Business Level Strategies – CA Inter SM Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Business Level Strategies – CA Inter SM Question Bank
Question 1.
Explain the factors that affect the strength of competitive pressures from substitute products. (Nov 2012, 3 marks)
Answer:
Substitute products are those products which are used in place of main product. They are a latent source of competition in an industry. Substitute products offering a price advantage and/or performance improvement to the consumer can drastically alter the competitive character of an industry.
According to Michael Porter. the state of competition In an industry is a composite of competitive pressures operating in five areas of overall market. One of the five areas is the threat of substitute products or services.
The threat of actual or potential substitutes needs to be examined carefully, as it may put a ceiling on the prices for a product, or make inroads into the market and reduce its demand, e.g.: PVC tubes making inroads into the market for steel tubes, or copper loosing Its market to aluminum and plastics.
Question 2.
What are the five competitive forces ¡n an Industry as identified by Michael Porter? Explain. (Nov 2009, 10 marks)
OR
Industry Is a composite of competitive pressures In five areas of the overall market. Briefly explain the competitive pressures. (Nov 2011, 3 marks)
OR
Explain briefly the competitive forces In any industry as identified by Michael Porter. (May 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
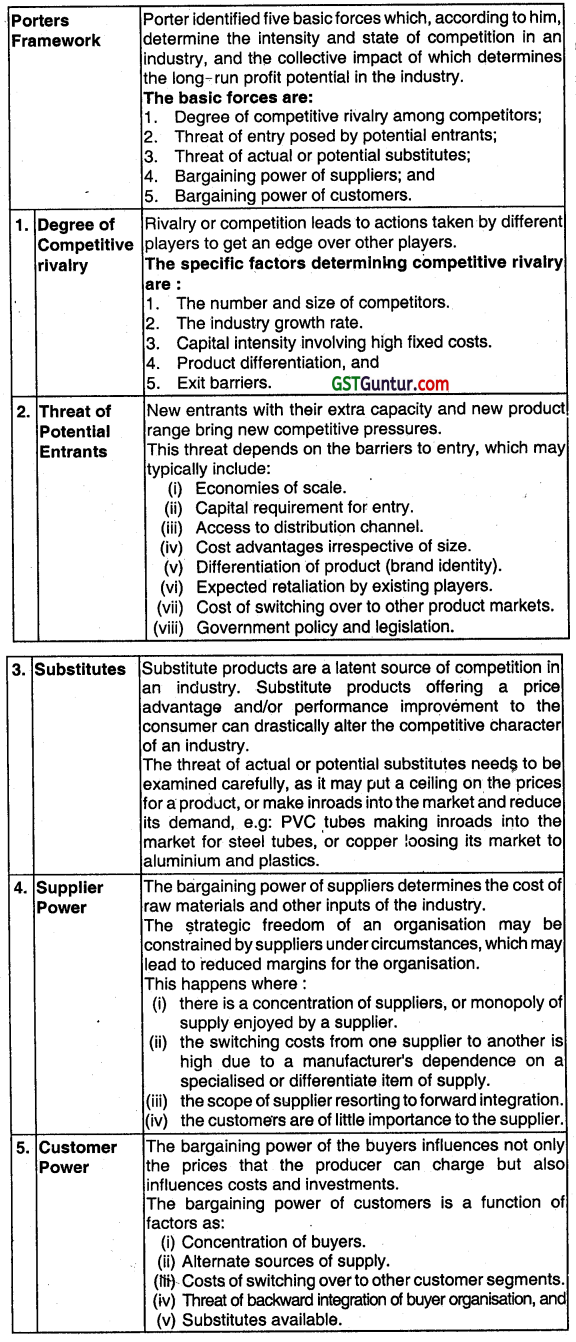
A structured approach to examining the competitive environment of an organization has been suggested by Michael Porter.
Logic of the Approach
The logic behind this approach is that for most organizations, the strategic competitive advantages enhance and ensure long-term profit potentials, and also because competitive forces happen to be more immediate external influences which organisations are likely to be able to overcome directly by their own actions.
Question 3.
Analyse the following cases in the context of Michael Porter’s Five Forces Model:
(i) A supplier has a large base of customers.
(ii) A manufacturer of sports goods has the advantage of economies of large-scale production.
