Automated Business Process – CA Inter EIS Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Automated Business Process – CA Inter EIS Question Bank
Question 1.
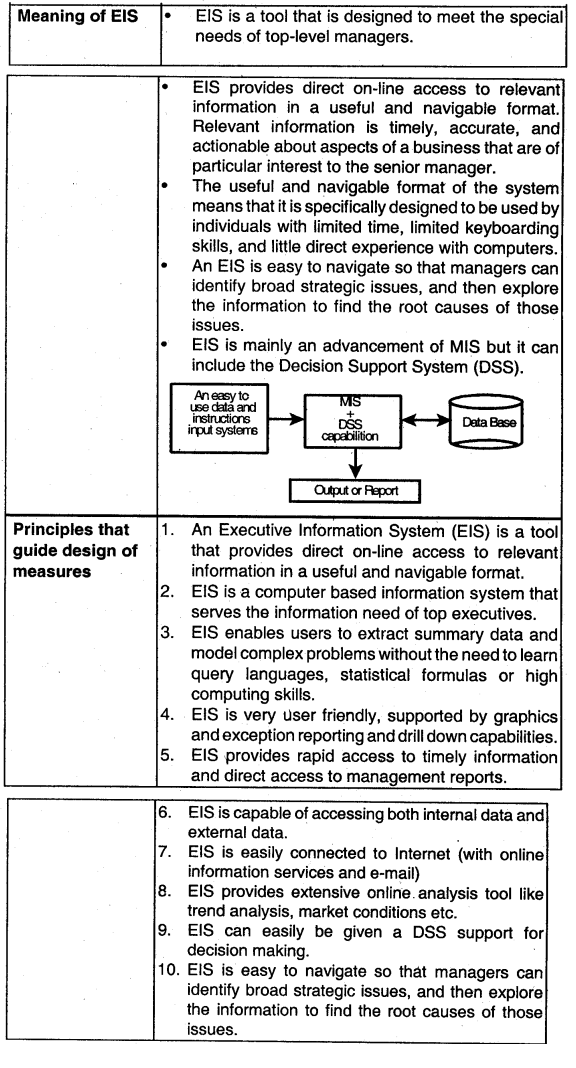
Briefly explain the principles to guide the design of measures and indicators to be included in EIS. (Nov 2007, 5 marks)
Answer:
Question 2.
Executive information systems (EIS) and its components.
Answer:
Executive Information Systems (EIS):
An Executive Information System (EIS) is the nature of Information System used by executives to access and administer the data they entail to make informed business decisions. In the hierarchical structure of information systems, the EIS is at the pinnacle and is designed to renovate all significant data (from project to process to budget) into aggregated information that makes sense and brings value to the by-and-large business strategy. EIS is able to link data from various sources both internal and external to provide the amount and kind of information executives find useful.
These systems are designed for top management easy to use present information in condensed view; access organization’s databases and data external to the organisation.
Components of an EIS
| Components | Description |
| Hardware | Includes Input data-entry devices. CPU. Data Storage files and Output Devices. |
| Software | Includes Text base software, Database, and Graphic types such as time series charts, scatter diagrams, maps, motion graphics, sequence charts, and comparison- oriented graphs (i.e., bar charts) Model base. |
| User Interface | Includes hardware (physical) and software (logical) components by which people (users) interact with a machine. Several types of interlaces can be available to the EIS structure, such as scheduled reports, questions/answers, menu driven, command language, natural language and input/output. |
| Tele- communication | Involves transmitting data from one place to another in a reliable networked system. |
Question 3.
What are the various key factors to be considered in implementing Business Process Management (BPM) in an enterprise? (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Various key factors to be considered in implementing Business Process Management (BPM) In an enterprise are as follows:
| Factors | Key Considerations |
| Scope | A single process, a department, the entire company. |
| Goals | Process understanding, Process Improvement, Process Automation! Optimization arid Process re-engineering. |
| Methods to be used | Six Sigma, BPM Life Cycle Method, TQM, Informal methods. |
| Skills Required | Consultants, Train Employees, Formal Certification. Basic Education, Existing Skill sets. |
| Tools to be used | White-Boards, Sticky Notes, Software for Mapping, Documenting, Software for Simulation. Comprehensive BPMS. |
| Investments to Make | Training, Tools, Time. |
| Sponsorship/Buy-in Needed | Executive Level, Department Level, Process Owner Level, Employee Level. |
Question 4.
What are the major reasons for failure of Business Process Management System (BPMS)? (Nov 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Reason for Failure of BPMS:
1. The consumer is often confronted with poor customer service due to broken processes, inefficient processes and manual processes- that is the customer is often confronted (challenged) with the silos of the organisation.
2. The same consumer is becoming more and more demanding with respect to delivery time and also demanding higher quality of the products or services.
3. The product or service is becoming more and more personalized supported by increased customer services.
4. Inadequate investment in ongoing training for involved personnel and deficient executive Involvement.
5. Breakdown in gap analysis due to deficient project management.
6. Inefficient corporate policy protecting the integrity of data in BPMS.
![]()
Question 5.
Write any two principles of Business Process Management. (May 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Principles of Business Process Management:
| 1. Principle of Context Awareness | BPM should light to the organizational context. It should be tailor-made and should not follow cookbook approach. |
| 2. Principle of Continuity | BPM should be a continuous and permanent practice. It should not be a one-off project. |
Question 6.
Define Business Process
Answer:
Business Process:
A Business Process Consists of a set of activities that are performed in coordination in an organizational and technical environment. These activities jointly realize a business goal. Each business process is enacted by a single organization, but It may interact with business processes performed by other organizations. To manage a process, the first task is to define it that involves defining the steps/ tasks in the process and mapping the tasks to the roles involved in the process.
Once the process is mapped and Implemented, performance measures are established. The last piece of the process management definitions describes the organizational setup that enables the standardization of and adherence to the process throughout the organization.
Question 7.
During a job interview, an interviewer asked Mr. A to list out all the risks and their controls associated with Order-To-Cash (O2C) business process. Prepare an appropriate draft reply.
Answer:
Risks and Controls related to the Order to Cash (O2C) business process are follows:
| Risks | Controls |
| 1. The Customer master file might not be maintained property and the Information might not be accurate. | The Customer master file is maintained properly and the information is accurate. |
| 2. Invalid changes are made to the customer master file. | Only Valid changes are made to the customer master file. |
| 3. All Valid changes to the customer master file are not processed. | All Valid changes to the customer master file are processed. |
| 4. Changes to the customer master tile might not be accurate. | Changes to the customer master file are made accurate. |
| Changes to the customer master file are not processed in a timely manner. | Changes to the customer master file are processed in a timely manner. |
| 5. Customer master file data might not be up-to-date and relevant | Customer master file data is up-to-date and relevant. |
Question 8.
What are the objectives of business process automation? (2014- Nov 2 marks)
Answer:
The success of any business process automation shall only be achieved when BPA ensures
| Confidentiality | To ensure that data is only available to persons who have right to see the same; |
| Integrity | To ensure that only authorized amendments can be made in the data; |
| Availability | To ensure that data is available when asked for; and |
| Timelines | To ensure that data Is made available at the right time. To ensure that all the above parameters are met, BPA needs to have appropriate internal controls put in place. |
![]()
Question 9.
Mention the challenges in implementing ‘Business Process Automation’. (Nov 2015, 2 marks)
Answer:
Challenges In Implementing Business Process Automation
| 1. Planning | It requires determining the goals, of the information system function and the means of achieving these goals. |
| 2. Organizing | it involves gathering, allocating, and coordinating the resources needed to accomplish the goals. |
| 3. Leading | In involves motivating, guiding, and communicating with personnel. |
| 4. Controlling | Comparing actual performance with planned performance as a basis for taking any corrective actions that are needed. |
| 5. Increase In Number of Interface with Customers | Since the number of interlace with customers is growing for e.g. phone, e-mail, SMS, Whatsapp, etc. It becomes difficult to handle. |
| 6. High Cost | It plays heavily on the budget of the company. |
Question 10.
