Performance Measurement and Evaluation – CA Final SCMPE Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Performance Measurement and Evaluation – CA Final SCMPE Question Bank
Question 1.
Write short note on:
Balanced Score Card; (Dec 2008, 5 marks) [CMAFG IV]
Answer:
Balanced Score Card:
- Balanced Score Card is a performance management and strategy development methodology that helps executives translate an organization’s mission statement and overall business strategy into specific, qualifiable goals and monitors the organization’s performancfe in terms of these goals.
- Balanced Score Card also aligns budgets to strategy and helps in developing an enterprise performance management system.
- It is a set of financial and non-financial measures relating to company’s critical success factors.
- As a management tool it helps companies to assess overall performance, improve operational processes and enable management to develop better plans for improvements.
- It offers managers a balanced view of their organization upon which they can base real change.
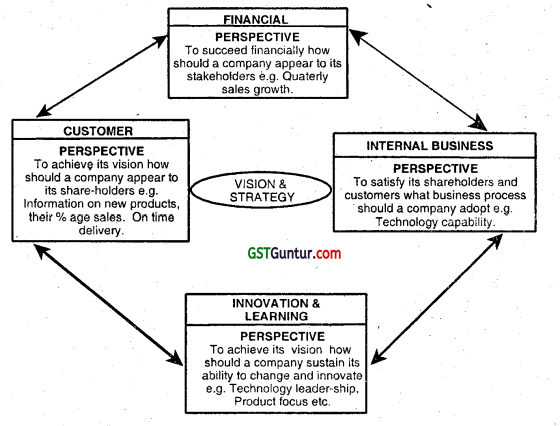
Balanced Score Card has the following four perspectives:
- Customer Perspective: i.e., How customers see us? The Customer Perspective considers the business through the eyes of the customers, measuring and reflecting upon customer’s satisfaction.
- Internal Business Perspective: i.e., In what processes must the firm excel? The Internal Business Perspective focuses attention on the performance of the key internal processes of the business.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: i.e., Can we continue to improve and create value? This perspective is a measure of potential future performance. It drives attention to the basis of all future success the organization’s people and its infrastructure.
- Financial Perspective: i.e., How do we look at our shareholders? The Financial Perspective measures the results that the organization delivers to its stakeholders.
![]()
Question 2.
Write short note on the following;
Advantages of balanced score card (Dec 2010, 5 marks) [CMAFG IV]
Answer:
Advantages of Balanced Score Card:
| 1. Wholistic approach | It brings strategy and vision as the center of management focus. It helps companies to assess overall performance, improve operational processes and enable management to develop better plans for improvements. It provides management with a comprehensive picture of business operation. |
| 2. Overall agenda | It brings together in a single management report, various aspects like customer oriented, shortening response time, improving quality, etc, of a competitive agenda. |
| 3. Objectivity | It emphasizes the need to provide the user with a set of information, which addresses all relevant areas of performance in an objective and unbiased manner. |
| 4. Management by objectives | The .methodology of BSC facilities communication and understanding of business goals and strategies at all levels of the firm. Thus it enables management by objectives. |
| 5. Feedback and learning | It provides strategic feedback and learning. BSC guards against sub-ordination. It emphasizes an integrated combination of traditional and non-traditiopal performance measures. |
| 6. System approach | It helps senior managers to consider all the important performance measures together, and allows them to see whether an improvement in one area has been achieved at the expense of another. |
![]()
Question 3.
Benchmarking exercise is based on “best exercise”and not on “best performances”. Explain. Also state briefly the important bench marking processes used in strategy implementation. (June 2009, 3 ÷ 8 = 11 marks) (CMAFG IV)
Answer:
The practice of setting targets, using external information is known as ‘Bench marking”. Bench marking is the establishment of targets, with which performance ¡s sought to be assessed. It is a continuous process of enlisting the best practices in the world for the process, goals and objectives, leading to world-class levels of achievement.
- Benchmarking can be defined as a tool for improving performance by continuously identifying, understanding, adopting and adapting best practices and processes followed by an entity internally and externally of a company.
- A benchmarking exercise is based on “best practices” and not on “best performances”.
- Best practice is a continuous process of learning, feedback, reflection and analysis of what works (or does not work) and why.
Types of Bench marking:
1. Strategic Benchmarking :
This aims at enhancing a company’s holistic performance by analyzing the long-term approaches and strategies adopted by the “best practice companies” for their success in any sector across the globe.
2. Product Benchmarking :
This is an age old practice of product oriented reverse engineering. Every organization buys its rival’s products and tears them down to find out the features and performances etc. compared with its products. This could be the starting point for improvement. When Ford Motor Company redesigned the Tauras in 1992, it benchmarked 209 features on the Car against 7 competitors.
The company then worked to match / excel the higher standard set by any of its rival, in each of these features with its own product.
Japanese seemed to have excelled at this practice but to their credit it must be said that they just do not imitate, but ingeniously innovate.
![]()
3. Competitive Benchmarking :
“A measure of organizational performance compared against competing organization; studies the target specific product designs, process capabilities or administrative methods used by a company’s direct competitors”. This is confined to the area relating to the performance characteristics of the company’s key products and services. So competitive benchmarking will involve the best practices of the companies in the same sector.
