significant amount of fresh produce.
Question 23.
Explain the Strategic Alliance. Describe the advantages of Strategic Alliance. (Nov 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
A strategic alliance is a relationship between two or more business that enables each to achieve certain strategic objectives which neither would be able to achieve on its own. The strategic partners maintain their status, as independent and separate entities, share the benefits and control over the partnership, and continue to make contributions to the alliance until It is terminated. Strategic alliances are often formed in the global marketplace between businesses that are based in different regions of the world.
Advantages of Strategic Alliance:
Strategic alliance usually are formed if they provide an advantage to all parties in the alliance. The advantages can be broadly categorised as follows:
1. Organisational
Strategic alliance helps to learn necessary skills and obtain certain capabilities from strategic partners. Strategic partners may also help to enhance productive capacity, provide a distribution system, or extend supply chain. Strategic partners may provide a good or service that complements thereby creating a synergy. Having a strategic partner who is well-known and respected also helps add legitimacy and credit ability to a new venture.
2. Economic
There can be reduction in costs and risks by disturbing them across the members of the alliance. Greater economies of scale can be obtained in an alliance, as production volume can Increase, causing the cost per unit decline. Finally, partners can take advantages of Co-specialization, creating additional value, such as when a leading computer manufacturer bundles its desktop with a leading monitor manufacturer’s monitor.
3. Strategic
Rivals can join together to cooperate instead of compete. Vertical integration can be created where partners are part of supply chain. Strategic alliances may also be useful to create a competitive advantage by the pooling of resources and skills. This may also help with future business opportunities and the developments of new products and technologies. Strategic alliances may also be used to get access to new technologies or to pursue joint research and development.
4. Political
Sometimes strategic alliances are formed with a local foreign business to gain entry into a foreign market either because of local prejudices or legal barriers to entry. Forming strategic alliances with politically – influential partners may also he improve your own influence and position.
Question 24.
Read the following case study and answer the questions given at the end:
Meters Limited is a company engaged in the designing, manufacturing, and marketing of instruments like speed meters, oil pressure gauges, and so on, that are fitted into two and four-wheelers. Their current Investment in assets la around ₹ 5 crores and their last year’s turnover was ₹ 15 crores, just adequate enough to break even. The company has been witnessing over the last couple of years, a fall In their market share prices since many customers are switching over to a new range of electronic instruments from the range of mechanical Instruments that have been the mainstay of Meters Limited. The company has received a firm otter of cooperation from a competitor who is similarly placed in respect of product range. The offer implies the following:
- transfer of the manufacturing line from the competitor to Meters Limited;
- manufacture of mechanical instruments by Meters Limited for the competitor to the latter as specifications and brand name; and
- marketing by the competitor.
The benefits that will accrue to Meters Limited will be better utilization of its installed capacity and appropriate financial compensation for the manufacturing effort. The production manager of Meters Limited has welcomed the proposal and points out that it will enable the company to make profits. The sales manager is doubtful about the same since the demand for mechanical Instruments Is shrinking. The Chief Executive is studying the offer.
(a) What is disinvestment strategy? Do you see it being practiced in the given case? Explain. (May 2009, 5 marks)
(b) What is stability strategy? Should Meters Limited adopt it? (May 2009, 5 marks)
(c) What is expansion strategy? What are the implications for Meters Limited in case it is adopted? (May 2009, 5 marks)
(d) What is your suggestion to the Chief Executive? (May 2009, 5 marks)
Answer:
(a) Disinvestment Strategy Involves the sale or liquidation of a portion of business or a major division to a profit center organization or SBU. Divestment s usually a part of rehabilitation or restructuring plan end is adopted by those organisations which are in loss or are unsuccessful in the Market.
Yes, It is being practiced In the given case study. Here the major reason leading to disinvestment Is change in technology. Meters Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing mechanical instruments which are not In demand in the present market. So the market price of instruments is declining and the company is In a situation to withdraw itself from the market. Hence, Meter Ltd’s. a competitor is offering divestment strategy and the company is ready to adopt a proposal of the competitor to withdraw its brand name and manufacture products in the name of the competitor.