(iii) Products offered by competitors are almost similar. (May 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
(i) A Supplier has a large base of customers:
Quite often suppliers, too, exercise considerable bargaining power over companies. The more specialized the offering from the supplier, greater is his power. If the suppliers are limited in number they stand a still better chance to exhibit their bargaining power. The bargaining power of suppliers determines the cost of raw materials and other inputs of the industry and, therefore, industry attractiveness and profitability.
(ii) A Manufacturer of sports goods has the advantage of economies of large-scale production:
Bargaining power of customers is another force that influences the competitive condition of the Industry. This force will become heavier depending on the buyers forming groups or cartels. Mostly, this is a phenomenon seen in industrial products. Quite often, users of industrial products come together formally or informally and exert pressure on the producer in matters such as price, quality, and delivery.
(iii) Products Offered by competitors are almost similar:
- Substitute products are a latent source of competition in an industry.
- In many cases, they become a major constituent of competition.
- Substitute products offering a price advantage and /or performance improvement to the consumer can drastically alter the competitive character of an Industry.
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following statement is ‘correct’ and which is ‘incorrect’? Give reason, in brief, for your answer:
Economies of scale discourage new entrants. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct
Economies of Scale refers to the dedine in the per-unit cost of production (or other activity) as volume grows. A large firm that enjoys economies of scale can produce high volumes of goods at successively lower costs. This tends to discourage new entrants.
Question 5.
What do you mean by economies of Scale’? (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Economies of Scale:
Economies of Scale refer to the decline in the per-unit cost of production (or other activity) as volume grows. A large firm that enjoys economies of scale can produce high volumes of goods at successively lower costs. For examples, In the semiconductor industry, larger companies, such as IBM, Intel, Samsung, and Texas Instruments, enjoy substantial economies of scale in the production of advanced microprocessors, communication chips, and integrated circuits that power most customer electronics, personal computers (PCs) and cellular phones. This acts as a barrier for new entrants.
Question 6.
Discuss in what conditions rivalry among competitors tends to be cut-throat and profitability of the industry goes down. (Nov 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Rivalry among competitors tends to be cutthroat and industry profitability goes down when:
(i) An industry has no clear leader.
(ii) Competitors in the industry are numerous.
(iii) Competitors operate with high Fixed costs.
(iv) Competitors face high exit barriers.
(v) Competitors have little opportunities to differentiate their offerings
(vi) The industry faces slow or diminished growth.
(i) Industry Leader: A strong industry leader can discourage price wars by disciplining initiators of such activity, Because of its greater financial resources, a leader can generally outlast smaller rivals fri price wars. Knowing this, smaller rivals often avoid initiating such a contest.
(ii) Number of Competitors: Even when an industry leader exists, the leader’s ability to exert pricing discipline diminishes with the increased number of rivals in the industry as communicating expectations to players becomes more difficult.
(iii) Fixed Costs: When rivals operate with high fixed costs, they feel strong motivation to utilize their capacity and therefore are Inclined to cut prices when they have excess capacity. Price cutting causes profitability to fall for all firms in the industry as firms seek to produce more to cover costs that must be paid regardless of industry demand. For this reasons, profitability tends to be lower In industries (for example, airline, and telecommunications) characterized by high fixed Costs.
(iv) Exit Barriers: Rivalry among competitors declines if some competitors leave an industry. Profitability therefore tends to be higher in industries with few exit barriers. Exit barriers come in many forms. Assets of a firm considering exit may be highly specialized and therefore of little value to any other firm. Such a firm can thus find no buyer for its assets. This discourages exit. When barriers to exit are powerful, competitors desiring exit may retrain from leaving. Their continued presence In an industry exerts downward pressure on the profitability of all competitors.
(v) Product Differentiation: Firms can sometimes insulate themselves from price wars by differentiating their products from those of rivals. As a consequence, profitability tends to be higher in industries that offer opportunities for differentiation profitability tends to be lower in industries involving undifferentiated commodities such as memory chips, natural
resources, processed metals, and railroads.
(vi) Slow Growth: Industries whose growth is slowing down tend to face more intense rivalry. As industry growth slows, rivals must often fight harder to grow or even to keep their existing market share. The resulting intensive rivalry tends to reduce profitability for all.
Question 7.
Explain Porter’s five forces model as to how businesses can deal with the competition.
