Students should practice Valuation of Goodwill & Shares – Corporate and Management Accounting CS Executive MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Valuation of Goodwill & Shares – Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
Question 1.
If the intrinsic value of a share of common stock is less than its market value, which of the following is the most reasonable conclusion?
(A) The stock has a low level of risk.
(B) The stock offers a high dividend payout ratio.
(C) The market is undervaluing the stock.
(D) The market is overvaluing the stock.
Answer:
(D) The market is overvaluing the stock.
Question 2.
Market-based methods of valuation should not be adopted when –
(A) When business is too small
(B) When assets are less than liabilities of the business
(C) In case of significant and unusual fluctuations in market price
(D) It is difficult to estimate the realizable value in case of going concerned.
Answer:
(C) In case of significant and unusual fluctuations in market price
Question 3.
Market value method is generally the most preferred method in case of –
(A) Frequently traded shares of companies listed on stock exchanges having nationwide trading
(B) Valuation of a division of a company
(C) Where the share are not listed or are thinly traded
(D) Where there is an intention to liquidate it and to realize the assets and distribute the net proceeds.
Answer:
(A) Frequently traded shares of companies listed on stock exchanges having nationwide trading
Question 4.
Which of the following is required to be taken into consideration while valuing equity shares of the company?
(A) Size of the block of shares
(B) Restricted transferability aspect
(C) Dividends
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 5.
Which of the following shall not be taken into consideration while calculating Capital Employed?
(A) Discount on issue of debentures
(B) Preliminary expenses
(C) Fictitious assets
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 6.
Goodwill is –
(A) Intangible asset
(B) Valuable asset
(C) Non-current asset
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 7.
Net asset value per share is also known as –
(A) Internal value per share
(B) Intrinsic value per share
(C) Economic value per share
(D) Recoverable value per share
Answer:
(B) Intrinsic value per share
Question 8.
Which of the following is deducted while calculating net assets available to equity shareholders?
(A) Proposed preference dividend
(B) Share suspense account
(C) Know-how
(D) Non-trading investment
Answer:
(A) Proposed preference dividend
Question 9.
Statement I:
Net Asset Method can be fairly used to value shares when the firm is liquidated.
Statement II:
This method does not give any weight to earning capacity of the company.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Statement I is correct but State-ment II is incorrect
(B) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(C) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(D) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Answer:
(D) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Question 10.
In which of the following cases valuation is essential?
(A) Conversion of debt instruments into shares.
(B) On directions of Tribunal or Authority or Arbitration Tribunals.
(C) When issuing shares to the public either through an Initial Public Offer or by the offer for sale.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 11.
While deciding net asset value, fictitious assets –
(A) Should be considered
(B) Should not be considered
(C) Added to total assets
(D) Valued separately
Answer:
(B) Should not be considered
Question 12.
For which one or more of the following reasons is the recognition as an asset of an internally generated intangible prohibited? ,
(a) Because there may not be an active market for that asset.
(b) Because its cost is usually relatively insignificant.
(c) Because it is difficult to reliably identify the related costs
(d) Because it is difficult to establish the probability of flow of economic benefits
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(A) (a) & (b)
(B) (c) & (d)
(C) (b) & (c)
(D) (b) & {d)
Answer:
(B) (c) & (d)
Question 13.
When controlling shares are to be sold then which of the following will be the appropriate base for valuation of shares:
(A) Rate of dividend
(B) Rate of earning
(C) Rate of gross profit
(D) Rate of risk-free return
Answer:
(B) Rate of earning
Question 14.
Fair value is the average of the –
(A) Intrinsic value and yield value
(B) Internal value and external value
(C) Capitalized value and earning value
(D) Notional value and book value
Answer:
(A) Intrinsic value and yield value
Question 15.
As per the valuation of equity shares based on the price-earnings ratio, the shares are valued on the basis of __ multiplied by the price-earnings ratio.
(A) Dividend per share
(B) Earnings per share
(C) Bonus per share
(D) Interest per share
Answer:
(B) Earnings per share
Question 16.
The market value of share =
(A) DPS × EPS
(B) P/E Ratio × DPS
(C) P/E Ratio × EPS
(D) (P/E Ratio ÷ EPS) × 100
Answer:
(C) P/E Ratio × EPS
Question 17.
Which of the following Accounting Standard deals with Intangible Assets?