4. Process Benchmarking :
‘The activity of measuring discrete performance and functionality against organizations through performance in excellent analogous business processes”.
This is attempted to improve specific key activities and operations culminating into processes with the help of best practice organizations that are engaged in similar activities and services.
5. Functional Benchmarking :
Optimization of functional processes or activities through benchmarking can be done by comparing with different business sectors but engaged in similar functions or processes.
6. Internal Benchmarking :
This involves benchmarking against the company’s own divisions or branches or strategic business units situated at different locations. The purpose is to develop a database which gives access to information and a cross fertilization of the managerial acumen within the company.
7. Global Benchmarking :
It is an extension of Strategic Benchmarking to include benchmarking partners on a global scale. E.g. Ford Co. of USA benchmarked it’s a/c payable functions with that of Mazda in Japan and found to its astonishment that the entire function, was managed by 5 persons as against 500 in Ford.
![]()
Question 4.
State briefly the shortcomings of Balance Scorecard. (Dec 2009, 5 marks) [CMAFG IV]
Answer:
Shortcomings of the Balanced Score Card: .
1. Community and environmental issues are missing ¡n BSC. These are very vital and critical issues today.
2. Competitors have not been included. Companies need to monitor the environment to track competitor’s activities and technological developments. These criticisms mainly stem from the fact that the BSC is not multiple stakeholders’ framework. Any performance measurement framework needs to reflect the needs of all the important stakeholders.
Conclusion: These shortcomings, however, should not detract from the inherent merits of the BSC, which helps to clarify, consolidate and gain consensus around the strategy of the organization. BSC is a powerful tool for strategy implementation. The shortcomings as pointed out may be added as its additional perspectives.
![]()
Question 5.
Attempt:
Explain the major components of balanced score card. (Nov 2010, 4 marks)
Question 6.
What are the stages involved in the creation of a Balanced Score Cara? Explain them briefly. (Dec 2010, 6 marks) [CMAFG IV]
Answer:
The stages involved in the creation of a Balanced Score Card are enumerated below:
- Identify a vision i.e. where an organization is going to?
- Identify organisation’s strategies: i.e. how. an Organization is planning to go there?
- Define Critical Success Factors and perspectives: i.e. what we have to do well in each Perspective-Customer perspective, Internal perspective, Innovation and Learning perspective and Financial perspective.
- Identify measures which will ensure that everything is going in the expected way.
- Evaluation of Balanced score card, i.e, ensuring what we are measuring is right.
- Create action plans and plan reporting of the Balanced score Card.
- Follow up and manage i.e, which person should have reports and what reports should look like
The diagram given below depicts various stages involved to create a balanced score Card:
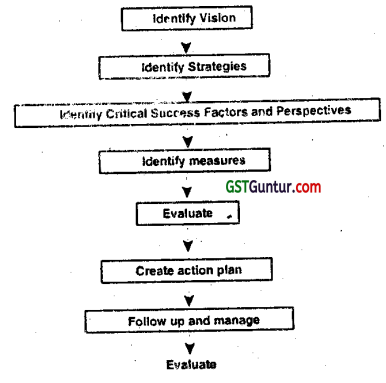
Although the process to create Balance Score card is the same for all organizations. However, each organizations must decide what are its critical success factors and what are its performance measures.
![]()
Question 7.
State whether each of the following independent activities is value-added or non-value-added:
(i) Polishing of furniture used by a systems engineer in a software firm.
(ii) Maintenance by a software company of receivables management software for a banking company.
(iii) Painting of pencils manufactured by a pencil factory.
(iv) Cleaning of customers’ computer key boards by a computer repair centre.
(v) Providing brake adjustments in cars received for service by a car service station. (May 2012, 5 marks)
Answer:
| Item | Activity |
| (i) Polishing furniture used by a Systems Engineer in a software firm | Non-value added |
| (ii) Maintenance by a software company of receivables management software for a banking company | Value-added |
| (iii) Painting of pencils manufactured by a pencil factory | Value-added |
| (iv) Customers’ computer key board cleaning by a computer repair centre | Value-added |
| (v) Providing brake adjustments in cars for repairs by a care service station. | Value-added |
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the features of a balanced score card. (May 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
A Balanced score card includes information, both financial and non-financial elements under 4 perspectives with a long term goal of improved financial performance.
| Perspective | Parameters |
| Customer | Sales % Delivery time New product information |
| Internal business perspective | Business process to be adopted Technological capability Internal efficiency parameters ‘ |
| Innovation/ learning perspective | How a company should sustain its ability to change and innovate Technology leadership Product focus Kaizen approach |
| Financial perspective | Sales growth How the company should appear to its shareholders Operating income by segments |
![]()
Question 9.
Explain briefly the major components of a Balanced Score Card. (Dec 2012, 5 marks) [CMAFG IV]
Question 10.
State the different types of Bench-marking, with a small write-up on each? (June 2016, 10 marks) [CMAFG IV]
Question 11.
What is ‘Bench Marking’? Describe briefly the different types of ‘Bench Marking’. (June 2017, 2 + 8 = 10 marks) [CMAFG III]
Question 12.
