Management of Inventory – CA Inter FM Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Management of Inventory – CA Inter FM Question Bank
Question 1.
A Ltd. uses inventory turnover as one performance measure to evaluate its production manager. Currently, its inventory turnover (based on cost of goods sold ÷ inventory) is 10 times per annum, as compared with industry average of 4. Average sales are ₹ 4,50,000 p.a. variable costs of inventory have consistently remained at 70% of Sales with fixed costs of ₹ 10,000. Carrying Costs of inventory (excluding financing costs) are 5% per annum. Sales force complained that low inventory levels are resulting in lost sales due to stock-outs. Sales manager has made an estimated based on stock-out reports as under:

On the basis of above estimates, assuming a 40% tax rate and an after-tax required return of 20% on investment in inventory, which policy would you recommend? (May 2002, 10 marks)
Answer:
For the identification of best policy, we would determine the incremental rate of return as comparison to current policy for Which, calculate cost of goods sold and investment level at various levels first.
Working Note:
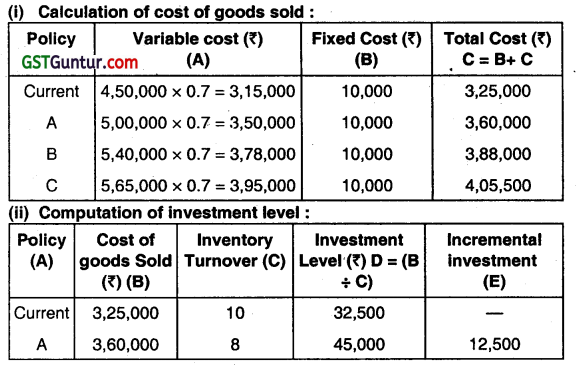

Recommendation: Policy ‘A’ should be followed because its incremental rate of return is highest.
Question 2.
Answer the following:
The demand for a certain product is random. It has been estimated that the monthly demand of the product has a normal distribution with a mean of 390 units. The unit price of product is ₹ 25. Ordering cost is ₹ 40 per order and inventory carrying cost is estimated to be 35 per cent per year.
Required:
Calculate Economic Order Quantity (EOQ). (Nov 2007, 2 marks)
Answer:
EOQ = \(\sqrt{\frac{2 A Q}{C}} \)
A = Annual requirement
= 390 × 12
= 4680
O = ordering cost
= ₹ 40/order
C = Carrying cost
= 25×35%
= ₹ 8.75
= \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 4680 \times 40}{8.75}}\)
= 207 unit
![]()
Question 3.
ZED Company supplies plastic crockery to fast food restaurants in metropolitan city. One of its products is a special bowl, disposable after initial use, for serving soups to its customers. Bowls are sold in pack 10 pieces at a price of ₹ 50 per pack. The demand for plastic bowls has been forecasted at a fairly steady rate of 40,000 packs every year. The company purchases the bowl directly from manufacturer at ₹ 40 per pack within a three-day lead time. The ordering and related cost is ₹ 8 per order. The storage cost is 10% per annum of average inventory investment.
Required:
(i) Calculate Economic Order Quantity.
(ii) Calculate number of orders needed every year.
(iii) Calculate the total cost of ordering and storage bowls for the year.
(iv) Determine when should the next order to be placed. (Assuming that the company does maintain a safety stock and that the present inventory level is 333 packs with a year of 360 working days. (May 2008, 2+1 +2+3 = 8 marks)
Answer:
(i) Computation of EOQ
U = Annual Requirement = 40,000
B = Buying Cost = 40 \(\sqrt{2,50,000}\)
O = Ordering cost = ₹ 8
PC = Carrying cost permit x % cost of cost price
= ₹ 40 × 10% = 4
EOQ = \(\sqrt{\frac{2 U O}{P C}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 40,000 \times 8}{4}}\) = 400
Therefore, EOQ = 400 units
(ii) No. of orders needed = \(\frac{40,000}{400} \) = 100 orders
(iii) Total Cost of Ordering

Alternatively: Total Cost = \(\sqrt{2 U O P C}\)
= \(\sqrt{2 \times 40,000 \times 8 \times 4}\)
= ₹ 1,600
(iv) Timing of next order
(a) Days requirement served by each order.
