AS 16: Borrowing Costs – CA Inter Accounts Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
AS 16: Borrowing Costs – CA Inter Accounts Study Material
Borrowing Costs (Based On Para Nos. S And 4)
Question 1.
Briefly indicate the items which are included in the expressions ‘Borrowing Cost’ as per AS 16. (2 Marks) (Nov. 2009)
Answer:
Borrowing costs are interest and other costs incurred by an enterprise in connection with the borrowing of funds.
Borrowing cost may include:
(a) Interest and commitment charges on bank borrowings and other short term and long-term borrowings.
(b) Amortisation of discounts or premiums relating to borrowings.
(c) Amortisation of ancillary costs incurred in connection with the arrange¬ment of borrowings.
(d) Finance charges in respect of assets required under finance leases or under other similar arrangements; and
(e) Exchange differences arising from foreign currency borrowings to the extent that they are regarded as an adjustment to interest costs.
![]()
Question 2.
Rutu Builders Limited has borrowed a sum of US$ 20,00,000 at the beginning of Financial year 2017-18 for its residential project at LIBOR +3%. The interest is payable at the end of the financial year.
At the time of availment exchange rate was 61 per US$ and the rate as on 31st March, 2018 was 65 per US $. If Rutu Builders Limited had borrowed the loan in India in Indian Rupee equivalent, the pricing of loan would have been @ 10.50%.
Compute Borrowing cost and exchange difference for the year ending 31st March, 2018 as per Accounting Standards 16. (Applicable LIBOR is 1%). (5 Marks) (May 2018)
Answer:
(i) Interest for the period 2017-18
= US $ 20 lakhs × 4% × ₹ 65 per US $ = ₹ 52 lakhs
(ii) Exchange Loss on principal amount
= US $ 20 lakhs × ₹ (65 – 61) = ₹ 80 lakhs.
(iii) Interest that would have resulted if the loan was taken in Indian currency
= US $ 20 lakhs × ₹ 61 × 10.5% = ₹ 128.1 lakhs
(iv) Difference between interest on local currency borrowing and foreign currency borrowing
= ₹ 128.1 lakhs – ₹ 52 lakhs = ₹ 76.1 lakhs.
Out of ₹ 80 lakhs increase in the liability towards principal amount, only ₹ 76.1 lakhs will be considered as the borrowing cost.
The remaining ₹ 3.9 lakhs (₹ 80 lakhs – ₹ 76.1 lakhs) would be considered as the exchange difference to be accounted for as per AS 11 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’.
![]()
Question 3.
Raj & Co. has taken a loan of US$ 20,000 at the beginning of the financial year for a specific project at an interest rate of 6% per annum, payable annually. On the day of taking loan, the exchange rate between currencies was ₹ 48 per 1 US$. The exchange rate at the closing of the financial year was ₹ 50 per 1 US$. The corresponding amount could have been borrowed by the company in Indian Rupee at an interest rate of 11% per annum. Determine the treatment of borrowing cost in the books of account. (4 Marks) (Nov 2013)
Answer:
The following computations would be made to determine the amount of borrowing costs for the purpose of AS 16 ‘Borrowing Costs’:
Interest for the period = US $ 20,000 × ₹ 50 per US $ × 6% = ₹ 60,000.
Exchange loss on principal amount
= US$ 20,000 × ₹ (50-48) = ₹ 40,000.
Interest that would have resulted if the loan was taken in Indian Currency
= US $ 20,000 × 48 × 11% = ₹ 1,05,600
Difference between interest on local currency borrowing and foreign currency borrowing
= ₹ 1,05,600 – ₹ 60,000 = ₹ 45,600 (B)
In the above case, ₹ 40,000 is less than ₹ 45,600, therefore the entire exchange difference of 40,000 would be considered as borrowing costs.
The total borrowing cost would be ₹ 100000 (₹ 60000 + ₹ 40000)
![]()
Question 4.
X Limited has borrowed a sum of US $ 10,00,000 at the beginning of Financial Year 2016-17 for its residential project at 4 %. The interest is payable at the end of the Financial Year. At the time of availment exchange rate was ₹ 56 per US $ and the rate as on 31st March, 2017 was ₹ 62 per US $. If Omega Limited borrowed the loan in India in Indian Rupee equivalent, the pricing of loan would have been 10.50%.
You are required to compute Borrowing Cost and exchange difference for the year ending 31st March, 2017 as per applicable Accounting Standards.
Answer:
(i) Interest for the period 2016-17
= US $ 10 lakhs × 4% × ₹ 62 per US$ = ₹ 24.80 lakhs
(ii) Exchange loss on principal amount
= US $ 10 lakhs × 7 (62 – 56) = ₹ 60 lakhs
(iii) Interest that would have resulted if the loan was taken in Indian currency
= US $ 10 lakhs × ₹ 56 × 10.5% = ₹ 58.80 lakhs
(iv) Difference between interest on local currency borrowing and foreign currency borrowing
= ₹ 58.80 lakhs – ₹ 24.80 lakhs = ₹ 34 lakhs.
Out of ₹ 60 lakhs increase in the liability towards principal amount, only ₹ 34 lakhs will be considered as the borrowing cost.
The remaining ₹ 26 lakhs (60 – 34) would be considered as the exchange difference to be accounted for as per AS 11.
![]()
Qualifying Asset (Based On Para Nos. 3 And 5)
Question 5.
A company capitalizes interest cost of holding investments and adds to cost of investment every year, thereby understating interest cost in profit and loss account. Comment on the accounting treatment done by the company in context of the relevant AS. (RTP)
Answer:
Investments other than investment properties are not qualifying assets as per AS-16 ‘Borrowing Costs’. Therefore, interest cost of holding such invest¬ments cannot be capitalized.
Question 6.
A company incorporated in June 2017, has setup a factory within a period of 8 months with borrowed funds. The construction period of the assets had reduced drastically due to usage of technical innovations by the company. Whether interest on borrowings for the period prior to the date of setting up the factory should be capitalized although it has taken less than 12 months for the assets to get ready for use. You are required to comment on the necessary treatment with reference to AS 16. (RTP)
Answer:
As per para 3.2 to 4S 16 ‘Borrowing Costs’, a qualifying asset is an asset that necessarily takes a substantial period of time to get ready for its intended use or sale.
Further, AS 16 states that what constitutes a substantial period of time primarily depends on the facts and circumstances of each case. However, ordinarily, a period of twelve months is considered as substantial period of time unless a shorter or longer period can be justified on the basis of facts and circumstances of the case.
Analysis:
In estimating the period, time which an asset takes, technologically and commercially, to get it ready for its intended use or sale is considered.
It may be implied that there is a rebuttable presumption that a 12 months period constitutes substantial period of time.
In the given case where construction period has reduced drastically due to technical innovation, the 12 months period should at best be looked at as a benchmark and not as a conclusive yardstick. It may so happen that an asset under normal circumstances may take more than 12 months to complete. However, an enterprise that completes the asset in 8 months should not be penalized for its efficiency by denying it interest capitalization and vice versa.
Conclusion:
Therefore, if the factory is constructed in 8 months then it shall be considered as a qualifying asset. The interest on borrowings for the same shall be capitalised although it has taken less than 12 months for the asset to get ready to use.
![]()
Specific And General Borrowings With Qualifying Asset Concept (Based On Para Nos. 3, 5, 10 And 12)
Question 7.
U Limited borrowed an amount of ₹ 150 crores on 1.4.2016 for construction of boiler plant @ 11% p.a. The plant is expected to be completed in 4 years. Since the weighted average cost of capital is 13% p.a., the accountant of Rainbow Ltd. capitalized ₹ 19.50 crores for the accounting period ending on 31.3.2017. Due to surplus fund out of ₹ 150 crores, income of ₹ 3.50 crores were earned and credited to profit and loss account. Comment on the above treatment of accountant with reference to relevant accounting standard. (RTP)
Answer:
Para 10 of AS 16 Borrowing Costs’ states ‘To the extent that funds are borrowed specifically for the purpose of obtaining a qualifying asset, the amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalisation on that asset should be determined as the actual borrowing costs incurred on that borrowing during the period less any income on the temporary investment of those borrowings.
Analysis and accounting treatment:
In the given case, treatment of accountant of U Ltd. is incorrect.
The amount of borrowing costs capitalized for the financial year 2016-17 should be calculated as follows:

Question 8.
Rohini Limited has obtained loan from an Institution for ₹ 500 lacs for modernization and renovation of its plant and machinery. The installation of plant and machinery was completed on 31.3.2009 amounting to ₹ 320 lacs and ₹ 50 lacs were advanced to suppliers of additional assets and the balance of ₹ 130 lacs have been utilized for working capital requirements. Total interest paid for the above loan amounted to ₹ 65 lacs during 2008-09. You are required to state how the interest on institutional loan is to be accounted for in the year 2008-09. (2 Marks) {May 2010)
Answer:
As per AS 16 ‘Borrowing Costs \ borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of qualifying assets should be capitalised as part of the cost of that asset. Other borrowing costs are recognized as expense in the period in which they are incurred.
Accounting Treatment:
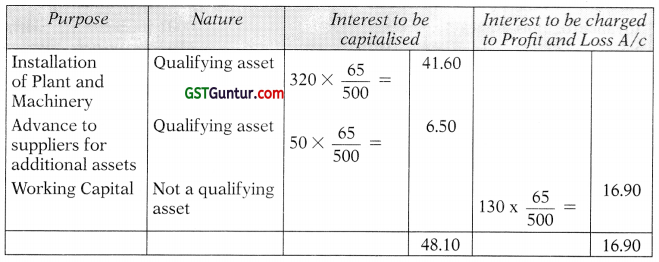
![]()
Question 9.
On 1st April, 2009, Amazing Construction Ltd. obtained a loan of ₹ 32 crores to be utilized as under:

Show the treatment of interest by Amazing Construction Ltd. (4 Marks) (Nov 2010)
Answer:
Accounting Treatment:
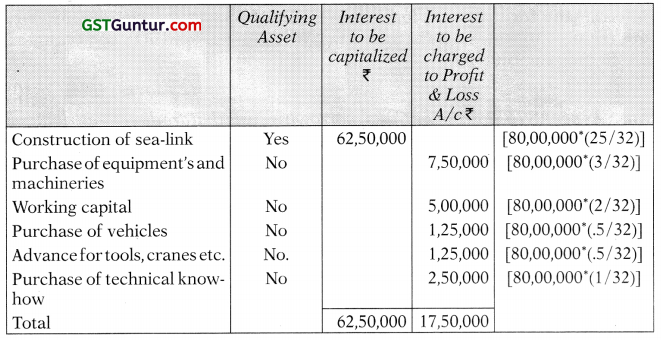
Question 10.
On 25th April, 2010, Neel Limited obtained a loan from the bank for ₹ 70 lakhs to be utilized as under:

In March, 2011, construction of shed was completed and machinery installed. Delivery of truck was not received. Total interest charged by the bank for the year ending 31st March, 2011 was ₹ 12 lakhs. Show the treatment of interest under Accounting Standard 16. (5 Marks) (Nov 2011)
Answer:
Accounting Treatment of Interest:
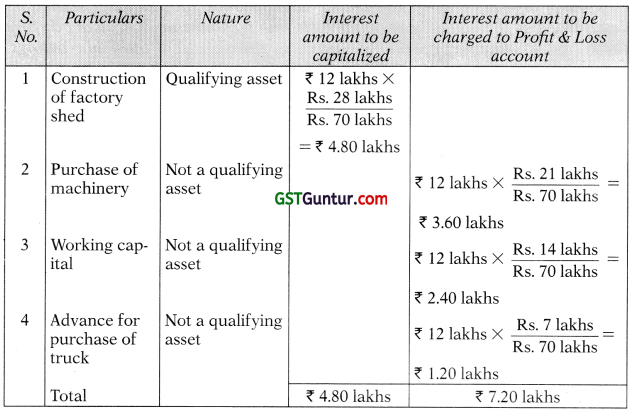
![]()
Question 11.
Suhana Ltd. issued 12% secured debentures of ₹ 100 Lakhs on 01.05.2013, to be utilized as under:

In March 2014, construction of the factory building was completed and machinery was installed and ready for its intended use. Total interest on debentures for the financial year ended 31.03.2014 was ₹ 11,00,000. During the year 2013-14, the company had invested idle fund out of money raised from debentures in banks’ fixed deposit and had earned an interest of ₹ 2,00,000.
Show the treatment of interest under Accounting Standard 16 and also explain nature of assets. (5 Marks) (May 2014)
Answer:
According to para 6 of AS 16 ‘Borrowing Costs’, borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of a qualifying asset should be capitalised as part of the cost of that asset. The amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalisation should be determined in accordance with this Standard. Other borrowing costs should be recognised as an expense in the period in which they are incurred.
Also para 10 of AS 16 ‘Borrowing Costs’ states that to the extent that funds are borrowed specifically for the purpose of obtaining a qualifying asset, the amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalisation on that asset should be determined as the actual borrowing costs incurred on that borrowing during the period less any income on the temporary investment of those borrowings.
Amount eligible for capitalization:
= ₹ 11,00,000 – ₹ 2,00,000
= ₹ 9,00,000
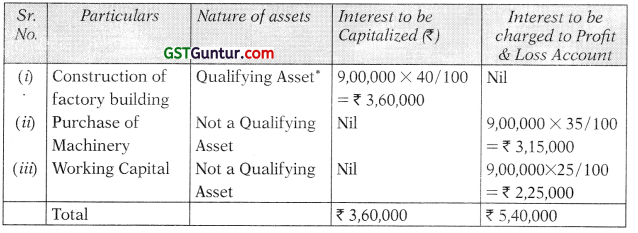
Question 12.
M/s. Zen Bridge Construction Limited obtained a loan of ₹ 64 crores to be utilized as under:

Show the treatment of Interest according to Accounting Standard by M/s. Zen Bridge Construction Limited. (5 Marks) (Nov 2016)
Answer:
Accounting Treatment:
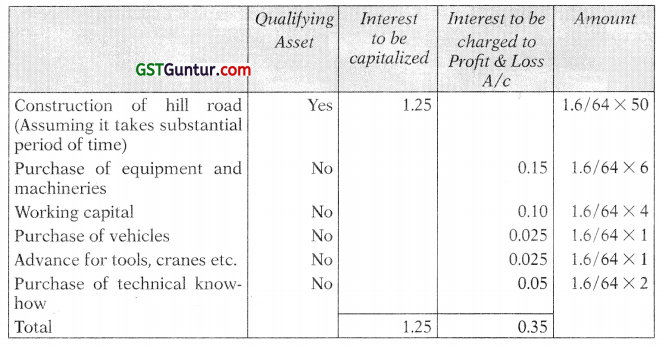
![]()
Question 13.
X Limited began construction of a new plant on 1st April 2012 and obtained a special loan of 8 lakhs to finance the construction of the plant. The rate of interest on loan was 10 per cent per annum.
The expenditure that was made on the construction project of plant was as follows:

The Company’s other outstanding non – specific loan was ₹ 46,00,000 at an interest of 12 per cent per annum.
The construction of the plant was completed on 31-3-2013. You are required to calculate the amount to be capitalized including amount of interest as per the provision of AS 16 ‘Borrowing Costs’. (RTP)
Answer:
Step 1:
Computation of weighted average accumulated expenses

Step 2:
Non-specific Borrowings utilized for construction of Plant
Non-specific Borrowings = Average accumulated capital expenses – Specific borrowings
= ₹ 27,00,000 – ₹ 8,00,000 = ₹ 19,00,000
Step 3:
Interest on weighted average accumulated expenses
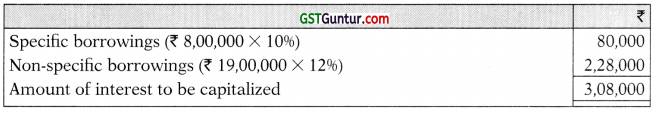
Step 4:
Total expenses to be capitalized for Plant

![]()
Question 14.
Axe Limited began construction of a new plant on 1st April, 2008 and obtained a special loan of ? 4,00,000 to finance the construction of the plant. The rate of interest on loan was 10%.
The expenditure that were made on the project of plant were as follows:

The company’s other outstanding non-specific loan was ₹ 23,00,000 at an interest rate of 12%.
The construction of the plant completed on 31st March, 2009.
You are required to:
(a) Calculate the amount of interest to be capitalized as per the provisions of AS 16 ‘Borrowing Cost’.
(b) Pass a journal entry for capitalizing the cost and the borrowing cost in respect of the plant. (5 Marks) (Nov 2009)
Answer:
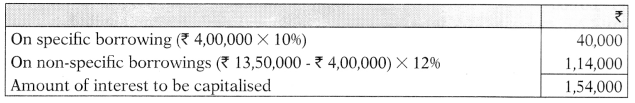
Total expenses to be capitalised:
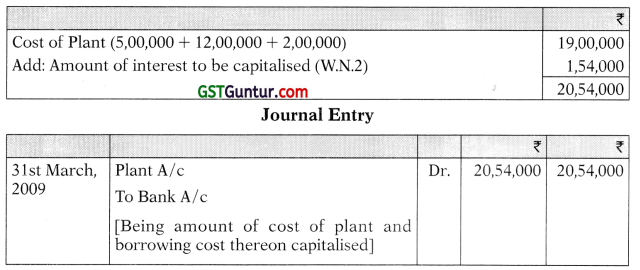
Working Notes :
1. Computation of average accumulated expenses
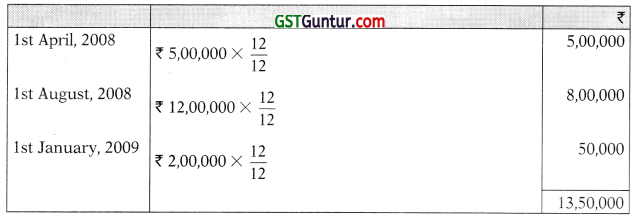
2. Amount of interest capitalised
![]()
Question 15.
M/s. Ayush Ltd. began construction of a new building on 1st January, 2014. It obtained ₹ 3 lakh special loan to finance the construction of the building on 1st January, 2014 at an interest rate of 12% p.a. The company’s other outstanding two non-specific loans were:
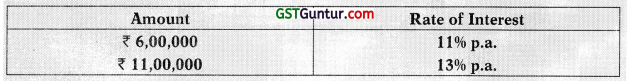
The expenditure that were made on the building project were as follows:
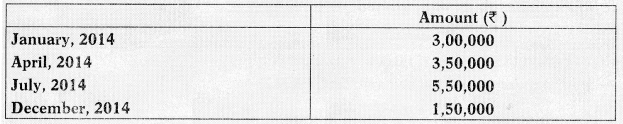
Building was completed on 31st December, 2014. Following the principles prescribed in AS 16 ‘Borrowing Cost’, calculate the amount of interest to be capitalized and pass one Journal entry for capitalizing the cost and borrowing in respect of the building. (5 Marks) (May 2015)
Answer:
(i) Computation of average accumulated expenses

(ii) Calculation of average interest rate other than specific borrowings
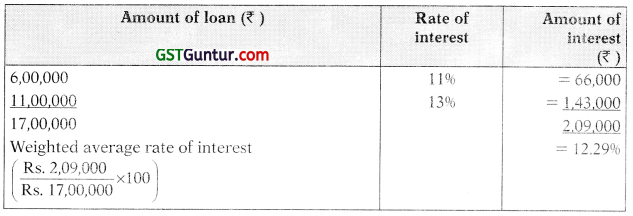
(iii) Interest amount eligible for capitalization

(iv) Journal Entry

![]()
Question 16.
Small Limited began construction of a building on 1st April, 2016 which is expected to cost ₹ 25,00,000. The construction of the building was financed through a special loan of ₹ 10,00,000 obtained at an interest rate of 10% per annum on 1st April, 2016. Further, expenditure on the building was financed through other non-specific finance arrangements of the company. Details of non-specific finance arrangements are as under:

Cumulative expenses incurred on the building were as follows:

Construction of the building was completed on 31st March, 2017. Following the principles specified in AS 16 ‘Borrowing Cost’, calculate the amount of interest to be capitalized. (5 Marks) (Nov 2017)
Answer:
Computation of average accumulated expenses

Non-specific Borrowings
Non-specific Borrowings = Average accumulated capital expenses – Specific borrowings
= ₹ 14,75,000 – ₹ 10,00,000 = ₹ 4,75,000
Interest amount eligible for capitalization

Working Note:
Computation of average interest rate other than for specific borrowings

![]()
Commencement, Suspension and Cessation of Borrowing Costs (Based on Para Nos. 14, 17, 19 and 21)
Question 17.
Write short note on ‘Suspension of Capitalisation’ in context of Accounting Standard 16. (4 Marks) (May 2016)
Answer:
Capitalization of borrowing costs should be suspended during extended periods in which active development is interrupted.
Borrowing costs may be incurred during an extended period in which the activities necessary to prepare an asset for its intended use or sale are interrupted. Such costs are costs of holding partially completed assets and do not qualify for capitalization.
However, capitalization of borrowing costs is not normally suspended during a period when substantial technical and administrative work is being carried out. Capitalization of borrowing costs is also not suspended when a temporary delay is a necessary part of the process of getting an asset ready for its intended use or sale.
For example, capitalization continues during the extended period needed for inventories to mature or the extended period during which high water levels delay construction of a bridge, if such high-water levels are common during the construction period in the geographic region involved.