Students should practice Working Capital Management – CS Executive Financial and Strategic Management MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Working Capital Management – Financial and Strategic Management MCQ
Question 1.
Working capital is also known as___
(A) Operation capital
(B) Operating capital
(C) Current assets capital
(D) Capital relating to main projects of the company
Answer:
(B) Operating capital
Question 2.
Positive working capital means that __
(A) The company is able to pay off its long-term liabilities.
(B) The company is able to select profitable projects.
(C) The company is unable to meet its short-term liabilities.
(D) The company is able to pay off its short-term liabilities.
Answer:
(D) The company is able to pay off its short-term liabilities.
Question 3.
Working capital =
(A) Core current assets less current liabilities
(B) Core current assets less core current liabilities
(C) Liquid assets less current liabilities
(D) Current assets less current liabilities
Answer:
(D) Current assets less current liabilities
Question 4.
Other things remaining constant, if the debtors increase as compared to last year it means –
(A) Company has a poor credit policy
(B) Company has a positive working capital
(C) Company has a negative working capital
(D) Company has no working capital
Answer:
(B) Company has a positive working capital
Question 5.
Which of the following will be considered while calculating working capital?
(1) Short Term Advances
(2) Stock of WIP
(3) Short Term Investments
(4) Perpetual inventory policy
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(A) (2) & (3)
(B) (1) & (3)
(C) (1),(2)&(3)
(D) All of the above except (4)
Answer:
(D) All of the above except (4)
Question 6.
Contingencies are –
(A) Added to gross working capital
(B) Deducted from gross working capital
(C) Contingencies are not considered in financial management; it is considered in accounts only
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Added to gross working capital
Question 7.
For reducing and controlling working capital requirement which of the following step is required to be taken –
(A) Increase in manufacturing cycle
(B) Increase of credit period allowed by creditors to the extent that does not affect the production.
(C) Increase in credit period given to customers
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(B) Increase of credit period allowed by creditors to the extent that does not affect the production.
Question 8.
Working capital is a highly effective barometer of a company’s efficiency and effectiveness.
(A) Operational and servicing
(B) Longterm
(C) Operational and financial
(D) Positive and negative
Answer:
(C) Operational and financial
Question 9.
Statement I:
Maintaining adequate working capital is not just important in the short term. Sufficient liquidity must be maintained in order to ensure the survival of the business in the long term as well.
Statement II:
Even a profitable business may fail if it does not have the adequate cash flow to meet its liabilities as they fall due.
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(A) Statement I is correct while Statement II is incorrect.
(B) Statement II is correct while Statement I is incorrect.
(C) Both Statement I and Statement II Eire correct.
(D) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Answer:
(C) Both Statement I and Statement II Eire correct.
Question 10.
While calculating working capital based on cash cost –
(A) Depreciation is ignored
(B) Non-cash items are not considered
(C) Debtors are calculated on the basis of the cost of goods sold and not on sale price
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 11.
Negative working capital means that –
(A) The company has no current assets at all
(B) The company currently is unable to meet its short-term liabilities
(C) The company has negative earnings before interest and tax
(D) The company currently is able to meet its short-term liabilities
Answer:
(B) The company currently is unable to meet its short-term liabilities
Question 12.
Which of the following analyzes the accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable cycles in terms of a number of days?
(A) Operation cycle
(B) Current asset cycle
(C) Operating cycle
(D) Business cycle
Answer:
(C) Operating cycle
Question 13.
Which of the following method is not used for calculating the working capital cycle?
(A) Percentage of sales method
(B) Regression analysis method
(C) Operating cycle approach
(D) Trial and error method
Answer:
(D) Trial and error method
Question 14.
Which of the following is the correct formula to calculate WIP Conversion Period?
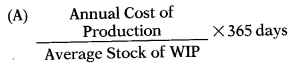
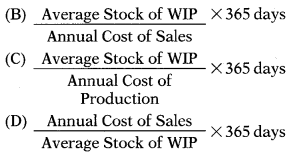
Answer:
(C)
Question 15.
Initial Working Capital
(A) Supplies the funds necessary to meet the current working expenses.
(B) Is used to raise the volume of production by improvement or extension of machinery.
(C) Is required at the time of the commencement of business
(D) Represents the amount utilized at the time of contingencies.
Answer:
(C) Is required at the time of the commencement of business
Question 16.
Which of the following is determinant of working capital?
(1) Nature and size of business
(2) Manufacturing cycle
(3) Credit policy
(4) Production policy
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(A) (1) only
(B) (1) and (2) only
(C) (1), (2), and (3) only
(D) (1), (2), (3), and (4)
Answer:
(D) (1), (2), (3) and (4)
Question 17.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) A desire to maintain an established dividend policy may affect the volume of working capital.
(B) Changes in working capital may bring about an adjustment of dividend policy.
(C) Payment of dividend may reduce cash in current assets consider-ably which in turn may reduce the available working capital for the company.
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 18.
Regular Working Capital:
(A) Supplies the funds necessary to meet the current working expenses le. for purchasing raw material and supplies, payment of wages, salaries, and other sundry expenses.
(B) Refers to the firm’s investment in current assets.
