Accounting Standards – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Accounting Standards – CMA Inter Financial Accounting Study Material
Short Notes
Question 1.
Write short note:
Recognition of Govt. grants related to specific fixed assets (PPE). (June 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Recognition of Govt. grants related to specific fixed assets (PPE):
Grants received specifically for fixed asset(PPE) is disclosed in the financial statement either
(i) by way of deduction from the gross block of the asset concerned, thus granted recognized in Profit and Loss Account through reduced depreciation (in case of funding of specific asset Cost entirely, the asset should be stated at a nominal value in Balance Sheet); or
(ii) the grant treated as deferred revenue income and charged off on a systematic and rational basis over the useful life of the asset, until appropriated disclosed as – Deferred Govt. grant under Reserves and Surplus in the Balance Sheet (grants relating to depreciable assets should be credited to Capital Reserve and suitably credited to Profit and Loss Account to offset the cost charged to income).
Question 2.
Write short note on the following:
Advantages of Accounting Standard (June 2017, 5 marks)
Answer:
Following are the Advantages of setting up Accounting Standards:
- Standards reduce to a reasonable extent or eliminate altogether confusing variations in the Accounting Treatment used to prepare the Financial Statements.
- There are certain areas where important information is not required by law to be disclosed. Standard may call for Disclosure that is beyond that is required by law.
- It facilitates comparison of Financial statements of different Companies at different places.
Question 3.
Write short note on the following:
Bearer Plant. (June 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
A bearer plant is a plant that:
- is used in the production or supply of agricultural produce;
- is expected to bear produce for more than a period of twelve months; and
- has a remote likelihood of being sold as agricultural produce, except for incidental scrap sales.
The following are not bearer plants:
- plants cultivated to be harvested as agricultural produce;
- plants cultivated to produce agricultural produce when there is more than a remote likelihood that the entity will also harvest and sell the plant as agricultural produce, other than as incidental scrap sales;
- annual crops.
![]()
Question 4.
Write short flotes on the following:
Objective and necessity for providing Depreciation (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Objective and Necessity for Providing Depreciation:
Eric Kohler defined depreciation as the lost usefulness, expired utility, the diminution in service yield.” Its measurement and charging are necessary for cost recovery. It is treated as a part of the expired cost for an asset. For determination of revenue, that part or cost should be matched against revenue.
The objects or necessities of charging depreciation are as given below:
- Correct calculation of cost of production: Depreciation is an allocated cost of a fixed asset. It is to be calculated and charged correctly against the revenue of an accounting period. It must be correctly included within the cost of production.
- Correct calculation of profits: Costs incurred for earning revenues must be charged properly for correct calculation of profits. The consumed cost of assets (depreciation) has to be provided for correct matching of revenues with expenses.
- Correct disclosure of fixed assets at reasonable value: Unless depreciation is charged, the depreciable asset cannot be correctly valued and presented in the Balance Sheet. Depreciation is charged so that the Balance Sheet exhibits a true and fair view of the affairs of the business.
- Provision of replacement cost: Depreciation is a non-cash expense. But net profit, is calculated after charging it. Through annual depreciation, cash resources are saved and accumulated to provide replacement cost at the end of the useful life of an asset.
- Maintenance of capital: A significant portion of Capital has to be invested for purchasing fixed assets. The values of such assets are gradually reduced due to their regular use and passage of time. Depreciation on the assets is treated as an expired cost and it is matched against revenue. It is charged against profits. if it is not charged the profits will remain inflated. This will cause capital erosion.
- Compliance with technical and legal requirements: Depreciation has to be charged to comply with the relevant provisions of the Companies Act and Income Tax Act.
Question 5.
Write short flotes on Borrowing Cost as per AS-16. (Dec 2021, 3 marks)
Answer:
Borrowing Cost as per AS-16:
Borrowing costs are interests and other costs incurred by an enterprise in connection with the borrowing of funds. The standard is applied in accounting for borrowing costs which include:
- interest and commitment charges on bank borrowing and other short-term borrowings;
- Amortization of discounts/premiums relating to borrowings;
- Amortization of ancillary cost incurred in connection with arrangement of borrowings;
- Finance charges for assets acquired under finance lease or other similar arrangement
- Exchange difference in foreign currency borrowing to the extent it relates to interest element
Descriptive Questions
Question 6.
Answer the following:
State the disclosure requirements under AS-12. (Dec 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Disclosure under AS-12:
- The accounting policy adopted for Gnvemment Grants including, method of presentation in the financial statement.
- The nature and extent of Govt. grants recognized in the financial statements, including grants of non-monetary assets given at a concessional rate or free of cost.
Question 7.
What are the disclosure requirements for an enterprise as per AS-11? (Dec 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Disclosure under AS -11:
An enterprise should disclose:
- The amount of exchange difference included in the net profit or loss for the period.
- The amount of exchange difference adjusted in the carrying amount of fixed assets (PPE) during the accounting period.
- The amount of exchange difference in respect of forward contracts to be recognized in the profit/loss for one or more subsequent accounting periods.
- Foreign currency risk management policy.
![]()
Question 8.
Answer the question:
What are disclosure requirements under AS-11? (Dec 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Disclosure under AS -11: An enterprise should disclose:
- The amount of exchange difference included in the net profit or loss for the period.
- The amount of exchange difference adjusted in the carrying amount of fixed assets (PPE) during the accounting period.
- The amount of exchange difference in respect of forward contracts to be recognized in the profit loss for one or more subsequent accounting periods.
- Foreign currency risk management policy.
Question 9.
What is a biological asset as per (AS-10)? (Dec 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
Biological assets is a living animals or plants.
Practical Questions
Question 10.
