Dynamics of Competitive Strategy – CA Inter SM Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Dynamics of Competitive Strategy – CA Inter SM Question Bank
Question 1.
What do you understand by ‘Competitive Landscape’? What are steps to understand the competitive landscape? (May 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Competitive landscape is a business analysis which identifies and understands the competitors.
It the comprehends their vision, mission, core values, niche market, strengths, and weaknesses.
Understanding of competitive landscape requires an application of “competitive intelligence”.
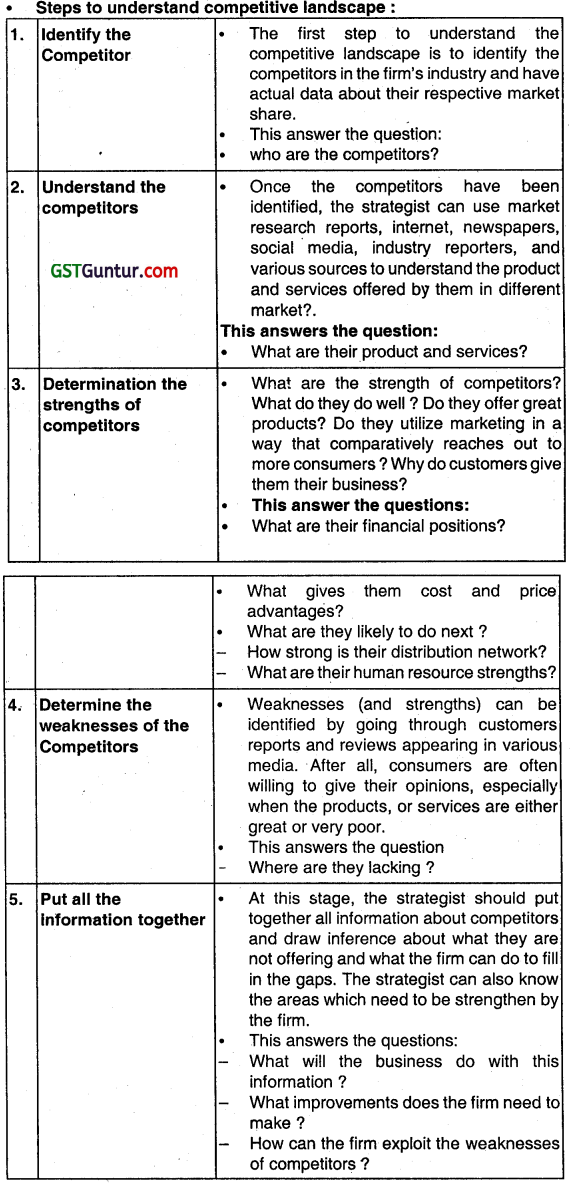
Question 2.
What are the different issues in strategic analysis.
Answer:
The following are the different Issues which must be considered In strategic analysis:
1. Timeline
There are different forces that drive and constrain strategy and that must be balanced In ‘my strategic decision. An important aspect of strategic analysis is to consider the possible implications of routine decisions. Strategy of a business, at a point of time, is result of a series of small decisions taken over an extended period. A manager who tries to Increase the growth momentum of an organization is materially changing strategy.
2. Balancing
The process of strategy formulation is often described as one of the matching the internal potential of the organization with the environmental opportunities. As perfect match between the two may not be feasible, strategic analysis involves a workable balance between diverse and conflicting considerations. A manager working on a strategic decision has to balance opportunities, influences and constraints. There are pressures that are driving towards a choice such as entering a now market. Simultaneously there are constraints that limit the choice such as existence of a big competitor.
3. Risk
The complexity and intermingling of variables in the environment reduces the strategic balance in the organization. Competitive markets, liberalization, globalization, booms, recessions, technological advancements, inter-country relationships all affect businesses and pose risk at varying degree. An important aspect all strategic analysis ‘s to identify potential imbalances or risks and assess their consequences. A broad classification of the strategic risk that requires consideration in strategic analysis is given below:
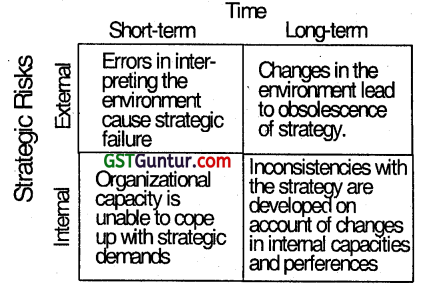
External risk is on account 0f Inconsistencies between strategies and the forces In the environment, Internal risk occurs on account of forces that are either within the organization or are directly interacting with the organization on a routine basis.
Question 3.
State with reason which of the following statement Is correct/Incorrect:
“industry is a grouping of dissimilar firms”. (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect: industry is a group of firms whose products have same and similar attributes such that they compete for the same buyers.
Question 4.
Briefly answer the following:
Strategic groups. (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
A Strategic Group consists of rival firms with similar competitive approaches and positions in the market, Companies in the same strategic group can resemble one another in any of several ways: they may have comparable product-line breadth, sell in the same price/quality range, emphasize the same distribution channels, use essentially the same product attributes to appeal to similar types of buyers, depend on identical technological approaches, or offer buyers similar services and technical assistance.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the meaning of the following concepts:
Strätegic Group Mapping (May 2011, May 2012, 1 mark each)
OR
Write short note on the following:
Strategic Group Mapping (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
A Strategic Group is a cluster of firms in an industry with similar competitive approaches and market positions. An industry contains only one strategic group when all sellers pursue essentially identical strategies and have comparable market positions. Strategic group mapping is a useful analytical tool for comparing the market positions If each firm separately and for grouping them into like positions when an industry has so many competitors that it‘s not practical to examine each one in depth.
It involves plotting firms on a two-variable map using pairs of differentiating characteristics such as price/quality range; geographic coverage and so on. Thus strategic group mapping is a technique for displaying the different market or competitive positions that rival firms occupy in the industry.
Question 6.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct or Incorrect:
E-commerce technology opens up a host of opportunities for reconfiguring industry and company value chains. (May 2012, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct: As more Industries go global, strategic management is becoming an increasingly crucial way to keep track of international development for long-term competitive advantage. The use of Internet for doing business is reshaping the global marketplace and that it will continue to do so for many years. It is believed that Internet would transform or have a major impact on their corporate strategy. The Internet Is changing the way customers. suppliers, and companies interact and It Is changing the way companies work internally.
Question 7.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
A strategic group consists of rival firms with similar competitive approaches and positions in the market. (May 2013, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct: A Strategic Group consists of those rival firms that have similar competitive approaches and positions in the market. Organizations in the same strategic group can resemble one another In several ways like offering buyers similar services and technical assistance.
Question 8.
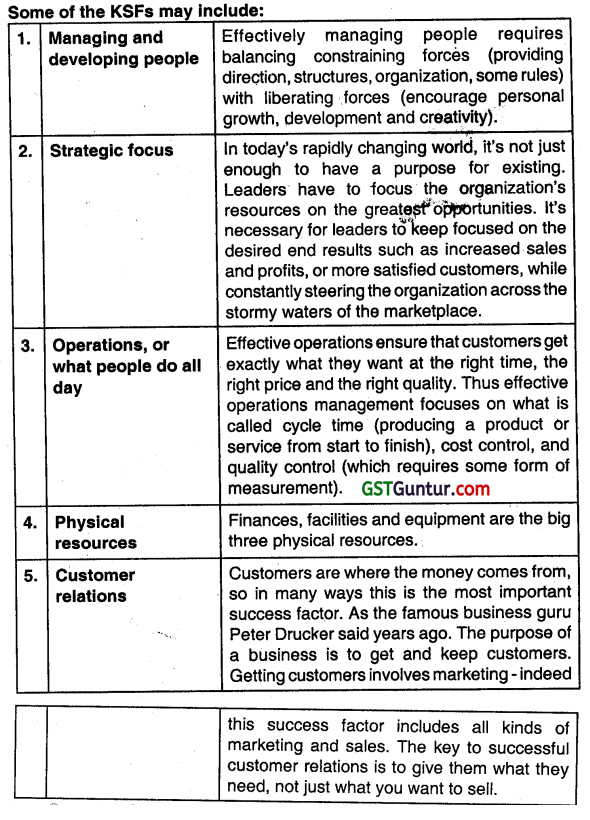
In your view what are the Key Success Factors for operating In a competitive marketplace? (2014 – Nov 3 marks)
OR
Examine the significance of KSFs (Key Success Factors) tar competitive success. ( 2018 – Nov3 marks)
Answer:
Key success factors are those few things that must go well to ensure success for an organization and, therefore, they represent those managerial or enterprise areas that must be given special and continual attention to bring about high performance. KSFs include issues vital to an organizations current operating activities and to its future success. The purpose of key success factors Is to inspire and incentive marketing and sales to a more robust business status. Products and services of businesses should not remain static or without evolution. Vigilance over key success factors helps business organisations to gauge business potential within the target market and also In the realm of business competition. Each business identifies key success factors differently, depending on their products and services.
Question 9.
State with reason which of the following statement Is correct or incorrect:
An industry can have more than one strategic group. (Nov 2014, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct: An industry can have more than one strategic group. An industry contains only one strategic group when all sellers pursue essentially identical strategies and have comparable market positions. On the other hand there are as many strategic groups as there are competitors when each rival pursues a distinctively different competitive approach and occupies a substantially different competitive position in a marketplace.
Question 10.
What steps would you take to construct a ‘Strategic Group Map’ for an industry? (May 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
Strategic group mapping is a useful analytical tool for comparing the market positions of each firm separately and for grouping them into like positions when an industry has so many corn petitions that ¡t is not practical to examine each one in depth. it involves plotting turns on a two-variable map using pairs of differentiating characteristics such as price/quality range: geographic coverage and so on.
Steps taken to construct a ‘Strategic Group Map’ for an industry:
- Identify the competitive characteristics that differentiate firms In the industry.
- Plot the firms on a two-variable map, using pairs of differentiating characteristics.
- classify firms that follows the same strategy, into one strategic group.
- Determine the position of each strategic group, by making it proportional to the size of the Group’s respective share of total industry sales revenues.
Question 11.
Key Success Factors (KSFs) are the rules that shape whether a company will be financially and competitively successful. Do you agree with tins statement? How to identify an industry’s key success factors? (Nov 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
Key Success Factors (KSFs):
An industry’s Key Success Factors are those things or strategic elements affect that the industry members’ ability to prosper in future in market place-based on particular industry elements, product attributes, resources, competencies, competitive capabilities, and business outcomes which defines the difference between profit and loss and ultimately between industry success and failure.
A company with a perceptive understanding of industry KSFs can gain sustainable competitive advantage by training its strategy on industry KSFs and devoting its energy better than rivals on one or more of these factors.
The main purpose of identifying KSFs is to make judgments about what things are more important to competitive success and what things are less important.
- Essentially live things or factors are needed by any organization wanting to succeed:
- People: those who make up the organization
- Purpose: a reason for organizing and working together
- Processes: activities which the people undertake to fulfill their purpose.
Physical Resources: a place to work, the right equipment, money to pay the bills, and the people who work there Customers: people outside the organization who are willing to pay money in return for the products and services the Organization provides; for government organizations taxpayers are the customers; many non-profits depend on contributions from donors who believe in the value of what the organization is doing.
