CA Final SCMPE Question Paper Nov 2022 – CA Final SCMPE Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
SCMPE CA Final Nov 2022 Question Paper
Question 1.
Rejuve Hotel is an Indian hotel chain of luxury hotels, based in New Delhi. With over 100 hotels, it is one of the largest hotel chain of the 5 Country. It has a franchise agreement to operate most of its hotels as part of “The Luxury Collection of Fruition International”. It is the biggest hotel business operator within the domestic and a well-established player in the international hotel business segment. From the past many decades, the hotel has been catering primarily to the business and premium segment travellers.
To create one-of-a-kind style experiences for the domestic and international travellers, the hotel offered exquisite services along with additional segment of services like in-room styling services by a local luxury boutique, provide exclusive hotel photo opportunities, create super personalized hotel amenities, include kid-friendly surprises, in house forex change services.
The hotel is liberal with the room stay timings such as early check-in and late check-out. They also offered option of auto-upgrade from deluxe joint room to suite class rooms, if available for free. A free shuttle pick up and drop services were provided for passengers from the domestic/ international airport.
Indian Hotel industry has been growing exponentially in the recent years due to growing economy. Consequently, there have been many new entrants in the domestic segment, offering low-cost rates to customers. These hotels have been offering rooms at huge discounts, thereby attracting a sizable chunk of customers away from the Rejuve Ho’ Vo counter this and maintain its market share, Rejuve Hotels also followed counter strategy.
For a period of six years, rooms for various domestic travellers were offered at low competitive prices. At the same time, low rates were offered only if it was profitable to do so. Therefore, certain cost management measures were undertaken. The hotel converted itself from “Create One-of-a-Kind Style Experiences” to limited services hotel.
Most of the previously offered exclusive free services by Rejuve Hotels were moved to “paid section”. Other measures taken were to immediately terminate the free shuttle pick-up and drop services and to offer last-minute deals for rooms at a heavy discount if the hotel was not fully booked for that date. Vacant rooms are “perishable”, therefore instead of letting them go empty, the hotel can be filled at cheaper rates. This yield management measure based on capacity utilization was expected to increase market share and also the hotel’s revenue. Rooms could be booked online using the internet or through any associate hotel reception maintained by the hotel group at various locations in selected cities.
In order to quickly respond to a competitor’s move, the pricing and marketing staff of the individual hotel were given sufficient autonomy to make this price war work. Therefore, in many situations, decisions could be taken even without the prior approval of the top management. Meanwhile adding to the stiff competition, prices due to inflation have been soaring in the last few years. Maintenance of Hotels, staff compensation and other overheads have also been increasing. Given this scenario, after six years of operations, the management at Rejuve Hotels found that they were not able to generate sufficient profits on many of the domestic hotel offers. A price discount by a competitor had to be matched with a similar price discount by Rejuve Hotels and vice versa. Offering last minute deals to fill up hotel to full capacity did not generate additional revenue. The volume of last-minute hotel bookers was low. It was found that most travellers booking at the last minute were anyway “price indifferent”. Had the deals not been offered, the traveller would have been willing to pay more money anyway to book the hotel. Therefore, neither did these deals generate extra customers nor any extra revenue.
Rejuve Hotels has always been perceived to cater the premium segment traveller, therefore participating in this price war had been contrary to its image of a luxurious hotel. This left a section of the customers confused about the product offering.
Therefore, the management of Rejuve Hotels decided to discontinue its discount pricing strategy and exit the “low cost” hotel business. The rooms are now being offered at its usual “full service” rates. This strategy is proposed to be followed for both current and prospective projects and operations.
In order to improve tourism within the country, the government has been formulating policies that are aimed at changing the landscape of the hospitality sector. Hotels are being built in smaller cities and towns that did not have any one till date. Concurrently with the expansion of its luxury hotel chain in the major metropolitan cities, the Rejuve Hotel Group also expanded its business hotels division in the secondary cities in India. The Rejuve Hotel Group continued to expand its geographic and market coverage in India. It developed specialized operations (such as wildlife lodges) and consolidated its position in established markets through the upgrading of existing properties and development of new properties.
In a new competitive market move, Rejuve Hotels proposed to develop a model where-in travellers booking rooms at smaller towns are redeemable at other hotels within the group in the same price range and category, subject to availability.
Under this policy, the hotels at the major metro cities will serve as a main hub for travellers touring different cities/towns in a sequence. Rejuve Hotels also proposes to develop few budgeted small rooms with limited amenities in its metropolitan hotels to cater budgeted travellers from small cities. The ultra-luxurious amenities in the hotel will remain paid for such budgeted travellers.
The travellers will have the advantage to relish the ultra-luxurious hotel environment in the metropolitan cities at a very budgeted price. More hotel options within the Rejuve Hotel group will now be available for 4 travellers. For example, a tourist from a smaller city, wanting to travel to X another smaller city can take a break at the nearest hub with Rejuve hotels under the same booking plan. For the tourist, this is a better alternative z as compared to staying in the hub at a small hotel with limited facilities. For Rejuve group of hotels, the proposition broadens its customer base.
To implement this effect, Rejuve began scouting the market for smaller hotels in small cities that can be operated more economically on the hub- spoke route under its brand.
Along wise, it discussed role for partnership with airlines, car rentals, city tour operators in order to offer attractive holiday packages to customers. Since most of the other hotels do not have the scale of operations to achieve the “hub-spoke” model or the ability to offer holiday packages, Rejuve Hotels identified this as a unique proposition that it can offer to its customers. The hotel proposed tag line for its advertisement as “REJUVENATE at REJUVE ANYWHERE, ANYDAY, ANYTIME”.
Room booking continued to be offered over the internet using various online digital payments services. In the past, customers liked this option due to the convenience it offered. Dedicated customer service lines available 24X7 to resolve issues is proposed. Pay@Hotel services were also proposed to ease and facilitate bookings by customers. The free shuttle pick-up and drop services were reinstated for passengers from the domestic/international airport and extended to city railway stations and city bus stands.
The management of Rejuve hotel wants to have a seamless implementation of this project. This could be a game changer for the company that will help it to consolidate its position in the hotel industry. Therefore, a meeting has been called to discuss critical reporting that needs to be in place for ensuring a successful launch.
Required :
(i) Evaluate the strategy adopted by Rejuve Hotels in becoming a “low-cost” hotel with limited services. (6 Marks)
(ii) Identify the strategy adopted by Rejuve Hotels for the proposed project. (4 Marks)
(iii) Recommend the company to adopt a mechanism to avoid errors in its strategy. (5 Marks)
(iv) Suggest a control reporting mechanism for timely corrections in the strategy. (5 Marks)
Answer:
(i) Evaluation of Strategy:
Rejuve Hotel is a premium segment hotel charging-full service “rates for its rooms. However, due to intense competition in the domestic market, it adopted a-low-cost advantage strategy. Low-cost advantage or cost lead-ership was achieved through following measures:
- Becoming a-no-frills hotel. All other facilities had to be purchased extra.
- Terminate the drop and pick up.
- Online ticket booking facilitated.
- Cost leadership enabled it to offer-low cost-rates to the customers that was generated through
(a) giving huge discounts on prices and
(b) yield management of price based on capacity utilization of the hotel.
Although, due to its long-standing image as a premium hotel, the transformation to a “no frills-airline” could have caused confusion about the product offering in the minds of customer, who expect higher service quality. This could have eroded the customer base in this segment.
This “Low-cost advantage”- strategy did not work due to the following reasons:
(a) Price war from competitors reduced the hotel prices to levels that were unviable to the company.
(b) Variable prices to fill up hotel capacity worked against the hotel. Since it was found that these customers, due to their immediate need, may have willing paid a higher price for the rooms what was offered as part of the deal. These customers were -price indifferent- which should have been used to hotel advantage & not against it.
(c) Costs of operations had been rising in recent years.
Due to the above reasons, the Hotel International’s venture as a low-cost Hotel became unviable.
(ii) Strategy for the proposed project:
Hotel plans to foray into offering its service to and from smaller cities. This time it has adopted a “differentiation advantage” strategy. It is marketing in the following ways as being different from its competitors:
(a) Offering a-full service- price where high quality facilities are provided to the traveller.
