Modern Business Environment – CA Final SCMPE Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Modern Business Environment – CA Final SCMPE Question Bank
Question 1.
What are the critical success factors for the implementation of a ‘Total Quality Management’ programme? (Nov 2009, 5 marks)
Answer:
Success Factors of TQM:
- Everyone within the organization should be involved in TQM.
- The focus should be on customer needs.
- The focus should be on continuous improvement.
- The aim should be to design and produce quality products.
- Appropriate training and education should be given so that everyone is aware of the aims of TQM.
- Existing rewards and performance measurements should be renewed to encourage quality improvements.
- Introduce an effective performance measurement system that measures continuous improvements from the customer’s perspective.
![]()
Question 2.
Answer the following:
Classify the following items under the three measures used in the.theory of constraints: (May 2011, 4 marks)
(i) Research and Development Cost
(ii) Rent/Utilities
(iii) Raw materials used for production
(iv) Depreciation
(v) Labour Cost
(vi) Stock of raw materials
(vii) Sales
(viii) Cost of equipments and buildings.
Answer:
The three key measures used in the theory of Constraints are:
Contribution
(iii) Raw Material for production
(vii) Sales
Operating Costs
(ii) Rent/utilities
(iv) Depreciation
(v) Labour
Investments
(i) R & D
(vi) Raw Material Stock
(viii) Building and Equipment Cost
![]()
Question 3.
Classify the following items under appropriate categories of quality costs viz. (Nov 2011, 5 marks)
Prevention Costs, Appraisal Costs, Internal Failure Costs and External Failure Costs:
(i) Rework
(ii) Disposal of scrap
(iii) Warranty Repairs
(iv) Revenue loss
(v) Repair to manufacturing equipment
(vi) Discount on defective sale
(vii) Raw material inspection
(viii) Finished product inspection
(ix) Establishment of quality circles
(x) Packaging inspection
Answer:
(i) Rework – Internal Failure
(ii) Disposal of Scrap – Internal Failure
(iii) Warranty Repairs – External Failure
(iv) Revenue Loss – External Failure
(v) Repairs to Manufacturing Equipment – Internal Failure
(vi) Discount on Defective Sales – External Failure
(vii) Raw Material Inspection – Prevention Cost
(viii) Finished Product Inspection – Appraisal Cost
(ix) Establishment of Quality Circles – Prevention Cost
(x) Packaging Inspection – Appraisal Cost
![]()
Question 4.
Answer the following:
What qualitative factors should be considered in an decision to out source manufacturing of a product? (Nov 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
Qualitative Factors for Outsourcing Decision:
The following qualitative factors should be considered in an outsourcing decision:
- Whether the vendor will acquire the technology and will emerge as a competitor?
- Whether the vendor will be able to maintain the quality? If the vendor fails to maintain the quality, will the company lose customers?
- Whether the company will lose its skills in manufacturing the product and it will find difficult to resume production internally?
- Whether laying off employees will demoralize the work force? .
- Whether the price quoted by the vendor is a penetrating price? If so, it is likely to increase i.e. whether price will increase.
![]()
Question 5.
Answer the following:
What are the focuses of Theory of Constraints? How it differs with regard to cost behaviour? (May 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Theory of Constraints:
- The theory of constraint focuses its attention on constraints and bottlenecks within ne organisation which hinder speedy production.
- The main concepts to maximize the rate of manufacturing output i.e. the throughput of the organisation.
- This requires examining the bottlenecks and constraints which are defined as:
(i) A constraint is a situational factor which makes the achievement of objectives/throughput more difficult than it would otherwise be. Constraints may take several forms such as lack of skilled employees, lack of customer orders or the need to achieve a high level of quality product output.
(ii) A bottleneck is an activity within the organisation where the demand tor that resource is more than its capacity to supply.
Therefore, a bottleneck is always a constraint but a constraints need not be a bottleneck. Throughput is thus related directly to the ability to cope with the constraint and to manage the bottleneck.
- The theory of constraints assumes few costs are variable-generally materials, purchased parts, piecework labour and energy to run machines. It assumes that most direct labour and overheads are fixed.
- This is consistent with the idea that the shorter the time period, the more costs are fixed and the idea that the theory of constraints focuses on the short run.
![]()
Question 6.
Answer the following:
Classify the following items appropriately under the three measures used in the Theory of Constraints : (May 2014, 4 Marks)
Sl. Nom – Item
(i) Research and Development
(ii) Cost Rent/Utilities
(iii) Finished goods inventory
(iv) Depreciation
(v) Labour Cost
(vi) Stock of Raw Materials
(vii) Sales
(vii) Cost of equipment and buildings
Answer:
| Item | Theory or Constraint | |
| 1. | R&D cost | Investments |
| 2. | Rent/Utilities | Operating cost |
| 3. | Finished goods inventory | investments |
| 4. | Depreciation | Operating cost |
| 5. | Labour cost | Operating cost |
| 6. | Stock of RM | Investments |
| 7. | Sales | Through put contribution |
| 8. | Cost of equipment and buildings | Investments. |
![]()
Question 7.