Number of days requirements = \(\frac{\text { No. of working days }}{\text { No. of order in a year }}\)
= \(\frac{360}{100}\)
= 3.6 days supply
This implies that each order of 400 packs supplies for requirements of 3.6 days only.
(b) Days requirement covered by Inventory

(c) Time interval for placing next order
Inventory left for day’s requirement – Lead time of delivery
3 days – 3 days = 0 days
This means that next order for the replenishment of supplies has to be placed immediately.
Question 4.
Answer the following:
The annual carrying cost of material ‘X’ is ₹ 3.6 per unit and its total carrying cost is ₹ 9,000 per annum. What would be the Economic order quantity for material ‘X’, if there is no safety stock of material X? (Nov 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
Computation of Economic Order Quantity
Average Inventory = \(\frac{\text { Total Carrying Cost }}{\text { Carrying Cost per unit }} \)
= \(\frac{₹ 9,000}{₹ 3.60}\)
= 2,500 Units
Economic Order Quantity = Average Inventory × 2 = 2,500 × 2 = 5,000 units.
Alternatively:
Total Carrying Cost = \(\frac{\text { Carrying cost per unit } \times \text { E.O.Q }}{2} \)
Or 9000 = \(\frac{3.6 \times EOQ}{2} \)
or E.O.Q. = \(\frac{9,000 \times 2}{3.6} \) = 5,000 units
Question 5.
Answer the following: .
The following information relating to a type of Raw material is available:
Annual demand 2000 units
Unit price ₹ 20.00
Ordering cost per order ₹ 20.00
Storage cost 2% p.a.
Interest rate 8% p.a.
Lead time Half-month
Calculate economic order quantity and total annual inventory cost of the raw material. (Nov 2009,3 marks)
Answer:
EOQ = \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times \text { Annual Consumption } \times \text { Buying CostperOrder }}{\text { Storage Cost per unit }}} \)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 2,000 \times 20}{₹ 20 \times\left(\frac{2+8}{100}\right)}}=\sqrt{\frac{80,000}{2}} \) = 200 Units
Total Annual Inventory Cost
Cost of 2,000 Units @ 20 (2,000 x 20) = ₹ 40,000
No.of Order \(\frac{2,000}{200} \) = ₹ 10
Ordering Cost 10 × 20 = ₹ 200
Carrying cost of average inventory \(\frac{200}{2} \) × 20 × \(\frac{10}{100} \) = ₹ 200
= ₹ 40,400
Question 6.
Answer the following:
ABC Limited has received an offer of quantity discounts on its order of materials as under:
| Price per tonne ₹ | Tonnes Nos. |
| 4,800 | Less than 50 |
| 4,680 | 50 and less than 100 |
| 4,560 | 100 and less than 200 |
| 4,440 | 200 and less than 300 |
| 4,320 | 300 and above |
The annual requirement for the material is 500 tonnes. The ordering cost per order is ₹ 6,250 and the stock holding cost is estimated at 25% of the material cost per annum.
Required:
(i) Compute the most economical purchase level.
(ii) Compute E.O.Q. if there are no quantity discounts and the price per tonne is ₹ 5,250. (Nov 2010, 5 marks)
Answer:
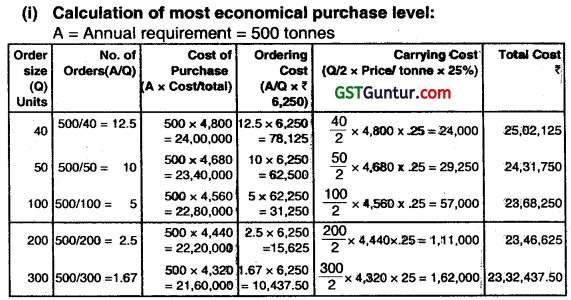
Since the total cost of Paradise, ordering cost and carrying cost of 500 tonnes is minimum ₹ 23,32,437.50 when the order size is 300 tonnes. Therefore most economical purchase level is 300 tonnes.