(b) Ability to offer more options of booking any hotel and going to smaller cities.
(c) Offer exchange with similar hotels.
(d) Few budget rooms and hotels are made in smaller cities to cater to budget customers but with an option to use paid services.
(e) Free shuttle pick was re-instated.
(iii) Mechanism to avoid errors:
Management control is required to set performance measure to determine if the desired objectives of the company are being achieved or not. Control is required at every stage before the activity commences. While the activity is being performed and after the activity has been completed. Accordingly, control reports generated could be Feed-f orward reports (prior), concurrent reports (during) and feedback reports (after).
When the management of Wings International wants to have a reporting system that enables them to take preventive pleasures. It would need to have a “Feed-forward” control. This control will help measure the error before it actually takes places. Preventive measure can then be taken to change the operational variables to achieve the desired result.
Guidelines to implement “Feed-forward” control are as follows:
(a) Thorough planning and analysis are required.
(b) Careful discrimination must be applied in selecting input variables. Planning and analysis should be done in an integrated fashion. There should be synergy in the thinking at an operational level and top management strategic level.
(c) Feed forward mechanism should be kept dynamic.
(d) A model control system should be developed.
(e) Data on input variables should be collected regularly. For example, Changes in rentals, electricity, commission. Which form a large share of expenses, have to be tracked continuously. If the prices are expected to fluctuate widely hedging options or long-term price agreements with suppliers can be considered.
Feed-forward control requires at the time of implementation, the control model developed should be followed in order to establish a systematic course of operations.
(iv) Feedback Control Report:
These are control reports that provide feedback about the operations. It tracks the actual Results with the budgeted/forecasted results. These reports in themselves do not cause a change in performance. The management has to take timely action to correct the errors and change its operations, if required. Guidelines to implement this reporting system are as follows:
(a) Feedback reports should disclose both accomplishment and responsibility. Performance should be tracked accordingly so that individual performance can be assessed.
(b) Feedback reports should be extracted promptly. The management has to decide the interval at which these reports need to be generated. The interval should be such that changes required can be assessed and action can be taken in a timely manner. In the previous instance, the hotel had given autonomy to the marketing and pricing division to make decisions to meet the competitors actions. It took six years to determine that the project was unviable. However, a timely reporting mechanism such as a feedback-report should have been in place to’ appraise the top management about the decisions taken. This information would have enabled the top management to make an earlier assessment as to the viability of ‘previous strategy’.
(c) Feedback reports should disclose trends and relationships. Trends could be customer travelling preferences, deals offered by competi-tors or other changes in operations. Relationships could be supplier relationships, customer relationships, strategic Partner relationships etc. Information generated from all these areas should be collated in order to provide proper feedback to the management.
(d) Feedback reports should disclose variations from standards. These standards could be from financial budgets or from non-financial metrics identified as key performance indicators. For example delay in flight operations could be a non-financial metric that can be tracked against an expected standard set in the planning stage. The information met¬ric for actual operations should be assessed in the same manner with
which the standard was set. For example a flight delay in operations could be a delay in arrival beyond 15 minutes. This same standard should be used to assess actual performance.
(e) Feedback reports should be in a standardised format. It should be easily understood and well presented to the management. Facts should be stated without ambiguity and in a standard manner.
![]()
Question 2(a).
Global Bakery is one of the largest bakery service providers for fresh breads. Among all the variants, the focaccia bread is very popular and is favourite of all its customers and envy of its rivals.
The firm has set a price of ₹ 629 for baking the focaccia breads. ‘Global Bakery’ derived this price as follows: Raw materials ₹ 40, labour (4 hrs @ ₹ 60 per hr.) ₹ 240, variable overheads ₹ 50, fixed overheads (2 hrs @ ₹ 20 per hr.) ₹ 40 plus mark-up 70% on total cost.
Global Bakery is known for its quality work and timely delivery; hence, customers are willing to pay this premium price. Firm’s employees receive a fixed salary. The hourly rate 160 is arrived by dividing the total salary by the total number of hours available. Variable overheads depend on the number of breads baked whereas fixed overheads rate is derived at by dividing the total cost of all related expenses by the number of labour hours available. Fixed overheads generally include office rent and administrative salary.
A local hotel approached ‘Global Bakery’ as the focaccia bread bakers of their hotel are on strike, about the possibility of delivering 120 focaccia breads in coming week and they need the work done on a rush basis. ‘Global Bakery’ has sufficient quantity of required raw material in stock for special order. It perceives that it could complete 70% of the special order during normal working hours. However, to complete the remaining 30%, some employees will have to work overtime. Overtime hours are paid at premium, which could be time and half the normal hourly rate.
Required :
(i) Advise the company to determine the price to be quoted for the special order. (5 Marks)
(ii) Comment on the suitability of special order decision to deal with excess supply or excess demand. (5 Marks)
Answer:
2(a)
(i) Firms can face situations where they are confronted with the opportunity of offering for a one-time special order. In this situation only the incremental costs of undertaking the order should be taken into consideration. Quote should be made at prices that exceeds incremental costs. Any excess of revenues over incremental costs will provide a contribution to committed fixed cost which would not otherwise have been gained.
‘Global Bakery’ can use the incremental cost numbers for pricing the ‘rush order’. The minimum price that firm would charge is ₹ 187.50 per suit (= ₹ 22,500/120). This price is well below normal price of ₹ 629.
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| Raw Materials (120 × ₹ 40) | 4,800 |
| Labour (120 × 4 × 30% × ₹ 60 × 1.5) | 11,700 |
| Variable overheads (120 Suits × 50) | 6,000 |
| Incremental cost | 22,500 |
However, in decision making other conditions are equally important. For instance, if this is a one-time deal with no prospect of repeat business, then ‘Pristine Makers’ might well charge a premium over the normal price. Long-term implications also mailer. The prospect of “getting a foot in the door” to quote for future business would push the price downward. Therefore, ‘Global Bakery’ can price based on both the short-run benefits from accepting the order and the long-run consequences.
(ii) Such special order definitely gives ‘Global Bakery’ opportunity to earn more profits, however, other aspects also need to be analysed. There is excess of cleaning material, if the current special order does not use up available stock, the firm could store the cleaning material for j later use. It is most likely that ‘Global Bakery’ fixed overhead costs will not change due to the special order which mainly consists of rent and administrative salaries. If 70% of the special order could be completed during normal working hours, then the firm clearly has some excess capacity in terms of labour hours. However, for the remaining 40% of the special order, labour will have to work overtime and will be paid 1.5 times. This clearly indicates that different resources in the ‘Global Bakery’ have differing capacity levels; a decision may impose constraints on particular resource. It is necessary to consider the opportunity cost of each resource when computing the total cost of a special order.
(iii) There are two sides in this scenario. On the one side, firm can earn more profits by taking the special order. On the other side, the order received heeds to be delivered urgently. Therefore, accepting such rush orders may affect the quality of service and also timely delivery may not be complied with. Hence, the goodwill and brand name will be affected which in turn will affect the future profitability. Though immediate monetary benefits are seen, long time consequences also need to be analysed before accepting such rush orders. The firm manager would need to consider both the short-run benefits from accepting the order and the long-run consequences on profitability.
Question 2(b).
A leading Beauty product company manufactures and sells cream.
It sells cream in a container of 200 ml. This container is of one time use. Raw material is procured locally. The raw material is blended with additives and fragrance at the manufacturing plant at specified temperatures to produce cream.
The plant has an automated packing facility. The operator is required to pre-set the quantity and number of ‘containers’ to be filled in a computerised system. No manual intervention is required thereafter. The cream is filled in ‘container’ at the first stage of packaging with 200 ml. Caps are fixed on the ‘Container’ and sealed at the second stage of packaging. The container is weighed at third stage of packaging. After weighing the containers are packed in cartons of 500 containers each.
Any ‘Container’ having lesser quantity of cream is removed before the ‘containers’ are packed into the cartons. The ‘containers’ which are short filled cannot be reused. Once the seal is broken, the ‘container’ is of no use. There is no process by which the cream in short filled ‘container’ could be reused. Hence the cream is wasted.