Answer the following:
Quality products can be determined by using a few of the dimensions of quality. Identify the following under the appropriate dimension: (May 2015, 4 Marks)
(i) Consistency of performance over time.
(ii) Primary product characteristics.
(iii) Exterior finish of a product.
(iv) Useful life of a product.
Answer:
Quality of Products with Appropriate Dimension
| Sl. No. | Quality of Products (Examples) | Dimension |
| (i) | Consistency of performance over time | Reliability |
| (ii) | Primary product characteristics | Performance |
| (iii) | Exterior finish of a product | Aesthetics |
| (iv) | Useful life of a product | Durability |
![]()
Question 8.
Answer the following question:
Classify the following items under the three measures used in the theory of constraints : viz Throughput Contribution, Operating Costs and Investments. (May 2017, 4 Marks)
(i) Research and Development Cost
(ii) Rent/Utilities
(iii) Raw materials used for production
(iv) Depreciation
(v) Labour Cost
(vi) Stock of raw materials
(vii) Sales
(viii) Cost of equipments and buildings
Answer:
| Item | Theory of Constraint | |
| (i) | Research and Development Cost | Investment |
| (ii) | Rent/Utilities | Operating costs |
| (iii) | Raw materials used for production | Through put contribution |
| (iv) | Depreciation | Operating cost |
| (v) | Labour Cost | Operating costs |
| (Vi) | Stock of raw materials | Investments |
| (vii) | Sales | Throughput contribution |
| (viii) | Cost of equipments and buildings | Investment |
![]()
Question 9.
Discuss the connection between Total Quality Management and Total Productive Maintenance. (Jan 2021, 5 marks)
Question 10.
A company produces three products A, B and C. The following information is available for a period: (Nov 2008, 5 Marks)

Estimated sales demand for A, B and C are 500 units each and machine capacity is limited to 6,000 hours for each machine.
You are required to analyse the above information and apply theory of constraints process to remove the constraints.
How many units of each product will be made?
Answer:
Throughput Accounting ratio is highest for ‘Machine 2′
∴ ‘Machine 2′ is the bottleneck
Contribution per unit of bottleneck machine hour:
Total ‘Machine 2’ hours available = 6,000

![]()
Question 11.
TQ Ltd. implemented a quality improvement programme and had the following results: (Nov 2008, 4 Marks)
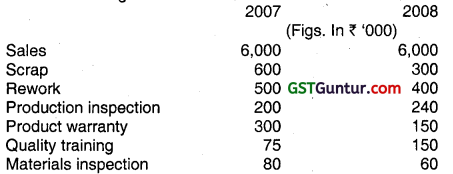
You are required to:
(i) Clasify the quality costs as prevention, appraisal, internal failure and external failure and express each class as a percentage of sales.
(ii) Compute the amount of increase in profits due to quality improvement.
Answer:
(i) Classification of Quality Costs
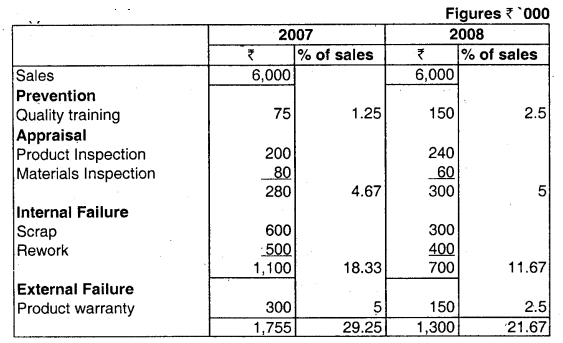
(ii) Cost reduction was effected by 7.58% (29.25 – 21.67) of sales, which is an increase in profit by ₹ 4,55,000.
![]()
Question 12.
Vikram Ltd. produces 4 products using 3 different machines. Machine capacity is limited to 3,000 hours for each machine. The following information is available for February, 2009: (May 2009, 7 Marks)

From the above information you are required to identify the bottleneck activity and allocate the machine time. (7 marks)
Answer:
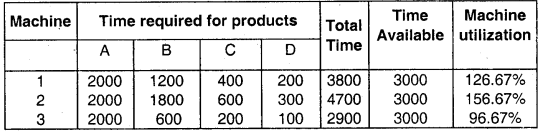
Since Machine 2 has the highest machine Utilization it represents the bottleneck activity hence product, ranking and resource allocation should be based on contribution/machine hour of Machine 2.