The answers of following 3 questions will help us to Identify KSFs.
1. One what basis do customers choose between the competing brand of sellers? What product, attributes are crucial?
2. What resources and competitive capabilities does a seller need to have to be competitive successful?
3. What does it take for seller to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage?
![]()
Question 12.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
E-commerce technology close up the opportunities for reconfiguring industry and company value chains. (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect: E-commerce technology doesn’t close up but open up the opportunities for reconfiguring industry and company value chains.
Question 13.
Write short note on the following:
Concept of driving forces. (May 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Concept of Driving Forces
The company shall determine the driving forces and their Impacts on competitions. This analysis is done in two steps:
- Identifying the most common driving forces causing the competition.
- Finding or analyzing their individual contribution to competition.
Some common Driving Forces
- Decreasing cost or price
- Increasing globalization
- Market innovations
- Product Innovations
- Change in long term industry growth rate
- Exit or entry of major firms
- The internet and new e-commerce opportunities and threats it breeds in the industry.
Question 14.
Assume that you are a manager making a business plan. Provide a checklist ot the important factors to be considered for conducting an analysis to make such plan. (Nov 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
| 1. Opportunity and issue Analysis | What are the current opportunities that are available in the market the main threats that business is facing and may face in the future, the strengths that the business can rely on and any weaknesses that may affect the business performance. |
| 2. Competitive Situation | Analyze main competitors of organization who are they what are they upto how do they compare. What are their competitive advantage? Analyze their strength and weakness. |
| 3. Product Situation | The details about current product. The details about current product may be divided into part audit as the core product and any secondary of supporting services or products that also make up what you sell. It is important to observe this in terms of its different parts in order to be able to relate this back of core needs of customers. |
Question 15.
Industry and competitive analysis begins with an overview of the industry’s dominant economic features.” Explain and also narrate the factors to be considered in profiling in industry’s economic features. (Nov 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Industry and competitive analysis begins with an overview of the industry’s dominant economic features. The factors to be considered ki profiling an industry’s economic features are fairly standard arid are given as follows:
- Size and nature of market
- Scope of competitive rivalry (local, regional, national, International or global).
- Market growth rate and position n the business life (early development, rapid growth arid takeoff, early maturity saturation and stagnation, decline).
- Number of rivals and their relative market share
- The number of buyers and their relative sizes. Whether and to what extent industry rivals have integrated backward and or forward.
- The types of distribution channels used to access consumers.
- The pace of technological change in both production process innovation and new product introductions.
- Whether the products and services of rival firms are highly differentiated, weakly differentiated, or essentially identical?
- Whether organization can realise economies of scale in purchasing, manufacturing, transportation, marketing or advertising?
- Whether key industry participants are dustered in a particular location, for example, lock Industry in Ali9arti. Saris and diamonds in Surat, information technology in Bangalore. Similarly, there is also concentration of business in different countries on account of geographical and other reasons?
Question 16.
What do you understand by Trigger of change? How is trigger related to driving force?
Answer:
Triggers of Change:
Triggers are fundamental character to make movements. The intensity of competition is determined by the triggers. Triggers hits the driving force and driving force creates impact on competition. This analysis has two steps:
- Identify most common driving torces causing the competition.
- Find how much it is creating Impact on competition.
There is popular concept of life cycle of the product. The life cycle change is applicable to the whole Industries. But we know that there are other factors also which provide stimulants for changes.
The trigger hits the driving force. Industry and competition changes because of force and motion In business. The most dominant force or reason for change is called driving force. This driving forces have biggest influences on kind of competition that will take place In industry. Most powerful driving force Is good enough to make quality upgradation. Some of the categories of drivers are to take the industry on the top in the quality, awareness, stability etc. Many events can affect an industry powerfully enough to qualify as driving force. Some of them can be Industry-specific and some of them can be general. Some of the categories of drivers are the following:
- The Internet and the new e-commerce opportunities and threats it breeds in the industry.
- Increasing globalization.
- Changes in the long-term industry growth rate.
- Product innovation.
- Marketing innovation.
- Entry or exit of major forms.
Question 17.
State with reasons which of the following statement is correct/incorrect:
A core competence is a unique opportunity of an organisation not shared by other. (Nov 2007, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct: Core competencies represent distinctive skills which helps a firm gain competitive advantage over the others. It Is thus not shared by others and if the competitors Imitate or develop similar core competencies, the firm has to continuously gain more and more competencies to stand aside.
Question 18.
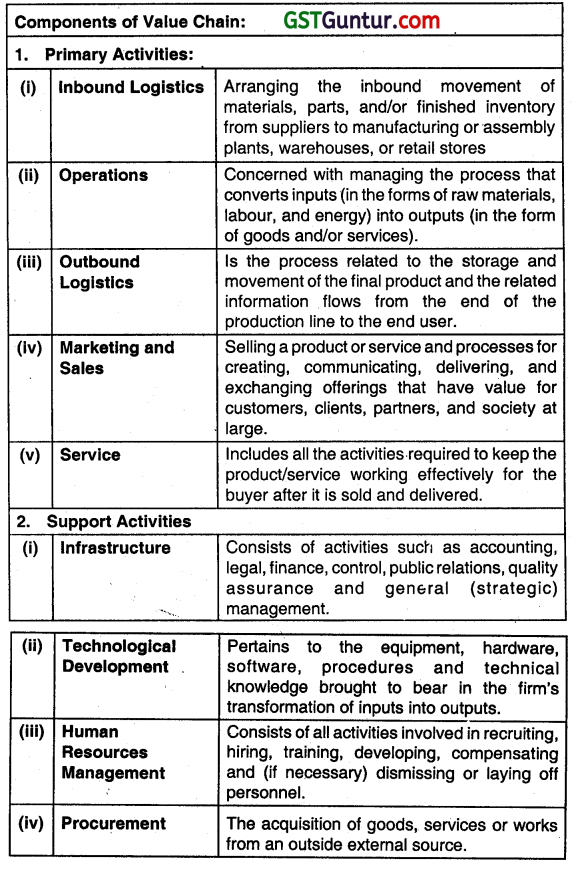
Briefly answer the following:
Components of a Value chain. (Nov 2008, 2 marks)
OR
Write short note on the following:
Components of Value Chain (Nov 2013, 3 marks)
Answer:
Question 19.
Explain the meaning of the following concepts:
Value Chain Analysis (Nov 2011, 1 mark)
Answer
Value Chain
A firm’s Value Chain forms a part of a larger stream of activities, which Porter calls a value system. A value system, or an industry value chain, includes the suppliers that provide the inputs necessary ro the firm along with their value chains. After the firm creates products, those products pass through the value chains of distributors (which also have their own value chains), all the way to the customers. All parts of these chains are included in the value system. To achieve and sustain a competitive advantage, and to support that advantage with information technologies, a firm must understand every component of this value system.
Question 20.
Management of internal linkages in the value chain could create competitive advantage In a number of ways. Briefly explain. (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Successful implementation of supply management systems require a change from managing individual function to integrating activities into key supply chain processes. It involves collaborative work between buyers and suppliers joint product development, common systems and shared information. A key requirement for successfully implementing supply chain will be network of information sharing and management of linkages.
Linkages are relationships between the way one value activity is performed and the cost or performance of another (e.g., purchasing high-quality, precut steel sheets can simplify manufacturing and reduce scrap). Linkages can lead to competitive advantage In two ways optimization and coordination.
Linkages among value activities arise from a number of generic causes, among them the following: the same function can be performed In different ways; the cost or performance of direct activities is improved by greater efforts in indirect activities; activities performed inside a firm reduce the need to demonstrate, explain, or service a product in the field; quality assurance functions can be performed in different ways.
The buyer’s Value Chain. Buyers also have value chains, and a firm’s product represents a purchased Input to the buyer’s chain. Understanding the value chains of industrial, commercial, and institutional buyers Is easy because of their similarities to that of a firm.
The Value Chain can be used to compare the firm’s current position with the strategy selected in order to assess the strategic gap. The use of activity-based cost measurement with value chain analysis will enable individual components of the business to be evaluated without losing sight of their holistic impact on the competitiveness of the business.
Finally, the basic concept of the Value Chain has been used by strategists to explain the success of various firms in pursuit of a differentiation or low-cost strategy.
Question 21.
Write short note on the following:
Value Chain Analysis. (Nov 2017, 3 marks)
Answer:
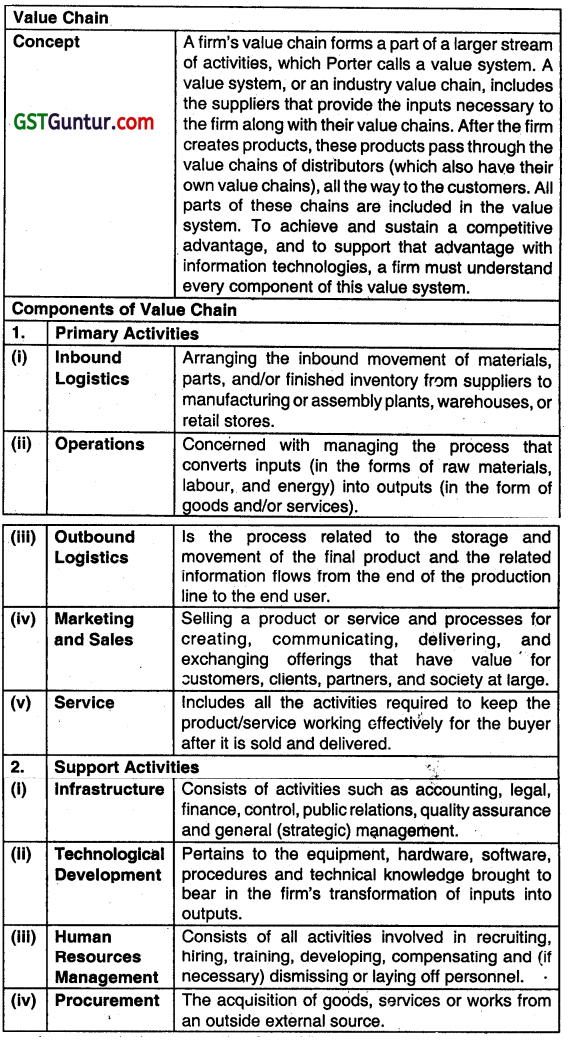
Question 22.
Explain the meaning of core competencies. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Core Competence:
A core competence is a unique strength of an organization which may not be shared by others. Core competencies are those capabilities that are critical to a business achieving competitive advantage. In order to quality as a core competence, the competency should differentiate the business from any other similar businesses.
Question 23.
Which of the following statement is ‘correct’ and which Is incorrects? Give reason, in brief, for your answer Human Resource Manager’s role is significant In building up core competency of the firm. (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct
The human resource manager has a significant role to play In developing core competency of the firm. A core competence Is a unique strength of an organization which may not be shared by others. Core- competencies can be generated and maintained only through the effective management of human resources and their skills.
![]()
Question 24.
Core competencies provide edge to a business over its competitors. Discuss. Also, briefly state the three areas in which major core competencies are identified. (Jan 2021, 5 marks)
Question 25.
