Chapter 4 Procedural Compliance under GST – CS Professional Advance Tax Law Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Procedural Compliance under GST – CS Professional Advance Tax Law Study Material
Question 1.
Determine with reason, whether the following statements are true or false with reference to provisions of GST law:
(i) “A registered person shall issue separate invoices for taxable and exempted goods when supplying both taxable as well as exempted goods to an unregistered person”. (June 2019, 2 marks)
(ii) “A Non- banking financial company (NBFC) can issue a consolidated
tax invoice at the end of every month for the supply made during that month”. (June 2019, 1 mark)
(iii) “It is mandatory to issue a tax invoice in case a registered person has opted for composition levy scheme”. (June 2019, 2 marks)
Answer:
(i) The given statement is false.
Where a registered person is supplying taxable as well as exempted goods or services or both to an unregistered person, a single “invoice cum bill of supply” may be issued for all such supplies (Rule 46A of the CGST Rules, 2017).
(ii) The given statement is true.
A non-banking financial corppany is allowed to issue a consolidated tax invoice or any other document In lieu thereof for the supply of services made during a month at the end of the month. [Rule 54(2) of the CGST Rules, 2017].
(iii) The given statement is false.
A registered person paying tax under the provisions of Section 10 of CGST Act, 2017 (composition levy) is required to issue, instead of tax invoice, a bill of supply containing the specified particulars in the prescribed manner [Section 31 (3)(c) read with Rule 49 of the CGST Rules, 2017].
Question 2.
State with brief reasons whether the following are true or false; as per GST law:
(i) When the refund is issued beyond 60 days from the date of application, interest is payable @ 8% per annum.
(ii) Final return has to be furnished within 3 months of the date of order of cancellation of registration of GST.
(iii) Commissioner can grant time for payment of GST liability in maximum of 20 instalments for the self assessed tax shown in the GST return, as per section 80.
(iv) Under section 10, the ‘due date for’ filing return by a registered person is 20 days after the end of each quarter. (Dec 2019, 1 mark each)
Answer:
(i) False. As per section 56 of the CGST Act, where any tax ordered to be refunded is not refunded to the applicant within 2 months from the date of the application, the applicant shall be paid interest at such rate not exceeding 6%. as may be prescribed by Board.
Vide Notification No. 13/2017-C.T., dated 28-6-2017, the Government has notified the rate of interest for the purpose of Section 56 @ 6%.
(ii) True. As per section 45 when a registration is cancelled such person shall furnish a final return within 3 months of the date of cancellation or date of order of cancellation – whichever is later.
(iii) False. As per Section 80 of the CGST Act, the Commissioner cannot grant payment of tax in instalments in respect of self assessed tax. However, In respect of any amount due other than self assessed tax the Commissioner can provide monthly instalments not exceeding 24 for the purpose of payment of tax.
(iv) False. As per section 39(2) the due date for filing return by the composition person is 18 days after the end of each quarter.
![]()
Question 3.
State with reasons whether the following statements are true or false under GST Law:
(ii) No e-way bill is required if a Registered person from West Bengal purchases goods from Delhi valuing ₹ 1,12,000 (including tax) and carries the same with him in train. (Aug 2021, 1 mark)
(iii) A person exclusively dealing in goods not liable to tax or wholly exempt from tax having a turnover of ₹ 1,00,00,000 is required to get registered under GST. (Aug 2021, 1 mark)
(iv) TCS is not required to be collected on supplies on which the recipient is liable to pay tax on Reverse charge basis. (Aug 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
(ii) False. E-way bill is necessary. It has to be generated by either the supplier or the recipient either before or after the commencement of the movement of goods when goods are transported by railways.
(iii) False. As per Section 23 (1) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, any person engaged exclusively in the business of supplying goods or services or both that are not liable to tax or wholly exempt from tax under this Act or under the Integrated Goods & Services Act, 2017 (IGST Act), is not liable for registration.
(iv) True. TCS is not required to be collected when the recipient is required to pay tax on Reverse charge basis as according to the explanation to section 52 of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 the expression net value of taxable supplies or when TCS is to be collected shall means the aggregate value of taxable supplies of goods or services or both other than services notified under section 9(5) made during any month by the registered person through the operator as reduced by aggregate value of taxable supplies returned to the supplies during the said month.
Question 4.
State with reasons, whether the following statement is true or false under GST law:
TDS under section 51 of CGST Act, should be paid to the Government by the deductor within 15 days after the end of the month in which the deduction is made. (Aug 2021, 1 mark)
Answer:
False. As per Section 51(2) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 the amount deducted as tax under Section 51 shall be paid to the Government by the deductor within ten days (10 days) after the end of the month in which deduction is made in such manner as may be prescribed.
Question 5.
Write short notes:
Common Portal (Dec 2017, 1 mark)
Answer:
“Common Portal” means the common goods and services tax electronic portal referred to in section 146. [Section2(26)]
Question 6.
Who are required to file Annual Return under CGST Act, 2017? Also explain the time limit for filing such return. Is there any requirement of furnishing of the audited annual accounts? (Dec 2017, 5 marks)
Answer:
Every registered person, other than an Input Service Distributor, a person paying tax under section 51 or section 52, a casual taxable person and a non-resident taxable person, shall furnish an annual return as specified under sub-section (1) of section 44 electronically through the common portal either directly or through a Facilitation Centre notified by the Commissioner.
Annual return for every financial year to be filed electronically in prescribed format and in such manner as may be prescribed on or before the 31st December of the next financial year.
Question 7.
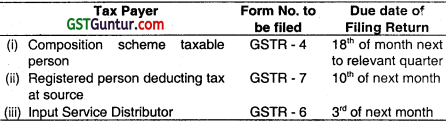
State the Form Number and the due date for its filing under CGST Act, 2017 of the return by:
(i) a composition scheme taxable person
(ii) a registered person deducting tax at source
(iii) an input service distributor. (June 2018, 1 mark each = 3 marks)
Answer:
Question 8.
Briefly explain provisions related to e-way bill as per CGST Act, 2017 relating to:
(i) What is e-way bill and when it is being required? (June 2018, 1 mark)
(ii) What is its validity period? (June 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
(i) E – way bill is an electronic way bill for movement of goods which is generated on the GSTN portal. It is required when a “movement” of goods is of more than ₹ 50,000 in value. A registered person cannot move goods without an e – way bill.
(ii) The validity period of e – way bill is tabulated as under:
Distance Validity period
Upto 100 kms One day
For every 100 kms or part thereof thereafter One additional day
![]()
Question 9.
Discuss the provisions relating to refund of balance in electronic cash ledger as per the GST law. (Dec 2018, 2 marks)
Answer:
As per Section 54 a registered person, claiming refund of any balance in the electronic cash ledger in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (6) of Section 49, may claim such refund by submitting a refund application form RFD-01.
Question 10.
What are the documents required to be prepared by the recipient of supplies from an unregistered person as per GST law? (Dec 2018, 3 marks)
Answer:
(i) A registered person who is liable to pay tax under reverse charge shall issue an invoice in respect of goods of services or both received by him from the supplier who is not registered on the date of receipt of goods or services or both;
(ii) A registered person who is liable to pay tax under shall issue a payment voucher at the time of making payment to the supplier.
Question 11.
Briefly discuss the provisions related to Levy of late fee as per section 46 of CGST Act, 2017 on a person who fails to furnish the details of outward or inward supplies required under section 37 or 38 or 39 or 45 of CGST Act, 2017. (Dec 2018, 3 marks)
Answer:
As per Section 47 of CGST Act, 2017 read with notification No. 64/2017- Central Tax and 4/2018 – Central Tax, any registered person who fails to furnish the return under Section 37 or 39 or 45 or 52 of CGST Act, 2017 shall pay the late fees of ₹ 25 for every day during which such failure continues and ₹ 10 in case of nil return subject to a maximum of ₹ 5,000.
As per Central Government notifications the late fees has been reduced to ₹ 25 for every day during which such failure continues and ₹ 10 in case of nil return subject to a maximum of ₹ 5,000.
Note: ₹ 25/₹ 10 is late fees in CGST Act, equal late fees shall be charged under respective SGST Act of the state.
Question 12.
