Bills of Exchange, Consignment, Joint Venture – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Bills of Exchange, Consignment, Joint Venture – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Bills of Exchange CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short flotes on the following:
(a) Accommodation Bill (June 2016, 5 marks)
(c) Rebate on Bills Discounted (June 2016, 5 marks)
Answer:
(a) Accommodation Bill: An Accommodation Bill is a bill of exchange signed by-a party as drawer, drawee, endorser to accommodate another party whose credit is not strong enough to enable him to borrow on his single name. It is drawn for the purpose, of arranging temporary finance.
Therefore, an Accommodation Bill is a Bill of exchange which has been drawn, on and accepted by a reputable party for the purpose of giving value to the bill so that it can be discounted. What actually happens In the case of an accommodation bill is that one party draws the bill and the other party accepts it.
Then, the drawing party gets it discounted from the bank and receives eady cash of which he is in need. The money received is either wholly utilized by the drawer, or by both, the drawee and the acceptor. Before the due date approaches, the required sum of money is sent to the acceptor in order to make him able to honour the bill and the bill is honoured on the due date. Thus, although there is no legal liability, there exists a strong moral understanding between the parties concerned.
(c) Rebate on Bills Discounted: When a bank discounts a bill of exchange, the full amount of the discount earned is credited to the Discount Account but some of the Bills discounted may not mature for payment by the close for the year; as a result, the amount of discount in respect of such bill would not have been earned during the year.
On this consideration, the unexpired portion of such discount is carried forward by Debiting the Discount Account and crediting Rebate on Bills Discounted Account. The latter account is shown on the liabilities side of the Balance Sheet as income received which had hot accrued before the close of the year. At the commencement of the period next following the account is close oft by transfer to the Discount Account.
Question 2.
Write short note:
(d) Features of a Bill of Exchange. (Dec 2022, 5 marks)
Practical Questions
Question 3.
(a) On 20th July, 2012, Sohan drew a bill for ₹ 50,000 on Mohan for the period of four months and Mohan accepted it. It was for mutual accommodation of both to the extent of 2/3rd and 1/3rd. On 23rd July, 2012, Sohan discounted the bill with the Bank @ 12% per annum and remitted one-third of proceeds to Mohan. On 18 November, 2012 Mohan drew another bill for ₹ 71,000 on Sohan to provide funds to meet the first bill, for the period of three months, which was accepted by Sohan. On 21st November 2012, Mohan discounted it with Bank @ 12% per annum. With this amount, the first bill was met out and ₹ 12,580 was remitted to Sohan.
On 1st February, 20131 Sohan became insolvent and Mohan received a dividend of 60 paise in a rupee in full settlement on 15th February 2013. Give journal entries to record the above transactions in the books of Sohan and prepare Sohan’s account in the ledger of Mohan. (Dec 2013, 10 marks)
Answer:
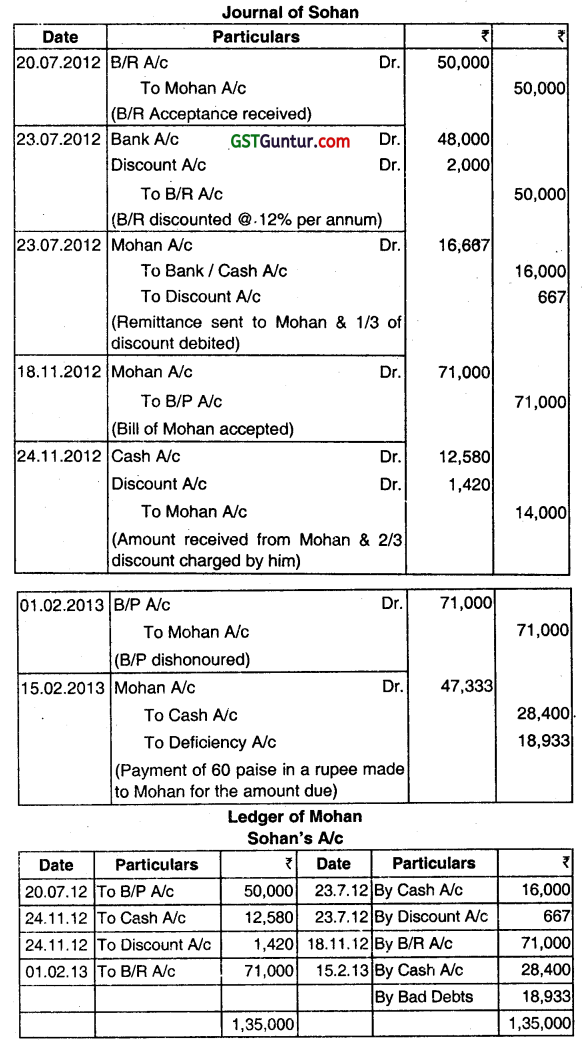
Calculation of distribution of discount
In case of accommodation bills, the proceeds of discounting are shared by parties as agreed. The discounting charges are also shared in agreed proportion. Here, the ratio between Sohan and Mohan is given as two-thirds and one-third.
![]()
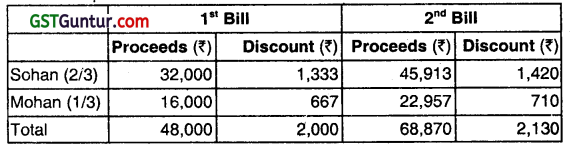
Question 4.
Big owes Fast ₹ 12,000 for which the former accepts a three months’ bill drawn by the latter. Fast immediately discounts the bill with his banker, Strong Bank, at 12% p.a. On the due date, the bill is dishonoured and Strong Bank pays ₹ 40 as noting charges. Big pays ₹ 2,360 including interest of ₹ 400 and gives another bill at three months’ for the balance.
Fast endorses the bill to his creditor Thin in full settlement of his debt for ₹ 10,200. Thin discounts the bil with banker Strong Bank who charges ₹ 80 as discount. Before maturity Big becomes bankrupt and first and final dividend of 20 paise in a ₹ is realized from his estate. Show the journal entries in the books of Thin and Strong Bank and the ledger account of Big in the books of Fast. (June 2014, 6 marks)
Answer:
Question 5.