(A) AS-22
(B) AS-24
(C) AS-26
(D) AS-28
Answer:
(C) AS-26
Question 18.
As per AS-26, there is a rebuttable presumption that the useful life of an intangible asset will not exceed___from the date when the asset is available for use.
(A) Ten years
(B) Five years
(C) Eight years
(D) Six years
Answer:
(A) Ten years
Question 19.
If control over the future economic benefits from an intangible asset is achieved through legal rights that have been granted for a finite period, the useful life of the intangible asset should not exceed the period of the legal rights unless:
(A) The legal rights are renewable and
(B) Renewal is virtually certain.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 20.
As per AS-26, the intangible asset can be recognized at –
(A) Research phase
(B) Development Phase
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Answer:
(B) Development Phase
Question 21.
As per AS-26, expenditure on research or on the research phase of an internal project should be recognized when it is incurred.
(A) An Asset
(B) An expense
(C) Profit
(D) Liability
Answer:
(B) An expense
Question 22.
Which of the following is NOT the method of valuation of Goodwill?
(A) Average profit Method
(B) Super profit Method
(C) Capitalization Method
(D) Straight-line Method
Answer:
(D) Straight-line Method
Question 23.
Super profit means –
(A) Future maintainable profit minus the normal return
(B) Weighted Average Profit
(C) Future maintainable profit minus net profit earned by the business
(D) Normal return plus PAT
Answer:
(A) Future maintainable profit minus the normal return
Question 24.
In the balance sheet shares appears at___
(A) Face value
(B) Adjusted market value
(C) Market price
(D) Paid-up value
Answer:
(D) Paid-up value
Question 25.
Which of the following is not required while calculating yield value per share?
(A) Expected return rate
(B) Normal return rate
(C) Superprofit
(D) Paid-up value per share
Answer:
(C) Superprofit
Question 26.
The profits of last 5 years are ₹ 60,000; ₹ 67,500; ₹ 52,500; ₹ 75,000 & ₹ 60,000. Find the value of goodwill, if it is calculated on average profits of last 5 years on the basis of 3 years of purchase.
(A) ₹ 63,750
(B) ₹ 1,91,250
(C) ₹ 1,89,000
(D) ₹ 2,13,750
Hint:
Average Profit = \(\frac{60,000+67,500+52,500+75,000+60,000}{5}\) = 63,000
Goodwill = Average Profit × No. of years purchases
= 63,000 × 3
= 1,89,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 1,89,000
Question 27.
It is agreed that goodwill of the company is to be valued at 3 years purchase of average profits for the last 5 years.
| Year ended | Profit/(loss) ₹ in ‘000 |
| 31st March 2015 | 16,110 |
| 31st March 2016 | 11,850 |
| 31st March 2017 | 8,145 |
| 31st March 2018 | (600) |
| 31st March 2019 | 12,750 |
Value of goodwill will be –
(A) ₹ 28,953 thousand
(B) ₹ 29,673 thousand
(C) ₹ 28,673 thousand
(D) ₹ 29,953 thousand
Answer:
(A) ₹ 28,953 thousand
Question 28.
It is agreed that goodwill of the firm is valued at 2 years purchase of weighted average profits for the last 3 years.
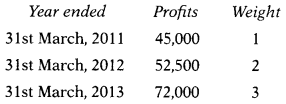
Value of goodwill will be –
(A) ₹ 1,22,000
(B) ₹ 2,22,000
(C) ₹ 1,22,222
(D) ₹ 1,20,000
Hint:
Average Profit = \(\frac{16,110+11,850+8,145 \cdot 600+12,750}{5}\)= 9,651 thousand
Goodwill = Average Profit × No. of years purchases
= 9,651 × 3
= 28,953 thousand
Answer:
(A) ₹ 1,22,000
Question 29.
Find the goodwill of the company from the following information:
Total Capital Employed = ₹ 8,00,000
Reasonable Rate of Return = 15%
Profits for the year = ₹ 12,00,000
Use capitalization method.
(A) ₹ 82,00,000
(B) ₹ 12,00,000
(C) ₹ 72,00,000
(D) ₹ 42,00,000
Hint:
Goodwill = [\(\frac{\text { Future maintainable profit }}{\text { Normal rate return }}\) × 100] – Capital Employed
= [\(\frac{12,00,000}{15}\) × 100] – 8,00,000
= 72,00,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 72,00,000
Question 30.