On 31st December, 2011 two machines which were purchased on 1.10.2008 costing ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 20,000 respectively had to be discarded and replaced by two new machines costing ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 25,000 respectively. One of the discarded machines was sold for ₹ 20,000 and other for ₹ 10,000. The balance of Machinery Account on April 1st, 2011 was ₹ 3,00,000 against which the depreciation provision stood at ₹ 1,50,000. Depreciation was provided @ 10% on Reducing Balance Method. Prepare the Machinery Account, Provision for Depreciation Account, and Machinery Disposal Account. (June 2013, 5 marks)
Answer:
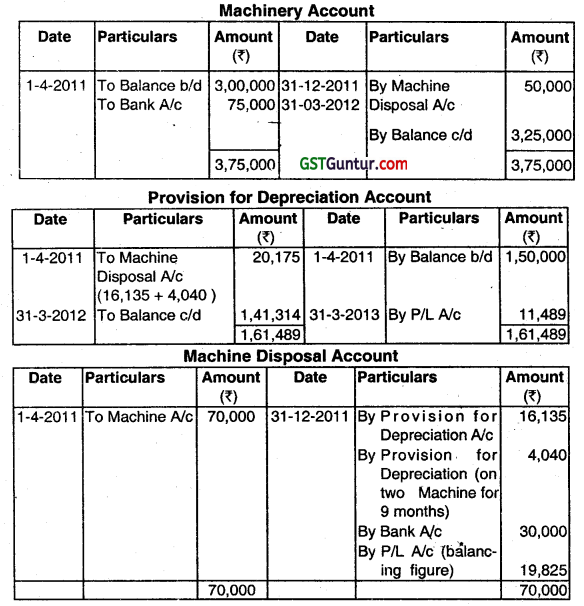

Question 11.
Answer the following question (give workings wherever required):
On 01.01.2010, M/s. Johnson arid Co. Ltd. purchased machinery for ₹ 1,00,000. Subsequently, 50,000 was paid for installation. Assuming that the rate of depreciation was 10% on Reducing Balance Method, determine the Closing Book Value of the Machine as at 31.12.2012. (Dec 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
| Year | ₹ | Rate | Depreciation | ₹ |
| 2010 | 1,50,000 | 10% | 15,000 | 1,35,000 |
| 2011 | 1,35,000 | 10% | 13,500 | 1,21,500 |
| 2012 | 1,21500 | 10% | 12,150 | 1,09,350 |
₹ 1,09,350
Question 12.
Answer the following:
From the following information for Rishab Ltd. for the year ended 31.03.2013, calculate the deferred tax asset/liability as per AS-22.
Accounting Profit ₹ 10,00,000
Book Profit as per MAT (Minimum Alternate Tax) ₹ 9,00,000
Profit as per Income Tax Act ₹ 1,00,000
Tax Rate 30%
MAT Rate 10%
(Dec 2013, 5 × 2 = 10 marks)
Answer:
Tax as per accounting profit 10,00,000 × 30% = ₹ 3,00,000
Tax as per income tax profit 1,00,000 × 30% = ₹ 30,000
Tax as pei MAT 9,00,000 × 10% = ₹ 90,000
Tax Expense = Current Tax + Deferred Tax
Therefore Deferred Tax Liability as on 31.3.2013= ₹ 3,00,000 – ₹ 30,000 = ₹ 2,70,000
Amount of Tax to be debited in Profit and Loss AIc for the year 31.3.2013:
= Current Tax + Deferred Amount of Tax liability + Excess of MAT over current tax
= 30,000 + 2,70,000 + (90,000 – 30,000) = ₹ 3,60,000
Alternative answer for second part of the answer
Amount of tax to be debited in Profit and Loss A/c for the year 31.3.2013
= Current Tax (MAT) + Deferred Tax = 90,000 + 2,70,000 = 3,60,000
Both the options can be considered favourably.
![]()
Question 13.
The following details are provided by an Import House:
| Particulars | Exchange rate |
| Goods purchase done 24th August,2012 | 1 Us Dollar = ₹ 47.10 |
| Us Dollar | 2,00,000 |
| Exchange rate on 31st March,2013 | ₹ 54.20 |
| Exchange rate on date of actual payment on 25th May, 2013 | ₹ 56.30 |
Calculate gain or loss for the financial years 201 2-13 and 2013-14 and its accounting treatment. (Dec 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
As per AS-11, all foreign currency transactions should be recorded by applying the exchange rate at the date of transaction. Therefore, goods purchased on 24m August, 2012 and corresponding creditor would be recorded at ₹ 47.10.
= 2,00,000 x 47.10 = ₹ 94,20,000
As per As-11, at the balance sheet date all monetary items should be reported using the closing rate. Therefore, the creditors of US $ 2,00,000 outstanding on 31st March, 2013 will be reported as:
= 2,00,000 x 54.20 = ₹ 1,08,40,000
Exchange loss ₹ 14,20,000(1,08,40,000 – 94,20,000) should be debited in profit and loss account for 2012-13.
As per AS-11, exchange difference on settlement on monetary items should be transferred to profit and loss account as gain or loss thereof:
= 2,00,000 x 56.30 = 1,12,60,000 – 1,08,40,000 = ₹ 4,20,000
₹ 4,20,000 should be debited to profit or loss for the year 201 3-14.
Question 14.
Answer the following question (give workings):
| Cost of Machine | ₹ 1,30,000 |
| Residual value | Nil |
| Useful life | 10 years |
| Method of Depreciation in use | Straight Line Method |
| After 8 years, the machine was revalued to | ₹ 80,000 |
Compute Depreciation as per AS-10. (June 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Computation of Depreciation as per AS- 10
| Particulars | Amount (₹) | |
| A | Original Cost | 1,30,000 |
| B | Less. Aggregate Depreciation up to 8 years (1,30,000-Nii) x 8/10 | 1,04,000 |
| C | Existing unamortized Depreciation Amount (A – B) | 26,000 |
| D | Add: Profit on Revaluation (80,000 -26000) | 54,000 |
| E | Revised unamortized depreciable amount (C + D) | 80,000 |
| F | Depreciation for 9th year (₹ 80,000/2) | 40,000 |
Question 15.
Jayakrishna Mills Ltd., runs a modern wheat flour mill. The CEO has prepared the draft accounts, duly considering the mandatory accounting standards. Following note appears: “The company purchased on 15.6.2013, a special purpose machinery for ₹ 75 lakhs. It received a State Government grant for 10% of the price. The machine has an effective lite of
10 years”. What is the proper method of accounting treatment for the above? (June 2014, 4 marks)
(ii) Springlily Ltd. borrowec US $ 6,00,000 on 31 .12.2013 which will be repaid (settled) as on 30.6.2014. The company prepares its financial statements ending on 31.3.2014.