Answer the question:
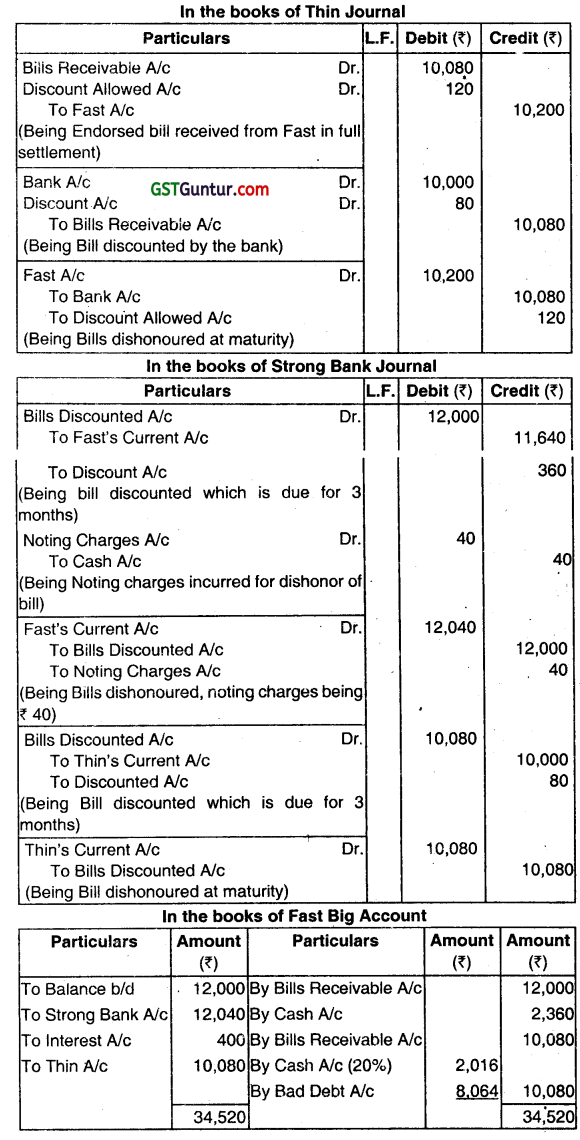
(a) BABAI sold goods to KACHARI for ₹ 90,000 on 1st April 2014 for which the later accepted three bills of ₹ 30,000 each due respectively in 1, 2 and 3 months. The first bill is retained by Babai and is duly met. The second bill was discounted (discount being ₹ 600) and is met in due course. The third bill is also discounted (discount being ₹ 900) and is dishonoured, the Noting charges being ₹ 150.
New arrangements were duly made whereby Kachan pays Cash ₹ 10,150 and accepts a new bill due in 2 months for the balance of the amount with interest at 15% p.a. The bill is retained. On due date the same is dishonoured, noting charges being ₹ 180. Kachari declared insolvent on 15th Sept 2014 and 35 paise in a rupee were received from his estate.
Required:
Pass Journal entries in the Books of BABAI. (June 2015, 8 marks)
Answer:
Question 6.
Answer the question:
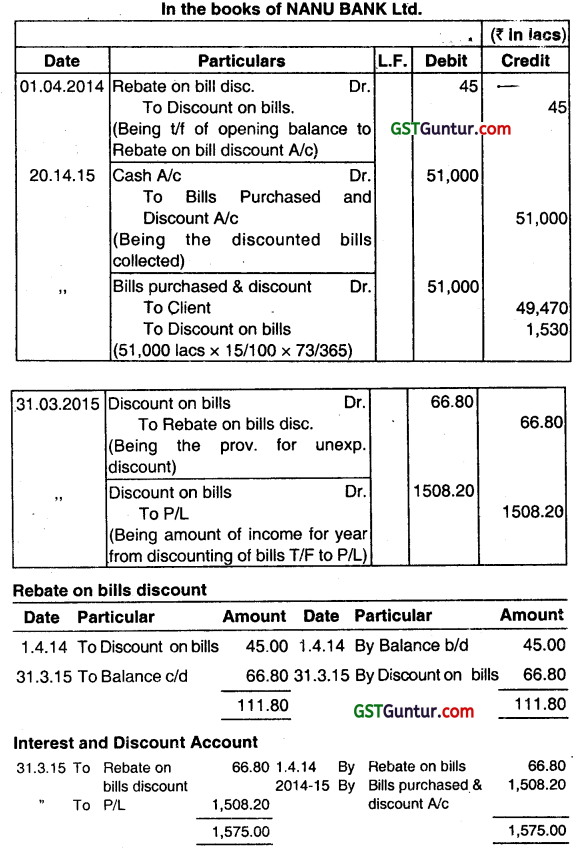
(a) On 1st April, 2014 NANU BANK LTD. had a balance of ₹ 45 Lakhs in ‘Rebate on Bills Discounted Account.’ During the year ended 31st March, 2015, Nanu Bank Ltd. discounted bills of exchange of ₹ 51,000 Lakh charging interest at 15% per annum, the average period of discount being for 73 days. Out of these, Bill of Exchange of ₹ 3,067 Lakh were due for realization from the acceptor/customers after 31st March, 2015, the average period outstanding after 31st March, 2015 being 53 days.
You are required to pass the necessary Journal Entries and show the Ledger Accounts in the Books of NANU BANK LTD. pertain to
(i) Rebate on Bills Discounted Account
(ii) Interest and Discount Account (June 2015, 4 + (2 + 2) = 8 marks)
Answer:
In the books of NANU BANK Ltd.
Question 7.
Answer the following question (Give workings):
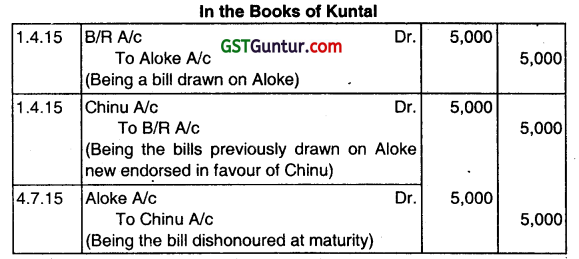
(g) On 1st April, 2015 ALOKE accepted a bill for ₹ 5,000 for 3 months drawn by KUNTAL. Kuntal endorses the bill in favour of Chinu. At maturity, the bill was dishonoured. Pass the Journal Entries in the Book of KUNTAL. (Dec 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Question 8.
