Regression Analysis – CA Foundation Statistics Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Regression Analysis – CA Foundation Statistics Notes
Previous Year Exam Questions
Question 1.
For some bivariate data, the following results were obtained for the two variables x and y : \(\bar{x}\) = 53.2, \(\bar{y}\) = 21.9, byx = -1.5, bxy = -0.2
The most probable value of y when x = 60 is [1 Mark, Nov. 2006]
(a) 17.7
(b) 13.4
(c) 19.7
(d) 15.6
Solution:
(a) 17.7
The regression equation of y of x is applicable.
∴ Y – \(\bar{Y}\) = byx(X – \(\bar{X}\))
⇒ Y – 27.9 = (-1.5)(X – 53.2)
or Y = 107.7 – 1.5X
when x = 60 then
y = 107.7 – 1.5 × 60 = 17.7
Question 2.
Two random variables have the regression lines 3x + 2y = 26 and 6x + y = 31. The coefficient of correlation between x and y is : [1 Mark, Feb. 2007]
(a) -0.25
(b) 0.5
(c) -0.5
(d) 0.25
Solution:
(c) -0.5
Let 3X + 2Y =26 be the Regr. line of Y on X & 6X + Y = 31 be the Regr. line of X on Y
bxy \(=-\frac{\text { Coefficient of } Y}{\text { Coefficient of } X}\) = \(\frac{-1}{6}\) ; byx = –\(\frac{3}{2}\)
Now r2 = byx.bxy = \(\left(-\frac{1}{6}\right) \cdot\left(\frac{-3}{2}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 0.25 < 1
(Hence, our assumption is true) r = – 0.5
∴ r = -0.5
Note : r is negative because byx and bxy are negative.
TRICKS : See Quicker BMLRS examples
![]()
Question 3.
The following data is given, based on 450 students for marks in Statistics and Economics at a certain examination:
Mean marks in Statistics = 40
Mean marks in Economics = 48
S.D. of marks (Statistics) = 12
Variance of marks (Economics) = 256
Sum of the products of deviations of marks from their respective mean = 42075
The average marks in Economics of candidates who obtained 50 marks in Statistics is: [1 Mark, May 2007]
(a) 45
(b) 54.5
(c) 54
(d) 47.5
Solution:
(b) 54.5
Let x = Marks in statistics and y = Marks in Economics
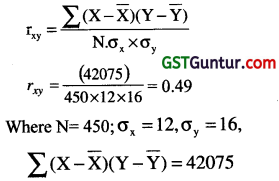
Now regression equation of Y on X
Y – \(\overline{\mathrm{Y}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{r} \cdot \sigma_y}{\sigma_x}\). (X – \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\))
⇒ Y – 48 = \(\frac{0.49 \times 16}{12}\)(X – 40)
⇒ Y = 0.65.X + 22
where x = 50, then y = 0.65 × 50 + 22 = 54.5
Question 4.
The lines of regression are as follows:
5x – 145 = – 10y ; 14y – 208 = -8x. The mean values \((\overline{x, y})\) is: [1 Mark, Nov. 2007]
(a) (12, 5)
(b) (5, 7)
(c) (7, 12)
(d) (5, 12)
Solution:
(d) (5, 12)
TRICKS : Go by choice.
for (d) Put X = 5 and Y =12 in the given Eqns.
They satisfy these eqns.
So, (d) is correct.
Question 5.
Given the following data:
bxy = 0.4 & byx = 1.6. The coefficient of determination is : [1 Mark, Feb. 2008]
(a) 0.74
(b) 0.42
(c) 0.58
(d) 0.64
Solution:
(d) 0.64
We know that,
Coefficient of determination r2 = byx × bxy = 1.6 × 0.4 = 0.64
![]()
Question 6.
The method applied for deriving regression equations is known as : [1 Mark, Feb. 2008]
(a) Concurrent deviation
(b) Product moment
(c) Least squares
(d) Normal equation
Solution:
(c) Least Squares
Question 7.
If the correlation coefficient between two variables is 1, then the two lines of regressions are: [1 Mark, June 2008]
(a) Parallel
(b) At right angles
(c) Coincident
(d) None of these
Solution:
(c) Coincident
- If r = 0, The Regression Lines are perpendicular to each other i.e. The Regression Lines are farther to each other
- If r = 1, The Regression Lines are Coincident; i.e. The Regression Lines are nearer to each other.
