Students should practice Custom Act, 1962 – CS Executive Tax Laws MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Custom Act, 1962 – CS Executive Tax Laws MCQ Questions
Question 1.
Customs Act, 1962 extends to
(A) Whole of India excluding Jammu & Kashmir
(B) Whole of India
(C) Whole of India excluding Jammu & Kashmir and Union Territories
(D) Whole of India excluding Jammu & Kashmir and Special Economic Zones
Answer:
(B) Whole of India
Question 2.
As per Section 2(1) of the Customs Act, 1962,____means any authority competent to pass any order or decision under this Act, but does not include the Board, Commissioner (Appeals), or Appellate Tribunal.
(A) Adjudicating Authority
(B) Proper Authority
(C) Proper Officer
(D) Custom Authority
Answer:
(A) Adjudicating Authority
Question 3.
As per Section 2(2) of the Customs Act, 1962, “assessment” includes
(I) Provisional assessment
(II) Self-assessment
(III) Reassessment
(IV) Any assessment in which the duty assessed is NIL.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (I) & (II)
(B) (I), (II) & (IV)
(C) (I), (II) & (III)
(D) All (I) to (IV)
Answer:
(D) All (I) to (IV)
Question 4.
The Customs Act, 1962, not only regulates the levy and collection of duties but also, serves equally important purposes like
(a) Regulation of imports & exports.
(b) Protection of domestic industry
(c) Prevention of smuggling
(d) Conservation & augmentation of foreign exchange
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) All (a) to (d)
(B) All except (a)
(C) All except (b)
(D) All except (c)
Answer:
(A) All (a) to (d)
Question 5.
It is Section 12 of the Customs Act, 1962 that provides duties of customs to be levied at such rates as may be specified under the____or other applicable Acts on goods imported into or exported from India.
(A) Customs Tariff Act, 1962
(B) Customs Tariff Act, 1975
(C) Customs Rates & Tariff Act, 1975
(D) Customs Rate Act, 1962
Answer:
(B) Customs Tariff Act, 1975
Question 6.
Under the Customs Act, 1962, the rulemaking power is delegated to
(A) Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC)
(B) Central Government
(C) Respective State Governments
(D) Partly to the Central Government and partly to the respective State Governments
Answer:
(B) Central Government
Question 7.
Under the Customs Act, 1962, the regulations making power is delegated to
(A) Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC)
(B) Respective State Governments
(C) Partly to the Central Government and partly to the respective State Governments
(D) Central Government
Answer:
(A) Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC)
Question 8.
For which of the following Rules can be made by the Central Government u/s 156 of the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) Transaction Value
(B) Form of Bill of Entry
(C) Import & export manifest
(D) Conditions for transshipment & removal of good without payment of duty
Answer:
(A) Transaction Value
Question 9.
As per Section 2(3) of the Customs Act, 1962, “baggage” includes
(P) unaccompanied baggage
(Q) motor vehicles
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (Q) only
(B) Both (P) & (Q)
(C) (P) but not (Q)
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) (P) but not (Q)
Question 10.
As per Section 2(4) of the Customs Act, 1962, “bill of entry” means a bill of entry referred to in ______
(A) Section 45
(B) Section 46
(C) Section 47
(D) Section 48
Answer:
(B) Section 46
Question 11.
As per Section 2(5) of the Customs Act, 1962, “bill of export” means a bill of export referred to in _____
(A) Section 53
(B) Section 52
(C) Section 51
(D) Section 50
Answer:
(D) Section 50
Question 12.
“Board” means the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs constituted under the____
(A) Central Boards Indirect Taxes Act, 1963
(B) Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963
(C) Central Boards Indirect Taxes & Customs Act, 1963
(D) Central Boards of Taxation Act, 1963
Answer:
(B) Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963
Question 13.
“Coastal goods” means
(A) Goods, other than imported goods, transported in a vessel from one port in India to another.
(B) Any goods including imported goods, transported in a vessel from one port in India to another.
(C) Goods, other than imported goods, transported in a vessel from one port in India to a place outside India.
(D) Any goods including imported goods, transported in a vessel from one port in India to a place outside India.
Answer:
(A) Goods, other than imported goods, transported in a vessel from one port in India to another.
Question 14.
As per Section 2(7A) of the Customs Act, 1962, Commissioner (Appeals) means a person appointed to be a Commissioner of Customs (Appeals) under subsection (1) of
(A) Section 3
(B) Section 4
(C) Section 5
(D) Section 7
Answer:
(B) Section 4
Question 15.
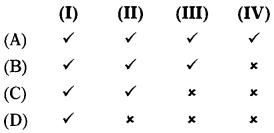
As per Section 2(9) of the Customs Act, 1962, “conveyance” includes
(I) Vessel
(II) Aircraft
(DO) Vehicle
(IV) Animal
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
Answer:
(B)
Question 16.
“ Customs Area” means
(A) Area of a Customs Station
(B) Area of a warehouse
(C) Any area in which imported goods or export goods are ordinarily kept before clearance by Customs Authorities
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 17.
“Customs Station” means
(A) Any customs port
(B) Any customs airport
(C) Any international courier terminal
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 18.
Which of the following is not included within the definition of “Customs Station” as defined in the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) Land customs station
(B) International courier terminal
(C) Foreign post office
(D) Are where goods are kept after custom clearance
Answer:
(D) Are where goods are kept after custom clearance
Question 19.
“Dutiable Goods” means
(A) All imported goods.
(B) Any goods which are chargeable to duty and on which duty has been paid.
(C) Any goods which are chargeable to duty and on which duty has not been paid.
(D) Any goods which are chargeable to duty and on which proper amount duty has been paid.
Answer:
(C) Any goods which are chargeable to duty and on which duty has not been paid.
Question 20.
“Entry” in relation to goods means an entry made in____and includes the entry made under the regulations made under section 84
(A) the case of goods imported or to be exported by post, the entry referred to in section 82
(B) a bill of entry, shipping bill, or bill of export
(C) bill of entry, import report, or bill of export
(D) import report, bill of export, bill of entry & import manifest
Answer:
(B) a bill of entry, shipping bill, or bill of export
Question 21.
As per Section 2( 17) of the Customs Act, 1962, “examination”, in relation to any goods, includes
(A) measurement
(B) weigh-ment
(C) measurement and weigh-ment
(D) measurement or weigh-ment
Answer:
(C) measurement and weigh-ment
Question 22.
“Export goods” means
(A) any goods which are to be taken out of India
(B) any goods which are to be taken out of India to a place outside India
(C) which exporter desires to take outside India
(D) none of the above
Answer:
(B) any goods which are to be taken out of India to a place outside India
Question 23.
Foreign going vessel or aircraft means any vessel or aircraft for the time being engaged in the carriage of_____between any port or airport in India and any port or airport outside India.
(A) Goods
(B) Passengers
(C) Goods or passengers
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) Goods or passengers
Question 24.
Which of the following is included within the definition of “foreign going vessel or aircraft” as defined in Section 2(21) of the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) Any naval vessel of any foreign government taking part in any naval exercises
(B) Any vessel engaged in fishing or any other operations in territorial waters of India
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer:
(A) Any naval vessel of any foreign government taking part in any naval exercises
Question 25.
As per Section 2(22) of the Customs Act, 1962, “goods” includes
(A) Vessels, aircraft and vehicles
(B) Currency & negotiable instruments
(C) Stores, baggage
(D) Any of the above
Answer:
(D) Any of the above
Question 26.
Imported goods means
(A) Any goods brought into India from a place outside India.
(B) Any goods brought into India from a place outside India and include goods that have been cleared for home consumption.
(C) Any goods brought into India from a place outside India but do not include goods that have been cleared for home consumption.
(D) None of the above is correct.
Answer:
(C) Any goods brought into India from a place outside India but do not include goods that have been cleared for home consumption.
Question 27.
Which of the following can be treated as Adjudicating Authority under the Customs Act, 1962?
(i) Board [Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC)]
(ii) Commissioner (Appeals)
(iii) Appellate Tribunal
(iv) Authority competent to pass any order or decision under the Act.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (i), (ii) & (iii)
(B) (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)
(C) (ii) & (iv)
(D) (iv)
Answer:
(D) (iv)
Question 28.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) All imported goods are dutiable goods.
(B) Market price, in relation to any goods, means the retail price of the goods in the ordinary course of trade in India.
(C) All dutiable goods are imported goods.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(C) All dutiable goods are imported goods.
Question 29.
Which of the following is included within the definition of “foreign going vessel or aircraft” as defined in Section
2(21) of the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) Any naval vessel of any foreign government taking part in any naval exercises.
(B) Any vessel engaged in fishing or any other operations outside the territorial waters of India.
(C) Any vessel or aircraft proceeding to a place outside India for any purpose whatsoever.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 30.