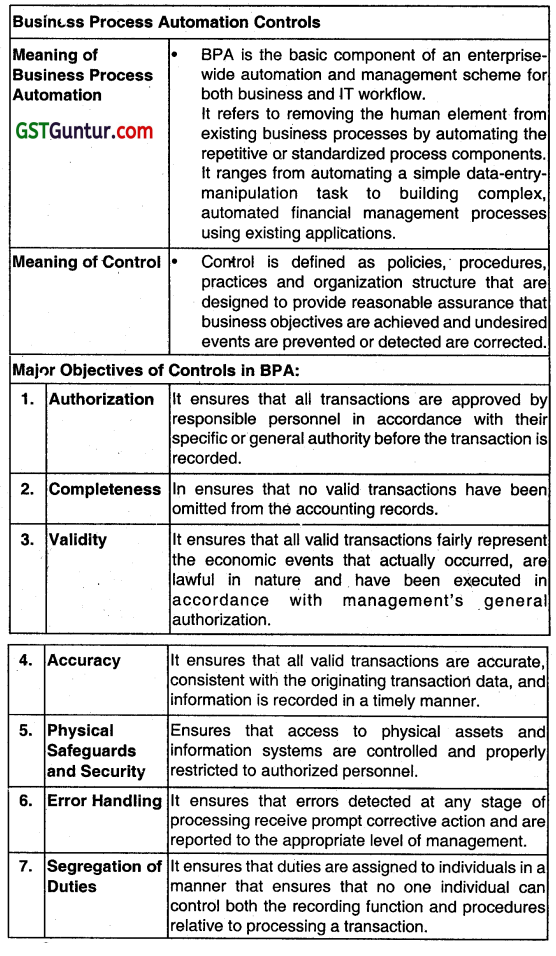
What is meant by ‘controls in BPA? What are their major objectives? (Nov 2015, 4 marks)
Answer:
Question 11.
What are the generic reasons for going for Business Process Automation? (May 2017, 4 marks)
Answer:
Business Process Automation
Meaning
BPA is the basic component of an enterprise-wide automation and management scheme for both business and PT workflow. It refers to removing the human element from existing
business processes by automating the repetitive or standardized process components. It ranges from automating a simple data-entry manipulation task to building complex, automated financial management processes using existinq applications.
| Need of BPA | |
| 1. Fast Service to customers | This was not the initial reason for adaption of BPA but gradually business managers realized that automation could help them to serve their customers faster and better. |
| 2. To Remain Competitive and enhancing goodwill | To provide the level of products and services as offered by competition and thus enhancing goodwill. |
| 3. Cost Saving | Automation leads to saving In time and labour costs. |
| 4. Error-free | To provide error-free services to the customer. |
| 5. Focus on key areas | Freeing people from routine and volume, and allow management to do what they are best at make decisions, analyze data Implications and trends and focus on providing better customer service. |
Question 12.
State the required characteristics of goals to be achieved by implementing Business Proc3ss Automation (BPA). (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
The characteristics of goals to be achieved by Implementing Business Process Automation (BPA), being:
S-Specific
M – Measurable
A – Attainable
R – Relevant
T-Timely
![]()
Question 13.
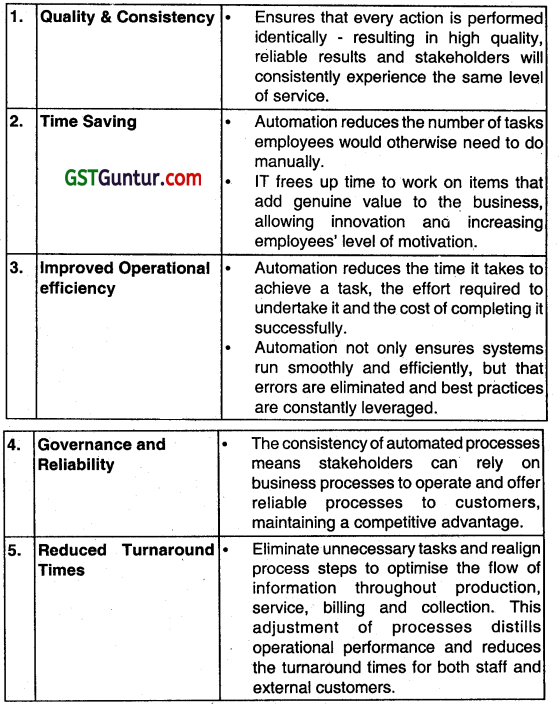
A business organization is planning to increase the accuracy of information transferred and certifies the repeatability of the value-added task performed by the automation of business. Being a management consultant, identify any four major benefits that the organization can achieve through the automation of a business process. (May 2019, 4 marks)
OR
Briefly discuss the benefits of Business Process Automation.
Answer: ‘
Major benefits that the organisation can achieve through the automation of a business process.
Question 14.
Using the automation technique in modem era of business, the business gets well developed with a great customer satisfaction of their services and products in which the customer-oriented supply chain plays a major role. List down the name of all the benefits of Automating Business processes by explaining any four benefits. (Jan 2021, 6 marks)
Question 15.
Discuss the steps in implementing Business Process Automation.
Answer:
The steps in Implementing Business Process Automation are:
Step 1: Define why we plan to implement a BPA?
The primary purpose for which an enterprise implements automation may vary from enterprise to enterprise. A list of generic reasons for going for BPA may include any or combination of the following:
- Errors in manual processes leading to higher costs.
- Payment processes not streamlined, due to duplicate or late payments, missing early pay discounts and losing revenue.
- Paying for goods and services not received.
- Poor debtor management leading to high invoice aging and poor cash flow.
- Not being able to find documents quickly during an audit or lawsuit or not being able to find all documents.
- A lengthy or incomplete new employee or new account onboarding.
- Unable to recruit and train new employees, but where employees are urgently required.
- Lack of management understanding of business processes.
- Poor customer service.
Step 2: Understand the rules regulations under which enterprise needs to comply with? One of the most important steps in automating any business process is to understand the rules of engagement, which include following the rules, adhering to regulations, and following document retention requirements. This governance is established by a combination of internal corporate policies, external industry regulations, and local, state, and central laws.
Regardless of the source. it is important to be aware of their existence and how they affect the documents that drive the processes. it is important to understand that laws may require documents to be retained for specified number of years and in a specified format. Entity needs to ensure that any BPA adheres to the requirements of law.
Step 3: Document the Process, we wish to automate At this step, all the documents that are currently being used need to be documented. The following aspects need to be kept in mind while documenting the present process:
- What documents need to be captured?
- Where do they come from?
- What format are they in Paper, Fax, email. PDF etc.?
- Who is involved in processing of the documents?
- What is the impact of regulations on processing of these documents?
- Can there be a better way to do the same job?
- How are exceptions In the process handled?
- The benefit of the above process for user and entities being that It provides clarity on the process, helps to determine the sources of inefficiency, bottlenecks, and problems, and allows tore design the process to focus on the desired result with workflow automation.
Step 4: Define the objectives! goals to be achieved by implementing BPA
Once the above steps have been completed, entity needs to determine the key objectives of the process improvement activities – SMART (Specific Clearly defined, Measurable: Easily quantifiable in monetary terms, Attainable: Achievable through best efforts, Relevant: Entity must be in need of these and Timely: Achieved within a given time frame.)
Step 5: Engage the business process consultant This is again a critical step to achieve BPA. To decide as to which company consultant to partner with depends upon the following:
Objectivity of consultant in understanding! evaluating entity situation.
- Does the consultant have experience with entity business process?
- Is the consultant experienced in resolving critical business issues?
- Whether the consultant is capable of recommending and implementing a combination of hardware, software, and services as appropriate to meeting enterprise BPA requirements?
- Does the consultant have the required expertise to dearly articulate the business value of every aspect of the proposed solution?