(b) Stability Strategy means sustaining moderate growth in line with the existing trends i.e. staying in the market with the same business, same product market posture and functions, and maintaining same level of effort as at present.
In the given case, the market share of Meter’s Ltd is declining day by day due to the increased demand of electronic instruments, and in this situation if the Company will adapt stability strategy It will sooner have a corporate death. So it is important for the company that it does not remain stable but take necessary steps to cope up with the changing
environment.
(c) Expansion Strategy is a true growth strategy and Involves a redefinition of the business. Expansion strategy is followed when an organisation broadens the scope of Its business in order to improve its performance.
In the given case, the market for ‘the products of Meters Ltd. is declining. So if it adopts expansion strategy It may go into mergers and acquisitions to increase its market share. The company adopts the different measures of expansion in order to maintain itself in the changing business environment.
(d) After the analysis of situation of Meters Ltd., it is advisable to adopt the expansion strategy in order to maintain their stake in the market. It is adopted because:
- It may become good when environment demands Increase In pace of activity.
- Increasing size may lead to more control over the market as compared to competitors. Chief executive shall accept the proposals to expand its market share and become a monopoly power in its own range of mechanical products.
Question 25.
Gautam and Siddhartha two brothers are the owners of a cloth manufacturing unit located in Faridabad. They are doing well and have substantial surplus funds available within the business. They have different approaches regarding corporate strategies to be followed to be more competitive and profitable in future.
Gautam is interested in acquiring another industrial unit located in Faridabad manufacturing stationery items such as permanent markers, notebooks, pencils and pencil sharpeners, envelopes and other office supplies. On the other hand, Siddhartha desires to start another unit to produce ready-made garments. Discuss the nature of corporate strategies being suggested by two brothers and risks involved In it. (May 2019,5 marks)
Answer:
In this case, Gautam and Siddhartha two brother running a cloth manufacturing unit In Faridabad, They have surplus and have different approaches between them regarding corporate strategies.
Gautam is interested in acquiring another industrial unit located In Faridabad manufacturing Stationery items such as permanent markers, notebooks, pencils, and pencil Sharpeners, envelopes, and other office supplies. So strategy adopted by Gautam is a conglomerate diversification.
Conglomerate mergers are the combination of organizations that are unrelated to each other. There are no linkages with respect to customer groups, customer functions, and technologies being used. There are no important common factors between the Organizations in production. marketing, research and development, and technology. In practice, however, there is some degree of overlap in one or more of these factors.
On the other hand, Siddhartha desires to start another unit to produce readymade garments. So strategy adopted by Siddhartha is vertically integrated diversification.
In vertically integrated diversification, firms opt to engage in businesses that are related to the existing business of the firm. The firm remains vertically within the same process sequence moves forward or backward in the chain and enters specific product process steps with the intention of making them into new businesses for the firm. The characteristic feature of vertically integrated diversification is that there, the firm does not jump outside the vertically linked product-process chain.
Risk Involved
In conglomerate diversification, there are no linkages with customer groups, customer marketing functions, and technology used, which is a risk. in the case of vertical Integrated diversification, there is a risk of lack of continued focus on the original business.
![]()
Question 30.
Discuss how mergers and acquisitions are used for business growth. What are the various types of mergers?
Answer:
Many organizations in order to achieve quick growth, expand or diversify use mergers and acquisitions strategies. Merger and acquisition in simple words are defined as a process of combining two or more organizations together. There is a thin line of difference between the two terms but the impact of combination is completely different in both the cases.
Merger is considered to be a process when two or more organizations join together to expand their business operations. In such a case the deal gets finalized on friendly terms. Owners of pre-merged entities have right over the profits of new entity. In a merger two organizations combine to increase their strength and financial gains.
When one organization takes over the other organization and controls all its business operations, it is known as acquisition. In the process of acquisition. one financially strong organization overpowers the weaker one. Acquisitions often happen during economic recession or during declining profit margins.
In this process, one that is financially stronger and bigger establishes it power. The combined operations then run under the name of the powerful entity. A deal In case of an acquisition is often done In an unfriendly manner, it is more or less a forced association.