Find the goodwill from the following information:
Capital employed – ₹ 11,00,000
Rate of normal return – 10%
Future Maintainable profit – ₹ 2,00,000 No. of year purchases – 3 years
(A) ₹ 6,00,000
(B) ₹ 2,70,000
(C) ₹ 9,00,000
(D) ₹ 3,70,000
Hint:
| Future maintainable profit | 2,00,000 |
| Less: Normal return (11,00,000 × 10%) | (1,10,000) |
| Super profit | 90,000 |
Goodwill = Super profit × No. of years purchases
= 90,000 × 3
= 2,70,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 2,70,000
Question 31.
Find the goodwill of the firm using the capitalization method from the following information:
Capital employed = ₹ 4,80,000.
Rate of normal return = 15%.
Profits for the year = ₹ 90,000
(A) ₹ 4,20,000
(B) ₹ 3,11,000
(C) ₹ 1,20,000
(D) ₹ 2,20,000
Hint:
Goodwill = [\(\frac{\text { Future maintainable profit }}{\text { Normal rate return }}\) × 100] – Capital employed
= [\(\frac{90,000}{15}\) × 100] – 4,80,000
= 1,20,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 1,20,000
Question 32.
The average profit of a firm is ₹ 1,20,000. The rate of capitalization is 12%. Assets and liabilities of the company are ₹ 10,00,000 & ₹ 4,25,000 respectively.
(A) ₹ 3,25,000
(B) ₹ 2,25,000
(C) ₹ 5,25,000
(D) ₹ 4,25,000
Hint:
Assets – Liabilities = Capital employed
10,00,000 – 4,25,000 = 5,75,000
Goodwill = [\(\frac{\text { Future maintainable profit }}{\text { Normal rate return }}\) × 100] – Capital employed
= [\(\frac{1,20,000}{12}\) × 100] – 5,75,000
= 4,25,000
Answer:
(D) ₹ 4,25,000
Question 33.
The profits for 2016-2017 is ₹ 2,000; for 2017-2018 is ₹ 26,100 and for 20182019 is ₹ 31,200. Closing stock for 2017-2018 and 2018-2019 includes the defective items of ₹ 2,200 and ₹ 6,200 respectively which were considered as having market value nil. Calculate goodwill on the average profit method.
(A) ₹ 23,700
(B) ₹ 17,700
(C) ₹ 13,700
(D) ₹ 17,300
Hint:
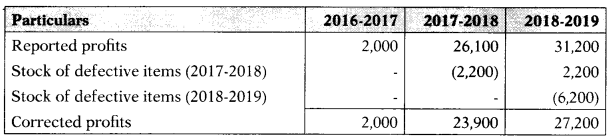
Note: Closing stock of one year is opening stock of next year. In next year it will be added
Averagc profit = \(\frac{2,000+23,900+27,200}{3}\)= 17,700
Goodwill = Average profit (As no. of year purchase is not given)
Answer:
(B) ₹ 17,700
Question 34.
A company has a total capital investment of ₹ 3,60,000. The company earned net profit during the last four years as ₹ 56,000, ₹ 64,000, ₹ 96,000 & ₹ 80,000. The fair return on the net capital employed is 15%. Value of goodwill if it is based on 3 years purchase of the average super-profits of past 4 years.
(A) ₹ 37,500
(B) ₹ 50,000
(C) ₹ 60,000
(D) ₹ 40,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 60,000
Question 35.
Find the goodwill from the following information:
Capital employed – ₹ 8,25,000
Rate of normal return – 10%
Future Maintainable profit – ₹ 1,50,000
Annuity factor – 3.17
(A) ₹ 4,75,500
(B) ₹ 2,61,525
(C) ₹ 3,13,975
(D) ₹ 2,13,975
Hint:
| Future maintainable profit | 1,50,000 |
| Less. Normal return (8,25,000 × 10%) | (82,500) |
| Super profit | 67,500 |
Goodwill = Super profit × Annuity Factor
= 67,500 × 3.17
= 2,13,975
Answer:
(D) ₹ 2,13,975
Question 36.
The net profits after tax of Z Ltd. for the past 5 years are as follows:
| Year | Profit |
| 2007-2008 | 2,56,000 |
| 2008-2009 | 2,64,000 |
| 2009-2010 | 3,76,000 |
| 2010-2011 | 4,86,000 |
| 2011-2012 | 5,30,500 |
The capital employed is ₹ 16,00,000. The rate of normal return is 15%. Calculate the value of the goodwill on the basis of the annuity method on a super-profits basis, taking the present value of an annuity of ₹ 1 for the 4 years at 15% as ₹ 2.855.