Prohibited goods mean any goods
(A) the import or export of which is subject to any prohibition under the Act
(B) the import or export of which is subject to any prohibition any other law for the time being in force
(C) any such goods in respect of which the conditions subject to which the goods are permitted to be imported or exported have not been complied with
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 31.
Proper officer
(A) in relation to any functions to be performed under the Act, means the officer of customs who is assigned those functions by the Board
(B) includes Principal Commissioner of Customs
(C) includes Commissioner of Customs
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 32.
As per Section 2(37) of the Customs Act, 1962, “Shipping bill” means a shipping bill referred to in_____
(A) Section 56
(B) Section 50
(C) Section 62
(D) Section 60
Answer:
(B) Section 50
Question 33.
As per Section 2(38) of the Customs Act, 1962, “Stores”
(A) Means goods for use in a vessel or aircraft
(B) Includes fuel and spare parts and other articles of equipment, whether or not for immediate fitting
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) (A) but not (B)
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 34.
Smuggling, in relation to any goods, means any act or omission which will render such goods liable to confiscation under_____or ______
(A) Section 111; Section 113
(B) Section 110; Section 111
(C) Section 113; Section 114
(D) Section 111; Section 115
Answer:
(A) Section 111; Section 113
Question 35.
A warehouse
(A) is a designated area where goods are allowed to be stored after landing, without the payment of duty.
(B) is a designated area where goods are allowed to be stored after payment of the proper amount of duty.
(C) is a designated area where goods are allowed to be stored after landing, without the payment of duty and in certain cases after payment of the proper amount of duty.
(D) is a designated area where imported goods are kept if the importer is unable to pay the proper amount of duty.
Answer:
(A) is a designated area where goods are allowed to be stored after landing, without the payment of duty.
Question 36.
Identify which of the following statement is correct (✓) and which is incorrect (✗).
(P) An exemption notification can be withdrawn.
(Q) Duty can be demanded with retrospective effect.
(R) The goods imported into India, are now subject to IGST and not CVD or SAD.
(S) The general basic rate of basic customs duty is 15%.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:

Answer:
(B)
Question 37.
Match the following:
List I
(P) Petroleum Product
(Q) Schedule I of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975
(R) Alcoholic liquor for human consumption
(S) Latter the Better Principle
(A) Where the declaration of such liability is made and the persons/ properties in respect of which the duty is to be levied are identified.
(B) Where actually import or export duties are paid.
(C) Where a bill of entry is submitted for duty assessment before goods come to India by sea.
(D) Where imported goods are kept before payment of duty.
Answer:
(A) Where the declaration of such liability is made and the persons/ properties in respect of which the duty is to be levied are identified.
Question 39.
The general basic rate of basic customs duty is
(A) 5%
(B) 10%
(C) 15%
(D) 7.5%
Answer:
(B) 10%
Question 40.
Basic Custom Duty could be levied at
(A) Standard Rate
(B) Preferential Rate
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Answer:
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Question 41.
The onus is on the______ to substantiate with the supporting evidence that the goods are chargeable with a preferential rate of duty.
(A) Person (owner)
(B) Government
(C) Custom Officials
(D) (B)or(C)
Answer:
(A) Person (owner)
Question 42.
Countervailing Duty (CVD) is subsumed under
(A) GST
(B) Excise
(C) Income Tax
(D) Local Duties
Answer:
(A) GST
Question 43.
Which of the following statement is/are correct?
(A) The goods imported into India, are now subject to IGST and not CVD or SAD.
(B) Petroleum is outside the scope of GST, and hence CVD and SAD are applicable to them.
(C) IGST is now payable on Assessable Value + Basic Customs Duty.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 44.
Classification
(A) Enables categorizing the goods into groups/subgroups, in order to apply a different rate of duty on goods following within the same group.
(B) Enables the proper officer to recover the duties of custom.
(C) Enables categorizing the goods into groups/subgroups, in order to apply a single rate of duty on each group/subgroup.
(D) Is based on the concept of MAT.
Answer:
(C) Enables categorizing the goods into groups/subgroups, in order to apply a single rate of duty on each group/subgroup.
Question 45.
Schedule II of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 specifies
(A) Rate applicable to imported goods
(B) Preferential rate of duty
(C) Rate applicable for export of goods
(D) List out the goods which are exempt from import or export duty as the case may be.
Answer:
(C) Rate applicable for export of goods
Question 46.
There are ______ Interpretation Rules under the Customs Tariff Act, 1975.
(A) Four
(B) Eight
(C) Six
(D) Three
Answer:
(C) Six
Question 47.
Rule 2(a) of the Interpretation Rules under the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 states that
(A) Goods shall be classified under the heading which is closest to the specific description.
(B) Any reference in a heading to an article shall be deemed to include a reference to that article in an unfinished stage too, as long as in the present stage, the incomplete article exhibits the essential character of that article incomplete/ finished form.
(C) Goods that cannot be classified in accordance with Rule 1 shall be classified under the heading which includes goods that are the most “akin or similar”.
(D) Any reference in a heading to a material or substance, shall be deemed to include a reference to the mixtures and combinations of that material/substance with other materials/substances.
Answer:
(B) Any reference in a heading to an article shall be deemed to include a reference to that article in an unfinished stage too, as long as in the present stage, the incomplete article exhibits the essential character of that article incomplete/ finished form.
Question 48.
Which of the following example is best suitable to the “Specific Identification Rule” of the Interpretation Rules under the Customs Tariff Act, 1975?
(A) Car without tires or without seats would be still construed as Cars, but not Cars without engines.
(B) Natural rubber would include its mixture with synthetic or other forms of rubber.
(C) If one imports ‘Liquor Gift Sets’ that have both, liquor and glasses, it should be classified under the heading, ‘Liquor’.
(D) Mint Tea is not separately classified, but the classification should be tea as the product is closest to the one under the heading “tea”, mint is only a flavor.
Answer:
(D) Mint Tea is not separately classified, but the classification should be tea as the product is closest to the one under the heading “tea”, mint is only a flavor.
Question 49.
If composite goods cannot be classified as per Rule 3(a) of the Interpretation Rules, then, shall be classified on the basis of material/substance. This rule is known as
(A) Latter the Better Principle
(B) Most Suitable Rule
(C) Essential Character Rule
(D) Akin Principle
Answer:
(C) Essential Character Rule
Question 50.
Rule 2(b) of the Interpretation Rules states that any reference in a heading to a material or substance shall be deemed to include a reference to the mixtures and combinations of that material/substance with other materials/substances. You are required to state which of the following example of this rule
(A) Natural rubber would include its mixture with synthetic or other forms of rubber
(B) Scooter without tires is classified as Scooter.
(C) Mint Tea is not separately classified, but the classification should be tea as the product is closest to the one under the heading “tea”, mint is only a flavor.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(A) Natural rubber would include its mixture with synthetic or other forms of rubber
Question 51.
______ states that the goods which cannot be classified in accordance with Rule 1,2 or 3, shall be classified under the heading which includes goods that are the most similar.
(A) Residual Rule
(B) Akin Rule
(C) Standard Rule
(D) Subheading Rule
Answer:
(B) Akin Rule
Question 52.
Which of the following is covered under Rule 3 of the Interpretation Rules?
(A) Specific Identification Rule
(B) Essential Character Rule
(C) Latter the Better Rule
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 53.
Valuation for Customs Duty begins with
(A) Determination of Import Value
(B) Determination of Transaction Value
(C) Determination of Invoice Value
(D) Interrogation of Importer.
Answer:
(B) Determination of Transaction Value
Question 54.
Custom value fixed as per Section 14 is the value that would be used for calculating the customs duty payable. This is also called
(A) Standard Value
(B) Assessable Value
(C) Nominal Value
(D) Any of the above
Answer:
(C) Nominal Value
Question 55.
Mr. Ramsay imported some goods from the USA for US$ 1,00,000. Advise him of the exchange applicable for converting foreign currency value into Indian currency?
(A) Rate of exchange in force as notified by RBI and approved by CBIC as on the date when the bill of entry is presented is considered for imports.
(B) Rate of exchange notified by the Government of India from time to time is relevant.
(C) Rate of exchange in force as notified by CBIC as on the date when the bill of entry is presented is considered for imports.
(D) Telegraphic transfer rate as notified by RBI as on the date when the bill of entry is presented is considered for imports
Answer:
(C) Rate of exchange in force as notified by CBIC as on the date when the bill of entry is presented is considered for imports.
Question 56.
Which of the following factor(s) is/ are essential to determine assessable Value in case of import and export under the Customs Act, 1962?
(1) Price at which such or like goods are ordinarily sold or offered for sale.
(2) Discount given by the exporter when goods are imported into India.
(3) Fact that Seller and Buyer are not be related to each other.
(4) Exchange rate prescribed by the RBI when the bill of entry is presented.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (2) & (1)
(B) (4) & (2)
(C) (3) & (1)
(D) (4), (1) & (3)
Answer:
(C) (3) & (1)
Question 57.