Types of Mergers:
1. Horizontal Merger
Horizontal mergers are combinations of firms engaged in the same Industry. It is a merger with a direct competitor. The principal objective behind this type of mergers is to achieve economies of scale In the production process by shedding duplication of Installations and functions, widening the line of products, decreasing working capital and fixed assets Investment, getting rid of competition, and so on.
2. Vertical Merger
It is a merger of two organizations that are operating in the same industry but at different stages of production of distribution system. This often leads to Increased synergies with the merging firms. If an organization takes over its supplier/producers of raw materials, then It leads to backward integration. On the other hand, forward Integration happens when an organization decides to take over its buyer organizations or distribution channels. Vertical merger results In operating and financial economies. Vertical mergers help to create an advantageous position by restricting the supply of inputs or by providing them at a higher cost to other ptayers.
3. Co-generic Merger
In co-generic merger two or more merging organizations are associated in some way or the other related to the production processes, business markets, or basic required technologies. Such mergers include the extension of the product line or acquiring components that are required in the daily operations, If offers great opportunities to businesses to diversity around a common set of resources and strategic requirements. For example. an organization rnanufacturing refrigerators can diversity by merging with another organization having business In kitchen appliances.
4. Conglomerate mergers
Conglome are the combination of rate Merger organizations that are unrelated to each other. There are no linkages with respect to customer groups, customer functions, and technologies being used. There are no important common factors between the organizations in production, marketing, research and development, and technology. In practice, however, there is some degree of overlap In one or more of these factors.
Question 31.
Vastralok Ltd. was started as a textile company to manufacture cloth. Currently, they are in the manufacturing of silk cloth. The top management desires to expand the business in the cloth manufacturing. To expand they decided to purchase more machines to manufacture cotton cloth. Identify and explain the strategy opted by the top management of Vastralok Ltd.
Answer:
Vastralok Ltd. is currently manufacturing silk cloth and its top management has decided to expand its business by manufacturing cotton cloth. Both the products are similar in nature within the same Industry. The strategic diversification that the top management of Vastralok Ltd. has opted is concentric in nature. They were in business of manufacturing silk and now they will manufacture cotton as well. They will be able to use existing infrastructure and distribution channels. Concentric diversification amounts to related diversification.
In concentric diversification, the new business is linked to the existing businesses through process, technology or marketing. The new product is a spin-ott from the existing facilities and products/processes. This means that in concentric diversification too, there are benefits of synergy with the current operations.
Question 32.
What is Divestment strategy? When is It adopted?
Answer:
Divestment Strategy:
Concept
Divestment strategy involves the sale or liquidation of a portion of business, or a major division, profit center or SBU. For a multiple-product company, divestment could be a part of rehabilitating or restructuring plan called turn around.
When Adopted
- divestment strategy may be adopted due to various reasons:
- When a turnaround has been attempted but has proved to be unsuccessful.
- A business that had been acquired proves to be a mismatch and cannot be integrated within the company.
- Persistent negative cash flows from a particular business create financial problems for the whole company.
- Severity of competition and the inability of a firm to cope with it.
- Technological upgradation is required if the business is survive but where it is not possible for the firm to invest in it.
- A better alternative may be available for investment.
Question 33.
Briefly answer the following:
What is meant by retrenchment strategy? (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
Retrenchment Strategy
Meaning
Retrenchment Strategy may require a firm to redefine its business and may involve divestment of a major product line or an SBU, abandonment of some markets or reduction of its functions, Retrenchment In pace may necessitate a firm to use layoffs, reduce R&D or marketing or other outlays, increase the collection of receivables etc. The efforts aimed at redefining the business and reducing the pace of activities can improve performance of a firm. Retrenchment In combination with expansion is not uncommon. Retrenchment alone is probably the least frequently used generic strategy.”
Reasons for following Retrenchment Strategy
- The firm is doing poorly.
- If there is pressure from various groups of stakeholders to improve performance.
- If better opportunities of doing business are available else where a firm can better utilize its strengths.