How does the core competency and value chain linked together helps th company to be unique?
Answer:
Core Competence:
A core competence is a unique strength of an ‘organization which may not be shared by others. Core competencies are those capabilities that are critical to a business achieving competitive advantage. In order to qualify as a core competence, the competency should differentiate the business from any other similar businesses.
Core competencies in Separate activities may provide competitive advantage for an organization, but nevertheless over time may be imitated by competitors. Core competencies are likely to be more robust and difficult to imitate if they relate to the management of linkages within the organization’s value chain and linkages into the supply and distribution chains. It Is the management of these linkages which provides ‘leverage’ and levels of performance which are difficult to match.
The Management of Internal Linkages In the value chain could create competitive advantage in a number of ways:
There may be Important linkages between the primary activities. For example, a decision to hold high levels of finished stock might ease production scheduling problems and provide for a faster response time to the customer. However, it will probably add to the overall cost of operations. An assessment needs to be macle of whether the value added to the customer by this faster response through holding stocks is greater than the added cost.
It is easy to miss this issue of managing linkages between primary activities in an analysis If, for example, the organization’s competencies in marketing activities and operations are assessed separately.
The Management of the linkages between a primary activity and a support activity may be the basis of a core competence. It may be key investments In systems or infrastructure which provides the basis on which the company outperforms competition. Computer-based systems have been exploited in many different types of service organization and have fundamentally transformed the customer experience. Linkages between different support activities may also be the basis of core competencies.
In addition to the management of internal linkage, competitive advantage may also be gained by the ability to complement/co-ordinate the organization’s own activities with those of suppliers, channels or customers.
Again, this could occur in a number of different ways:
Vertical integration attempts to improve performance through ownership of more parts of the value system, making more linkages internal to the organization. However, the practical difficulties and costs of co-ordinating a wider range of internal activities can outweigh the theoretical benefits.
Within manufacturing industry, the competence In closely specifying requirements and controlling the performance of suppliers (sometimes linked to quality checking and/or penalties for poor performance) can be critical to both quality enhancement and cost reduction.
A more recent philosophy has been total quality management, which seeks to improve performance through closer working relationships between the specialists within the value system. For example, many manufacturers will now involve their suppliers and distributors at the design stage of a product or project.
The merchandising activities which manufacture undertakers with their distributors are now much improved and are an important.
Question 26.
‘Value for Money’ is a leading retail chain, on account of its ability to operate its business at low costs. The retail chain aims to further strengthen Its top position in the retail industry. Marshal, the CEO of the retail chain is of the view that to achieve the goals they should focus on lowering the costs of procurement of products. Highlight and explain the core competence of the ‘Value for Money retail chain.
Answer:
A Core Competence is a unique strength of an organization which may not be shared by others. Core Competencies are those capabilities that are critical to a business achieving competitive advantage. In order to qualify as a core competence, the competency should differentiate the business from any other similar businesses. A core competency for a firm is whatever it does is highly beneficial to the organisation.
‘Value for Money’ is the leader on account of Its ability to keep costs low. The cost advantage that ‘Value for Money’ has created for itself has allowed the retailer to price goods lower than competitors. The core competency in this case is derived from the company’s ability to generate large sales volume, allowing the company to remain profitable with low profit margin.
Question 27.
Explain the concept of competitive advantage, (2 marks)
Answer:
Competitive Advantage:
Competitive advantage ¡s the position of a firm to maintain and sustain a favourable market position when compared to the competitors. Competitive advantage Is ability to offer buyers something different and thereby providing more value for the money. It is the result of a successful strategy. This position gets translated Into higher market share, higher profits when compared to those that are obtained by competitors operating in the same industry. Competitive advantage may also be In the form of low-cost relationships In the industry or being unique in the industry along dimensions that are widely valued by the customers in particular and the society at large.
Question 28.
Mohan has joined as the new CEO of XYZ Corporation and aims to make it a dominant technology company in the next five years. He aims to develop competencies for managers for achieving belier performance and a competitive advantage for XYZ Corporation. Mohan is well aware of the importance of resources and capabilities In generating competitive
advantage.
Discuss the four major characteristics of resources and capabilities required by XYZ Corporation to sustain the competitive advantage and its ability to earn profits from it. (Jan 2021, 5 marks)
Question 29.
Briefly answer the following:
Growth phase of product life cycle (May 2008, 2 marks)
Answer:
Growth Phase of Product Lite Cycle:
After the product is introduced in the market, the product enters the second stage i.e. growth stage. Under this stage the product gains popularity and recognition. As a resuft the demand and sales go up tremendously. Consequently, profit of the firm starts going up. However, high profit also attracts competitors to enter the field. Thus expenditure on advertisement
and sales promotion programme should be Increased.
Question 30.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
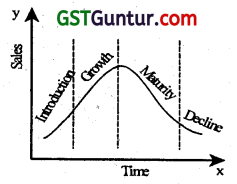
PLC is an S shaped curve. (May 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct:
PLC is a S-shaped curve showing graphical representation of sales over time that passes through four stages that is, Introduction, growth, maturity and decline phase. Identification of PLC stages of any product or service Is very helpful In marketing management.
Question 31.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements with the most appropriate word:
Product Life Cycle portrays the distinct ……………. In the sales history of a product. (Nov 2010, 1 mark)
Answer:
Stages.
Question 32.
Explain the concept of Experience Curve and highlight its relevance in strategic management. (Nov 2012, 3 marks)
OR
Write short note on the following:
Experience Curve (May 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Experience Curve
| Meaning | Experience curve is a concept which explains the phenomena of efficiency increase gained by workers through repetitive productive work. It is a portfolio approach. |
| Based on | Experience curve is based on the commonly observed phenomenon that unit costs decline as a firm accumulates experience in terms of a cumulative volume of production. |
| Implication | The implication is that larger firms in an industry would tend to have lower unit costs as compared to those of smaller organizations, thereby gaining a competitive cost advantage. |
| Results from | Experience curve results from a variety of factors such as learning effects, economies of scale, product redesign and technological improvements in production. |
| Relevance In Strategic Management | 1. With implementation of experience curve larger firms in an industry tend to have lower cost per unit as 2. compared to smaller companies thus gaining a competitive cost advantage. Thus it builds market share and discourages competition by building a barrier for new firms. |
Question 33.
Write short note on the following:
Product Life Cycle (Nov 2013, 4 marks)
OR
Write short note on the following:
Product Life Cycle (PLC) arid its significance in portfolio diagnosis. (May 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
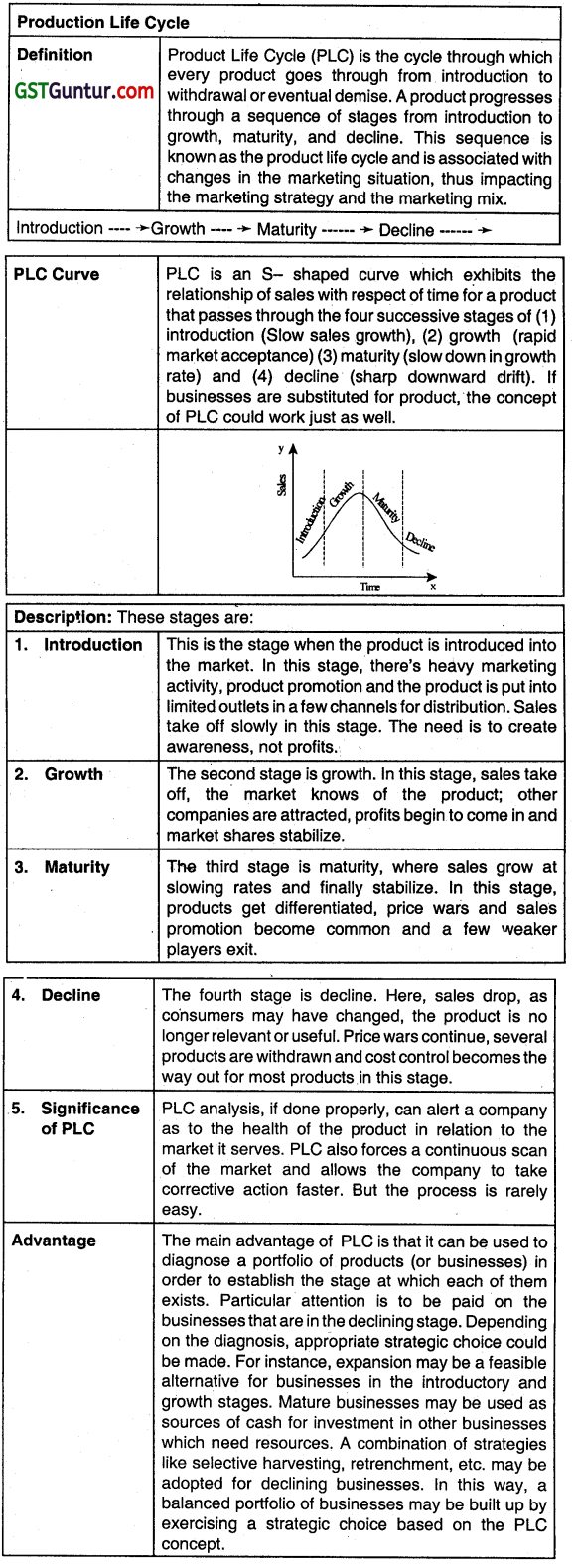
Question 34.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
Portfolio analysis helps the strategists in identifying and evaluating various businesses of a company. (Nov 2012, Nov 2015, 2 marks each)
Answer:
Correct:
Corporate portfolio analysis (or simply, portfolio analysis) is a set of techniques that evolved during the mid-1960s.
Corporate portfolio analysis could be defined as a set of techniques That help strategists in taking strategic decisions with regard to individual products or businesses in a firm’s portfolio.
Question 35.
Discuss with example the relevance of experience curve in strategic management. (Nov 2017, 3 marks)
Answer:
Experience Curve:
| Meaning | Experience curve is a concept which explains the phenomena of efficiency increase gained by workers through repetitive productive work. It is a portfolio approach. |
| Based On | Experience curve is based on the commonly observed phenomenon that unit costs decline as a firm accumulates experience in terms of a cumulative volume of production. |
| Relevance | The concept of experience curve is relevant for a number of areas in strategic management for instance, experience curve is considered a barrier for new firms contemplating entry in an industry. It is also used to build market share and discourage competition. |
| Example | In the contemporary Indian two-wheeler market, the experience curve phenomenon seems to be working in favour of Bajaj Auto, which for the past decade has been selling, on an average, five lakh scooters a year and retain more than 60 percent of market. Its only serious competitor is LML Vespa Ltd., which has a far lesser share of the market. The primary strategic advantage that Bajaj Auto has is in terms of costs, other competitors like Gujarat Narmada and Kinetic Honda find it extremely difficult to compete due to the cost differentials the currently exist. The likely strategic choice for underdog competitors could be a market-nice approach or segmentation based on demography. |
Question 36.
