Supply under GST – CA Final IDT Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Supply under GST – CA Final IDT Study Material
Question 1.
How the tax liability on composite and mixed supplies is determined under GST law? Answer in single sentence each. [Nov. 2017, 2 Marks]
Answer:
As per section 8 of CGST Act, 2017:
Composite Supply
- As per Section 8(a), “Composite supply comprising two or more supplies, one of which is a principal supply, shall be treated as a supply of such principal supply.”
- Thus, tax liability shall be on the basis of rate of GST Principal supply.
Mixed Supply
- As per Section 8(b), “A mixed supply comprising of two or more supplies shall be treated as supply of that particular supply that attracts highest rate of tax.”
- Thus, tax liability shall be on the basis of that supply that attracts highest rate of tax.
Question 2.
Sharma Carriers is a Good Transport Agency engaged in transportation of goods by road. As per the general business practice, Sharma carriers also provides intermediary and ancillary services like loading/ unloading, packing/ unpacking, transhipment and temporary warehousing in relation to transportation of goods by road.
With reference to the provisions of GST law, analyse whether such services are to be treated as part of the GTA services, being a composite supply or as mixed supply. [Nov. 2018 (Old), 5 Marks]
Answer:
Facts of the given Case Study
- Sharma Carriers (Good Transport Agency) is engaged in transportation of goods by road.
- It also provides intermediary and ancillary services.
- Question arises whether such services are to be treated as part of the GTA services. (composite supply or mixed supply)
Related Provisions
(a) As per Section 2(30) of the CGST Act, 2017:
- Composite supply means a supply made by a taxable person to a recipient
- consisting of two or more taxable supplies of goods or services or both, or any combination thereof
- which are naturally bundled and supplied in conjunction with each other in the ordinary course of business
- one of which is a principal supply.
(b) As per Section 2(74) of the CGST Act, 2017 :
- Mixed supply means two or more individual supplies of goods or services, or any combination thereof,
- made in conjunction with each other
- by a taxable person for a single price
- where such supply does not constitute a composite supply.
Decision
Principal Service: Transportation of goods by road.
Other Service: intermediary and ancillary services.
- The various Intermediary and ancillary services provided by GTA are not provided as independent services but as ancillary to the principal service, namely, transportation of goods by road.
- The invoice issued by the GTA includes the value of intermediary and ancillary services.
- Thus, any intermediary and ancillary service would form part of the GTA service, and thus will be composite supply.
Examiner’S Comment
Most of the examinees exhibited lack of knowledge of the provisions relating to composite and mixed supply and thus, failed to elaborate the conditions to be satisfied for a supply to be classified as a composite supply and mixed supply.
![]()
Question 3.
A professional training institute gets its training material printed from a printing press. The content of the material is provided by the training institute who owns the usage rights of the same while the physical inputs including paper used for printing belong to the printer.
Ascertain whether supply of training material by the printing press constitutes supply of goods or supply of services. [MTP, May 2018, 5 Marks]/[RTP, Nov. 19, 5 Marks]
Answer:
Facts of the given Case Study
- A printing press supplies printing services.
- Content of the material is provided by the recipient of service.
- Paper and other physical inputs belong to the printer.
- The question is whether it is supply of goods or services.
Related Provisions
(a) As per Circular No. 11/11/2017 GST dated 20.10.2017:
The supply of books printed with contents supplied by the recipient of such printed goods is a composite supply and the question, whether such supplies constitute supply of goods or services would be determined on the basis of what constitutes the principal supply.
(b) As per section 2(90) of the CGST Act:
Principal supply is the supply of goods or services which constitutes the predominant element of a composite supply and to which any other supply forming part of that composite supply is ancillary.
Decision
- Supply of printing (of the content supplied by the recipient of supply) is the principal supply.
- Therefore, such supplies would constitute supply of service.
Question 4.
X, a registered dealer offers a Desktop Computer (for ₹ 50,000 before tax) and a wooden table (for ₹ 5,000 before tax) for a consolidated price of ₹ 52,500 plus tax. The rates of GST applicable on desktop computer and wooden table are 28% and 18% respectively.
(i) Determine whether the supply is a mixed supply or a composite supply.
(ii) Is it beneficial for the customer to avail the offer or buy them separately?