Question 34.
Under what conditions would you recommend the use of Turn around strategy in an organisation? What could be a suitable work plan for this? (May 2008, 5+5=10 marks)
Answer:
Turnaround Strategies
Meaning
Retrenchment may be done either internally or externally. For Internal retrenchment to take place, emphasis is laid on improving internal efficiency, known as turnaround strategy. The overall goal of turnaround strategy is to return an underperforming or distressed company to normalcy in terms of acceptable levels of profitability, solvency, liquidity, and cash flow.
In order to achieve its objectives, turnaround strategy must reverse causes of distress, resolve the financial crisis, achieve a rapid improvement in financial performance, regain stakeholder support, and overcome internal constraints and unfavorable industry characteristics.
Condition or Indicators
There are certain conditions or indicators which point out that a turnaround is needed If the organization has to survive. Those danger signs are:
- Persistent negative cash flow
- Negative profits
- Declining market share
- Deterioration, in physical facilities
- Overmanning, high turnover of employees, and low morale
- Uncompetitive products or services
- Mismanagement
Focus
For turnaround strategies to be successful, it is imperative to focus on the short and long-term financing need as well as on strategic issues. A workable action plan for turnaround should include:
- Analysis of product, market, production processes, competition and market segment positioning.
- Clear thinking about the marketplace and production logic.
- implementation of plans by target-setting feedback, and remedial action.
Elements Contributing towards Turnaround
A set of ten elements that contribute to turnaround are:
- Changes in the top management
- Initial credibIlity – building actions
- Neutralising External Pressures
- Internal control
- Identifying quick pay-off activities
- Quick cost reductions
- Revenue generation
- Asset liquidation for generating cash
- Mobilization of the organizations
- Better internal coordination.
Question 35.
Briefly answer the following:
Need for Turnaround Strategy (May 2010, 2 marks)
Answer:
Need for Turnaround Strategy:
Need for Turnaround Strategy is when an enterprise’s performance deteriorates to a point that it needs a radical dange of direction in strategy, and possibly in structure and culture as well. A turnaround strategy is a highly targeted effort to return an organization to profitability and increase positive cash flows to a sufficient level. It is used when both threats and weaknesses adversely affect the health of an organization so much that its basic survival is difficult.
Question 36.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements with the most appropriate word:
Divestment is a part of rehabilitation and is adopted when a …………………… has been attempted but has proved tobe unsuccessful. (Nov 2011, 1 marks)
Answer:
Turnaround.
![]()
Question 37.
What is Divestment strategy? When is it adopted? (Nov 2012, 3 marks)
Answer:
Divestment Strategy is also known as Retrenchment strategy.
Retrenchment
Retrenchment strategy may require a firm to redefine its Strategy business and may involve divestment of a major product line or an SBU, abandon some markets or reduce its functions. Retrenchment in pace may necessitate a firm to use layoffs, reduce R&D or marketing or other outlays, Increase the collection of receivables, etc. The efforts aimed at redefining the business and reducing the pace of activities can improve performance of a firm. Retrenchment in combination with expansion is not uncommon. Retrenchment alone Is probably the least frequently used generic strategy.”
Features
1. Retrenchment Strategy Involves a partial or total withdrawal either from products, markets or functions in one or more of a firm’s businesses.
2. Retrenchment Strategy Is generally followed during the period of decline of a business when It is thought possible to bring profitability back to the firm. if the prospects of restoring profitability are not good, abandoning market share, reducing expenses and assets can use controlled divestment.
Reasons for Following Retrenchment Strategy
- The firm Is doing poorly.
- If there is pressure from various groups of stakeholders to improve performance.
- If better opportunities of doing business are available elsewhere, a firm can better utilize Its strengths.
The retrenchment strategy is particularly followed for dealing with crises. For minor crises pace retrenchment will be suitable, for moderate crises, divestiture of some divisions or units may be Inevitable whereas, for serious crises, a liquidation strategy will be imperative.
Question 38.