Based on the above information and using a Strategy Map tabulate two objectives and two measures for each perspective across the four dimensions of a balanced scorecard in the following format: (Nov 2019, 8 marks)
| Perspective | Strategic Objective | Measure |
Answer:
| Perspective | Strategic Objective | Measure |
| Learning and Growth perspective | Increase the Number of New Products or Services sold | Number of customers Buying the New products or services |
| Customer perspective | Increase Customer Loyalty | Number of Account closed or closure Request Received |
![]()
Question 13.
Sure Success & Co. is a team of professionals engaged in coaching the students of CMA Final Examinations. They offer coaching facilities in the main cities of the country. Though they have been in this profession for a long time, there is a lot of competition from many o+her coaching centres.
You are required to design a Balanced Score Card for Sure Success to readily read the parameters and implement its performance. (June 2015, 20 marks) [CMAFG IV]
Answer:
The Balanced Score Card suggests that we view the organization from 4 perspectives and to develop metrics, collect data and analyze it relative to each of the following perspectives:
(i) Customer Perspectives: Recent management philosophy has shown an increasing realization of the importance of customer focus and customer satisfaction in any business. This is the leading indicator. If the customers are not satisfied, they will eventually find other suppliers that will meet their needs. In developing metrics for satisfaction, customers should be analyzed in terms of customers and the kinds of processes for which we are providing a product or service to those customer groups.
(ii) Financial Perspectives/Owner’s Perspectives: There is always the traditional need for financial data. Timely and accurate funding data will always remain to be a. priority and the managers will do whatever necessary to provide it.
(iii) Learning and Innovative Perspectives: This perspective includes employees training and the corporate cultural attitudes related to both individual and corporate self-improvement. In all organization, People are the only repository of knowledge and remain the main resource.
(iv) Internal Business Perspectives: Metrics based on this perspectives allow the managers to know how well their business is running and whether its products and services conform to customer requirements. These metrics have to be carefully designed by those who know these processes most intimately.
![]()
Based on the above, we have designed a Balance Score Card for the Coaching Centre namely Sure Success & Co., as per below:
| Perspective | Key Performance Indicator | Target | Actual | Deviation |
| 1. Customer Perspective (Customers are the Students and their Parents) | No. of Students enrolled No. of Passes per class No. of Marginal failures No. of Good students who have failed No. of Rank holders No. of Students who drop out midway Increase in Student Strength over last period No. of Cancelled classes No. of Delayed classes due to late coming of faculty |
|||
| 2. Financial Perspectives/ Owners’ Perspectives | Revenue per person Gross Revenue Direct Expenses-like Study material, Remuneration Rental of the premises Gross and net margin Returns after taxes Growth of returns |
|||
| 3. Learning and Innovation Perspectives | New subjects offered E-learning growth Video lessons offered No. of faculty added Capital/Infrastructure expenditure Training & Development of Faculty |
|||
| 4. Internal Business Perspectives | Average no- of hrs/session. No, of sessions Seating conveniences Optimality of batch size Effectiveness of batch size |
The Balanced Score Card Implementation process is quite simple in so far as it involves:
- Agreeing to a set of performance measures as per above.
- Agreeing to a performance targets for each measure.
- Recording actual performance for each performance measure and
- Regularly reporting and acting on any performance deviation.
![]()
Question 14.
Answer the following:
In the context of a balanced scorecard, identify the perspectives of the following independent situations: (May 2015, 4 marks)
| Organization | Target Parameter | Perspective |
| (i) Courier Company | 100% on-time delivery of priority dispatches | |
| (ii) Tuition Centre | Set up class-on-internet facility for better reach of more number of students and absentees. | |
| (iii) Computer Manufacturing Company | Set up service centres is all major cities for after sales support. | |
| (iv) Government Taxation Department | Ensure Computer training to all officers above a certain rank to improve their capabilities. |
(Candidates need to only write the 1st and last columns in the answer books.)
Answer:
Identification of Perspectives of Independent Situation – ‘Balance Scorecard’:
Answer:
| Organisation | Perspective |
| (i) Courier Company | Customer Perspective |
| (ii) Tuition Centre | Learning and Growth Perspective |
| (iii) Computer Manufacturing Company | Internal Business Perspective |
| (iv) Government Taxation Department | Learning and Growth Perspective |
![]()
Question 15.
ABC Airlines has two divisions organized as profit centres, the Passenger Division and the Cargo Division. The following divisional informations were given for the year ended 31st March 2018 : (May 2018)
| Cargo Division | Passenger Division | Total | |
| Number of personnel trained | 200 | 800 | 1000 |
| Number of flights | 350 | 250 | 600 |
| Number of reservations requested | NIL | 7000 | 7000 |
| Revenue | ₹ 42,00,000 | ₹ 42,00,00 | ₹ 84,00,000 |
| Operating Expenses (excluding service department charges) | ₹ 36,00,000 | ₹ 28,50,000 | ₹ 64,50,000 |
| Service Department Charges | |||
| Training | ₹ 3,20,000 | ₹ 3,20,000 | ₹ 6,40,000 |
| Flight Scheduling | ₹ 1,50,000 | ₹ 1,50,000 | ₹ 3,00,000 |
| Reservation | ₹ 1,05,000 | ₹ 1,05,000 | ₹ 2,10,000 |
The service department charge rate for the service department costs was based on revenue. Since the revenue of both the divisions were the same, the service department charges to each to division were also the same.