Rate of exchange between reporting currency (Rupee) and foreign currency (US $) on different dates are as under:
31.12.2013 1 US$=₹ 64.00
31.03.2014 1 US$=₹ 64.50
30.06.2014 1 US $ = ₹ 6475
State the aspects to be noted while preparing the financial statements due to the applicable AS. How should the difference in exchange rates be treated? (June 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) AS-12 prescribes two methods in accounting treatment of Government grants for specific fixed assets(PPE).
Method I: Government grants related to depreciable fixed assets (PPE) to be treated as deferred income which is to be recognized in the Protit and Loss Account in proportion in which depreciation on those assets is charged over the useful life of the asset.
The deferred income pending its apportionment to Profit and Loss Account to be disclosed in the balance sheet separately with a suitable description, e.g. Deferred Government Grants, to be shown after “Reserves & Surplus” but before” Secured Loans”.
Method II: Grants received specifically for Fixed Asset(PPE) may be disclosed in the financial statement by way of deduction from the gross block of the asset concerned, thus grant is recognised in P/L Account through reduced depreciation.
In this case machinery will be recognised at ₹ 67.5 lakhs i.e. after deduction of ₹ 7.5 lakhs Govt. Grants ånd depreciation will be calculated on that ₹ 67.5 lakhs.
Answer:
(ii) As per AS-11, all foreign currency transactions should be recorded by applying the exchange rate at the date of transaction. Therefore, amount borrowed on 31.12.2013 and corresponding lender would be recorded at ₹ 64.00
= 6,00,000 x 64.00 = 3,84,00,000
As per AS-11, at the balance sheet date all monetary items should be reported using the closing rate. Therefore, the lenders of US $ 6,00,000 outstanding on 31 .3.14 will be reported as:
= 6,00,000x 64.50 = 3,87,00,000.
Exchange loss 300,000 = (3,87,00,000- 3,84,00,000) should be debited in profit and loss account for 2013-14.
As per AS-11, exchange difference on settlement on monetary items should be transferred to profit and loss account as gain or loss thereof:
6,00,000 x 64.75 = 3,88,50,000 – 3,87,00,000 = ₹ 1,50,000 should be debited to profit or loss for the year 2014-15.
![]()
Question 16.
Answer the following questions (Give workings):
A machine costing ₹ 13,75,000 is depreciated on a straight-line basis assuming 8 years working life and zero residual value. After third year machine’s remaining useful life was reassessed at 7 years. Calculate the amount of depreciation charged for 4e year. (Dec 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
(a) WDV of Machinery at the end of 3rd year
= \(13,75,000-3\left(\frac{13,75,000-0}{8}\right) \)
= 8,59,375
Depreciation for 4th year
= \(\left(\frac{8,59,375-0}{7}\right) \)
= 1,22,768
Question 17.
Answer the questions:
During the year 2013-14, Purvi Limited received a grant from the Government of India aríounting to ₹ 35 lakh towards purchase of a piece of land for ₹ 140 lakh. You are required to show the accounting treatment of the above transaction in the books of PuM Limited, as per AS-12. (Dec 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
As per AS-12, accounting for Government Grants reLated to non- depreciable assets should be credited to capital reserve.

Question 18.
Answer the question:
(a) A company writes off depreciation at 10% p.a. on the diminishing balance. On 1st January, 2011 the machinery account showed a balance of ₹ 1,49,000. It was discovered in 2011 that:
(i) A heavy repairs effected to plant and machinery account (completed on 30th June, 2009), were debited to the machinery. The amount was ₹ 15,000; and
(ii) A machine cost ₹ 6,000 was entered in the purchases on 15th October 2009. The expenses on installation, ₹ 400 were debited to General Expenses Account. Necessary corrections were to be made in 2011. On 3Qth June 2011, a machine which had cost ₹ 20,000 on 1st January, 2009 was disposed of for ₹ 15,000 and a machine costing ₹ 30,000 was installed on the same date, the expenses on installing the same being ₹ 500. Show Machinery Account for the year ended 31st December, 2011. Please show your working in detail. (Dec 2014, 12 marks)
Answer:
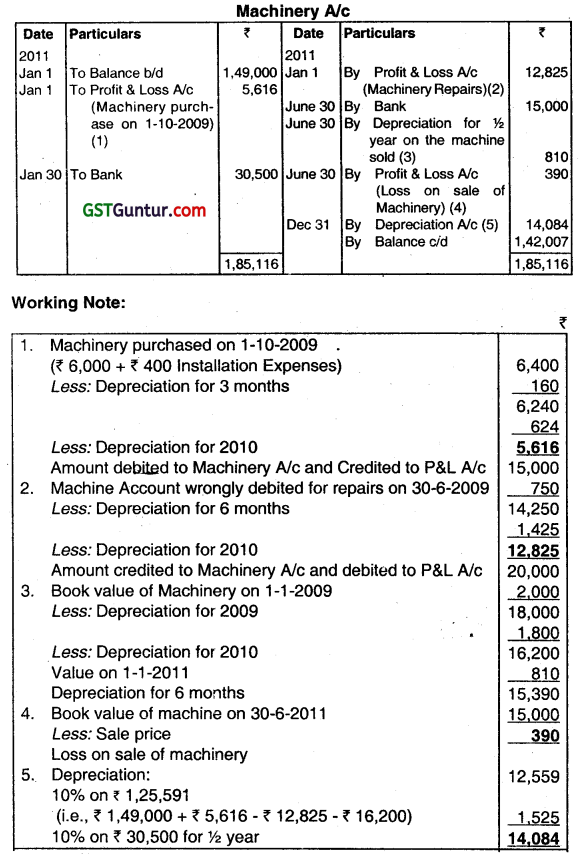

Note: As per AS-10 an item of property, plant, and equipment should be recognized as an asset if and only if it is probable that future economic benefits associated with the item will flow to the enterprise and cost of the item can be measured reliably.
Question 19.
Answer the questions:
Rukmani Limited purchased a plant for US $ 2,50,000 on 1st March, 2015, payable after three months. Company entered into a forward contract for three months @ ₹ 54.10 per dollar. Exchange rate per dollar on 1st March, 2015 was ₹ 53.74. Compute amount of profit or loss on forward contract as per AS-11. How will you recognise the same in the books of the company? (June 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Forward Premium = (54.10 – 53.74) x 2,50,000 = ₹ 90,000
As per AS- 11 this should be expended over the tenor of contract i.e. three months (01.03.2015 to 31 .05.2015).
![]()
Question 20.