The company is considering a proposal to add a machinery in its packaging unit to avoid losses arising out of quantity issues in packaging. The machinery will be installed after the first stage of packaging. The machinery will measure the volume of cream and will forward the ‘container’ for capping and sealing only if the quantity in ‘container’ is correct. In case the ‘container’ does not have required volume of cream, the ‘container’ will j be topped up with balance cream before the capping and sealing process. By this the company will be able to achieve 0% wastage due to short filling after implementation of new system.
Required :
Identify and Explain the type of existing control system in the company and also the type of control system proposed. (10 Marks)
Answer:
2(b)
Control is a management function of establishing benchmarks and com-paring actual performance against the benchmarks and taking corrective actions. Control is required at all levels of organisation to ensure that the organisation achieves its intended objective. There are two types of control systems – Feedback Control and Feed-forward Control.
Feedback Control is a control activity that takes place after a process is complete. It is also known as post action control. If any problem is identi-fied after a process is complete, a corrective action is taken to rectify the problem. Feedback control provides information only after the process is complete and sometimes a significant time is lost to take corrective action. Feedback-based systems have the advantage of being simple and easy to implement.
In the given case, the company currently has a feedback control mechanism in place. The actual volume of the product is measured at the end of the packaging process. The current control process is that any ‘Container’ which is short filled is not packed in the carton. This ensures that a lower quantity of product is not supplied into the market. The current control system, however leads to product losses as identification of short-filled ‘Container’ at the end of process is not useful to the production process. In case, there is a huge variation in the final packaging, the packaging system can be reviewed to ensure that such problems do not acquire in the future.
Feed-forward Control is also referred to as a preventive control The rationale behind feed forward control is to foresee potential problems and take corrective action to ensure that the final output is as expected. Feed-forward controls are desirable because they allow management to prevent problems rather than having to cure them later. Feed-forward control are costly to implement as it requires additional investment and resources. These are designed to detect deviation some standard or goal to allow correction to be made before a particular sequence of actions is completed.
The proposed system in the company is a Feed-forward control. In this case, any short filling is identified in the packaging process itself and corrective action is taken to ensure that the final packed ‘Container’ has proper quantity of product. The new process is beneficial to the company as the wastage arising out of the packaging process can be avoided. The savings must be compared with the cost required to modify the packaging process before finalising on whether the new system should be implemented or not.
Question 3.
A new startup venture ABC Ltd. has successfully entered into their first contract with an offshore pharmaceutical company to supply one of the high demand generic medicines. Expected demand for the medicine will be 98,000 units annually. The plant holds the maximum capacity to 25,200 units per quarter but it can additionally produce 14,000 units per quarter in overtime. Total fixed overheads are expected to be 116,80,000 for all the quarters. Each unit produced in overtime would incur an additional cost equivalent to 32% of the expected variable cost per unit of that quarter.
Expected sales and variable cost per unit for all quarters are given as under:
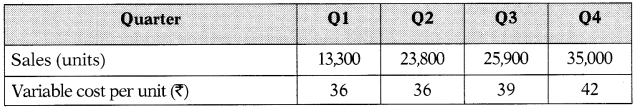
The production manager has to decide about the production plan. The choices are :
Plan 1 : Produce at a constant rate of 24,500 units per quarter. Inventory holding costs will be ₹ 7.80 per unit of average inventory per quarter.
Plan 2 : Use a Just-in-Time (JIT) system
Assume that there is no balance of opening inventory.
Required :
(a) Calculate the incremental production cost and the savings in inventory holding cost by JIT production system. (6 Marks)
(b) Advise the company on the choice of the plan. (3 Marks)
(c) State, any four pros and cons of the JIT Inventory Management. (4 Marks)
(d) State why Kanban and machine cells are critical elements for the JIT Inventory System. (3 Marks)
(e) State the difference between Just-in-Time Inventory v. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) ? (2 Marks)
(f) State any four areas in which JIT purchasing may reduce cost significantly to bring the cost efficiency. (2 Marks)
Answer:
(a) Workings:
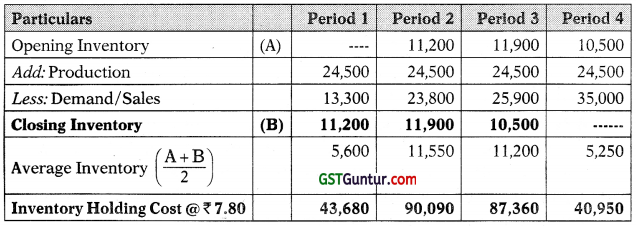
Statement Showing ‘Additional Cost-Overtime’ under Plan 2 (JIT System)
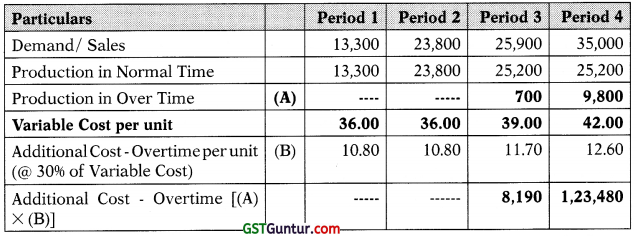
Statement Showing ‘Additional Variable Cost’ under Plan 2 (JIT System)
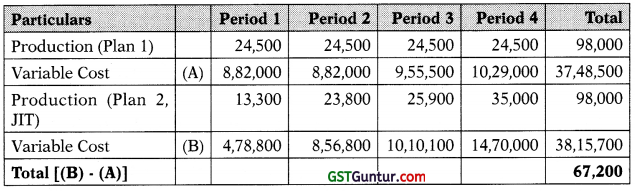
# excluding overtime cost
Incremental Production Cost in JIT System = ₹ 1,31,670 + ₹ 67,200 = ₹ 1,98,870
Therefore, Saving in JIT System (Net) = ₹ 2,62,080 – ₹ 1,98,870 = ₹ 63,210
(b) Advise:
Though ABC Ltd. is saving ₹ 63,210 by changing its production system to Just-in-Time but it has to consider other factors as well before taking any final call which are as follows:
- ABC Ltd. has to ensure that it receives materials from its suppliers on the exact date and at the exact time when they are needed. Credentials and reliability of supplier must be thoroughly checked.
- To remove any quality issues, the engineering staff must visit supplier’s sites and examine their processes, not only to see if they can reliably ship high-quality parts but also to provide them with engineering j assistance to bring them up to a higher standard of product.
- ABC Ltd. should also aim to improve quality at its process and design levels with the purpose of achieving “Zero Defects” in the production process.
- ABC Ltd. should also keep in mind the efficiency of its work force. ABC j Ltd. must ensure that labour’s learning curve has reached at steady rate so that they are capable of performing a variety of operations at effective and efficient manner. The workforce must be completely retrained and focused on a wide range of activities.
(c) Advantages of JIT System:
The use of just-in-time inventory has the following advantages:
- There should be minimal amounts of inventory obsolescence, since the high rate of inventory turnover keeps any items from remaining in stock and becoming obsolete.
- Since production runs are very short, it is easier to halt production of one product type and switch to a different product to meet changes in customer demand.
- The very low inventory levels mean that inventory holding costs (such as warehouse space) are minimized.
- The company is investing far less cash in its inventory, since less inventory is needed.
- Less inventory can be damaged within the company, since it is not held long enough for storage-related accidents to arise. Also, having less inventory gives materials handlers more room to maneuver, so they are less likely to run into any stored inventory and cause damage.
- Production mistakes can be spotted more quickly and corrected, which results in fewer products being produced that contain defects.
Disadvantages of JIT System
Despite the magnitude of the preceding advantages, there are also some disadvantages associated with just-in-time inventory, which are:
- A supplier that does not deliver goods to the company exactly on time and in the correct amounts could seriously impact the production process.
- A natural disaster could interfere with the flow of goods to the company from suppliers, which could halt production almost at once.
- An investment should be made in information technology to link the computer systems of the company and its suppliers, so that they can coordinate the delivery of parts and materials.
- A company may not be able to immediately meet the requirements of a massive and unexpected order, since it has few or no stocks of finished goods.
(d) Kanban (Japanese for sign) is an inventory control system used in just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing to track production and order new shipments of parts and materials. Kanban was developed by Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, and uses visual cues to prompt the action needed to keep a process flowing.
Cellular Manufacturing results in following benefits to improve productivity. It may be noted that all of these are critical:
- Reduce setup times by using part family tooling and sequencing.