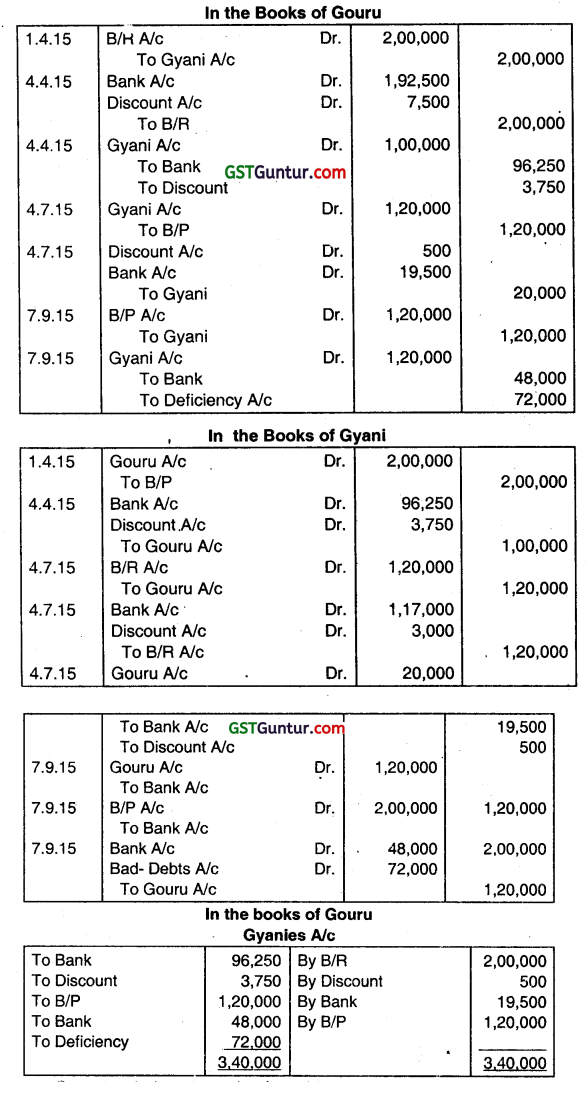
GOURU and GYANI were friends and in need of funds. On 1st April, 2015 Gouru drew a BOL for ₹ 2,00,000 for three months on Gyani. On 4.4.15 Gouru got the bill discounted at 15% per annum and remitted half of the proceeds to Gyani. On the due date, Gyani could not meet the bill, instead, Gouru accepted Gyani’s bill for ₹ 1,20,000 on 4th July, 2015 for two months. This was discounted by Gyani at 15% per annum and out this ₹ 19,500 was paid to Gouru after deducting ₹ 500 discounting charges. Due to financial crisis, Gouru became insolvent and the bill drawn on him was dishonoured and his estate paid 40%. Days of grace for discount purposes may be ignored.
Required:
(i) Give Journal Entries and
(ii) Prepare Gyani’s Account in the books of Gouru. (Dec 2015, 6 + 2 = 8 marks)
Answer:
Question 9.
VISHAN for mutual accommodation of TITHAN and himself drew upon the latter a three-months bill for ₹ 24,000 on is’ 1st July 2015, which was duly accepted. Vishan discounted the bill at 6% p.a. on 4th July 2015 and remitted 1 of the proceeds to Tithan. On 1st August 2015, Tithan drew and Vishan accepted a bill at 3 months for ₹ 9,600. On 4th August 2015, Tithan discounted the bill at 6% p.a. and remitted half the proceeds to Vishan.
At maturity, Vishan met his acceptance, but Tithan failed to meet his and Vishan had to take up. Vishan drew and Tithan accepted a new bill at two months on 4th November, 2015, for the amount due to Vshan plus ₹ 200 as interest. On 1st’ January, 2016, Tithan became insolvent and a first and final dividend of 40 paise in the rupee was received from his estate on 31st March, 2016. Note: Days of grace for discounting purposes may be ignored.
Required:
Pass the necessary Journal Entr,es in the Books of VISHAN. (Dec 2016, 4 + 3 =7 marks)
Answer:
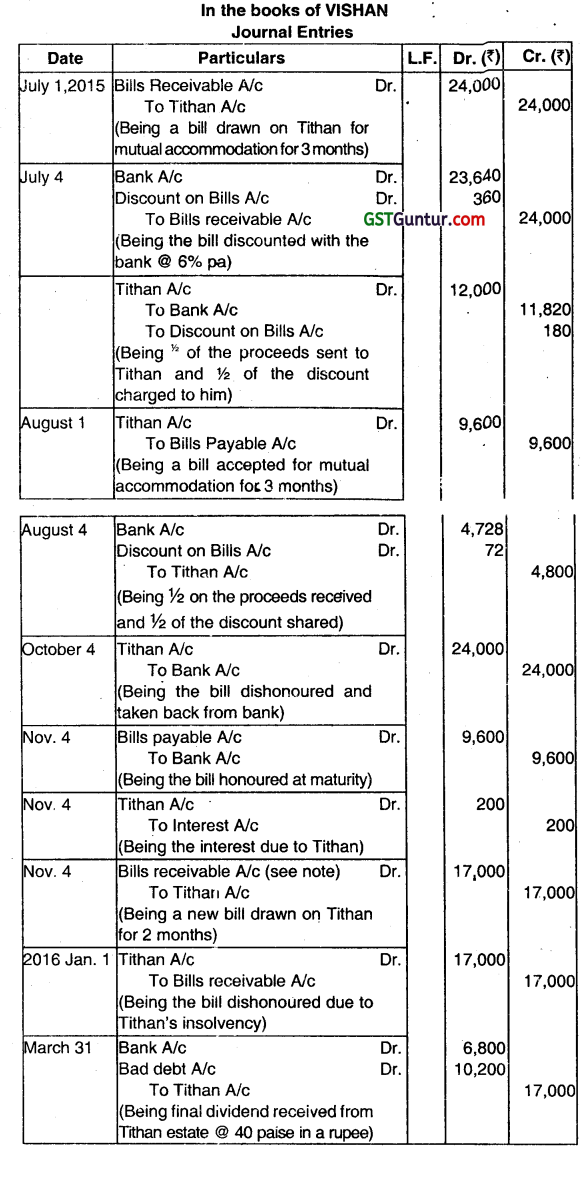
Note: Value of the new bill will be 12,000 for 1 bill + 4,800 for 2 bills + 200 for interest = 17,000.