When can Summary Assessment order be made by the proper Officer under the provisions of the CGST Act, 2017? Can such an order be requested to be withdrawn and if yes, then how and before which authority? (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
As per Section 64 of the CGST Act, 2017, ‘Summary Assessments’ can be initiated by the proper officer to protect the interest of revenue when:
(a) has evidence that a taxable person has incurred a liability to pay tax under the Act, and
(b) believes that the delay in passing an assessment order will adversely affect the interest of revenue.
Such order can be passed after seeking permission from the Additional Commissioner /Joint Commissioner.
In certain cases, like when goods are under transportation or are stored in a warehouse, and the taxable person in respect of such goods cannot be ascertained, the person in charge of such goods shall be deemed to be the taxable person and will be assessed to tax.
A taxable person against whom a summary assessment order has been passed can apply for its withdrawal to the Jurisdictional Additional/Joint Commissioner within thirty days of the date of receipt of the order.
The Jurisdictional Additional/Joint Commissioner, if finds that the order is erroneous, he can order for withdrawal and direct the proper officer to carry out determination of tax liability in terms of Section 73 or 74 of CGST Act. The Additional/Joint Commissioner can follow a similar course of action on his own motion, if he finds the summary assessment order to be erroneous.
Question 13.
Discuss and explain in brief the provisions relating to refund of the amount of advance tax deposited by a casual taxable person under section 27(2) of the CGST Act, 2017. (Dec 2020, 4 marks)
Answer:
As per provisions of section 54(13) of CGST Act, 2017, the amount of advance tax deposited by a casual taxable person under section 27(2), shall be refunded only when such person has, in respect of the entire period for which the certificate of registration granted to him had remained in force, furnished all the returns required under section 39 of the CGST Act, 2017.
Further, as per 4th proviso to Rule 89 of the CGST Rules, 2017, refund of any amount, after adjusting the tax payable by the applicant out of the advance tax deposited by him under section 27 at the time of registration, shall be claimed in the last return required to be furnished by him.
![]()
Question 14.
(i) Discuss briefly the salient features of Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) scheme under GST. (Aug 2021, 2 marks)
(ii) Explain the provisions of CGST Act, and rules regarding Annual Return for the financial year 2021 -22. (Aug 2021, 3 marks)
Answer:
(i) Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) Scheme
To help the small tax payers whose aggregate annual turnover is up to ₹ 5 crore in the preceding financial year 2021-22. CBIC has launched Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) scheme under GST. This scheme allows the taxpayers to file form GSTR-3B on a quarterly basis and pay tax every month. This is an optional scheme. Registered person opting for the scheme would be required to furnish the details of outward supply in FORM GSTR-1 quarterly as per Rule 59 of the GST Rules. At the same time, the tax payer has been given a facility to upload their tax invoices on monthly basis on Invoice Furnishing Facility available on GSTN Portal.
(ii) Annual Return
Every Registered person otherthan an Input Service Distributor (ISD), a person paying tax under section 51 or section 52 a casual taxable person shall furnish an annual return as specified under section 44 (1) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 electronically in FORM GSTR – 9. However a person paying tax under section 10 shall furnish the annual return in FORM GSTR – 9A and every electronic commerce operator requires to deduct tax at source under section 52 shall furnish the annual return in FORM GSTR – 9B.
The due date in above cases is 31st day of December following the end of such Financial Year.
As per section 44 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 and notifications issued thereunder. Annual return for Financial year 2021-22 was required to be filed by all registered person whose aggregate annual turnover during the year 2021 -22 did not exceed two crore rupees shall have the option to furnish the annual return.
In other words, filing GSTR-9 was optional for registered persons having turnover upto rupees Two Crores and mandatory for registered person having turnover above 2 crores. The last date for furnishing the Annual Return for 2021-22 was 31.03.2023. However registered Person having turnover below Rupees two crore would be deemed to have furnished their Annual Return if they fail to do so.
In case of registered person whose turnover exceeds Five crores it is also mandatory to get their accounts audited under GST from a practicing Chartered Accountant or a practicing Cost and Management Accountant and to submit a copy of Audited Annual Accounts and a reconciliation statement duly certified in FORM GSTR – 9C for the financial year 2021-22.
Question 15.
State briefly the features of Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) scheme of furnishing GST return under CGST Act, 2017. (Aug 2021, 4 marks)
Answer:
A new scheme named Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) under GST has been launched recently to help small taxpayers having aggregate annual turnover up to ₹ Five Crores in the preceding Financial Year 2021 -22.
- The scheme allows the taxpayers to file Form GSTR – 3B on a quarterly basis and pay taxes every month.
- It is an optional scheme.
- The registered persons opting for the scheme would be required to furnish the details of outward supply in Form GSTR -1 on a quarterly basis.
- However, the registered persons opting for such scheme can furnish the details of outward supply on Invoice Furnishing Facility.
Question 16.
Explain the system prescribed under the CGST Act, 2017 to facilitate smaller dealers or dealers having no IT infrastructure and who are also not Information Technology Savvy to comply with the procedural requirement under the CGST Act, 2017. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
Under the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 to facilitate smaller dealers or dealers having no IT infrastructure and who are. also not Information Technology Savvy following facilities shall be made available:
(i) Tax Return Preparer (TRP) : A taxable person may prepare his registration application/ returns himself or can approach the TRP for assistance. TRP will prepare the registration document/ return in prescribed format on the basis of the information furnished by the taxable person. The legal responsibility of the correctness of information contained in the forms prepared by the TRP will remain with the taxable person only and the TRP shall not be liable for any errors or incorrect information.
(ii) Facilitation Centre (FC): GST Facilitation Centre shall be responsible for the digitization and/ or uploading of the forms and documents including summary sheet duly signed by the Authorized Signatory and given to it by the taxable person.
After uploading the data on common portal using the ID and Password of FC, a print-out of acknowledgement will be taken and signed by the FC and handed over to the taxable person for his records.
The FC will scan and upload the summary sheet duly signed by the Authorized Signatory
(iii) Further, the Government has introduced facility of Nil returns throuqh SMS.
Question 17.
XYZ Ltd. a taxable person registered under GST is eligible to get refund from the proper authority. Manager Finance of the company seeks your opinion to know whether there is any provision under the Act for obtaining a provisional sanction of refund. Advice the company suitably in the context of provisions contained under the CGST Act, 2017. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
XYZ Ltd. can obtain a provisional sanction for the refund as the proper officer may sanction refund of an amount up to ninety percent of the total amount of refund so claimed as reduced by the amount of Input Tax Credit (ITC) accepted on a provisional basis in case of Zero Rated Supplies.
This provisional refund shall be granted subject to the following conditions:
(i) The person claiming refund has not been prosecuted for any offence under the Act or under any earlier law prior to GST where the amount of tax evaded exceeds ₹ 250 Lakhs during the period of five years immediately preceding the tax period to which the claim for refund relates.
(ii) GST Compliance rating of the applicant is not less than five on a scale of ten.
(iii) Issues for which refund is claimed are not pending under proceedings of any appeal, review or revision and if pending, the same has not been stayed by any court or appropriate authority.
Question 18.
State the rate of tax for collection of tax at source applicable to electronic commerce operator (ECO) under the CGST Act, under the SGST Act and under the IGST Act, 2017. Also specify when and on which of the value the rate of tax for collection at source be applicable. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
The rate of tax collection at source (TCS) is 0.5% under CGST Act, 2017; 0.5% under SGST Act, 2017 and 1% under IGST Act, 2017.
TCS would be on the net value of taxable supplies made, through the electronic commerce where the consideration with respect to such supplies is to be collected by the electronic commerce operator.
The net value of taxable supplies is the aggregate value of taxable supplies of goods or services or both made during any month by all registered taxable persons through the operator as reduced by the aggregate value of taxable supplies returned to the suppliers during the said month.
Question 19.
State few cases where refundable amount shall be paid to the applicant, instead of being credited to Consumer Welfare Fund under CGST Act, 2017. (June 2022, 5 marks)
Answer:
Section 54(8) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, provides that the refundable amount shall be paid to the Applicant, instead of being credited to the Consumer Welfare Fund, if such amount is relatable to-
(a) Refund of tax paid on export of goods and/or services or on inputs or input services used in making such exports
(b) Refund of unutilized ITC in case of zero-rated supplies made without payment of tax or accumulated ITC on account of inverted duty structure
(c) Refund of tax paid on a supply which is not provided, either wholly or partially, and for which invoice has not been issued, or where a refund voucher has been issued
(d) Refund of tax paid on a transaction treating it to be an intra-Stale supply, but which is subsequently held to be an inter-State supply or vice-versa.