In the case of exports
(A) Rate of exchange in force as notified by CBIC as on the date on which is shipping bill is submitted to the Proper Officer makes the clearance order is relevant.
(B) Rate of exchange in force as notified by RBI as on the date on which bill of export is submitted to the Proper Officer is relevant.
(C) Rate of exchange in force as notified by CBIC as on the date on which bill of export is submitted to the Proper Officer is relevant.
(D) Rate of exchange in force as notified by CBIC as on the date on which the Proper Officer makes the clearance order is relevant.
Answer:
(D) Rate of exchange in force as notified by CBIC as on the date on which the Proper Officer makes the clearance order is relevant.
Question 58.
Value of Imported Goods shall be the Transaction Value adjusted in accordance with provisions of
(A) Rule 8 of Customs Valuation Rules
(B) Rule 10 of Customs Valuation Rules
(C) Rule 6 of Customs Valuation Rules
(D) Rule 12 of Customs Valuation Rules
Answer:
(B) Rule 10 of Customs Valuation Rules
Question 59.
CIF Value means
(A) Price paid/payable for delivery at the time and place of importation, which essentially implies that the price up to a port in India when goods are imported.
(B) Price paid / payable for delivery at the time and place of exportation, which essentially implies that the price up to a port in India when goods are exported
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Price paid/payable for delivery at the time and place of importation, which essentially implies that the price up to a port in India when goods are imported.
Question 60.
CIF Value = _____
(A) FOB Value Cost of Transport + Insurance
(B) FOB Value + Cost of Transport Insurance
(C) FOB Value Cost of Transport Insurance
(D) FOB Value + Cost of Transport +Insurance
Answer:
(D) FOB Value + Cost of Transport +Insurance
Question 61.
FOB Value = ?
(A) CIF Value Cost of Transport Insurance
(B) CIF Value + Cost of Transport + Insurance
(C) CIF Value Cost of Transport + Insurance
(D) CIF Value + Cost of Transport Insurance
Answer:
(A) CIF Value Cost of Transport Insurance
Question 62.
In the case of export if the transaction value is not acceptable then value as per Export Valuation Rules has to be taken. Determine the proper sequence of such values.
1. Value arrived by Residual Method
2. Value of Similar Goods
3. Value of Identical Goods
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) 3, 2, 1
(B) 1,2,3
(C) 2, 1, 3
(D) 3, 1, 2
Answer:
(A) 3, 2, 1
Question 63.
If more than one transaction value of identical goods is found then which of the following shall be used to determine the value of imported goods?
(A) Value which importer agrees to apply with the permission of Proper Officer.
(B) Highest of such value.
(C) Value which Proper Officer deems fit.
(D) Lowest such value
Answer:
(D) Lowest such value
Question 64.
Computed Value =?
(A) Cost of production + Reasonable profit + Post importation transport charges
(B) Cost of production + Charges for design or brand + Reasonable profit
(C) Cost of production + Charges for design or brand + Actual profit earned by the importer on resale in the domestic market
(D) Cost of production + Charges for design or brand + Reasonable profit + Actual profit earned by the importer on resale in domestic market Marketing charges
Answer:
(B) Cost of production + Charges for design or brand + Reasonable profit
Question 65.
Safeguard duty is a duty paid on___
(A) Import of goods into India
(B) Export of goods out of India
(C) (A)or(B)
(D) (A) and (B)
Answer:
(A) Import of goods into India
Question 66.
Safeguard duty is levied on goods imported into India
(A) When such goods are imported from countries listed as noncooperative countries.
(B) When Central Government introduces an ordinance in the Parliament and goods are imported from countries listed as noncooperative countries.
(C) To protect the domestic industries in India from goods imported in mass quantities from China and other countries listed as non-cooperative countries and later appropriate Act is passed by the
Central Government with two-third majority in the Parliament.
(D) When such goods are already manufactured in India, but the cost is higher as compared to import prices. It is levied to ensure that the Indian manufacturers don’t suffer owing to the import of cheaper goods from outside and therefore aims to create a level playing field for the Indian manufacturers and importers, thereby with the intent of safeguarding the National interest.
Answer:
(D) When such goods are already manufactured in India, but the cost is higher as compared to import prices. It is levied to ensure that the Indian manufacturers don’t suffer owing to the import of cheaper goods from outside and therefore aims to create a level playing field for the Indian manufacturers and importers, thereby with the intent of safeguarding the National interest.
Question 67.
Antidumping duty
(A) prevents the predatory pricing measures/discriminatory pricing, that could be unfair for the local goods and markets
(B) is levied on goods imported into India, when such goods are already manufactured in India, but the costs are higher as compared to import prices.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Answer:
(A) prevents the predatory pricing measures/discriminatory pricing, that could be unfair for the local goods and markets
Question 68.
Central Government may, by special order, exempt from duty, any goods, on which duty is leviable only under exceptional circumstances. Further, no duty is to be collected, if the amount of duty leviable is less than or equal to_______
(A) US $ 100
(B) INR 100
(C) INR 1,000
(D) US $ 1,000
Answer:
(B) INR 100
Question 69.
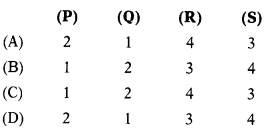
Match the following in relation to the person in charge as defined in the Customs Act, 1962:
| List I | List II |
| (P) Master | 1. In the case of an aircraft |
| (Q) Commander or Pilot | 2. In the case of a Vessel |
| (R) Conductor, guard, or any other person having the chief direction of the train | 3. In case of any other conveyance |
| (S) Driver or other people in charge of the conveyance | 4. In the case of a train |
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
Answer:
(A)
Question 70.
Which of the following is the duty or responsibility of a person in charge under the Customs Act, 1962?
1. To submit Import/Export Manifest.
2. To pay import duty on all goods contained in vessel or ship.
3. To ensure that the conveyance lands at the appropriate place
4. Ensure that the Goods are loaded or unloaded only after proper permissions or orders.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) 1,2 & 3
(B) 4, 2 & 1
(C) 2, 3 & 4
(D) 3, 1 & 4
Answer:
(D) 3, 1 & 4
Question 71.
As per Section 4 of the Customs Act, 1962, who may appoint persons as officers of customs?
(A) Board
(B) Central Government
(C) Board with prior approval of the Central Government
(D) Board with prior approval of the respective State Governments
Answer:
(A) Board
Question 72.
As per Section 6 of the Customs Act, 1962, to whom the Central Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, entrust either conditionally or unconditionally any functions of the Board or any officer of customs under the Act.
(A) to any officer of the Central
(B) to any officer the State Government
(C) to any officer of a local authority
(D) any of the above
Answer:
(D) any of the above
Question 73.
Which of the following is the charging section of the Customs Act, 1962 for levy of customs duty?
(A) Section 12
(B) Section 13
(C) Section 11
(D) Section 10
Answer:
(A) Section 12
Question 74.
The Import Manifest or Import Report is required to be delivered under
(A) Section 29
(B) Section 30
(C) Section 31
(D) Section 35
Answer:
(B) Section 30
Question 75.
In case of a vessel or the aircraft, Import Manifest is required to be delivered
(A) within twelve hours after its arrival in the customs station
(B) prior to the arrival of the vessel or the aircraft, as the case may be
(C) within twelve hours after its arrival in the customs water
(D) none of the above
Answer:
(B) prior to the arrival of the vessel or the aircraft, as the case may be
Question 76.
In case of vehicle Import Report is required to be delivered:
(A) within twelve hours after its arrival in the customs water
(B) within twelve hours after its arrival in the customs station
(C) within twelve hours after proper officer pass appropriate order
(D) within twenty-four hours after its arrival in the customs station.
Answer:
(B) within twelve hours after its arrival in the customs station
Question 77.
Custom ports or airports are appointed by the
(A) Central Government
(B) Board [CBIC]
(C) Respective State Governments with prior approval of Central Government
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Answer:
(B) Board [CBIC]
Question 78.
Entry Inward granted by the Customs
(A) acts as permission for unloading the goods.
(B) is the date that is construed as the relevant date for the arrival of goods in India.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Only (A) but not (B)
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 79.
The Custodian
(A) would be responsible for keeping a proper records of unloaded goods.
(B) is responsible to ensure that the goods don’t leave the customs area without proper authorization from the Customs Officer
(C) is appointed by the Principal Commissioner of Customs or Commissioner of Customs
(D) all of the above
Answer:
(D) all of the above
Question 80.
Assessed duty is paid to vide
(A) TR6 Challan
(B) TR5 Challan
(C) TR6A Challan
(D) TR5A Challan
Answer:
(A) TR6 Challan
Question 81.
Demurrage charges are levied by the port authorities if goods are not cleared within____of unloading.
(A) 3 days
(B) 5 days.
(C) 7 days
(D) 10 days
Answer:
(A) 3 days
Question 82.