Question 8.
Given the regression equations as 3x + y = 13 and 2x +5y = 20. Find regression equation of y on x.
(a) 3x + y = 13
(b) 2x + Y = 20
(c) 3x + 5y = 13
(d) 2x + 5y = 20
Solution:
(d) 2x + 5y = 20
Let us assume that 2X + 5Y – 20 = 0 represents the regression line of Y on X and 3X + Y-13 = 0 represent the line of X on Y.
Now, 2X + 5Y – 20 = 0
∴ byx = \(\frac{-2}{5}\) (See Quicker BMLRS example TRICK)
Again, 3X + Y – 13 = 0
∴ bxy = \(\frac{-1}{3}\) \(=-\frac{\text { co-efficient of } y}{\text { co-efficient of } x}\)
Thus, r2 = byx × bxy
= \(\frac{-2}{5} \times \frac{-1}{3}\) = \(\frac{2}{15}\) < 1
Since |r| ≤ 1 ⇒ r2 ≤ 1, our assumptions is correct. Thus, 2X + 5Y – 20 = 0, truly represents the regression line of Y on X.
Question 9.
The two regression equations are: [1 Mark, June 2009]
2x + 3y+ 18=0
x + 2y – 25 = 0
find the value of y if x = 9
(a) -8
(b) 8
(c) -12
(d) 0
Solution:
(b) 8
To find the value of Y when X’s value is given, regression equation of Y on X should be known.
Let 2X + 3Y + 18 = 0 represents the regression line of Y on X and X + 2Y – 25 = 0 represents line of X on Y.
Now, for 2X + 3Y + 18 = 0 ∴ byx = \(\frac{-2}{3}\)
Again for x + 2y – 25 = 0
x = 25 – 2y
∴ bxy = -2
Thus, r2 = byx × bxy
= \(\left(\frac{-2}{3}\right) \times(-2)\) = \(\frac{4}{3}\) > 1
∴ Our assumption is wrong. Thus, 2x + 3y + 18 = 0 really shows the regression line of X on Y and x + 2y – 25 = 0 the regression line of Y on X.
Putting x = 9 in x + 2y – 25 = 0
9 + 2y – 25 = 0
2y = 25 – 9 = 16, So y = 8
Question 10.
The correlation coefficient between x and y is -1/2. The value of bxy = -1/ 8. Find byx.
[1 Mark, June 2009]
(a) -2
(b) -4
(c) 0
(d) 2
Solution:
(a) -2
∵ r2 = bxy × byx
∴ \(\left(\frac{-1}{2}\right)^2\) = \(\frac{-1}{8} \times b_{y x}\)
or; \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{-1}{8}\) × byx ; So, byx = -2
Question 11.
Which of the following regression equations represent regression line of Y on X: [1 Mark, June 2009]
7x + 2y + 15 = 0, 2x + 5y + 10 = 0
(a) 7x + 2y + 15 = 0
(b) 2x + 5y +10 = 0
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Solution:
(b) 2x + 5y +10 = 0
Let 7x + 2y + 15 = 0 is the regression line X on Y and 2x + 5y + 10 = 0, is the regression line of Y on X.
bxy = \(-\frac{2}{7}\); byx = \(-\frac{2}{5}\) [Tricks]
r2 = bxy × byx = \(\left(-\frac{2}{7}\right) \times\left(-\frac{2}{5}\right)\) = \(\frac{4}{35}\) < 1
So, our assumption is correct.
So, 2x + 5y + 10 = 0 is the regression line of Y on X.
Question 12.
The two regression line are 7x – 3y – 18 = 0 and 4x – y -11 = 0. Find the value of bx and bxy [1 Mark, June 2009]
(a) 7/3, 1/4
(b) -7/3, -1/4
(c) -3/7,-1/4
(d) None of them
Solution:
(a) 7/3, 1/4
Let 7x – 3y -18 = 0 be the regression line of Y on X and 4x – y – 11 = 0 is of X on Y.
TRICKS : See QUICKER BMLRS Examples.
byx = \(-\frac{7}{-3}=\frac{7}{3}\), bxy = \(-\frac{-1}{4}=\frac{1}{4}\)
r2 = bxy × byx = 0.583 <1
So, our assumption is correct.
So, byx \(=\frac{7}{3}\) and bxy = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
![]()
Question 13.