(e) The tax and interest, if any, or any other amount paid by the applicant, if he had not passed on the incidence of such tax and interest to any other person, or
(f) The tax or interest borne by such other class of applicants as the Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify.
Answer:
Composition of total supplies of vinod
| Particulars | ( ₹ in Lakhs) |
| Value of Supply of goods chargeable to GST
Goods to be supplied to World Heath Organisation [Though this is an exempt SUPPLY BUT INCLUDIBLE for ascertaining aggregate turnover] |
38
4 |
| Aggregate Turnover | 42 |
It is to be noted that aggregate turnover would include, Taxable Supplies, Exempt Supplies, Zero Rated Supplies and Inter State Supplies, but not supplies through the Reverse Charge mechanism route.
Since the aggregate turnover during third and fourth quarter of 2022 -23 of Mr. Vinod exceeds ₹ 40 Lakhs, he is advised to apply for registration under GST laws.
![]()
Question 20.
M/s Nose Ltd. reduced the amount of ₹ 2,25,000 from the output tax liability in contravention of the provisions of section 42(10) of the CGST Act, 2017 in the month of January 2022 (vide invoice dated 12th January, 2022), which is ineligible credit at invoice level. As a result a show cause notice was issued by the Central Tax Department under section 74 of the CGST Act, 2017 along with interest. M/s Nose Ltd. paid the tax and interest on 5th March, 2022. Find the interest liability if any? Ignore penalty. (Dec 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
As per Section 42(10) read with Section 50(3) of CGST Act, 2017 amount reduced from the output tax liability in contravention of the provisions of Section 42(7) shall be added to the output tax liability of the recipient in his return for the month in which such contravention takes place and such recipient shall be liable to pay interest on the amount so added at the rate specified in the Section 50(3) of CGST Act, 2017.
- Therefore, applicable interest rate shall be 24% per annum.
- January month return due date is 20th of February, 2022.
- Interest = ₹ 1,923 (₹ 2,25,000 × 24% × 13/365)
- From 21st February 2022 to 5th March 2022 = 13 days
Question 21.
Amar Publishing House, registered under CGST Act, 2017 in Delhi is engaged in printing and selling of books as well as trading of stationery items. It has provided following information of a single consignment which is to be supplied to a person in Jaipur (Rajasthan):
- Value of exempted supplies of ₹ 12,000 and value of taxable supplies of ₹ 32,000 are indicated on tax invoice.
- Value of goods to be sent to unregistered job worker on delivery challan having value of ₹ 16,000.
Note: All amounts given above are excluding GST.
Calculate the consignment value, for the purpose of generating e-way bill for Interstate supply of goods. Take rate of tax on taxable goods of IGST @ 12%. Legal provision explained in brief should form part of the answer.
(June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Determination of the value of consignment for E-way Bill:
As per Rule 138 of the CGST Rules, 2017, Consignment value of goods shall be the value, determined in accordance with the provisions of Section 15 of the CGST Act, 2017, declared in an invoice, a bill of supply or a delivery challan, as the case may be, issued in respect of the said consignment and also includes the Central tax, State or Union Territory tax, integrated tax and cess charged, if any, in the document and shall exclude the value of exempt supply of goods where the invoice is issued in respect of both exempt and taxable supply of goods.
Hence, according to the above rule, consignment value shall be:
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| Taxable Value of Supply | 32,000 |
| Add: IGST on taxable value of supply @ 12% on 32,000 | 3,840 |
| value of goods to be sent to job worker on delivery challan | 16,000 |
| Total value of consignment | 51,840 |
Question 22.
Jayant Pvt. Ltd. of Jaipur (Rajasthan) provides the following information of the supplies made for the year 2022-23:
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| (i) Sale of high speed diesel on which Sales Tax (VAT) levied by Rajasthan Government | 8,00,000 |
| (ii) Supply of goods directly by principal from the place of Jayant Pvt. Ltd. after completion of Job work done by Jayant Pvt. Ltd. | 9,00,000 |
| (iii) Taxable outward supply within Rajasthan | 6,00,000 |
| (iv) Inward supply of services on which GST to be paid by Jayant Pvt. Ltd. under reverse charges | 5,00,000 |
| (v) Outward supply on which GST to be paid by recipient under reverse charges | 1,00,000 |
Calculate the aggregate turnover for the purpose of registration under CGST Act, 2017 and state whether Jayant Pvt. Ltd. is liable for registration or not. Also provide brief reasons for the treatment of various items given above in the context of Provisions of CGST Act, 2017.
Note: All the above amount are exclusive of taxes of any nature. (June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Calculation of Aggregate Turnover
| Particulars | Amount (₹) |
| (i) Sale of high speed diesel on which sales tax (VAT) levied by Rajasthan Government | 8,00,000 |
| (ii) Taxable outward supply within Rajasthan | 6,00,000 |
| (iii) Outward supply within State on which GST to be paid by recipient under reverse charge (RCM) | 1,00,000 |
| Aggregate turnover | 15,00,000 |
1. As per Section 2(6) of the CGST Act, 2017, aggregate turnover includes the aggregate value of all exempt supplies. Thus, sale of high speed diesel is an exempt supply and is, therefore, includible while calculating the aggregate turnover.
2. The aggregate turnover exclude the value of inward supplies on which tax is payable under reverse charge but include outward supply on which GST to be paid by recipient under reverse charge.
3. Supply of goods after completion of job work by registered job worker shall be treated as the supply of goods by the principal in terms of explanation (ii) to Section 22 of the CGST Act, 2017.
As per Section 22 of the CGST Act, 2017, a supplier is liable to be registered, if his aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds ₹ 20 lakhs. However, if supplier receives any inward supply on which GST to be paid by recipient under reverse charge then he is compulsory required for registration even if its aggregate turnover is below ₹ 40 lakhs. Hence, Jayant Pvt. Ltd. needs to be compulsory registered even though his turnover is less than the limit of ₹ 40 lakhs.
![]()
Question 23.
Badrinath Filters Ltd., a registered supplier of industrial air filters, is required to send from Mumbai (Maharashtra), a consignment of parts of air filters to be replaced under warranty at various client locations in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. The value of consignment declared in delivery challan accompanying the goods is ₹ 52,000.
Badrinath Filters Ltd. is of the view that since movement of goods to Gujarat is caused due to reasons other than supply, e-way bill is not mandatorily required to be generated in this case.
You are required to examine whether the aforesaid view is correct. (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
E-way bills:
The goods to be moved to another State for replacement under warranty is not a ‘supply’. However, Rule 138(1) of the CGST Act, 2017. inter alia, stipulates that every registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value exceeding ₹ 50,000 :
- in relation to a supply; or
- for reasons other than supply; or
- due to inward supply from an unregistered person,
Shall, generate an electronic way bill (E-way Bill) before commencement of such movement.
CBIC vide Q 9. of FAQs on E-way Bill has also clarified that even if the movement of goods is caused due to reasons others than supply [including replacement of goods under warranty, e-way bill is required to be issued.
Thus, in the given case, since the consignment value exceeds ₹ 50,000, e-way bill is required to be mandatorily generated.
Therefore, the contention of Badrinath Filters Ltd. that e-way bill is not mandatorily required to be generated as the movement of goods is caused due to reasons other than supply, is not correct.
Question 24.
Anand Kumar, a regular tax payer, filed his return of outward supplies (GSTR-1) for the month of August, 2021 before the due date. Later on, in February, 2022 he discovered certain error in the GSTR-1 return of the month of August, 2021 so filed before the due date and thus intends to correct the GSTR-1 and consults you to seek an opinion.
You are required to advise as to the suitable course of action to be taken according to statutory provisions contained under the CGST Act, 2017 so as to enable him to rectify the error so noticed in the already filed GSTR-1 return of the month of August, 2021. (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
As per Section 37(3) of the CGST Act, 2017, any registered person, who has furnished the details for any tax period of the CGST Act, 2017 shall upon discovery of any error or omission therein rectify such error or omission in such manner as may be prescribed in the tax period in which it is noticed.
The tax payer shall also be paying the tax and interest, if any, in case there is a short payment of tax on account of such error or omission, in the return to be furnished for such tax period.