Required:
(i) Does the income from operations for the two divisions accurately measure performance? (3 marks)
(ii) Prepare the divisional income statement using activity bases provided. above in revising the service department charges. (7 marks)
Answer:
(i) The reported income from operations does not accurately measure performance because the service department charges are based on revenue. Revenue is not associated with the profit centre manager’s use of the service’ department services. For example, the Reservations Department serves only the Passenger Division and number of reservation requested by Cargo Division is NIL.
Thus, by charging this cost based on revenue, these costs are incorrectly charged to the Cargo Division. Further, the Passenger Division requires additional personnel. Since these personnel must be trained, the training costs assigned to the Passenger Division should be greater than the Cargo Division.
(ii) ABC Airlines Divisional Income Statement For the Year Ended March 31, 2018
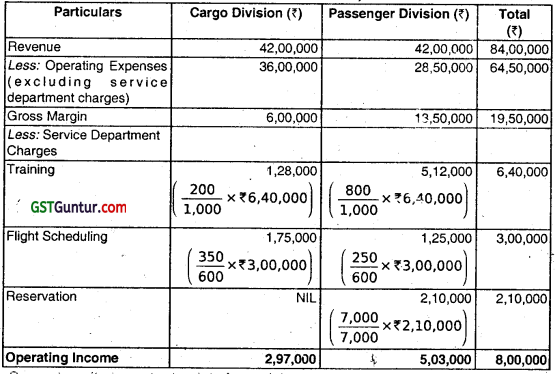
![]()
Question 16.
Cure Hospital is running under private-public-partnership (PPP) model-providing treatment for non-communicable diseases. ABCO Hospitals Limited is the private partner which runs a chain of hospitals on profit basis in major cities in India. The public partner is the State Government. Cure Hospital is a “not- for-profit” hospital. (Nov 2019)
Private partner is to invest in upgrading and equipping the facility and responsible for operational management and service delivery. Government to provide physical space and other infrastructure in “as is where is” condition, provide support facilities and hospital amenities. Private partner assumes the entire responsibility for a full range of investment, operation and maintenance functions. Private partner has the authority to make daily management decisions.
The hospital is funded to a great extent by the State Government and a fixed level of funding is received from the government each year out of the State budgetary allocation. It is up to the hospital to allocate this fund to different areas such as doctors’ and other staff salaries, medicines and all other costs required to run a hospital.
Cure Hospital’s objectives are:
- to give prompt access to high quality medical treatment for patients.
- to provide free treatment to poor patients in line with government policy of inclusive development.
- to provide value for money for the taxpayer-measured by the 3 Es framework of Economy, Efficiency and Effectiveness.
- to contribute to medical science by developing innovative ways to deliver treatment to patients.
Except select surgeries, all services are free for poor patients that are below poverty line (BPL) card holders. 40% beds are reserved for poor patients. Free out patient department (OPD) services to poor. CT Scan and MRI diagnostics are free for poor patients, subsidised rates for others. Cure Hospital also runs a generic medicine shop inside the hospital premises which sells medicines to all patients at discount ranging from 40% to 56% – the only shop of this kind in the city.
WHO has agreed to provide financial and technical support to the neonatal care unit. The hospital enabled it to obtain five accreditation certificates from various leading authorities On different aspects of hospital management. Feedback is taken from each in-patient about the quality of service provided by the hospital and the satisfaction level is taken in 1 to 10 point scale. 1 being the least satisfied and 10 represents totally satisfied.
In.a recent meeting of the managing committee of the hospital, discussions were held about inadequate performance measurement systems in place to assess whether the hospital is achieving its objectives and that insufficient attention is given to the importance of non-financial performance indicators. A four member team consisting of a performance management expert and three senior doctors was created to give their advice in these aspects.
![]()
The four member team met with doctors, staff and other stakeholders at length and breadth. Some of the conversations were as below :
Doctor A : I think the hospital always delivers value for money. We have always achieved our total financial budgets.
Doctor B : We work here much longer hours than doctors in other hospitals, often without being paid for working overtime.
Doctor C : There is not enough government and private partner funding to recruit more doctors and paramedic staff.
Doctor D : Number of out-patients has increased considerably. Earlier an out-patient had to wait for an average period of 2 hours 20 minutes and now the same has increased to 3 hours.
Senior Doctor K : I do not know how much time we spend developing innovative ways to deliver treatment to patients though, as most of the performance data we doctors receive relates to financial targets.
In-patient H : Incompetent paramedic staff, poor quality of food and bed linen. Staff M : Management undermines our role in running the hospital.