Export General Manifest (EGM) is generally filed on the basis of?
(A) Bill of Entry
(B) Bill of Lading
(C) Airway Bill
(D) Either (B) or (C)
Answer:
(D) Either (B) or (C)
Question 83.
As per provisions of Chapter VII of the Customs Act, 1962, in____, the goods remain in the same vessel and consequently reach the port of clearance.
(A) transshipment
(B) transit
(C) transport
(D) traveling
Answer:
(B) transit
Question 84.
As per provisions of Chapter VLH of the Customs Act, 1962, in_____, the vessel after reaching an intermediate port, transfers the goods to another vessel and the second vessel into which the goods are transferred (loaded) from the first vessel, carries the goods to the destination port.
(A) transit
(B) transshipment
(C) traveling
(D) transport
Answer:
(B) transshipment
Question 85.
As per Section 53 of the Customs Act, 1962, subject to the provisions of section 11, where any goods imported in a conveyance and mentioned in the arrival manifest or import manifest or the import report, as for transit in the same conveyance to any place outside India or to any customs station, the Proper Officer may allow the goods and the conveyance to transit_____ subject to such conditions, as may be prescribed.
(A) without payment of duty
(B) after payment of duty
(C) without filing bill of transit
(D) after filing a bill of transit
Answer:
(A) without payment of duty
Question 86.
Which of the following section of the Customs Act, 1962 deals with transshipment of goods without payment of duty?
(A) Section 53
(B) Section 54
(C) Section 55
(D) Section 56
Answer:
(B) Section 54
Question 87.
In transshipment
(A) Goods are transferred to a different vessel at the intermediate port.
(B) Bill of Transhipment/declaration is also required to be submitted.
(C) A different vessel reaches the destination port
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 88.
In transit
(A) Goods remain in the same vessel at the intermediate port.
(B) Import manifest is not required to be submitted for entry.
(C) Double duty bond would also be required.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(A) Goods remain in the same vessel at the intermediate port.
Question 89.
Which of the following types of goods can be warehoused?
(A) Only dutiable goods
(B) All types of imported goods whether dutiable or not
(C) Only goods to be exported
(D) Only prohibited goods
Answer:
(A) Only dutiable goods
Question 90.
Section 57 of the Customs Act, 1962 provides that the_____may, subject to such conditions as may be prescribed, license a public warehouse wherein dutiable goods may be deposited.
(A) Principal Commissioner of Customs or Commissioner of Customs
(B) Central Government
(C) Central Government or Commissioner of Customs
(D) Commissioner (Appeal) or Commissioner of Customs
Answer:
(A) Principal Commissioner of Customs or Commissioner of Customs
Question 91.
As per Section 58B(4) of the Customs Act, 1962, where the license issued u/s 57 or 58 or 58A is canceled, the goods warehoused shall, within_____from the date on which order of such cancellation is served on the licensee or within such extended period as the proper officer may allow, be removed from such warehouse to another warehouse or be cleared for home consumption or export
(A) Seven days
(B) Ten days
(C) Thirty days
(D) One month
Answer:
(A) Seven days
Question 92.
The importer of any goods in respect of which a bill of entry for warehousing has been presented u/s 46 and assessed to duty u/s 17 or 18 shall execute a bond in a sum equal to
(A) thrice the amount of the duty assessed on such goods
(B) twice the amount of the duty assessed on such goods
(C) thrice the amount of assessable value of such goods
(D) twice the amount of assessable value of such goods
Answer:
(A) thrice the amount of the duty assessed on such goods
Question 93.
In the case of capital goods intended for use in any 100% EOU, such goods can be stored up to a period of_____
(A) 1 year
(B) Till the clearance of such goods from the warehouse
(C) 3 years
(D) Till the expiry of 1 year from the date of order u / s 60( 1) permitting removal of goods from customs station for deposit in a warehouse
Answer:
(B) Till the clearance of such goods from the warehouse
Question 94.
In the case of goods other than capital goods intended for use in any 100% EOU, such goods can be stored up to a period of_____
(A) Till the clearance of such goods from the warehouse
(B) Till the consumption of such goods from warehouse
(C) Till the clearance or consumption of such goods from the warehouse
(D) 3 years
Answer:
(C) Till the clearance or consumption of such goods from the warehouse
Question 95.
In the case of any goods not intended for use in any 100% EOU, such goods can be stored up to a period of ______
(A) 2 years
(B) 1 year
(C) 6 months
(D) 3 months
Answer:
(B) 1 year
Question 96.
What is the maximum rate of the drawback of duty as per Section 74 of the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) 90%
(B) 80%
(C) 95%
(D) 98%
Answer:
(D) 98%
Question 97.
The owner of any warehoused goods may, after warehousing the same
(a) inspect the goods
(b) sale the goods
(c) deal with their containers to prevent loss/deterioration/damage to the goods
(d) consume the goods
(e) sort the goods
(f) show the goods for sale.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (a), (c), (e) & (f)
(B) (a), (b), (d) & (f)
(C) (a), (b), (c), (e) & (f)
(D) (a), (e) & (f)
Answer:
(A) (a), (c), (e) & (f)
Question 98.
As per Section 74 of the Customs Act, 1962, duty drawback is allowed
(A) On re-export of duty paid goods
(B) On material used in the manufacture of exported goods.
(C) Only respect of notified goods.
(D) As per All Industry Rate.
Answer:
(A) On re-export of duty paid goods
Question 99.
As per Section 75 of the Customs Act, 1962, duty drawback is allowed
(A) Only respect of notified goods.
(B) As per All Industry Rate.
(C) If minimum value addition is achieved
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 100.
Which of the following is an eligible condition for availing drawback u/s 74?
(A) The goods must be capable of being easily identified.
(B) The goods must be exported within 2 years from the date of payment of duty.
(C) There is no requirement of value addition.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 101.
If goods are used for less than 3 months then how much percentage of import duty can be paid as a drawback as per the rate notified by the Central Government u/s 74(2)?
(A) 98%
(B) 95%
(C) 90%
(D) 88%
Answer:
(B) 95%
Question 102.
If goods are used for more than 3 months but for less than 6 months then how much percentage of import duty can be paid as a drawback as per the rate notified by the Central Government u/s 74(2)?
(A) 95%
(B) 85%
(C) 80%
(D) 75%
Answer:
(B) 85%
Question 103.
If goods are used for more than 18 months then how much percentage of import duty can be paid as a drawback as per the rate notified by the Central Government u/s 74(2)?
(A) 60%
(B) 50%
(C) 10%
(D) Nil
Answer:
(D) Nil
Question 104.
Which of the following goods are not eligible for drawback? if reexported after use.
(I) Wearing apparel
(II) Tea chests
(III) Exposed cinematograph film
(IV) Unexposed photographic film
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (I)
(B) (I), (II)
(C) (I), (II), (III)
(D) (I), (II), (III) & (IV)
Answer:
(D) (I), (II), (III) & (IV)
Question 105.
Where any drawback payable to a claimant under section 74 or section 75 is not paid within a period of one month from the date of filing a claim for payment of such drawback, there shall be paid to that claimant in addition to the amount of drawback, interest at the rate of
(A) 12%
(B) 15%
(C) 10%
(D) 6%
Answer:
(D) 6%
Question 106.
Where any drawback has been paid to the claimant erroneously or it becomes otherwise recoverable under the Act or the rules made thereunder, the claimant shall, within a period of 2 months from the date of demand, pay in addition to the said amount of drawback, interest at the rate of
(A) 15%
(B) 12%
(C) 10%
(D) 8%
Answer:
(A) 15%
Question 107.
No drawback shall be allowed
(A) In respect of any goods the market price of which is less than the amount of drawback due thereon
(B) Where the drawback due in respect of any goods is less than ₹ 50
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 108.
Where any duty has not been levied or not paid or short-lived or short paid or erroneously refunded, or any interest payable has not been paid, part-paid or erroneously refunded, for any reason other than the reasons of collusion or any wilful misstatement or suppression of facts, the proper officer shall, within_____from the relevant date, serve notice on the person chargeable with the duty or interest which has not been so levied or paid or which has been short levied or short paid or to whom the refund has erroneously been made, requiring him to show cause why he should not pay the amount specified in the notice.
(A) 1 year
(B) 2 years
(C) 3 years
(D) 6 months
Answer:
(B) 2 years
Question 109.
Section 28(1) of the Customs Act, 1962 provides that the proper officer shall not serve such show cause notice, where the amount involved is less than ______
(A) ₹ 10
(B) ₹ 100
(C) ₹ 1,000
(D) ₹ 10,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 100
Question 110.
Generally, the show-cause notice, should be served within_____from the relevant date as provided in Section 28(1)(a)
(A) 1 year
(B) 3 years
(C) 4 years
(D) 2 years
Answer:
(D) 2 years
Question 111.