![]()
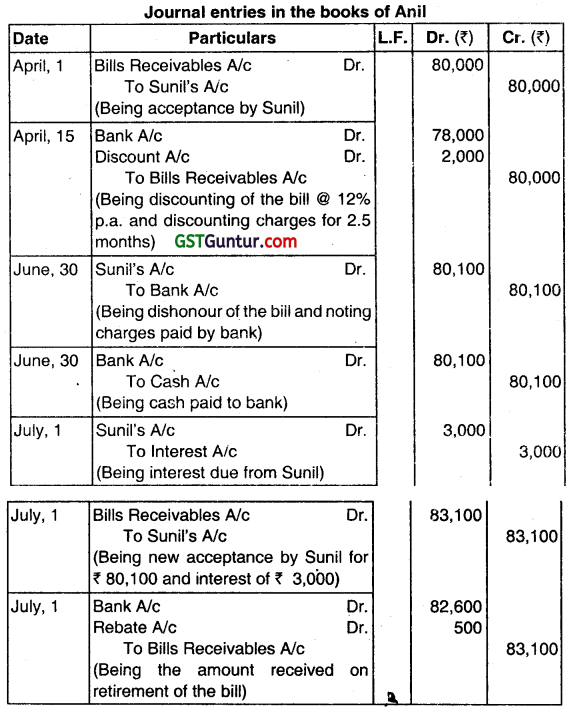
Question 10.
Sunil owed Anil ₹ 80,000. Anil draws a bill on Sunil for that amount for 3 months on 1st April. Sunil accepts it and returns it to Anil. On 1st April Anil discounts it with Citi Bank at a discount of 12% p.a. On the due date the bill was dishonoured, the bank paid noting charges ₹ 100. Anil settled the bank’s claim along with noting charges in cash. Sunil accepted another bill for 3 months for the amount due plus interest of ₹ 3,000 on 1st July. Before the new bill becomes due, SunD retires the bill with a rebate of ₹ 500. Show journal entries in books of Anil. (June 2017, 9 marks)
Answer:
Question 11.
(A) X sells goods toY for ₹ 2,00,000. Instead of one bill of ₹ 2,00,000, X draws three bills of exchange on Y for ₹ 40000; ₹ 60,000 and ₹ 1,00,000. What is the value involved in drawing three bills instead of one?
(B) Sunny draws a bill on Vivek for three months. On the due date, Vivek finds himself in financial difficulties and requests Sunny to renew the bill for a further period of one month. Sunny agrees to his request. What is the virtue involved in renewing the bill?
(C) What is the value involved in accepting an accommodation bill?
(D) What is the reason that a drawer cannot file a suit against drawee in case of dishonour of an accommodation bill? (June 2018, 1 x 4 = 4 marks)
Answer:
(A) Any of three bills may be put to different uses i.e., any of the bill may either be discounted, endorsed or kept till the date of maturity. For example, if X is in need of 30,000 he may get only the first bill discounted from the bank.
(B) Virtue involved is the expression of morality and humanism towards a fellow businessman by helping him in case of need.
(C) Value involved in accepting an accommodation bill is helping a friend who is temporarily in need of money.
(D) Because accommodation bills are drawn without consideration.
Question 12.
X draws a bill on Y. Y accepts the same. Can Y endorse the bill to Z? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
No, Y cannot endorse the bill to Z because Y is drawee only. X, the drawer can do so.
Question 13.
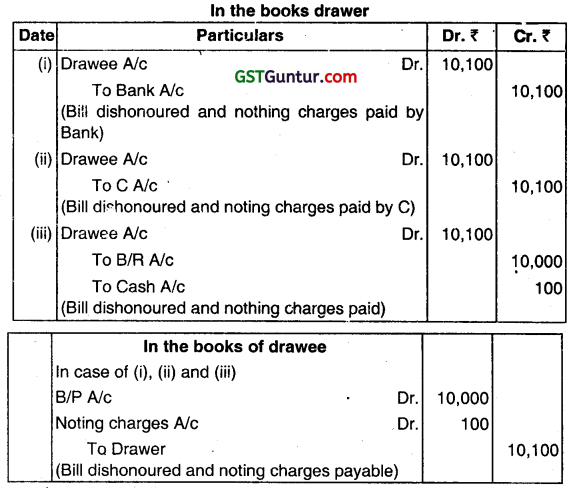
What journal entry will be passed in the books of a drawer and drawee at the time of dishonour of Bill of Exchange in the following cases?
(i) If Bill of ₹ 10,000 was discounted from the bank and the noting charges paid by the bank was ₹ 100.
(ii) If B/R of ₹ 10,000 was endorsed in favour of C. Noting charges paid by ₹ 1o0.
(iii) If B/R is retained with a drawer and noting charges was ₹100 (Dec 2021, 4 marks)
Answer:
Consignment Accounting CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short note on the following:
Treatment of Abnormal Loss in case of Consignment Account. (June 2017, 5 marks)
Answer:
Abnormal Losses arises as a result of negligence) accident etc., e.g., theft, fire etc. Before ascertaining the result of the consignment, value of abnormal loss should be adjusted. The method of calculation is similar to the method of calculating unsold stock. Sometimes insurance company admits the claim in part or in full. The same should also be adjusted against such abnormal loss.
While valuing the abnormal loss the proportionate expenses are taken only up to the stage of the loss. For example, if goods are lost in the transit on way to the consignee’s place, the value of abnormal loss will include the basic cost of the goods plus proportionate expenses of the consignor only and not the proportionate expenses of consignee because consignee has spent nothing on account of these goods.
Treatment of Abnormal Loss
(i) For Abnormal Loss –
Abnormal Loss A/c Dr,
To Consignment A/c
(ii) For the insurance claim due I received by the consignor –
Insurance Co./Bank A/c Dr.
To Abnormal Loss A/c
(iii) It goods are not insured –
Profit & Loss A/c Dr.
To Abnormal Loss A/c
(iv) For transferring the net loss –
Profit & Loss A/c Dr.
To Abnormal Loss A/c
Question 2.
Write short note on the following:
Operating cycle of Consignment Arrangement. (June 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
- Operating Cycle of Consignment Arrangement:
- Goods are sent by consignor to the consignee
- Consignee may pay some advance or accept a bill of exchange
- Consignee will incur expenses for selling the goods
- Consignee maintains records of all cash and credit sale
- Consignee prepares a summary of results called as Account sales
- Consignor pays commission to the consignee.