Recent performance data of the hospital vis-a-vis national average are as follows:
| Cure Hospital | National average of other PPP run hospitals | |
| Number of doctors | 80 | 76 |
| Average doctors salaries per month including overtime | ₹ 1,20,000 | ₹ 1,60,000 |
| Average doctors salaries including overtime as per budget | ₹ 1,20,000 | ₹ 1,25,000 |
| Number of in-patients treated | 8,360 | 6,369 |
| Average satisfaction rating of in- patients | 6 | 9 |
| Number of patients readmitted for treatment of the same ailment within short period of time after discharge from the hospital | 627 | 128 |
| Average staff satisfaction rating (0% represents totally dissatisfied and 100% represents totally satisfied) | 16% | 86% |
| Number of out-patients treated | 76,212 | 63,318 |
Required :
(a) Explain why non-financial performance indicators are particularly important
to measure the performance of “not-for-profit” organisations such as Cure Hospitals. (4 marks)
(b) Evaluate whether Cure Hospital is delivering value for money for each of the components of the value for money framework. (12 marks)
(c) The CEO of the hospital intends to introduce a nominal fee for out patient treatment given to poor patients and remove subsidised rate of CT Scan and MRI diagnostic for other patients in order to achieve its objectives in a better way ‘Evaluate the proposal of the CEO. (4 marks)
Answer:
(a) Lack of profit-making objective:
Not-for-profit organisations do not, by definition, have profit as an overriding motive. Patients are not charged for receiving treatment, so Cure Hospital does not have a revenue stream. It may also be difficult to define a cost unit as this could be cost per patient arriving at hospital or cost per patient successfully treated.
Not-for-profit public sector organisations, such as Cure Hospital, have strict constraints on the amount of funding they receive, such as a fixed, amount of funding received entirely from the State Government. They cannot obtain funding from elsewhere, so financial measures cannot be ignored completely. Cure Hospital must exist within its financial means, and the use of budgets to control costs is critical.
![]()
Cure Hospital provides an essential public service. Political, legal and social influences would prevent it from closing down a service just because it became more expensive or uneconomic to provide it. For all of these reasons, financial objectives are less relevant than for most commercial organisations, and its objectives are mainly non-financial in nature.
Not-for-profit organisations also undergo more public scrutiny and have multiple stakeholders, so non-financial indicators will be necessary to manage expectations. For example, patients are stakeholders who will have relatively little interest in how Cure Hospital exists within its financial constraints.
They will have much more interest in non-financial performance, such as how quickly and successfully they are treated.
Due to its objective of public service, measurement of appropriate non-financial metrics are equally important. The reasons are:
(i) Benefits cannot be quantified: Cure Hospital essentially provides public healthcare service to the economically weaker sections of the society. Due to political, legal, and social reasons, not-for-profit organizations like Cure Hospital cannot be shut down merely for not being economically / financially viable. Therefore, financial measures are less relevant. Due to its non-financial objective, -appropriate non-financial measures become more important. For example, the benefits of saving lives cannot be quantified in financial terms.
(ii) Benefits may accrue over long term: The expenditure incurred in one year may yield benefits over several years. For example, the investment in an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) facility may accrue of multiple years. Neonatal care unit have been given financial and technical support from WHO which will give long term benefits to hospital.
(iii) Measurement of utilization of funds and expenditure: In the case of Cure Hospitals, many hospital services are free, allocation of capacity is aimed at providing free service to the BPL section of the society, medicines are provided at discounted rates. Therefore, Cure Hospital does not have a substantial revenue stream to earn from its patients. It gets a fixed budget allocation from the State Government, while ADCO Hospital allocates these funds for various investments and expenditures.
The assessment whether the spending have been appropriate is a key challenge. Defining cost per unit would be subjective since it could be cost of patients arriving at the hospital or cost of patients successfully treated at the hospital. Either figure could be tweaked to make it seem that the objectives are being met. The management may resort to rampant spending simply to meet the expenditure targets. Therefore, non-financial measure need to be put in place help stakeholders scrutinize whether the objectives for which funds have been given are being met.
(iv) Multiple objectives: Not-for-profit organizations have multiple objectives. It may be unclear which are the most important. Cure Hospital aims at . providing high quality treatment to its patients while also’ developing innovative ways to deliver treatment to its patients. Both objectives are equally important and inter-related. Non-financial measures provide better information about how each of these objectives have-been met. The benefits of organizations like Cure Hospital are non-financial in nature. Except for providing fiduciary information to the stakeholders, all other objectives of Cure Hospital can be measure only using non-financial measures.
![]()
(b) Value for money in public sector organisations can be measured using the ‘three Es’; economy, efficiency and effectiveness.
(i) Economy:
Economy means obtaining resources at the lower cost. Doctors’ salaries will be a significant expense for Cure Hospital and salary per doctor is a suitable measure of economy. Doctors at Cure Hospital have an average salary of ₹ 18,000 (₹ 1,20,000 × 12/80), compared to the national average of ₹ 25,263 (₹ 1,60,000 × 12/76).
The relatively lower salaries of doctors may be due to differences in levels of experiences or they work unpaid overtime. It may also be one of the reasons why the staff Satisfaction is so much lower at 16% as compared to the national level of 86%.
(ii) Efficiency:
Efficiency refers to obtaining the greatest possible outputs from the resources available. Treating patients is a key objective of Cure Hospital, and the number of doctors is important resource. The number of patients treated per year by each doctor is a good measure of efficiency. In Cure Hospital, each doctor treats an average of 952 (76,212/80) patients per year, 14.29% more than the national average 833 (63,318/76). This may be because they work longer hours than their colleagues in other hospitals.