(A) ₹ 7,65,000
(B) ₹ 8,67,800
(C) ₹ 5,70,000
(D) ₹ 4,06,838
Hint:
| Future maintainable profit | 3,82,500 |
| Normal return (16,00,000 × 15%) | (2,40,000) |
| Super profit | 1,42,500 |
Goodwill = 1,42,500 × 2.855 = 4,06,838
Answer:
(D) ₹ 4,06,838
Question 37.
The following particulars are available in respect of the business carried on by X Ltd.:
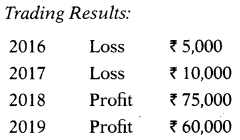
You are required to compute the value of goodwill on the basis of 5 years purchase of average profit.
(A) ₹ 1,25,000
(B) ₹ 1,50,000
(C) ₹ 10,000
(D) ₹ 1,20,000
Hint:
Goodwill = 30,000 × 5 = 1,50,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 1,50,000
Question 38.
The net profits after tax of NZ & Co. for the past 3 years are as follows:
| Year | Profit (₹) |
| 2010-2011 | 20,000 |
| 2011-2012 | 2,61,000 |
| 2012-2013 | 3,12,000 |
Closing stock for 2011-2012 and 20122013 includes the defective items of ₹ 22,000 and ₹ 62,000 respectively which were considered as having no market value. Calculate goodwill on the average profit method.
(A) ₹ 2,37,000
(B) ₹ 1,77,000
(C) ₹ 1,37,000
(D) ₹ 1,73,000
Hint:
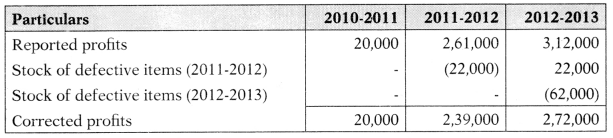
Note: Closing stock of one year is opening stock of next year. In next year it will be added.
Average profit = \(\frac{20,000+2,39,000+2,72,000}{3}\) = 1,77,000
Goodwill = Average profit (As no. of year purchase is not given)
Answer:
(B) ₹ 1,77,000
Question 39.
Profits & losses for the last years are:
2011- 2012 Losses ₹ 10,000
2012- 2013 Losses ₹ 2,500
2013- 2014 Profits ₹ 98,000
2014- 2015 Profits ₹ 76,000
The average capital employed in the business is ₹ 2,00,000. The rate of interest expected from capital invested is 12%. The remuneration of partners is estimated to be ₹ 1,000 per month. Calculate the value of goodwill on the basis of four years purchase of super-profits based on the annuity of the four years. Take discounting rate as 10%.
(A) ₹ 13,500
(B) ₹ 13,568
(C) ₹ 13,668
(D) ₹ 13,868
Hint:
| Future maintainable profit | 40,375 |
| Remuneration of partners | (12,000) |
| Normal return (2,00,000 × 12%) | (24,000) |
| Super profit | 4,375 |
Goodwill = 4,375 × 3.1698 = 13,868
Answer:
(D) ₹ 13,868
Question 40.
The following information is available for N Ltd.:
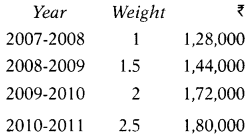
Capital employed is ₹ 5,40,000. A standard rate of return on capital employed in this type of business is 12%. The above net profit included a fixed income on non-trading investment of ₹ 8,000 per year. At the end of the year, 2008-2009 closing stock was overvalued by ₹ 25,000. Calculate goodwill on a weighted average super profit basis at 3 years of purchase. Ignore taxation.