Answer:
(i) Mixed or Composite Supply: The two items “computer and table” can be supplied separately and is not dependent on each other. Hence, the offer of “computer and table” at consolidated price is not naturally bundled. Therefore, it is mixed supply.
(ii) Comparative Analysis: In order to compare the two alternatives, there is a need to calculate the total amount payable by the recipient under the same.
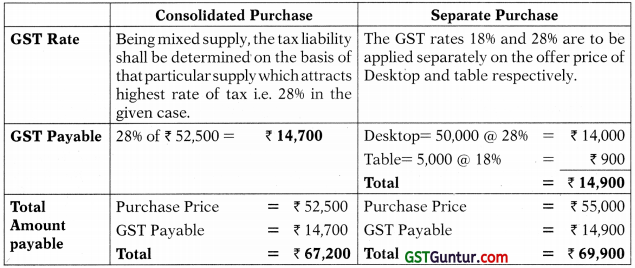
Comment: It is beneficial to customer to avail the offer.
Question 5.
Mr. Rajesh Surana has a proprietorship firm in the name of Surana & Sons in Jaipur. The firm, registered under GST in the State of Rajasthan, manufactures taxable products. The firm also provides taxable consultancy services.
Mr. Rajesh Surana has provided the consultancy service to his brother – Mr. Akhilesh Surana (located in USA) without any consideration. The products manufactured by Mr. Akhilesh are similar to the ones manufactured by Mr. Rajesh Surana. Mr. Surana charges ₹ 3,00,000 for providing similar consultancy services to other independent customers located in USA.
Answer:
Facts of the given Case Study
- “Surana and Sons” has provided the consultancy service to ’Mr. Akhilesh Surana” without any consideration.
- Mr. Akhilesh Surana is located in USA and is the brother of proprietor.
- The question is whether export of service will fall under Schedule I and liable to tax?
Related Provisions
As per Schedule I of the CGST Act, 2017: The activities to be treated as supply even if made without consideration. Accordingly, Para 2 of Schedule I treats supply of goods or services or both between related persons or between distinct persons as specified in section 25, when made in the course or furtherance of business as a supply even if made without consideration.
Decision
- Consultancy service to Mr. Akhilesh Surana (located in USA) has been provided without any consideration.
- However, a brother who is not dependent on the person supplying the service, does not come within the purview of term family as defined under section 2(49) of the CGST Act, 2017 and hence, is not a related person.
- Therefore, the export of service to an independent brother without any consideration will not fall under Para 2 of the Schedule I to CGST Act, 2017.
- Hence, the activity is not a supply and is thus, not liable to any tax.
![]()
Question 6.
Mr. Z, a supplier registered in Hyderabad (Telangana), procures goods from China and directly supplies the same to a customer in US. With reference to the provisions of GST law, examine whether the said activity of supply of goods by Mr. Z to customer in US is taxable under GST. If yes, determine the place of supply of the same. [RTP, Nov. 19]
Answer:
Facts of the given Case Study
- Mr. Z has procured goods from China and supplied directly to customer in USA.
- The question is whether it is taxable under GST laws.
Related Provisions
- The Schedule III specifies transactions/activities which shall be neither treated as supply of goods nor supply of services.
- The Entry 7 of this Schedule includes supply of goods from a place in the non-taxable territory to another place in the non-taxable territory without such goods entering into India.
Decision
- The activity given in question comes under purview of schedule III.
- Therefore, the transaction is neither supply of goods nor services.
- Thus, the question arises about place of supply.
Question 7.
Examine whether the following activities would amount to supply under section 7 of the CGST Act:
(а) Damodar Charitable Trust, a trust who gets the eye treatment of needy people done free of cost, donates clothes and toys to children living in slum area.
(b) Sulekha Manufacturers have a factory in Delhi and a depot in Mumbai. Both these establishments are registered in respective States. Finished goods are sent from factory in Delhi to the Mumbai depot without consideration so that the same can be sold.
(c) Raman is an Electronic Commerce Operator in Chennai. His brother who is settled in London is a well-known lawyer. Raman has taken legal advice from him free of cost with regard to his family dispute.
(d) Would your answer be different if in the above case, Raman has taken advice in respect of his business unit in Chennai?