Answer the question:
Patta Ltd. purchased a piece of Land for ₹ 25,00,000 for which it received a grant from the State Government amounting to ₹ 6,00,000. How will you treat government grant in the accounts as per AS-12? Also pass the necessary journal entries of the above in the books of the company. (June 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
Grant related to non-depreciable Fixed Assets (PPE). (AS-12) Grant is shown as deduction from the gross value of assets in arriving at its book value when grant is equal to the cost of asset, the asset should be shown in the balance sheet at nominal value.
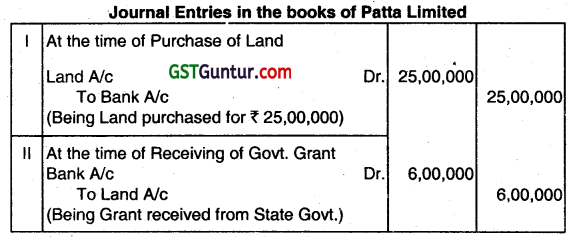
Question 21.
Answer the question:
JIMIRA LTD. bought a Machine on 30.09.2014 at a price of ₹ 248 Lakh after charging 6% Sales Tax and giving a trade discount of 1.3% on the quoted price. Transport charges and installation charges were 0.30% and 0.75% respectively on the quoted price. To meet machine purchase a loan of ₹ 240 Lakh was taken from the bank on which interest at 12%
P.A. was to be paid. Expenditure incurred on trial run was materials, wages and overheads ₹ 24,000, ₹ 18,000 and ₹ 11,000 respectively. Machine was ready for use on 01-12-2014. However, it was actually put to use only on 01-05-201 5. Entire loan amount remain unpaid on 01-05-2015.
Required:
Find the cost of machine as per AS-10 (June 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
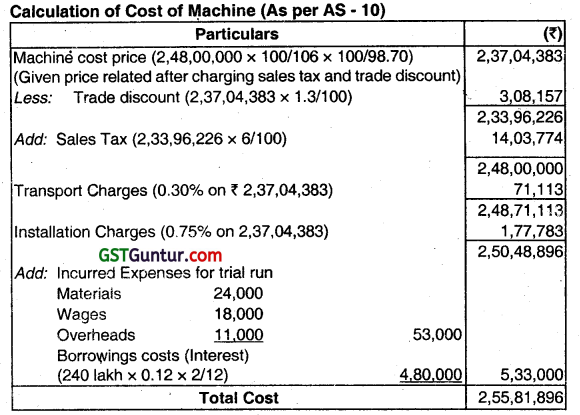
Question 22.
Answer the questions:
Shiva Limited has received a grant of ₹ 15 crores from the Government for setting up a manufacturing unit in a backward area. Out of this grant, the company distributed ₹ 4 crores as dividend. Also, Shiva Limited received land free of cost from the State Government but it has not recorded it at all in the books as no money has been spent. In the light of AS-12 examine, whether the treatment of both the grants is correct. (Dec 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
As per AS -12 “Accounting for Government Grants,’ when Government Grant is received for a specific purpose, it should be utihzed for the same. So, the Grant received for setting up a manufacturing unit is not available for distribution of dividend. In the case, even if the company has not spent money for the acquisition of land, land should be recorded in the books of accounts at a nominal value. The treatment of both the elements in the treatment of the grant is incorrect as per AS -12.
Question 23.
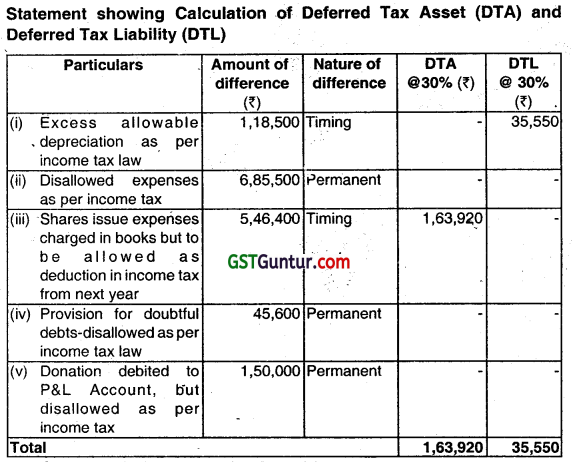
M/s. Eagle Ltd. gives you the following information as on 31.03.2015:
(i) The Company has charged depreciation of ₹ 6,45,600 in its books of accounts, while as per income-tax computation, the depreciation available to the company is ₹ 7,64,100.
(ii) The expense of ₹ 6,85,500 has been charged to profit and loss account which are disallowed under the Income-tax Ad.
(iii) The Company has debited share issue expenses of ₹ 5,46,400, which will be available for deduction under the Income-tax Act for the next year.
(iv) The Company has made provision for doubtful debts for ₹ 45,600 during the year.
(v) The Company has made donation of ₹ 3,00,000, which has been debited to profit and loss account and only 50% thereof will be allowed as deduction as per Income-tax law.
You are required to compute the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liability as on 31.03.2015. The tax rate applicable is 30%. (Dec 2015, 5 marks)
Answer:
![]()
Question 24.
Answer the following questions (Give workings):
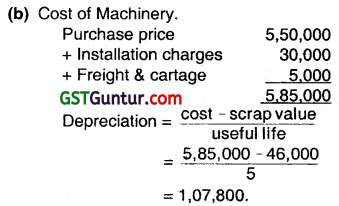
On April 1, 2014, ZOOM LTD. purchased a Machine for ₹ 5,50,000 and spent ₹ 30,000 on its installation, ₹ 5,000 for freight and cartage and ₹ 10,000 for Insurance Charges. The expected life of the Machine is 5 years, at the end of which the estimated scrap value will be ₹ 46,000. Calculate the amount of Annual Depreciation under Straight Line Method. ( Dec 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Question 25.
Answer the following:
From the following details ‘of Zebra Ltd., calculate the deferred tax asset/liability as per AS-22 and the amount of tax to be debited in the Profit & Loss A/c under different heads for the year ended 31-03 2016.