(A) ₹ 2,74,671
(B) ₹ 2,47,671
(C) ₹ 2,74,167
(D) ₹ 2,47,716
Hint:
Normal return = 5,40,000 × 12% = 64,800
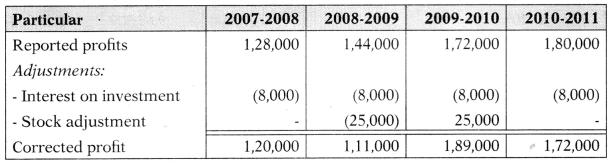
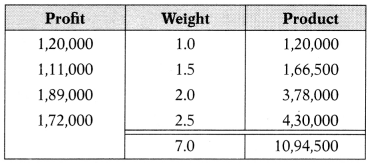
Weighted average profit = \(\frac{10,94,500}{7}\) = 1,56,357
| Future maintainable profit | 1,56,357 |
| (-) Normal return | (64,800) |
| Super profit | 91,557 |
Goodwill = Super profit × No. of years purchases
= 91,557 × 3
= 2,74,671
Answer:
(A) ₹ 2,74,671
Question 41.
Profit after tax of Z Ltd. for the 3 financial years are as follows:
| 2013 | ₹ 4,41,000 |
| 2014 | ₹ 6,45,000 |
| 2015 | ₹ 4,80,000 |
Capital employed is ₹ 29,25,000. The normal rate of return is 10%. The tax rate is 40%. 10% of profits for the year 2014 arose from a transaction of non-recurring nature. A provision of ₹ 31,500 on sundry debtors was made in the financial year 2005 which is no longer required. A claim of ₹ 16,500 is to be provided against profit for the year 2015. Goodwill may be calculated at 3 times adjusted average profits of 3 years.
(A) ₹ 6,33,000
(B) ₹ 15,10,500
(C) ₹ 7,22,667
(D) ₹ 15,50,100
Hint:
Normal return = 29,25,000 × 10% = 2,92,500
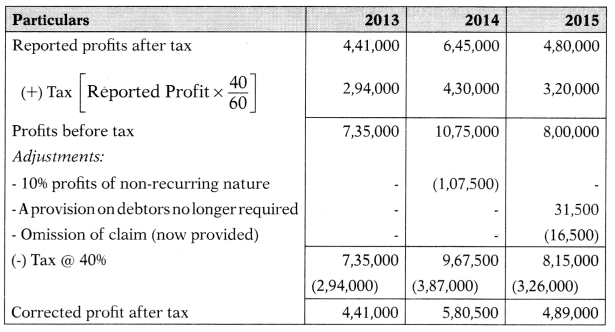
Average profit = \(\frac{4,41,000+5,80,500+4,89,000}{3}\) = 5,03,500
Goodwill = Adjusted average profits × No. of years purchases
= 5,03,500 × 3 = 15,10,500
Answer:
(B) ₹ 15,10,500
Question 42.
The average net profit before adjustments is ₹ 5,14,000. Profit includes interest at 8% on non-trading investments. The cost of these investments is ₹ 1,98,200 while the face value is ₹ 2,00,000. Expenses amounting to ₹ 7,000 per annum are likely to be discontinued in the future. The provision for income tax to be made at 30%. The normal rate of return may be taken at 10%. The average capital employed in the business (including investments) is ₹ 18,98,200. Assuming 4 years purchase of super-profits, what is the value of goodwill?
(A) ₹ 7,43,000
(B) ₹ 8,34,000
(C) ₹ 7,34,000
(D) ₹ 8,43,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 7,34,000
Question 43.
The average net profit of a business as adjusted for valuation of goodwill amounted to ₹ 2,35,000. Net tangible assets employed were of the value of ₹ 4,50,000. But upon valuation, they amounted to ₹ 15,00,000. Assuming that 10% represented a fair commercial return, the value of goodwill by capitalizing super-profits will be___
(A) ₹ 8,75,000
(B) ₹ 8,25,000
(C) ₹ 8,90,000
(D) ₹ 8,50,000
Hint:
| Future Maintainable Profit | 2,35,000 |
| (-) Normal return (15,00,000 × 10%) | (1,50,000) |
| Super profit | 85,000 |
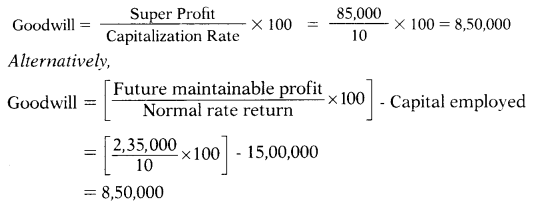
Answer:
(D) ₹ 8,50,000
Question 44.
From the following particulars, calculate goodwill on the basis of 3 years purchase of super-profits:
Capital employed: ₹ 50,000
Trading profit (after tax):
2011: ₹ 12,200
2012: ₹ 15,000
2013: ₹ 2,000 (loss)
2014: ₹ 21,000
The normal rate of interest on investment 10% p.a. Remuneration from alternative employment: ₹ 3,600 p.a. (included in above profit).
