Scope and Objectives of Financial Management – CA Inter FM Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Scope and Objectives of Financial Management – CA Inter FM Notes
1. Financial Management:
Financial management refers to that managerial activity which is concerned with the arrangement of funds from various sources with consideration of cost, control and risk involved with such sources and application of these funds in an effective manner to maximize shareholders earning and wealth (EPS and MPS).
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
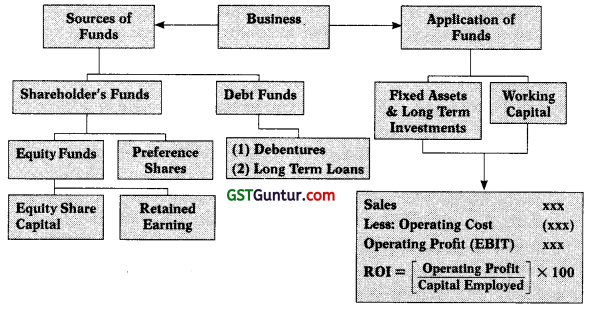
2. Sources of Funds
- Equity Share Capital
- Retained Earnings
- Preference Share Capital
- Debentures
- Funding from banks
- International Funding
3. Application of Funds:
- Investment in Fixed Assets
- Investment in Working Capital
![]()
4. Evolution of Financial Management: Evolution of financial management took 50 years and can be divided into three stages:
- The Traditional Phase: In traditional phase, financial management was relevant only for big decisions like: takeovers, mergers, expansion, liq-uidation, etc.
- The Transitional Phase: In transitional phase, importance of day to day financial decisions increased, small decisions also got more attention. Like: funds analysis, planning and control etc.
- The Modern Phase: It is current phase today and is still going on. In today’s world importance and scope of financial management greatly increased due to globalization, heavy foreign exchange transfers, capital market transactions etc. Many new theories have been developed regarding efficient markets, capital budgeting, option pricing, valuation models and also in several other important fields in financial management.
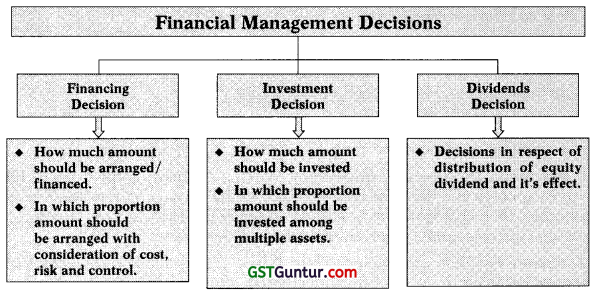
5. Finance Functions or Finance Decisions: we can classify finance decisions into two categories:
- Long term finance decisions: It can be further divided into three categories:
- Investment decisions (I): Selection of assets and investment of long term funds into these assets.
- Financing decisions (F): Selection of optimum capital structure on the basis of cost of fund, risk associated with these funds and control.
- Dividend decisions (D): Decisions related to distribution of profit as dividend.
- Short term finance decisions: Decisions related to management of cur-rent assets and current liabilities. It is also known as Working Capital Management (WCM).
6. Importance of Financial Management due to following tasks:
- Look after not to over-invest in fixed assets,
- Maintain balancing of cash outflow with cash inflows,
- Maintaining sufficient level of short term working capital,
- Preparation of growing sales budget,
- Set correct pricing for products or services to increase gross profit,
- Look after and control general and administrative expenses, and
- Focusing on tax planning to minimize the taxes.
![]()
7. Scope of Financial Management:
- Determination of size of the enterprise and determination of rate of growth,
- Determining the composition of assets of the enterprise,
- Determining the mix of enterprise’s financing,
- Analysis, planning and control of financial affairs of the enterprise.
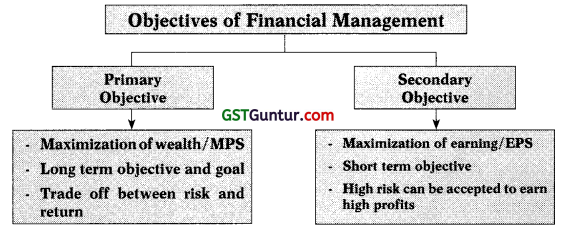
8. Objectives of Financial Management: Main two objectives of financial management are profit maximization and wealth maximization.
9. Role of Finance Executive:
- Financial analysis and planning,
- Investment decisions,
- Financing and capital structure decisions,
- Management of financial resources (such as working capital),
- Risk management.
![]()
10. Financial Distress and Insolvency: When a company cannot pay its day to day expenses and financial expenses like: salaries, rent, interest on debt etc. smoothly, then this situation is known as financial distress. Continuation of financial distress create insolvency situation in long term.
11. Agency Problem and Agency Cost: When management is focusing their salaries, perks etc. instead of maximization of shareholders wealth and profit then this situation is known as agency problem. Agency cost is the additional cost borne by the shareholders to monitor the manager and control their behaviour so as to maximise shareholders wealth.