Briefly answer the following:
Explain the term star in the context of BCG matrix. (Nov 2007, 2 marks)
Answer:
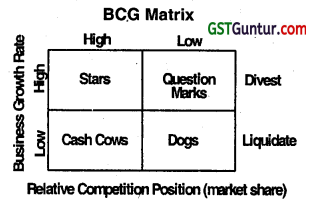
| Star | Stars are high growth- high market share businesses which are growing rapidly. |
| Cow | Cash Cows are businesses which generate large amount of cash but their rate of growth is slow. |
| Dog | These are low growth and low share business and products. They may generate enough cash to maintain themselves in the market but do not have much future. |
Question 37.
Describe the construction of BCG matrix and discuss its utility in strategic management. (May 2009, 5 + 5 = 10 marks)
Answer:
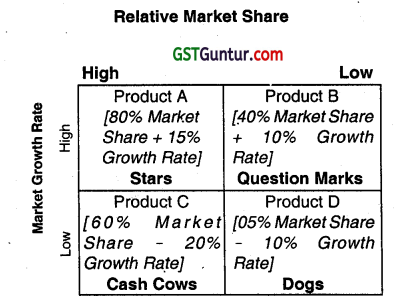
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix provides a graphic representation for an organization to examine different businesses in its portfolio on the basis of their relative market shares and industry growth rates. The result of the combination of industry growth rate and relative market share, each along a high and low dimension, is a four-cell matrix. Each cell of the matrix has been given an appropriate name by the Boston Consulting Group.
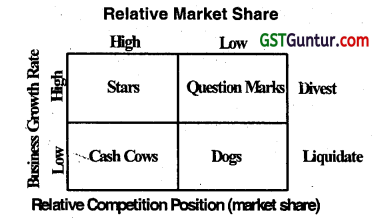
The vertical axis denotes the rate of growth of sales In percentage for particular Industry.
The horizontal axis denotes the relative market share and serve as a measure of company Strength in the Market.
The Four Cells of the BCG Matrix are:
| 1. Star | Stars are high growth- high market share businesses which are growing rapidly. |
| 2. Cow | Cash Cows are businesses which generate large amount of cash but their rate of growth is slow. |
| 3. Question Marks | Business with high Industry growth but low market share for a company are questions marks which are also called ‘Problem Children’. They require large amounts of cash to maintain or gain market share. These are usually new products or services so they need heavy investment. It is for business organisations to turn them into the stars and then to cash cows when the growth rate reduces. |
| 4. Dogs | These are low-growth and low-share business and products. They may generate enough cash to maintain themselves in the market but do not have much future. |
![]()
Question 38.
In the Ught of BCG Growth Matrix state the situation under which the following strategic options are suitable:
(i) Build
(ii) Hold
(iii) Harvest
(iv) Divest (Nov 2011, May 2017, 4 x 1 4 marks each)
Answer:
In the light of BCG Growth Matrix, once an organisation has classified its products or SBUs, It must determine what role each will play in the future.
The Four Strategies that can be pursued are:
| (i) Build | Create a new brand and a new target audience by means of a Question Mark. Here the objective Is to increase market share, even by forgoing short-term earnings in favour of building a strong future with large market share. |
| (ii) Hold | Maintain this success and benefit from market growth by means of a star. Here the objective Is to preserve market share. |
| (iii) Harvest | Make as much money as possible with the product by means of the Cash Cow. This can be achieved by improving or renewing the product or by manufacturing by-products. Here the objective is to increase short-term cash flow regardless of long-term effect. |
| (iv) Divest | Abandon the Investment in the product by means of a Dog: the market is saturated or there is no or little interest in the product. Here the objective is to sell or liquidate the business because resources can be better used elsewhere. |
Question 39.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements with the most appropriate word:
Market penetration refers to a ……………………. where the business focuses on selling existing products into existing market. (May 2012, 1 mark)
Answer:
Growth Strategy.
Question 40
What does the concept of ‘question marks’ In the context of BCG Growth-Share matrix signify? What strategic options are open to a business firm which has some ‘question marks’ In the portfolio of its businesses? (May 2015, 3 marks)
Answer:
- The Concept of ‘question marks’ in the context of BCG growth-share matrix is high growth & low market share.
- They require huge amount of cash to maintain or gain market share.
- Question marks are generally new goods and services which have a good commercial prospect.
- There is no specific strategy which can be adopted. If the firm thinks it has dominant market share, then It can adopt expansion strategy, else retrenchment strategy can be adopted.
- Most businesses start as question marks as the company tries to enter a high-growth market in which there is already a market share.
- If ignored, the question marks may become dogs, while if huge Investment is made, they have the potential of becoming stars.
Question 41.
To which industries the following environmental changes will otter opportunities and pose threats (name any two industries in each case).
Give reasons for your answer.
(i) Significant reduction in domestic air-tares spanning over a long period.
(ii) Cut in interest rates by banks. (May 2015, 2 x 2 = 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) If there la changes In significant reduction In domestic air-fares spanning over a long period:
- Airline Industries: As an opportunity because it creates profit in future and service can be improved.
- Service industries: It creates opportunity for them in the future a service communication can be improved by providing better and speedier services.
(ii) Cut in interest rates by banks:
- Banking Section: Cut in interest rate can be favourable to banking Industries as It attracts and pleases the customers for more loans and advances. So, they can earn good amount on fund.
- Manufacturing Industries: Main requirement of manufacturing industries is a fund at its lower cost. So, when there is change in Bank interest Rate, Manufacturing Industries can avail such fund and grow In an economy.
Question 42.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
BCG Growth-Share Matrix is popularly used for resource allocation. (May 2016, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct:
BCG Growth-Share Matrix is popularly used for resource allocation.
Question 43.
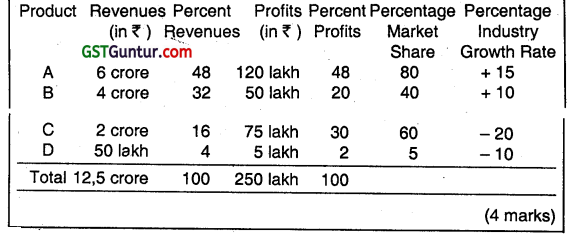
An industry comprises of only two firms – Soorya Ltd. and Chandra Ltd. From the following information relating to Soorya Ltd., prepare BCG Matrix:
(May 2010, 4 marks)
Answer:
On implementation of BCG approach, a company classifies its different businesses on a two-dimensional growth-share matrix. In the matrix, the vertical axis shows market growth rate arid provides a measure of market attractiveness. The horizontal axis shows relative market share and serves as a measure of company strength In the market. Using the given data on market share and industry growth rate of Soorya Ltd., its four products are placed in the BCG matrix as follows:
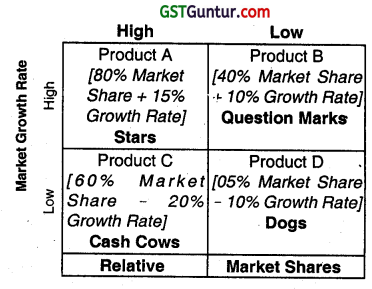
Analysis:
(i) Product A is in best position as it has a high relative market share and a high industry growth rate.
(ii) On the other hand, product B has a low relative market share, yet competes in a high-growth industry.
(iii) Product C has a high relative market share, but competes In an industry with negative growth rate. The company should take advantage of its present position that may be difficult to sustain in long run.
(iv) Product D is in the worst position as it has a low relative market share, and competes in an industry with negative growth rate.
Question 44.
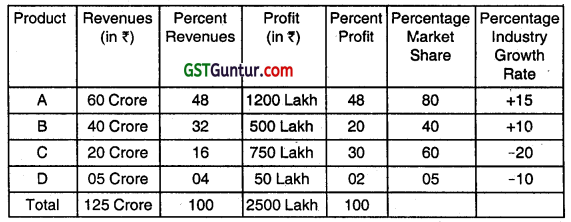
From the following information relating to X Ltd. company, prepare BCG Matrix and also analyse It.
(Nov 2013, 4+ 3=7 marks)
Answer:
Using the BCG approach, a company classifies Ils different businesses on a two-dimensional Growth-Share Matrix, in the Matrix, the vertical axis represents market growth rate and provides a measure of market attractiveness. The horizontal axis represents relative market share and serves as a measure of company strength in the market. With the given data
on market share and industry growth rate of X Ltd., its four products are placed in the BCG matrix as follows:
Product A: It falls ¡n the Star category arid is In the best position with high relative market share and a high industry growth rate. This product has the best opportunities for expansion. It will require heavy investment to maintain its present position.
Product B: It is a question mark product that has a relatively low market share, yet competes in a high-growth industry. This product will also need lot of cash to hold its share. If unattended, it is capable of becoming a cash trap.
Product C: It is a cash cow for the business, has a relatively high market share competing ¡n an Industry with negative growth rate. The company should take advantage of its present position that may be difficult to maintain in the long run. Currently, it needs less investment to maintain its market share.
Product D: It is presently placed in the Dog category, is in the worst position as it has relatively a low market share, and competes in an industry with negative growth rate. This product does not have much future. It should be minimized by means of divestment or liquidation.
![]()
Question 45.
Aurobindo, the pharmaceutical company wants to grow its business. Draw Ansoff s Product Market Growth Matrix to advise them of the available options. (Nov 2010, 4 marks)
OR
“The Ansoff’s product market growth matrix is a useful tool that help businesses their product and market growth strategy.” Elucidate this statement. (May 2013, 3 marks)
OR
How Ansoff’s Product Market Growth Matrix is a useful tool for business organisations? (May 2017, 3 marks)
Answer:
The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic planning tool that provides a framework to help executives, senior managers, and marketers devise strategies for future growth. It is named after Russian American Igor Ansoff, who came up with the concept. Ansoff, in his 1957 paper, provided a definition for product-market strategy as “a joint statement of a product line and the corresponding set of missions which the products are designed to fulfill.
Ansoff’s Product Market Growth Matrix is useful tool that helps businessmen decide their product and market growth strategy. This two-dimensional matrix gives us four strategic options.