In specific cases, where the duty or interest is not paid, or short paid, by reason of collusion, willful suppression of facts, or misstatement, then the notice could be served within a period of
(A) 5 years
(B) 4 years
(C) 3 years
(D) 2 years
Answer:
(A) 5 years
Question 112.
Where notice has been served and the Proper Officer is of the opinion that the amount of duty along with interest payable thereon u/s 28AA or the amount of interest, as specified in the notice, has been paid in full within____from the date of receipt of the notice, no penalty shall be levied and the proceedings against such person or other persons to whom the said notice is served shall be deemed to be concluded.
(A) 30 days
(B) 15 days
(C) 60 days
(D) 45 days
Answer:
(A) 30 days
Question 113.
As per Section 28(7A) of the Customs Act, 1962, the proper officer may issue a____under such circumstances and in such manner as may be prescribed.
(A) Show cause notice
(B) Proper notice
(C) Supplementary notice
(D) Demand notice
Answer:
(C) Supplementary notice
Question 114.
Which of the following section of the Customs Act, 1962 deals with “confiscation of improperly imported goods?
(A) Section 110
(B) Section 111
(C) Section 111A
(D) Section 112
Answer:
(B) Section 111
Question 115.
As per Section 112 of the Customs Act, 1962, what is the penalty for ‘prohibited goods?
(A) Value of goods or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(B) 1096 of the duty sought to be evaded or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(C) Value of goods or ₹ 10,000, whichever is higher.
(D) 10% of the duty sought to be evaded or ₹ 10,000, whichever is higher.
Answer:
(A) Value of goods or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Question 116.
As per Section 112 of the Customs Act, 1962, what is the penalty for ‘dutiable goods’ other than prohibited goods?
(A) 10% of the duty sought to be evaded or ₹ 10,000, whichever is higher.
(B) Value of goods or ₹ 10,000, whichever is higher.
(C) 10% of the duty sought to be evaded or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(D) Value of goods or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Answer:
(C) 10% of the duty sought to be evaded or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Question 117.
As per Section 112 of the Customs Act, 1962, what is the minimum penalty for ‘prohibited goods’?
(A) ₹ 5,000
(B) ₹ 10,000
(C) ₹ 50,000
(D) ₹ 1,00,000
Answer:
(A) ₹ 5,000
Question 118.
As per Section 112 of the Customs Act, 1962, what is the penalty for “Goods for which value stated in Bill of Entry or baggage declaration is greater than the actual value”?
(A) Actual Value less Declared Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(B) Actual Value of the goods, or Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(C) Actual Value less Declared Value, or ₹ 10,000, whichever is higher.
(D) Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Answer:
(D) Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Question 119.
As per Section 112 of the Customs Act, 1962, what is the penalty for “Prohibited goods in respect of which value stated in Bill of Entry or baggage declaration is greater than the actual value”?
(A) Actual Value of the goods, or Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(B) Value of goods or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(C) Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 10,000, whichever is higher.
(D) Actual Value of the goods, or Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 10,000, whichever is higher.
Answer:
(A) Actual Value of the goods, or Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Question 120.
As per Section 112 of the Customs Act, 1962, what is the penalty for “Prohibited goods (not dutiable) in respect of which value stated in Bill of Entry or baggage declaration is greater than the actual value”?
(A) Actual Value of the goods, or Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(B) Duty sought to be evaded, or Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
(C) Duty sought to be evaded, or Actual Value of the goods, whichever is higher.
(D) Duty sought to be evaded, or Actual Value of the goods, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Answer:
(B) Duty sought to be evaded, or Declared Value less Actual Value, or ₹ 5,000, whichever is higher.
Question 121.
Section 123 of the Customs Act, 1962 clearly states that if goods are seized, the onus is on the —
(A) Owner to prove that they were not smuggled
(B) Person in possession of the goods to prove that they were not smuggled
(C) Proper officer prove that goods are smuggled goods
(D) CBIC to prove that goods are smuggled goods
Answer:
(A) Owner to prove that they were not smuggled
Question 122.
Central Government may prohibit,_____, the import/ export of goods of the specified description
(A) absolutely
(B) subject to such conditions specified in the notification
(C) either absolutely or subject to such conditions specified in the notification
(D) none of the above
Answer:
(C) either absolutely or subject to such conditions specified in the notification
Question 123.
Which of the following section of the Customs Act, 1962 deals with the option to pay a fine in lieu of confiscation?
(A) Section 121
(B) Section 123
(C) Section 125
(D) Section 127
Answer:
(C) Section 125
Question 124.
Section 125 of the Customs Act, 1962 provides that redemption fine shall not exceed the
(A) Market price of the goods confiscated
(B) Declared Value less Actual Value
(C) Actual Value of the goods
(D) The Market price of the goods confiscated, less in the case of imported goods the duty chargeable thereon
Answer:
(D) The Market price of the goods confiscated, less in the case of imported goods the duty chargeable thereon
Question 125.
A refund application must be filed within______from the date of payment of duty.
(A) 1 year
(B) 6 months
(C) 2 years
(D) 3 months
Answer:
(A) 1 year
Question 126.
_____of the Customs Act, 1962 prescribes the method for self-assessment of duty.
(A) Section 15
(B) Section 17
(C) Section 19
(D) Section 16
Answer:
(B) Section 17
Question 127.
Self-assessed goods may be_____by the proper officer.
(A) Verified
(B) Examined
(C) Tested
(D) Verified, examined, or tested
Answer:
(D) Verified, examined, or tested
Question 128.
Which of the following can be classified as ‘criminal liability’ under the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) Recovery of duties short paid
(B) Punishment up to 7 years
(C) Confiscation of import/export goods
(D) The Interest charge
Answer:
(B) Punishment up to 7 years
Question 129.
Which of the following can be classified as ‘civil liability under the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) Recovery of duties short paid
(B) Confiscation of import/export goods
(C) Confiscation of conveyances used for smuggling
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 130.
Advance Ruling refers to the determination, by the authority, of a_____specified in the application, regarding the liability to pay duty in relation to an activity proposed to be undertaken by an applicant.
(A) Question of law
(B) Question of fact
(C) Any question raised by the applicant
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Answer:
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Question 131.
The advance ruling application can be withdrawn within_____of the application.
(A) 10 days
(B) 60 days
(C) 30 days
(D) 45 days
Answer:
(C) 30 days
Question 132.
The advance ruling must be pronounced made within_____of the application.
(A) 3 months
(B) 4 months
(C) 2 months
(D) 6 months
Answer:
(A) 3 months
Question 133.
The Central Government may if it deems necessary to do so in the general interest of the public, exempt goods
(A) Generally
(B) Specifically
(C) Generally or specifically
(D) Bypassing appropriate order
Answer:
(C) Generally or specifically
Question 134.
Offenses under the Customs Act, 1962 could attract
1. Civil Liabilities
2. Criminal Liabilities
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) 1 only
(B) Either 1 or 2
(C) 2 only
(D) Either 1 or 2 or both
Answer:
(D) Either 1 or 2 or both
Question 135.
Which of the following duty is/ are now subsumed under GST?
(I) Countervailing duty (CVD)
(II) Special Additional Duty (SAD)
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (II) only
(B) (I) only
(C) Both (I) & (II)
(D) Neither (I) nor (II)
Answer:
(C) Both (I) & (II)
Question 136.
Under the Customs Act, 1962, the relevant date for determining the rate of exchange in case of imported goods is:
(A) Date when the vessel arrives in India
(B) Date of presentation of Bill of entry
(C) Date of examination of goods by the proper officer
(D) Date of deposit of duty
Answer:
(B) Date of presentation of Bill of entry
Question 137.
AntiDumping duty is calculated as
(A) Higher of margin of dumping or injury margin
(B) Lower margin of dumping or injury margin
(C) Higher export price or normal value
(D) Lower export price or normal value
Answer:
(B) Lower margin of dumping or injury margin
Question 138.
Which of the following has to be taken as an assessable value under the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) FOB Value
(B) CIF Value
(C) Landed Value
(D) Import Value
Answer:
(B) CIF Value
139.
If the goods are imported by Air, the freight cannot exceed
(A) 20% of FOB Value
(B) 20% of CIF Value
(C) 10% of FOB Value
(D) 15% of CIF Value
Answer:
(A) 20% of FOB Value
Question 140.
In which of the following cases, the refund under section 27 of the Customs Act, 1962 is credited to the Consumer Welfare Fund?
(A) If the importer proves that there is no unjust enrichment.
(B) Where goods are imported for nonpersonal use of an individual.
(C) If the amount of refund relates to drawback under sections 74 and 75 of the Customs Act, 1962.
(D) If the amount relates to export duty paid on goods which have been returned to the exporter as specified under section 26 of the Customs Act, 1962.
Answer:
(B) Where goods are imported for nonpersonal use of an individual.
Question 141.
Which of the following goods are not mandatorily required to be deposited in a special warehouse under section 58A of the Customs Act, 1962?