(C) Is amount over and above the per¬manent level of working capital
(D) Refers to the difference between current asset and Current liabilities
Answer:
(A) Supplies the funds necessary to meet the current working expenses le. for purchasing raw material and supplies, payment of wages, salaries, and other sundry expenses.
Question 19.
Which of the following is the correct formula to calculate working capital leverage?
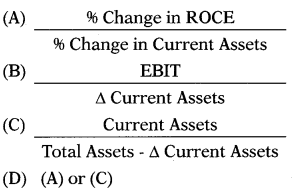
Answer:
(D)
Question 20.
One of the important objective(s) of working capital management is/are –
(A) To maintain the optimum levels of investment in current assets.
(B) To reduce the levels of current liabilities
(C) Improve the return on capital employed
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 21.
Fluctuating Working Capital is also called as –
(A) Reserve Margin Working Capital
(B) Temporary Working Capital
(C) Permanent Working Capital
(D) Variable working capital
Answer:
(D) Variable working capital
Question 22.
Operating cycle is also called as –
(A) Working cycle
(B) Business cycle
(C) Current asset cycle
(D) Working capital cycle
Answer:
(D) Working capital cycle
Question 23.
For reducing and controlling working capital requirement which of the following step is required to be taken –
(I) Reduction of the manufacturing cycle.
(II) Increase of credit period allowed by creditors to the extent that does not affect the production.
(Ill) Reduction in credit period given to customers.
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(A) (I) &(III)
(B) (II) & (III)
(C) (I) & (II)
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 24.
The capital which is needed to meet the seasonal requirements of the business –
(A) Gross Working Capital
(B) Reserve Margin Working Capital
(C) Net working capital
(D) Fluctuating Working Capital
Answer:
(D) Fluctuating Working Capital
Question 25.
A higher current assets/fixed assets ratio indicates –
(A) Hedging Approach
(B) Conservative Approach
(C) Matching/hedging Approach
(D) Aggressive Approach
Answer:
(B) Conservative Approach
Question 26.
The aggressive approach covers those policies –
(A) Where the firm relies heavily on short term bank finance
(B) Seeks to increase dependence on long-term financing.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer:
(A) Where the firm relies heavily on short term bank finance
Question 27.
Gross working capital refers to –
(A) The amount utilized at the time of contingencies.
(B) The firm’s investment in current assets.
(C) The capital which is required at the time of the commencement of business.
(D) The working capital which is necessary on a continuous and uninterrupted basis.
Answer:
(B) The firm’s investment in current assets.
Question 28.
A conservative policy implies –
(A) Greater liquidity and lower risk
(B) Greater risk and lower liquidity
(C) Negligible risk
(D) No risk at all with low liquidity
Answer:
(A) Greater liquidity and lower risk
Question 29.
If a firm has insufficient working capital and tries to increase sales, it can easily over-stretch the financial resources of the business. This is called –
(A) Over rating
(B) Overtrading
(C) Overcoming
(D) Overtone
Answer:
(B) Overtrading
Question 30.
Which of the following represents the amount utilized at the time of contingencies?
(A) Reserve Working Capital
(B) Net working capital
(C) Extra working capital
(D) Fixed working capital
Answer:
(A) Reserve Working Capital
Question 31.
Permanent Working Capital is also known as –
(A) Fixed working capital
(B) Temporary working capital
(C) Long term funds
(D) Gross margin working capital
Answer:
(A) Fixed working capital
Question 32.
A lower current assets/fixed assets ratio means –
(A) Matching/hedging Approach
(B) Aggressive current assets policy
(C) Riskier current assets policy
(D) Conservative current assets pol-icy
Answer:
(B) Aggressive current assets policy
Question 33.
Any amount over and above the permanent level of working capital is known as working capital.
(A) Temporary
(B) Fluctuating
(C) Variable
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 34.
Current assets are those assets –
(A) Which can be sold by the companies.
(B) Which are less important from a production angle.
(C) Which are held by the companies to pay off current liabilities.
(D) Which are converted into cash within a period of one year.
Answer:
(D) Which are converted into cash within a period of one year.
Question 35.
Current assets are usually financed through –
(A) equity capital, preference capital, debentures, bonds, and long-term bank loans.
(B) (A) and (C)
(C) mode of the overdraft, cash credit, public deposits, etc.
(D) money market instrument and long-term securities.
Answer:
(C) mode of the overdraft, cash credit, public deposits, etc.
Question 36.
To carry on a business, a certain minimum level of working capital is necessary on a continuous and uninterrupted basis. This requirement is referred to as –
(A) Permanent working capital
(B) Long term working capital
(C) Fixed working capital
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Question 37.
Which of the following is/are methods of maximum permissible bank finance as recommended by the Tandon Committee?
(A) 75% of (Current Assets – Current Liabilities)
(B) 50% of (Current Assets – Current Liabilities)
(C) 75% of (Core Current Assets – Current Liabilities)
(D) 50% of (Core Current Assets – Current Liabilities)
Answer:
(A) 75% of (Current Assets – Current Liabilities)
Question 38.
_____varies inversely with profitability.
(A) Liquidity
(B) Risk
(C) Gross profit
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Liquidity
Question 39.