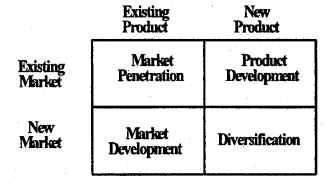
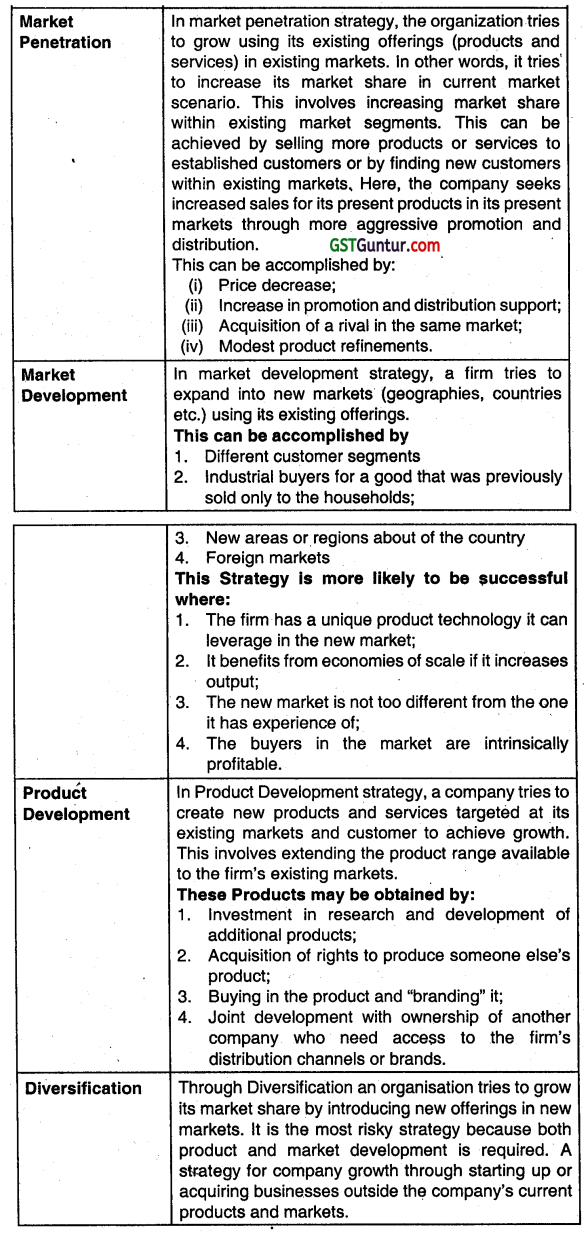
Advise: Based on the matrix, Aurobindo may segregate its different products. Being In pharmaceuticals, development of new products is result of extensive research and involves huge costs. There are also social dimensions that may influence the decision of the company. It can adopt penetration, product development. market development or diversification simultaneously for its different products.
Question 46.
Explain the meaning of following concepts:
Market Penetration (May 2012, 1 mark)
Answer:
Market Penetration: Market penetration as a deliberate strategy involves gaining market share through improving quality or productivity, and increasing marketing activity. This is true for the long-term desirability of obtaining a dominant market share. However, the nature of the market and the position of competitors determine the ease with which a business can pursue a strategy of market penetration.
Question 47.
Distinguish between the following:
Market development’ and ‘Product development’. (May 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Market Development and Product Development
| Market Development | Product Development | |
| 1. Meaning | This strategy Involves marketing existing products to customer In related market areas, by adding different channels of distribution or by changing the content of advertising or promotional media | This involves substantial modification of existing products or creation of new but related products that can be marketed to current customers through established level |
| 2. Market Change | Here, the existing market changes because firms enters into new market. | Here, market doesn’t change, firm agrees to offer in same market |
| 3. Product | Here products are offered i.e. existing product offered in new markets. | Here, new products are offered in existing markets. |
Question 48.
Explain the meaning of the following concepts:
ADL Matrix (Nov 2012, 1 mark)
Answer:
The matrix suggested by Arthur D. Little Company for portfolio analysis is a four-by-five matrix and is aimed at linking stages in the product life cycle with the competitive strength of businesses. The matrix is illustrated below:
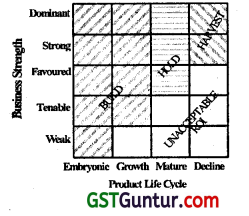
Classified according to their business strength. SBUs may be plotted on the vertical axis which is divided into five segments-Weak, Tenable, Favourable. Strong and Dominant. The stages In life cycle of the products are plotted on the horizontal axis in four segments-Embryonic, Growth, Maturity and Decline.
Question 49.
Describe the various competitive positions and its assessment criteria as per ADL Matrix. (Nov 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Competitive Positions and their Assessment Criteria for ADL Matrix:
| 1. Dominant | This is a comparatively rare position and in many cases is attributable either to a monopoly or a strong and protected technological leadership. |
| 2. Strong | By virtue of this position, the firm has a considerable degree of freedom over its choice of strategies and is often able to act without its market position being unduly threatened by its competitors. |
| 3. Favourable | This position, which generally comes about when the industry is fragmented and no one competitor stand out clearly, results in the market leaders a reasonable degree of freedom. |
| 4. Tenable | Although the firms within this category are able to perform satisfactorily and can justify staying in the industry. |
| 5. Weak | The performance of firms In this category is generally unsatisfactory although the opportunities for Improvement do exist. |
Question 50.
In the context of Ansoff’s Product-Market Growth Matnx, identify with reasons, the type of growth strategies followed in the following cases:
(i) A leading producer of toothpaste, advises its customers to brush teeth twice a day to keep breath fresh.
(ii) A business giant in hotel Industry decides to enter into dairy business.
(iii) One of India’s premier utility vehicles manufacturing company ventures to foray into foreign markets.
(iv) A renowned auto manufacturing company launches ungeared scooters in the market. (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
(i) Market Penetration
Refers to a growth strategy where the business focuses on selling existing products Into existing markets.
(ii) Diversification
Diversification refers to a growth strategy where a business markets new products In new markets.
(iii) Market Development
Market Development refers to a growth strategy where the business seeks to sell its existing products Into new markets.
(iv) Product Development
Product Development refers to a growth strategy where business alms to Introduce new products into existing markets.
Question 51.
Discuss General Electric’s model of analyzing current business portfolio. (May 2016, 3 marks)
OR
Explain GE model. How is it useful in making strategic choices?
Answer:
General Electric Model:
This model is used by General Electric Company (developed by GE with the assistance of the consulting firm McKinsey & company). This model, is also known as Business Planning Matrix, GE Nine cell Matrix and GE Electric Model. The strategic planning approach in this model has been inspired from traffic control lights. The hghts that are used at crossing to manage traffic are; green for go, amber or yellow for caution, and red for stop.
This model uses two factors while taking strategic decision:
Business strength and market attractiveness. The vertical axes indicates market attractiveness and horizontal axis shows the business strength in the industry.
The Market attractiveness le measured by a number of factors like:
- Size of the market.
- Market growth rate.
- Industry profitability.
- Competitive intensity.
- Availability of technology.
- Pricing trends.
- Overall risk-off returns in the inustry.
- Opportunity for differentiation of products and services.
- Demand variability.
- Segmentation.
- Distribution structure (e.g. retail, direct, wholesale) etc.
Business Strength Is measured by drivers like:
- Market share.
- Market share growth rate.
- Profit margin.
- Distribution efficiency.
- Brand image.
- Ability to compete on price and quality.
- Customer loyalty.
- Production capacity.
- Technological capability.
- Relative cost position.
- Management caliber etc.
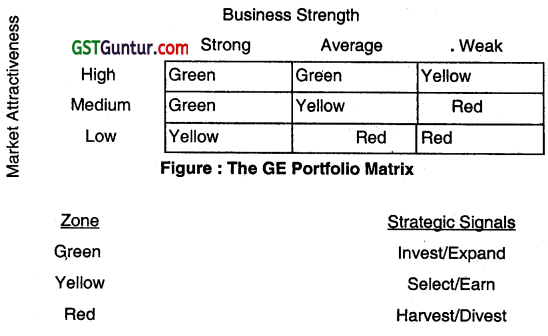
If e product falls In the green section, the business is at advantageous position. To reap the benefits, the strategic decision can be to expand, to invest and grow.
If a product Is In the amber or yellow zone, it needs caution and managerial discretion Is called for making the strategic choices.
If e product Is In the red zone, ¡t will eventually lead to losses that would make things difficult for organisations. In such cases, the appropriate strategy should be retrenchment, divestment or liquidation.
![]()
Question 52.
State with reáson which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The purpose of SWOT analysis is to rank organizations. (May 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
Incorrect:
Organisations use SWOT analysis to understand the external and internal environment. SWOT refers to strength, weakness, opportunities and threats. Through this analysis, the strengths and weaknesses existing within an organisation can be matched with the opportunities and threats operating In the environment so that an effective strategy can be formulated.
Question 53.
To which industries the following development otters opportunities and threats? The number of nuclear families, where husband and wife both are working, is fast increasing. (Nov 2010, 3 marks)
Answer:
Different developments ¡n the environment can offer different opportunities and threats to businesses. An opportunity is a favourable condition in the organisation’s environment which enables it to strengthen Its position with respect to its competitors. A threat is an unfavourable condition in the which causes a risk for, or damage to, the organization’s position.
The Situation in the question relates to threats and opportunities of social environment. in the present social environment, there is growth of nuclear families. This is away from the joint family system when both husband & wife are working It Increases their spending capacity.
Opportunity: Such developments bring direct opportunities to different businesses such as Ready to eat food, fast-to-cook items, dishwashers, washing machines, crashes for children and so on. Indirect opportunities exists for other lifestyle products.
Threat: At the same time, such development also acts as threat to traditional raw food suppliers, kitty party organizers and so on.
Question 54.
Explain the significance of SWOT analysis. (May 2014, 3 marks)
Answer:
SWOT Analysis
Meaning SWOT analysis (alternatively SWOT matrix) Is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and is a structured planning method that evaluates those five elements of a project or business venture. A SWOT analysis can be carried out for a company, product, place, industry, or person. It involves specifying the objective of the business venture or project and identifying the internal and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieve that objective. SWOT analysis aims to identify the key internal and external factors seen as important to achieving an objective.
Categories
SWOT analysis groups key pieces of information Into two main categories:
1. Internal factors: the strengths and weaknesses internal to the organization.
2. External factors: the opportunities and threats presented by the environment external to the organization.
Significance of SWOT analysis
It provides logical framework for systematic and sound of issues having bearing on the business Analysis situation, generation of alternative strategies and the choice of strategy.
It presents information about both external and internal environment in a structured firm where it is possible to compare external opportunities and threats with internal strengths and weaknesses.
It guides the strategist In strategy identification. It is natural that a strategist faces a problem when his organization cannot be matched In the firm patterns.
It is possible that the organization may have several opportunities and some serious threats. It Is equally true that the organisation may have powerful strengths coupled with major weaknesses ¡ri the light of critical success factors.
Question 55.
To Which industries the following developments offer opportunities and threats? Increasing trend In India to organize IPL (Cricket) type of tournaments In other sports also”. (Nov 2014, 3 marks)
Answer:
Opportunities An opportunity is a favourable condition in the organisation’s environment which enables it to strength then its position. The opportunities through IPL (cricket) tournaments are as follows:
- Growth of the Nation.
- Growth of Indian Cricket Industry.
- Growth of Stadiums,
- Growth of Sports industry.
- Growth of Media Industry.
- Growth of tourism and hotel industry.
Threats A threat is an unfavorable condition In the organisations environment which causes a risk for or damage to organisation.
- Increase In corruption.
- Increase in betting.
- Time wasting of people.
Question 56.
Write short note on the following:
SWOT analysis. (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
OR
Write a short note on SWOT analysis. (May 2018, 3 marks)
Answer:
SWOT Analysis:
1. Concept SWOT analysis (alternatively SWOT matrix) is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and is a structured planning method that evaluates those four elements of a project or business Venture. A SWOT analysis can be carried out for a company, product, place, industry, or person. It involves specifying the objective of the business venture of project and Identifying the internal and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieve that objective.
2. Aim
SWOT analysis alms to identify the key Internal and external factors seen as important to achieving an objective.
3. Categories
SWOT analysis groups key pieces 0f information into two main categories:
1. Internal factors: the strengths and weaknesses Internal to the organization.
2. External factors: the opportunities and threats presented b the environment external to the organization.
4. Strength
Strength is an inherent capability of the organization which it can use to gain strategic advantage over its
competitors.