______ of the regression Coefficient is greater than the correlation coefficient [1 Mark, June 2010]
(a) Combined mean
(b) Harmonic mean
(c) Geometric mean
(d) Arithmetic mean.
Solution:
(d) Arithmetic mean.
r = ±\(\sqrt{b_{x y} b_{y x}}\) = GM of Regression Coefficients.
∵ AM > GM> HM
∴ AM of regression coefficients is greater than correlation coefficient.
Question 15.
Regression coefficient are _______ [1 Mark, Dec. 2010]
(a) dependent of change of origin and of scale.
(b) independent of both change of origin and of scale.
(c) dependent of change of origin but not of scale.
(d) independent of change of origin but not of scale
Solution:
(d) independent of change of origin but not of scale
Regression coefficient are independent of change of origin but changes with respect to scale. [Properties of regression co-efficients]
Question 16.
Given:
\(\bar{X}\) =16, σx =4.8, \(\bar{Y}\) = 20, σY = 9.6
The coefficient of correlation between x and y is 0.6. What will be the regression [1 Mark, Dec. 2010]
(a) 0.03
(b) 0.3
(c) 0.2
(d) 0.05
Solution:
(b) 0.3
bxy = r × \(\frac{\sigma_{\mathrm{x}}}{\sigma_{\mathrm{y}}}\)
bxy = 0.6 × \(\frac{4.8}{9.6}\) = 0.3
Question 17.
If the two line of regression are x + 2y – 5 =0 and 2x + 3y – 8 =0. The regression line of y on x is [1 Mark, Dec. 2010]
(a) x + 2y – 5 = 0
(b) 2x + 3y – 8 = 0
(c) Any of the two line
(d) None of the two line
Solution:
(a) x + 2y – 5 = 0
Let x + 2y – 5 =0 be Regression equation of Y on X .
byx \(=\frac{-\text { coeff. of } x}{\text { coff. of } y}\) = \(\frac{-1}{2}\) = -0.5
Let 2x + 3y – 8 = 0 be Regression equation of X on Y .
bxy = \(-\frac{3}{2}\) = -1.5
bxy.bxy
= (-0.5).(-1.5)
= 0.75
∴ byx.bxy < 1
∴ 1st line is Y on X.
Question 18.
For a bivariate data two lines of regression are 40x – 18y = 214 and 8x – lOy + 66 = 0, then find the values of x and y [1 Mark, June 2011]
(a) 17 and 13
(b) 13 and 17
(c) 13 and-17
(d) -13 and 17
Solution:
(b) 13 and 17
TRICKS : Go by choices,
X = 13 and Y = 17; satisfy both Regression Lines.
∴ \(\overline{\mathbf{X}}\) = 13 and \(\overline{\mathbf{Y}}\) = 17
Question 19.
Out of the following which one affects the regression co-efficient.
(a) Change of origin only
(b) Change of scale only
(c) Change of scale & origin both
(d) Neither change of origin nor change of scale [1 Mark, Dec. 2011]
Solution:
(b) Change of scale only
The regression coefficients does not change due to a shift of origin but changes due to a shift of scale.
Question 20.
For a bivariate data, the line of regression of Y on X, and of X on Y are respectively 2.5Y – X = 35 and 10X – Y = 70, then correlation coefficient r is equal to:
Solution:
(a) The equation of regression line Y on X is 2.5 Y – X = 35
byx = \(-\left(\frac{-1}{2.5}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{2.5}\) = 0.4
The equation of Regression line X on Y is 10x – y = 70
bxy = \(-\left(\frac{-1}{10}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{10}\) = 0.1
Both Regression Coefficients are positive.
r = +\(\sqrt{b_{x y} \times b_{y x}}\) = \(\sqrt{(0.4) \cdot(0.1)}\) = 0.2
![]()
Question 21.
If one of regression coefficient is ____ unity, the other must be ____ unity. [1 Mark, Dec. 2011]
(a) more than, more than
(b) Less than, Less than
(c) more than,less than
(d) Positive, Negative
Solution:
(c) more than,less than
If one regression co-efficient is more than unity, the other must be less than unity.
Question 22.