Answer:
To gain a deep understanding of a company’s industry and competitive environment, managers do not need to gather all the information they can find and waste a lot of time digesting it. Rather, the task is much more focused.
A powerful and widely used tool for systematically diagnosing the significant competitive pressures in a market and assessing the strength and Importance of trade is the Porter’s five-forces model of competition.
This model holds that the state of competition in an industry is a composite of competitive pressures operating in five areas of the overall market:
- Competitive pressures associated with the market maneuvering and jockeying for buyer patronage that goes on among rival sellers in the industry.
- Competitive pressures associated with the threat of new entrants Into the market.
- Competitive pressures coming from the attempts of companies in other industries to win buyers over to their own substitute products.
- Competitive pressures stemming from supplier bargaining power and supplier-seller collaboration.
- Competitive pressures stemming from buyer bargaining power and seller-buyer Collaboration.
![]()
Question 8.
Michael E. Porter has suggested three generic strategies. Briefly explain them. What is the basic objective to follow a generic strategy? in what situations can the three strategies be used? Identify the type of strategy used in the following examples:
(a) Dell Computer has decided to rely exclusively on direct marketing. (May 2010, 4 marks)
(b) “Our basic strategy was to charge a price so low that microcomputer makers couldn’t do the software Internally for that cheaply.” (May 2010, 3 marks)
(c) NDTV, a TV Channel has identified a profitable audience niche in the electronic media. It has further exploited that niche through the addition of new channels like ‘NDTV Profit’ and ‘Image’. (May 2010, 3 marks)
Answer:
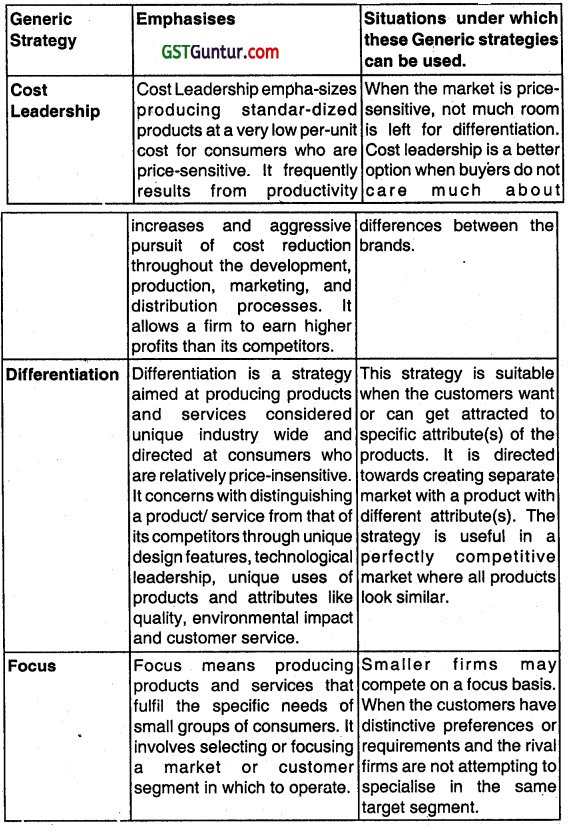
Michael E. Poiler describes that strategies allow organizations to gain competitive advantage from three different bases:
(i) Cost leadership,
(ii) Differentiation, and
(iii) Focus.
The basic purpose of following a generic strategy is to gain competitive advantage so as to ensure the long-term survival and growth of the organisation.
In the given examples the generic strategies that are being followed are given as follows:
(a) Differentiation: Deli Compiters is differentiating on product delivery. The computer market is highly competitive and the products are very similar.
(b) Cost Leadership: By Keeping the prices low, microcomputer makers acquire the software rather than developing themselves Is a case of cost leadership.
(c) Focus: NDTV has identified a profitable area (audience niche) and is focusing on It.
Question 9.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements with the most appropriate word:
Michael Porteras Generic strategies allow organizations to gain competitive advantages by cost leadership, and focus. (May 2011, 1 mark)
Answer:
Differentiation.
Question 10.
According to Michael Porter, strategies allow organizations to gain competitive advantages from different bases. Explain these bases as mentioned by Porter. (May 2013, 3 marks)
OR
Michael Porter has suggested three generic strategies. Explain them with examples. (May 2017, 4 marks)
OR
Discuss strategic alternatives with reference to Michael Porter’s strategies.