Rectification of details furnished in GSTR-1 shall not be allowed after:
- 30th day of November following the end of the financial year to which such details pertain; or
- filing of the relevant annual return. Due date of filing of the annual return in this case is 31.12.2022; whichever is earlier.
In the present case, the error has been noticed in the GSTR-1 for August 2021. Such error can be corrected on or before 30th November 2022 or before the filing of annual return for 2021 -22. In case, Mr. Anand Kumar can very well make the required corrections in GSTR-1 of August 2021 through “Amendment Tables” in GSTR-1 to be filed for the month of February 2022.
He should also pay the tax and interest, if any, in case there is short payment, in the return to be furnished for February 2022.
Question 25.
Radhey Gobind & Co. engaged in the wholesale business particularly dealing in the product of which supply was exempt from tax under GST. Subsequently, tax was imposed on the sale of the product by a notification issued from 01-10-2021. Radhey Gobind & Co. continued to sell the product without making any change in the selling price of the product.
Later, in the month of March, 2022 they realised that because of no change in the selling price, they had paid higher quantum of tax and therefore decided to file an application for refund claim by stating that there was no change in the price before and after imposition of tax and hence the burden of tax had not been passed on to the buyer.
Discuss and explain in the context of provisions of the CGST Act, 2017 supported with a decided case law, if any, whether the stand taken for refund claim by Radhey Gobind & Co. shall be acceptable. (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
Section 54 read with section 77 and Rule 89(2) under the CGST Act, 2017 1 allows refund of tax under various conditions which mainly cover payment of wrong tax by a registered person. One of the conditions for grant of refund to the applicant is that the burden of tax so claimed as refund should not have been passed on to any other person.
Apex Court in the case of CCE v. Allied Photographic 2004 166 ELT3 has held that even if there is no change in the price before and after the assessment (before and after imposition of tax), it does not lead to the irrebuttable conclusion that incidence of tax has not been passed on to the buyer as such uniformity may be due to various factors.
Thus, even if the price remains the same before and after imposition of tax, the assessee has to establish with tangible evidence that he has not passed on the burden of tax to the buyer in any manner to the satisfaction of the proper officer.
Thus, in the ordinary course, the refund claim made by Radhey Gobind & Co. will be sanctioned but credited to the consumer welfare fund. However, if Radhey Govind & Co. adduces sufficient evidence to prove that such tax has not been recovered from the buyer, the refund claim can be granted thereto.
Question 26.
Trident Beauty Cosmetics Ltd. operating multiple wholesale outlets of cosmetic products in different suburbs in Mumbai, Maharashtra received an order worth ₹ 3,54,000 (inclusive of GST leviable @ 18%) for supply of different cosmetic products from Prasanna Cosmetics Store of Delhi.
Trident Beauty Cosmetics Ltd. while checking the stocks found that order worth ₹ 1,18,000 can be fulfilled from the company’s Dadar (Mumbai) store and remaining goods worth ₹ 2,36,000 can be supplied from its Malad (Mumbai) store. Both the stores were instructed to issue separate invoices for the goods supplied and sent by them to Prasanna Cosmetics Store of Delhi. The goods are required to be transported to Delhi in a single conveyance owned by Radhey Transport Carriers of Dadar (Mumbai).
You are required to advise Trident Beauty Cosmetics Ltd. as per provision under the CGST Act, 2017 with regard to issuance of e-way bill/(s). (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
Trident Beauty Cosmetics Ltd. would be required to prepare two separate e- way bills since value of each of the invoice exceeds ₹ 50,000 and each invoice is to be considered as separate consignment for the purpose of generating e-way bill.
Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) has clarified that if multiple invoices are being issued by the supplier to one recipient, then for the movement of goods of more than one invoice multiple e-way bills have to be generated.
One e-way bill has to be generated for each invoice, irrespective of the fact whether same or different consignors or consignees are involved. Multiple invoices cannot be clubbed to generate one e-way bill.
However, Rule 138(6) CGST Rules, 2017 provides that after e-way bill has been generated for each invoice/ consignment, where multiple consignments are intended to be transported in one conveyance, the transporter may indicate the serial number of e-way bills generated in respect of each such consignment electronically on the common portal and a consolidated e-way bill in FORM GST EWB-02 may be generated by him on the said common portal prior to the movement of goods.
Thus, after generating all these separate e-way bills, one consolidated e-way bill can be generated/prepared by the transporter for transportation purpose, where the goods are transported in one vehicle.
Therefore, in the present case both the stores issuing the invoice will generate separate e-way bill and thereafter one consolidated e-way bill can also generated by Radhey Transport Carriers of Dadar (Mumbai) as the goods from both the stores be transported to Delhi in one conveyance.
![]()
Question 27.
A.K. Services registered under GST in Chennai is engaged in supply and service of various goods and services. For the month of November, 2022. it has provided the following data:

If the goods and services supplied by A.K. Services are taxable under GST @ 12%:
(i) Calculate the TDS deductible by the recipients, who are notified under Section 51 of the CGST Act, 2017, if any, in respect of the aforesaid two independent contracts.
(ii) State whether the deductee can claim credit of TDS deducted under GST. (Aug 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
(i) Acording to Section 51 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, TDS is to be deducted @ 1 % by the recipient from the payment made or credited to the supplier (Deductee) of taxable goods or services or both, where the total value of such supply under a contract exceeds two lakh and fifty thousand (2,50,000) rupees.
Since in this case of Contract 1 the contract value including goods and services (excluding GST) is ₹ 2,50,000 (1,80,000+70,000) it does not fall under the provisions of TDS. Hence no, tax at source is required to be deducted in this case.
As per the provision in section 51(1) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 no deduction of tax at source shall be made if the location of the supplier and the place of supply is in a State or Union Territory which is different from the State or as the case may be Union Territory of registration of the recipient.
Since in the case Contract 2 the location of the supplier is in Chennai and the place of supply also is in Chennai but the place of location of the recipient is in Karnataka it appropriately falls in the exception envisaged in this provision and therefore, no tax is liable to be deducted.
(ii) According to section 51 (5) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 the deductee shall claim credit in his electronic cash ledger, of the tax deducted and reflected in the tax return of the deduct or furnished under section 39 (3) in such manner as may be prescribed.
Question 28.
Discuss the provisions of GST laws in respect of the following circumstances:
(i) R.K. Steel company received an order for supply of 1000 ton steel and supplied the same in installments as a continuous, supply. What will be the due date of invoice in such transaction?
(ii) What will be the due date of invoice if goods sent on approval for sale or return?
(iii) Farmer A is engaged in farming and cultivates agricultural produce from his, own land. He supplies agricultural produce worth Rupees 41 lakh cultivated by him and Rupees 6 lakh belonging to his friend to Traders. Whether he has to get registered under GST Act?
(iv) W Ltd. provides consultancy services without consideration to V Ltd. in which W Ltd. has holding rights. These technical services have been provided for the benefit of the entire group. Analyse the taxability of the service to determine whether it constitutes a supply under GST (Aug 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
(i) As per Section 31 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 in case of continuous supply of goods where successive statements of accounts or successive payments are involved the invoice shall be issued before or at the time each such statement is issued or as the case may be each such payment is received.
Hence, in this case, R. K. Steel Company shall issue invoice either before or at the time of issuance of account statement or at the time of receipt of each payment.
(ii) Section 31(7) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 provides that where the goods are being sent or taken or approved for sale or return are removed before the supply takes place, then the invoice shall be issued before or at the time of supply or six month from the date of removal whichever is earlier.
(iii) In terms of section 23(i) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, farmer shall not be liable to get registered under GST Act being an agriculturist to the extent of supply of produce out of cultivation of land. In this given case however, as the farmer has also supplied agricultural products processed by his friend his total turnover crosses rupees Forty lakhs (₹ 41 lakh + ₹ 6 lakh), which is beyond the threshold limit for getting registered. Hence, he will be liable to get registered.
(iv) As per section 7(1) (c) read with schedule I of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 supply of goods or services between related person is treated as supply even if it is without consideration. As per explanation to Section 15 of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 person shall be deemed to be related persons if one of them directly or indirectly controls the other.
Since, W Ltd. holds rights of V Ltd., they will be treated as related person and the said transaction will qualify as supply even though no consideration s involved.
Question 29.