Step 6: Calculate the Return on Investment (ROI) for project:
The right stakeholders need to be engaged and involved to ensure that the benefits of BPA are dearly communicated and implementation becomes successful. Hence, the required business process owners have to be convinced so as to justify the benefits of BPA and get approval from senior management. Some of the methods for justification of a BPA proposal may include cost savings in terms of eliminating fines to be paid by entity due to delays, cost of audits and lawsuits and reduced cost of space regained from paper, tile cabinets; reduction in required manpower leading to no new recruits; ensuring complete documentation for all new accounts; taking advantage of early payment discounts and eliminating duplicate payments;
ensuring complete documentation for all new discounts; ensuring complete documentation for all new accounts; building business by providing superior levels of Customer service and charging for Instant access to records etc.
![]()
Step 7: Developing the BPA
Once the requirements have been documented, ROI has been computed and top management approval to go ahead has been received the consultant develops the requisite BPA. The developed BPA needs to meet the objectives for which the same is being developed.
Step 8: Testing the BPA
Once developed, it is important to test the new process to determine how well it works and identify where additional exception processing” steps need to be included. The process of testing is an iterative process, the objective being to remove all problems during this phase.
Testing allows room for improvements prior to the official launch of the new process, increases user adoption, and decreases resistance to change. Documenting the final version of the process will help to capture all of this hard work, thinking, and experience which can be used to train new people.
Question 16.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) does not create a risk-free environment; rather ¡t enables management to operate more effectively in environments filled with risks. In view of this statement, explain the various benefits, which Board of Directors and Management of an entity seek to achieve by implementing the ERM process within the entity. (Nov 2018, 6 marks)
Answer:
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) does not create a risk-free environment, rather it enables management to operate more effectively in environments filled with risks. The Board of Directors and Management achieve the following benefits by implementing the ERM process within the entity:
| 1. Align risk appetite and strategy | Risk appetite is the degree of risk, on a broad-based level that an enterprise (any type of entity) is willing to accept in pursuit of its goals. Management considers the entity’s risk appetite First in evaluating strategic alternatives, then it setting objectives aligned with the selected strategy and in developing mechanisms to manage the related risks. |
| 2. Link growth, risk, and return | Entities accept risk as part of value creation and preservation and they expect return commensurate with the risk. ERM provides an enhanced ability to identify and assess risks and establish acceptable levels of risk relative to growth and return objectives. |
| 3. Enhance risk response decision | ERM provides the rigor to identify and select among alternative risk- responses risk avoidance, reduction, sharing, and acceptance. ERM provides methodologies and techniques for making these decisions. |
| 4. Minimize operational surprises and losses | Entities have enhanced capability to identify potential events, assess risk and establish responses, thereby reducing the occurrence surprises and related costs or losses. |
| 5. identify and manage cross-enterprise risks | Every entity faces a myriad of risks affecting different parts of the enterprise. Management needs to not only manage individual risks but also understand interrelated impacts. |
| 6. Provide Integrated responses to multiple risks | Business processes carry many inherent risks, and ERM enables integrated solutions for managing the risks. |
| 7. Seize opportunities | Management considers potential events, rather than just risks, and by considering a full range of events, management gains an understanding of how certain events represent opportunities. |
| 8. Rationalize capital | More robust information on an entity’s total risk allows management to more effectively assess overall capital needs and improve capital allocation. |
Question 17.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework consists of integrated components that are derived from the way management runs a business and are Integrated with the management process. Define any six components of ERM framework. (Nov 2020, 6 marks)
Question 18.
Risks involved in Implementing Business Process Automation. (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
Risks involved In Implementing Business Process Automation
| 1. Risk to Jobs | Jobs that were earlier performed manually by several employees would post-automation would be mechanized, thereby posing a threat to jobs. |
| 2. False Sense of Security | Automating poor processes will not gain better business practices. |
Question 19.
How the inherent risks involved in BPA can be classified? Discuss any four. (Nov 2019, 2 marks)
Answer:
The inherent risks involved in BPA are classified below
| 1. Input & Access | All input transaction data may not be accurate, complete and authorized. |
| 2. File & Data Transmission | All files and data transmitted may not be processed accurately and completely, due to network error. |
| 3. Processing | Valid input data may not have been processed accurately and completely due to program errors or bugs. |
| 4. Output | Is not complete and accurate due to program errors or bugs and is distributed to unauthorised personnel due to weak access control. |
Question 20.
After defining risk appetite, strategies are set to manage risks. Explain any four risk management strategies. (Nov 2020, 4 marks)
Question 21.
Explain the following in brief:
Risk Assessment (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Risk Assessment
Risk may be defined as the possibility that an event will occur and adversely affect the achievement of objectives. Risk assessment involves a dynamic and interactive process for identifying and assessing risk to the achievement of objectives. Risks to the achievement of these objectives from across the entity are considered relative to established risk tolerances.
Thus, risk assessment forms the basis for determining how risks will be managed. A precondition to risk assessment is the establishment of objectives, linked at different levels of the entity. Management specifics objectives within categories of operations, reporting, and compliance with sufficient clarity to be able to identify and assess risks to those objectives. Risk assessment also requires management to consider the impact of possible changes in the external environment and within Its own business model that may render internal control ineffective.
Question 22.
An electric supply company charges the following rates from its consumers:

If the consumer pay his bill within 15 days from the bill date. 10% discount is given. If he makes the payment after 15 days from the bill date, 5% surcharge is levied. Draw a Flow chart to calculate the net amount of the bill for each consumer and print it. (Nov 2007, 10 marks)
Answer:
![]()
Question 23.
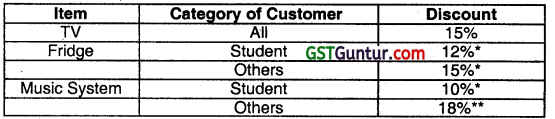
A Book publisher offers discounts to customers on the basis of customer type and number of copies ordered as shown below:
| Customer type | Number of Copies Ordered | % of Discount |
| Book Seller | More than 10 | 25 |
| Less than of equal to 10 | 15 | |
| More than 5 | 20 | |
| Library | Less than or equal to 5 | 10 |
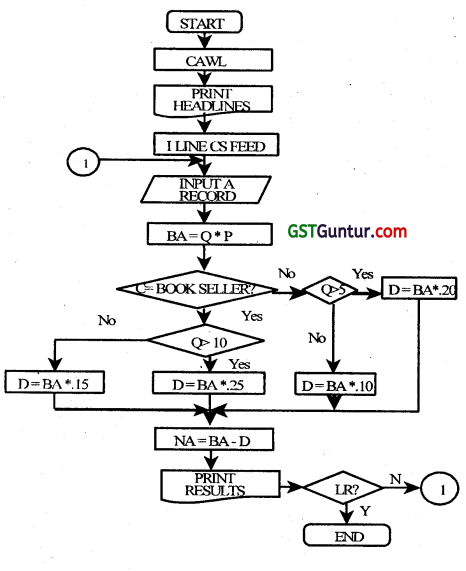
Customer number, name, type, book number, number of copies ordered, and unit price are given as input. Draw a flow chart to calculate the net amount of the bill for each customer and print it. The above is to be carried out for 50 customers. (2008 Nov, 10 marks)
Answer:
Please see answer on next page
Question 24.
Frame the problem for which the given Flowchart has been drawn. See the Abbreviations defined below:
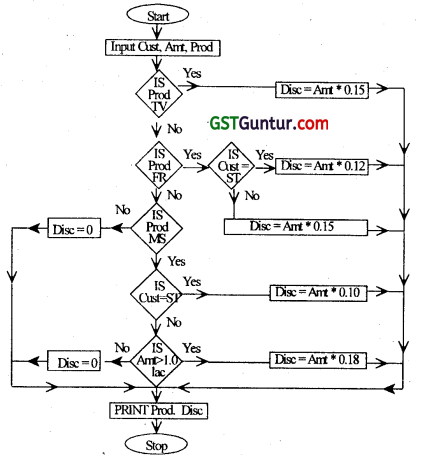
Cust. : Customer,
Prod: Product,
Amt: Amount,
Disc: Discount,
TV: Television,
FR: Fndge,
MS: Music System,
ST: Student (May 2009, 10 marks)
Answer:
The problem relates to the ‘Discount Policy’ of a company engaged in selling electronic items.
irrespective of order value
subject to order value being more than ₹ 1 lakh.