Allocation of Resources
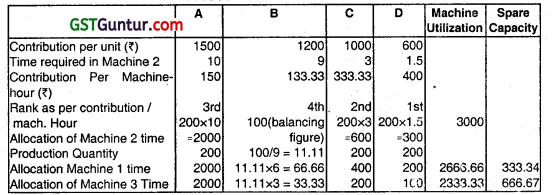
![]()
Question 13.
H Ltd. manufactures three products. The material cost, selling price and bottleneck resource details per unit are as follows: (Nov 2010, 5 Marks)
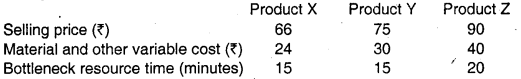
Budgeted factory costs for the period are ₹ 2,21,600. The bottleneck resources time available is 75120 minutes per period.
Required:
(i) Company adopted throughput accounting and products are ranked according to ‘product return per minute’. Select the highest rank product.
(ii) Calculate throughput accounting ratio and comment on it.
Answer:
(i) Computation of Rank according to product return per minute
| Particulars | X | Y | Z |
| Selling Price | 66 | 75 | 90 |
| Variable Cost | 24 | 30 | 40 |
| Throughput Contribution | 42 | 45 | 50 |
| Minutes per unit | 15 | 15 | 20 |
| Contribution per minute | 2.8 | 3 | 2.5 |
| Ranking | II | I | III |
(ii)
| Particulars | X | Y | Z |
| Contribution/minute | 2.80 | 3.00 | 2.50 |
| Factory Cost per minute (221600/75120) | 2.95 | 2.95 | 2.95 |
| TA Ratio = Contribution per min / cost per minute | 0.95 | 1.02 | 0.85 |
| Ranking based on TA Ratio | II | I | III |
Comment: Product Y yields more contribution compared to average factory contribution per minute, whereas X and Z yield less.
![]()
Question 14.
A company makes a single product which sells at ₹ 800 per unit and whose variable cost of produetion is ₹ 500 per unit. Production and sales are 1000 units per month. Production is running to full capacity and there is market enough to absorb an additional 20% of output each month.
The company has two options: (May 2011, 5 marks)
Option -I
Inspect finished goods at ₹ 10,000 per month. 4% of production is detected as defectives and scrapped at no value. There will be no warranty replacement, since every defect is detected. A small spare part which wears out due to defective material is required to be replaced at 2,000 per spare for every 20 units of scrap generated. This repair cost is not included in the manufacturing cost mentioned above.
Option -II
Unift the finished goods inspection at no extra cost, to raw material inspection, (since defective raw materials are entitled to free replacement by the supplier), take up machine set-up tuning and machine inspection at an additional cost of 8,000 per month, so that scrap of finished goods is completely eliminated. However, delivery of uninspected finished products may result in 1% of the quantity sold to be replaced under free warranty due to minor variation in dimensions, which does not result in the wearing out of the spare as stated in
Option -I
(i) Using monthly figures relevant for decision making, advise which option is more beneficial to the company from a financial perspective.
(ii) Identify the quality costs that can be classified as
(a) appraisal costs and
(b) external failure costs.
Answer:
| Option 1 | Option II | |||
| Production | 1000 Units | 1000 Units | ||
| Finished Goods Inspection | ‘10000 | Appraisal | – | |
| Raw Material Inspection scrap 4% = 40 units × variable cost per unit 500 | 20000 | Appraisal | 10000 | |
| Contribution lost 300 × 40 | 12000 | Appraisal | ||
| Machine repair | 4000 | Appraisal | – | |
| Machine set up | 8000 | |||
| Warranty replacement | – | |||
| 1% × 1000 = 10 unit | ||||
| Contribution lost 10 x 300 | 3000 | External failure | ||
| Variable Cost lost 10 × 500 | 5000 | External failure | ||
| Quality Cost | 46000 | 26000 | ||
Better Option II
![]()
Question 15.
Gupta Ltd. produces 4 products P, Q, R and S by using three different machines X, Y and Z. Each machine capacity is limited to 6000 hours per month. The details given below are for July, 2013: (May 2013, 8 marks)
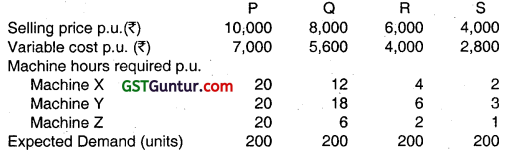
Required:
(i) Find out the bottleneck activity.
(ii) Allocate the machine hours on the basis of the bottleneck.
(iii) Ascertain the profit expected in the month if the monthly fixed cost amounts to ₹ 9,50,000.
(iv) Calculate the unused spare hours of each machine.