(ii) EOQ = \(\times \sqrt{\frac{2 A O}{C \times i}}=\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 500 \text { tonnes } \times ₹ 6,250 \text { per order }}{₹ 5,250 \times 0.25}} \) = 69 tonnes
A is the annual requirement for the material.
O is the ordering Cost per order
Ci is the carrying Cost per unit per annum.
Question 7.
KL Limited produces product ‘M’ which has a quarterly demand of 8,000 units. The product requires 3 kgs. quantity of material ‘X’ for every finished unit of product. The other information are follows:
Cost of material ‘X’: ₹ 20 per kg.
Cost of placing an order: ₹ 1000 per order
Carrying Cost: 15% per annum of average Inventory
You are required:
(i) Calculate the Economic Order Quantity fur material ‘X’.
(ii) Should the company accept an offer of.2 percent discount by the supplier, if he wants to supply the annual requirement of material ‘X’ in 4 equal quarterly installments? (Nov 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
Annual demand of material ‘X’
= 8000 units (per quarter) × 4 (No. of Quarter ¡n a year) × 3 kgs. (for every finished product) = 96,000 kgs.
(i) Calculation of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) for material ‘X’
EOQ = \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times \text { Annual demand } \times \text { Ordering cost }}{\text { Carrying cost per unit per annum }}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 96,000 \times 1000}{20 \times 15 \%}}\)
= 8,000kg.
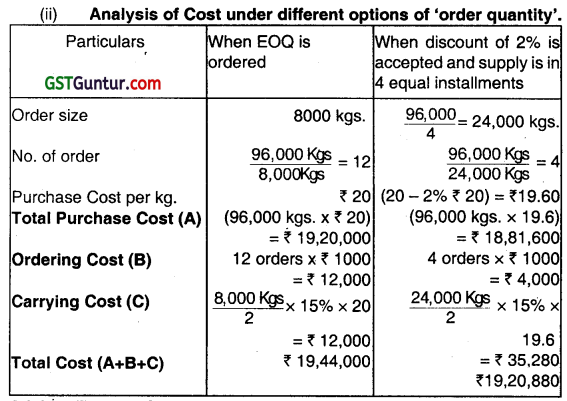
Advice: The total Cost is lower if Company accepts an offer of 2% discount by the supplier when supply of the annual requirement of material ‘X’ is made in 4 equal installments. Hence, the company should accept the offer of 2% discount.
![]()
Question 8.
A company manufactures a product from a raw material, which is purchased at ₹ 80 per kg. The company incurs a handling cost of ₹ 370 plus freight of ₹ 380 per order. The incremental carrying cost of inventory of raw materials is ₹ 0.25 per kg per month. In addition, the cost of working capital finance on the investment in inventory of raw materials is ₹ 12 per kg per annum. The annual production of the product is 1,00,000 units and 2.5 units are obtained from one kg. of raw material.
Required:
(i) Calculate the economic order quantity of raw materials;
(ii) Advise, how frequently company should order for procurement to be placed.
(iii) If the company proposes to rationalize placement of orders on quarterly basis, what percentage of discount in the price of raw materials should be negotiated? Assume 360 days in a year. (May 2014, 8 marks)
Answer:
(I) Economic Order Quantity:
EOQ = \(\sqrt{\frac{2 A C a}{\mathrm{C}}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 40,000 \times 750}{15}}\)
= 2,000 Kg.
A = Annual units required
= \(\frac{1,00,000}{2.5} \)
= 40,000 Kg.
Ordering Cost = Ca = 370 + 380 = ₹ 750
Carrying Cost = Ci = 12 + 3 = 15
(∵ incremental carrying cost = 0.25 p.m. /per Kg.)
(ii) Computation of days of placing Next Order
for 40,000 units → 360 days.
for 2,000 units → ? days
∴ Days required = \(\frac{2,000 \times 360}{40,000} \)
= 18 days.
Alternative Solution
Frequency of placing orders for procurement:
Annual consumption (A) = 40,000 Kg.