- Reduce flow times by reducing material handling and transit time and using smaller batch sizes (even single piece flow – this also results in the requirement of less floors pace).
- Reduced work-in-process inventory.
- Better use of human resources. Hence, reduced direct labour but heightened sense of employee participation.
- Better scheduling easier to control, and automate.
- Increased use of equipment & machinery, hence reduced investment on machinery & equipment.
(e) Differences between JIT and EOQ:
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a production method that aims at maintaining the amount of materials at a desired level at a minimum cost.
Just-in-Time (JIT) is a Japanese management philosophy which aims at providing customers with the right kind and amount of stocks at the right time.
The following are the differences:
(1) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a production method that aims at maintaining the amount of materials at a desired level at a minimum cost while Just-in-Time (JIT) is a Japanese management philosophy which aims at providing customers with the right kind and amount of stocks at the right time.
(2) EOQ maintains a fixed amount of material in its inventory and has a reorder level wherein it must be replenished to avoid shortages and extra costs while JIT focuses on meeting customers’ demands on time with the right quality and quantity with minimum resource, time, and material wastes.
(3) Both are intended to reduce costs and increase the company’s profitability. While EOQ is dependent on financial and marketing strategy, JIT is dependent on the work ethics and commitment of the entire workforce of the company.
(f) Areas in which JIT purchasing may reduce cost significantly:
Short production times, Streamlined supply chain management, Accurate demand and inventory forecasting, Efficient order fulfilment, including batch picking.
![]()
Question 4(a).
Supreme Automation Limited (SAL) is a leading AI based home automation-based manufacturing firm. SAL started its business around 5 years back when it was the only manufacturer of such home automation- based systems. SAL manufactures all assembly components themselves, irrespective of fact that these components can be acquired from market j at a cheaper rate. Major component of total costs in manufacturing of such automation systems is variable in nature. Company was performing well, earning reasonably and enjoyed a large market share up-till two 4 years ago majorly due to the first mover advantage. However, with rough macro-economic conditions, an increase in rival competition and more new g entrants coming into the market, the resultant market share and thereby, § profitability has started shrinking. If no major steps are immediately taken, f then company may run into red in a year to come.
The CEO of SAL attended a workshop where he learnt about the lean management techniques of Cost Management. He asked Mr. X the Chief Management Accountant to report on underlying reasons behind the S company’s current performance with available set of possible solutions.
Mr. X immediately convened a meeting with top ranked officers to address the issues.
The Marketing department confirmed that it is difficult to maintain the same level of sales in upcoming years because the price of SAL automation systems is much higher than price offered by its competitors in the market with similar Quality and features.
The Customer Relations department conveyed that the popularity of their product is declining. They quoted that they receive lot of complaints from buyers in e-mails and tele-calls due to manufacturing defects, which arise in the product within a month period of purchase & frequency of such calls and emails have increased in recent years. They also mentioned that in some cases, customer reported that assembled part did not belong to model they purchased, and some customers say, assembly is not as per the 1 specifications provided in the product datasheet.
In addition, the maintenance department affirms that the repair issues in case of recently sold products have increased drastically.
The Operations department testifies that firstly large percentage of workers employed with the company are unskilled; secondly, large number of raw materials in each category are dumped by store at the production floor; that’s too well prior to requirement. These two reasons cause worker catastrophe in differentiating among parts which appear similar. They also mentioned the entire business process, especially production process is quite old and contains certain activities which are purely unnecessary. To its defence, the purchase department argued about the economics of discount involved behind purchase of large quantities of raw material and also mentioned about possibility of buying too less quantities may lead to stock-out situations.
Required :
Prepare a report to advise the CEO pointing out the factors influencing the current performance and policies of the company and also with available set of possible solutions. (5 Marks)
Answer:
4(a)
Report
Addressed to:
Office of CEO,
Supreme Automation Limited (SAL)
Dated: 19th Dec. 2022
Report on underlying reasons behind current performance and Lean Man: agement, Cost Management tools:
(i) First reason behind weak financial performance is price of SAL’s product is much higher than the price offered by all the competitors in the market. Quality and features of other products are also similar.
Target Costing as cost management technique can be applied. Since market conditions are stiff and bargaining power of customers is high due to multiple competitors. These competitors are selling the product at less than price offered by SAL. Hence, price offered by such vendors should be considered as “Target Price” and after reducing “Target Profit” from the same Target Cost can be identified, production, operations facilities along with product need to be re-engineered to achieve such Target Cost.
(ii) Second reason is that SAL manufactures all assembly components themselves, irrespective of the fact that these components can be acquired from the market at a cheaper rate. Relevant cost of both.
“Make or Buy” needs to be compared. As mentioned, the major of total costs in manufacturing is variable in nature. Hence, such a major component of costs can be controlled if SAL buys all the components instead of Making them.
Only those products need to be made in house whose variable cost of manufacturing is less than market price and vice versa.
(iii) Third and major reason is the popularity of their product is declining this is evident from declining market share and a lot of complaints from buyers in e-mails and tele-calls for manufacturing defects.
Since these defects arise in the product within the month period of purchase. Hence, the product needs to be looked at. Further, in some cases customers reported that assembled part is not belonging to model they purchased and some customers say assembly part is not as per specification provided. Hence quality is needed to be ensured in the product delivered.
One of way to look at ‘Quality’ is conformance to need of customer, to ensure same Total Productivity Management/Total Quality Man-agement supported by Six Sigma need to be applied as part of Lean System Management.
Total Quality Management is management of the entire process in-cluding planning process, to meet customer’s requirements. PRAISE analysis can be used in order to achieve improve quality.
Using DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve and Control) methodology of Six Sigma, existing business process can be improved to ensure customer satisfaction, reducing cycle time and reduction’ in waste also.
(iv) Fourth reason being a large percentage of workers are unskilled, each worker should be provided with requisite’ training. Through Kaizen, workers should be involved in the improvement of existing processes so that they become able to address small problems or improve a process.
(v) Fifth and second major reason is large amounts and categories of raw materials, dumped by stores on the production floor; that’s too well prior to need. This reason may be the root cause of one complaint by a customer that the assembled part does not belong to the model they purchased.
JIT can be implemented as part of the lean system. JIT is a pull system of production, with single piece flow after considering TAKT time. In JIT, the production facility needs to be integrated with a vendor system for signal (Kanban) based automatic supply which depends upon demand-based consumption. Under JIT system of inventory, storage cost is at lowest level due to direct issue of material to production department as and when required and resultantly less/no material lying over. In store or production floor.
Cost benefit analysis of reduction in storage cost along with opportunity cost saved and increase in ordering cost, purchase cost along with stock-out cost’ need to be made.
(vi) Sixth reason for low performance is Old established business processes. especially production processes and contains certain activities which are purely unnecessary.
Value Analysis needs to be applied in order to ensure maximum value to customers by eliminating activities which are not value generating this will control cost also, that’s too strategically.
Process Innovation and Business Process Re-engineering can also be applied. Re-engineering is rethinking and radical design of business processes in order to achieve improvement. It will help the SAL to keep them at par with changing technology by synchronisation along with redesign, retooling the business process.
Further details can be tabled on requisition basis.
Closure of Report Mr. X
Chief Management Accountant
(For Management Accounting Division)
Supreme Automation Limited
Question 4(b).
TSK Limited is a mobile manufacturing company. The company using budgets for control which are prepared on traditional basis. The new CEO of the company wants to change the budgeting system from traditional budgeting to Beyond Budgeting in the company on experimental basis.
Therefore, as the management accountant of the company you have been assigned to explore the possibilities of introducing Beyond Budgeting system 1 in the company.
You are required to explain reasons for taking approval of change the budgeting system from Traditional to Beyond Budgeting on following points:
- The advantages and benefits available in Beyond Budgeting, (3 Marks)
- The suitability of Beyond Budgeting to the company. (2 Marks)
Answer:
4(b)
Advantages of Beyond Budgeting (BB):
- It is a more adaptive process than traditional budgeting.
- It is a decentralised process, unlike traditional budgeting where leaders plan and control organisations centrally.