Question 25.
Write the output sequence (at least first five numbers) for the given flow chart, if N = 0 is selected as the value for N as Input.
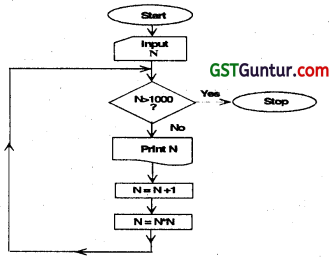
(Nov 2009,5 Marks)
Answer:
If N = 0 then the output sequence will be:
0 1 4 25 676
Question 26.
If the statement N. = N * N In the computation box of the flowchart is modified as N = N * (N – 1)n. Write the output sequence (at least first five numbers) for the flowchart with N = 0 as the input value for N.
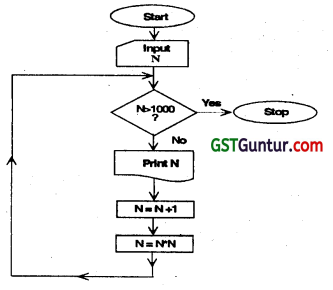
(Nov 2009, 5 Marks)
Answer:
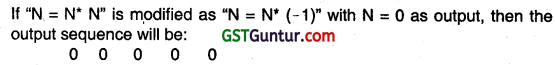
Question 27.
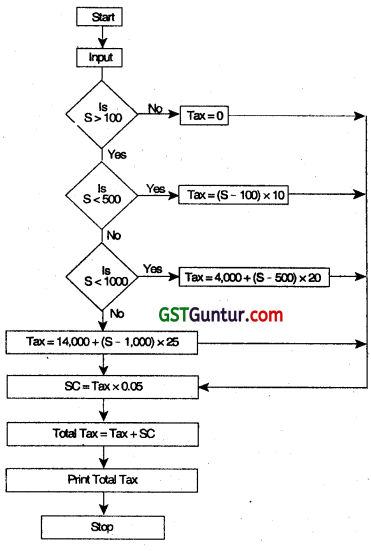
The Income-tax for the employees of an organization is calculated on the basis of their Gross Income and the Investments made by them, under Section 80G. The taxable income is calculated according to the following rules:
Taxable Income = Gross Income – Investments provided investments a less than 1.5 lac. Otherwise
Taxable Income = Gross Income – 1.50,000
Following rules are applied to calculate the Income-tax, on the Taxable Income:

Also, an educational cess of 4% of Income-tax is levied on all the employees, irrespective of the income. Employee number, Name, Gross Income, Investment amount is given as input. Draw a flow chart to calculate the Income-tax payable by each employee. (May 2010, 10 marks)
Answer:
Please see answer on next page
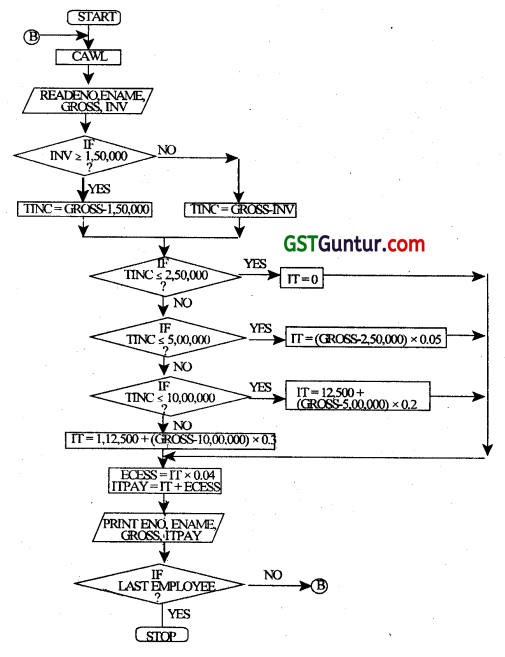
Terms used:
ENO = Employee Number
ENAME = Employee Name
GROSS = Gross Income
INV = Investment made
TINC = Taxable Income
IT = Income Tax
ECESS = Education Cess
ITPAY = Total Income Tax payable
CAWL = Clear All Working Locations
Question 28.
What do you mean by term flow chart? Draw a program flow chart to find the sum of first 50 odd numbers. (Nov 2010, 2 +6 =8 marks)
Answer:
Flow Chart:
Flow chart is a diagram that shows sequence of steps required to solve a particular problem.
It is a logical flow of steps which shows sequence of operations of a program by using symbols and interconnectivity lines. It is like a blueprint that shows the general plan and essential details of the proposed structure. It allows the programmer to compare different approaches and alternatives on paper and often shows inter-relationships that are not immediately apparent.
The required flowchart to find the sum of first 50 odd numbers is drawn below:
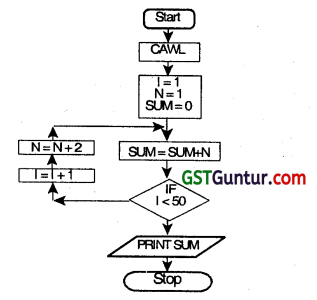
Question 29.
What is Program debugging? Explain it briefly. (Nov 2010, 2 marks)
OR
Write short note on Program Debugging (May 2013, 2 marks)
Answer
Program Debugging:
It is a process of finding errors in program and rectifying them by using diagnostic routine before putting the program into use. There is a real necessity to debug a program, i.e. to cleanse it from errors. For this purpose the programmers device a set of test data transactions to test the various alternative branches in the program. The results got from the computer are
compared with one derived manually prior to computer processing. When the results do not match for any reason, the programmer then verifies the flowchart and coding sheet to hunt for the bugs. This process is called program debugging.
![]()
Question 30.
For computing custom duty, the imported items are classified into 4 categories. The rate of duty to be levied on each category of items is given below:
| Category | Class of goods | % customs duty on the (K) value of goods (V) |
| 1 | Food and beverages | 10 |
| 2 | Textile and leather goods | 15 |
| 3 | Heavy machinery | 20 |
| 4 | Luxury items | 40 |
Draw a flowchart to compute the custom duty. (May 2011, 4 marks)
Answer:
Please see answer on next page
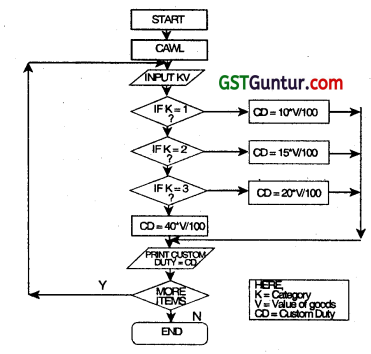
Question 31.
A housing society having 400 members pay electricity bills at the following rates:
No. of units consumed Charges/unit (₹)
For the first 200 units 2.65
For the next 300 unIts 3.90
Over 500 units 4.75
Surcharge @ 5% of the bill Is to be added to the charges.
Draw a flow chart which will read the house number and the number of units consumed. Print the total charges with the house number and the units consumed. (Nov 2011, 8 marks)
Answer:
Abbreviations used:
House No. – House Number
Units – No. of units consumed
Amt – Amount
Chrg – Charges
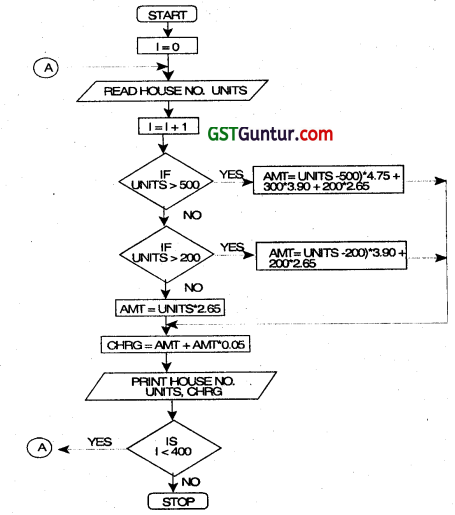
Question 32.