Distinguish between the following:
Expansion Strategy and Retrenchment Strategy (May 2012, 3 marks)
Answer:
Turnaround Strategies:
Meaning
Retrenchment may be done either internally or externally. For internal retrenchment to take place, emphasis is laid on improving internal efficiency, known as turn around strategy. The overall goal of turnaround strategy is to return an underperforming or distressed company to normalcy in terms of acceptable levels of profitability, solvency, liquidity and cash flow. In order to achieve its objectives, a turnaround strategy must reverse causes of distress, resolve the financial crisis, achieve a rapid improvement in financial performance, regain stakeholder support, and overcome internal constraints and unfavourable industry characteristics.
Condition or Indicators
There are certain conditions or indicators which point out that a turnaround is needed if the organization has to survive. These danger signs are:
- Persistent negative cash flow
- Negative profits
- Declining market share
- Deterioration, in physical facilities
- Overmanning, high turnover of employees, and low morale
- Uncompetitive products or services
- Mismanagement
Focus
For turnaround strategies to be successful, it is imperative to focus on the short and long-term financing need as well as on strategic issues. A workable action plan for turnaround should include:
Analysis of product, market, production processes,
competition and market segment positioning.
Clear thinking about the marketplace and production logic. Implementation of plans by target-setting feedback, and remedial action.
Elements Contributing towards Turnaround
A set of ten elements that contribute to turnaround are:
- Changes in the top management
- Initial credibility – building actions
- Neutralising External Pressures
- Internal control
- Identifying quick pay-off activities
- Quick cost reductions
- Revenue generation
- Asset liquidation for generating cashs
- Mobilization of the organizations
- Better internal coordination.
Question 39.
The Management of a sick company manufacturing various electrical home appliances seeks your advice for an appropriate retrenchment strategy. What will be your advice and why? (May 2015, 7 marks)
Answer:
- Retrenchment Strategy may require a firm to redefine its business and may involve divestment of a major product line or an SBU, abandon some markets or reduce its functions.
- The efforts aimed at redefining the business and reducing the pace of activities can Improve performance of a firm.
- Sometimes businesses have products or units which are not performing as per their expectation.
- In this situation, business may divest such business units from their portfolio, as stop loss strategy.
- The retrenchment over here is not related to the retrenchment of staff but the retrenchment of business unit.
- The nature, extent, and timing of retrenchment are matters to be carefully decided by management, depending upon each contingency.
The sick company manufacturing various electrical home appliances seeks so management follows as per following:
- First of all, the enterprise withdrawing from some marginal markets.
- withdrawal of some brands and sizes of products, withdrawal of even some slow-moving poducts, winding up some branch offices, abolition of some executive positions, and so on.
- Next, the enterprise may resort to sale of some manufacturing facilities and individual product divisions which are a drag on the enterprise’s resources.
- It may also seek retirement either from Production on the marketing stage.
- It is also possible to think of offering itself for takeover by another more viable enterprise.
- At a last option, an enterprise may seek liquidation which means corporate death.
Question 40.
Write short note about the following:
Reasons to adopt Turnaround Strategies. (Nov 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Reasons for adopting turnaround strategy are as follows:
- Turnaround is needed when an enterprise’s performance deteriorates to a point that it needs a radical change of direction In strategy and possibly in structure and culture as well.
- To return an underperforming or distressed company to normalcy in terms of acceptable levels of profitability, solvency, liquidity and cash flow.
- To achieve its objectives, turnaround strategy must reverse, causes of distress, resolve the financial crisis, achieve a rapid improvement.
Question 41.
State the reasons in which a company thinks for going to divestment strategy. (Nov 2017, 3 marks)
Answer:
Divestment Strategy involves the sale or liquidation of a portion of business, or a major division, profit centre or SBU. Divestment is usually a part of rehabilitation or restructuring plan.
A Divestment Strategy may be adopted due to various reasons:
- When a turnaround has been attempted but has proved to be unsuccessful.
- A business that had been acquired proves to be a mismatch and cannot be integrated within the company.
- Persistent negative cash flows from a particular business create financial problems for the whole company.
- Severity of competition and the Inability of a firm to cope with it.