____refers to the difference between current asset and current liabilities.
(A) Differential working capital
(B) Net working capital
(C) Operation working capital
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B) Net working capital
Question 40.
Permanent working capital –
(A) Varies with seasonal needs.
(B) Includes fixed assets.
(C) Is the number of current assets required to meet a firm’s long-term minimum needs.
(D) Includes accounts payable.
Answer:
(C) Is the number of current assets required to meet a firm’s long-term minimum needs.
Question 41.
Financing a long-lived asset with short-term financing would be
(A) an example of “moderate risk – moderate (potential) profitability” asset financing.
(B) an example of “low risk – low (potential) profitability” asset financing.
(C) an example of “high risk – high (potential) profitability” asset financing.
(D) an example of the “hedging approach” to financing.
Answer:
(C) an example of “high risk – high (potential) profitability” asset financing.
Question 42.
Hardcore working capital is also known as –
(A) Hard current assets
(B) Core current assets
(C) Core current liabilities
(D) Hard current liabilities
Answer:
(B) Core current assets
Question 43.
An aggressive policy indicates –
(A) Higher liquidity and poor-risk
(B) Higher risk and poor liquidity
(C) Higher risk and higher liquidity
(D) Lower risk with lower liquidity
Answer:
(B) Higher risk and poor liquidity
Question 44.
Tandon Committee Report on Working Capital relates to norms for
(A) Inventory and receivables bank finance as recommended by the Tandon Committee?
(B) Gross profit and inventory
(C) Receivable, gross profit, and inventory
(D) Net profit and receivables
Answer:
(A) Inventory and receivables bank finance as recommended by the Tandon Committee?
Question 45.
In deciding the appropriate level of current assets for the firm, management is confronted with –
(A) Trade-off between profitability and risk.
(B) Trade-off between liquidity and marketability.
(C) Trade-off between equity and debt.
(D) Trade-off between short-term versus long-term borrowing.
Answer:
(A) Trade-off between profitability and risk.
Question 46.
Which of the following is not correct with the matching strategy?
(A) All assets should be financed with permanent long-term capital.
(B) Temporary current assets should be financed with temporary working capital.
(C) Long-term assets should be Financed from long-term capital.
(D) Permanent current assets should be financed with permanent working capital.
Answer:
(A) All assets should be financed with permanent long-term capital.
Question 47.
The paucity of working capital may lead to a situation where –
(A) The firm may not be able to its long term finance
(B) The firm may not be able to meet its liabilities
(C) The firm may not be able to achieve its sale target
(D) The firm may take on some different projects with a low internal rate of return.
Answer:
(B) The firm may not be able to meet its liabilities
Question 48.
Which of the following is/are method of maximum permissible
(A) [50% of (Current Assets – Core Current Assets)] – Current Liabilities
(B) [7596 of (Core Current Assets – Current Assets)] – Current Liabilities
(C) [7596 of (Current Assets – Core Current Assets)] – Current Liabilities
(D) [8096 of (Current Assets – Core Current Assets)] – Current Liabilities
Answer:
(C) [7596 of (Current Assets – Core Current Assets)] – Current Liabilities
Question 49.
What is the difference between the current ratio and the quick ratio?
(A) The current ratio includes inventory and the quick ratio does not.
(B) The current ratio does not include inventory and the quick ratio does.
(C) The current ratio includes physical capital and the quick ratio does not.
(D) The current ratio does not include physical capital and the quick ratio does.
Answer:
(A) The current ratio includes inventory and the quick ratio does not.
Question 50.
It is understood that a current ratio of _____ for a manufacturing firm implies that the firm has an optimum amount of working capital.
(A) 1 (one)
(B) 2 (two)
(C) 3 (three)
(D) 2.5 (two and half)
Answer:
(B) 2 (two)
Question 51.
If raw material consumed is ₹ 8,42,000; cost of production is ₹ 14,25,000; Stock of raw material & WIP is ₹ 1,24,000 and ₹ 72,000 respectively then Raw Material Conversion period will be –
Note: 1 Year = 365 days
(A) 54 days
(B) 18 days
(C) 29 days
(D) 49 days
Hint:
Raw material conversion period:
\(\frac{\text { Raw Material Stock }}{\text { Raw Material Consumed }}\) × 365 = \(\frac{1,24,000}{8,42,000}\) × 365 = 54 days
Answer:
(A) 54 days
Question 52.
Calculate the working capital from the following data:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Raw Material Stock | 11,70,000 |
| WIP Stock | 9,58,750 |
| Finished Goods Stock | 26,65,000 |
| Debtors | 55,12,000 |
| Cash & Bank | 6,00,000 |
| Creditors | 17,55,000 |
| Outstanding expenses | 14,95,000 |
(A) 76,75,550
(B) 76,55,750
(C) 75,65,750
(D) 77,55,650
Hint:
Working capital = 11,70,000 + 9,58,750 + 26,65,000 + 55,12,000 + 6,00,000 – 17,55,000 – 14,95,000 = 76,55,750
Answer:
(B) 76,55,750
Question 53.