Quantity per order (E.O.Q) = 2,000 Kg.
No. of orders per annum \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{EO} \cdot \bar{Q}}\right)=\frac{40,000 \mathrm{Kg}}{2,000 \mathrm{Kg}}\) = 20 Orders
Frequency of placing orders (in days) = \(\frac{360 \text { days }}{20 \text { orders }} \) = 18 days.
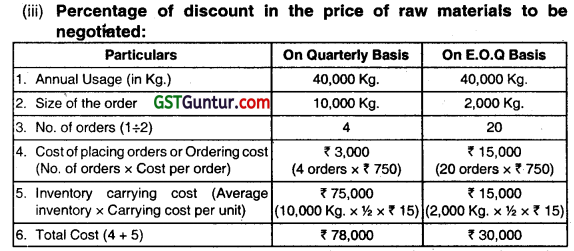
When order is placed on quarterly basis the ordering cost and carrying cost increased by ₹ 48,000 (₹ 78,000 – ₹ 30,000).
So, discount required = ₹ 48,000
Total annual purchase = 40,000 Kg. x ₹ 80 = ₹ 32,00,000
Therefore, Percentage of discount to be negotiated
= \(\frac{₹ 48,000}{₹ 32,00,000} \times 100 \) = 1.5%
Question 9.
A company manufactures a product from a raw material, which is purchased at ₹ 60 per kg. The company incurs a handling cost of ₹ 360 plus freight of ₹ 390 pe order. The incremental carrying cost of inventory of raw material is ₹ 0.50 per kg per month. In addition, the cost of working capital finance or the investment in inventory of raw material is ₹ 9 per kg. Per annum, the main production of the product is 1,00,000 units and 2.5 units are obtaIradftom one kg of raw material.
Required:
(i) Calculate the economic order of raw materials.
(ii) Advise, how frequently should orders for procurement be placed.
(iii) If the company proposed to rationalise placement of orders on quarterly basis, what percentage of discount in the price of raw materials should be negotiated?
Answer:
A = Annual requirement of raw material in kgs. = 1 kg × 1,00,000 units/ 2.5 units = 40,000 kgs
O = (handling and freight cost per order) =₹ 360 + ₹ 390 = ₹ 750
C = Carrying cost per unit per annum + Investment cost per Kg. per annum
= (0.5 × 12 months) + ₹ 9 = ₹ 15 per unit
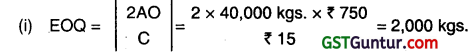
(ii) Frequency of orders for procurement
= 365 days/No. of orders = 3651(40,000/2,000) = 18 days (App.)
(iii) Percentage of discount in the price of raw materials to be negotiated:
Quarterly orders (40,000 kgs/4 orders) = 10,000 kgs. per order
No. of orders = 4
Total Cost (When order size is 10,000 units)
= (4 orders × 750) + (10,000/ 2 × ₹15)
= ₹ 78,000
Total Cost (When order size is equal to EOQ) = (20 orders × ₹ 750) + (2,000/2 × ₹ 15)
= ₹ 30,000
Increase in cost to be compensated by discount = ( ₹ 78,000- ₹ 30,000) = ₹ 48,000
Reduction per kg. in the purchase price of raw material = ₹ 48,000/40,000 kgs = ₹ 1.20 per kg.
Percentage of discount in the price of raw material to be negotiated = \(\frac{1.20}{60} \times 100 \) = 2% discount.
![]()
Question 10.
Following details are available in respect of a firm:
(i) Annual requirement of Inventory 40,000 units
(ii) Cost per unit (other than carrying and ordering cost) ₹16
(iii) Carrying cost are likely to be 15% per year
(iv) Cost of placing order ₹ 480 per order.
Determine the economic ordering quantity.
Answer:
ECO = \(\frac{\sqrt{2 \times \text { Total consumption p. } a \times \text { ordering cost per order }}}{\text { Carrying cost per unit }} \)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 40,000 \times 480}{₹ 16 \times 0.15}} \)
= 4,000 units