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Accounting profit | 15,00,000 |
| Book profit as per MAT | 13,50,000 |
| Profit as per Income-tax Act | 2,00,000 |
| Tax rate | 30% |
| MAT rate | 7.50% |
(Dec 2016, 5 marks)
Answer:
| Tax expense as per accounting profit | 15,00,000 x 30% | = ₹ 4,50,000 |
| Tax as per Income tax profit | 2,00,000 x 30% | = ₹ 60,000 |
| Tax as per MAT | 13,50,000 x 7.5% | = ₹ 1,01,250 |
| Deferred tax liability as on 31-03-2016 (Tax expense – Current tax) | 4,50,000 – 60,000 | = ₹ 3,90,000 |
Amount of tax to be debited in the Profit & Loss A!c under different heads for the year ended 31-03-2016.
| Current tax | ₹ 60,000 |
| Deferred tax liability | ₹ 3,90,000 |
| Excess of MAT over current tax | ₹ 41,250 |
| Total | ₹ 4,91,250 |
Question 26.
Answer the following questions:
The following information relate to ZOOM Ltd.
Imported Raw materials on 25.02.2015 for US $ 10,000;
Exchange Rate on 25.02.2015 ₹ 60 per US $;
Exchange Rate on 31.03.2015 ₹ 60.50 per US $;
Date of Actual payment for import: 15.06.2015;
Exchange Rate on 15.06.2015 ₹ 61 per US $;
Calculate the (Loss)/Gain for the financial year 2015-16 (as per AS-11).
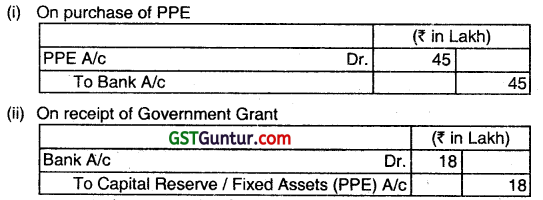
ATIMA LTD. purchased a fixed asset (PPE) for ₹ 45 Lakh on 05.04.201 5. The company received a grant from the Government of West Bengal during the year amounting to ₹ 18 Lakh. Show the accounting treatment of the above if it is non-depreciable asset as per AS-12. (Dec 2016, 2 marks each)
Answer:
As per AS-1 1 outstanding liability for creditors as on 31.03.2015 will be reported (10,000 × 60.50) = ₹ 6,05,000.
Hence (loss) /Gain for the year 2015-16 will be 10,000 × (61 -60.50) = (₹ 5,000)
As per AS-12 accounting for Government Grants related to non-depreciable assets should be credited to Capital Reserve.
Accounting entries:
Question 27.
Answer the following questions (Give workings):
BHARAT TUSHAR LTD. which depreciates its machinery at 10% p.a. on diminishing balance method, had on 1st April, 2015, ₹ 29,160, to the debit of Machinery Account. On 31st March, 2016, the company decided to change the method of depreciation to straight line method, the rate of depreciation remaining the same. Pass the necessary Journal entry for Depreciation on 31st March 2016. (Modified) (Dec 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:

Question 28.
Z Ltd. sold goods to a US Company for US $ 50000 on 10.02.2017 and realized the due on 30.06.2017. Z Ltd. closes the books of accounts on 31st March. Exchange rates were as follows:
| Date | Rate |
| 10.02.2017 | 65.40 |
| 31.03.2017 | 66.00 |
| 30.06.2017 | 65.80 |
Calculate the exchange loss/gain the reporting date and on the settlement date and comment on their treatment as per AS 11. (Dec 2017, 3 marks)
Answer:
As per AS 11, transactions such as purchase, sales etc. are to be recorded in the books of accounts at the exchange rate pfevailing on the date of transaction. Any exchange gain/ loss arising subsequently is to be transferred to Income Statement.
Value of the goods sold = $ 50000
Exchange rate on the date of transaction = ₹ 65.40/$
So sales to be recorded in the books = 50000 x 65.40 = ₹ 3,270.000
Exchange rate on the date of reporting (31.03.17) = ₹ 66.00/$’
Value of the receivables on 31.03.17 = 5000 x 66 = ₹ 3,300,000
Exchange gain on 31.03.2017 = (33,00,000 – 32,70,000) = ₹ 30,000, to be credited to P/L A/c.
Exchange rate on the date of settlement (30.06.17) = ₹ 65.80/$
Exchange loss on 30.06.17 = 50000 x (66.00 – 65.80) = 10.000 to be debited to P/L A/c.
![]()
Question 29.
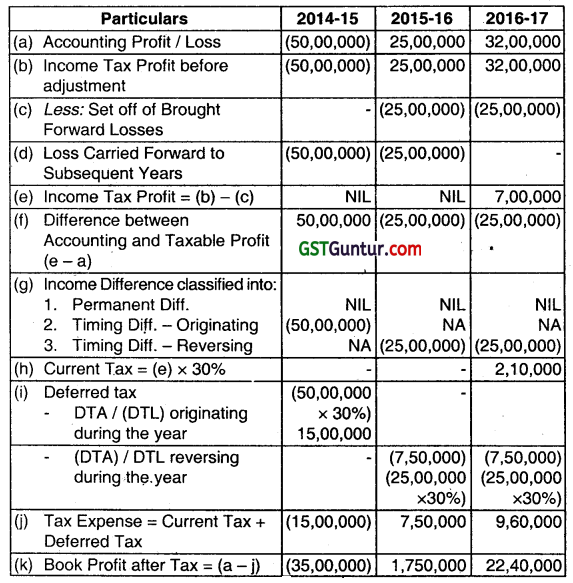
Sanwar Ltd. made a loss of ₹ 50 Lakhs for the year ending 31st March, 2015. For the year ending 31 March, 2016 and 31 March, 2017 it made profits of ₹ 25 Lakhs and ₹ 32 Lakhs respectively. It is assumed that the loss of a year can be carried forward for eight years and tax rate is 30%. By the end of the 31.03.2015, the company feels that there will be sufficient taxable income in the future years against which carry forward loss can be set off. There is no difference between taxable income and accountimg income except that the carry forward loss is allowed in the years ending on 31st March, 2016 and 2017 for tax purposes. Prepare a statement showing Profit and Loss before Tax and after Tax for the years ending 31st March, 2015, 2016 and 2017. (Dec 2017, 8 marks)
Answer:
Question 30.