Answer:
(i) Computation of Machine Utilisation:
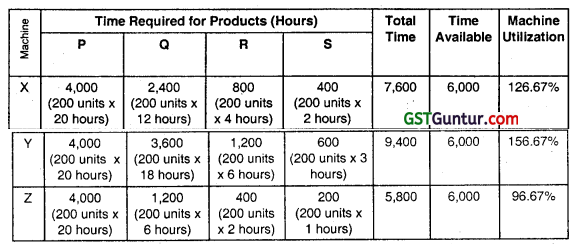
Because of Machine Y has the highest machine utilization it represents the bottleneck activity.
Therefore Product Ranking and Resource Allocation should be based on Contribution / Machine Hour of Machine Y.
(ii) Allocation of Resources:
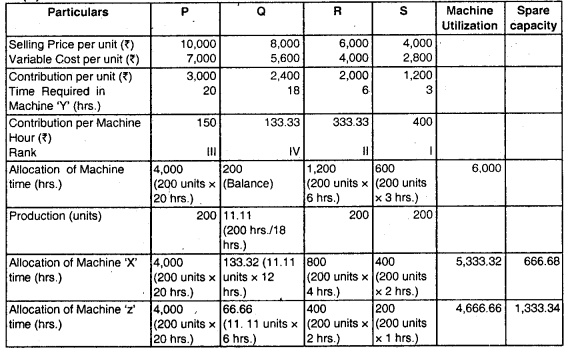
![]()
(iii) Calculation of Expected Profit
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| P (200 units × ₹ 3,000)
Q (1.1.11 units × ₹ 2,400) R (200 units × ₹ 2,000) S (200 units × ₹ 1,200) |
6,00,000
26,664 4,00,000 2,40,000 |
| Total Contribution
Less: Fixed Cost |
12,66,664
9,50,000 |
| Expected Profit | 3,16,664 |
(iv) Unused Spare Hours
Machine ‘X’
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| Machine Hours Available
Less: Machine Hours Utilized |
6,000.00 hrs.
5,333.32 hrs. |
| Spare Hours | 666.68 hrs. |
Machine ‘Z’
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| Machine Hours Available
Less: Machine Hours Utilized |
6,000.00 hrs.
4,666.66 hrs. |
| Spare Hours | 1,333.34 hrs. |
Note: At the time of computation of Production (units) of Product ‘Q’ on the basis of allocated hours, round figure (complete units) can also be considered. Then remaining solution will be changed accordingly.
![]()
Question 16.
A Ltd. is going to introduce Total Quality Management (TQM) in its company. State whether and why the following are valid or not for the successful implementation of TQM. (May 2014, 5 Marks)
(i) Some departments serve both the external and internal customers. These departments have been advised to focus on satisfying the needs of the external customers.
(ii) Hold a training program at the beginning of a production cycle to ensure the implementation of TQM.
(iii) Implement Management by Objectives for faster achievement of TQM.
(iv) Appoint the Head of each department as the person responsible to develop improvement strategies and performance measures.
(v) Eliminate wastage of time by avoiding documentation and procedures.
Answer:
Total Quality Management:
(i) Invalid : TQM advocates focus to be given on both external and internal customers. Hence, focus satisfying the needs of the external customers only will not be valid for the successful implementation of TQM.
(ii) Valid: Hold a training program at the beginning of the production cycle is necessary for effectiveness and accuracy of process.
(iii) Invalid: For implementation of TQM, Management by Objectives should be eliminated as targets of production will encourage delivery of poor quality goods and thus will defeat the collective nature of TQM.
(iv) Invalid: For achievement of goals each and every person of organisation is responsible, not a single person. So all persons of organisation make a group efforts for success. So appointment of head of each department is not necessary.
(v) Invalid: Documentation, procedures and awareness of current best practice are essential in TQM implementation. If documentation and procedures are in place then only improvement can be monitored and measured and consequently deficiency can be corrected.
![]()
Question 17.
Genex Limited produces 3 products X, Y and Z using three different machines M1, M2 and M3. Each machine’s capacity is limited to 6000 hours dunng the production period. The details given below are for the production period: (May 2015, 8 Marks)
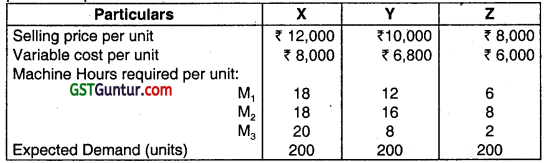
(i) Determine the bottleneck activity.
(ii) Allocate the machine hours on the basis of the bottleneck.
(iii) Determine the unused spare capacity, If any, of each machine.