- Technological upgradation is required It the business is to survive but where it is not possible for the firm to Invest In it.
- A better alternative may be available for Investment.
![]()
Question 42.
XYZ Ltd. is a multi-product company, suffering from continuous losses since last few years and has accumulated heavy losses which have eroded its net worth. What strategic option is available to me management of this sick company? Advise with reasons. (May 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
This sick company (XYZ Ltd.) has huge accumulated losses that have eroded its net worth. The multi-product company may analyse Its various products to take decisions on the viability of each. Retrenchment becomes necessary for coping with hostile and adverse situations in th environment and when any other strategy is likely to be suicidal. The nature, extent, and timing of retrenchment are matters to be carefully decided by management, depending upon each contingency.
Retrenchment strategy is adopted because:
The management no longer wishes to remain In business either partly or wholly due to continuous losses and unviability. The environment faced is threatening. Stability can be ensured by reallocation of resources from unprofitable to profitable businesses. A retrenchment strategy is followed when an organization substantially reduces the scope of Its activity. This is done through an attempt to find out the problem areas and diagnose the causes of the problems. Next steps are taken to solve the problems. These steps result in different kinds of retrenchment strategies.
Turnaround Strategy:
If the organization chooses to transform itself into a leaner structure and focuses on ways and means to reverse the process of decline, it adopts a turnaround strategy. It may try to reduce costs, eliminate unprofitable outputs, generate revenue, improve coordination, better control, and so on. It may also involve changes in top management and reorienting leadership.
Divestment Strategy:
Divestment Strategy Involves the sale or liquidation of a portion of business, or a major division, Profit Center or SBU. Divestment is usually a part of rehabilitation or restructuring plan and is adopted when a turnaround has been attempted but has proved to be unsuccessful.
Liquidation Strategy:
In the retrenchment strategy, the most extreme and unattractive is liquidation strategy. It involves closing down a firm and selling its assets. It is considered as the last resort because it leads to serious consequences such as loss of employment for workers and other employees, termination of opportunities where a firm could pursue any future activities, and the stigma of failure. Many small-scale units, proprietorship firms, and partnership ventures liquidate frequently but medium and large-sized companies rarely liquidate in India. The company management, government, banks and financial institutions, trade unions, suppliers and creditors, and other agencies are extremely reluctant to take a decision, or ask, for liquidation.
Liquidation strategy may be unpleasant as a strategic alternative but when a dead business is worth more than ahve, it is a good proposition. The management of a sick company manufacturing multiple products be explained about the each of the above three options of retrenchment strategy with their pros and cons. But the appropriate advice with respect to a particular option of retrenchment strategy will depend on the specific circumstances of each such multi-product and management goals of the company.
Question 43.
An XYZ Company is facing continuous losses. There is decline in sales and product market share. The products of the company became uncompetitive and there is persistent negative cash flow. The physical facilities are deteriorating and employees have low morale. At the board meeting the board members decided that they should continue the organization and adopt such measures that the company functions properly. The board has decided to hire young executive Shayamli for improving the functions of the organization. What corporate strategy should Shayamli adopt for this company and what steps to be taken to implement the corporate strategy adopted by Shayamli? (Nov 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
For the purpose of strategy adoption, if the company faces the following dangers signals then turnaround strategy need to be adopted,
- Persistent negative cash flow from business
- Uncompetitive products or services.
- Declining market share
- Deterioration in physical facilities
- Over-staffing, high turnover of employees, and low morale
- Mismanagement.
In this case, XYZ company faces the same above-mentioned issued so turnaround strategy is to be adopted for the company. For turnaround strategies to be successful, It is imperative to focus on the short and long-term financing need as well as on strategic issues.
A workable plan for turnaround would Involve the following five stages:
- Stage 1 – Assessment of current problems
- Stage 2 – Analyzing the situation arid develop a strategic plan
- Stage 3 – Implementing an emergency action plan
- Stage 4 – Restructuring the business
- Stage 5 – Returning to normal.