Question 3.
Write short notes on Overriding Commission. (Dec 2021, 3 marks)
Answer:
Overriding Commission: It is an extra commission allowed over and above, the normal Commission is generally offered for the following reasons:
- When the agent is required to put in hard work in introducing a new product in the market.
- Where he is entrusted with the work of šupervising the performance of other agents in a particular area.
- For effecting sales at prices higher than the price fixed by the consignor.
Distinguish Between
Question 4.
Differences between sale arid consignment. (Dec 2017, 5 marks)
Answer:
Difference between Sale and Consignment:
1. In sale the property in goods is transferred to the buyer immediately where as in consignment the property transferred to the buyer only when goods are sold by the consignee. The ownership of goods remains with the consignor when goods are transferred to the consignee by the consignor.
2. In sale, the risk attaching to the goods passes with ownership to the buyer, in case of a consignment, the risk attaching to the goods does not pass to the consignee who acts as a mere agent. it there is any damage or loss to the goods it is borne by the consignor provided the consignee has taken reasonable care of the goods and the damage or loss is not due to his negligence.
3. The relationship of consignor and consignee is that of a principal and an agent as in a contract of agency whereas the relationship of buyer and seller is governed by the Sale of Goods Act.
4. Unsold goods on consignment are the property of the consignor and may be returned if not saleable in the market whereas goods sold on sale basis are normally not returnable unless there is some defect in them.
![]()
Question 5.
Difference between Sale and Consignment (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Difference between Sale and Consignment:
1. In sale the property in goods is transferred to the buyer immediately where as in consignment the property transferred to the buyer only when goods are sold by the consignee. The ownership of goods remains with the consignor when goods are transferred to the consignee by the consignor.
2. In sale, the risk attaching to the goods passes with ownership to the buyer, in case of a consignment, the risk attaching to the goods does not pass to the consignee who acts as a mere agent. it there is any damage or loss to the goods it is borne by the consignor provided the consignee has taken reasonable care of the goods and the damage or loss is not due to his negligence.
3. The relationship of consignor and consignee is that of a principal and an agent as in a contract of agency whereas the relationship of buyer and seller is governed by the Sale of Goods Act.
4. Unsold goods on consignment are the property of the consignor and may be returned if not saleable in the market whereas goods sold on sale basis are normally not returnable unless there is some defect in them.
Descriptive Questions
Question 6.
What is Del Credere commission? (Dec 2013, 3 marks)
Answer:
Sometimes the consignor allows an extra commission to the consignee in order to cover the risk of collection from customers, on account of credit sales which is known as Del Credere Commission. Naturally, if debt is found to be irrecoverable the same must be borne by the consignee. There will be no effect in the books of consignor. In short, the credit sales will be treated as cash sales to consignor. If no Del Creciere Commission is given by the consignor to the consignee, the amount of Bad Debts must be borne by the consignor.
Practical Questions
Question 7.
Answer the following question (give workings wherever required):
From the following particulars, calculate the value of unsold goods on consignment:
| ₹ | |
| Goods sent on consignment (1500 kgs.) | 3,30,000 |
| Consignor’s expenses | 13,000 |
| Consignee’s non-recurring expenses | 7,000 |
| Consignee’s recurring expenses | 3,500 |
| Goods sold by consignee (1000 kgs.) | 3,50,000 |
| Wastage treated as normal (100 kgs.) | – |
(Dec 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Value of unsold Goods:
Unsold quantity = 1,500 -1,000 – 100 = 400 Kgs.
Cost of goods sent (3,30,000) + Consignor’s Exp. (13,000) + Consignee’s
non-recurring exp. (7,000) = 3,50,000.
Value of unsold goods = [3,50,000 / (1,500 – 100)] × 400 = ₹ 1,00,000.
Question 8.
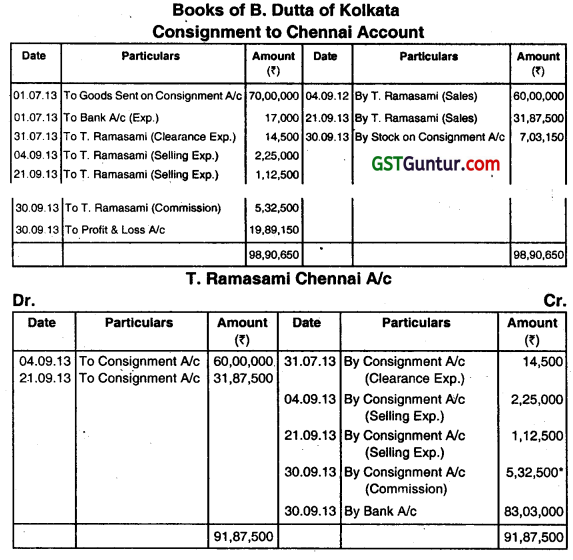
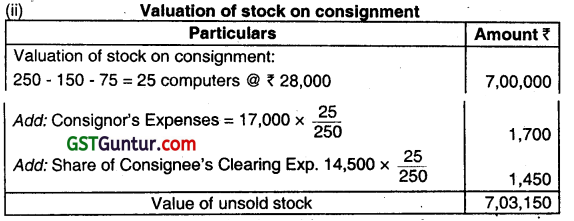
On 1st July, 2013 B. Dufta of Kolkata consigned 250 Computers costing ₹ 28,000 each to T. Ramasami, Chennal. Expenses of ₹ 17,000 were met by the consignor. T. Ramasami spent ₹ 14,500 for clearance on 31st July 2013 and selling expenses were ₹ 1,500 per computer as and when the sale made by consignee. T. Ramasami sold on 4th September 2013, 150 computers at ₹ 40,000 per computer and again on 21st September, 75 computers at ₹ 42,500.
Mr. Ramasami was entitled to a commission of ₹ 1,500 per computer sold plus one-fourth of the amount by which the gross sale proceeds less total commission thereon exceeded a sum calculated at the rate of ₹ 35,000 per computer sold. T. Ramasami sent the account sale and the amount due to B. Dutta on 30th September 2013 by bank demand draft. You are required to show the consignment account and T. Ramasami’s account in the books of B. Dutta. (June 2014, 8 marks)
Answer:
Working Notes:
(i) Calculation of Commission
Let ‘x’ be total commission
x = (225 × 1,500) + \(\frac{1}{4} \) [60,00,000 + 31,87,500 – x – 1 (35,000 × 225)]
x = 3,37,500 +\(\frac{1}{4} \) (91,87,500 – x – 78,75,000)
x = 3,37,500 + 3,28,125 – \(\frac{x}{4} \)
\(\frac{5}{4} \)x=6,65,625
x = 5,32,500
Question 9.