Answer:
(i) Calculation of Bottleneck Activity
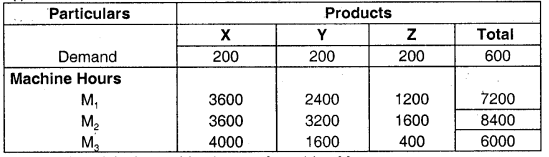
Bottleneck activity is machine hours of machine M2.
(ii) Allocation of Machine Hours on the basis of Bottleneck Activity: Ranking
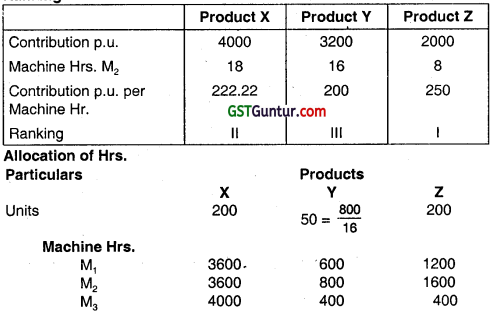
(iii) Calculation of unused capacity of each machine
Machine – Unused capacity
M1 – 6000 – 3600 – 600 – 1200 = 600 hrs.
M2 – 6000 – 3600 – 800 – 1600 = Nil
M3 – 6000 – 4000 – 400 – 400 = 1200 hrs.
![]()
Question 18.
Classify the following items under appropriate categories of quality costs, viz., Prevention Costs (PC), Appraisal Costs (AC), Internal Failure Costs (IFC) and External Failure Costs (EFC): (Nov 2015, 5 Marks)
(i) Unplanned replacement to customers
(ii) Correction of a bank statement
(iii) Design review
(iv) Equipment accuracy check
(v) Staff training
(vi) Reprocessing of a loan operation
(vii) Product liability warranty (viii) Product acceptance
(ix) Wastage of material
(x) Planned maintenance of equipment
(Candidates may opt for the following format and fill in the appropriate Roman numerals under each column)
| Costs → | PC | AC | IFC | EFC |
| Q. Nos. → |
Answer:
Appropriate Categories of Quality Costs
| Costs | PC | AC | IFC | EFC |
| Q. Nos. | (iii) | (iv) | (ii) | (i) |
| (v) | (viii) | (vi) | – | |
| (x) | ‘ – | (ix) | (vii) |
![]()
Question 19.
A company produces and sells a single product. The cost data per unit for the year 2017 is predicted as below: (May 2016, 8 Marks)
₹ Per unit
Direct material – 35
Direct labour – 25
Variable overheads – 15
Selling price – 90
The company has forecast that demand for the product during the year 2017 will be 28,000 units. However, to satisfy this level of demand, production quantity will be increased?
There are no opening stock and closing stock of the product.
The stock level of material remains unchanged throughout the period.
The following additional information regarding costs and revenue are given:
- 12. 5% of the items delivered to customers will be rejected due to specification failure and will require free replacement. The cost of delivering the replacement item is ₹ 5 per unit.
- 20% of the items produced will be discovered faulty at the inspection stage before they are delivered to customers.
- 10% of the direct material will be scrapped due to damage while in storage.
Due to above, total quality costs for the year is expected to be ₹ 10,75,556.
The company is now considering the following proposal:
- To introduce training programmes for the workers which, the management of the company believes, will reduce the level of faulty production to 10%. This training programme will cost ₹ 4,50,000 per annum.
- To avail the services of quality control consultant at an annual charges of ₹ 50,000 which would reduce the percentage of faulty items delivered to customers to 9.5%.
You are required to:
(i) Prepare a statement of expected quality costs the company would incur if it accepts the proposal. Costs are to be calculated using the four recognised quality costs heads.
(ii) Would you recommend the proposal? Give financial and non-financial reasons.