For the flow chart given below:
(a) Print the output displayed for using the given two sets of data:
| X | Y | |
| 1st Set: | 15 | 20 |
| 2nd Set: | 35 | 30 |
(May 2012, 4 marks)
(b) What interpretation do you make from the instructions given in the flow chart? (May 2012, 3 marks)
(c) Comment about the storage of the variables used in the instructions of the flow chart. (May 2012,1 mark)
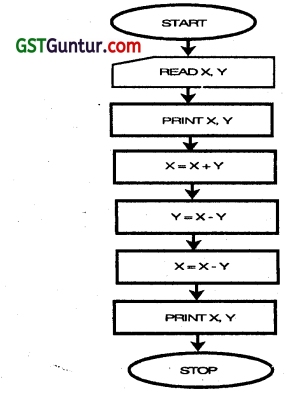
Answer:
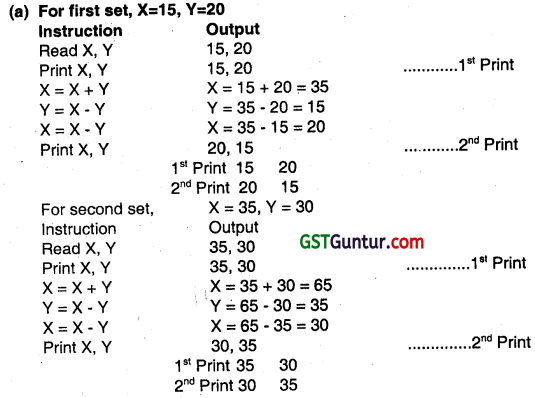
Answer:
(b) The given set of instructions in the flow chart is the steps for swapping/interchanging the values of two variables without involving the third variable. As clearly interpreted from the output, the values of X and Y in the both the value sets have got interchanged.
Note: The interpretation involves two important factors:
(i) Interchange of values of two variables X and Y.
(ii) Without involving the third or temporary storage/variable.
Answer:
(c) The comments about the storage of the variables used In the instructions of the flow chart are as follows
X = X + Y // The value of X has been assigned the value of (X+Y) …………………… (i)
Y = X – Y // The value of Y has been assigned the value of (X-Y) …………………… (ii)
X = X – Y //The value of X has again been assigned the value of (X-Y), where the value of X and Y are calculated from the statement (i) and (ii)
Question 33.
Draw a flow chart to print the square of odd numbers between 10 to 50 and also print the sum of their square. (Nov 2012, 8 marks)
Answer:
The required flowchart is as follows:
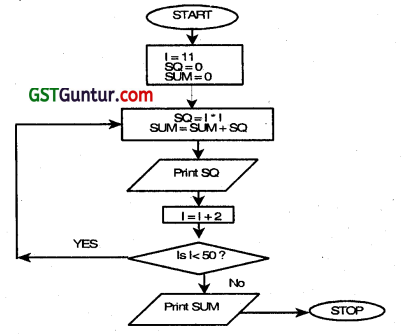
I: Stores the value of odd number between 10 to 50 at each step.
SQ: Stores the calculated value of square of each odd number at each step.
SUM: Stores the sum of the squares of all the odd numbers till that step.
Question 34.
Describe briefly System Flow Chart (Nov 2012, 2 marks)
Answer:
System Flowchart:
- System flowchart depicts the electronic flow of data and processing steps in Information systems.
- It is used by System Analysts to describe the data flow and operations for a data processing cycle.
- It defines the broad processing in the organizations.
- It shows the origin of data, filing structure, processing to be performed, output that is to be generated and necessity of any offline operation.
Question 35.
Top town Municipality, is levying annual House Tax, as per following rules:
| Size of House in Sq. Metre | House tax rate per Square Metre |
| Less than 100 | Nil |
| Up to Next 400 | ₹10 |
| Up to Next 500 | ₹ 20 |
| More than 1000 | ₹ 25 |
There is a surcharge of 5% of the value of House Tax. Taking into account the above factors, draw a flow chart to compute appropriate total House Tax including surcharge for any one house. (May 2013, 6 marks)
Answer:
Please see answer on next page
![]()
Question 36.
A book publisher of Information Technology offers discounts to its customers on the basis of customer type as detailed below:
| Customer Type | Discount |
| Book Seller | 30% |
| Library | 20% |
| Student | 10% |
Further, If number of copies purchased is more than 20. then additional discount of 5% is allowed Irrespective of customer type. Number of books, unit price of each book, and customer type are given as input. Draw a flow chart to calculate the net amount after all discounts and print customer type, number of copies, and net amount. (Nov 2013, 8 marks)
Answer:
Please see answer on next page
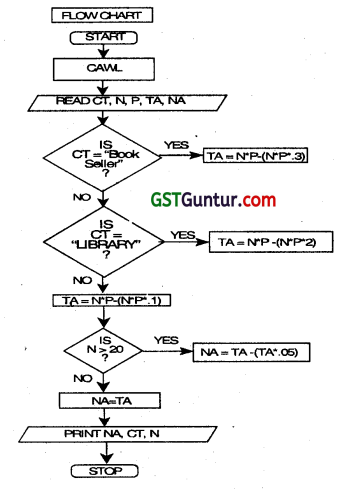
Question 37.
ABC Limited is a software development company, which appointed 50 software engineers in August 2014 at a monthly salary of ₹ 30,000. All these engineers shall be entitled for an increment in their monthly salary after six months. The increment on present monthly salary shall be based on their performance to be evaluated on a 100 marks scale as per details
given below:
– Performance Marks <70. then increment shall be 10% of present salary.
– 70 Performance marks < 80, then increment shall be 20% of present salary.
– Performance Marks 80. then increment shall be 30% of present salary.
Draw a Flow-Chart to enable to print the details like Name of the engineer. performance marks, monthly increment amount and revised monthly salary for each of these 50 engineers. (May 2015, 8 marks)
Answer:
Let us define the variables first
PM: Performance Marks
RESAL: Revised Monthly Salary.
INCAMT: Increment Amount,
NAME: Name of Engineer.
N: Pointer to track number of Engineers,
INCREMENT = 0
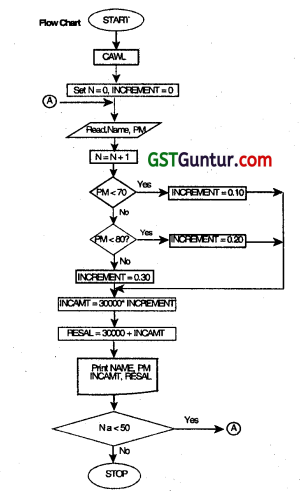
Question 38.
An E-Commerce site has the following cash back otters.
(i) If the purchase mode is via website, an Initial discount of 10% is given on the bill amount.
(ii) If the purchase mode is via phone app, an Initial discount of 20% is given on the bill amount.
(iii) It done via any other purchase mode, the customer is not eligible for any discount. Every purchase eligible to discount is given 10 reward points.
(a) If the reward points are between 100 and 200 points, the customer is eligible for a further 30% discount on the bill amount after initial discount.
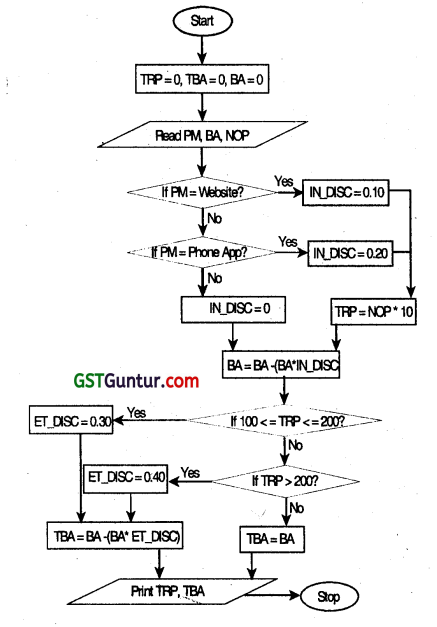
(b) If the reward points exceed 200 points, the customer is eligible for a further 40% discount on the bill amount after Initial discount. Taking purchase mode, bill amount, and number of purchases as Input, draw a flowchart to calculate and display the total reward points and total bill amount payable by the customer after all the discount calculations. (Nov 2015, 8 marks)
Answer:
Let us define the variables first:
PM: Purchase Mode BA: Bill Amount TBA: Total Bill Amount
NOP: Number of Purchases TAP: Total Reward Points
IN DISC: Initial Discount
ET- DISC: Extra Discount on purchases eligible to Initial Discount
N: Counter (to track the number of purchases)
Question 39.