Answer the following questions (Give workings):
Ajay of Jaipur sent goods of ₹ 2,50,000 to Vijay of Mumbai on consignment. Ajay paid ₹ 8,500 as railway freight and ₹ 4,240 as insurance. 2% goods are damaged In the Vijay’s godown due to normal circumstances. Vijay incurred cartage ₹ 5,140 and selling expenses ₹ 14,700. Calculate the value of stock of unsold 15% of goods sent to Vijay. ₹ 3,25,000 is total cost of 6500 units, consignor’s expenses are ₹ 65,000, units lost in transit was 700 units and consignee’s non-recurring expenses amounted to ₹ 4,300, what will be the value of stock? (Dec 2014, 2 marks each)
Answer:

(h) Cost of 6500 units = Total cost + Consigner expenses = 3,25,000 + 65,000 = ₹ 3,90,000
Cost of 700 units = ( 3,90,000 ÷ 6.500) × 700 = ₹ 42,000
Value of closing stock = 6500 unit cost price Cost of units lost in transit = ₹ 3,90,000 – ₹ 42,000 = ₹ 3,48,000
Add: Non-recurring expenses = ₹ 4,300
Total cost price of 5800 units = ₹ 3,52,300
![]()
Question 10.
Answer the question:
MR NAITIK sends goods to the value of ₹ 9,37,500 at cost to MR JATIN on a consignment basis to be sold at 5% commission on sales on 01.01.2015. Jatln accepted a bill of ₹ 2,50,000 drawn by Naitik for 4 months on the same date. Naitik discounted the bill with his banker @ 15% p.a. on 04.02.2015. Naltik Incurred ₹ 75,000 by way of freight and other expenses, whereas expenses of Jatin were ₹ 50,000 out of which 60% were non-recurring. Jatin sent the final balance of ₹ 7,68,750 to Naitik on 31.03.15 along with account sales. The Gross Profit margin is 25% on Sales and 10% of Goods Remaining unsold with Jatin.
You are required to prepare:
(i) Consignment Account and
(ii) Jatin Account-in the books of Mr. Naitik. (June 2015, 8 marks)
Answer:
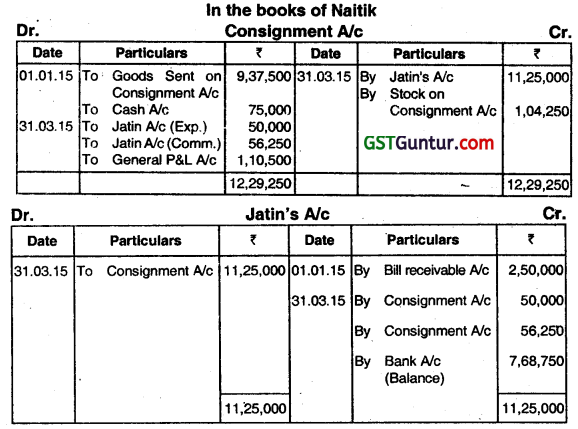
Working Notes:
1. Calculation of amount of goods sold on consignment:
\(\frac{9,37,500}{1-0.25} \times 0.90\) = ₹ 11,25,000
Question 11.
IRANI & Co., of Chennal, had consigned 6000 shirts to Vikram of Jaipur at cost of ₹ 425 each. Irani & Co., paid freight ₹ 50,000 and insurance ₹ 7,500. During the transit 550 shirts were totally damaged by fire. Vikram took delivery of the remaining shirts and paid ₹ 82,000 on customs duty. Vikram had sent a bank draft to Iraní & Co., for ₹ 3,50,000 as advance payment. 5000 shirts were sold by him at 550 each. Expenses incurred by Vikram on godown rent and advertisement, etc., amounted to ₹ 12,000. He is entitled to a commission of 5%. One of the customer to whom the goods were sold on credit could not pay the value of 40 shirts which is not recoverable. Vikram settled his account immediately. Nothing was recovered from the insurer for the damaged goods.
You are required to prepare:
(i) Consignment to Vlkram Account.
(ii) Vikram Account – in the book of IRANI & Co. (June 2016, (4+1)+2 = 7 marks)
Answer:
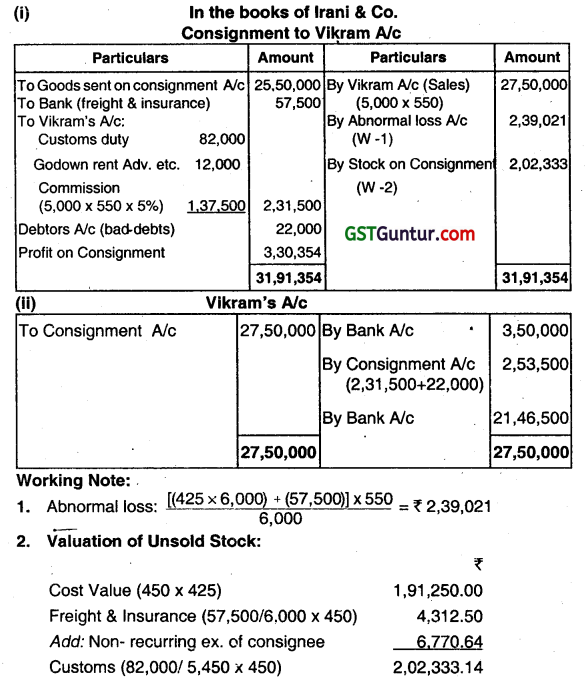
Question 12.
From the following particulars unsold stock on Consignment.
| Goods sent (1000 kgs.) | ₹ 20,000 |
| Consignor’s expenses | ₹ 4,000 |
| Consignees non-recurring expenses | ₹ 3,000 |
| Sold (800 kgs.) | ₹ 40,000 |
| Loss due to natural wastage (100 kgs.) | – |
(June 2019, 3 marks)
Answer:
Value of Unsold Stocks
| ₹ | |
| Total cost of goods sent | 20,000 |
| Add: Consignor expenses | 4,000 |
| Add: Non-recurring expenses | 3,000 |
| Cost of (1,000 Kgs – 100 Kgs) = 900 Kgs | 27,000 |
∴ Value of unsold stock (1,000- 800- 100) = 100 Kgs. will be = 27,000 × (100 Kgs. / 900 Kgs.) = ₹ 3000.
| Repeatedly Asked Questions | |
| Question | Frequency |
| 1. Difference between Sale and Consignment 17- Dec, 19- Dec | 2 Times |
Joint Venture CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Practical Questions
Question 1.