Annual credit sales = ₹ 19,50,000
Cash sales = ₹ 11,50,000
Debtors = ₹ 1,60,000
Bills receivable = ₹ 1,00,000
Finished goods = ₹ 11,22,000
Collection Period = ₹
Note: 1 Year = 360 days
(A) 29 days
(B) 30 days
(C) 48 days
(D) Data given is not sufficient
Hint:
Debtors Collection Period:
\(\frac{\text { Debtors }}{\text { Annual Credit Sales }}\) × 360 = \(\frac{2,60,000}{19,50,000}\) × 360 = 48 days
Answer:
(C) 48 days
Question 54.
Financial statement of A Ltd. shows the following data:
Opening stock ₹ 1,75,000, Total purchase ₹ 10,75,000 including cash purchase ₹ 1,75,000, total sales ₹ 15,00,000 out of which 2096 are on cash basis. Closing stock is ₹ 1,50,000. Stock turnover ratio =?
(A) 7.67
(B) 6.77
(C) 7.76
(D) 7.66
Hint:
Stock turnover ratio:
\(\frac{\text { Material Consumed }}{\text { Average Stock }}=\frac{11,00,000}{1,62,500}\) = 6.77
Answer:
(B) 6.77
Question 55.
WIP Conversion Period = 18 days
Raw Material Consumed = ₹ 8,42,000
Stock of WIP = ₹ 72,000
Cost of Production = ?
(A) ₹ 14,00,000
(B) ₹ 22,67,000
(C) ₹ 5,83,000
(D) ₹ 14,60,000
Hint:
WIP Conversion Period:
\(\frac{\text { Average Stock of WIP }}{\text { Annual Cost of Production }}\) × 360 days
18 = \(\frac{72,000}{x}\) × 365 days
x = Annual Cost of Production = 14,60,000
Answer:
(D) ₹ 14,60,000
Question 56.
A Ltd. financial statement shows the following data:
Equity ₹ 5,67,500, Reserve & surplus ₹ 3,87,850, total debt ₹ 5,88,778 out of which ₹ 2,88,778 are long term debt, fixed assets are ₹ 11,44,128.
Current Ratio =?
(A) 2.48
(B) 1.92
(C) 3.68
(D) 1.33
Hint:
Current liabilities = 5,88,778 – 2,88,778 = 3,00,000
Total assets = 5,67,500 + 3,87,850 + 5,88,778 = 15,44,128
Current assets = 15,44,128 – 11,44,128 = 4,00,000
Current ratio = \(\frac{4,00,000}{3,00,000}\) = 1.33
Answer:
(D) 1.33
Question 57.
Total sales of OLX Ltd. are ₹ 31,248 out of which 2596 are cash sales. The closing balance of debtors is ₹ 9,468. Debtors collection period =?
Note: 1 Year = 365 days
(A) 4.2 months
(B) 157 days
(C) 148 days
(D) 4.43 months
Hint:

Answer:
(C) 148 days
Question 58.
Raw material consumption = ₹ 6,48,000
Raw material purchase = ₹ 8,42,000
Annual cost of production = ₹ 14,42,000
Creditors = ₹ 75,000
Bills payable = ₹ 25,000
Creditors Payment Period = ?
Note: 1 Year = 360 days
(A) 34 days
(B) 43 days
(C) 40 days
(D) 39 days
Hint:
Creditors Payment Period:
\(\frac{\text { Accounts Payable }}{\text { Annual credit purchase }}\) × 365 days = \(\frac{1,00,000}{8,42,000}\) × 365 days = 43 days
Answer:
(B) 43 days
Question 59.
The following information is available for your calculation.
Level of activity = 1,56,000 units
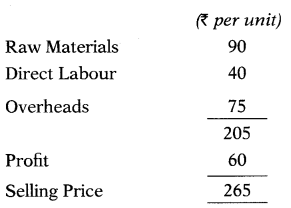
Raw materials are in stock on average for two months and Materials are in process, on average half a month.
Calculate the value of ‘Raw Material Stock’ for working capital purposes.
(A) ₹ 26,65,000
(B) ₹ 23,40,000
(C) ₹ 6,45,250
(D) ₹ 9,58,750
Hint:
Raw Material Stock (1,40,40,000 × \(\frac{2}{12}\)) = 23,40,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 23,40,000
Question 60.
From the following data calculate the finished goods conversion period for the years 2019 & 2020.
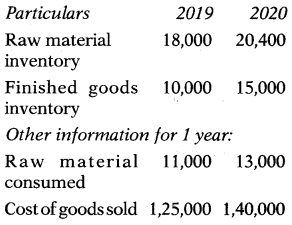
Note: 1 Year = 360 days
(A) 29 days & 39 days
(B) 39 days & 29 days
(C) 25 days & 35 days
(D) 35 days & 25 days
Hint:
Finished Goods Conversion Period:
\(\frac{\text { Stock of Finished Goods }}{\text { Annual Cost of Goods Sold }}\) × 360 days

Answer:
(A) 29 days & 39 days
Question 61.
Maximum permissible bank finance as per the first method of Tandon Committee norms was ₹ 57,41,813 while current liabilities are reported at ₹ 32,50,000. Current assets =?