Benefits of the ‘Beyond Budgeting’ Model:
- Beyond budgeting helps managers to work in coordination to beat the competition. Internal rivalry between managers is reduced as target shifts to competitors.
- Helps in motivating individuals by defining clear responsibilities and challenges.
- It eliminates some behavioural issues by making rewards team-based.
- Proper delegation of authority to operational managers who are close to the concerned action and can react quickly.
- Operational managers do not restrict themselves to budget limits and focus on achieving key ratios.
- It establishes customer-orientated teams.
- It creates information systems which provide fast and open information throughout the organization.
Suitability of Beyond Budgeting to TSK Limited:
Since TSK Ltd. is a mobile manufacturing company and presently adopting Traditional Costing system. Moreover, telecom industry goes through rapid j changes in its business environment. So, the company can definitely use Beyond Budgeting to improve the control system and beat the competition. Beyond Budgeting lies an agile, holistic approach based on self-organisation, This will also help the managers to work in close coordination with each j other with motivation which in turn will beat the competition.
OR
Question 4(b).
HRY Limited is a leading company in the kitchenware industry. Due to competition in the market, company is continuously making R&D to develop new products. Product “Aiken” is currently being developed and is about to be launched in the market. The company has made very heavy expenditure to develop this product. This is a highly-innovative product which the company believes that it will change the market and consumer behaviour. Production and promotional costs in the launching year are likely to be very high. The CEO of the company has decided to use a market skimming approach for pricing this product during its induction stage.
You are required to analyze the reasons for going with market skimming approach of pricing by the CEO of HRY Limited. (5 Marks)
Answer:
4(b)
While preparing to enter the market with a new product, management must decide whether to adopt a skimming or penetration pricing strategy. The CEO of HRY Limited has decided to use a market skimming approach for pricing this product. Basically, the Skimming Pricing is a policy of high prices during the early period of a product’s existence. This can be synchronised with high promotional expenditure and in the later years the prices can be gradually reduced.
The HRY Limited should follow skimming approach due to following reasons:
- Aiken is an innovative product. The demand is likely to be inelastic in the earlier stages till the product is established in the market.
- It is expected to change the consumer behaviour,
- Since the production and marketing cost is expected to be high, this kind of strategy is required to sustain.
- The research and development cost is very high.
- The charge of high price in the initial periods serves to skim the cream of the market that is relatively insensitive to price. The gradual reduction in price in the later year will tend to increase the sales.
- This method is preferred in the beginning because in the initial periods when the demand for the product is not known the price covers the initial cost of production.
- High initial capital outlays, needed for manufacture, results in high cost of production. Added to this, the manufacturer has to incur huge promotional activities resulting in increased costs. High initial prices will be able to finance the cost of production particularly when un-certainties block the usual sources of capital.
![]()
Question 4(c).
ABC Ltd. is a manufacturer of motorbikes. It has two divisions, Assembly division ‘A’ and manufacturing division ‘P’. Division ‘P’ manufactures the part which may be used by division ‘A’ as well as outside customers. Division ‘A’ gets its entire requirement for the part from division ‘P’. The Division ‘P’ operates at full capacity, with no inventory at the beginning and end of the year. As per company policy, demand from Division ‘A’ has priority over external customers. The data of Division ‘P’ during 2021-22 is as under :
| Production Capacity | 1,50,000 Units |
| Sales price to external customers | ₹ 6,000 per unit |
| Variable cost of production per unit | ₹ 4,125 |
| Transfer price to Division ‘A’ | Any opportunity cost in the form of lost sales. |
| Total Sales including transfer to division ‘P’ | ₹ 81 crores |
| Sales made to the external customers | 75,000 Units. |
This year, there was an additional demand from external customers for 27,000 components. However, since Division ‘C’ operated at full capacity, this demand was not catered to.
Required :
(i) Analyse the Sales in terms of ₹ and units made by Division’P’to both external and internal customers. (3 Marks)
(ii) Recommend the transfer pricing range that would promote goal congruence between divisions A and P. (2 Marks)
(iii) Discuss the effect of changes in external demand on the transfer price for the company, assuming the current policy continues. (2 Marks)
(iv) Discuss the advantages, disadvantages and behavioural Consequences of Transfer Pricing at Variable Cost method. (3 Marks)
Answer:
4(c)
(i) Sales Analysis of Division P
Total annual capacity and actual production of Division P is 1,50,000 units f of components. Zero inventory implies that sales for the year was also 1,50,000 units of components. Sales to external customers was ₹ 45 crores, at ₹ 6,000 per unit.
Therefore, units sold to external customers would be 75,000 units this year.
Therefore, internal sales can be derived to be 75,000 units for the year (annual sales 1,50,000 units less external sales 75,000 units). For the year, value of sales made to Division A is ₹ 36 crores (Division P’s total sales of ₹ 81 crores less external sales of ₹ 45 crores). Had there been no extra demand, opportunity cost for Division P would have been nil. Therefore, transfer price would only be the variable cost of ₹ 4,125 per unit of component. However, given in the problem, that there was excess demand for 27,000 units of components from external customers, that could not be met since Division P had to give priority to internal demand. Had these sales been made Division P would have earned ₹ 1,875 per unit contribution (Sale price ₹ 6,000 per unit less variable cost ₹ 4,125 per unit). This lost contribution of ₹ 1,875 per unit is the opportunity cost per unit for Division P. Due to company’s policy of giving priority to internal demand, Division P lost a profit of ₹ 5.0625 crore during the year. (27,000 units × contribution of ₹ 1,875 per unit).
Therefore, internal sales comprise of two parts:
48,000 units of components transferred at variable cost of ₹ 4,125. This amounts to ₹ 19.8 crore. 27,000 units of components transferred factoring any opportunity cost = variable cost +contribution per unit = external sale price = ₹ 6,000 per unit. This amounts to ₹ 16.2 crores.
Therefore, internal sales = ₹ 19.8 crores + ₹ 16.2 crores = ₹ 36 crores.
Summarizing
External sales are 75,000 units amounting to ₹ 45 crores annual sales value. Internal sales are 75,000 units amounting to ₹ 36 crores annual sales value. Transfer price for 48,000 units is at variable cost of ₹ 4,125 per unit while for 27,000 units is at external sales price of ₹ 6,000 per unit.
(ii) Transfer Price Range for Divisions A and B Division A procures its entire demand of 75,000 units from Division P. Out of this, 27,000 units at market price of ₹ 6,000 per unit while 48,000 units are procured at a lower rate of ₹ 4,125 per unit. Had Division A procured 48,000 units from the market, the additional cost of procurement would be d ₹ 9 crores {(External price of ₹ 6,000 per unitless internal transfer price at £ variable cost of ₹ 4,125 per unit ₹ 48,000 units}. Only Division A currently enjoys this benefit of lower procurement cost. Financials of Division P show no profit from such internal transfers. This may skew the performance assessment of the divisions, if it is based primarily on financial metrics of each division. In order, promote goal congruence, some portion of this benefit can be shared with Division P.
Division P will at the minimum want to recover its variable cost of ₹ 4,125 I per unit, while Division A will be ready to pay only up to external market price of ₹ 6,000 per unit.
Therefore, transfer price range can be set between ₹ 4,125-₹ 6,000 per unit. Division A enjoys lower procurement rate while Division P financial reflect J some benefit of transferring components internally to Division A.
(iii) Impact of External Demand on Transfer Price
1 As per the company’s transfer pricing policy, Division P gives priority to demand from Division A. The division has a production capacity of 1,50,000 units annually. If there is no external market for Division P’s components, then transfer price for the entire internal transfer would be the variable cost of ₹ 4,125 per unit plus portion of the fixed cost (if any). This is the minimum cost that Division P would like to recover from Division A.
When there is an external market, transfer price would depend on whether Division P had to incur any opportunity in the form of lost sales. When total demand (internal and external) is within production capacity of 1,50,000 units, the entire demand can be met. There would be no lost sales for Division P, no opportunity cost. Therefore, transfer price for the entire internal transfer would be the variable cost of ₹ 4,125 per unit. This is the minimum cost that Division P would like to recover from Division A.