A person dealing in supply of taxable goods is doing business since 01.01.2023. He crossed the mandatory thresholds for registration of ₹ 40 Lakhs on 22.01.2023. He was required to get registered under GST within one month i.e. by 21st February 2023. He did not get himself registered. If his tax liability is of ₹ 85,900, state the consequences of his not registering under GST laws. (Aug 2021, 4 marks)
Answer:
According to Section 22 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 every person making supply of taxable goods or services beyond the threshold limit of ₹ 40 Lakhs in a financial year is required to get registered under the Act.
Further according to section 25 every person liable to be registered under the Act shall apply for registration within thirty days from the date on which he becomes liable for registration.
According to Section 122(1)(xi) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 if a taxable person who is liable to be registered under CGST Act, 2017 but fails to obtain registration he shall be liable to pay a penalty of ten thousand rupees or an amount equivalent to the tax evade or the tax not deducted or short deducted but not paid to the Government, etc. Hence, in this case the person is liable to a penalty of ₹ 85,900.
Question 30.
A registered person under GST failed to file his returns for a period of the last six consecutive months. For this period his liability under GST works out to ₹ 20,000 (CGST ₹ 10,000, SGST ₹ 10,000). The department blocked his facility to generate e-way bills and the appropriate authority also issued a show cause notice to him as to why his registration should not be cancelled and afforded him an opportunity to present his case.
As the registered person failed to respond to the notice his registration was cancelled. The registered person is of the view that since his registration has been cancelled he is not required to pay anything to the Government. Advise the registered person in this context as per the CGST Act, 2017. (Aug 2021, 4 marks)
Answer:
According to Section 29 of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 the proper officer may cancel the registration of a person from such date, including any retrospective date, as he may deem fit, where any registered person has not furnished returns for such continuous tax period as may be prescribed after giving him an opportunity of being heard.
The section further provides that cancellation of registration hereunder shall not affect the liability of the person to pay tax and other dues under this Act or to any obligation under this Act or Rules made thereunder for any period prior to the date of cancellation whether or not such tax and dues are determined before or after the date of cancellation. Hence, in this case the dealer has to pay the tax of ₹ 20,000 along with interest to the Government.
Question 31.
ABC Ltd. of Jaipur, Rajasthan engaged in business was making till 28.02.2023 Intra-state supplies of the taxable goods. Total value of taxable supplies of goods till 28.02.2023 was of ₹ 16,50,000. However, on 01.03.2023, it has effected Inter-state supply of taxable goods amounting in total of ₹ 3,00,000. Manager (Taxation) of ABC Ltd. is of the view that it is not required to get registered under GST law since its aggregate turnover is not likely to exceed ₹ 20,00,000 during the financial year 2022-23.
However to become sure seeks your opinion as a consultant relating to his view as to requirement of registration under GST. Advise suitably to the company ABC Ltd. in the matter of requirement of registration as per provisions contained under the CGST Act, 2017. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
The opinion of the Manager (Taxation) of ABC Ltd. is not correct. As per provisions of section 24 of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 person making inter-state taxable supply are compulsorily required to obtain registration.
Section 24 of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 is an overriding section that makes it mandatory to obtain registration by certain prescribed persons even though the conditions prescribed under Section 22 are not fulfilled. Hence, ABC Ltd. despite having the turnover below the thresh hold limit of 20 lakh is mandatorily required to obtain registration.
As per provisions of Section 25 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 every person who is liable to be registered under section 22 or section 24 shall apply for registration in every such State or Union territory in which he is so liable within 30 days from the date on which he becomes liable to registration, in such manner and subject to such conditions as may be prescribed.
Thus, ABC Ltd. is required to obtain registration up-to 31.03.2023, because of making of Inter State supply of taxable goods on 01.03.2023.
![]()
Question 32.
Goyal Fashions, a registered supplier of designer outfits in Delhi, decided to exhibit its products in a Fashion Show being organized at Hotel Part Royal, Delhi on 04.01.2023 Goyal Fashion for the occasion, gets the makeover of its models done by Galaxy Beauty Services Ltd., Ashok Vihar, Delhi for which a consideration of ₹ 5,00,000 (excluding GST) has been charged. Galaxy Beauty Services Ltd., issued a duly signed tax invoice on 10.02.2022 showing the lumpsum amount of ₹ 5,90,000 inclusive of CGST and SGST @ 9% each. Goyal Fashions made the payment the very next day.
Answer the following questions in the context of provisions of the CGST Act, 2017:
(a) Examine and state whether the tax invoice has been issued within the time limit prescribed under the law by Galaxy Beauty Services Ltd.
(b) Tax consultant of Goyal Fashions objected to the invoice raised suggesting that the amount of tax charged in respect of the taxable supply should be shown separately in the invoice raised by Galaxy Beauty Services Ltd.
However, Galaxy Beauty Services Ltd, contended that there is no mandatory requirement of showing tax component separately in the invoice. Examine and State the validity of the objection raised by tax consultant of Goyal Fashions. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
IF CANDIDATES ASSUMED DATE OF ISSUE OF COMPLETION OF SERVICE: 04.01.2023 & DATE OF ISSUE OF INVOICE: 10.02.2022
(a) As per Section 31 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 read with the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017, in case of taxable supply of services, invoices should be issued before or after the provision of service, but within a period of 30 day (45 days in case of insurer, Banking company or financial institutions including NBFCs) from the date of supply of service.
In the present case, the tax invoice should have been issued in the prescribed time limit of 30 days from the date of supply of service i.e., up-to 03.02.2023 and invoice has been issued on 10.02.2022. This is issued wjthin time limit.
(b) Section 31 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 read with the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017, inter alia, provides that tax invoice shall contain the following particulars:
- Total value of supply of goods or services or both
- Rate of tax (Central tax, State tax, Integrated tax, Union territory Tax or Cess)
- Amount of tax charged in respect of taxable goods or services (Central tax, State tax, Integrated tax, Union Territory Tax or Cess)
The objection raised by the tax consultant of Goyal Fashions suggesting that the amount of tax charged in respect of the taxable supply should be shown separately in the invoice raised by Galaxy Beauty Services Ltd, is valid in law. In the present case, the tax amount has not been shown separately in the invoice.
Question 33.
Aryan & Sons is an unregistered dealer of taxable supplies in Delhi. On 10th September, 2022 aggregate turnover of Aryan & Sons exceeded ₹ 20,00,000. The firm applied for registration on 27th September, 2022 and was granted the registration certificate on 1st October, 2022. Under CGST Rules 2017, you are required to advise Aryan & Sons as to what is the effective date of registration in its case. It has also sought your advice regarding period for issuance of revised tax invoices. (June 2022, 5 marks)
Answer:
Section 22(1) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, provides that every supplier is liable to be registered under this act in the State or Union Territory, other than special category States, from where he makes a taxable supply of goods or services or both, if his aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds the threshold limit.
Section 25(1) of Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, provides that a supplier whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds the threshold limit in the State or Union Territory is liable to apply for registration within 30 days from the date of becoming liable to registration (i.e. the date of crossing the threshold limit).
Where the application is submitted within the same period, the effective date of registration is the date on which the person becomes liable to registration vide Central Goods and Services Tax, Rule 10(3).
In the given case, since Aryan & Sons have applied for registration on 27th September, 2022 which is within 30 days from the date of becoming liable to registration (10th September), its effective date of registration is 10th September, 2022.
Further, every registered person who has been granted registration with effect from a date earlier than the date of issuance tax of registration certificate to him, may issue revised tax invoices in respect of taxable supplies affected during this period within one month from the date of issuance of registration certificate [Section 31(3)(a) read with rule 53(2)].
In view of the same, Aryan & Sons may issue revised tax invoices against the invoices already issued during the period between effective date of registration (10th September, 2022) till the date of issuance of registration certificate (1st October, 2022) within one month from the date of issuance of certificate of registration, i.e. on or before 1st November, 2022.
Question 34.