Answer:
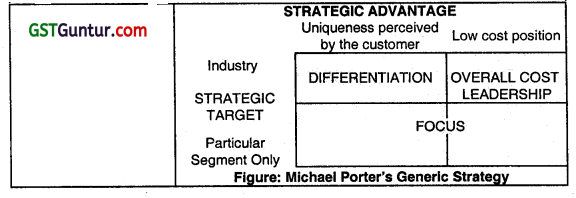
According to Porter, strategies allow organizations to gain competitive advantage from three different bases: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.
1. Cost Leadership
Cost leadership emphasizes producing standardized products at a very low per-unit cost for consumers who are price-sensitive. It frequently results from productivity increases and aggressive pursuit of cost reduction throughout the development, production, marketing, and distribution processes. It allows a firm to earn higher profits than its competitors.
2. Differentiation
Differentiation is a strategy aimed at producing products and services considered unique Industry-wide and directed at consumers who are relatively price-insensitive. It concerns with distinguishing product/service from that of its competitors through unique design features, technological leadership, unique uses of products, and attributes like quality,
environmental impact, and customer service.
3. Focus
Focus means producing products and services that fulfill the specific needs of small groups of consumers. In involves selecting or focusing on a market or customer segment in which to operate.
Question 11.
Explain the meaning of following concepts:
Cost Leadership Strategies (May 2012, 1 mark)
Answer:
Cost Leadership Strategy:
When the competitive advantage of a firm lies in a lower cost of products or services relative to what the competitors have to offer, it is termed as cost leadership. A firm which finds and exploits all sources of cost advantage and aims at becoming a low-cost producer in the industry is said to pursue a sustainable cost leadership strategy. It implies achieving the lowest cost in production and marketing to gain a large market share compared with competitors over time. It a firm can achieve and sustain overall cost leadership then it will be an above-average performer in the industry provided 11 can command prices at or near the industry average.
![]()
Question 12.
Identify the Generic Strategy used In the following examples:
(i) Bell Computer has decided to rely exclusively on direct marketing.
(ii) Our basic strategy was to charge a price so low that microcomputer makers couldn’t do the software internally for that cheaply.
(iii) MD TV, a TV channel has identified a profitable audience niche in the electronic media. It has further exploded that niche through the addition of new channels like MD TV’s Profit and Image. (Nov 2013, 3 marks)
Answer:
(i) Differentiation Strategy
Bell Computers is differentiating on product delivery as computer market is highly completive and the competitive and the products are very similar.
(ii) Cost Leadership
Keeping the prices low so that microcomputer makers acquire the software rather than developing themselves is a case of cost leadership.
(iii) Focused Differentiation
MD TV has identified a profitable area (audience range) and is focusing on it.
Question 13.
Distinguish between the following:
C0st Leadership and Differentiation Strategies (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Cost Leadership:
A primary reason for pursuing forward, backward, and horizontal integration strategies is to gain cost leadership benefits. A number of cost elements affect the relative attractiveness of generic strategies, including economies of scale achieved. Learning and experience Curve affects the percentage of capacity utilization achieved and linkage with suppliers and distributors. A successful cost leadership strategy usually permeates the entire firm, as evidenced by high efficiency, low overhead, limited perks, intolerance of waste, intensive screening at budget requests, wide sponsor control, rewards linked to cost containment, and broad employee participation in cost control efforts.
Differentiation Strategies: It offers different degrees of differentiation. Differentiation does not guarantee competitive advantages, especially if standard products sufficiently meet customer needs or if rapid imitation by competitors is possible.
Question 14.
What do you mean by differentiation strategy? How it is achieved? (May 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Differentiation is a strategy aimed at producing products and services considered unique industry-wide and directed at consumers who are relatively price-insensitive. It concerns with distinguishing a product service from that of its competitors through unique design features, technological leadership, unique uses of products, and attributes like quality, environmental impact, and customer service.
This strategy is suitable when the customers want or can get attracted to specific attributes (s) of the products. It Is directed towards creating separate market with a product with different attribute(s). The strategy is useful in a perfectly competitive market where all products look similar. To achieve differentiation, following ere the measures that could be adopted by an organization to Incorporate:
- Offer utility for the customers and match the products with their tastes and preferences.
- Elevate the performance of the product.
