Students should practice Introduction to Corporate Accounting – Corporate and Management Accounting CS Executive MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Introduction to Corporate Accounting – Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
Question 1.
An asset shall be classified as current:
(A) If it is held primarily for the purpose of being traded.
(B) If it is not possible to classify such an asset as a non-current asset.
(C) If for the asset normal operating cycle cannot be identified.
(D) If such asset is expected to be realized twelve months after the reporting date.
Answer:
(A) If it is held primarily for the purpose of being traded.
Question 2.
A copy of the financial statements, including consolidated financial statement, along with all the documents attached to financial statements, duly adopted at the AGM, shall be filed with the Registrar within_____of the date of AGM in a prescribed manner along with prescribed fees.
(A) 10 days
(B) 30 days
(C) 60 days
(D) 90 days
Answer:
(B) 30 days
Question 3.
As per Schedule HI of the Companies Act, 2013, where the normal operating cycle cannot be identified, it is assumed to have a duration of –
(A) 3 months
(B) 6 months
(C) 9 months
(D) 12 months
Answer:
(D) 12 months
Question 4.
As per Rule 12 of the Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014, a financial statement shall be filed in_____which should be pre-certified by Practicing CA.
(A) Form AOC-3
(B) Form AOC-4
(C) Form AOC-5
(D) Form AOC-6
Answer:
(B) Form AOC-4
Question 5.
Liability shall be classified as current when it satisfies any of the following criteria:
(A) It is expected to be settled in the company’s normal operating cycle.
(B) It is due to be settled within twelve months after the reporting date
(C) The company does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting date.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 6.
OPC shall file a copy of the financial statements duly adopted by its member, along with all the documents which are required to be attached to such financial statements, within_____from the closure of the financial year.
(A) 30 days
(B) 60 days
(C) 120 days
(D) 180 days
Answer:
(D) 180 days
Question 7.
Which of the following is required to be disclosed in notes to accounts in respect of ‘Share Capital?
(A) A reconciliation of the number of shares outstanding at the beginning and at the end of the reporting period
(B) Aggregate number and class of shares bought back
(C) Shares in the company held by each shareholder holding more than 5%.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 8.
As per Rule 3 of the Companies (Filing of Documents and Forms in Extensible Business Reporting Language) Rules, 2015, all companies having_____has to file their Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss A/c, and other documents with the Registrar using the Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL).
(A) Issued capital of ₹ 5 Crore or above
(B) Authorized capital of more than ₹ 10 Crore
(C) Paid-up capital of ₹ 5 Crore or above
(D) Subscribed capital of ₹ 25 Crore or above
Answer:
(C) Paid-up capital of ₹ 5 Crore or above
Question 9.
Which of the following appears under the heading ‘Reserves & Surplus’ in the balance sheet?
(A) Share Options Outstanding Ac-count
(B) Share Application Money Pending Allotment
(C) Long Term Provisions
(D) Secrete Reserves
Answer:
(A) Share Options Outstanding Ac-count
Question 10.
As per Schedule in of the Companies Act, 2013, a Company shall disclose by way of notes additional information regarding aggregate expenditure and income in relation to any item of income or expenditure which exceeds:
(A) 0.5% of the revenue from operations
(B) ₹ 10,000
(C) 1% of the revenue from operations ₹ 1,00,000, whichever is higher
(D) 0.5% of the revenue from operations ₹ 10,000, whichever is less.
Answer:
(C) 1% of the revenue from operations ₹ 1,00,000, whichever is higher
Question 11.
As per Rule 3 of the Companies (Filing of Documents and Forms in Extensible Business Reporting Language) Rules, 2015, all companies having turnover of_____has to file their Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss A/c, and other documents with the Registrar using the Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL)
(A) ₹ 50 Crore or above
(B) ₹ 100 Crore or above
(C) ₹ 250 Crore or above
(D) ₹ 500 Crore or above
Answer:
(B) ₹ 100 Crore or above
Question 12.
As per Section 128 of the Companies Act, 2013, every company shall prepare and keep at its_____books of account and other relevant books and papers and financial statement for every financial year,
(A) Corporate Office
(B) Registered Office
(C) Corporate Office or Registered Office
(D) Head Office
Answer:
(B) Registered Office
Question 13.
Which of the following will be shown in the balance sheet under the heading ‘cash and cash equivalents?
(A) Earmarked balances with banks
(B) Bank deposits with more than twelve months of maturity
(C) Cheques, drafts on hand
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 14.
Which of the following type of companies is required to file their accounts in Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) format?
(A) Banking companies
(B) Insurance companies
(C) Non-Banking Financial companies
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 15.