M/s. Ayush Ltd. began construction of a new building on 1st January, 2017. It obtained 3,00,000 lakh special loan to tinnce the construction of the building on 1st January ,201 7 at an Interest rate of 12% p.a. The company’s other outstanding two non-specific loans were:
| Amount | Rate of Interest |
| ₹ 6,00,000 | 11%p.a. |
| ₹ 11,00,000 | 13%p.a. |
The expenditure that were made on the building project were as follows: Building was completed on 31 December, 2017. Following the principles prescribed in AS 16 on ‘Borrowing Cost’, calculate the amount of interest to be capitalized and pass one Journal entry for capitalizing the cost and borrowing in respect of the building. (June 2018, 6 marks)
Answer:
| Amount (₹) | |
| January, 2017 | 3,00,000 |
| April, 2017 | 3,50,000 |
| July, 2017 | 5,50,000 |
| December, 2017 | 1,50,000 |
Building was completed on 31st December, 2017. Following the principles prescribed in AS 16 on ‘Borrowing Cost’, calculate the amount of interest to be capitalized and pass one Journal entry for capitalizing the cost and borrowing in respect of the building. (June 2018, 6 marks)
Answer:
(i) ComputatIon of average accumulated expenses:
| ₹ | |
| ₹ 3,00,000 × 12/12 | 3,00,000 |
| ₹ 3,50,000 × 9 / 12 | 2,62,500 |
| ₹ 5,50,000 × 6 / 12 | 2,75,000 |
| ₹ 1,50,000 × 1/12 | 12,500 |
| ₹ 13,50,000 | 8,50,000 |
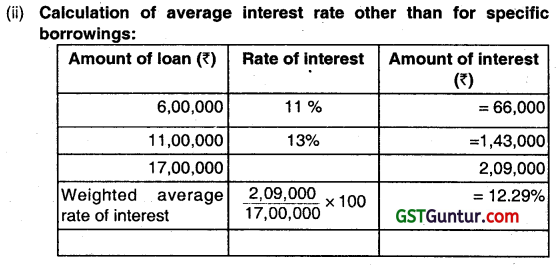
(iii) Interest amount to be capitalized:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Specific borrowings (₹ 3,00,000 × 12%) | = 36,000 |
| Non-specific borrowings [ (₹ 5,50,000 (₹ 8,50,000 – ₹ 3,00,000) × 12.29%] | = 67,595 |
| Amount of interest to be capitalized | = 1,03,595 |
(iv) Computation of actual Interest costs incurred during the year:
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| ₹ 3,00,000 × 12% | 36,000 |
| ₹ 6,00,000 × 11% | 66,000 |
| ₹ 11,00,000 × 13% | 1,43,000 |
| 2,45,000 |
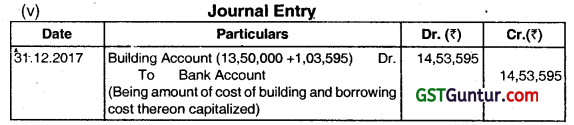
Amount to be capitalized is ₹ 13,50,000 +₹ 1,03,595 i.e. ₹ 14,53,595 which is not more than ₹ 2,45,000.
![]()
Question 31.
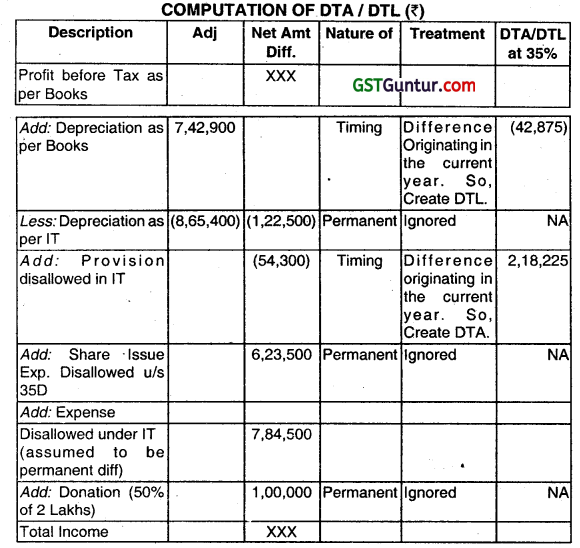
From the given information, you are required to compute the Deferred Tax Assets and Deferred Tax Liability for Ramanujam Limited as on 31st’ March, 2018. The tax rate applicable is 35%
(i) The Company has charged Depreciation of ₹ 7,42,900 in its Books of Accounts while as per Income Tax computation, the Depreciation available to the Company is ₹ 8,65,400.
(ii) The Company has made Provision for Doubtful Debts for ₹ 54,300 during the year.
(iii) The Company has debited Share Issue Expenses of ₹ 6,23,500 which will be available for deduction under the Income Tax Act from the next year.
(iv) The expenses of ₹ 7,84,500 has been charged to Profit and Loss Account which are disallowed tinder the Income Tax Act.
(v) The Company has made Donation of ₹ 2,00,000 which has been debited to Profit and Loss Account and only 50% thereof will be allowed as deduction as per Income Tax Law. (June 2018, 8 marks)
Answer:
Question 32.
K Ltd. purchased goods from a US Company for US $ 50000 on 10.02.2019 and settled the due on 30.06.2019. K Ltd. closes the books of accounts on 31st March. Exchange rates were as follows:
| Date | Rate |
| 10.02.2019 | 47.4 |
| 31.03.2019 | 46 |
| 30.06.2019 | 47.8 |
Calculate the exchange loss/gain on the reporting date and on the settlement date and comment on their treatment as per AS 11. (Dec 2019, 4 marks)
Answer:
As per AS 11, transactions such as purchase, sales, etc. are to be recorded in the books of accounts at the exchange rate prevailing on the date of transaction. Any exchange gain loss arising subsequently is to be transferred to Income Statement.
Value of the goods purchased = $ 50,000
Exchange rate on the date of transaction = ₹ 47.40/$
So, purchase to be recorded in the books = 50,000 × 47.40 = ₹ 23,70,000
Exchange rate on the date of reporting (31 .03.19) = ₹ 46.00/$
Value of the payables on 31.03.19 = 50,000 × 46 = ₹ 23,00,000
Exchange gain on 31.03.2019= (23,70,000 – 23,00,000) = ₹ 70,000, to be credited to P/L A/C.
Exchange rate on the date of settlement (30.06.19) = ₹ 47.80/$
Exchange loss on 30.06.19 – 50,000 × (47.80 – 46.00) = ₹ 90,000 to be debited, to P/L A/c.