(A) ₹ 1,09,05,750
(B) ₹ 81/79,313
(C) ₹ 1,09,07,550
(D) ₹ 1,05,09,750
Hint:
Maximum permissible bank finance as per first method = 75% of (Current Assets – Current Liabilities)
57,41,813 = 0.75 × (x – 32,50,000)
57,41,813 = 0.75 – 24,37,500
0.75 = 81,79,313
x= Current Assets = 1,09,05,750
Answer:
(A) ₹ 1,09,05,750
Question 62.
Current assets of Z Ltd. are ₹ 3,70,000 which includes stock ₹ 1,00,000 and prepaid expense ₹ 70,000. Its current liability are ₹ 1,60,000 which includes provision for tax ₹ 60,000.
Liquid Ratio =?
(A) 1.25
(B) 1.52
(C) 1.22
(D) 0.95
Hint:
Liquid ratio = \(\frac{\text { Liquid Assets }}{\text { Current Liabilities }}=\frac{2,00,000}{1,60,000}\) = 1.25
Answer:
(A) 1.25
Question 63.
The following information is provided by DPS Ltd. for the year ending 31st March 2019.
Raw material storage period 55 days WIP conversion period 18 days
Finished goods storage 22days period
Debt collection period 45 days
Creditor’s payment period 60 days
Annual operating cost including depreciation of ₹ 2,10,000 was ₹ 21,00,000.
[1 Year = 360 days]
You are required to calculate working capital on a cash cost basis.
(A) ₹ 4,20,000
(B) ₹ 4,66,667
(C) ₹ 7,35,000
(D) ₹ 8,16,667
Hint:
Operating Cycle Period = 55 + 18 +22 +45 – 60 80 days
Working Captial = \(\frac{\text { Operating Cost }}{360 \text { days }}\) × Operating Cycle days
= \(\frac{18,90,000}{360 \text { days }}\) × 80 days
= 4,20,000
Answer:
(A) ₹ 4,20,000
Question 64.
KT Ltd.’s opening stock was ₹ 2,50,000 and the closing stock was ₹ 3,75,000. Sales during the year were ₹ 13,00,000 and the gross profit ratio was 25% on sales. Average accounts payable are ₹ 80,000. Creditors Turnover Ratio =?
(A) 13.75
(B) 14.33
(C) 13.33
(D) 14.44
Hint:
| Sales | 13,00,000 |
| (-) Gross profit | (3,25,000) |
| Cost of goods sold | 9,75,000 |
2,50,000 + Cost of production/purchase – 3,75,000 = 9,75,000
Cost of production/purchase = 11,00,000
Creditors Turnover Ratio = \(\frac{11,00,000}{80,000}\) =13.75
Answer:
(A) 13.75
Question 65.
The raw material conversion period is 36 days. Raw material consumed and cost of goods sold in the year is ₹ 1,80,000 & ₹ 2,16,000 respectively. How much raw material stock will appear in the working capital statement?
Note: 1 Year = 360 days
(A) ₹ 18,000
(B) ₹ 20,000
(C) ₹ 21,600
(D) ₹ 19,800
Hint:
Raw material conversion period:
\(\frac{\text { Raw Material Stock }}{\text { Raw Material Consumed }}\) × 360
36 = \(\frac{x}{1,80,000}\) × 360
x = Raw Material Stock = 18,000
Answer:
(A) ₹ 18,000
Question 66.
Creditors payment period = 60 days
Material consumed = ₹ 1,20,000
Material purchased in cash = ₹ 10,000
Material purchased on = ₹ 90,000 credit
Creditors that will appear in balance sheet and working capital statement = ?
Note: 1 Year = 360 days
(A) ₹ 16,667
(B) ₹ 15,000
(C) ₹ 20,000
(D) ₹ 36,667
Hint:
Creditors payment period = \(\frac{\text { Creditors }}{\text { Credit purchase }}\) × 360
60 = \(\frac{\text { Creditors }}{90,000}\) × 360
Creditors = 15,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 15,000
Question 67.
Opening and closing balance of creditors are ₹ 2,00,000 & ₹ 2,40,000 respectively. Raw material purchased on credit was ₹ 11,00,000. Creditors payment period for the purpose of the working capital statement will be –
[l Year =360 days]
(A) 72 days
(B) 32 days
(C) 65 days
(D) 78 days
Hint:
Creditors payment period = \(\frac{\text { Average Creditors }}{\text { Credit purchase }}\) × 360
= \(\frac{2,20,000}{11,00,000}\) × 360
= 72 days
Answer:
(A) 72 days
Question 68.
N Ltd. gives the following information:
Current Ratio 2.8
Total assets ₹ 60,00,000
Fixed assets ₹ 32,00,000
Current liabilities =?
(A) ₹ 28,00,000
(B) ₹ 10,00,000
(C) ₹ 18,00,000
(D) ₹ 12,00,000
Hint:
Current assets = 60,00,000 – 32,00,000 = 28,00,000
2.8 = \(\frac{28,00,000}{x}\)
x = Current liabilities = 10,00,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 10,00,000
Question 69.