(iii) Effectiveness:
Effectiveness means how well Cure Hospital achieves its objectives. Cure Hospital has multiple objectives, one of which is to provide high quality medical treatment for patients. Where patients are re-admitted to Cure Hospital because their treatment had failed, this represents a failure to provide high quality medical care, so the rate of re-admission of patients is a measure of effectiveness. The rate of readmission at Cure Hospital is 0.82% (627/76,212) much higher than the national average of 0.20% (128/63,318). Cure Hospital seems to have performed relatively very poorly in this respect.
Summary:
Overall, the results from the measurement of the 3Es are consistent with the doctor’s comments that they are working without being paid overtime and treating more patients than their colleagues in other hospitals. Cure Hospital appears to deliver better economy and efficiency than the national average. This seems to be reducing performance, however, in respect of providing high-quality medical treatment for patients, where Cure Hospital is less effective than the national average.
![]()
(c) A budget constrained management style emphasises the need to achieve short-term performance measures, for example, the annual financial budgets.
The doctor said that Cure Hospital has always achieved its total financial budgets,, and this is supported by the fact that the doctor’s salaries equalled the budget set for the period. Though it is unclear what NFPIS are measured at Cure Hospital as a whole, doctors receives only a limited set of financial and non-financial performance data.
The discussion about this data, however, is mainly related to financial targets. This implies greater emphasis is given to performance against financial targets, rather than non-financial ones.
Ali of this suggests that Cure Hospital has a budget constrained management style. An advantage of this is that it ensures Cure Hospital operates with the financial constraints of the fixed amount of funding received from the Government.
This management style encourages short-termism, by encouraging doctors to work long hours without being paid overtime, or not making funding available to recruit new doctors to alleviate the situation.
An implication of this is that Cure Hospital may reduce its performance against its objectives, and this is already seen by the relatively high rates of re-admission as an indicator of a reduced quality of medical treatment. Job-related tension is a consequence of a budget-constrained management style, and the low staff satisfaction score could have resulted from this.
This management style encourages manipulation of results, or the way they are measured, to show better performance. At busy times, more patients are referred to the nearby larger hospital. There is apparently no medical need for this, which is inconsistent with the objective to deliver high-quality treatment. It appears to be a way to distrot waiting times to demonstrate improved performance in treating patients promptly. From patients perspective, though, this will mean they are treated less promptly than if treated at Cure Hospital.
Being unable to recruit new doctors reduces Cure Hospital’s flexibility in reducing waiting times at busy periods, as the steps already taken seem to have minimal effect.
This management style does not encourage innovation, probably because doctors have insufficient time for this. Though this may have long-term benefits, it seems to be taken as less important than the other key objectives, to provide prompt high quality treatment.
![]()
Question 17.
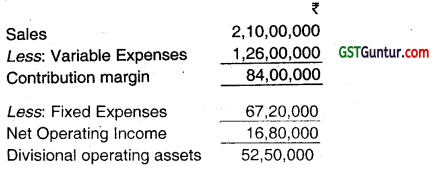
AKG Limited has three autonomous divisions. The divisions are evaluated on the basis of ROI, with year end bonuses given to divisional managers who have the highest ROI. Operating results of Division II for the last year are given below: (Nov 2019)
The company’s overall ROI for the last year was 18% (considering all divisions). Division II has an opportunity to add a new product line that would require an investment of ? 30,00,000. Other details of the new product line are as follows:
Sales – ₹ 90,00,000 per annum
Variable Expenses – 65% of sales
Fixed Expenses – ₹ 25,20,000 per annum
Life cycle of the product line 5 years
Though Division II is performing well, but many a times, the customers complained that they had to wait for long after placing the orders. The company is interested in cutting the amount of time between when a customer places an order and when the order is completed. For the last year, the following data were reported in respect of Division II
Inspection time = 0.5 days per batch
Process time = 2.8 days per batch
Wait time = 16.0 days per batch
Queue time = 4.0 days per batch
Move time = 0.7 days per batch
In addition to financial performance measures, the company wishes to introduce a variety of non-financial performance measures.
The company has set aggressive targets in both sales growth and ROI for the coming year. The company’s strategy for achieving these goals includes a campaign aimed at building brand recognition, customer retention, improvement in product quality, on time delivery to customers, expansion of eco-friendly product line and introduction of limited edition items.
Required:
(i) Calculate last year’s ROI of Division II (1 mark)
(ii) Discuss whether the manager of Division II would accept or reject the new product line, if he takes his decision based solely on divisional ROI. (2 marks)
(iii) Advise how residual income approach can be used as an alternative financial measure for evaluation of managerial performance in the best interest of the company. , (2 marks
(iv) Calculate Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency (MCE) and interpret the result. (3 marks)
(v) State what percentage of the production time is spent in non-value added activities. (1 mark)
(vi) Calculate the delivery cycle time. (1 mark)
(vii) Calculate the new MCE if by using Lean Production all queue time can be eliminated. (2 marks)
Answer:
(i) Last year’s ROI of Division II:
= \(\frac{\text { Net Operating Income }}{\text { DivisionalOperating Assets }}\)
= \(\frac{₹ 16,80,000}{₹ 52,50,000}\)
ROI = 32%
![]()
(ii) Calculation of ROI of new product line:
| ₹ | |
| Sales
Less: Variable Expenses Contribution Less: Fixed Expenses Operating Income (Net) Investment New product line ROI (%) ‘ |
90,00,000
58,50,000 |
| 31,50,000
25,20,000 |
|
| 6,30,000 30,00,00021% |
The manager of Division II should reject the new product line as the ROI of new product line i.e. 21% ¡s less than last year ROI of Division II i.e. 32%.