(A) Gold and silver articles
(B) Supply as stores to vessels/air crafts
(C) Supply to duty-free shops in a customs area
(D) Supply meant for Government use
Answer:
(D) Supply meant for Government use
Question 142.
The integrated tax leviable on imported goods is levied
(A) As an additional duty of customs u/s 3(7) of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975
(B) As integrated tax u/s 5 of the IGST Act, 2017
(C) As a duty of customs under the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 read with IGST Act, 2017
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) As an additional duty of customs u/s 3(7) of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975
Question 143.
Which of the following statement is correct?
I. Customs area does not include a warehouse.
II. A beneficial owner of imported goods is a person on whose behalf the goods are being imported but cannot be exported.
m. Customs station includes an international courier terminal but does not include the foreign post office.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 144.
The Supreme Court in____has held that importation gets complete when goods become part of the mass of goods within the country.
(A) Weston Components Ltd. v. CC
(B) Garden Silk Manufacturing Ltd. v. UOI
(C) Garden Silk Milk v. UOI
(D) Weston Silk Mills v. UOI
Answer:
(C) Garden Silk Milk v. UOI
Question 145.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) Proper officer has right to reject transactional value.
(B) Transactional value shall be accepted even where the buyer and seller are related if the relationship has not influenced the price.
(C) A bill of entry shall include all the goods mentioned in the bill of lading.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 146.
What is the interest rate for late payment of customs duty?
(A) 10%
(B) 12%
(C) 15%
(D) 22%
Answer:
(C) 15%
Question 147.
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(I) Transit is allowed in every port normally.
(II) Transhipment is allowed in specified ports only.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (II) only
(B) Both (1) and (II)
(C) (I) only
(D) Neither (I) nor (II)
Answer:
(D) Neither (I) nor (II)
Question 148.
Warehouse means
(A) A public warehouse licensed u/s 57
(B) A private warehouse licensed u/s 58
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (II) only (C) A special warehouse licensed u/s
(B) Both (I) and (II) 58A
(C) (I) only
(D) (A) or (B) or (C)
Answer:
(D) (A) or (B) or (C)
Question 149.
Following data is available for import from USA:
FOB Value = ₹ 12,70,000
Freight = ₹ 2,54,000
Insurance = ₹ 6,000
Calculate CIF Value.
(A) ₹ 10,10,000
(B) ₹ 15,18,000
(C) ₹ 10,22,000
(D) ₹ 15,30,000
Hint:
CIF Value = FOB Value + Cost of Transport + Insurance
= 12,70,000 + 2,54,000 + 6,000
= 15,30,000
Answer:
(D) ₹ 15,30,000
Question 150.
Following data import from USA: is available for
CIF Value = US $ 5,400
Freight = US $ 600
Insurance = US $ 1,800
Calculate FOB Value.
(A) US$3,000
(B) US$7,800
(C) US$4,200
(D) US$6,600
Hint:
FOB Value = CIF Value – Cost of Transport – Insurance
= 5,400 – 600 – 1,800
= 3,000
Answer:
(A) US$3,000
Question 151.
KPMG Ltd. imports equipment by Air. CIF price is US $ 6,000, freight paid is US $ 1,200 and insurance is US $ 1,800. RBI prescribes the exchange rate as ₹ 68. CBIC notifies the exchange rate as ₹ 65. What is assessable value under the Customs Law?
(A) ₹ 3,90,000
(B) ₹ 1,95,000
(C) ₹ 3,51,000
(D) ₹ 2,80,000
Hint:
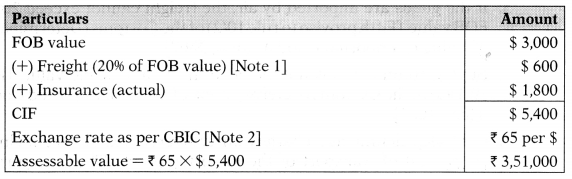
Note 1: If the goods are imported by air, the freight cannot exceed 2096 of FOB price. [Fifth proviso to Rule 10(2) of the Customs (Determination of Value of Imported Goods) Rules, 2007],
Note 2: The rate of exchange determined by CBIC is considered. [Clause (a) of the explanation to Section 14 of the Customs Act, 1962].
Answer:
(C) ₹ 3,51,000
Question 152.
Parag International Ltd. exported some goods to the USA by air at a FOB price of US $ 1,00,000. Other details are as follows:
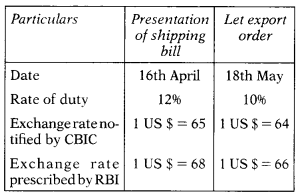
Basic export duty payable by Parag International Ltd. is:
(A) ₹ 6,50,000
(B) ₹ 7,80,000
(C) ₹ 7,68,000
(D) ₹ 6,40,000
Hint:
1,00,000 × 65 = 65,00,000.
Answer:
(A) ₹ 6,50,000
Question 153.
Shubham Ltd. has imported a machine from the UK. Details of Import as follows:
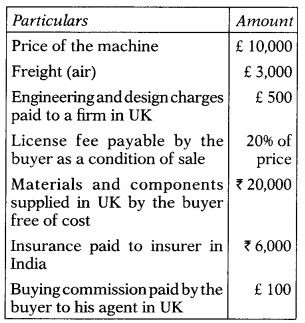
Interbank k exchange rate: £ 1 = 98
CBIC notified exchange rate: £ I = 100
Importer paid ₹ 5,000 towards demurrage charges for delay in clearing the machine from the airport. Assessable value =?
(A) ₹ 12,70,000
(B) ₹ 15,30,000
(C) ₹ 15,70,000
(D) ₹ 12,30,000
Hint:
| Particulars | Amount (£) |
| Price of the machine | 10,000 |
| (+) Engineering and design charges paid in the UK [Note 1] | 500 |
| (+) License fee payable by the buyer as a condition of sale (2096 of the price of machine) [Note 1] | 2,000 |
| Total | 12,500 |
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| Value in Indian currency [£ 12,500 × ₹ 100] [Note 2] | 12,50,000 |
| (+) Materials and components supplied by the buyer free of cost [Note 1] | 20,000 |
| FOB | 12,70,000 |
| (+) Freight [Note 3] | 2,54,000 |
| Insurance paid to the insurer in India [Note 1] | 6,000 |
| CIF value/Assessable value | 15,30,000 |
Notes:
- Engineering and design charges paid in the UK, license fee relating to imported goods payable by the buyer as a condition of sale, materials, and components supplied by the buyer free of cost, and actual insurance charges paid are all includible in the assessable value. [Rule 10 of the Customs (Determination of Value of Imported Goods) Rules, 2007],
- As per explanation to section 14(1) of the Customs Act, 1962, the assessable value should be calculated with reference to the rate of exchange notified by the CBIC.
- If the goods are imported by air, the freight cannot exceed 2096 of FOB value. [The fifth proviso to rule 10(2) of the Customs (Determination of Value of Imported Goods) Rules, 2007]
- Buying commission is not included in the assessable value. [Rule 10( 1 )(a) of the Customs (Determination of Value of Imported Goods) Rules, 2007]
- Only ship demurrage charges on chartered vessels are included in the cost of transport of the imported goods. Thus, demurrage
charges for delay in clearing the machine from the airport will not be includible in the assessable value [Explanation to rule 10(2) of the Customs (Determination of Value of Imported Goods) Rules, 2007],
Answer:
(B) ₹ 15,30,000
Question 154.
A person makes an unauthorized import of goods liable to confiscation. After adjudication, Assistant Commissioner provides an option to the importer to pay a fine in lieu of confiscation. It is proposed to impose a fine (in lieu of confiscation) equal to 50% of the margin of profit. The following particulars are
(A) ₹ 1,00,000
(B) ₹ 84,192
(C) ₹ 15,808
(D) ₹ 19,192
Hint:
Option to pay fine in lieu of confiscation [Section 125]: Whenever confiscation of any goods is authorized by the Act, the officer adjudging it may give to the owner of the goods or where such owner is not known, the person from whose possession or custody such goods have been seized an option to pay in lieu of confiscation such fine as the said officer thinks fit.
However, such a fine shall not exceed the ‘market price of the goods confiscated less ‘import duty’.
Since the proposed fine is less than the maximum fine permissible, the redemption fine payable by the importer would be ₹ 9,596.
Total payment to be made by the importer = ₹ 15,808 (Duty) + ₹ 9,596 (Fine) = ₹ 25,404.
Answer:
(B) ₹ 84,192
Question 155.