The declared dividend must be paid within_____of declaration.
(A) 5 days
(B) 10 days
(C) 30 days
(D) 60 days
Answer:
(C) 30 days
Question 16.
Retained earnings are –
(A) An indication of a company’s liquidity.
(B) The same as cash in the bank.
(C) Not important when determining dividends.
(D) The cumulative earnings of the company after dividends.
Answer:
(D) The cumulative earnings of the company after dividends.
Question 17.
Which of the following type of companies is required to file their accounts in Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) format?
(I) Subsidiary of Indian Listed Company
(II) Companies that are required to prepare their financial statements in accordance with the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015
(III) Private company having turnover of ₹ 99 Crore.
(IV) Public companies having paid-up capital of ₹ 3 Crore.
Select the correct answer from the options given below –
(A) (I) & (II)
(B) (II) & (IV)
(C) (II) & (III)
(D) (I), (II) & (III)
Answer:
(A) (I) & (II)
Question 18.
The primary goal of a publicly-owned firm interested in serving its stockholders should be too:
(A) Maximize expected total corporate profit
(B) Maximize expected EPS
(C) Maximize the stock price per share
(D) Maximize expected net income.
Answer:
(C) Maximize the stock price per share
Question 19.
In the real world, we find that dividends –
(A) Usually exhibit greater stability than earnings.
(B) Fluctuate more widely than earnings
(C) Tend to be a lower percentage of earnings for mature firms
(D) Are usually set as a fixed percentage of earnings
Answer:
(A) Usually exhibit greater stability than earnings.
Question 20.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) A company may, if so authorized by its articles, pay dividends in proportion to the amount paid upon each share.
(B) Dividend cannot be paid on calls- in advance.
(C) All the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 that are applicable to the final dividend are also applicable to the interim dividend.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 21.
As per the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013, the amount of the dividend, including interim dividend, shall be deposited in a scheduled bank in a separate account within_____from the date of declaration of such dividend.
(A) 30 days
(B) 15 days
(C) 10 days
(D) 5 days
Answer:
(D) 5 days
Question 22.
After the declaration of the dividend, the company has to pay dividends within_____of declaration of dividend. If the amount of dividend remains unpaid or unclaimed for 30 days of declaration of dividend, then in next_____the company has to transfer the amount unclaimed to a special account in any scheduled bank to be called the “Unpaid Dividend Account”.
(A) 5 days; 5 days
(B) 30 days; 7 days
(C) 30 days; 5 days
(D) 10 days; 7 days
Answer:
(B) 30 days; 7 days
Question 23.
In the Balance Sheet, Corporate Dividend Tax will be shown as a liability under the heading –
(A) Current Liabilities
(B) Non-Current Liabilities
(C) Tax Liabilities
(D) Deferred Liabilities
Answer:
(A) Current Liabilities
Question 24.
Any money transferred to the unpaid dividend account of a company that remains unpaid or unclaimed for a period of_____from the date of such transfer must be transferred by the company to Investor Education and Protection Fund
(A) 3 years
(B) 5 years
(C) 7 years
(D) 10 years
Answer:
(C) 7 years
Question 25.
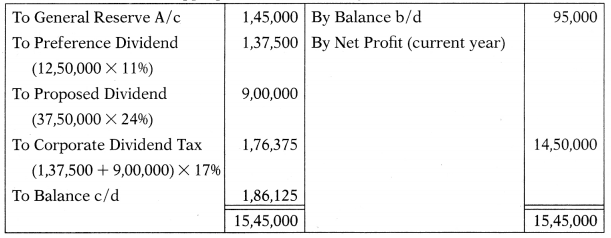
A Company has a paid-up equity share capital of ₹ 37,50,000 (of ₹ 10 each) and 11% preference share capital of ₹ 12,50,000 (of ₹ 100 each). The balance of profit brought forward from the previous Balance Sheet was ₹ 95,000. Profit for the year ended on 31.3.2018 amounted to ₹ 14,50,000 after tax. The directors proposed a dividend of 24% on equity share capital, after the following provisions:
(i) Transfer 10% of current profits to general reserves.
(ii) Provision of dividend on preference shares
Assume corporate dividend tax rate 17%. Closing balance of Profit & Loss A/c will be –
(A) ₹ 1,86,125
(B) ₹ 3,62,500
(C) ₹ 2,48,350
(D) ₹ 1,75,425
Hint:
Dr. Profit and Loss Appropriation A/c for the year ended 31.3.2018 Cr.
Answer:
(A) ₹ 1,86,125
Question 26.