If Y is dependent variable and X is Independent variable and the S.D of X and Y are 5 and 8 respectively and Co-efficient of co-relation between X and Y is 0.8. Find the Regression co-efficient of Y on X. [1 Mark, Dec. 2011]
(a) 0.78
(b) 1.28
(c) 6.8
(d) 0.32
Solution:
(b) 1.28
Given, σx = 5 ; σy = 8; r = 0.8
Regression Co- eff. of Y on X
byx = r.\(\frac{\sigma_y}{\sigma_x}\) = \(\frac{0.8 \times 8}{5}\) = \(\frac{6.4}{5}\) = 1.28
Question 23.
If the regression lines are 8x -10y + 66 = 0 and 40x – 18y = 214, the correlation coefficient between ‘x’ and ‘y’ is : [1 Mark, June 2012]
(a) 1
(b) 0.6
(c) -0.6
(d) -1
Solution:
(b) 0.6
8x – 10y + 66 = 0 be the Regression eqn. of Y on X
byx = \(-\frac{8}{-10}\) = 0.8 and
40x – 18y = 214; be Regression eqn. of X on Y .
bxy = \(-\frac{-18}{40}\) = 0.45
r = ± \(\sqrt{b_{y x} \times b_{x y}}\) [Both Regr. Coef. are + ve.]
= +\(\sqrt{0.8 \times 0.45}\) = + 0.6
[r is also +ve.]
Question 24.
The coefficients of correlation between two variables X and Y is the simple ____ of the two regression. [1 Mark, June 2012]
(a) Arithmetic Mean
(b) Geometric Mean
(c) Harmonic Mean
(d) None of the above
Solution:
(b) Geometric Mean
The coefficient of correlation between two variables X and Y is the simple geometric mean of the two regression coefficient.
Question 25.
If 2 variables are uncorrelated, their regression lines are: [1 Mark, June 2012]
(a) Parallel
(b) Perpendicular
(c) Coincident
(d) Inclined at 45 degrees
Solution:
(b) Perpendicular
If two variables are uncorrelated, (it means r = 0). Hence regression lines are perpendicular
Question 26.
If x, y denote the arithmetic means, σx ; σy denote the standard the deviations, ; bxy : byx denote the regression coefficients of the variables ‘x’ and ‘y’ respectively, then the point of intersection of regression lines X on Y & Y on X is
(a) \((\overline{\mathrm{X}} ; \overline{\mathrm{Y}})\)
(b) (σx, σy)
(c) (σx ; σy)
(d) \(\left(\sigma_x^2, \sigma_y{ }^2\right)\) [1 Mark, June 2012]
Solution:
(a) \((\overline{\mathrm{X}} ; \overline{\mathrm{Y}})\)
∵ Two lines of regression pass through the point of intersection of Regression lines \((\bar{X}, \bar{Y})\).
Question 27.
For certain x and y series which are correlated, the two line of regression are 5x – 6y + 9 = 0 1
5x – 8y – 130 = 0
The correlation coefficient is [1 Mark, Dec. 2012]
(a) 4/5
(b) 3/4
(c) 2/3
(d) 1/2
Solution:
(c) 2/3
Let 5x – 6y + 9 = 0; be a Regression eqn. of Y on X .
byx = \(-\frac{5}{-6}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\)
And 15x – 8y – 130 = 0, be a Regression eqn. of X on Y
bxy = \(\frac{8}{15}\)
r = ±\(\sqrt{b_{y x} \times b_{x y}}\) = +\(\sqrt{\frac{5}{6} \times \frac{8}{15}}\) = +\(\frac{2}{3}\) (r is positive because regression-coefficients are positive).
![]()
Question 28.
The coefficient of correlation between X and Y series is – 0.38. The linear relation between X & V are 3X + 5U = 3 and -8Y – 7V = 44, what is the coefficient of correlation between U & V ? [1 Mark, Dec. 2012]
(a) 0.38
(b) -0.38
(c) 0.40
(d) None of these
Solution:
(b) -0.38
Given rxy = -0.38
TRICKS : 3X + 5U = 3 and -8Y – 7V = 44
8Y + 7V = 44
r = – 0.38
Note :- See QUICKER BMLRS Examples .
Question 29.
If Y = 18X + 5 is the regression line of X on Y ; The value of bxy is [1 Mark, Dec. 2012]
(a) 5/18
(b) 18
(c) 5
(d) 1/18
Solution:
(d) 1/18
If Y = 18X + 5
18X – Y – 5 = 0
bxy = \(-\left(\frac{-1}{18}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{18}\)
Question 30.