(A) ₹ 10,250
(B) ₹ 8,850
(C) ₹ 7,450
(D) ₹ 12,350
Hint:
Average Profit = \(\frac{12,200+15,000-2,000+21,000}{4}\) = 11,550
| Future Maintainable Profit (i.e. Average Profit) | 11,550 |
| (-) Remuneration from alternative employment | (3,600) |
| (-) Normal Return (50,000 × 10%) | (5,000) |
| Super Profit | 2,950 |
Goodwill = Average Profit × No. of years purchases
= 2,950 × 3
= 8,850
Answer:
(B) ₹ 8,850
Question 45.
Compute the amount of goodwill based on 3 years purchase of super profit from the following:
Future maintainable profit after tax: ₹ 15,00,000;
Normal pre-tax rate of return: 20%;
Capital employed: ₹ 60,00,000; Tax rate: 30%
(A) ₹ 12,30,000
(B) ₹ 21,40,000
(C) ₹ 19,80,000
(D) ₹ 14,70,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 19,80,000
Question 46.
Total assets of X Ltd. are ₹ 10,00,000 and total liabilities are ₹ 4,00,000. Expert valued goodwill of the company at ₹ 2,00,000. The company has two types of equity shares:
50,000 shares of ₹ 10 each fully paid-up
50,000 shares of ₹ 10 each, ₹ 7 paid up.
Intrinsic value per share of ₹ 7 paid- up is:
(A) ₹ 3.5
(B) ₹ 4.5
(C) ₹ 6.5
(D) ₹ 7.5
Hint:
| Capital employed (10,00,000 – 6,00,000) | 4,00,000 |
| (+) Goodwill | 2,00,000 |
| (+) Notional call (50,000 × 3) | 1,50,000 |
| Net assets available to equity shareholder | 7,50,000 |
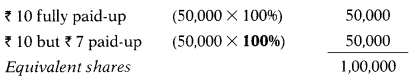
Note: In the case of ₹ 10 but ₹ 7 paid-up shares 100% has been taken as notional call ₹ 3 has been considered while calculating “’ Net Assets” hence shares are fully paid-up.
Intrinsic value per share = \(\frac{\text { Net assets }}{\text { No. of shares }}\)
₹ 10 fullv paid-up = \(\frac{7,50,000}{1,00,000}\) = 7.5
₹ 10 share, ₹ 7 paid-up = 7.5 – 3 = 4.5
Answer:
(B) ₹ 4.5
Question 47.
The profit available for equity share-holder of JK Ltd. is ₹ 1,27,500. The company has two types of equity shares:
50,000 shares of ₹ 10 each fully paid-up
50,000 shares of 10 each, ₹ 7 paid up.
Other companies in the same industries pay dividends @ 20%.
Yield value per share of ₹ 7 paid-up share is –
(A) 4.50 per share
(B) 6.25 per share
(C) 5.25 per share
(D) 3.50 per share
Hint:
Paid-up equity share capital = (50,000 × 10) + (50,000 × 7) = 8,50,000
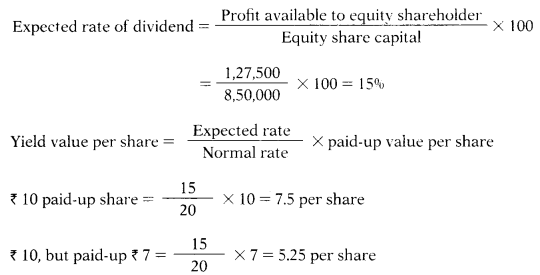
Answer:
(C) 5.25 per share
Question 48.
Total assets of X Ltd. are ₹ 23,00,000 and total liabilities are ₹ 12,00,000. Expert valued goodwill of the company at ₹ 6,50,000. The company has two types of equity shares:
25.000 shares of ₹ 10 each fully paid-up
25.000 shares of ₹ 5 each, ₹ 3 paid-up.