![]()
(iii) To overcome some of the dysfunctional consequences of ROI, the residual income approach can be used. For the purpose of evaluating the performance of divisional managers, residual income is defined as controllable contribution less a cost of capital charge on the investment controllable by the divisional manager. For evaluating the economic performance of the division residual income can be defined as divisional contribution less a cost of capital charge on the total investment in assets employed by the division.
If residual income is used to measure the managerial performance of investment centres, there is a greater probability that managers will be encourged, when acting in their own best interests, also to act in the best interests of the company.
Here, the AKG Limited should follow the residual income approach, as considering the following:
Proposed Investment = ₹ 30,00,000
Controllable = ₹ 31,50,000
Cost of Capital (21%) = ₹ 6,30,000
Residual Income = ₹ 25,20,000
(iv) Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency = \(\begin{aligned}
& \frac{\text { ProcessingTime }}{\text { ProcessingTime+Inspection Time }} \\
& \text { Waiting Time + Move Time Queue Time }
\end{aligned}\)
= \(\frac{2.8}{2.8+0.5+16+0.7+4}\)
= \(\frac{2.8}{24}\) × 100
= 11.67%
(v) Non-Value added Activities = InspectionTlme + WaitingTime – MoveTime + QueueTime
= 0.5 days + 16 days + 0.7 days + 4 days
= 21.2 days
Total Production Time = 0.5 + 2.8 + 16 + 4 + 0.7
= 24 days
% = \(\frac{21.1}{24}\) × 100
% of production time spent on non-value added activities = 88.33%
(vi) Delivery Time Cycle = Inspection Time + Processing Time + Waft Time + Queue Time + Move Time
= 0.5 days + 2.8 days + 16 days + 4 days + 0.7 days
= 24 days
(vii) MCE if Queue time is eliminated = \(\frac{2.8 \text { days }}{2.8+0.5+16+0.7}\)
= \(\frac{2.8}{20}\) × 100
= 14%
![]()
Question 18.
The triple bottom line recognises that a company’s performance should not only be viewed in terms of its ability to generate economic profits for its owners, but also by its impact on people and the planet (Nov 2019, 5 marks)
(i) Reduced the amount of plastic usage in the peanut butter jars.
(ii) Provided financial support to hospital run by local authority in the vicinity of the factory.
(iii) Constructed solar powered warehouse.
(iv) Generated profit for the company’s shareholders.
(v) Started child care unit for the benefit of women employees as well as for the neighbourhood community.
Required:
Identify whether this initiative would primarily impact people, planet or profit.
Answer:
| Initiatives | Impact |
| (i) Reduced the amount of plastic usage in the peanut butter jars | Planet |
| (ii) Provided financial support to hospital run by local authority in the vicinity of the factory | People |
| (iii) Constructed solar powered warehouse | Planet |
| (iv) Generated profit for the company’s shareholders | Profit |
| (v) Started child care unit for the benefit of women employees as well as for the neighbourhood community | People |
![]()
Question 19.
The world fame Taj Mahal is situated on the banks of Yamuna River in the city of Agra, Uttar Pradesh, known for its beautiful design and is counted as one of the Seven Wonders of the World; the city attracts a lot of tourist from all around the world. The Tourism is one of the main sources of livelihood for its residents. Consequently, cleanliness and maintenance of garden area within the Taj Mahal campus is of prime importance in order to sustain and develop this industry. (Nov 2020)
The local government has recently employed a contractor to clean and maintain the garden area within the Taj Mahal campus. The contractor uses cleaning machines pulled by horses to avoid pollution. The contractor has been selected through an online competitive tendering/bidding process. Majority of the litter comprises of plastic waste (bags, bottles etc.) while some portion also includes glass, aluminium cans, paper and cardtoard. A detailed log is held by the contractor about the waste that has been cleaned, time taken for the cleanup, number of horses used, etc. This log is also checked and signed by local government officials. This record is used to process payments at the end of the month.
In addition to contracting, the local government has also placed bins at various locations within the campus for the public to dispose their waste. The Nagar Nigam’s workers clean these bins every morning. Again, detailed logs of the man power and other resources employed are kept by the respective department. In addition, the government has started a mobile messaging system, whereby the public can message the concerned department if they find litter anywhere in the campus. Depending on whether it is from overflowing bins or scattered waste, the Nagar Nigam’s workers will take action to clean it within 12 hours. A detailed log of these operations is also maintained. Patrons can also suggest measures for improving cleanliness on the above mentioned areas.
Due to its importance to the economy, the local government has allotted substantial budget for these operations. At the same time, it is essential to know if this is sufficient for the purpose of maintaining the cleanliness of the campus. Therefore, the government wants to assess whether the city is getting “good value for money” from expenditure.