8x – 3y + 7 = 0, 14x – 7y + 6 =0 are two regression equation then the correlation coefficient, r = [1 Mark, June 2013]
(a) 0.86
(b) -0.86
(c) 0.45
(d) -0.45
Solution:
(a) 0.86
(a) is correct
Let 8x – 3y + 7 = 0; be Regression Eqn. of y on x
∴ byx = \(-\frac{8}{-3}\) = \(\frac{8}{3}\)
and 14x – 7y + 6 = 0; the Regression Eqn. of x on y
∴ bxy = –\(\frac{-7}{14}\) = \(\frac{7}{14}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
bxy.bxy = \(\frac{8}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{4}{3}\) > 1
:-Our Assumption is wrong
So; bxy = \(\frac{2}{1}\) = 2 & byx = \(\frac{3}{8}\)
∴ r2 = bxy.byx = 2.\(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) = 0.75
:- r = +0.86
Question 31.
If r = + 1 or -1 then the two regression lines _____ [1 Mark, Dec. 2013]
(a) Have 30% angle between them
(b) Have 45% angle between them
(c) Coincide
(d) Perpendicular to each other
Solution:
(c) Coincide
For r = + 1 or -1
Regression Lines Coincide.
Question 32.
If mean of X and Y variables is 20 and 40 respectively and the regression coefficient Y on X is 1.608 then the regression line of Y on X is: [1 Mark, Dec. 2013]
(a) Y = 1.608X + 7.84
(b) Y = 1.56X + 4.84
(c) Y = 1.608X + 4.84
(d) Y = 1.56X + 7.84
Solution:
(a) Y = 1.608X + 7.84
(a) is correct
Tricks : See Quicker BMLRS
check which option is correct
for x = 20 ; y = 40
For (a); \(\bar{y}\) = 1.608 × 20 + 7.84 = 40 which is correct
![]()
Question 33.
The equations two lines of regression for x & y are 5x = 22 + y and 64x = 24 + 45y, then the value of regression coefficient of y on x will be [1 Mark, June 2014]
(a) 5
(b) \(\frac{1}{5}\)
(c) \(\frac{64}{65}\)
(d) \(\frac{45}{64}\)
Solution:
(c) \(\frac{64}{65}\)
(c) is correct
Let 5x = 22 + y be a regression Eqn. of X on Y
∴ bxy = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
and 64x = 24 + 45y be a Regression Eqn. of y on x
∴ 45y = -24 + 64x
byx = \(\frac{64}{65}\)
∴ r2 = bxy.byx = \(\frac{1}{5} \cdot \frac{64}{45}\) = \(\frac{64}{225}\) < 1
∴ Our assumption is correct
∴ byx = \(\frac{64}{65}\)
Question 34.
Two regression lines for a bivariate data are 2x – 5y +6 = 0 and 5x – 4y + 3 = 0. Then the coefficient correlation shall be _____. [1 Mark, June 2014]
(a) \(\frac{-2 \sqrt{2}}{5}\)
(b) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
(c) \(\frac{+2 \sqrt{2}}{5}\)
(d) \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{5}\)
Solution:
(c) \(\frac{+2 \sqrt{2}}{5}\)
(c) is correct Tricks : (See Quicker BMLRS)
Let 2x – 5y + 6 = 0 be a Regression
Eqn. of x on y
bxy = \(-\frac{(-5)}{2}\) = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
and 5x – 4y + 3 = 0 be a Regression
Eqn. of y on x
byx = \(-\frac{5}{-4}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\)
r2 = bxy.byx = \(\frac{5}{2}\) . \(\frac{5}{4}\) = \(\frac{25}{8}\) > 1
∴ Our assumption is incorrect
∴ Correct bxy = \(\frac{4}{5}\) and byx = \(\frac{2}{5}\)
∴ r2 = bxy.byx = \(\frac{4}{5}\) . \(\frac{2}{5}\)
∴ r = +\(\frac{2 \sqrt{2}}{5}\)
Question 35.
If the mean of two variables x & y are 3 and 1 respectively. Then the equation of two regression lines are _____
[1 Mark, June 2014]
(а) 5x + 7y – 22 = 0 & 6x + 2y – 20 = 0
(b) 5x + 7y – 22 = 0 & 6x + 2y + 20 = 0
(c) 5x + 7y + 22 = 0 & 6x + 2y – 20 = 0
(d) 5x + 7y + 22 = 0 & 6x + 2y + 20 = 0
Solution:
(а) 5x + 7y – 22 = 0 & 6x + 2y – 20 = 0
(a) is correct
Tricks : Go by choices
For (a) x = 3; y = 1 Satisfy eqns. of (a)
As LHS = 5 x 3+7-22 = 0 (RHS) and LHS = 6×3 + 2x 1-20 = 0 (RHS)
∴ (a) is correct.