N Ltd. gives the following information:
Liquid ratio 1.6
Current Assets ₹ 28,00,000
Current Liabilities ₹ 10,00,000
Stock = ? .
(A) ₹ 28,00,000
(B) ₹ 10,00,000
(C) ₹ 18,00,000
(D) ₹ 12,00,000
Hint:
Liquid Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Current Assets – Stock }}{\text { Current Liabilities }}\)
1.6 = \(\frac{28,00,000-\text { Stock }}{10,00,000}\)
Stock = 12,00,000
Answer:
(D) ₹ 12,00,000
Question 70.
S Ltd. gives the following information:
Networking capital ₹ 2,80,000
Current ratio 2.4
Liquid ratio 1.6
Current Assets =?
(A) ₹ 2,00,000
(B) ₹ 2,80,000
(C) ₹ 4,80,000
(D) ₹ 3,60,000
Hint:
Current Ratio =\(\frac{x}{y}\)
2.4y = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
2.4y = x
Working Capital = CA – CL
2,80,000 = 2.4y – y
2,80,000 = 1.4y
y = 2,00,000
x = Current Assets = 2,00,000 × 2.4 = 4,80,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 4,80,000
Question 71.
Debtors as per working capital statement = ₹ 3,00,000
Debtors collection period = 45 days
Gross profit ratio = 20%
Cash sales = ₹ 5,00,000
Note: 1 Year = 365 days Total sales = ?
(A) ₹ 24,00,000
(B) ₹ 19,00,000
(C) ₹ 29,00,000
(D) ₹ 25,00,000
Hint:
Debtors Collection Period = \(\frac{\text { Debtors }}{\text { Credit Sales }}\) × 365 days
45 = \(\frac{3,00,000}{\text { Credit Sales }}\) × 365 days
Credit Sales = 24,00,000
Total sales = 24,00,000 + 5,00,000 = 29,00,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 29,00,000
Question 72.
The operating cycle days of Ramji Ltd. is 167 days. Other details are as follows:
Raw material stock velocity 79 days
Debtors collection period 70 days
WIP conversion period 3 6 days
Finished goods 29 days
conversion period
Creditors payment period =?
(A) 47 days
(B) 94 days
(C) 52 days
(D) 59 days
Hint:
Let the creditors payment period be ‘x’.
79 + 70 + 36 + 29 – x = 167
– x = – 47
x = Creditors payment period = 47 days
Answer:
(A) 47 days
Question 73.
Operating cost is ₹ 18,90,000.
Current assets are ₹ 5,20,000
Current liabilities are ₹ 1,00,000
Operating cycle days =?
(Assume a 360 day year.)
(A) 80 days
(B) 99 days
(C) 19 days
(D) 70 days
Hint:
Working capital = 5,20,000 – 1,00,000 = 4,20,000
Working Capital = \(\frac{\text { Operating Cost }}{360 \text { days }}\) × Operating Cycle days
4,20,000 = \(\frac{18,90,000}{360 \text { days }}\) × Operating Cycle days
Operating Cycle days = 80 days
Answer:
(A) 80 days
Question 74.
NS Ltd. gives the following information:
Current Ratio = 2.4
Quick Ratio =1.0
Stock = ₹ 5,60,000
Current Assets = ?
(A) ₹ 9,60,000
(B) ₹ 6,90,000 .
(C) ₹ 4,00,000
(D) ₹ 4,60,000
Hint:
Current Ratio = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
2.4 = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
2.4y = x
Quick Ratio = \(\)
1 = \(\)
y = 4,00,000
x Current Assets = 4,00,000 × 2.4 = 9,60,000
Answer:
(A) ₹ 9,60,000
Question 75.
Gross profit ratio = 20%.
Stock velocity = 6 month
Gross profit for the year ended amounts to ₹ 5,00,000. The stock of the year is ₹ 20,000 more than what it was at the beginning of the year.
Closing stock =?
(A) ₹ 10,00,000
(B) ₹ 9,90,000
(C) ₹ 10,10,000
(D) ₹ 10,20,000
Hint:
| Sales | 25,00,000 |
| (-) Gross profit 20% | (5,00,000) |
| Cost of goods sold | 20,00,000 |
Stock velocity = \(\frac{\text { Average Stock }}{\text { Cost of goods sold }}\) × 12
6 = \(\frac{x}{20,00,000}\) ×12
x = Average Stock 10,00,000
Let Opening stock be = x
Closing stock = x + 20,000
Average Stock = \(\frac{\text { Opening Stock }+\text { Closing stock }}{2}\)
10,00,000 = \(\frac{x+(x+20,000)}{2}\)
20,00,000 = 2x + 20,000
19,80,000 = 2x
x = Opening stock 9,90,000
Closing stock = 9,90,000 + 20,000 = 10,10,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 10,10,000
Question 76.
No. of operating cycle in a year=4.5
No. of days in year = 360 days
Working capital = 8,40,000
Operating cost =?