- Offer the promise of high-quality product/service for buyer satisfaction.
- Rapid product Innovation.
- Taking steps for enhancing image and its brand value.
- Fixing product prices based on the unique features of the product and buying capacity of the customer.
Question 15.
Write a short note on the concept of cost leadership strategy and how to achieve it? (Nov 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Cost Leadership Strategy:
When the competitive advantage of a firm lies In a lower cost of products or services relative to what the competitors have to offer, it is termed as cost leadership. A firm which finds and exploits all sources of cost advantage and aims at becoming a low-cost producer in the industry is said to pursue a sustainable cost leadership strategy. It implies achieving the lowest cost in production and marketing to gain a large market share compared with competitors over time. If a firm can achieve and sustain overall cost leadership then it will be an above-average performer in the industry provided it can command prices at or near the industry average.
Achieving Cost Leadership Strategy;
To achieve Cost Leadership, following are the actions that could be taken:
- Forecast the demand of a product or service promptly.
- Optimum utilization of the resources to get cost advantages.
- Achieving economies of scale leads to lower per unit cost of product/service.
- Standardization of products for mass production to yield lower cost per unit.
- Invest In cost-saving technologies and try using advanced technology for smart working.
- Resistance to differentiation till It becomes essential.
Question 16.
Sohan and Ramesh are two friends who are partners in their business of making biscuits. Sohan believe In making profits through selling more volume of products. Hence. he believes in charging lower price to the customers. Ramesh, however of the opinion that higher price should be charged to create an image of exdusivity and for this, he proposes that the product to undergo some change. Analyse the nature of generic strategy used by Sohan and Ramesh. (Nov 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
The Generic, Competitive Strategies or Best-cost provider Strategy involves providing customers more value for the money by emphasizing low cost and better quality difference. It can b. done:
- through offering products at lower price than what 18 being offered by rivals for products with comparable quality and features or.
- charging similar price as by the rivals for products with much higher quality and better features.
Generic Strategy adopted by Sohan and Ramesh:
1. As Sohan Is opinion of making profits through selling more volume of products by charging less prices of biscuits. The strategy adopted here is to take competitive advantage. It provides more value for the money and having lower costs than competitors.
2. As Ramesh is of the opinion that higher price should be charged to create an image of exclusivity and for this, he proposes that the product to undergo sorne change. Here, Ramesh build in whatever features buyers are willing to pay for and charges a premium price for to cover extra costs of differentiating features. The firm shall require to either under-price rival brands with comparable features or match the price of rivals and provide better features to build a reputation for delivering the best value. This strategy focuses on Market Emphasis.
![]()
Question 17.
Gennex is a company that designs, manufactures, and sells computer hardware and software. Gennex is well known for its innovative products that has helped the company to have advantage over Its competitors. It also spends on research and development and concerned with innovative softwares. Often the unique features of their product, that are not available with their competitors helps them to gain competitive advantage. Gennex using the strategy is consistently gaining its position in the industry over its competitors. Identify and explain the Porter’s generic strategy which Gennex has opted to gain the competitive advantage.
Answer:
According to Porter, strategies allow organizations to gain competitive advantage from three different bases: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Porter called these base generic strategies.
Gennex has opted differentiation strategy, Its products are designed and produced to give the customer value and quality. They are unique and serve specific customer needs that are not met by other companies in the industry.
Highly differentiated and unique hardware and software enables Gennex to charge premium prices for its products hence making higher profits and maintaining its competitive position in the market.
Differentiation strategy is aimed at broad mass market and involves the creation of a product or service that is perceived by the customers as unique. The uniqueness can be associated with product design, brand image, features, technology, dealer network, or customer service.
Question 18.
Explain the meaning of the following concepts:
Best-cost provider strategy (Nov 2012, 1 mark)
Answer;
The Best cost Provider strategy is an advancement of Porter’s generic strategy.
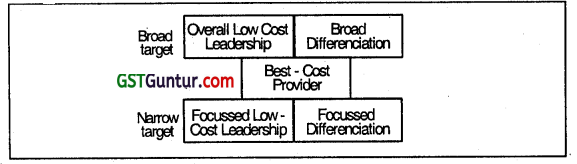
Best Cost Provider:
It targets the value-conscious buyer by either underpricing the competitor’s brand with comparable features or matching the price of the competitor by providing better features.