Question 36.
Two regression equations are x + y = 6 and x + 2y = 10 then correlation coefficient between X any Y is [1 Mark, Dec. 2014]
(a) -1/2
(b) 1/2
(c) –\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
(d) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Solution:
(c) –\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
(c) is correct
Tricks : See Quicker QA book
1x + 1y = 6 ⇒ y = -x + 6
1x + 2y = 10 ⇒ 2y = -x + 10
r = \(-\sqrt{\frac{1 \times 1}{1 \times 2}}\) = \(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) (x & y have opposite signs)
![]()
Question 37.
Correlation coefficient between x and y is zero the two regression lines are [1 Mark, Dec. 2014]
(a) Perpendicular to each other
(b) Coincide to each other
(c) Parallel to each other
(d) None of these
Solution:
(a) Perpendicular to each other
(a) is correct.
Question 38.
The two regression lines are 16x – 20y + 132 = 0 and 80x – 30y – 428 = 0, the value of correlation coefficient is [1 Mark, June 2015]
(a) 0.6
(b) -0.6
(c) 0.54
(d) 0.45
Solution:
(c) 0.54
(c) is correct
see Quicker BMLRS book
Tricks r = +\(\sqrt{\frac{16 \times 30}{20 \times 80}}\) = 0.547
Question 39.
Which of the following is true: [1 Mark, Dec. 2015]
(a) bxy = r.\(\frac{\sigma_y}{\sigma_x}\)
(b) bxy = r.\(\frac{\sigma_x}{\sigma_y}\)
(c) bxy = \(\pi \cdot \frac{\sum x y}{\sigma_x}\)
(d) bxy = \(\pi \cdot \frac{\sum x y}{\sigma_y}\)
Solution:
(b) bxy = r.\(\frac{\sigma_x}{\sigma_y}\)
(b) is correct.
Question 40.
The regression are as follows
Regression equation of X on Y : 6X – Y = 28
Regression equation of Y on X : 64X – 45Y = 24
What will be the mean X and Y ? [1 Mark, June 2016]
(a) \(\overline{\mathbf{X}}\) = 8, \(\overline{\mathbf{Y}}\) = 6
(b) \(\overline{\mathbf{X}}\) = 6, \(\overline{\mathbf{Y}}\) = 6
(c) \(\overline{\mathbf{X}}\) = 6, \(\overline{\mathbf{Y}}\) = 8
(d) \(\overline{\mathbf{X}}\) = 8, \(\overline{\mathbf{Y}}\) = 8
Solution:
(c) \(\overline{\mathbf{X}}\) = 6, \(\overline{\mathbf{Y}}\) = 8
(c) is correct.
Tricks: Go by Choices
X = 6 and Y = 8 satisfy both Regression Eqns.
∴ \(\overline{\mathbf{X}}\) = 6; \(\overline{\mathbf{Y}}\) = 8 is correct
Question 41.
The two lines of regression become identical when [1 Mark, June 2016]
(a) r = 1
(b) r = -1
(c) r = 0
(d) (a) or (b)
Solution:
(d) (a) or (b)
(d) is correct.
![]()
Question 42.
Regression coefficients are affected by _____ [1 Mark, Dec. 2016]
(a) Change of origin
(b) Change of Scale
(c) Both origin & scale
(d) Neither origin nor scale
Solution:
(b) Change of Scale
(b) is correct.
Question 43.
Regression lines are passes through the ____ points [1 Mark, Dec. 2016]
(a) Mean
(b) Standard deviation
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None
Solution:
(a) Mean
(a) is correct.
Question 44.
If the regression line of x ony is 3x + 2y = 100, then find the value of ?
(a) \(\frac{-2}{3}\)
(b) \(\frac{10}{3}\)
(c) \(\frac{3}{2}\)
(d) \(\frac{2}{3}\) [1 Mark, Dec. 2016]
Solution:
(a) \(\frac{-2}{3}\)
(a) is correct.
Tricks : Quicker BMLRS
bxy = \(\frac{-2}{3}\)
Question 45.