Answer:
(i) Statement Showing ‘Expected Quality Costs’
| Particulars | Current Situation (₹) | Proposed Situation (₹) |
| Prevention Costs | — | 4,50,000 |
| Appraisal Costs | — | 50,000 |
| External Failure Costs | 3,20,000 | 2,35,120 |
| Internal Failure Costs | 7,55,556 | 3,91,538 |
| Total Quality Costs | 10,75,556 | 11,26,658 |
![]()
Workings
External Failure Cost
| Particulars | Current Situation | Proposed Situation |
| Customer’s Demand …(A) | 28,000 units | 55,000 units |
| Number of units Dispatched to Customers …(B) \(\left(\frac{28,000 \text { units }}{87.5 \%}\right) ;\left(\frac{28,000 \text { units }}{90.5 \%}\right)\) |
32,000 units | 30,939 units |
| Number of units Replaced …(B) – (A) | 4,000 units | 2,939 units |
| External Failure Cost {4,000 units × ₹ (35 + 25 + 15 + 5)}; {2,939 units × ₹ (35 + 25 + 15 + 5)} |
₹ 3,20,000 | ₹ 2,35,120 |
Internal Failure Cost
| Particulars | Current Situation | Proposed Situation |
| Number of units Dispatched to Customers …(A) | 32,000 units | 30,939 units |
| Number of units Produced & Rejected …(B) \(\left(\frac{32,000 \text { units }}{80 \%}\right) ;\left(\frac{30,939 \text { units }}{90 \%}\right)\) |
40,000 units | 34,377 units |
| Number of units Discovered Faulty … (B) – (A) | 8,000 units | 3,438 units |
| Cost of Faulty Production …(D) {8,000 units × ₹ (35 + 25+15)}; {3,438 units × ₹ (35+25+15)} |
₹ 6,00,000 | ₹ 2,57,850 |
| Material Scrapped \(\left(\frac{40,000 \text { units }}{90 \%} \times 10 \%\right) ;\left(\frac{34,377 \text { units }}{90 \%} \times 10 \%\right)\) | 4,444.44 units | 3,819.67 units |
| Cost of Material Scrapped …(E) {4,444.44 units × ₹ 35}; (3,819.67 units × ₹ 35} |
₹ 1,55,556 | ₹ 1,33,688 |
| Internal Failure Cost …(D) + (E) | ₹ 7,55,556 | ₹ 3,91,538 |
(ii) Recommendation:
On purely financial grounds the company should not accept the proposal because there is an increase of ₹ 51,102 in quality costs. However there may be other factors to consider as the company may enhance its reputation as a company that cares about quality products and this may increase the company’s market share.
On balance the company should accept the proposal to improve its long-term performance.
![]()
Question 20.
ABC Ltd. produces three products A, B and C. The following information is available for a period: (Nov 2016, 6 marks)
| Product | A | B | C |
| Contribution per unit (Sales – Direct Materials) (?) | 30 | 25 | 15 |
Machine hours required per unit of production:
| Machine hours required per unit | Through put Accounting ratio | |||
| Product | A | B | C | |
| Machine 1 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 133.33% |
| Machine 2 | 15 | 3 | 6 | 200.00% |
| Machine 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 66.67% |
Estimated sales demand for A, B and C are 500 units each and machine capacity limited to 6000 hours for each machine.
Required:
Analyse the above information and apply theory of constraints process to remove the constraints. How many units of each product will be made?
Answer:
Note: TA Ratio is highest for Machine 2. So, ‘Machine 2’ is the bottleneck.
Total ‘Machine 2’ hours available = 6,000.
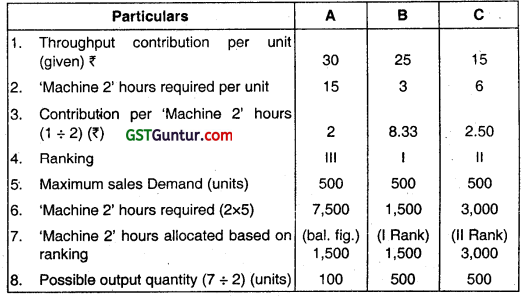
![]()
Question 21.
Rohni Steel Company produces three grades of steel-super, good and normal grade. Each of these products (Grades) has high demand in the market and company is able to sell as much as it can produce these products.
The furnace operation is a bottle-neck in the process. The company is running at 100% of capacity. The company wants to improve its profitability. The variable conversion cost is ₹ 100 per process hour. The fixed cost is ₹ 48,00,000. In addition, the Cost Accountant was able to determine the following information about the three products (grades): (May 2018)
| Super Grade | Good Grade | Normal Grade | |
| Budgeted Units Produced | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 |
| Total process hours per unit | 12 | 12 | 10 |
| Furnace hours per unit | 6 | 5 | 4 |
| Unit Selling Price | ₹ 3,600 | ₹ 3,400 | ₹ 3,000 |
| Direct Material cost per unit | ₹ 2,100 | 7 1,900 | ₹ 1,720 |
The furnace operation is part of the total process for each of these three products. Thus furnace hours are the part of process hours.