(A) ₹ 35,00,000
(B) ₹ 37,80,000
(C) ₹ 36,40,000
(D) ₹ 38,80,000
Hint:
No. of operating cycle in a year = \(\frac{360 \text { days }}{\text { Operating Cycle days }}\)
4.5 = \(\frac{360 \text { days }}{\text { Operating Cycle days }}\)
Operating Cycle days = 80 days
Working Capital = \(\frac{\text { Operating Cost }}{360 \text { days }}\) × Operating Cycle days
8,40000= \(\frac{\text { Operating Cost }}{360 \text { days }}\) × 80
Operating Cost = 37,80,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 37,80,000
Question 77.
If current assets are ₹ 1,09,05,750 and current liabilities are ₹ 32,50,000 then maximum permissible bank finance as per first method of Tandon Committee norms is –
(A) ₹ 57,41,813
(B) ₹ 49,29,313
(C) ₹ 52,29,813
(D) ₹ 49,41,813
Hint:
Maximum permissible bank finance as per Tandon Committee norms:
Method 1: 15% of (Current Assets – Current Liabilities)
= 0.75 × (1,09,05,750 – 32,50,000)
= 57,41,813
Answer:
(A) ₹ 57,41,813
Question 78.
Debtors velocity = 3 months Sales = ₹ 25,00,000
Bills receivable & Bills payable were ₹ 60,000 and ₹ 36,667 respectively.
Sundry debtors =?
(A) ₹ 6,25,000
(B) ₹ 5,25,000
(C) ₹ 5,65,000
(D) ₹ 6,65,000
Hint:
Debtors Velocity = \(\frac{\text { Account Receivable }}{\text { Credit Sales }}\) × 12
3 = \(\frac{x}{25,00,000}\) × 12
x = Account Receivable = 6,25,000
Debtors + Bills Receivable = Account Receivable
x + 60,000 = 6,25,000
x = Debtors = 5,65,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 5,65,000
Question 79.
Creditors velocity = 2 months.
Cost of goods sold = ₹ 20,00,000
Opening stock = ₹ 9,90,000
Closing stock = ₹ 10,10,000
Bills receivable & Bills payable were ₹ 60,000 and ₹ 36,667 respectively.
Creditors =?
(A) 3,36,667
(B) 3,66,333
(C) 3,30,367
(D) 3,00,000
Hint:
Opening stock + Purchase – Closing stock = Cost of goods sold
9,90,000 + x – 10,10,000 = 20,00,000 .
x = Purchase = 20,20,000
Creditors Velocity = \(\frac{\text { Accounts Payable }}{\text { Credit Purchases }}\) × 12
2 = \(\frac{x}{20,20,000}\) × 12
x = Accounts Payable = 3,36,667
Creditors + Bills Payable = Account Payable
x + 36,667 = 3,36,667
x = Creditors = 3,00,000
Answer:
(D) 3,00,000
Question 80.
If current assets are ₹ 1,09,05,750 and current liabilities are ₹ 32,50,000 then maximum permissible bank finance as per second method of Tandon Committee norms is ___
(A) ₹ 57,41,813
(B) ₹ 49,29,313
(C) ₹ 52,29,813
(D) ₹ 49,41,813
Hint:
Maximum permissible bank finance as per Tandon Committee norms:
Method 2: 15% of Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= (0.75 × 1,09,05,750) – 32,50,000
= 49,29,313
Answer:
(B) ₹ 49,29,313
Question 81.
When the current ratio is 2:5, and the amount of current liabilities is ₹ 25,000, what is the amount of current assets?
(A) ₹ 62,500
(B) ₹ 12,500
(C) ₹ 10,000
(D) None of these
Answer:
(C) ₹ 10,000
Question 82.
Toted ‘cost of sales’ and ‘sales’ of Gama Ltd. is ₹ 3,19,80,000 and ₹ 4,13,40,000 respectively. It makes 20% sales on a cash basis. Debtors are allowed 2 months credit period. If the company calculates working capital on a cash cost basis then debtors are __
(A) ₹ 55,12,000
(B) ₹ 42,12,000
(C) ₹ 42,64,000
(D) ₹ 55,64,000
Hint:
| Total Cost | 3,19,80,000 |
| (-) 20% Cash Sales Cost | (63,96,000) |
| Cost of Credit Sales | 2,55,84,000 |
Debtors = (2,55,84,000 × \(\frac{2}{12}\)) = 42,64,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 42,64,000
Question 83.
If credit sales for the year are ₹ 5,40,000 and Debtors at the end of the year are ₹ 90,000 the Average Collection Period will be?
Note: 1 year = 365 days
(A) 30 days
(B) 61 days
(C) 90 days
(D) 120 days
Answer:
(B) 61 days
Question 84.
Total wages for the year of Rakshit Ltd., a listed company are ₹ 64,80,000 out of which ₹ 2,40,000 are paid in cash immediately after they became due.
Lag in payment of wages -1 month. If you are appointed to prepare a working capital statement for the company, then how much outstanding wages you will take while preparing a working capital statement?
(A) ₹ 5,40,000
(B) ₹ 5,50,000
(C) Not enough data
(D) ₹ 5,20,000
Hint:
Wages on credit = 64,80,000 – 2,40,000 = 62,40,000
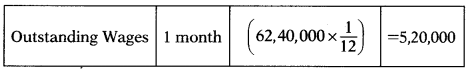
Answer:
(D) ₹ 5,20,000
Question 85.