Trial Balance of Complex Ltd., as of 31.3.2019 shows the following item:
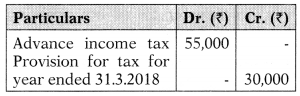
(1) Advance payment of income tax includes ₹ 35,000 for 2017-20 18.
(2) Actual tax liability for 2017-2018 amounts to ₹ 3 8,000 and no effect for the same has so far be given in accounts.
(3) Provision for income tax has to be made for 2018-2019 for ₹ 40,000.
You are required to calculate:
(a) Liability for taxation for last year ie. 2017-2018;
(b) Extra provision to be made in the current year for last year.
(A) ₹ 8,000; ₹ 3,000
(B) ₹ 5,000; ₹ 12,000
(C) ₹ 3,000; ₹ 8,000
(D) ₹ 12,000; ₹ 5,000
Hint:
| Adjustment for advance tax | ₹ |
| Assessment finalized for last year | 38.000 |
| Advance tax paid for last year | 35.0 |
| Tax to be paid | 3,000 |
| Adjustment for provision for tax | ₹ |
| Assessment finalized for last year | 38.000 |
| Provision for tax made for last year | 30.000 |
| Extra provision to be made for last year | 8,000 |
Answer:
(C) ₹ 3,000; ₹ 8,000
Question 27.
A company had made provision for tax ₹ 70,000 for last year. Actual tax liability for the last financial year settled at ₹ 68,000. It had paid advance tax for last year ₹ 65,000. Which of the following statement is correct in relation to tax treatment in accounts of the company?
(A) Liability for taxation for the last year is ₹ 3,000
(B) Provision to write back for the last year ₹ 2,000
(C) Adjustment entry is required to be passed in the current year by debiting Provision for Tax A/c and crediting Advance Income Tax A/c ₹ 65,000.
(D) All of the above are correct.
Hint:
| Adjustment for advance tax | ₹ |
| Assessment finalized for last year | 68,000 |
| Advance tax paid for last year | 65,000 |
| Tax to be paid | 3,000 |
| Adjustment for provision for tax | ₹ |
| Assessment finalized for last year | 68,000 |
| Provision for tax made for last year | 70,000 |
| Provision to write back for the last year | 2,000 |
Answer:
(D) All of the above are correct.
Question 28.
Yash Ltd. has only one type of capital, viz. 40,000 equity shares of ₹ 100 each. It also has got reserves totaling ₹ 20,00,000. The company closes its books on 31st March each year. It has paid dividends @ 15% up to 2015-2016 and 20% thereafter. In 2018-2019, the company suffered a loss of ₹ 2,50,000; therefore, it wishes to draw the required amount out of the reserves to pay the dividend at 12%. As the Companies (Declaration of Dividend Out of Reserves) Rules, 2014 how much maximum percentage of dividend can be paid by the company out of reserves.
(A) 12%
(B) 10%
(C) 8.75%
(D) 6.55%
Hint:
Dividends can be declared out of past years’ profits transferred to reserves. In this case, the company has to comply with the Companies (Declaration of Dividend Out of Reserves) Rules, 2014. It lay down the following conditions subject to which a dividend may be declared by a company in the event of inadequacy or absence of profits in any year out of the profits earned by it in previous years and transferred to reserves.
1. The rate of dividend declared shall not exceed the average of the rates at which the dividend was declared by it in the 3 years immediately preceding that year.
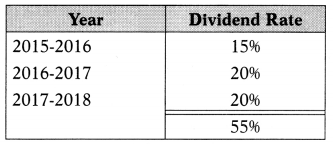
Average rate of dividend = 55/3 = 18.33%
So, an 18.33% dividend can be paid in the first instance.
Amount required for dividend at 18.33% = 40,00,000 × 18.33% = ₹ 7,33,200.
2. The total amount to be drawn from such accumulated profits shall not exceed 1/10th of the sum of its paid-up share capital and free reserves as appearing in the latest audited financial statement.
1/10th of (Paid up capital + Free Reserve) = (40,00,000 + 20,00,000) × 1/10 = 6,00,000.
Thus, the above amount in condition (1) will be restricted to ₹ 6,00,000.