Required:
(i) Determine the unit contribution margin for each product. . (5 marks)
(ii) Give an analysis to determine the relative product profitability, assuming that the furnace is a bottleneck. (5 marks)
(iii) Management wishes to improve profitability by increasing prices on selected products. At what price would super and good grades need to be offered in order to produce the same relative profitability as normal grade steel? (10 marks)
Answer:
(i) Contribution Marging per unit
| Particulars | Super Grade (₹) | Good Grade (₹) | Normal Grade (₹) |
| Selling Price per unit | 3,600 | 3,400 | 3,000 |
| less: Variable Conversion Cost per unit | 1,200 (₹ 100 × 12 hrs.) | 1,200 (₹ 100 × 12 hrs.) | 1,000 (₹ 100 × 10 hrs.) |
| Less: Direct Material Cost per unit | 2,100 | 1,900 | 1,720 |
| Contribution Margin per unit | 300 | 300 | 280 |
![]()
(ii) The contribution margin per unit may give false signals when an organization has production bottlenecks. Instead, Company should use the contribution margin per bottleneck hour to determine relative product profitability, as follows:
| Particulars | Super Grade | Good Grade | Normal Grade |
| Contribution Margin per unit (₹) | 300 | 300 | 280 |
| Furnace Bottleneck hrs. per unit | 6 | 5 | 4 |
| Contribution Margin per furnace hour | 50 | 60 | 70 |
Analysis
The Super and Good Grade steel have the highest contribution margin per unit (₹ 300); however, the normal grade has the highest contribution margin per furnace hour (₹ 70), Thus, using production bottleneck analysis indicates that the Normal Grade is actually more profitable at a ₹ 70 contribution margin per furnace hour than Super Grade’s ₹ 50 or Good Grade’s ₹ 60 contnbution margin per furnace hour.
Therefore, the company would want to sell product in the following preference order:
I. Normal Grade
II. Good Grade
III. Super Grade
(iii) One way is to revise the pricing would be to increase the price to the point where all three products produce profitability equal to the highest profit product. This would be determined as follows:
Contribution Margin per furnace hour for Normal Grade

Or, ₹ 420 = Revised Price of Super Grade – ₹ 3,300
Super grade steel would require a revised price of ₹ 3,720 in order to deliver the same contribution margin per bottleneck hour as does Normal Grade steel.
Contribution Margin per furnace hour for Normal Grade =

Good grade steel would require a revised price of ₹ 3,450 in order to deliver the same contribution margin per bottleneck hour as does Normal Grade steel.
![]()
Question 22.
JK Ltd. produces and sells a single product. Presently the company is having its quality control system in a small way at an annual external failure and internal failure costs of ₹ 4,40,000 and ₹ 8,50,000 respectively. As the company is not able to ensure supply of good quality products upto the expectations of its customers and wants to manage competition to retain market share considers an alternative quality control system. It is expected that the implementation of the system annually will lead to a prevention cost of ₹ 5,60,000 and an appraisal cost of ₹ 70,000. The external and internal failure costs will reduce by ₹ 1,00,000 and ₹ 4,10,000 respectively in the new system. All other activities and costs will remain unchanged. (May 2018)
Required:
(i) Examine the new quality control proposal and recommend the acceptance or otherwise of the proposal both from financial and non- financial perspectives. (6 marks)
(ii) What is your advice to the company, if the company wants to achieve zero defect through a continuous quality improvement programme? (2 marks)
(iii) Suggest a suitable quality control level at a minimum cost. (2 marks)
Answer:
(i) Implementation of new system will reduce costs of the non – conformance (internal and external failure) by ₹ 5,10,000 (-40%). However, this will also increase costs of conformance by ₹ 6,30,000. There is inverse relationship between the costs of the conformance and the costs of non-conformance. JK Ltd. should try to avoid costs of non-conformance because both internal and external failure affect customer’s satisfaction and organisations profitability.
The company should focus on preventing the error such that it ensures that product is of good quality when it reaches the customer at the very first instance. This enhances the customer experience and therefore eliminating the scope for external failures like sales returns and warranty claims. Better quality can yield further sales. Therefore, an increase in spending on quality measures is justified since it not only yields significant improvements to quality but also brings in more sales orders.
Accordingly, from the financial perspective point of view the new proposal for quality control should not be accepted as it will lead to an additional cost of ₹ 1,20,000 (₹ 6,30,000 – ₹ 5,10,000). However, from non-financial perspective point of view as stated above the company should accept the new proposal.
(ii) It is possible to increase quality while at the same time reducing both conformance and non-conformance costs if a programme of aiming for zero defect/ and or continuous improvement is followed. Zero defect advocates continuous improvement. To implement this elimination of all forms of waste, including reworks, yield losses, unproductive time, over-design, inventory, idle facilities, safety accidents, etc. is necessary.
(iii) To achieve 0% defects, costs of conformance must be high. As a greater proportion of defects are accepted, however, these costs can be reduced. At a level of 0% defects, cost of non-conformance should be nil but these will increase as the accepted level of defects rises. There should therefore be an acceptable level of defects at which the total costs of quality are at a minimum.
![]()
Question 23.
TSC Box Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of android set up boxes for various DTH operators. This is very popular with the operators as it converts normal TV to a smart TV. To ensure supply of good quality products to meet the expectations of the viewers, it has set up quality control department that regularly conducts quality inspection and submits it report to the management on weekly basis.