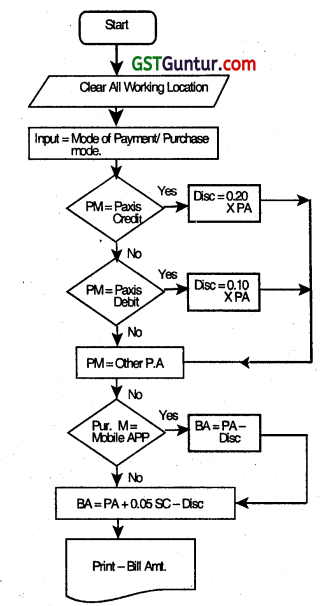
Draw a Flowchart for the following process:
Leebay is a new e-commerce website that is setting up business in India. Leebay and their partner bank Paxis have come up with a joint promotion plan for which the following offers are proposed. Customers can either log in through a mobile app or directly from the website:
(1) If the payment mode chosen is ‘Paxis Credit’, then a 20% discount is given to the user.
(2) If the payment mode chosen is ‘Paxis Debit’, then a 10% discount is given to the user.
(3) If other payment modes are used, then no discount is given.
Also, to promote the downloads of its new smartphone app, the company has decided to give the following offer:
1. If the purchase mode is ‘Mobile App’, then no surcharge is levied on the user.
2. If any other purchase mode is used, then additional 5% surcharge is levied on the user. This surcharge is applied on the bill after all necessary discounts have been applied. With bill amount, payment mode, and purchase mode as inputs, draw a flowchart for the billing procedure for Leebay. (Nov 2018, 1 x 8 = 8 marks)
Answer:
Please see answer on next page
Question 40.
What is a Data Flow Diagram. Explain the four major components of a Data Flow Diagram. (Nov 2016, 4 marks)
Answer:
Type of Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
There are two types of Data Flow Diagrams:
1. Logical Data Flow Diagram.
2. Physical Data Flow Diagram.
| Logical Data | Flow Diagram |
| 1. Logical Data flow Diagram | A logical DFD focuses on the business and how the business operates. It describes the business events that take place and the data required and produced each event. The logical model reflects the business. |
| 2. Physical Data Flow Diagram | A physical DFD shows how the system will be implemented. The physical model depicts the system. |
Major Component of DFD
Data Flow Diagrams
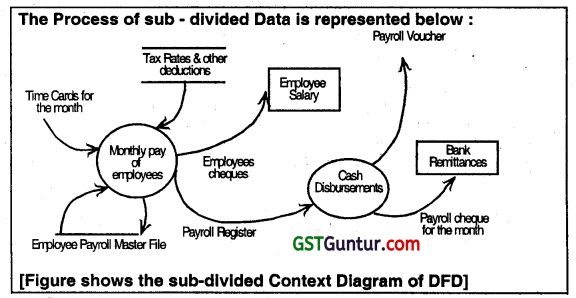
1. Concept of Data Flow Diagram (DFD):
A Data flow diagram graphically describes the flow of data within an organization. It is used to document existing systems and to plan and design new ones. There is no ideal way to develop a DFD; different problems call for different methods. A DFD Is composed of four basic elements: data sources and destinations, data flows, transformation processes, and data stores. Each is represented on a DFD by one of the symbols shown in figure given below.




![]()
Question 41.
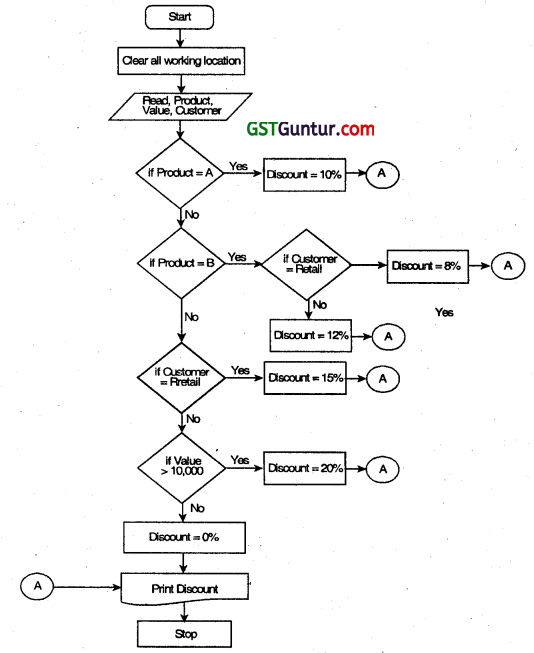
A company is selling three types of products, namely, A, B, and C to two different types of customers viz, dealers and retailers. To promote the sales, the company is offering the following discounts:
(i) 10% discount Is allowed on Product A, irrespective of the category of customers and the value of order.
(ii) On product B, 8% discount Is allowed to retailers and 12% discount to dealers, irrespective of the value of order.
(iii) On product C, 15% discount Is allowed to retailers irrespective of the value of order and 20% discount to dealers If the value of order is minimum of ₹ 10,000. Draw a flowchart to calculate the discount for the above policy.(May 2017, 8 marks)
Answer:
Please see answer on next page
Question 42.
(a) Draw a flow chart to incorporate for the following steps:
L1N=1 .
L2 PRINT N
L3 N = N x (N + 1)
L4 STOP when N exceeds 100
L5 GOTO L2
Note that In step L3, ‘x’ denotes the multiplication sign. (Nov 2017, 4 marks)
(b) List the output for the above program. (Nov 2017, 2 marks)
(c) List the output If the above program Is modified in the step L1 as N’ = 0.
(Nov 2017, 2 marks)
Answer:
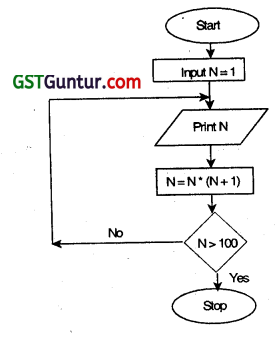
(b) Output=1,2,6,42
(c) Output = O (it will continue as the loop doesn’t end)
| 2. Effective Analysis | The flow chart becomes a blueprint of a system that can be broken down into detailed parts for study. Problems may be identified and new approaches may be suggested by flowcharts. |
| 3. Communication | Flow charts and In communicating the facts of a business problem to those whose skills are needed for arriving at the solution. |
| 4. Documentation | Flow charts serve as a good documentation which and greatly in future program conversions. In the event of staff changes, they serve as a training function by helping new employees in understanding the existing programs. |
| 5. Efficient Coding | Flow charts act as a guide during the system analysis and program preparation phase. Instructions, coded in a programming language may be checked against the flowchart to ensure that no steps are omitted. |
| 6. Program Debugging | Flowcharts serve as an important tool during program debugging. They help in detecting, locating, and removing mistakes. |
Question 43.
The Goods and Service Tax (GST) rate in India for various goods and services is divided broadly under 4 categories, draw a flow chart to compute Goods and Service Tax for the goods manufactured as per table below.
| Category (K) | Rate |
| A | 5% |
| B | 12% |
| C | 18% |
| D | 28% |
(Jan 2021, 6 marks)
Question 44.
Distinguish Between Data flow of DFD and Datastore of DFD.
Answer:
Data Flow of DFD: Data Flow is the movement of data between the entity, the process and the data store. Data flow portrays the interface between the components of the DFD. The flow of data in a DFD Is named to reflect the nature of the data used (these names should also be unique within a specific DFD). Data flow ¡s represented by an arrow, where the arrow Is annotated with the data name.