Question 33.
Total borrowing and interest cost for the year ending on 31.03.2020 are given below:
| Borrowing | Date of Borrowing | Amount (₹) | Interest (₹) |
| 8% Term Loan | 1.4.2019 | 20,00,000 | 1,60,000 |
| 8% Bank Loan | 1.7.2019 | 60,00,000 | 3,60,000 |
| 6% Debentures | 1.10.2019 | 40,00,000 | 1,20,00,000 |
| 1,20,000 | 6,40,000 |
Qualifying assets in which these funds are utilized are:
| Particulars | Amount (₹) | Period |
| Factory Shed | 20,00,000 | 12 months |
| Plant A | 14,00,000 | 8 months |
| Plant B | 9,00,000 | 6 months |
From the above information calculate
(i) Capitalization rate
(ii) Total Interest Cost to be capitalized. (Dec 2021, 6 marks)
Answer:
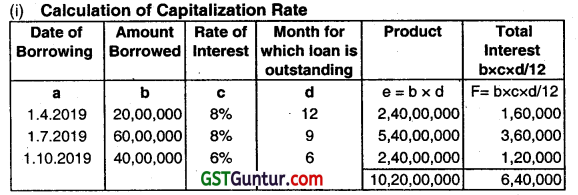
Average amount outstanding = \(\frac{10,20,00,000}{85,00,000} \) = 85,00,000
Capitalisation Rate = \(\frac{640,000}{85,00,000} \times 100 \) = 7.5% Approx.
(ii) Total interest cost to be capitalised
| Particulars | Expenditure incurred | Month | Product |
| a | b | c | d =(b x c) |
| Factory Shed | 20,00,000 | 12 | 2,40,00,000 |
| Plant A | 14,00,000 | 8 | 1,12,00,000 |
| Plant B | 9,00,000 | 6 | 54,00,000 |
| 4,06,00,000 |
Average amount of Assets during a period
= \(\frac{4,06,00,000}{12} \) = 33,83,333
Interest to be capitalized = Average amount of Asset x Capitalization Rate
= 33,83,333 x 0.075 =2,53,750
Question 34.
M Ltd. sold goods to a US Company for US $1,00,000 on 10.01.2021 and realized the due on 30.06.2021. Y Ltd. closes the books of accounts on 31st March every year. Exchange rates were as follows:
| Date | Rate (₹) |
| 10.01.2021 | 69.2 |
| 31 .03.2021 | 76.1 |
| 30.06.2021 | 74.3 |
(i) Calculate the exchange loss/gain on the reporting date.
(ii) Calculate the exchange loss/gain on the settlement date. (Dec 2021, 4 marks)
Answer: ‘
(i) Calculation of exchange gain on the reporting date (31.3.2021)
Value of the goods sold = $ 1,00,000
Exchange rate on the date of transaction = ₹ 69.20 $
So sales to be reported ¡n the books 1,00,000 x 69.20 = ₹ 69,20,000
Exchange rate on the date of reporting (31.3.2021) – ₹ 76.10$
Value of the receivable on 31 .3.2021 = 1,00,000 x 76.10 = ₹ 76,10,000
Exchange gain on 31.3.2021
= 76,10,000 – 69,20,000 = ₹ 6,90,000
(ii) Calculation of loss on settlement date (30.6.2021)
Exchange rate on date on the date of settlement = ₹ 74.30$
Exchange loss on 30.6.2021 = 1,00,000 x (76.10 – 74.30) = ₹ 1,80,000
![]()
Question 35.
State your views with reasons whether the following statements are in line with the provisions of AS-1.
(i) Certain fundamental accounting assùmptions underline the preparation and presentation of financial statements. They are usually specifically stated because their acceptance and use are not assumed.
(ii) If fundamental accounting assumptions are not followed in presentation and preparation of financial statements, a specific disclosure is not required.
(iii) All significant accounting policies adopted ¡n the preparation and presentation of financial statements should form part of the financial statements.
(iv) Any change in an accounting policy, which has a material effect should be disclosed. Where the amount by which any item in the financial statements is affected by such change is not ascertainable, wholly or in part, the fact need not to be indicated.
(v) There is no single list of accounting policies which are applicable to all circumstances. (Dec 2022, 10 marks)
Question 36.
Omega Ltd, a supermarket chain, is renovating one of its major stores. The store will have more available space for store promotion outlets after the renovation and will include a restaurant. Management is preparing the budgets for the year after the store reopens, which include the cost of remodelling and the expectation of a 15% increase in sales resulting
from the store renovations, wh1ch will attract new customers. Decide whether Omega Ltd. can capitalize the remodelling cost or not as per provisions of AS-10 ‘Property Plant & Equipment’. (Dec 2022, 3 marks)
Accounting Standards CMA Inter Financial Accounting Notes
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) is a collection of commonly followed accounting rules and standards meant for accounting of transactions and ultimately their reporting.
Accounting Standards (AS)
Accounting Standards are written policy documents which discuss the aspects of recognition, measurement and treatment of specific accounting transactions, along with the presentation and disclosure there of in the financial statements of an entity.
Fundamental Accounting Assumptions
- Going Concern
- Consistency
- Accrual
Factors governing the selection and application of accounting policies are:
- Prudence
- Substance over form
- Matenality
- AS1
Changes in Accounting Policies
Any change in the accounting policies which has a material effect in the current period or which is reasonably expected to have a material effect in the later period should be disclosed, In the case of a change in accounting policies, having material effect in the current period, the amount by which any item in the financial statements, is affected by such change should also be disclosed to the extent as ascertainable, otherwise the fact that the effect is not (wholly or partially) ascertainable, should be disclosed.
![]()
Property Plant and Equipment (AS -10)
Property, plant and equipment are tangible items that:
- are held for use in the production or supply of goods or services, for rental to others, or for administrative purposes; and
- are expected to be used during more than a period of twelve months. Recoverable amount is the higher of an asset’s net selling price and its value in use.
Useful life is:
- the period over which an asset is expected to be available for use by an enterprise; or
- the number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the asset by an enterprise.
Cost Model
After recognition as an asset, an item of property, plant and equipment should be carried at its cost less any accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
Revaluation Model
After recognition as an asset, an item of property, plant and equipment whose fair value can be measured reliably should be carried at a revalued amount, being its far value at the date of the revaluation less any subsequent accumulated depreciation and subsequent accumulated impairment losses.