Thereby creating more value for money.
Multiple Choice Question
Question 1.
Michael Porter’s Generic Strategies comprises except:
(a) Cost Leadership Strategy
(b) Best Cost Provider Strategy
(c) Focus Strategy
(d) Differentiation Strategy.
Answer:
(b) Best Cost Provider Strategy
Question 2.
Common barriers to entry represents hurdles that slow down entry by other firms except:
(a) Capital requirements
(b) Switching cost
(c) Added Production Capacity
(d) Brand identity.
Answer:
(c) Added Production Capacity
![]()
Question 3.
Suppliers can influence the profitability of an Industry in various way except:
(a) Buyers have full knowledge of the sources of products and their substitutes
(b) They can erect high switching cost
(c) They are more concentrated their buyers
(d) Their products are crucial to the buyer and substitutes are not available.
Answer:
(a) Buyers have full knowledge of the sources of products and their substitutes
Question 4.
Business Level Strategy Is concerned with the issue such as
(a) Achieving advantage over competitors
(b) Avoiding competitive disadvantage
(c) Meeting the needs of key customers
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 5.
…………………… is very important in obtaining arid sustaining a Competitive advantage.
(a) Knowing general Customers
(b) Knowing Sellers
(c) Knowing Producers
(d) Knowing one’s customers.
Answer:
(d) Knowing one’s customers.
Question 6.
…………………. are the foundation of an organization’s business-level strategies.
(a) Business Structure
(b) Customers
(c) Competitive environment
(d) Business Scale.
Answer:
(b) Customers
Question 7.
Porter’s Generic Strategies allow organisations to gain competitive advantage from different bases, except:
(a) Customers
(b) Cost Leadership
(c) Differentiation
(d) Focus.
Answer:
(a) Customers
Question 8.
Producing products and services that fulfill the needs of small groups of customers is termed as:
(a) Cost Leadersilp
(b) Differentiation
(c) Competitive advantage
(d) Focus.
Answer:
(d) Focus.
Question 9.
Cost Leaders tend to keep their costs low by minimizing advertising, market research, and research and development, but this approach can prove to be expensive in the long run. Is this method Is good for long term?
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) Practically yes
(d) Non.
Answer:
(b) No
![]()
Question 10.
Differentiations strategy should be made on the basis of ………………….. .
(a) Product
(b) Pricing
(c) Organisation
(d) Any of the above.
Answer:
(d) Any of the above.
Question 11.
A successful ……………….. strategy depends on an industry segment that is of sufficient size, has good growth potential, and is not crucial to the success of other major competitors.
(a) Customer
(b) Cost Leadership
(c) Focus
(d) Differentiation
Answer:
(c) Focus
Question 12.
Best-Cost Provider Strategy is directed towards giving customers more value for the money by emphasizing
(a) Differentiation Strategy
(b) Low cost
(c) upscale differences
(d) Both Low Cost and upscale
Answer:
(d) Both Low Cost and upscale
Question 13.
Cost Leadership strategy is a low-cost competitive strategy that aims at ………………….. .
(a) Customer-centric market
(b) Specialised market
(c) Specific market area
(d) Broad mass market
Answer:
(d) Broad mass market
Question 14.
Differentiation strategy is aimed at broad man market and involves the creation of a product of service that is perceived by …………………….. as unique.
(a) Customers
(b) Supplier
(c) Producer
(d) Management
Answer:
(a) Customers
Question 15.
Which is not a disadvantage of Differentiation strategy?
(a) In long term, uniqueness ¡s difficult to sustain.
(b) Substitute products can’t replace differentiated products which have high brand value and enjoy customer loyalty
(c) Charging too high a price for different differentiated features may cause the customers to switch off to another alternative.
(d) Differentiation fails to work it its basis Is something that is not valued by the customers.
Answer:
(b) Substitute products can’t replace differentiated products which have high brand value and enjoy customer loyalty
Question 16.
Focus strategies are most effective when:
(a) Consumers have distinctive preferences or requirements
(b) When rival firms are not attempting to specialize in the same target segment.
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b).
![]()
Question 17.
Objective of the Best -Cost Provider strategy is to keep cost and price those of other sellers of comparable products.
(a) Higher than
(b) Lower than
(c) Equal to
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Lower than