Answe the question:
X and Y entered into a joint venture for purchase and sale of some household items. They agreed to share profits and losses in the ratio of their respective contributions. X contributed ₹ 10,000 in cash and Y ₹ 13,000. The whole amount was placed in a Joint Bank Account. Goods were purchased by X for ₹ 10,000 and expenses paid by Y amounted to ₹ 2,000. They also purchased goods for ₹ 15,000 through the Joint Bank Account. The expenses on purchase and sale of the articles amounted to ₹ 6,000 (including those met by Y). Goods costing ₹ 20,000 were sold for ₹ 45,000 and the balance were lost by fire. Prepare Joint Venture Account, Jo1nt Bank Account and the Ventures’ Accounts closing the venture. (Dec 2014, 8 marks)
Answer:
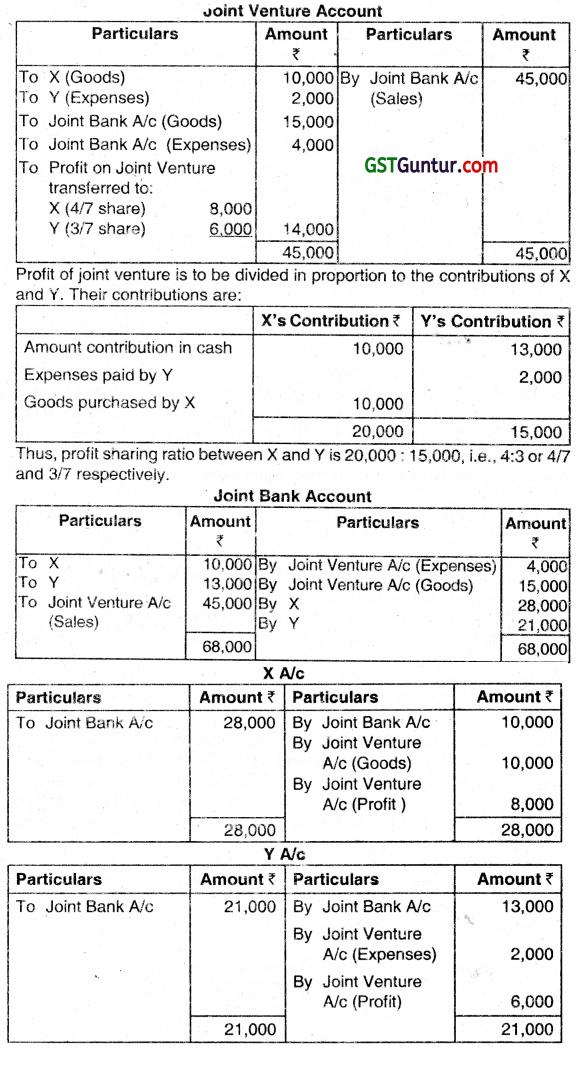
Question 2.
JIBAN and MITRIK decided to work in joint venture with the following scheme, agreeing to share profits in the ratio of 2/3 and 1/3. They guaranteed the subscription aL par of 50 lakhs shares of ₹ 10 each in RAINBOW LTD. and to pay all expenses up to allotment in consideration of RAINBOW LTD. issuing to them 3,00,000 other shares of ₹ 10 each fully paid together with a commission @ 5°’ in cash which will be taken by J IBAN and MITRIK in 3:2.
Co-ventures introduced cash as follows:
JIBAN: Stamp charges, etc. ₹ 1,65,000
Advertising charges ₹ 1,35,000
Car expenses ₹ 1,54,000
Printing charges ₹ 1,88,000
MITRIK: Rent ₹ 1,30,000
Solicitor’s charges ₹ 80,000
Application tell short of the 50 lakhs shares by 1,20,000 shares and MITRIK. introduced ₹ 12,00,000 for the purchase of those shares.
The guarantee having been fulfilled, Rainbow Ltd. handed over to the venturers 3,00,000 shares and also paid the Commission in cash. All their holdings were subsequently sold by the venturer MITRIK receiving ₹ 12,50,000 and JIBAN ₹ 25,00,000.
You are required to prepare the:
(i) Memorandum Joint Venture Account and
(ii) Joint Venture Account with MITRIK – in the Books of JIBAN. (Dec 2015, 6 + 2 = 8 marks)
Answer:
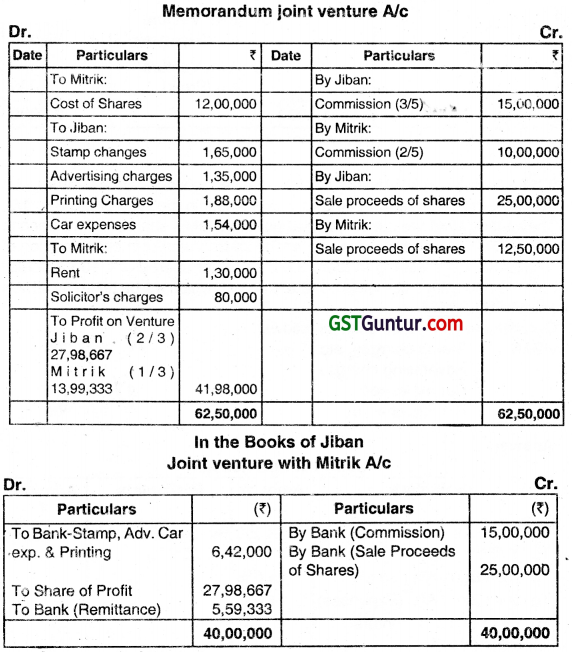
Question 3.