Nizam Traders, registered in New Delhi, is engaged in supply of taxable goods. Its turnover in the preceding FY 2021-2022 was ₹ 230 lakh and was furnishing its GST return on monthly basis. In the beginning of April month in the current FY 2022-2023, it sought advice from its tax consultant. Vaibhav Consultants, whether it can furnish its GST on quarterly basis from now onwards. Vaibhav Consultants advised Nizam Traders that it cannot furnish its return on quarterly basis as the GST law does not provide for quarterly return any circumstances. Discuss the technical veracity of the advice given by Vaibhav Consultants. (June 2022, 5 marks)
Answer:
No, the advice given by Vaibhav Consultants is not valid in law. With effect from 01.01.2021, a quarterly return has been introduced under GST law where the payment of tax is to be made on monthly basis. The scheme is known as Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) Scheme.
The scheme has been introduce as a trade facilitation measure and in order to further case the process of doing business. It is an optional return filing scheme, introduced for small taxpayers having aggregate annual turnover (PAN based) of upto ₹ 5 crore in the current and preceding financial year to furnish their Form GSTR-1 and Form GSTR- 3B on a quarterly basis while paying their tax on a monthly basis through a simple challan. Thus, the tax payers need to file only four GSTR-3B returns in a year. Similarly, they would be required to file only four GSTR-1 returns since Invoice Furnishing Facility (IFF) is provided under this scheme.
Opting of QRMP Scheme is GSTIN wise. Distinct person can avail QRMP Scheme option for one or more GSTINs for a PAN can opt for the QRMP Scheme and remaining GSTINs may not opt for the said scheme. Since, the aggregate turnover of Nizam Traders does not exceed ₹ 5 crores in the preceding financial year, it is eligible for furnishing the return on quarterly basis till the time its turnover in the current financial year does not exceed ₹ 5 crores. In case its aggregate turnover crosses ₹ 5 crore during a quarter in the current financial year, it shall no longer be eligible for furnishing of return on quarterly basis from the first month of the succeeding quarter and needs to opt for furnishing of return on a monthly basis.
Question 35.
Suncity Private Ltd., a manufacturer registered in the state of Rajasthan, sold synthetic cloth to a retail seller in Maharashtra, at a value of ₹ 49,000 (excluding IGST leviable @ 5%). Now, it wants to send the consignment of such cloth to the retail seller in Maharashtra.
You are required to advise Suncity Private Ltd. on the following issues with reference to the provisions relating to the electronic way bill (c-way bill) as prescribed under the GST law:
(i) Whether a-way bill is mandatorily required to be generated in respect of such movement of goods ?
(ii) If yes, who is required to generate the e-way bill ?
(iii) What will be the consequences for non-issuance of e-way bill ? (Dec 2022, 5 marks)
Question 36.
From the following information of independent cases, your expert advice, with appropriate reasoning is sought on the applicability of TDS/TCS provisions of the CGST Act, 2017.
You shall also quantify the amount of TDS/TCS, as the case be, if the same is applicable.
Note: Rate is CGST, SGST and IGST are 9%, 9% and 18% respectively. All the amounts given are exclusive of taxes.
(i) Avis Fashions, a designer cloth dealer registered in the state of Rajasthan, effected supply through ‘FARE DEAL’, an electronic commerce operator (ECO). Net value of taxable Intra-State supplies effected for the month of October, 2022 was ₹ 2,00,000. (Dec 2022, 2 marks)
(ii) Tarun, a registered supplier in Maharashtra, was awarded a work contract by Government of Maharashtra amounting ₹ 4,00,000. Of this, value of exempt supply was ₹ 1,00,000. (Dec 2022, 3 marks)
Question 37.
Raj, a registered supplier, runs a general store in Bhilwara, Rajasthan. Some of the goods sold by him are exempt whereas some are taxable. You are required to advise him on the following issues:
(a) Whether Raj is required to issue a tax invoices in all cases, even if he is selling the goods to the end consumers?
(b) Raj sells some exempted as well as taxable goods valuing ₹ 6,000 to a school student. Is he mandatorily required to issue two separate GST documents?
(c) Raj wishes to know whether it is necessary to show tax amount separately in the tax invoices issued to the customers? (Dec 2022, 5 marks)
Question 38.
Whether the Department through the proper officer, can suo moto proceed to register of a Person under this Act?
Answer:
Yes. In terms of sub-section (8) of Section 25, where a person who is liable to be registered under this Act fails to obtain registration, the proper officer may, without prejudice to any action which may be taken under this Act, or under any other law for the time being in force, proceed to register such person in the manner as is prescribed in the Registration rules.
Question 39.
Whether the proper officer can reject an Application for Registration?
Answer:
Yes. In terms of sub-section 10 of section 25 of the CGST/SGST Act, the proper officer can reject an application for registration after due verification.
Question 40.
Whether the Registration granted to any person is permanent?
Answer:
Yes, the registration Certificate once granted is permanent unless surrendered, cancelled, suspended or revoked.
![]()
Question 41.
Whether Amendments to the Registration Certificate is permissible?
Answer:
Yes. In terms of Section 28, the proper officer may, on the basis of such information furnished either by the registrant or as ascertained by him, approve or reject amendments in the registration particulars within a period of 15 common working days from the date of receipt of application for amendment.
It is to be noted that permission of the proper officer for making amendments will be required for only certain core fields of information, whereas for the other fields, the certificate of registration shall stand amended upon submission of application in the GST common portal.
Question 42.
Whether Cancellation of Registration Certificate is permissible?
Answer:
Yes. Any Registration granted under this Act may be cancelled by the Proper Officer, in circumstances mentioned in Section 29 of the CGST/SGST Act. The proper officer may, either on his own motion or on an application filed, in the prescribed manner, by the registered taxable person or by his legal, heirs, in case of death of such person, cancel the registration, in such manner and within such period as may be prescribed.
As per the Registration Rules, an order for cancellation is to be issued within 30 days from the date of receipt of reply to SCN (in cases where the cancellation is proposed to be carried out suo moto by the proper officer) or from the date of receipt of application for cancellation (in case where the taxable person/legal heir applies for such cancellation)
Question 43.
Can the proper Officer Cancel the Registration on his own?
Answer:
Yes, in certain circumstances specified under section 29(2) of the CGST/SGST Act, the proper officer can cancel the registration on his own. Such circumstances include contravention of any of the prescribed provisions of the CGST Act or the rules made there under, not filing return by a composition dealer for a financial year beyond 3 months from the due date of furnishing the said return or non-furnishing of returns by a regular taxpayer for a continuous period of six months, and not commencing business within six months from the date of voluntary registration. However, before cancelling the registration, the proper officer has to follow the principles of natural justice, (proviso to Section 29(2)(e)).
Question 44.
Can unutilized Input tax credit be allowed as refund?
Answer:
Unutilized input tax credit can be allowed as refund in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (3) of section 54 in the following situations:
- Zero rated supplies made without payment of tax;
- Where credit has accumulated on account of rate of tax on inputs being higher than the rate of taxes on output supplies (other than nil rated or fully exempt supplies)
However, no refund of unutilized input tax credit shall be allowed in cases where the goods exported out of India are subjected to export duty, and also in the case where the supplier of goods or services or both avails of drawback in respect of central tax or claims refund of the integrated tax paid on such supplies.
Question 45.
Whether principle of unjust enrichment will be applicable in refund?
Answer:
The principle of unjust enrichment would be applicable in all cases of refund
except in the following cases:
- refund of tax paid on zero-rated supplies of goods or services or both or on inputs or input services used in making such zero-rated supplies
- unutilized input tax credit in respect of
- zero rated supplies made without payment of tax or,
- where the credit has accumulated on account of rate of tax on inputs being higher than the rate of tax on output supplies
- refund of tax paid on a supply which is not provided, either wholly or partially, and for which invoice has not been issued;
- refund of tax in pursuance of Section 77 of CGST/SGST Act i.e. tax wrongfully collected and paid to Central Government or State Government
- if the incidence of tax or interest paid has not been passed on to any other person;
- such other class of persons who has borne the incidence of tax as the Government may notify.
Question 46.
If a person is operating in different states, with the same PAN number, can he operate with a single Registration?
Answer:
No. Every person will have to get registered separately for each of the State from where he makes taxable supply if he is liable for registration in terms of Sub-section (1) of Section 22 of the CGST Act.
Question 47.
If a person is registered under earlier law, whether he needs to be registered under GST law compulsorily?
Answer:
Yes. As per section 22 (2) of the CGST Act, every person who, on the day immediately preceding the appointed day, is registered or holds a license under an earlier law, shall be liable to be registered under this Act with effect from the appointed day.
Question 48.