Data Store of DRD: A Datastore is where a process stores data between processes for later retrieval by that same processor another one. Files and tables are considered data stores. Data store names (plural) are simple but meaningful, such as customers, orders and products. Data stores are usually drawn as a rectangle with the right-hand side missing and labeled by the name of the data storage area it represents, though different notations do exist.
Question 45.
Discuss advantages arid limitations of using Data Flow Diagram.
Answer:
Advantages of using Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
- It aids in describing the boundaries of the system.
- It is beneficial for communicating existing system knowledge to the users.
- A straightforward graphical technique which is easy to recognize.
- DFDs can provide a detailed representation of system components.
- it is used as the part of system documentation file.
- DFDs are easier to understand by technical and non-technical audiences
- It supports the logic behind the data flow within the system.
Limitations of using Data Flow Diagram
- it makes the programmers little confusing concerning the system
- The biggest drawback of the DFD is that It simply takes a long time to create, so long that the analyst may not receive support from management to complete it.
- Physical considerations are left out.
![]()
Question 46.
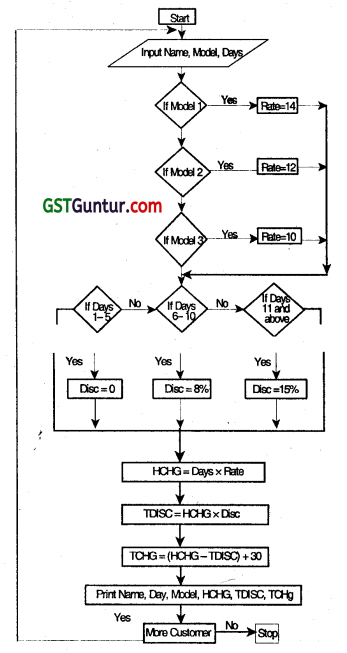
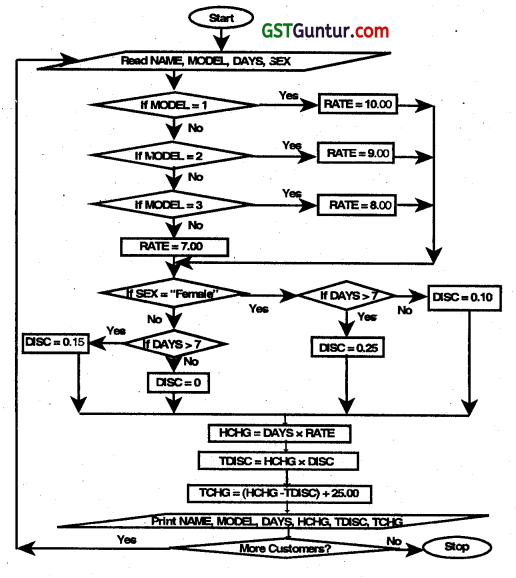
A bicycle shop in a city provides rental facility to its customers at different rates for different models as given below:
| Model No. | Hire Ratio per day |
| Model No.1 | ₹ 10 |
| Model No.2 | ₹ 9 |
| Model No.3 | ₹ 8 |
| Model No.4 | ₹ 7 |
To attract customers, the shopkeeper gives a discount of 15 percent to all those customers, who hire a bicycLe for more than one-week period. Further to attract women customer, he gives additional discount of 10 percent irrespective of hire period. For every bicycle hired, a security deposit of 25 must be paid. Draw a flow chart to print out the details of each customer such as name of customer, bicycle model number, number of days a bicycle is hired for, hire charges, disc’ount and total charges including deposits.
Answer:
Abbreviations used are as follows:
HCHG: Hire Charges
DAYS: No. of days a bicycle Is hired for
NAME: Name of Customer
TCHG: Total Charges
MODEL: Bicycle Model No.
TDISC: Total Discount
SEX: Gender of the Customer
The flowchart Is available on the next page.
Question 47.
Give two examples of the Risks and Control objectives for Human Resource Process at configuration level. (Nov 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Example of Risks and control objectives for Human Resource Process at configuration level
Risks objectives for Human Resource Process at configuration level:
Employees who have left the company continue to have system access.
Employees have system access in excess of their job requirements.
Control objectives for Humen Resource Process at configuration level:
System access to be Immediately removed when employees leave the company. Employees should be given system access based on a need to know’ basis and to perlorm their job function.
Question 48.
Corporate governance Is the framework of rules and practices, by which a board of directors ensures accountability, fairness, and transparency in a company’s relationship with all its stakeholders. List out the rules and procedures that constitute corporate governance framework. (May 2019, 3 marks)
Answer:
Corporate Governance Is the framework of rules and practices by which a board of directors ensures accountability, fairness, and transparency in a Company’s relationship with its all stakeholders (financiers, customers, management, employees, government, and the community). The corporate governance framework constitutes the following rules and procedures:
| 1. Contract | Explicit and Implicit contracts between the company and the stakeholders for distribution of responsibilities, rights and rewards. |
| 2. Reconciling | Procedures for reconciling the sometimes-conflicting interests of stakeholders in accordance with their duties, privileges and roles, and |
| 3. Supervision and Control | Procedures for proper supervision, control and information flows to serve as a system of checks and balances. |
Question 49.
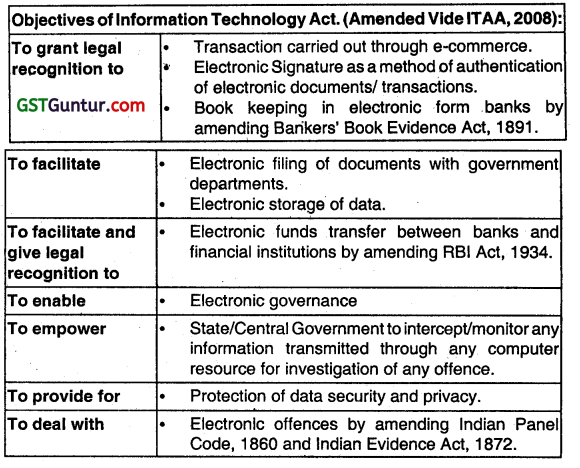
Write short note on the following:
Objectives of Information Technology Act, 2000. (Nov 2007, 5 marks)
Answer:
Question 50.
Explain the following In brief:
Cyber Crime (May 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
Cyber Crimes: Cyber Crimes also known as Computer Crime is a crime that involves use of a computer and a network. Is the reputation of the victim or cause physical or mental harm, or loss, to the victim directly or indirectly using modem telecommunication networks such as Internet (chat rooms, email, notice boards, and groups) and mobile phones.
Question 51.
Explain the positive aspects contained In the IT Act 2000 and its provisions, from the perspective of e-commerce in India. (May 2018, 4 marks)
Answer:
From the perspective of e-commerce In India, the IT Act, 2000 and Its provisions contain many positive aspects which are as follows:
- The implications for the e-businesses would be that email would now be a valid and legal form of communication in India that can be duly produced and approved in a Court of Law.
- Companies shall now be able to carry out electronic commerce using the legal infrastructure provided by the Act.
Digital signatures have been given legal validity and sanction in the Act. - The Act throws open the doors for the entry of corporate companies in the business of being Certifying Authorities for issuing Digital Signatures Certificates.
- The Act now allows Government to issue notifications on the web thus. heralding e-governance.
- The Act enables the companies to file any form, application oc any other document with any office, authority, body or agency owned or controlled by the appropriate Government in electronic form by means of such electronic form as may be prescribed by the appropriate Government.
- The IT Act also addresses the important issues of security, which are so critical to the success of electronic transactions.
- The Act has given a legal definition to the concept of secure digital signatures that would be required to have been passed through a system of a security procedure, as stipulated by the Government at a later date.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
……………….. may be defined as any kind of information system which improves the functions of an enterprise business process by Integration.
(a) Management Information System
(b) Enterprise Information System
(c) Enterpreneur Information System
(d) Corporate Information System
Answer:
(b) Enterprise Information System
Question 2.
Enterprise Information System p4ovide a technology platform that enable organizations to Integrate and co-ordinate their business processes on a ……………….. .
(a) Robotic System
(b) Robotic foundation
(c) Robust foundation
(d) Robust management system
Answer:
(c) Robust foundation
Question 3.