5. Weakness
A weakness is an inherent limitation or constraint of the organisation which creates strategic disadvantage for it.
6. Opportunity
An opportunity Is a favourable condition in the organisatioWs environment which enables it to strengthen its position.
7. Threat
A threat is an unfavourable condition ¡n the organisation environment wiich causes a risk for, or damage to the organisation position.
Question 57.
Read the following case arid answer the questions given at the end:
In 2006-07 PTC Food division decided to enter the fast-growing (20- 30% annually) snacks segment, an altogether new to it. It had only one national competitor-Trepsico’s Trito. After a year Its wafer snack brand-Ringo fetched 20% market share across the country. Ringo’s introduction was coincided with the cricket world cup. The water snacks market Is estimated to be around ‘₹ 250 crores.
The company could take the advantage of its existing distribution network and also source potatoes from farmers easily. Before the PTC could enter the market a cross-functional team made a customer survey through a marketing research group in 14 cities of the country to know about the snacks of eating habits of people. The result showed that the customers within the age group of 15-24 years were the most promising for the product as they were quite enthusiastic about experimenting new snack tastes. The company reported to its chefs and the chefs came out with 16 flavours with varying tastes suiting to the targeted age group.
The company decided to target the youngsters as primary target on the assumption that once they are lured in, it was easier to reach the whole family.
Advertising in this category was extremely crowded. Every week two-three Focal products in new names were launched, sometimes with similar names. To break through this clutter the company decided to bank upon humour appeal.
The Industry sources reveal that PTC spent about ₹ 50 crores on advertisement and used all possible media -print and electronic, both including the creation of its own website. Ringoringoyoungo.com with offers of online games, contests etc. Mobile phone tone downloading was also planned which proved very effective among teenagers. The site was advertised on all dot-com networks. Em TV, Shine TV, Bee TV, and other important channels were also used for its advertisement along with FM radio channels In about 60 cities with large hoardings at strategic places.
Analysts believes that Ringo’s success story owes a lot to PTC’s widespread distribution channels and aggressive advertisements. Humour appeal was a big success. The ‘Ringo’ was made visible by painting the Railway bogies passing across the States. It has also been successful to induce Lovely Brother’s Future Group to replace Trito in their Big Bazaar and chain of food Bazaars. PTC is paying 4% higher margin than Trepsico to Future group and other retailers.
Ringo to giving Trepsico a run for its money. Trito’s share has already been reduced considerably. Retail tie-ups, regional flavours, and regional humour appeals have helped PTC. But PTC still wants a bigger share in the market and In foreign markets also, if possible.
Questions:
(a) What is SWOT Analysis? (May 2008, 4 marks)
(b) What are the strength of PTC? (May 2008, 4 marks)
(c) What are the weaknesses of PTC for entering into the branded snacks market? (May 2008, 4 marks)
(d) What kind of marketing strategy was formulated and implemented for Ringo?
What else need to be done by Ringo so as to enlarge its market? (May 2008,8 marks)
Answer:
(a) The comparison of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is normally referred to as a SWOT analysis.
Strength: Strength is an inherent capability of the organization which it can use to gain strategic advantage over its competitors.
Weakness: A weakness is an inherent limitation or constraint of the organization which creates strategic disadvantage to it.
Opportunity: An opportunity is a favorable condition in the organization’s environment which enables it to strengthen its position.
Threat: A threat is an unfavorable condition In the organization’s environment which causes a risk for, or damage to, the organization’s position.
The central purpose of SWOT analysis is to Identity the strategies that will create a firm-specific business model that will best align, fit, or match a companys resources and capabilities to the demands of the environment in which it operates. Strategic managers compare and contrast the various alternative possible strategies against each other with respect to their ability to achieve major goals and superior profitability.
(b) The strength of PTC:
- Widespread distribution network
- Aggressive advertisements
- Easy availability of raw material
- Ringo’s introduction coincided with Cricket Woki Cup.
(c) The main weakness was the presence of strong national competitors. The company has only targeted youngsters. Heavy advertisement cost is not required. It is unusually increasing the expenditure of the company.
(d) The company’s marketing strategy targeted the youngster on the assumption that once they are lured in, it would be easier to reach the whole family. For this their decision to bank upon humour appeal clicked. The following measures can be taken by Ringo so as to enlarge its market.
- Making the product available in public places and other crowded areas and organising street shows etc.
- Attention should also be paid towards the preference and lastes of foreign buyers for exploring the foreign market.
![]()
Question 58.
Read the following case and answer the questions given at the end:
Subhiksha (prosperity in Sanskrit) began with a single grocery store at Chennai in 1997. Subiksha stores increased from 50 in 2000 to 140 by 2002-03 (spread across 30 towns in Tamilnadu) to 670 by 2006-07 to 1650 by September 2008. Its early success was due to Its business model based upon no-frills/deep discounts and high level of neighborhood focus.
Its decision in 2004 to go national from a regional player at a rapid pace proved wrong. With the growing ambition to go national, focus shifted from value to customers to creating valuation for self. The company had recruited all the employees to foray into consumer durables also. Its revenue increased from ₹ 278 crore from 140 stores in 2005 to ₹ 2305 crore in 2008 with a capital base of ₹ 32 crore. Subhiksha’s profit after tax for 2007-08 was ₹ 41 crore. It had invested heavily, largely using debt, and paybacks took longer than expected. Repayment of debt had no relationship to cash flow. In the end the company had liabilities of ₹ 900 crore.
Around January, 2009, the company had started to shut down stores pan-India arid in February, the top management quit the firm, not just because it defauLted on rentals of its outlets and salaries since October, 20o8. Today all the stores are closed. Major suppliers had stopped supplies after it defaulted on payments. It asked its employees to take home groceries; and go on leave without pay. Many employees did not get their salaries. Initially the company was confident to restructure and remain in business.
Indian retail industry comprises 0112 million mom-and-pop stores and kirana stores (many of whom have also started Innovating) and unknown number of hawkers in the unorganized sector working on small-size stores and with low or no rentals and salaries and the organized retailers (market share not more than 5%).
The emergence of a large young population and a growing middle class with strong disposable incomes and credit card culture are the drivers of the organized retail, a mix of two types – ones going in for huge
expansion announcements and others following “slow and steady wins the race strategy. The industry operates not on a very hefty margin. The yearly top-line growth Is likely to remain around 10-15% as against forecasted 35% this year. Compared with players like Pantaloon, Rsliance, More, RPG and even Nilgiri’s (which has private equity funding), Subhiksha has no large group’s backing (except Shri Azim Premji having 10% stake). The strategy was to raise more debt and keep equity low. During 2006, Subhiksha had a good chance to make an initial IPO or raise private equity money, but it was in quest of creating higher valuations.
Suddenly retail was no longer so hot arid the capital tap had gone dry. Due to inability to raís9 more debt, working capital was diverted to expand. Many of the organized retailers have survived the downturn through transformation in their strategies and tactics. However, one thing is certain that footfalls have daclined for the organized retail.
Debt-ridden retailer Subhiksha Trading Services Ltd. has begun Its second innings in February, 2010, with the launch of its first cash-and- carry store (the board outside the outlet reads Subhlksha Maligal Ansi
Mandi) in Thiruvanmiyur in Chennai – at its first ever retail outlet). “Subhiksha’s model will be different this time around and will not directly engage with customers, said an industry source.
Questions:
(a) To understand the nature of competition certain questions need to be answered. What those questions are? (May 2010, 3 marks)
(b) Who were the competitors of Subhiksha? Do you think they were better equipped than it? (May 2010, 5 marks)
(c) What, where and how the business strategy of Subhiksha might have gone wrong? (May 2010,4 marks)
(d) If you were the strategy consultant to the Organised Retailers Association of India, what will you advise to control the cost and convert the threat of dropping footfalls and declining sales into an opportunity? (May 2010,6 marks)
(e) How is a Cash-and-carry store different from a Retail store? Name any other such Cash-and-carry store in India. 2010- May (May 2010,2 marks)
Answer:
(a) The nature of competition can be visualised in terms of SWOT (strength, weakness, opportunities and threats). The questions frequently asked are as follows:
- What are the strengths? What are the strengths of the competitors?
- What are the weaknesses? What are the weaknesses of the competitors?
- What are the opportunities that are available? What ¡s the position of opportunities when compared to competitors?
- What are the threats that are available? What ¡s the position of threats when compared to competitors?
Alternatively: Alternative questions that can be answered to understand the nature of competition are:
- Who are the competitors?
- What are their market shares?
- What are their products and services?
- What gives them cost arid price advantage?
- What are their financial positions?
- What are they likely to do next?
- Who are the potential future competitors?
(b) Subhiksha was facing competition on two fronts:
- Organized sector: Big departmental stores.
- Unorganized sector: Weekly markets, street vendors etc.
Different vendors in organised and unorganised sector enjoyed a number of distinct advantages in comparison with Subhlksha. There are many players in the organized retailing such as ‘Big Bazaar’, ‘Spencer’, More’, etc. These had support of established big business houses. They also took better strategic decisions. All of them competed with Subhiksha and were not short of finances.
The unorganised sector’s benefit is their own low costs and reach to the customers. Mom-and-Pop stores are small-sized retailers that are spread around nook and comer of the country. They enjoy personal relationships touch with the customers, and have cost advantage due to no or low rentals and salaries. They also normally work with their own funds and do not have any interests costs. Weekly Bazaars, frequently named after the days of weeks such as Manga/Budh Bazaar, also enjoy similar position. Hawkers lined up along streets, spread out on temporary platforms and illuminated by gas lamps also offer bargains. The street vendors offer the unparalleled convenience as they serve at the door of
the users.
(c) Subhiksha’s business model was working fine till it was a regional player. It did try to look at the things with long-term perspective but that landed them in trouble. Problems arose when It tried to expand rapidly. It was their aggressive growth strategy that had gone awry because they opened too many stores in too short a period without realising the potential of the company. Outlets were opened for sake of expansion, inspite of focus on sustainable growth.
Subhiksha’s financial strategy also proved to be problematic. Retail sector needs cash infusion. Subhiksha expanded by diverting working capital and rising high costs debts. To leverage on a small equity base of ₹ 32 crore only was bound to put them in difficulty. Recession made it faster. The strategy of Subhiksha of raising funds with more debt and less equity was wrong. It also did not go for the IPO to manage their finances in a better manner.
(d) in order to control the costs Organised Retailers Association of India can make several recommendations to its members. A strategist may suggest the following points:
1. Reduce Inventory: With proper Inventory management, the cost of obsolescence and reduce financing cost of Inventory.
2. Efficient utilisation of facilIties: Expenditure on account of power can be reduced by optimum usage of air-conditioning, lifts, lighting. etc.
3. Procure directly from the source: To reduce the costs and take advantages of bulk purchases, the products may be purchase directly from the manufacturers and producers.
4. Lease out excess space to manufacturers and other marketers:
Extra space may be leased out at a price to others. This will generate extra revenue and efficient utilization of space. Many organised retailers otter separate space to the sellers of cosmetic or small eateries. This also Improves footfalls.
5 Offer discounts: Hefty discounts can be offered on the products that are brought at low costs to Improve the interest and footfalls. It improves the sales even with falling footfalls.