What is the time limit for taking registration under GST Law?
Answer:
Every Person who is liable to be registered under Section 22 or Section 24 shall apply within 30 days from the date on which he becomes liable to registration in such manner and subject to such conditions as may be prescribed.
Further, a casual taxable person or a non-resident taxable person shall apply for registration at least 5 days prior to the commencement of business. Furthermore, every person who makes a supply from the territorial waters of India shall obtain registration in the coastal State or Union territory where the nearest point of the appropriate baseline is located.
Question 49.
Whether a person having multiple business verticals in a State or Union territory can obtain different registrations for each of such vertical?
Answer:
Yes. As per proviso to Section 25 (2) of the CGST Act, a person having multiple business verticals in a State or Union territory, may obtain a separate registration for each business vertical, subject to such conditions as may be prescribed.
![]()
Question 50.
Is possession of a Permanent Account Number (PAN) mandatory for obtaining a Registration?
Answer:
Yes. Every person should have a Permanent Account Number issued under the Income Tax Act, 1961 in order to be eligible for grant of registration under Section 25 of the CGST Act.
Provided that a person required to deduct tax under section 51 may have, in lieu of a Permanent Account Number, a Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number issued under the said Act in order to be eligible for grant of registration.
However, as per section 25 (7) the CGST Act, PAN is not mandatory for a non-resident taxable person for obtaining registration.
Question 51.
Whether all persons are mandatorily required to obtain registration?
Answer:
(a) Yes
(b) Not required if he is an agriculturist or person exclusively engaged in supplying exempt goods or services, if specified threshold limit does not exceeds in a financial year.
(c) Not required if he is an agriculturist or person exclusively engaged in supplying exempt goods or services.
(d) No, only if specified threshold exceeds in a financial year then only need to obtain.
Space to write important points for revision
Question 52.
Should every registered person required to maintain books of account?
Answer:
Yes, as per Section 35 of the CGST Act, 2017 every registered person is required to keep and maintain books of account at his principal place of business, as mentioned in the certificate of registration.
Question 53.
What are the basic accounts required to be maintained by a person at the principal place of business?
Answer:
As per Section 35 of the CGST Act, 2017 read with the CGST Rules, 2017, the following accounts need to be maintained on a true and correct basis:
(a) Production or manufacture of goods;
(b) Inward or outward supply of goods or services of both;
(c) Stock of goods;
(d) Input tax credit availed;
(e) Output tax payable and paid;
(f) Such other particulars as may be prescribed.
Question 54.
Where are the books of account liable to be maintained?
Answer:
The books of account are to be maintained at principal place of business, as mentioned in the certificate of registration. Provided that where more than one place of business is specified in the certificate of registration, the accounts relating to each place of business shall be kept at such places of business.
Question 55.
Whether accounts can be maintained in the electronic form?
Answer:
Yes, the registered person may keep and maintain such accounts and other particulars in the electronic form and must be digitally signed. Proper’ electronic back-up of records shall be maintained and presented. The same must be produced on demand along with its sample hard copy and passwords, codes, etc.
Question 56.
The books and other records U/S 35 are to be maintained at:
(a) Place where the books and accounts are maintained
(b) Place of address of the Proprietor/ Partner/Director/Principal Officer
(c) Principal place of business mentioned in the Certificate of Registration
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(c) Principal place of business mentioned in the Certificate of Registration
Question 57.
In case, more than one place of business situated within a state specified in the Registration Certificate, the books and Accounts shall be maintained at
(a) Each place of business pertaining to such place
(b) Place where the books of accounts are maintained for all places situated within a state
(c) At principal place of business covered mentioned in the Registration Certificate for all places of business in each state
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(a) Each place of business pertaining to such place
Question 58.
What are the various returns prescribed under the GST Act?
Answer:
The various returns prescribed under GST Act read with Chapter VIII Returns of the CGST Rules, 2017 are as follows:
| Return | Particulars | Due date |
| GSTR-1 | Furnishing details outward supplies of goods or services or both | 10th of succeeding tax period |
| GSTR-1A (auto-drafted) | Communication to supplier of goods and services for any addition/ deletion/ modification made by the recipient in FORM GSTR-2 | Accept or reject before 17th of the succeeding tax period |
| GSTR-2 | Furnishing details of inward supplies | Before 15th of succeeding tax period |
| GSTR-2A(auto-drafted) | Part A: Communication to receiver of goods and services in respect of goods and services procured by it and uploaded by the supplier.
Part B: Communication to the receiver of credit in case of distribution of credit by Input Service Distributor in FORM GSTR-6 Part C: Communication of details of tax deducted at source from the payments to the receiver based on FORM GSTR-7 of the deductor Part D: Communication of details of tax collected at source on payments received by the supplier from the e-commerce operator, based on FORM GSTR-8. |
|
| GSTR-3 | Monthly return after finalization of outward supplies and inward supplies | 20th of succeeding tax period |
| GSTR-3A | Notice sent to registered taxable persons who fails to furnish return under section 39 or section 44 or section 45 or section 52 of the CGST Act, 2017 | |
| GSTR-3B | Return to be filed in lieu of FORM GSTR-3 when the due date for filing FORM GSTR-1 and FORM GSTR-2 has been extended by the Commissioner | Due date shall be notified by the Commissioner |
| GSTR-4 | Return to be furnished by a registered taxable person under composition scheme | 18th of the month succeeding the quarter |
| GSTR-4A | Communication to the person registered under composition scheme in respect of inward supplies procured by it and uploaded by the supplier | |
| GSTR-5 | Return to be furnished by non-resident taxable person | 20th of the month succeeding the tax period & within 7 days after expiry of registration |
| GSTR-6 | Return to be furnished by Input Service Distributor | 13th of succeeding tax period |
| GSTR-6A | Communication to Input Service Distributor in respect of inward supplies procured by it and uploaded by the supplier | |
| GSTR-7 | Return to be furnished by persons liable to deduct tax at source under Section 51 of the CGST Act | 10th of succeeding tax period |
| GSTR-7A | Certificate to be issued to the recipient by the person deducting tax at source | Within 5. days of remitting the amount deducted |
| GSTR-8 | Return to be furnished by persons liable to collect tax at source under Section 52 of the CGST Act | 10th of succeeding tax period |
| GSTR-9 | Annual return | 31st December of subsequent year |
| GSTR-9A | Annual return for composition dealers | 31st December of subsequent Year |
| GSTR-9B | Annual Return for electronic commerce operator required to collect tax at source | 31st December of subsequent year |
| GSTR-9C | Furnish a copy of audited annual accounts and a reconciliation statement, duly certified, | 31st December of subsequent year |
| GSTR-10 | Final Return | 3 months from the date of cancellation /order of cancellation, whichever later |
| GSTR-11 | Return to be filed by persons having Unique Identity Number and claiming refund on inward supplies | To be submitted along with Refund Application |
Question 59.
Is the word refund defined in the CGST Act?
Answer:
Yes, the word refund is defined in explanation to Section 54 of the CGST Act, 2017. As per the said definition, refund includes refund of tax and interest paid on:
- Zero-rated supplies of goods or services or both; or
- Inputs or input services used in the effecting such zero-rated supplies of goods or services or both; or
- Supply of goods regarded as deemed exports; or
- Refund of unutilized input tax credit at the end of any tax period in case the rate of output tax is less than the rate of input tax.
Question 60.
Is there any time limit to claim refund under Section 54?
Answer:
Yes, as per Section 54, refund application is to be filed before the expiry of two years from the relevant date.
![]()
Question 61.
Can United Nations Organisation claim refund?
Answer:
Yes. UNOs are entitled to claim refund of IGST/CGST/SGST paid on inward supplies (notified) of goods and/or services.
Question 62.
Who needs to file Return in GST regime?
Answer:
Every person registered under GST will have to file returns in some form or other. A registered person will have to file returns either monthly (normal supplier) or quarterly basis (Supplier opting for composition scheme). An ISD will have to file monthly returns showing details of credit distributed during the particular month. A person required to deduct tax (TDS) and persons required to collect tax (TCS) will also have to file monthly returns showing the amount deducted/collected and other details as may be prescribed. A non-resident taxable person will also have to file returns for the period of activity undertaken.
Question 63.
Is an Annual Return and a Final Return one and the same?