The important elements of turnaround strategy are as follows:
- Changes In top management
- Initial credibility – building actions
- Neutralizing external pressures
- Identifying quick payoff activities
- Quick Cost reductions
- Revenue generation
- Asset liquidation for generating cash
- Better internal coordination
Question 44.
Briefly describe the meaning of divestment and liquidation strategy and establish difference between the two. (Nov 2020, 5 marks)
Question 45.
Spacetek Pvt. Ltd. is an IT company, Although there is cutthroat competition in the IT sector, Spacetek deals with distinctive niche clients and is generating high efficiencies for serving such niche market. Other rival firms are not attempting to specialize in the same target market. Identify the strategy adopted by Spacetek Pvt. Ltd. and also explain the
advantages and disadvantages of that strategy. (Jan 2021, 5 marks)
Question 46.
Distinguish between Divestment strategy and liquidation strategy.
Answer:
Divestment Strategy:
Divestment strategy involves the sale or liquidation of a portion of business, or a major division, profit centre or SBLJ. Divestment is usually a part of rehabilitation or restructuring plan and is adopted when a turnaround has been attempted but has proved to be unsuccessful. The option of a turnaround may even be ignored If it is obvious that divestment is the only answer.
Liquidation Strategy:
Liquidation as a form of retrenchment strategy is considered as the most extreme and un attractive. If involves dosing down a firm and selling its assets. It is considered as the last resort because it leads to serious consequences such as loss of employment for workers and other employees, termination of opportunities a firm could pursue, and the stigma of failure.
Question 47.
Devise an ideal work plan for implementing a turnaround strategy in an organisation.
Answer: .
Work Pien for Implementing e-Turnaround Strategy:
Stage One – Assessment of current problems: The first step is to assess the current problems and get to the root causes and the extent of damage the problem has caused. Once the problems are identified, the resources should be focused toward those areas essential to efficiently work on correcting and repairing any Immediate issues.
Stage Twos Analyze the situation and develop a strategic plan:
Before you make any major changes; determine the chances of the businesss survival. Identify appropriate strategies and develop a preliminary action plan. For this one should look of or the viable core businesses, adequate bridge financing and available organizational resources. Analyze the strengths and weaknesses in the areas of competitive position. Once major problems and opportunities are identified, develop a strategic plan with specific goals and detailed functional actions.
Stage Three – Implementing an Emergency Action Plan:
If the organization Is In a critical stage, an appropriate action plan must be developed to stop the bleeding and enable the organization to survive. The plan typically includes human resource, financial, marketing and operations actions to restructure debts, improve working capital, reduce costs, improve budgeting practices, prune product lines, and accelerate high-potential products. A positive operating cash flow must be established as quickly as possible and enough funds to implement the turnaround strategies must be raised.
Stage Four – Restructuring the business:
The financial state of the organization’s core business is particularly Important. Prepare cash forecasts, analyze assets and debts, review profits, and analyze other key financial functions to position the organization for rapid Improvement. During the turnaround, the “product mix” may be changed, requiring the organization to do some repositioning. Core products neglected over time may require immediate attention to remain competitive.
Organisations may also withdraw from some markets, close some facilities, or discontinue some products. The “people mix” is another important ingredient in the organization’s competitive effectiveness. Reward and compensation systems that encourage dedication and creativity encourage employees to think profits and return on investments.
Stage Five- Returning to normal:
In the final stage of turnaround strategy process, the origination should begin to show signs of profitability, return on investments and enhancing economic value-added. Emphasis is placed on a number of strategic efforts such as carefully adding new products and improving customer service, creating alliances with other organizations, increasing the market share, etc.
Question 48.
A large textile mill, which is in the verge of collapse, has approached you to suggest turnaround strategies. What can be the action plan while recommending turnaround strategies for such a firm?
Answer:
A textile mill which is on the verge of collapse should carefully analyse its present position, gravity of problems, whether there exist ways to overcome these problems, available resources and so on. The action plan for turn around strategy can be as follows:
1. Assessment of Current Problems:
The first step is to assess the current problems and get to the root causes and the extent of damage the problem has caused. Once the problems are identified, the resources should be focused toward those areas essential to efficiently work on correcting and repairing any immediate issues. The problems can be internal such as low morale of workers in the textile or environmental driven such as huge Influx of cheap both from foreign markets.