Intrinsic value per share of ₹ 3 paid- up is:
(A) ₹ 22 per share
(B) ₹ 8 per share
(C) ₹ 6 per share
(D) ₹ 4 per share
Hint:
| Capital employed (23,00,000 – 12,00,000) | 11,00,000 |
| (+) Goodwill | 6,50,000 |
| (+) Notional call (25,000 × 2) | 50,000 |
| Net assets available to equity shareholder | 18,00,000 |
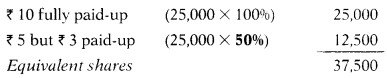
Note: In case of ₹ 5 but ₹ 2 paid-up shares notional call ₹ 2 has been considered while calculating “Net Assets” hence shares are fully paid-up i.e. ₹ 5. However, the face of these shares is half of the face values of other shares; hence 50% shares in terms of ₹ 10 paid-up shares will have to be taken.
Net assets
Intrinsic value per share =
₹ 10 fullv paid-up = = 48
₹ 5 fully paid-up = 48 × 5/10 = 24
₹ 5 but ₹ 3 paid-up = 24 – 2 = 22
Answer:
(A) ₹ 22 per share
Question 49.
Total assets of X Ltd. are ₹ 5,00,000 and total liabilities are ₹ 2,00,000. The company has three types of equity shares:
36,000 shares of ₹ 10 each fully paid-up
18,000 shares of ₹ 10 each, ₹ 8 paid up.
30,000 shares of ₹ 5 each, ₹ 5 paid up.
The company has earned ₹ 2,94,300 as profit after tax, which can be considered to be normal for the company. Average
EPS for a fully paid share of ₹ 10 of a Company in the same industry in ₹ 2.
Value per share on EPS basis of 30,000 shares of 10 each, ₹ 5 paid-up is –
(A) ₹ 22.5 per share
(B) ₹ 11.25 per share
(C) ₹ 18 per share
(D) ₹ 17.5 per share
Hint:
As there are different types of shares ₹ 10, ₹ 8 & ₹ 5, we have to convert it into ₹ 10 shares as follows:
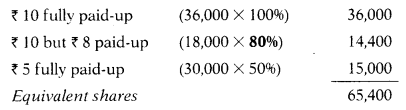
Note: In the case of ₹ 10 but ₹ 8 paid-up shares, 80% has been taken as notional call ₹ 2 has not been considered hence shares are partly paid-up.
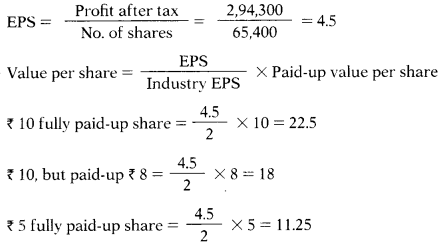
Answer:
(B) ₹ 11.25 per share
Question 50.
The capital Structure of SZ Ltd. is as follows:
| Types of capital | ₹ |
| 2,500 Equity shares (₹ 10) fully paid-up | 25,000 |
| 2,500 Equity shares of (₹ 10) paid-up | ₹ 8 20,000 |
| 2,500 Equity shares of (₹ 10) paid-up | ₹ 6 15,000 |
| 12% Debentures paid-up | 5,000 |
| 100, 9% Preference shares (₹ 100) | 10,000 |
| Expected profit per year before interest & tax: | ₹ 30,600 |
Rate of tax: 40%
Transfer to reserve: 10% of profit
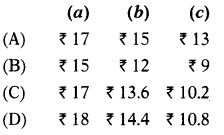
The normal rate of dividend: 15%
What is value per share as per yield method for
(a) ₹ 10 fully paid-up shares
(b) ₹ 8 paid-up shares
(c) ₹ 6 paid-up shares?
Hint:
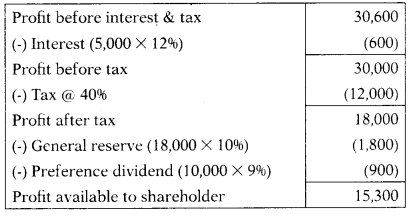
Expected rate of dividend = \(\frac{\text { Profit available to equity shareholder }}{\text { Equity share capital }}\) × 100
= \(\frac{15,300}{60,000}\) × 100 = 25.5%
Yield value per share = \(\frac{\text { Expected rate }}{\text { Normal rate }}\) × Paid-up value per share
₹ 10 paid-up share = \(\frac{25.5}{15}\) × 10 = 17
₹ 8 paid-up share = \(\frac{25.5}{15}\) × 8 = 13.6
₹ 6 paid-up share = \(\frac{25.5}{15}\) × 6 = 10.2
Answer:
(C)