Answer:
Activity given in questionWhether supply under section 7Reason
| (a) | Free eye treatment of needy people and donation of clothes, toys, etc. | No | Since it is without consideration, NOT covered in section 7 and also does not come under the purview of Schedule I. |
| (b) | Finished goods transferred from factory to depot (Both are in different states) | Yes | ♦ Schedule I of CGST Act, inter alia, stipulates that supply of goods or services or both between related persons or between distinct persons as specified in section 25, is supply even without consideration provided it is made in the course or furtherance of business.
♦ Further, where a person who has obtained or is required to obtain registration in a State in respect of an establishment, has an establishment in another State, then such establishments shall be treated as establishments of distinct persons [Section 25 of the CGST Act], ♦ In view of the same, factory and depot of Sulekha Manufacturers are establishments of two distinct persons. ♦ Therefore, supply of goods from Delhi factory of Sulekha Manufacturers to Mumbai Depot without consideration, but in course/ furtherance of business, is supply under section 7 of the CGST Act. |
| (c) | Legal advice received by Raman for personal purposes from brother free of cost. | No | ♦ Schedule I of CGST Act, inter alia, stipulates that import of services by a taxable person from a related person located outside India, without consideration is treated as supply if it is provided in the course or furtherance of business.
♦ In the given case, Raman has received legal services from his brother free of cost in a personal matter and NOT in course or furtherance of business. ♦ Hence, services provided by Raman’s brother to him would not be treated as supply under section 7 of the CGST Act. |
| (d) | Import of service by Raman for business purposes from brother free of cost. | Yes | ♦ In the above case, if Raman has taken advice with regard to his business unit, services provided by Raman’s brother to him would be treated as supply under section 7 of the CGST Act as the same are provided in course or furtherance of business though received from a related person. |
Question 8.
Determine whether the following supplies amount to composite supplies/mixed supplies:
(a) A hotel provides 4 days-3 nights package wherein the facility of breakfast and dinner is provided along with the room accommodation.
(b) A toothpaste company has offered the scheme of free toothbrush along with the toothpaste.
Answer:
Activity Nature Reason
| Activity | Nature | Reason | |
| (a) | 4 days-3 nights package with breakfast/Dinner along with room accommodation | Composite | The supply of breakfast and dinner with the accommodation in the hotel are naturally bundled. |
| (b) | free toothbrush along with the toothpaste | Mixed | The supply of toothbrush along with the toothpaste is NOT naturally bundled. |
Question 9.
Define the meaning of Related Parties and Distinct Person as per the CGST Act?
Answer:
Related Persons [Section 15 of CGST Act, 2017]
A person shall be deemed to be related if,
(a) such persons are officers or directors of one another’s businesses
(b) such persons are legally recognized partners in business
(c) such persons are employer and employee
(d) any person directly or indirectly owns, controls or holds twenty-five percent or more of the outstanding voting stock or shares of both of them
(e) one of them directly or indirectly controls the other
(f) both of them are directly or indirectly controlled by a third person
(g) together they directly or indirectly control a third person; or they are members of the same family
(h) persons who are associated in the business of one another in that one is the sole agent or sole distributor or sole concessionaire, howsoever described, of the other, shall be deemed to be related.
Distinct Persons Specified [SECTION 25 of CGST Act, 2017]
Separate Registration make Distinct Person u/s 25(4): A person who has obtained/is required to obtain more than one registration, whether in one State/Union territory or more than one State/Union territory shall, in respect of each such registration, be treated as distinct persons.
Separate Establishment u/s 25(5):- Separate establishment in another state/UT whether registered or unregistered, such Establishment shall be treated as DP.
![]()
Question 10.
Can Priority Sector Lending Certificate (PSLCs) be termed as Supply of Service?
Answer:
- PSLC are akin to freely tradable duty scrips, Renewable Energy Certificates, REP license or replenishment license, which earlier attracted VAT.
- RBI’s FAQ on PSLCs have construed PSLCs to be in the nature of goods,
- In GST, there is no exemption to trading in PSLCs.
- Thus, PSLCs are taxable as goods.
- GST payable on the certificates would be available as ITC to the bank buying the certificates [Circular No. 34/08/2018 GST dated 01.03.2018].