3. The amount is so drawn shall first be utilized to set off the losses incurred in the financial year in which a dividend is declared before any dividend in respect of equity shares is declared.
| Total amount to be drawn from such accumulated profits | 6,00,000 |
| (-) Losses incurred | (2,50,000) |
| (-) Preference dividend | – |
| The amount that can be drawn,n from accumulated profits | 3,50,000 |
So, rate of dividend = 3,50,000/40,00,000 × 100 = 8.75%
4. The balance of reserves after such withdrawal shall not fall below 15% of its paid-up share capital as appearing in the latest audited financial statement.
| Reserves | 20,00,000 |
| The amount that can be drawn from accumulated profits | (3,50,000) |
| Balance of reserve | 16,50,000 |
Paid-up capital × 15% = 40,00,000 × 15% = 6,00,000
As balance of reserve i.e. 16,50,000 is more than 6,00,000. This condition is fulfilled.
So, the rate of dividend can be 8.75%.
Answer:
(C) 8.75%
Question 29.
Due to paucity of profits, MUSKAT LTD. an Indian company proposes to declare dividends out of its general reserves.
10% pref. shares (₹ 100 each): ₹ 10,00,000
Equity shares (₹ 100 each): ₹ 30,00,000
General reserve: ₹ 8,00,000
Securities premium: ₹ 2,00,000
Credit balance of P & L A/c: ₹20,000
Net profit for the year (after tax): ₹ 1,80,000
Average dividend for last 3 years: 15%
As the Companies (Declaration of Dividend Out of Reserves) Rules, 2014 how much maximum percentage of dividend can be paid by the company out of reserves.
(A) 10%
(B) 8%
(C) 12%
(D) 15%
Hint:
Dividends can be declared out of past years’ profits transferred to reserves. In this case, the company has to comply with the Companies (Declaration & Payment of Dividend) Rules, 2014. It lay down the following conditions subject to which a dividend may be declared by a company in the event of inadequacy or absence of profits in any year out of the profits earned by it in previous years and transferred to Reserves.
- The rate of dividend should not exceed the average rate of a dividend of the last 3 years:
- The total amount to be drawn from the accumulated profits = up to 1 /10th of the sum of the paid-up capital and free reserves of the company. The amount so drawn shall first be utilized to set off the losses incurred in the financial year before any dividend in respect of preference or equity shares is declared.
- The balance of reserves after such draw shall not fall below 15% of the paid-up share capital of the company.
Condition 1:
Average rates of dividend i.e. 15%
So 15% dividend can be paid at first instance.
Condition 2:
| 1 /10th of (Paid up capital + Free Reserve) (40,00,000 + 10,00,000) × 1 /10 | 5,00,000 |
| (-) Losses incurred in past | – |
| (-) Preference dividend | (1,00,000) |
| The amount that can be drawn from accumulated profits | 4,00,000 |
So, rate of dividend = 4,00,000/40,00,000 × 100 = 10%
Condition 3: The balance of reserves after such draw shall not fall below 15% of the paid-up share capital of the company.
| Balance of reserve | 10,00,000 |
| The amount that can be drawn from accumulated profits | (4,00,000) |
| 6,00,000 |
Paid-up capital × 15% = 40,00,000 × 15% = 6,00,000. As balance of reserve is not less than ₹ 6,00,000, this condition is fulfilled. So rate of dividend can be 10%.
Answer:
(A) 10%
Question 30.
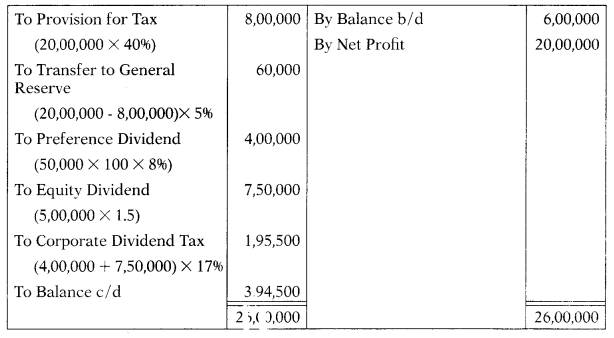
The paid-up capital of Apsara Ltd. consisted of ₹ 5,00,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each and 50,000, 8% preference shares of ₹ 100 each. The statement of profit and loss of the company for the year ended 31.3.2019 showed a net profit before tax of ₹ 20,00,000. Net profit brought forward from the previous year’s balance sheet amounted to ₹ 6,00,000. The company makes a provision of 40% for income tax. Following appropriations were proposed by the company:
(a) To pay final dividend @ ₹ 1.50 per share to equity shareholders.
(b) To transfer 5% of net profit to general reserve.
Assume corporate dividend tax rate 17%. Closing balance of Profit & Loss A/c will be:
(A) ₹ 3,94,500
(B) ₹ 2,94,500
(C) ₹ 4,94,500
(D) ₹ 1,94,500
Hint:
Dr. Profit & Loss Appropriation A/c Cr.
Answer:
(A) ₹ 3,94,500