An Enterprise Information System can be used to
(a) increase business productivity
(b) reduce service cycle
(c) reduction In product development cycle and marketing life cycles
(d) All of them.
Answer:
(d) All of them.
![]()
Question 4.
Business Processes has been categorized
(a) Operational and Supporting Processes
(b) Management processes
(c) Only (a) not (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 5.
Operational processes deal with the core business and value chain, which deliver value to the customer by helping to produce a product or service. It is also known as ………………. .
(a) Primary Processes
(b) Secondary Processes
(c) Tertiary Processes
(d) Supporting Processes
Answer:
(a) Primary Processes
Question 6.
Secondary processes is a back core processes and functions within an organisation, is also known as ……………… .
(a) Management Processes
(b) Operational Processes
(c) Supporting Processes
(d) Helping Processes
Answer:
(c) Supporting Processes
Question 7.
Processes measure, monitor and control activities related to business procedures and system, is known as …………………… .
(a) Operational Processes
(b) Supporting Processes
(c) Management Processes
(d) Controlling Processes
Answer:
(c) Management Processes
Question 8.
Management Processes do not provide value directly to the customer but has a direct impact on ……………….. .
(a) operation of the enterprise
(b) efficiency of the management
(c) efficiency of the enterprise
(d) effectiveness of the enterprise
Answer:
(c) efficiency of the enterprise
Question 9.
……………………. is the technology-enabled automation of activities that accomplish a specific function and can be implemented for many different functions of company activities including sales, management, operations, HA etc.
(a) Business Processes
(b) Business Processes Technology
(c) Business Process Automation
(d) Automated Business Technology
Answer:
(c) Business Process Automation
Question 10.
Business Process Automation is a process of ………………….. and then automating business processes.
(a) analyzing
(b) documenting
(c) optimizing
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
![]()
Question 11.
Success of any Business Process Automation (BPA) shall only be achieved when BPA ensures the
(a) Confidentiality
(b) Integrity and Availability
(c) Timeliness
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 12.
The ………………. is the flow of information, customized by value-added tasks, that begins with the primary contact with a potential customer and continues through deliverance of a finished product.
(a) Business Process
(b) Business Information Process
(c) Business Process Automation
(d) Automated Business Control
Answer:
(a) Business Process
Question 13.
………………. may be defined as a process, effected by an entity’s BOD, management, and other personnel, applied In strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risk to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives.
(a) Information Risk Management
(b) Align Risk Appetite and Strategy
(c) Entitys Risk Management
(d) Enterprise Risk Management
Answer:
(d) Enterprise Risk Management
Question 14.
Enterprise Risk Management provides a framework for management to ……………….. .
(a) effectively deal with uncertainty
(b) associated risk and opportunity
(c) enhance Its capacity to build value
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 15.
Enterprise Risk Management consists of ………………….. interrelated components. Such components are derived from the way management runs a business, arid are integrated with the management process.
(a) Four
(b) Five
(c) Seven
(d) Eight
Answer:
(d) Eight
![]()
Question 16.
Which of the following is not a component of Enterprise Risk Management?
(a) Internal Management
(b) Event Identification
(c) Organ Isatlonal Ctart
(d) Objective Setting.
Answer:
(c) Organ Isatlonal Ctart
Question 17.
Risk is any event that may result in a significant deviation from a …………………………. resulting in an unwanted negative consequence.
(a) Planned Objective
(b) Unplanned Objective
(c) Planned Consequences
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Planned Objective
Question 18.
………………….. is defined as policies, procedures, practices and organisation structure that are designed to provide reasonable assurance that business objectives are achieved and undesired events are prevented or detected and corrected.
(a) Risk Assessments
(b) Monitoring
(c) Operation
(d) Control
Answer:
(d) Control
Question 19.
…………….. defines the system of internal control as the plan of enterprise arid all the methods and procedures adopted by the management of an entity to assist achieving management’s objective of ensuring, as far as practicable, the orderly and efficient conduct of Its business.
(a) SA-310
(b) SA-315
(c) SA-320
(d) SA-700
Answer:
(b) SA-315
Question 20.
An Internal Control System:
(a) Facilitate the effectiveness and efficiency of operations.
(b) Assists compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
(c) Helps safe guarding the assets of the entity.
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 21.
Which one of the following ¡s not an objective of Internal Control?
(a) Compliance with applicable laws and regulations
(b) Meeting Sales Target
(c) Effectiveness and efficiency of operations
(d) Reliability of reporting.
Answer:
(b) Meeting Sales Target
Question 22.
The extent and nature of the risks to internal control vary depending on the nature and characteristics of the ……………….. .
(a) entity’s Information system
(b) entity’s control system
(c) entity’s management system
(d) entity’s risk control system
Answer:
(a) entity’s Information system
Question 23.
According to ………………. explains tine components of any internal control as they relate to a financial statement audit.
(a) SA-300
(b) SA – 305
(c) SA- 310
(d) SA- 315
Answer:
(d) SA- 315
Question 24.
Flowcharts are used in designing and documenting simple processes or ……………… .
(a) Progress
(b) Production
(c) Procedures
(d) Programs
Answer:
(d) Programs
![]()
Question 25.
Most common type of boxes used in a flow chart.
(a) A decision, usually denoted as a diamond
(b) A processing step, usually called activity, and denoted as a rectangular box
(c) A control step, usually denoted as circular box.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 26.
A flowchart is described as ……………… when the page is divided Into different swim lanes describing the control of different organizatioial units.
(a) Activity function
(b) Mutual-functional
(c) Cross-functional
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Cross-functional
Question 27.
Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) show the flow of data or information from
(a) beginning to the end
(b) one place to another
(c) establishment to customer
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) one place to another
Question 28.
…………………. is the methodical process of defining options that are provided. When any software is installed, value for various parameters should be set up as per policies and business process workflow and business process rules of the enterprise
(a) Master
(b) Transactions
(c) Control Objectives
(d) Configuration
Answer:
(d) Configuration
Question 29.
…………………………. refer to the actual transactions entered through menus and functions in the application software, through which all transactions for specific modules are initiated, authorised or approved.
(a) Master
(b) Transactions
(c) Control Objectives
(d) Configuration.
Answer:
(b) Transactions
Question 30.
A process of obtaining and managing the raw materials needed for manufacturing a product or providing a servce. is known as …………….. .
(a) Purchase to Pay P2P,
(b) Order to Cash or O2C
(c) Master O2C
(d) Transactions O2C
Answer:
(a) Purchase to Pay P2P,
![]()
Question 31.
A set of business processes that involve receiving and fulfilling customer requests for goods or services, is called.
(a) Purchase to pay or P2P
(b) Order to cash or 02C
(c) Master O2C
(d) Transaction O2C.
Answer:
(d) Transaction O2C.
Question 32.
A process of accurately trackIng the on-hand inventory levels for an enteyprise,is known as ………………… .
(a) Inventory Control
(b) Stock Process and Control
(c) inventory Cycle
(d) Masters-Inventory
Answer:
(c) inventory Cycle
Question 33.
…………………….. process refers to the process of recording the transactions In the system t finally generating the reports from financial transactions in the system.
(a) Inventory Cycle
(b) General Ledger
(c) Fixed Asset Cycle
(d) Master-General Ledger
Answer:
(b) General Ledger
Question 34.
Which one of the following Is not defined as Sensitive Personal Information?
(a) Home address
(b) Financial information
(c) Biometric information
(d) Password
Answer:
(a) Home address
Question 35.
Which one of the following deals with Section 143 of the Companies Act, 2013?
(a) Powers and duties at auditors and auditing standards
(b) Acquisition and Mergers
(c) Powers and duties of Board of Directors
(d) Penalties due to non-compliance.
Answer:
(a) Powers and duties at auditors and auditing standards
![]()
Question 36.
……………………. is the framework of rules and practices by which a board of directors ensures accountability, fairness, and transparency in a company’s relationship with its all stakeholders.
(a) Management’s Framework
(b Privacy Policy
(c) Risk Monitoring
(d) Corporate Governance
Answer:
(d) Corporate Governance