6. Combination offers: Offers can be made to combine low-moving products with fast-moving products and sell them at discount.
7. A balanced capital structure: The debt-equity ratio should be properly maintained with future perspective so that the scarce financial resources can be utilized in an optimum manner.
8. Organise special events to improve sales: Special events can be launched. These can have direct effect increasing footfalls and the sales. For example, an exhibition can be organised inviting mobile manufacturers to showcase their new products. Events such as painting competition for school kids, magic shows can also be organised to attract visitors to the stores.
9. Have proper security: Proper security system should be maintained to reduce the losses on account of pilferages.
(e) A cash-and-carry store is different from a retail store. Cash and carry store is one where customer pays in cash and cames away the purchases. The term is basically being used for the stores (wholesalers) that are making bulk sales to the retailers, caterers and institutional buyers. Therefore the business model is business-to-business. No credit period is given and invoice is settled on the spot in cash. The goods are carried away by the purchasers themselves. The store works as a bulk supplier rather than a retailer selling small quantities directed towars consumers.
Question 59.
Read the following case and answer the questions given at the end:
Godrej, still managed by a family board, is a 113-year-old brand and has a great brand value. But younger generation’s reaction has been – ‘it’s my parents’ or my grandparent& brand. Hence the Group launched a re branding exercise in 2008, the most visible part being a new logo, uniform across all group companies. it has well-diversified businesses – cyclical (property: owning 3000 acres in Mumbal’s Vikhroli alone, Ahmedabad, Pune and Kalyan), stable (fast moving consumer goods), rural (Agrovat stores) and urban (organised retail stores-Natures Basket, domestic appliances and furniture). The group sells fatty acidš to tyre manufacturers; animal feed to 1,00000 farmers: and premium wine in Mumbai and Delhi. Its customers range from five-year-olds (nutrine), ageing man (hair dye), to housewives (soaps & locks). IT companies (renting sprawling spaces), to Government of India (like rockets for Chandrayan), and to 50,000 barbers (Godrej dye). But it abstains in new-age, sunrise industries like health care and information technology.
Godrej Consumer Products Limited (GCPL) has adopted a ‘3 by 3’ strategy, sticking to emerging markets in three regions – Asia, Africa, and Latin America as their culture, tastes and even skin colours are quite similar to India and in three categories-personal care, hair-care and insecticides. Since 2005, GCPL has made seven acquisitions, including its biggest acquisition of Indonesia’s Megasarl Group for ₹ 1200 crore, in 2010. “Acquisitions overseas add status and pedigree to brand-owners in the domestic market” says an expert.
Prashant Goenka (Emami) questions “When Indian companies such as Dabur, Godrej, and Manco can make it big in international markets, why can’t Emami ? Anil Chug (Wipro) says. “by having a presence in multiple markets our risk assessment is neutralized”. Marico’s Harish opines- “the global play has helped Marico expand its footprint and given it another avenue for growth.”
Recently Godrej’s top honchos toured the hinterlands, an indicator of the renewed focus on consumer. To reach out to new customers, especially in rural India, it has gone in for destructive innovation. The group has been manufacturing refrigerators for more than 50 years, but its penetration has been only 18%. If found out that people do not need a 180-liter fridge due to space and cost constraints. It came out with ‘Chotukool’ – a square 45-litre mini fridge priced at just ₹ 3,250.
Another example of destructive innovation Is the launch of ‘U & Us’ – a ‘by appointment design studio where customers co-design their furniture as customers see furniture as an extension of their personality. Thus Godrej group is transiting from manufacturing-oriented to consumer-oriented.
Questions:
(i) What are the strengths of Group Godrej? (Nov 2010, 3 marks)
(ii) What are the weaknesses of Group Godrej? (Nov 2010, 3 marks)
(iii) What is the Group Godrej’s perception with regard to innovation and consumers now? (Nov 2010,3 marks)
(iv) Why do firms go global? (Nov 2010, 6 marks)
Answer:
(i) Strengths of the Godrej group are:
a. The group is into well diversified businesses, The businesses are both cyclical and stable in nature. The group also has presence in both rural and urban markets with different product offerings.
b. Godrej is more than 113-year-old brand.
c. Godrej enjoys trust and goodwill and has great brand value.
d. Godrej has 3000 acres of own land In VlkhroH, a developing suburb in Mumbai.
e. Godrej is growing internationally and Is concentrating on emerging markets of three regions – Asia, Africa, & Latin America.
(ii) Weaknesses of the group are:
a. Godrej is managed by members of a family. Unlike professional management the family considerations may play important role in the decisions of the company.
b. Godrej has made some aggressive acquIsitions in recent tithes.
How these are assimilated will be crucial for its business.
c. Lacks a significance presence ¡n new-age, sun-rise industries like health care, information technology and automobile Industry.
(iii) Godrej group Is shifting from being manufacturing-oriented to consumer-oriented. The company is focusing on customers and innovation. A business must understand what its customers want and keep innovating new products to satisfy the identified wants. If a company fails to do this, it will get extinct. For innovation, Godrej has adopted destructive innovation. The capacity to Innovate is a fundamental source of competitive advantage.
(iv) There are many reasons due to which the companies go global:
a. To increase the returns through higher margins or lower costs through large scale of operations.
b. Firms having surplus resources or capabilities developed at home may deploy them abroad for expansion.
c. Due to imposition of trade barriers by an importing state, the exporters from abroad decide to build manufacturing plants in the importing country.
d. Firms facing stiff domestic competition often decide to go international in search of new markets.
e. International presence dilutes local risk
f. Development of Institutions to support and facilitate International business.
g. Availing advantages of the liberalization initiatives of various governments across the world.
h. Attractive opportunities may exist in form of businesses in managerial or financial difficulty.
Question 60.
Read the following case and answer the questions given at the end:
Sharp Corporation is a worldwide developer of innovative products and core technologies that play a key role m shaping the future of electronics. As a leader in liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and digital technologies, Sharp offers one of the broadest and most advanced lines of consumer electronics, information products, and electronic components, while also creating new network businesses. Sharp Corporation has traveled a long way from an assembler of televisions to a leading TV manufacturer. In its early days as business enterprise, the company was making low-quality and low-price TVs and was, thus overshadowed by the giants like Sony, Samsung, and Matsushita. It was a technology follower in the beginning and was using secondary technology, The brand image, too, was not very high. Sharp, under the leadership of Machida, went for a brand image makeover by using innovation. The new leader has concentrated on R & D, in addition to enhancing its market coverage.
Its innovation In liquid crystal display (LCD) technology and developing products featuring LCD’s made at the reputed electronics company in Japan. Sharp is now the world’s largest manufacturer of LCD TVs. The company has very well succeeded and sustaining its success is a major critical factor: its focus on innovation. Unfortunately, the global economic downturn has hit Sharp worse than the most American Companies. The industry as a whole, and Sharp In particular, realised the fact that only innovation in terms of quality, cost and competitive strength is the main survival factor. At the same time, the Industry is not unaware of the fact that every new technology will obsolete laster. Average life of every new
technology is becoming shorter and shorter.
The ever-changing competitive scenario with the global competitors waging to dethrone Sharp and the entry of low cost manufacturers from Asia have created some of the biggest challenges for Sharp. Newer display technologies with superior quality at a lesser price are emerging in the international market. Sharp has taken the first mover advantage, but is facing competition from the late entrants.
Questions:
(i) What are the strengths of Sharp Corporation? (May 2011, 3 marks)
(ii) What are the weaknesses of Sharp Corporation? ((May 2011,3 marks)
(iii) What should be the next move of Sharp Corporation? ((May 2011,3 marks)
(iv) Analyse the key success factors for LCD TV Industry. ((May 2011,6 marks)
Answer:
(i) A positive aspect or strong capacity of a business which helps It overcome difficulties and gain strategic advantage over the others is known as strength of any business.
Eg.: Excellent workforce, strong R & D.
The strengths of Sharp Corporation are as follows:
(a) It is the leader In LCD and digital technologies.
(b) Broadest and advanced product line
(c) Wide market coverage
(d) Focus on innovation through R & D.
(ii) The term weakness refers to a negative aspect or limitation of a business which keeps it way behind its competitor.
Eg: Lise of old technology or techniques of production.
The weaknesses of Sharp Corporation are as follows:
(a) Brand image was not high in the beginning and was thus overshadowed by giants like Sony. Samsung, Matsushita.
(b) It was technology follower in.the beginning and was using secondary technology.
(c) Global economic turndown hit it worse than other American Company.
(d) Not able to cépe up with ever-changing technology.
(iii) The next move of Sharp Corporation should be to renew its value chain management in order to create competitive edge both in terms of high-quality product as wel’ as In terms of low cost. It can also explore areas where competition is low and also think about alliances, merger and takeovers.
(iv) Key success factors of LCD TV Industry.
(a) High quality accomplished with low cost and competitive strength.
(b) Constant upgradation In its technology.
(c) First moves advantage.
![]()
Question 61.
Discuss the relevance of Tows MatrIx In strategic planning process. (Nov 2009, 2 marks)
Answer:
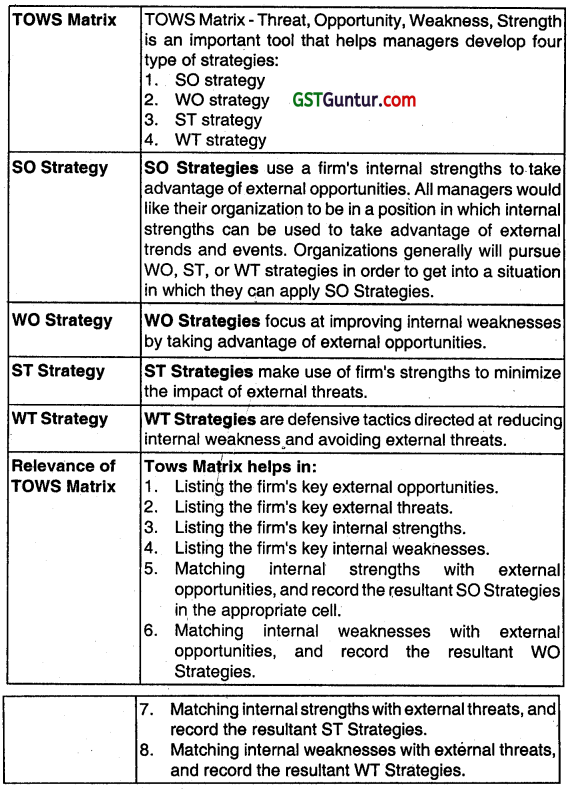
Question 62.
How is TOWS Matrix an improvement over the SWOT Analysis? Describe the construction of TOWS Matrix. (May 2013,2+2 = 4 marks)
OR
Explain how Tows matrix can generate strategic options with in external and internal environment.
Answer:
TOWS Matrix – an Improvement over the SWOT Analysis,
The basic objective of SWOT analysis is to provide a framework to reflect on the f irm8 ability to overcome
barriers or threats and avail the opportunities emerging in the environment.
However
While conducting the SWOT analysis managers are often not able to come to terms with the strategic choices that the outcomes demand. Heinz Welhrich developed a matrix called TOWS matrix by matching strengths and weaknesses of an organization with the external opportunities and threats.