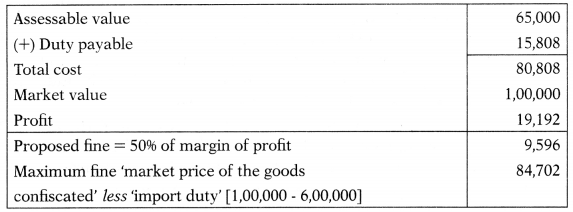
A person makes an unauthorized import of goods liable to confiscation. After adjudication, Assistant Commissioner provides an option to the importer to pay a fine in lieu of confiscation. It is proposed to impose a fine (in lieu of confiscation) equal to 50% of the margin of profit. The following particulars are made available:
(i) Assessable value: ₹ 65,000
(ii) Total duty payable: ₹ 15,808
(iii) Market value: ₹ 1,00,000
Calculate the total payment to be made by the importer to clear the consignment.
(A) ₹ 19,192
(B) ₹ 9,596
(C) ₹ 15,808
(D) ₹ 25,404
Hint:
Option to pay fine in lieu of confiscation [Section 125]: Whenever confiscation of any goods is authorized by the Act, the officer adjudging it may give to the owner of the goods or where such owner is not known, the person from whose possession or custody such goods have been seized an option to pay in lieu of confiscation such fine as the said officer thinks fit.
However, such a fine shall not exceed the ‘market price of the goods confiscated less ‘import duty’.

Since the proposed fine is less than the maximum fine permissible, the redemption fine payable by the importer would be ₹ 9,596.
Total payment to be made by the importer = ₹ 15,808 (Duty) + ₹ 9,596 (Fine) = ₹ 25,404.
Answer:
(D) ₹ 25,404
Question 156.
Certain goods were imported by air. The free on board value of goods is ₹ 100. The cost of transport, loading, unloading, and handling charges up to the place of importation is ₹ 25. The cost of insurance is ₹ 10. For the purposes of Rule 10(2) of the Customs Valuation (Determination of Value of Imported Goods) Rules, 2007, which of the following shall be added to the value of imported goods?
(A) Cost of transport, loading, unloading & handling charges ₹ 25 and Cost of insurance ₹ 10.
(B) Cost of transport, loading, unloading & handling charges ₹ 25 and Cost of insurance ₹ 1.125.
(C) Cost of transport, loading, unloading & handling charges ₹ 20 and Cost of insurance ₹ 1.125.
(D) Cost of transport, loading, unloading & handling charges ₹ 20 and Cost of insurance ₹ 10.
Answer:
(D) Cost of transport, loading, unloading & handling charges ₹ 20 and Cost of insurance ₹ 10.
Question 157.
ABC Ltd. imports equipment by air. CIF price of the equipment is US$ 6,000, freight paid is US$ 1,200 and insurance cost is US$ 1,800. CBIC notifies the exchange rate as ₹ 70 per $. ABC Ltd. expends ₹ 56,000 in India for certain development activities with respect to the imported equipment. Basic customs duty is 10%, Integrated tax is leviable @12% and social welfare surcharge is 10% on duty. GST Compensation Cess is leviable @ 15%. Compute the amount of total duty payable by ABC Ltd.
(A) ₹ 1,54,867
(B) ₹ 50,350
(C) ₹ 91,930
(D) ₹ 40,900
Hint:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| CIF | 6,000 |
| (-) Freight | 1,200 |
| (-) Insurance | 1,800 |
| FOB | 3,000 |
| Add: Freight (20% of FOB value) [Note 1] | 600 |
| Add: Insurance (actual) | 1,800 |
| CIF Value | 5,400 |
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| Assessable value = $ 5,400 × ₹ 70 | 3,78,000.00 |
| (+) Basic customs duty @ 10% | 37,800.00 |
| (+) Social Welfare Surcharge @10% | 3,780.00 |
| Sub-total | 4,19,580.00 |
| Integrated tax u/s 3(7) of the Customs Tariff Act @ 1296 of 4,19,580 [Note 4] | 50,349.60 |
| GST Compensation Cess [4,19,580 × 1596] | 62,937 |
| Total duty [37,800 + 3,780 + 50,349.60 + 62,937] | 1,54,854.60 |
| Total customs duty and integrated tax payable (rounded off) | 1,54,867 |
Notes:
- If the goods are imported by air, the freight cannot exceed 2096 of FOB price.
- The rate of exchange determined by CBIC is considered.
- Rule 10(l)(Z?)(iv) of the Customs Valuation (Determination of Value of Imported Goods) Rules, 2007 inter alia provides that value of development work undertaken elsewhere than in India is includible in the value of the imported goods. Thus, development charges of 156,000 paid for work done in India have not been included for the purposes of arriving at the assessable value.
- Integrated tax leviable u/s 3(7) of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 is levied on the sum total of the assessable value of the imported goods, customs duties, and applicable social welfare surcharge.
Answer:
(A) ₹ 1,54,867
Question 158.
From the following information, you are required to determine the Basic Export Duty.
(i) FOB Price of goods US$1,20,000
(ii) Shipping Bill presented electronically on 26th April
(iii) Proper officer passed the order permitting clearance and loading of goods for export on 5th May.
(iv) Rate of exchange and rate of export duty are as under:
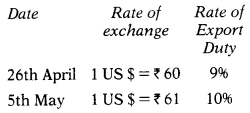
(v) No GST Compensation.
(A) ₹ 6,48,000
(B) ₹ 7,20,000
(C) ₹ 7,32,000
(D) ₹ 6,58,800
Hint:
Transactional value = FOB Price of goods = $ 1,20,000.
The rate of exchange will be the date of presentation of the Shipping Bill ie. 26.4.2018: 1$ = ?60.
Value in Indian currency = $ 1,20,000 × ₹ 60 = ₹ 72,00,000.
Rate of export duty will be the date on which the proper officer passed the order permitting clearance and loading of goods for export ie. 5.5.2018 = 1096
Export Duty = ₹ 72,00,000 × 1096 = ₹ 7,20,000.
Note: Education cess is not levied on export duty.
Answer:
(B) ₹ 7,20,000
Question 159.
Priya imported certain goods weighing 1,000 kgs having a CIF value of US $ 40,000. The exchange rate of 1 US $ was ₹ 65 on the date of presentation of a bill of entry. Basic customs duty chargeable is @ 10% and Social Welfare surcharge as applicable. There is no Integrated tax and GST compensation payable on these goods if supplied in India. However, vide Notification issued by the Government of India, anti-dumping duty has been imposed on these goods. The anti-dumping duty will be equal to the difference between the amount calculated @ the US $ 60 per kg and the ‘landed value’ of goods. You are required to compute the amount of customs duty and of the antidumping duty payable by Priya.
(A) ₹ 10,14,000
(B) ₹ 12,67,800
(C) ₹ 2,86,000
(D) ₹ 13,00,000
Hint:
| Assessable value ie. CIF Value [$ 40,000 × 65] | 26,00,000 |
| (+) Basic Custom Duty @ 10.396 | 2,60,000 |
| (+) Social Welfare Charge @ 10% of basic duty | 26,000 |
| Landed value/cost of the goods | 28,86,000 |
| Cost of goods for anti-dumping duty [1,000 kg × $ 60 × $ 65] | 39,00,000 |
| Anti-dumping duty [39,00,000 – 28,86,000] | 10,14,000 |
| Total customs duty [2,60,000 + 26,000 + 10,14,000] | 13,00,000 |
Notes:
- As per question only basic customs duty (including cess) and anti-dumping duty are leviable on goods. Additional duty u/s 3(5) is not leviable.
- Cess is not levied on anti-dumping duty.
- Landed value includes all duties of customs except duties levied under sections 3, 8B, 9 & 9A.
Answer:
(D) ₹ 13,00,000
Question 160.
Jaggi Mehta imported a car from the UK for his personal use and paid ₹ 4,50,000 as import duty on the car. However, the car was being re-exported immediately without bringing it into use by Mr. Mehta. Calculate the amount of duty drawback allowable under the Customs Act, 1962.
(A) ₹ 4,41,000
(B) ₹ 4,50,000
(C) ₹ 4,27,500
(D) ₹ 3,60,000
Hint:
As per Section 74 of the Customs Act, 1962, when any goods capable of being easily identified which have been imported into India and upon which any duty has been paid on the importation, are to be exported, 98% of duty shall be re-paid as a drawback, if:
- the goods are identified to the satisfaction of the AC/DC as the goods which were imported; and
- the goods are entered for export within 2 years from the date of payment of duty on the importation thereof.
Thus, Jaggi Mehta can claim drawback off 4,41,000 ie. 98% off 4,50,000.
Answer:
(A) ₹ 4,41,000
Question 161.
Meenakshi imported a music player from Dubai and paid ₹ 12,000 as import duty. She used it for 4 months and thereafter reexported the same after 4 months. Calculate the amount of duty drawback allowable under the Customs Act, 1962.