If the two regression lines are x + y = 1 and x – y = 1 then \(\bar{x}\) and \(\bar{y}\) are [1 Mark, June 2017]
(a) 1, 0
(b) 0, 1
(c) 1, 1
(d) None
Solution:
(d) None
(d) is correct.
Sign of both Regression lines x + y = 1 and x – y = 1 are different. It means ; x & y are not correlated ∴ \((\bar{x} ; \bar{y})\) cannot be determined.
Question 46.
The correlation coefficient is the ____ of the two regression coefficients byx and bxy : [1 Mark, Dec. 2017]
(a) AM
(b) GM
(c) HM
(d) None of these
Solution:
(b) GM
Question 47.
Regression coefficient are independent of _____: [1 Mark, Dec. 2017]
(a) Change of origin
(b) Change of scale
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of these
Solution:
(a) Change of origin
![]()
Question 48.
5y = 9x – 22 & 20x = 9y + 350 are two regression lines. Find the correlation coefficient between x & y : [1 Mark, Dec. 2017]
(a) 0.9
(b) 0.1
(c) -0.9
(d) -0.1
Solution:
(a) 0.9
Tricks : See Quicker BMLRS
(Chapter Regression Analysis)
9x – 5y = 22
20x – 9y = 350
∴ r = +\(\sqrt{\frac{81}{100}}\) = \(\frac{9}{10}\) = 0.9
Question 49.
Regression lines are parallel then r = :
(a) ±1
(b) -1/2
(c) 0
(d) None [1 Mark, June 2018]
Solution:
(a) ±1
Question 50.
The two lines of regression intersect at the point:
(a) Mean
(b) Median
(c) Mode
(d) None of the these [1 Mark, Nov. 2018]
Solution:
(a) Mean
Question 51.
If the two lines of regression are x + 2y – 5 = 0 and 2x + 3y – 8 = 0, then the regression line of y on x is [Nov. 2018]
(a) x + 2y – 5 = 0
(b) x + 2y = 0
(c) 2x + 3y – 8 = 0
(d) 2x + 3y = 0
Solution:
(a) x + 2y – 5 = 0
Let x + 2y — 5 = 0 is the
Regression Eqn. of y on x then 2x + 3y – 8 = 0 should be the Regression
Eqn. of x on y.
∴ byx = \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
and bxy = \(-\frac{3}{2}\)
∴ Our assumption is correct.
So ; x + 2y — 5 = 0 is the Regression Eqn. ofy on x.
Question 52.
If the two regression lines are 3X = Y and 8Y = 6X, then the value of correlation coefficient is [Nov. 2018]
(a) -0.5
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.75
(d) -0.80
Solution:
(b) 0.5
Regr. Eqns. are
3x – y = 0 &
6x – 8y = 0
Tricks : See Quicker BMLRS chapter
Regression Analysis
r = +\(\sqrt{\frac{1 \times 6}{3 \times 8}}\) = +\(\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}}\) = +\(\frac{1}{2}\) = 0.5
“+” Sign because X & Y have same sign.
![]()
Question 53.
The regression coefficient is independent of the change of [1 Mark, Nov. 2018]
(a) Origin
(b) Scale
(c) Scale and origin both
(d) None of these
Solution:
(a) Origin
Question 54.
A.M of regression coefficient is [1 Mark, June 2019]
(a) Equal to r
(b) Greater than or equal to r
(c) Half of r
(d) None
Solution:
(b) Greater than or equal to r
Question 55.
If the regression line of Y on X is given by Y = X + 2 and Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation is 0.5 then \(\frac{\sigma_y^2}{\sigma_x^2}\) = _____
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) None
Solution:
(c) 4
The regression line of y on x is given by y = x + 2 [It is in the form Y = a + bX]
byx = Coefficient of X = 1
Coeff. of correlation (r) = 0.5
then Regression coefficient Y on X
= byx = r \(\frac{\sigma_y}{\sigma_x}\)
1 = 0.5 \(\frac{\sigma_y}{\sigma_x}\)
\(\frac{\sigma_y}{\sigma_x}\) = \(\frac{1}{0.5}\) = \(\frac{10}{5}\) = 2
\(\left(\frac{\sigma_y}{\sigma_x}\right)^2\) = (2)2
\(\frac{\sigma_y^2}{\sigma_x^2}\) = 4.