When there is an external market, such that total demand (internal and external) is more than production capacity of 1,50,000 units, due to priority given to internal transfer, some portion of the external demand might not be ) met. This would be lost sales for Division P, opportunity cost would be the contribution lost from such sales at ₹ 1,875 per unit. This opportunity cost would be passed onto Division A. As explained in part (ii) above, transfer price range will be from ₹ 4,125 – ₹ 6,000 per unit. More lost sales for Division P would keep the average transfer price higher towards ₹ 6,000 per unit. Lesser lost sales for Division P would keep the average transfer price towards the lower bound of ₹ 4,125 per unit. Therefore, the proportion of external demand that could not be catered to, would determine the average transfer price. Higher the demand from external customers would drive p up the average transfer price within the company.
Question 5(a).
Aeron Electrical Solutions (AES) is a renowned firm for manufacturing a wide range of electrical appliances for professional and domestic use. The Scriver division of Aeron Electrical Solutions is engaged in the manufacturing of motorized screw driving machines capable of handling high-end commercial loads. They are particularly very popular in automation plants where the tasks are pre-defined and accuracy is the primary concern. The Scriver division is presently manufacturing only three models namely SD-100, SD-200 and SD-500 based on the increasing order of incorporated features and complexities.”
During the manufacturing process, each screw driving machine needs to pass through various level of steps, before it gets ready. One of the manufacturing steps involved manual intervention wherein the programming of the processing chip for automation is done post installation and tested before passing to the next stage. This process is termed as Processor Manual Programming for Automation (PMPA). The production capacity of Scriver division is constrained by PMPA.
The basic information pertaining to top-line and prime cost is as follows :
| Particulars | SD-100 | SD-200 | SD-500 |
| Sale price per unit | 168 | 240 | 540 |
| Material cost per unit | 86.4 | 124.8 | 240 |
| Labour cost per unit | 36 | 63 | 90 |
All the process and division at AES are operating for a single shift of 8 hours in a day. Conversion cost per hour (including labour cost) is ₹ 6,720. The standard out-put for PMPA during a day is the processing of either 960 units of SD-100 or 672 units of SD-200, or 384 units of SD-500.
AES is capable of sale more than, what they are presently capable to produce in all range of models.
The CEO of AES recently attended a science exhibition, Robo-tech 2022; where he saw a Robot developed by Micro Robotics Limited, capable to assembly including installation and programming of processing chip to any sort of device.
You are required to advise the company as management accountant on following aspects:
(i) On a random day if 576 units, 168 units and 144 units of SD-100, SD- 200 and SD-500 respectively are produced and sold, CALCULATE at what efficiency level current constraint (bottleneck) is operational. INTERPRET the same. COMPUTE profit earned during such day. (3 Marks)
(ii) Considering the ranking based upon throughput performance ratio, find production of which model is more beneficial for the firm ? (3 Marks)
(iii) Apply Goldratt’s five steps to remove the bottleneck at Scriver Division. (4 Marks)
Answer:
5(a)
(i) Efficiency level can be measured with help of Efficiency Ratio, which is one among the control ratios. Efficiency ratio indicates the degree of efficiency attained in production. It is expressed in term of standard hours for actual production as a percentage of the actual hours spent in producing that work.
Standard hours for actual production
= \(\frac{\text { Standard hours for actual production }}{\text { Actual hours worked }}\) × 100
= (9.8/8) × 100
= 122.5%
Working Note
Standard hour required for actual production.
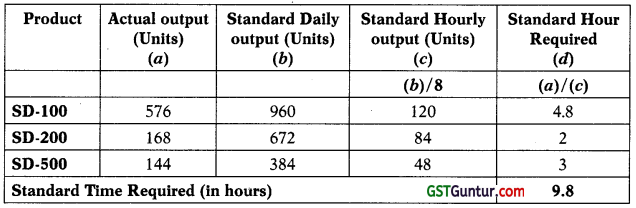
Interpretation: 122.5% signifies that efficiency (usage) of exploiting bottleneck activity is 22.5% better than the standard use. PMPA is producing output which require 9.8 hours, in 8 hours.
Profit earned during the day
| Particulars | Amount in ₹ |
| Revenue [(576 × 168) + (168 × 240) + (144 × 540)] | 2,14,848.00 |
| Less: Material Cost [(576 × 86.4) + (168 × 124.8) + (144 × 240)] | (1,05,292.80) |
| Less: Conversion Cost (including labour cost) [6,720 × 8 hrs.] | (53,760.00) |
| Profit | 55,795.20 |
(ii) Statement of ranking, based upon throughput performance ratio (using throughput contribution)
TA Ratio = (Throughput contribution)/Conversion cost
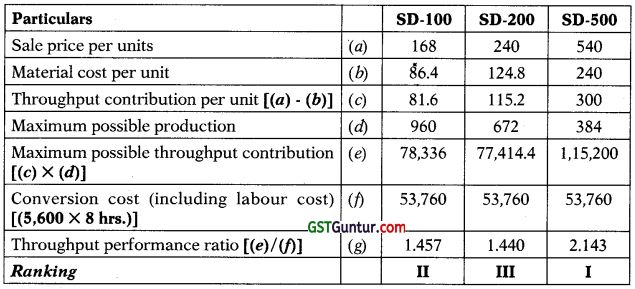
Rule for interpretation: Higher the throughput performance ratio (or TA ratio) is better and beneficial. All the products /models which have through-put performance ratio (or TA ratio) more than one may be produced/ continued to produce, depending upon constraint function.
Ranking: Considering the throughput performance ratio (or TA ratio) and ranking above, the most beneficial model to produce is SD-500 followed by SD-100 and SD-200.
It may be noted that the “Theory of Constraints” consider short-run time horizons and assume other current operating cost to be fixed costs.
(iii) Application of Goldratt’s five steps to remove the bottleneck at Scriver
Goldratt’s theory of constraints describes the following mentioned five steps process of identifying and taking steps to remove the bottlenecks i that restrict output.
1. Identifying the System Bottlenecks – At Scriver division of AES, PMPA is bottle neck.
2. Exploit the Bottlenecks – Bottleneck activities’ capacity must be fully utilised. Although the efficiency of bottleneck activity is already 122.5% but further attention on the possibility to enhance the flow of products from bottleneck activity is needful.
3. Non-bottleneck activities are subordinate – Bottleneck activity should S setup the pace for non-bottleneck activities. Scriver shall plan its pro¬gs duction keeping PMPA at the centre point, because even if the efficiency of other activities which are non-bottleneck enhanced beyond current level; the output can be maximum possible by MPA.
4. Elevate the bottleneck – Eliminate the bottleneck by enhancing the capacity and efficiency. Major change (business reengineering) or continuous minor change (kaizen) may do. In the case of Seriver, the introduction of the robot may be a way to elevate the bottleneck.
Note – There will always be one bottleneck in the system, if such bottleneck is eliminated then a new constraint emerges as a bottleneck. Hence this process continues. Ultimately improvement is a never-ending continues process.
5. Repeat the process – Apply step 1 to new bottleneck activity which emerges at Scriver and repeat the process.
![]()
Question 5(b).
The TVA Multiplex Pvt. Ltd. (TMPL) is a movie theatre chain in India with its headquarter located in Mumbai. Each centre has a cinema with a minimum of 8 screens equipped with IMAX & 4DX technologies, and mainstream auditoriums. It is the biggest chain of Multiplexes showing latest released movies across the country. The business of cinema is extremely competitive in all regions. Each centre operates autonomously and managers are able to offer best services in terms of customer experience and cleanliness.
TMPL’s mission statement is “to inspire and enhance customer experience by 1 using latest technologies and experience”. To establish long term relationship of trust and commitment with clients, TMPL wants to provide their client highest level of satisfaction with emphasis on:
- Best in class Audio and Video Services
- Professionalism, Comfort and Hygiene
- Client’s Feedback
Company has developed a website where it creates blogs, post high-quality content related to newly released movies. Website is also connected to social media to reach customers. If a customer searches TMPL’s services on search engine, it automatically redirects to the place of nearest TMPL cinema for customers comfort and ease. TMPL’s majority of tickets are booked through online channel.