As per the latest quality inspection report submitted by the department, it reflects that the current rejection rate is 7% of units input into the manufacturing system due to poor quality. 3,000 units of input go through the process every day. As per analysis, for each rejection, there is loss of ₹ 150 to the company. The management is very much worried due to high rate of rejection of input units.
The management has asked for suggestions from the quality control department in this regard. The department has suggested implementation of new system for inspection for early detection of defective units. This change would result in drop of rejection rate to 4% from earlier 7%. The cost of new system will be ₹ 12,000 per day. (Nov 2020)
Required:
(i) Analyse the proposed new system for inspection and suggest if it would be beneficial for the company. (3 marks)
(ii) Also Calculate the minimum reduction in number of rejections each day upto which the proposed system will be beneficial. (2 marks)
![]()
Question 24.
RS Tools Ltd. is a leading force in manufacture and supply of modern agriculture equipment like Power Tillers, Kisan Krafts, Agriculture Reaper and other Lawn Care equipment. The company grew substantially over the course of decades and presently ranked 20lh by size in the global arena and has become a household name in every agriculture family in the country. As commonly happens when an enterprise goes in leaps and hounds in a way like this, RS Tools Ltd. is experiencing an increasing degree of supply chain complexities and for many years it did nothing to address the difficulties of its decentralized and fragmented network.
The top management decided recently to enter into small irrigation components segment with the brand name ‘SIRI’, the demand for which is extremely seasonal and majority of sales are forecasted to occur between April to July every year. The company currently is replenishing dealer’s inventory every month, using direct shipment from its central warehouse which is not order driven and is not in sync with the industry average. This kind of dispatching the orders is proving too costly and too slow and not in consonance with the demand pattern.
The top management of RS Tools Ltd. has started getting doubts about the company’s ability to supply its existing 300 plus dealer network, to meet the consistent market demand of its regular agriculture equipment along with the seasonal demand of its new branded products ‘SIRI’. They recognized that this state of affairs cannot be allowed to continue in the long run and decided to adopt a long term program of strategic optimization. (Jan 2021)
The company has launched an initiative to achieve a targeted 15% reduction in supply chain cost within next 3 years and constituted an expert group to oversee this task. Mr. Karthik, the management consultant, is unanimously appointed at the board meeting to head the expert group formed to revamp the supply chain management. The management is squarely convinced with three of his bold and frank remarks to the board that:
(a) “Most Companies begin with the best intentions to achieve successful and sustainable supply chain cost management, but somehow lose momentum, only to see costs increase in short term due to the implementation costs of SCM”.
(b) “If you tell me your company hasn’t been able to sustain any progress in supply chain cost reduction in short run, I wouldn’t be surprised at air.
(c) “No producer has the ability to give the customers what they want, when they want and at the price they want unless the value chains also have been encouraged”.
![]()
When the expert team haded by Mr. Karthik began investigation they found three areas of feasible leverage to reduce supply chain costs which are listed below-
(i) Consolidating shipments and use of third party logistic providers as the existing decentralized environment of sourcing and inbound logistics are being managed by teams in different places with insufficient transparency in supply chain.
(ii) Leveraging on maintaining optimum inventory by bringing the order cycle time down to an industry average of 15 days.
(iii) The existing supply chain has evolved rather than grown by design and hence had become unnecessarily complex and the enterprise as a whole is not taking the advantage of synergies and economies of scale.
Mr. Karthik undertook a supply chain network redesigning program
- to reorganize the supply chain,
- to reduce cost to serve and
- to lay the groundwork for future capability in the supply chain.
He is determined to revitalize the Supplier Relationship management as well as the numbers of suppliers are very large in number and the company is burdened with quality, delivery and payment issues from the suppliers. He has decided to suggest the use of E-procurement process as a part of upstream supply chain as a remedy to this hiccup.
You being an associate consultant in his office have been asked by Mr. Karthik, to help him by preparing a briefing to be given to the board based on the above facts with particular reference to the following:
(a) List the critical issues being faced by RS Tools Ltd. under the present setup based on the facts of the above case. (3 marks)
![]()
(b) In the light of the initial remarks made by Mr. Karthik at the time of he being designated to head the expert group, explain the supply chain management and analyze the validity of the views expressed by Mr. Karthik. (4 marks)
(c) List the major benefits that RS Tools Ltd. would reap by energizing the Supply Chain Management. (3 marks)
(d) Evaluate how Supplier Relationship Management is going to help RS Tools Ltd. (4 marks)
(e) Describe E procurement and its process in the context of upstream supply chain management and discuss its constituents. (3 marks)
(f) Advise whether the outsourcing as suggested by Mr. Karthik would help RS Tools Ltd. in settling logistic constraints. (3 marks)