2. Analyze the Situation and Develop a Strategic Plan:
Before you make any major changes; determine the chances of the business’s survival. Identify appropriate strategies and develop a preliminary action plan. For this one should look for the viable core businesses, adequate bridge financing, and available organizational resources. Analyze the strengths and weaknesses in the areas of competitive position. Once major problems and opportunities are identified, develop a strategic plan with specific goals and detailed functional actions.
3. Implementing an Emergency Action Plan:
If the organization is in a critical stage, an appropriate action plan must be developed to stop the bleeding and enable the organization to survive. The plan typically includes human resource, financial, marketing, and operations actions to restructure debts, improve working capital, reduce costs, improve budgeting practices, prune product lines, and accelerate high-potential products. A positive operating cash flow must be established as quickly as possible and enough funds to implement the turnaround strategies must be raised.
4. RestructurIng the Business:
The financial state of the organization’s core business is particularly important. If the core business is irreparably damaged, then the outlook for the entire organization may be bleak. Prepare cash forecasts, analyze assets and debts, review profits, and analyze other key financial functions to position the organization for rapid Improvement. During the turnaround, the “product mix” may be changed, requiring the organization to do some repositioning. The ‘people mix’ is another important ingredient in the organization’s competitive effectiveness.
5. Returning to Normal: In the final stage of turnaround strategy process, the organization should begin to show signs of profitability, return on investments, and enhancing economic value-added. Emphasis is placed on a number of strategic efforts such as carefully adding new products and improving customer service, creating alliances with other organizations, increasing the market share, etc.
Question 49.
Explain the meaning of the following concepts:
Combination Strategies (May 2011, 1 mark)
Answer
Combination strategies:
When an organization adopts a mlx of stability, expansion arid retrenchment either simultaneously or sequentially for the purpose of improving its performance, it is said to follow the combination generic strategy. With combination strategies, the strategists consciously apply several generic strategies to different parts of the firm or to different future periods. For example, a paint company adopts combination strategies when it augments its offering of decorative paints to provide a greater variety to its customers (stability) and increases Its product range to add industrial and automotive paints (expansion), and closes down the paint-contracting division (retrenchment).
![]()
Question 50.
X Pvt. Ltd. had recently ventured into the business of co-working spaces when the global pandemic struck. This has resulted in the business line becoming unprofitable and unviable, and a failure of the existing strategy. However, the other businesses of X Pvt. Ltd. are relatively less affected by the pandemic as compared to the recent co-working spaces. Suggest a strategy for X Pvt. Ltd. with reasons to justify your answer. (Jan 2021, 5 marks)
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
“Strategy is a deliberate search for a plan of action that will develop a business competitive advantage and compound it is defined by
(a) Louis Pasteur
(b) Bruce D Henderson
(c) William F. Glueck
(d) Lawrarce R Jauch.
Answer:
(b) Bruce D Henderson
Question 2.
In a corporate units competitive strategies includes:
(a) Cost Leadership
(b) Differentiation
(c) Focus Cost Leadership
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 3.
Which is not a basic feature of corporate strategies?
(a) Stability
(b) Expansion
(c) Combination
(d) Procurement
Answer:
(d) Procurement
![]()
Question 4.
A stability strategy is followed by the firm specially when
(a) The strategic decisions focus on incremental improvement of functional performance.
(b) It continues to serve in the same or similar markets and deals in same or similar products and services.
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) Either (a) or (b)
Question 5.
Which is the most highly versatile strategy?
(a) Stability Strategy
(b) Expansion Strategy
(c) Divestment Strategy
(d) Turnaround Strategy
Answer:
(b) Expansion Strategy
Question 6.
Which is the best reason for combination strategy?
(a) The organisation is composed of different businesses, each of which lies in a different industry requiring a different response.
(b) The organization is large and faces complex environment.
(c) Both of (a and (b)
(d) None of above
Answer:
(d) None of above