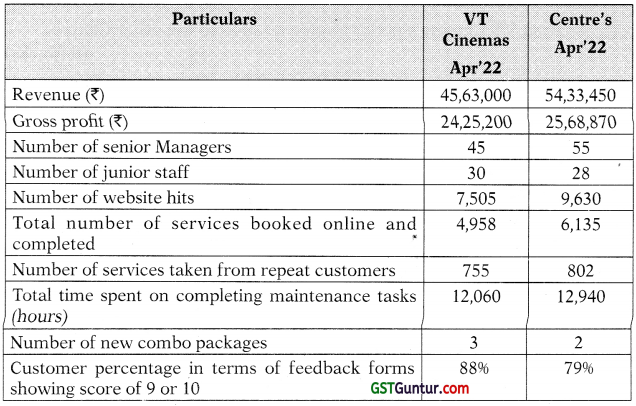
Notes:
(i) Managers are categorized as ‘senior’ if they have been qualified for more than five years.
(ii) Junior staff includes both trainees and staff who have been qualified for less than five years.
(iii) The VT Cinemas launched three new combo packs during the year :
- free food coupon of worth ₹ 450 for bookings over and above ₹ 1,000.
- a Premium Recliner seat costing only ₹ 260, instead of the usual ₹ 520, for 5 days advanced bookings.
- a Popcorn meal charged at ? 100, which usually costs ₹ 300, for all customers booking for minimum of 6 tickets.
These three new combo packs produced revenues off ₹ 3,96,000; ₹ 3,48,000 and ₹ 3,24,000 respectively, Two comparable new combo packs developed by other centre’s produced revenues of ₹ 2,64,000 and ₹ 2,52,000.
(iv) Customers to rate the particular centre from 1 to 10 in an online feedback form with 10 being the best.
Required :
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of TMPL has recently attended a webinar and heard about Building Block Model of Performance Management. The CEO is interested to know how the dimensions block could be applied at TVA Multiplex Pvt. Ltd.
(i) Analyse VT Cinema’s performance relative to the other Centres. (8 Marks)
(ii) Explain how the Standards and Rewards block support the Dimensions block in case of Building Block Model. (2 Marks)
Answer:
5(b)
(i) Analysis Competitiveness
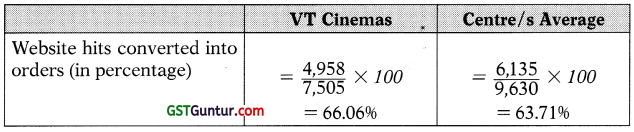
This ratio shows whether VT Cinema’s services are attractive compared to its competitors, which is essential if it is going to persist in such a competitive market.
It has performed considerably better than Centre/s average, having con-verted 66.06% of website hits into jobs, compared to the 63.71% converted by other Centre/s. This is a good outcome.
Financial Performance
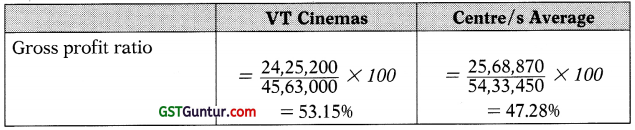
Gross profit ratio is the measure for financial performance. It indicates the percentage of revenue which exceeds the cost of goods sold.
VT Cinema’s gross profit ratio is 5.87% higher than the average, which is a good result. This could be because of new service pack sales. It is also likely to be because of ratio of senior managers to junior staff (1.5), which is lower than the average (2) and junior staff will invariably be paid less than senior ones.
Quality is a key aspect of VT Cinema’s service to customers and if it is poor, customers will not return.
Again, VT Cinemas has surpassed the other Centre/s on average by 2.15 percentage points. Though, it has a lower ratio of senior managers to junior staff (1.5) than other Centre/s (2), it might be possible that VT Cinemas has a portfolio of enthusiastic staff. So, the quality of work is probably belter, thus the higher level of repeat customers.
Flexibility
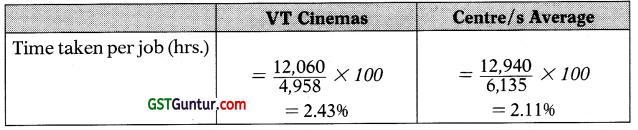
The comparison shows that VT Cinemas takes longer time to complete a job than the other Centre/s average, which is not really good, and is probably because of they have slightly less experienced station the whole, but it could also be that they do a more comprehensive job than other Centre/s.
Given the fact that they have a higher % of return customers than the other Centre/s and they are also graded 9 or 10 by most of the customers (86%).
Therefore, this cannot be viewed as too adversely.
Resource Utilization
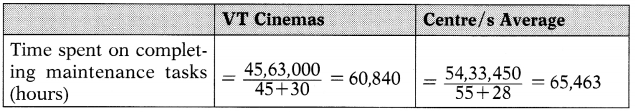
The crucial resource in a service company is its staff and so these indicators measure how this resource is being utilized.
VT Cinema’s utilisation of its staff is lower than that of the other Centre/s by ₹ 5,020 per staff. This clearly links in with the point that the average time to complete a job is longer at VT Cinemas than other Centre/s. However, given that VT Cinemas uses a slightly less experienced staff than other Centre/s and the fact that its gross margin is higher than the average, this should not also be viewed too adversely.
Innovation
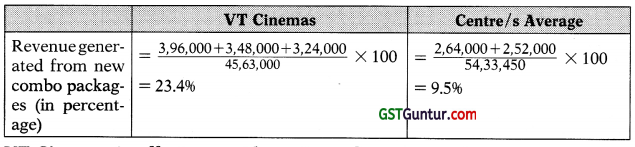
VT Cinemas is offering a wide variety of service packs to its customers. The ratio of 23.496 indicates that VT Cinemas has really outperformed other Centre/s on this front, generating a far larger part of its revenue by the introduction of new combo packages, which must have attracted customers. This is a really good performance.
(ii) Building Block Model:
- The standards block fixes the target for the performance indicators chosen for each of the dimensions. The targets must meet three criteria – they must be achievable, fair and encourage employees to take ownership. The performance of the organization could suffer if the targets set do not meet these criteria.
- The rewards block makes sure that employees are motivated to attain the standards. It also examines the properties of good reward schemes which are that they should be clear, motivating and based on controllable factors.
- If standards and rewards are set appropriately, the staff will be engaged and motivated and it is then more likely that the goals, Le., dimensions, of the organisation will be achieved.
Question 6(a).
During the second peak wave of Covid-19 in April 2021 in the country, many patients were deprived of oxygen due to its non-sufficient availability at the hospitals. A private company ABC Limited offers the government to manage the delivery and ensuring the availability of liquid j oxygen at all hospitals of locale within the expected time limit.
ABC Limited plans to manage 1,68,750 metric tons of liquid oxygen at the rate of ₹ 6.00 per metric ton. The company estimates that variable cost (all resources) will be equal to ₹ 1.50 per metric ton and that fixed costs (Cryogenic Oxygen tanker rent, driver wages, fuel and maintenance charges) will be equal to ₹ 1,04,400 per month.
In April 2021, ABC Limited managed 2,02,500 metric ton liquid oxygen and received ₹ 10,12,500 as total revenue. However, ABC Limited paid ₹ 3,24,000 on resources (including urgent purchase of PPE kits and other safety equipment). In addition, ABC Limited paid ₹ 1,10,000 for Cryogenic Oxygen tanker rent, fuel and maintenance charges under fixed costs. This past April was unusually high with infections and more than expected hospitals needed oxygen urgently. Due to the time constraint and urgency, ABC Limited resorted to use extra Cryogenic Oxygen tankers than expected which were partially filled with liquid oxygen. As a result, ABC limited g has to incur extra expenses for Cryogenic Oxygen tanker rent, fuel and § additional driver’s wages.
Required:
Prepare a budget reconciliation report along with suitable analysis. (10 Marks)
Answer:
6(a)
Workings
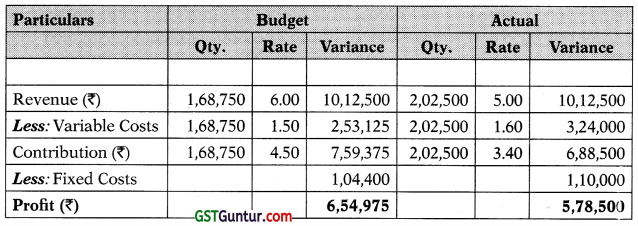
The following table shows ABC Ltd.’s budget profit and actual profit for j the month of September, 2020:
Analysis:
(1) Selling Price Variance:
ABC Ltd.’s standard selling is ₹ 1 more than the actual selling price. The actual quantity is 2,02,500. Therefore, ABC Ltd.’s selling price variance is ₹ 2,02,500 (A). It has been calculated as 2,02,500 × ₹ 1.00 = ₹ 2,02,500.