Depreciation
Each part of an item of property, plant and equipment with a cost that is significant in relation to the total cost of the item should be depreciated separately.
The depreciation charge for each period should be recognised in the Statement of Profit and Loss unless it is included in the carrying amount of another asset.
Property Plant and Equipment (AS -10)
Property, plane and equipment are tangible items that:
- are held for use in the production or supply of goods or services, for rental to others, or for administrative purposes; and
- are expected to be used during more than a period of twelve months. Recoverable amount is the higher of an asset’s net selling price and its value in use.
Useful life is:
- the period over which an asset is expected to be available for use by an enterprise; or
- the number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the asset by an enterprise.
![]()
Cost Model
After recognition as an asset, an item of property, plant and equipment should be carried at its cost less any accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
Revaluation Model
After recognition as an asset, an item of properly, plant and equipment whose fair value can be measured reliably should be carried at a revalued amount, being its far value at the date of the revaluation less any subsequent accumulated depreciation and subsequent accumulated impairment losses.
Depreciation
Each part of an item of property, plant and equipment with a cost that is significant in relation to the total cost of the item should be depreciated separately. The depreciation charge for each period should be recognised in the Statement of Profit and Loss unless it is included in the carrying amount of another asset.
The Effects of Changes In Foreign Exchange Rate (AS 11)
Foreign Currency Transactions
Meaning:
A foreign currency transaction is a transaction which is denominated in or requires settlement in a foreign currency, including transactions arising when an enterprise either:
- buys or sells goods or services whose price is denominated in a foreign currency;
- borrows or lends funds when the amounts payable or receivable are denominated in a foreign currency;
- becomes a party to an unperformed forward exchange contract; or
- otherwise acquires or disposes of assets, or incurs or settles liabilities, denominated in a foreign currency.
Integral foreign operations
A foreign operation that is integral to the operations of the reporting enterprise carries on its businos as if it were an extension of the reporting enterprise’s operations.
Non-integral foreign operations
A non-integral foreign operation accumulates cash and other monetary items, incurs expenses, generates income and arranges borrowings, all substantially in its local currency.
![]()
Accounting for Government Grants (AS 12)
Government grants are assistance by government in cash or kind to an enterprise for past or future compliance with certain conditions. They exclude those forms of government assistance which cannot reasonably have a value placed upon them and transactions with government which cannot be distinguished from tie normal trading transactions of the enterprise.
Methods of Accounting for Government Grants
Capital approach
Under this approach, a grant is treated as part of shareholders’ funds. This approach is followed because many government grants are in the nature of promoters’ contribution
Income approach
Under this approach, a grant is considered to be an item of income over one or more periods. This approach is followed when the government grants are not gratuitous in nature. The enterprise earns them through compliance with their conditions and meeting the envisaged obligations.
Non-monetary Government Grants
Government grants may take the form of nonmonetary assets, such as land or other resources, given at concessional rates. In these circumstances, it is usual to account for such assets at their acquisition cost. Non-monetary assets given tree of cost are to be recorded at a nominal value.
Presentation of Grants Related to Specific Fixed Assets
First method
The grant is shown as a deduction from the gross value of the asset concerned in arriving at its book value. The grant is thus recognised in the profit and loss statement over the useful life of a depreciable asset by way of a reduced depreciation. Where the whole, or virtually the whole, of the cost of the asset, the asset is shown in the balance sheet at a nominal value.
Second method
Grants related to depreciable assets are treated as deferred income which is recognised ¡n the profit and loss statement on a systematic and rational basis over the useful life of the asset. Such allocation to income is usually made over the periods and in the proportions in which depreciation on related assets is charged.
Refund of Government Grants
Government grants sometimes become refundable because certain conditions do not get fulfilled. A government grant that becomes refundable is treated as an extraordinary item (and treated accordingjy as per AS 5).
Borrowing Costs (AS 16)
Borrowing costs are interest and other costs that. an entity incurs in connection with the borrowing of funds.
Qualifying Asset —
A qualifying asset is an asset that necessarily takes a substantial period of time to get ready for its intended use or sale.
Inclusions in Borrowing Coste Borrowing costs may include:
- interest and commitment charges on bank borrowings and other short-term and long-term borrowings;
- amortization of discounts or premiums relating to borrowings;
- amortization of ancillary costs incurred in connection with the arrangement of borrowings;
- finance charges in respect of assets acquired under finance leases or under other similar arrangements; and
- exchange differences arising from foreign currency borrowings to the extent that they are regarded as an adjustment to interest costs.
Capitalization of Borrowing Costs
1. Specific Borrowing:
To the extent that funds are borrowed specifically for the purpose of obtaining a qualifying asset, the amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalization on that asset should be determined as the actual borrowing costs incurred on that borrowing during the period less any income on the temporary investment of those borrowings.
2. General borrowing:
To the extent that funds are borrowed generally and used for the purpose of obtaining a qualifying asset, the amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalisation should be determined by applying a capitalisation rate to the expenditure on that asset.
![]()
Accounting for Taxes on In come (AS 22).
Accounting income (loss) is the net profit or loss for a period, as reported in the statement of profit and loss, before deducting income tax expense or adding income tax saving.
Taxable Income (tax loss) is the amount of the income (loss) for a period, determined in accordance with the tax laws, based upon which income tax payable (recoverable) is determined.
Tax expense (tax saving) is the aggregate of current tax and deferred tax charged or credited to the statement of profit and loss for the period.
Current tax is the amount of income tax determined to be payable (recoverable) in respect of the taxable income (tax loss) for a period.
Deferred tax is the tax effect of timing differences.
Timing differences are the differences between taxable income and accounting income for a period that originate in one period and are capable of reversal in one or more subsequent periods.
Permanent differences are the differences between taxable income and accounting income for a period that originate in one period and do not reverse subsequently.
Timing differences arise because the period in which some items of revenue and expenses are included in taxable income do not coincide with the period in which such items of revenue and expenses are included or considered in arriving at accounting income.
Recognition
Tax expense for the period, comprising current tax and deferred tax, should be included in the determination of the net profit or loss for the period. Taxes on income are considered to be an expense incurred by the enterprise in earning income and are accrued in the same period as the revenue and expenses to which they relate. Such matching may result into timing differences.