K Ltd. had sales last year of ₹ 26,50,000, including cash sales of ₹ 2,50,000. If its average collection period was 36 days, its ending accounts receivable balance is closest to
(Assume a 365 days year.)
(A) ₹ 2,40,000
(B) ₹ 2,36,712
(C) ₹ 2,63,127
(D) ₹ 2,40,721
Answer:
(A) ₹ 2,40,000
Question 86.
Outstanding overheads appearing in the balance sheet are 9,75,000. Lag in payment of overheads is 30 days. Overheads accrue evenly throughout the year. Total overheads incurred by the company are –
(A) ₹ 1,17,00,000
(B) ₹ 32,500
(C) ₹ 2,92,50,000
(D) ₹ 1,92,50,000
Hint:
Outstanding Overheads = \(\frac{\text { Total Overheads } \times \text { Lag in payment of overheads }}{360}\)
9,75,000 = Total Overheads × \(\frac{30}{360}\)
Total Overheads = 1,17,00,000
Answer:
(A) ₹ 1,17,00,000
Question 87.
From the information given below calculate the amount of fixed assets.
Fixed assets to proprietors fund = 1.25 Net Working Capital = ₹ 6,00,000
(A) 20,00,000
(B) 24,00,000
(C) 3,42,857
(D) 8,00,000
Hint:
Fixed Assets to Proprietors Funds = \(\frac{\text { Fixed Assets }}{\text { Proprietors Funds }}\)
1.25 = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
1.25 y = x
Proprietors Funds = Fixed Assets – Working Capital
y= 1.25y – 6,00,000
0.25y = 6,00,000
y = 24,00,000
Answer:
(B) 24,00,000
Question 88.
If a firm has ₹ 100 in inventories, a current ratio equal to 1.2, and a quick ratio equal to 1.1, what is the firm’s Net Working Capital?
(A) ₹ 10
(B) ₹ 100
(C) ₹ 200
(D) ₹ 1,200
Hint:
Current Ratio = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
1.2 = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
1.2y = x
Quick Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Current Assets – Stock }}{\text { Current Liabilities }}\)
1.1 = \(\frac{1.2 y-100}{y}\)
1.1y = 1.2y – 100
y= 1,000
x = Current Assets = 1,000 × 1.2 = 1,200
Working Capital = 1,200 – 1,000 = 200
Answer:
(C) ₹ 200
Question 89.
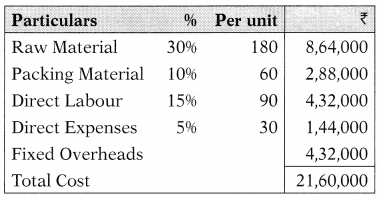
A company plans to manufacture andsell400unitsofdomesticappliances per month at a price of ₹ 600 each. The ratios of cost to selling price are:
| (% of the selling price) | |
| Raw materials | 30% |
| Packing material | 10% |
| Direct labor | 15% |
| Direct expenses | 5% |
Fixed overhead are ₹ 4,32,000 p.a.
Finished goods stock = 200 units
Working days in a year are taken as 300 days for the budget year. Norms maintained for work-in-progress is 7 days. Finished goods stock and WIP stock will appear in the balance sheet and working capital of the company at –
(A) ₹ 31,920; ₹ 80,000
(B) ₹ 80,000; ₹ 31,920
(C) ₹ 90,000; ₹ 67,200
(D) ₹ 90,000; ₹ 31,920
Hint:

Cost Structure for the year: (400 × 12 = 4,800 units)
Cost Structure for WIP:
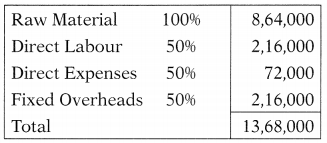
Note: Packing material will not be considered while calculating WIP.
Answer:
(D) ₹ 90,000; ₹ 31,920
Question 90.
Following is the balance sheet of PBX Ltd. Calculate maximum permissible bank finance by the Third Method of Tandon Committee norms. Assume the level of Core Current Assets to be ₹ 60 lakhs.
| Liabilities | ₹ Lakhs |
| Equity Shares (₹ 10 each) | 400 |
| Retained Earnings | 1,000 |
| Public Deposits | 200 |
| Trade Creditors | 160 |
| Bills Payable | 200 |
| 1,960 |
| Assets | ₹ Lakhs |
| Fixed Assets | 1,000 |
| Current Assets: Raw Material |
200 |
| Work-in-progress | 300 |
| Finished Goods | 150 |
| Debtors | 200 |
| Cash at Bank | 110 |
| 1,960 |
(A) ₹ 450 lakhs
(B) ₹ 360 lakhs
(C) ₹ 315 lakhs
(D) ₹ 425 lakhs
Hint:
Current Assets = 960 Lakhs; Current Liabilities = 360 Lakhs
Maximum permissible bank borrowing as per 3rd method of Tandon Committee norms:
= [75% of (Current Assets – Core Current Assets)] – Current Liabilities
= [0.75 × (960 – 60)] – 360
= 315 Lakhs
Answer:
(C) ₹ 315 lakhs