Answer:
No. Annual Return has to be filed by every registered person paying tax as a normal taxpayer. Final Return has to be filed only by those registered persons who have applied for cancellation of registration. The Final return has to be filed within three months of the date of cancellation or the date of cancellation order.
Question 64.
What is the consequence of not filing the return within the prescribed date?
Answer:
A registered person who files return beyond the prescribed date will have to pay late fees of rupees one hundred for every day of delay subject to a maximum of rupees five thousand. For failure to furnish Annual returns by due date, late fee of ₹ One hundred for every day during which such failure continues subject to a maximum of an amount calculated at a quarter percent [0.25%] of his turnover in a state, will be levied.
Question 65.
Who is the person responsible to make assessment of taxes payable under the Act?
Answer:
Every person registered under the Act shall himself assess the tax payable by him for a tax period and after such assessment he shall file the return required under section 39.
Question 66.
What is meant by commencement of audit?
Answer:
The term ‘commencement of audit’ is important because audit has to be completed within a given time frame in reference to this date of commencement. Commencement of audit means the later of the following:
(a) the date on which the records/accounts called for by the audit authorities are made available to them, or
(b) the actual institution of audit at the place of business of the taxpayer.
Question 67.
When can a taxable person pay tax on a provisional basis?
Answer:
As a taxpayer has to pay tax on self-assessment basis, a request for paying tax on provisional basis has to come from the taxpayer which will then have to be permitted by the proper officer. In other words, no tax officer can suo-moto order payment of tax on provisional basis.
This is governed by section 60 of CGST/SGST Act. Tax can be paid on a provisional basis only after the proper officer has permitted it through an order passed by him. For this purpose, the taxable person has to make a written request to the proper officer, giving reasons for payment of tax on a provisional basis. Such a request can be made by the taxable person only in such cases where he is unable to determine:
(a) the value of goods or services to be supplied by him, or
(b) determine the tax rate applicable to the goods or services to be supplied by him.
In such cases the taxable person has-to execute a bond in the prescribed form, and with such surety or security as the proper officer may deem fit.
Question 68.
Under what circumstances can a tax officer initiate Summary Assessment?
Answer:
As per section 64 of CGST/SGST Act, Summary Assessments can be initiated to protect the interest of revenue when:
(a) the proper officer has evidence that a taxable person has incurred a liability to pay tax under the Act, and
(b) the proper officer believes that delay in passing an assessment order will adversely affect the interest of revenue.
Such order can be passed after seeking permission from the Additional Commissioner / Joint Commissioner.
![]()
Question 69.
Who can conduct audit of taxpayers?
Answer:
There are two types of audit prescribed in the GST Act(s) as explained below:
(a) Audit by Department: The Commissioner or any officer of CGST or SGST or UTGST authorized by him by a general or specific order, may conduct audit of any registered person. The frequency and manner of audit will be prescribed in due course. (Section 65 of the CGST/SGST Act)
(b) Special Audit: If at any stage of scrutiny, inquiry, investigations or any other proceedings, if department is of the opinion that the value has not been correctly declared or credit availed is not with in the normal limits, department may order special audit by chartered accountant or cost accountant, nominated by department. (Section 66 of the CGST/SGST Act)
Question 70.
What are the obligations of the taxable person when he receives the notice of audit?
Answer:
The taxable person is required to:
(a) facilitate the verification of accounts/records available or requisitioned by the authorities,
(b) provide such information as the authorities may require for the conduct of the audit, and
(c) render assistance for timely completion of the audit.
Question 71.
Under what circumstances can a special audit be instituted?
Answer:
A special audit can be instituted in limited circumstances where during scrutiny, investigation, etc. it comes to the notice that a case is complex or the revenue stake is high. This power is given in section 66 of CGST ISGST Act.
Question 72.
What is the time limit to submit the audit report?
Answer:
The auditor will have to submit the report within 90 days or within the further extended period of 90 days.
Procedural Compliance under GST Notes
Enhanced threshold for supplier of goods [Notification No. 10/2019-CT dated 7.3.2019]
Effective, 1.4.2019, the Central Government has increased threshold for taking registration for person, who is engaged in exclusive supply of goods and whose aggregate turnover in the financial year does not exceed forty lakh rupees, except, –
(a) persons required to take compulsory registration under section 24 of the said Act;
(b) persons engaged in making the following supplies:
- Ice cream and other edible ice, whether or not containing cocoa falling under tariff 21050000
- Pan masala falling under tariff 21069020
- All goods, i.e. Tobacco and manufactured tobacco substitutes falling under Chapter 24
(c) persons engaged in making intra-State supplies in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Puducherry, Sikkim, Telangana, Tripura, Uttarakhand; and
(d) persons who opt to take registration voluntarily by exercising option under the provisions of sub – Section (3) of Section 25, or such registered persons who intend to continue with their registration under the said Act.
Supplier
According to Section 2(105) of the CGST Act, “supplier” in relation to any goods or services or both, shall mean the person supplying the said goods or services or both and shall include an agent acting as such on behalf of such supplier in relation to the goods or services or both supplied.
Location of the supplier of services
Section 2(71) of the CGST Act defines location of the supplier of services, which means:
- where a supply is made from a place of. business for which the registration has been obtained, the location of such place of business;
- where ‘a supply is made from a place other than the place of business for which registration has been obtained (a fixed establishment elsewhere), the location of such fixed establishment;
- where a supply is made from more than one establishment, whether the place of business or fixed establishment, the location of the establishment most directly concerned with the provisions of the supply; and
- in absence of such places, the location of the usual place of residence of the supplier;
![]()
Agent
In terms of Section 2(5) of the CGST Act, “agent” means a person, including a factor, broker, commission agent, arhatia, del credere agent, an auctioneer or any other mercantile agent, by whatever name called, who carries on the business of supply or receipt of goods or services or both on behalf of another.
Special Category States
Article 279A (4) (g) of the Constitution of India specifies the name of 11 States which have been put under the ‘special category States’. The name of these States are: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
Common Portal
According to Section 2(26) “common portal” means the common goods and services tax electronic portal referred to in section 146.
Compulsory Registration
The following categories of persons are required to be registered compulsorily irrespective of the threshold limit:
- persons making any inter-State taxable supply, except persons making inter-state supply of certain handicraft goods, and services;
- casual taxable persons except persons making supply of certain handicraft goods;
- persons who are required to pay tax under reverse charge;
- persons who are required to pay tax under sub-section (5) of Section 9;
- non-resident taxable persons making taxable supply;
- persons who are required to deduct tax under Section 51;
- persons who make taxable supply of goods or services on behalf of other registered taxable persons whether as an agent or otherwise;
- Input service distributor (whether or not separately registered under the Act);
- persons who supply goods, other than supplies specified under Section 9(5), through such e-commerce operator who is required to collect tax at source under Section 52;
- every electronic commerce operator;
- every person supplying online information and data base retrieval services from a place outside India to a person in India, other than a registered person.
Persons not liable for registration
Section 23(1) of the CGST Act states that the following persons shall not be liable to registration, namely: –
any person engaged exclusively in the business of supplying goods or services or both that are not liable to tax or wholly exempt from tax under this Act or under the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act (In short IGST Act)
an agriculturist, to the extent of supply of produce out of cultivation of land.
The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify the category of persons who may be exempted from obtaining registration under this Act.
Registration to be cancelled in certain cases
Rule 21 of the CGST Rules states that the registration granted to a person is liable to be cancelled, if the said person,-
- does not conduct any business from the declared place of business; or
- issues invoice or bill without supply of goods or services in violation of the provisions of this Act, or the rules made thereunder; or
- violates the provisions of Section 171 of the Act or the rules made thereunder. .
Disadvantage for not getting Registration
Where a person is not registered under the GST regime, he can neither collect GST from his customers nor can claim any input tax credit of GST paid by him.
“Refund”
“Refund” includes,
(a) any balance amount in the electronic cash ledger so claimed in the returns,
(b) any unutilized input tax credit in respect of
(i) zero rated supplies made without payment of tax or,
(ii) where the credit has accumulated on account of rate of tax on inputs being higher than the rate of tax on output supplies (other than nil rated or fully exempt supplies), (c) tax paid by specialized agency of United Nations or any Multilateral Financial Institution and Organization notified under the United Nations (Privileges and Immunities) Act, 1947, Consulate or Embassy of foreign countries on any inward supply.