(2) Total Profit Variance:
ABC Ltd.’s standard selling (packing) price is ₹ 5 per metric ton and her standard variable cost is ₹ 1.50 per metric ton. Therefore, ABC Ltd.’s budgeted revenue = 1,68,750 × ₹ 6 = ₹ 10,12,500 and its budgeted variable costs = 1,68,750 × ₹ 1.50 = ₹ 2,53,125. From the table, we can identify that ABC Ltd.’s actual profit for September 2020 was ₹ 76,475 lower than his budgeted profit (₹ 5,78,500 -16,54,975) ie., ABC Ltd.’s total profit variance is ₹ 76,475 (A).
(3) Contribution volume variance:
ABC Ltd.’s sales contribution volume variance equals to the difference between his standard contribution and budgeted contribution. Each item is budgeted to contribute ₹ 4.50 toward profit; since ABC Ltd. sold 33, 750 metric tons more items than budgeted, the increase in volume should have contributed ₹ 1,51,875 = 33,750 × ₹ 4.50 to actual profit. Therefore, ABC Ltd.’s sales contribution volume variance is ₹ 1,51,875 (F).
(4) Variable cost variance:
ABC Ltd.’s overall variable cost variance equals to the difference between its standard variable costs and its actual variable costs, or ₹ 3,03,750 – 13,24,000 = ₹ 20,250 (A). But there is not adequate data to segregate ABC Ltd.’s variable cost variance into price and quantity elements. To compute these variances, we would require the amount of resources ABC Ltd. budgets to use per metric ton managed and the actual & budgeted price of each resource (ie., an adverse variable cost variance can arise as the company used more resources per metric ton managed and/or it paid more than budgeted for the resources used). While the issue appears to suggest that ABC Ltd.’s adverse variable cost variance arose due to spending more on liquid oxygen than planned, it is not sure that the entire ₹ 20,250 variance is attributable to this. In fact, it is likely that the liquid oxygen price variance was greater than ₹ 20,250 (A) and that ABC Ltd. had a favourable resource quantity variance to offset this.
(5) Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance:
ABC Ltd.’s fixed cost expenditure variance equals the difference between budgeted and actual fixed costs, or ₹ 1,04,400 – ₹ 1,10,000 = ₹ 5,600 (A).
We can now prepare the following Budget reconciliation report:
| Item | Amount (₹) | Amount (₹) |
| Budgeted Profit | 6,54,975 | |
| Selling Price Variance | 2,02,500 (A) | 76,475 (A) |
| Sales Volume Variance | 1,51,875 (F) | |
| Variable Cost Variance | 20,250 (A) | |
| Fixed Cost Expenditure Variance | 5,600 (A) | |
| Actual Profit | 5,78,500 |
![]()
Question 6(b).
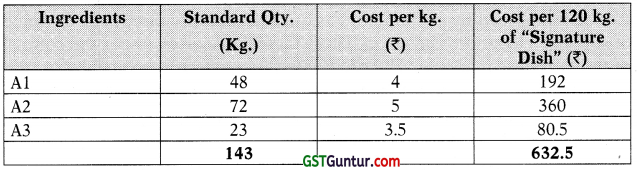
Yummy Foods Limited (YFL) is known to be the leading restaurant in India offering best in quality foods to its customers at very reasonable prices. YFL has made its credit pioneering effort and service for over one decade in development of domestic and international cuisines with its decade old unique recipes & hygiene. One of its Signature dishes is produced by mixing and cooking with three main ingredients: A1, A2 and A3. It uses a standard costing system to monitor its costs. The standard material cost for 120 kg. of the Signature dish is as follows :
Notes:
A1, A2 and A3 are organic & region-specific products. Their quality and price change significantly every year. Standard’prices are determined at the average market price over the last three years YFL has a purchasing manager responsible for purchasing and pricing. The standard mix is decided by the Managing Partner having 15 years rich experience in food recipes. The last time this was done at time of launching the signature dish was six years back. The standard mix has not been changed since.
Mixing and cooking process are subject to some evaporation losses.
In current month 5,520 kg. of “Signature dish” was produced, using the following ingredients :
| Ingredients | Standard Qty. (Kg.) | Cost per kg. (₹) | Cost per 120 kg. of “Signature Dish” (₹) |
| Al | 48 | 4 | 192 |
| A2 | 72 | 5 | 360 |
| A3 | 23 | 3.5 | 80.5 |
| 143 | 632.5 |
At every month end, the production manager receives a statement from the Managing Partner. This statement contains material price and usage variances for the month and no other feedback on the efficiency of the processes is provided.
Required:
Evaluate the performance measurement system in YFL. (10 Marks)
Answer:
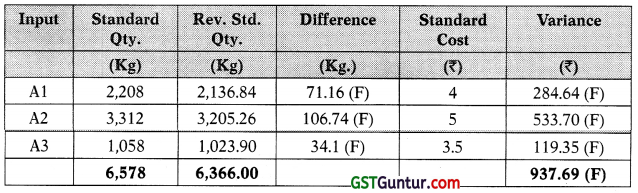
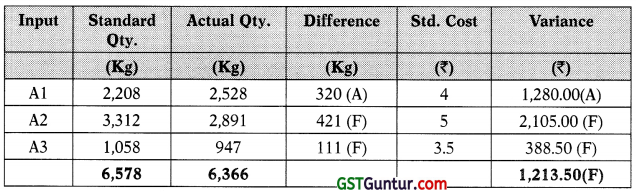
6(b) The statement reported, ₹ 2,953.60adverse material price variance. The responsibility for controlling the materials price variance usually lies J with the purchasing manager. Undoubtedly, incurrent scenario, the price of 25 materials is largely beyond his or her control; however, the price variance g can be influenced by such factors as quality, quantity discounts, distance of supplier’s location, and so on. These factors are often under the control of the purchase manager. The production manager is responsible for material usage and cannot be held responsible for the material price variance.
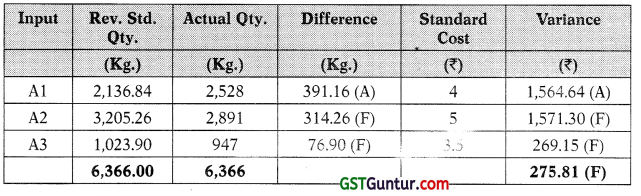
Since total usage variance reported, ₹ 1,213.50 favourable, production manager could assume good performance. However, if usage variance is considered in more detail, through the mix and yield calculations, it can be observed that variance was driven by a change in the mix and by using a mix of ingredients which was different from standard, it has resulted in a saving of ₹ 275.81. Similarly, it has led to a favourable yield. It is worthwhile to note that changing the mix could impact the product quality and sales as well, however, no information has been given about this.
Prices and quality of three agriculture ingredients are changing significantly every year. Using ex ante prices and usage standards can implicit an outdated 1 view of variances. Failing to separate variances caused by uncontrollable factors and planning errors from variances caused by controllable factors can be demoralizing for the managers.
In addition, managers are not involved in setting the standard mix and the same has not been changed for six years despite continuous changes in the quality and prices of the ingredients. This can also mislead the managers i. e., to carry out control activities which are based on the outdated standards.
Furthermore, a true image is missing in relation to managers’ performance as statement does not include any feedback or comments on the variances. Even no follow up is being taken on the same. Overall, it appears that YFL is NOT having comprehensive performance measurement system and this could adversely impact the firm in long run.
Workings:
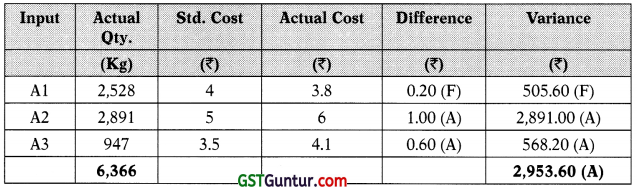
Usage Variance
Mix Variance
Yield Variance