The benefit of TOWS matrix lies in systematically identifying relationships between these factors and selecting strategies on their basis. Thus SWOT analysis is a planning tool while TOWS matrix is an action tool having a wider scope than SWOT.
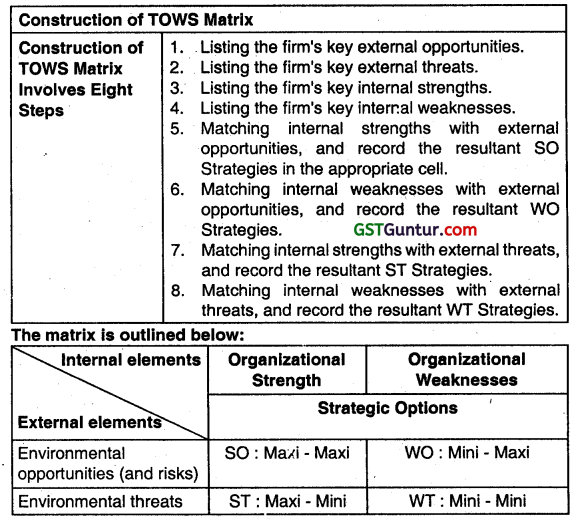
Question 63.
What is meant by a Global Company? Explain briefly different strategic approaches for Globalisation by a Company. (Nov 2008, 4+6 = 10 marks)
Answer:
Meaning of Global Company:
A Company is said to be a Global Company when:
(i) The company has several manufacturing locations around the world and offers productsn several diversified industries, and
(ii) It is able to compete in domestic markets with foreign competitors. A company which has gone global is called a Multinational (MNC) or a Transnational (TNC).
Different Stretelc Approaches for Globalisation by Company:
1. Configuring anywhere in the world
An MNC can locate its different operations in different countries on the basis of raw material availability, consumer markets and low-cost labour.
2. Interlinked and Independent economies
In terms of economies – welfare, globalization refers to the unique economically interdependent international environment. Each countrys prosperity is interlinked with the rest of the world. No nation can any longer hope to lead an existence of solitude and isolation in which only domestic industries can function.
3. Lowering of trade and tariff barriers
The apparent and real collapse of international trade barriers proposes a new global cooperative arrangement and a redefinition of roles of state and industry. The trend is towards increased privatization of manufacturing and services sectors, less government interference in business decisions and more dependence on the value-added sector to gain market place competitiveness world over, governments we pulling out from commercial business. The trade tariffs and custom barners are getting lowered, resulting in cheaper and abundant supply of goods.
4. infrastructural resources an inputs at International prices
Infrastructural Inputs must be ensured at competitive prices, if the companies were to compete globally. The advantages of cheap labour (and other inputs) evaporate ¡n the face of continuous inflation and high infrastructural costs.
5. Market side Efficiency
Integration of global markets implies that costs, quality processing time, and terms of business because dominant competition drivers customers can make a genuine choice products and services on the basis of maximum value for money. The inexorable pressure of technology and need for its integration means that customers no longer have to be satisfied with shoddy products, and services provided by the monopolies.
6. Formation of regional blocks
Countries, like corporations, have to form strategic alliances to ward off economic and technological threats and leverage their respective comparative and competitive advantages. The signing of NAFTA (North American Free Trade Area) among N America, Canada, and Mexico creates new markets and manufacturing opportunities for these countries and threatens to disrupt the plans and strategies of world powers such as Japan.
Question 64.
State with reason which of the following statement is correct or incorrect:
Globalization means different things to different people. (May 2010, 2 marks)
Answer:
Correct: Globalization means the process of integration of the world into one huge market. Globalization helps for removal of all trade barriers among countries. Globalization is an opportunity for organizations to expand their markets and reach out to different customers. Globalization can also have other meanings. For some Globalization Is a new paradigm- a set of fresh beliefs, working methods, and economic, political, and socio-cultural realities in which the previous assumptions are no longer velid. For developing countries, Globalization means integration with the world economy.
Question 65.
Write short note on the following:
Role of Global Industries (May 2012, 3 marks)
Answer:
Role of Global Industries:
Global industries are those which operate at the transnational, cross-culture, and across the border level. They Integrate the world into one huge market. They are committed to the International market to offer quality product in several diversified Industries. The influence of global Industries studied in terms of operating in the international environment is as below.
- Process of globalization.
- Global economic forces.
- Global trade and commerce.
- Global financial system, sources of financing, and accounting standards.
- Geo-political situation, strategic interests of nations.
- Global demographic patterns.
- Global human resource.
- Global information systems, communication networks.
- Global technological and quality systems and standards.
- Global markets and competitiveness.
- Global legal system, adjudication, and arbitration mechanisms.
- Globalisation of management.
Question 66.
Write short note on the following:
Characteristics of a Global Company. (Nov 2012, 3 marks)
OR
A global company has three characteristics. Explain. (Nov 2013, 3 marks)
OR
State three characteristics that are specific to a global company. (Nov 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Meaning of Global Company:
A Company is said to be a global company when:
- The company has several manufacturing locations around the world and otters products in several diversified industries, and
- It is able to compete in domestic markets with foreign competitors. A company which has gone global is called a Multinational (M NC) or a Transnational (TNC).
Chaiacterlstlca of Global Company:
A Global Company has three characteristics:
- It is a conglomerate of multiple units but all linked by common ownership.
- Multiple units draw on a common pool of resources, such as money, credit, information, patents, trade names and control systems.
- The units respond to some common strategy. Nestle International is an example of an enterprise that has become multinational.
A global company Is, therefore, one that, by operating in more than one country gains R&D, production, marketing arid financial advantages in its cost and reputation that are not available to purely domestic competitors.
The global company views the world as one market, minimises the importance of national boundaries, sources, raises capital and markets wherever It can do the job best.
Question 67.
Elaborate the reasons necessary for the globalization of companies. (May 2016, 3 marks)
Answer:
Reason for Globalization of Companies:
- Rapid shrinking of time and distance across the globe.
- Domestic markets are no longer adequate and rich.
- Development of attractive new products to attract customers internationally.
- To reduce high transportation cost.
- Cheaper labour available in other country to produce the product.
Question 68.
Why companies should go global? Mention any five reasons. (Nov 2020, 5 marks)
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Competitive advantage comes from a firm’s ………………………. to perform activities more effectively than rivals.
(a) Vision
(b) Capacity
(c) Ability
(d) Strategies
Answer:
(c) Ability
Question 2.
A competitive strategy consists of moves to:
(a) Attract customers
(b) Withstand competitive pressures
(c) Strengthen market position.
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
![]()
Question 3.
Understanding of competitive Landscape requires an application of ………………… .
(a) Competitive intelligence
(b) Competitive attitudes
(c) Competitive vigilance
(d) Competitive comparison
Answer:
(a) Competitive intelligence
Question 4.
………………… is the way of Identifying and understanding the competitors and at the same time, it permits the comprehension of their vision, mission, core values niche market, strengths and weakness.
(a) Competitive Dynamics
(b) Competitive Strategy
(c) Competitive Intelligence
(d) Competitive Landscape
Answer:
(d) Competitive Landscape
Question 5.
Analytical sequence is form strategic appraisal of the external and internal situation:
(a) To evaluation of alternatives
(b) To Choice of strategy
(c) To evaluation of dynamics
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 6.
Issue must consider for Strategic Analysis
(a) Balance of external and Internal factors
(b) Strategy evolves over a period of time
(c) Strategic decision at a point of time
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 7.
Which is/are the most Important question which helps to identify an industry’s key success factor?
(a) What does it take for sellers to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage?
(b) One what basis do customers choose between the competing brands of sellers?
(c) What resources and competitive capabilities does a seller need to have to be competitively successful?
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 8.
A strategic group consists of those rival firms which have ……………….. .
(a) Similar competitive approaches
(b) Positions in the market
(c) (a) or (b)
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) (a) and (b)
Question 9.
Mayor core competencies are Identified in the area of …………………….. .
(a) Competitor differentiation
(b) Customer values .
(c) Application to other marker
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 1o.
……………………….. are the knowledge, skills, and facilities necessary to design and produce core products.
(a) Competitors’s competence
(b) Core competencias
(c) Core Intelligence
(d) Core market
Answer:
(b) Core competencias
Question 11.
Which concept Is a kin to a learning curve which explains the efficiency Increase gained by workers through repetitive productive work?
(a) Experience curve
(b) Strategic curve
(c) Portfolio analysis
(d) Product life cycle
Answer:
(a) Experience curve
![]()
Question 12.
Product life cycle a
(a) U Shaped curve
(b) S Shaped curve
(c) Cyclic shaped curve
(d) Down shaped curve
Answer:
(b) S Shaped curve
Question 13.
BCG matrix is the simplest way to portray a …………………… .
(a) Market Growth Rate
(b) Relative Market Analysis
(c) Corporation’s portfolio of investment
(d) Business Expansion opportunities
Answer:
(c) Corporation’s portfolio of investment
Question 14.
BCG growth-share matrix also known for its …………………….. .
(a) Cash Cows metaphors.
(b) Cow and Dog metaphors
(c) Stars metaphors
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) Cow and Dog metaphors
Question 15.
Under BCG matrix low-growth, high market share business or pioducts is represented by.
(a) Dogs
(b) Stars
(c) Cash Cows
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(c) Cash Cows
Question 16.
Product Market Growth Matrix is Proposed by …………………. .
(a) Boston Consulting Group
(b) Igor Ansoff
(c) Arthur D. Little
(d) McKinsey and company
Answer:
(b) Igor Ansoff
Question 17.
The ADL matflx ¡s a portfolo analysis technique is based On ………………….. .
(a) Business life cycle
(b) Market life cycle
(c) Product life cycle
(d) Industry’s life cycle
Answer:
(c) Product life cycle
![]()
Question 18.
SWOT analysis referred to ………………… .
(a) Strength, Weakness, option and threat analysis
(b) Strength, Weakness, opportunity and threat analysis
(c) Strength, Worstness, opportunity and threat analysis,
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(b) Strength, Weakness, opportunity and threat analysis
Question 19.
In a market place organisation’s performance Is Influenced by:
(a) The Organisation’s correct market position
(b) The nature of environmental opportunities and threat
(c) The organisatiorl’s resource capability to capitalize the opportunities and to protect against the threats.
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(d) Any of the above
Question 20.
TOWS Matrix is developed by
(a) Heinz Weihrich
(b) Igor Ansoff
(c) Arthur D. Little
(d) S.W. Smith
Answer:
(a) Heinz Weihrich
Question 21.
SWOT analysis is a planning tool TOWS analysis is a/an ………………….. .
(a) Procedure tool
(b) Functional tool
(c) Action tool
(d) System tool
Answer:
(c) Action tool
Question 22.
Globalised company is also called ………………………. .
(a) Multinational (MNC)
(b) Transnational (TNC)
(c) Universonal (VNC)
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Question 23.
Which is the ¡mpoctant charactenstics of a Global company?
(a) Multiple units draw on a common pool of resources, such as money, credit information, patents trades marks and control system.
(b) The units respond to some common strategy, besides, Its managers and shareholders are also based in different nations.
(c) It is a conglomerate of multiple units but all linked by common ownership
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above