(A) ₹ 12,000
(B) ₹ 11,040
(C) ₹ 960
(D) Nil
Hint:
In respect of a motor car or goods imported for personal use, drawback ‘ of duty shall be allowed equal to import duty paid as reduced by 4%, 3%, 2.5% & 2% respectively for use for each quarter or part thereof during the first year, the second year, third year and fourth year respectively. Thus, Meenakshi will be allowed drawback as calculated below:
| Duty paid | 12,000 |
| (-) Reduction for two quarters of the first year | (960) |
| 11,040 |
Answer:
(B) ₹ 11,040
Question 162.
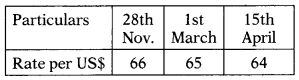
Balaram imported certain goods in November, and an ‘into bond’ bill of entry was presented on 28th November. Assessable value was US $ 1,00,000. The order permitting the deposit of goods in the warehouse for 3 months was issued on 2nd Dec. Bholaram neither obtained an extension of the warehousing period nor cleared the goods within the permitted warehousing period of 1 st March. Only after a notice was issued under section 72 of the Customs Act, 1962 demanding duty and other charges, Bholaram removed the goods on 15th April. No additional duty or special additional duty is payable. You are supplied with the following information:
(A) ₹ 67,98,000
(B) ₹ 66,95,000
(C) ₹ 66,00,000
(D) ₹ 64,00,000
Hint:
Rate of exchange = Rate of exchange in force on the date of presentation of a bill of entry for warehousing shall apply Le. $ 1 = ₹ 66. [Section 14]
Rate of duty = Goods are deemed to be removed on expiry of warehousing period Le. on 1.3.2017 and hence the rate of duty will be 10% including cess of 3%. Net rate = 10.3%. [Section 72]
Assessable value = $1,00,000 × 66 = ₹ 66,00,000.
Answer:
(C) ₹ 66,00,000
Question 163.
Calculate FOB Value, Cost of Insurance, Cost of Freight, and Assessable Value where only the CIF value is given as the US $ 5,000. The exchange rate notified by RBI and CBEC is ₹ 70 and ₹ 68 respectively for one US $.
(A) ₹ 2,17,600, ₹ 43,520, ₹ 2,448
(B) ₹ 2,41,264, ₹ 48,253, ₹ 2,714
(C) ₹ 2,80,702, ₹ 56,140, ₹ 3,158
(D) ₹ 2,69,144, ₹ 53,829, ₹ 3,028
Hint:
CIF Value in Indian currency = $ 5,000 × 68 = ₹ 3,40,000.
CIF Value = FOB Value + Cost of transport + Cost of Insurance
Let the FOB value be ‘x’.
| FOB Value | x |
| (+) Cost of transport [Note 1] | 0.2x |
| (+) Cost of Insurance [Note 2] | 0.01125x |
| CIF Value | 3,40,000 |
1.21125x = 3,40,000
x = FOB Value = 2,80,702
Cost of transport = 2,80,702 × 20% = 56,140
Cost of Insurance = 2,80,702 × 1.125% = 3,158
Note 1: Cost of transport will be 20% of FOB Value if not ascertainable. Note 2: Cost of insurance will be 1.125% of FOB Value if not ascertainable.
Answer:
(C) ₹ 2,80,702, ₹ 56,140, ₹ 3,158
Question 164.
From the following details calculate total customs duty payable:
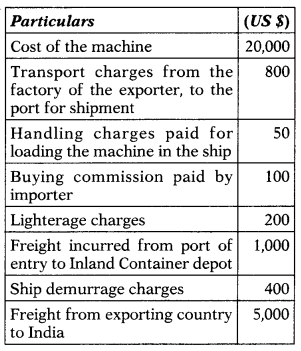
Date of the bill of entry: 20th February (BCD 20%; Exchange rate ₹ 60 per US $) Date of entry inward: 25th January (BCD 12%; Exchange rate ₹ 65 per the US $) Rate of IGST= 12%.
Ignore GST Compensation Cess.
(A) ₹ 5,86,633
(B) ₹ 5,86,366
(C) ₹ 5,68,633
(D) ₹ 5,68,366
Hint:
Computation of assessable value:
| Particulars | $ |
| Cost of the machine at the factory of the exporter | 20,000 |
| (+) Transport charges | 800 |
| (+) Handling charges | 50 |
| FOB Value | 20,850 |
| (+) Lighterage charges paid by the importer | 200 |
| (+) Ship demurrage charges | 400 |
| (+) Freight charges from exporting country to India | 5,000 |
| (+) Insurance @ 1.125% of FOB Value | 234.5625 |
| CIF Value/Assessable value | 26,684.5625 |
Computation of total customs duty payable:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Assessable value in Indian currency [26,684.5625 × 60] | 16,01,073.75 |
| (+) Basic custom duty [16,01,073.75 × 20%] | 3,20,214.75 |
| (+) Social Welfare Charge [3,20,214.75 × 10%] | 32,021.48 |
| 19,53,309.98 | |
| (+) Integrated tax u/s 3(7) [19,53,309.98 × 12%] | 2,34,397.20 |
| Total cost of import | 21,87,707.18 |
| Total Custom Duty Payable [3,20,214.75 + 32,021.48 + 2,34,3 97.20] | 5,86,633 |
Notes:
- Buying commission is not included in the assessable value.
- Freight incurred from the port of entry to the Inland Container depot is not included in the assessable value.
- No landing charges are added to the CIF Value due to amendment in Rule 10(2).
Answer:
(A) ₹ 5,86,633
Question 165.
Sai Cars Ltd. is a dealer in cars. They import cars from abroad and sell them to customers in India. On 20th March, they have imported cars from Japan, as per the following details:
Customs duty 10%
IGST 28%
Compensation cess 20%
Assessable value of cars = ₹ 4,00,00,000
Sai Cars Ltd. is eligible to claim an input tax credit (ITC). Their output IGST liability, before taking credit for ITC is ₹ 130 lakh. Compute the net liability towards customs duty and IGST.
(A) ₹ 2,57,12,000; ₹ 1,24,32,000
(B) ₹ 2,57,12,000; ₹ 5,68,000
(C) ₹ 1,24,32,000; ₹ 1,24,32,000
(D) ₹ 88,80,000; ₹ 5,68,000
Hint:
Computation of total customs duty payable:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Assessable value in Indian currency | 4,00,00,000 |
| (+) Basic custom duty [4,00,00,000 × 10%] | 40,00,000 |
| (+) Social Welfare Charge [40,00,000 × 10%] | 4,00,000 |
| 4,44,00,000 | |
| (+) Integrated tax u/s 3(7) [4,44,00,000 × 28%] | 1,24,32,000 |
| (+) Compensation cess [4,44,00,000 × 20%] | 88,80,000 |
| Total cost of import | 6,57,12,000 |
| Total Custom Duty Payable | 2,57,12,000 |
True Sai Cars Pvt. Ltd. can take credit of integrated tax paid of 11,24,32,000.
Computation of net IGST payable:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Output IGST liability | 1,30,00,000 |
| (-) Integrated tax paid on import | (1,24,32,000) |
| 5,68,000 |
Answer:
(B) ₹ 2,57,12,000; ₹ 5,68,000
Question 166.
Section 110 of Finance Act, 2018 w.e.f. 2nd February 2018 have levied……….on imported goods which is a duty of customs levied for the purpose of the union on the goods specified in the first schedule with the Customs Performing Act, 1975 being goods imported into India.
(A) Anti Dumping Duty
(B) Paid Command Duty
(C) IGST and GST Compensation Cess
(D) Social Welfare Surcharge [Dec. 2019]
Answer:
(D) Social Welfare Surcharge
Question 167.
Find from the following list which is treated as Port under the provisions of the Customs Act, 1962 :
(A) Land Station
(B) Land Customs Stations (LCS)
(C) Container Freight Stations (CFS) not attached to Port
(D) None of the above [Dec. 2019]
Answer:
(B) Land Customs Stations (LCS)
Question 168.
Duty Drawback under the Customs Act, 1962 shall be allowed on the imported goods, where such imported goods are being used for a period of eight months before the same were reexported @ …………
(A) 85%
(B) 70%
(C) 60%
(D) 40% [Dec. 2019]
Answer:
(B) 70%
Question 169.
Selfassessment of duty as per section 17 of the Customs Act, 1962 is being done by Importer and Exporter relating to the goods subject to duty and after final assessment of duty if any, amount refundable is not refunded within………..from the date of assessment of duty finally there shall be paid interest on such unrefunded amount by Central Government.
(A) 1 month
(B) 2 months
(C) 6 months
(D) 3 months [Dec. 2019]
Answer:
(D) 3 months
Question 170.
The offenses committed under the Customs Act, 1962 are having criminal liability as well as civil liability. However, the offenses involving duty evasion of more than ₹…………or/ and of……………….are nonbailable of fences under criminal liabilities.
(A) 50 lakh, Prohibited goods
(B) 50 lakh, Smuggled goods
(C) 100 lakh, Smuggled goods
(D) 100 lakh, Prohibited goods
Answer:
(A) 50 lakh, Prohibited goods