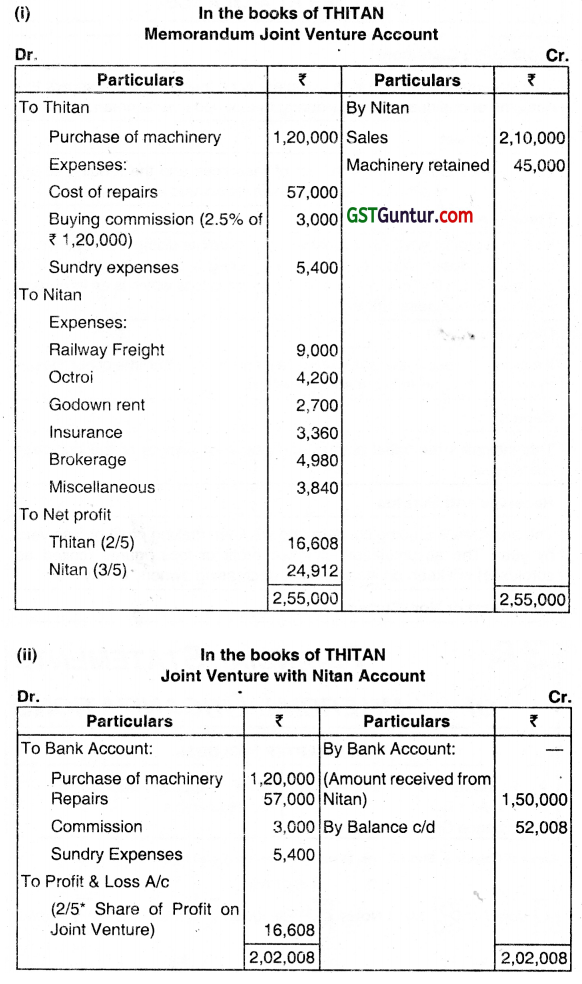
THITAN of Tatanagar and NITAN of Nagpur entered into a Joint Venture to trade together in the buying and receiving of cheap machinery. Profit or loss to be shared in the ratio of 2:3. Thitan undertook to make the purchases and Nitan to effect sales.
NITAN remitted ₹ 1,50,000 to Thtan towarus the Joint Venture. Thitan Purchased machinery worth ₹ 1,20,000 and paid ₹ 57,000, for repairs of these, 2.5% as buying commission and ₹ 5,400 for other Sundry expenses. He then sent all the machines purchased and repairtd to Nitan of Nagpur. While taking delivery of the machinery at Nagpur, Nitan incurred ₹ 9,000 towards Railway Freight and ₹ 4,200 towards Octroi. He sold part of the machinery for ₹ 2,10,000 and kept the remaining for himself at an agreed value of ₹ 45,000. Other exprises of Nitan were:
(i) Godown rent ₹ 2,700
(ii) Insurance ₹ 3,360
(iii) Brokerage ₹ 4,980; and
(iv) Miscellaneous ₹ 3,840
Both the parties decided to close the venture at this stage.
You are required to prepare the
(i) Memorandum Joint Venture Account showing profit of me Business.
(ii) Joint Venture with Nitan Account in the Books of Thitan. (Dec 2016, 5+2 = 7 marks)
Answer:
Bills of Exchange CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Bill of Exchange
An instrument in writing containing an unconditional order signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain some of money only to the order of the certain person or to the bearer of the instrument”.
Discounting a Bill
If the holder of a bill wants to get the money of the bill before its due date, he can do so by selling the bill to a bank or a Discounting House who in consideration of a charge called discount, provides him with ready cash. This is known as discounting the bill.
Dishonour of Bill
Dishonour of a Bill means that the acceptor refuses to honour his commitment on due date and for this, payment of the bill on presentation does not take place.
![]()
Renewal of Bills
Sometimes the drawee of a bill is not able to meet the budget on due date. He may request the drawer to draw a new Bill for the amount due. Sometimes he pays a certain amount out and accepts a first bill for the balance for which he has to pay a certain amount of interest which is either paid in cash or is included with the fresh bill. This bill is known as Renewal of Bills.
Retirement of Bill
Sometimes the drawee pays the bu! before the date of maturity. Under the circumstances, the drawer allows certain amount of rebase or discount which is calculated on certain percentage p.a. basis. The rebate is calculated from the date of payment to the date of maturity.
Types of Bills of Exchange
- Trade bill: This bill is drawn to settle a trade transaction.
- Accommodation bill: This bill is used without a trade transaction and is for mutual benefit.
Insolvency of Drawee (Acceptor)
Insolvency of acceptor means that he cannot pay the amount owed by him. Therefore, on insolvency of the acceptor, bill will be treated as dishonoured and entries for dishonour of bill will be passed in the books of respective parties.
Consignment Accounting CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Consignment Accounting
In case of direct selling, the company usually has depots all over. The stocks are transferred to these depots and from there finally sold to ultimate customers, This involves huge expenses and arid problems of maintaining the same on a permanent basis. Hence, the firm could appoint agents to whom stocks will be given. These agents distribute the products to ultimate customers and receive commission from the manufacturer. One such way of indirect selling is selling through consignment agents.
Consignor
He is the person who sends goods to agents e.g. a manufacturer or wholesaler.
Consignee
He is the agent to whom goods are sent for selling.
Proforma Invoice
When the consignor sends the goods to the consignee, he prepares only a proforma invoice and not an invoice. A proforma invoice looks like an invoice but is really not one.
Account Sales
This is a periodical statement prepared by consignee to be sent to the consignor giving details of all sales (cash and credit), expenses incurred and commission due for sales, destroyed-in-transit or in godown and deducting the amount of advance remitted by him.
Normal Loss
Normal Losses arise as a result of natural causes, e.g. evaporation, leakage, breakage etc., and they are inherent in nature. Since normal loss is a charge against gross profit no additional adjustment is required for this purpose.
![]()
Abnormal Losses –
Abnormal Losses arises as a result of negligence/accident etc., e.g., theft, fire etc. Before ascertaining the result of the consignment, value of abnormal loss should be adjusted.
Joint Venture CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Joint Venture Accounts
A Joint Venture is a temporary form of business organization. Two or more people having requisite skill sets come together to form a temporary. partnership. This is called a Joint Venture.
Basic Features
The basic features of a Joint Venture business are:
- It is done for a specific purpose and hence has a limited duration.
- The partners are called co-venturers.
- The profit or loss on a joint venture is shared between the co-venturers in the agreed ratio.
- The co-venturers may or may not contribute initial capital.
- The JV is dissolved once the purpose of the business is over.
- The accounts of the co-venturers are settled immediately on dissolution.
- A joint venture has no name.