The “value for money” concept can be looked at from three perspectives: (i) economy, (ii) efficiency and (iii) effectiveness. The internal audit department that has been requested to undertake this study has requested for guidelines on whether the audit should focus on economy and efficiency of the Taj Mahal campus cleaning operations or on effectiveness of the same. Economy and efficiency audit assess whether the same level of service can be procured at lower cost or resources while effectiveness audit assess whether better service can be procured at same cost.
Depending on the outcome of the audits, if required, policy decisions like requesting for additional funding from the state government, alternate policy measures like levying penalty for littering etc. can be taken.
Required:
(i) Recommend guidelines to assess economy, efficiency and effectiveness of Taj Mahal and campus cleaning operations. (8 marks)
(ii) Identify challenges involved in assessment of effectiveness. (6 marks)
(iii) Recommend general guidelines, how the audit team may conclude the audit based on the combined outcomes of economy, efficiency and effectiveness. . (6 marks)
![]()
Question 20.
Jal Cleaning and Distribution Services Ltd. (JCDSL) was established with an aim for supply and distribution of water in Nagpur and as well as supply of water to the various local authorities for distribution to villages and other small cities adjacent to Nagpur under “MISSION PAANI”. This involved planning, operating, treating, maintaining, and distributing water resources in the country’s urban centres and other areas mandated by State Government. The mission statement is “To provide clean and economical water for healthy life to the public”. (Nov 2020)
There are two operational divisions of JCDSL viz Water Distribution Operation (WDO) for distribution of water through pipes and Water Packaging Operation (WPO) for supplying water in packaged drinking water bottles. The state government ensures that JCDSL does not take advantage of its monopoly position in the regional area by increasing prices.
The government controls majority of services through its water regulatory body which determines an acceptable margin level (ROCE) and ensures that the pricing of JCDSL within these areas does not break this level. The other operation i.e. Water Packing Operation (WPO) is not regulated by government and JCDSL is free to charge a market rate for water supply in bottles.
The company is free to use water for Water Packaging Operation but the total use of water for Water Packing Operation (WPO) cannot exceed 35% of the total supply of water by the company. The company is presently using 20% of total water supply for packaging operation. The brand name of packaged drinking water is “Swachh- Jai” which is packed in transparent plastic bottles.
The water regulator calculates Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) of JCDSL based on its own valuation and assessment of the capital assets which are used in operation and profit from these services. Acceptable level of ROCE set by the regulator is 6.50%. If JCDSL breach this level, then the company would be heavily penalized. JCDSL board is making sincere efforts to improve the performance of the company for the benefit of the shareholders. The board of directors have decided to consider economic value added (EVA) as the key performance indicator, in order to meet the objective of maximizing shareholders’ wealth.
![]()
Key Financial data for the year ending 31st March, 2020 is given below:
| Particulars | Water Distribution Operation (₹ In Crore) | Water Packing Operation (₹ In Crore) | Total (₹ In Crore) |
| Revenue | 585.00 | 212.00 | 797.00 |
| Less: Operating Cost | 475.00 | 146.00 | 621.00 |
| Operating Profit | 110.00 | 66.00 | 176.00 |
| Less: Interest Cost | 42.00 | ||
| Profit before tax | 134.00 | ||
| Less: Tax @ 30% | 40.20 | ||
| Profit after tax | 93.80 |
| Capital Employed for the last two years | 2019-20 (₹ In Crore) | 2018-19 (₹ In Crore) |
| As per Audited Accounts | 2,040.00 | 1,940.00 |
| As calculated by Water Regulator (for WDO operations only) | 1,812.00 | 1,760.00 |
The following notos are to be taken into consideration in the analysis:
1. Operating Cost includes:
| Particulars | 2019-20 (₹ In Crore) | 2018-19 (₹ In Crore) |
| Depreciation | 124.00 | 118.00 |
| Provision for bad and doubtful debts | 6.00 | 2.00 |
| R&D Cost ‘ | 20.00 | — |
| Other Non-Cash items | 22.00 | 11.00 |
![]()
2. Economic depreciation is ₹ 156.00 Crore in 2019-20. In the F.Y. 2018-19, economic and accounting depreciation were assumed to be the same.
3. Current year’s tax paid is ₹ 23.00 Crore and deferred tax provisions of ₹ 2.00 Crore have been adjusted. There was no deferred tax balance before 2019-20.
4. The provision for doubtful debts was ₹ 12.00 Crore in the 2019-20 Balance Sheet.
5. Research and development has been non-capitalized. It belongs to a new project that will be developed over six years and is expected to be of long-term benefit to the company. 2019-20 is the first year of this project.
6. Cost of Capital:
| Equity | 15% |
| Debt (Post Tax) | 5% |
7. Gearing of JCDSL
| Equity | 30% |
| Debt | 70% |
Required :
(i) Calculate EVA of JCDSL for the year ending 31 March, 2020 based on the above information. (6 marks)
(ii) Evaluate the financial performance of JCDSL using EVA. (4 marks)
(iii) Assess whether JCDSL comply with its acceptable ROCE level. (3 marks)
(iv) Advise how JCDSL can improve its performance in terms of profitability and EVA in future. (7 marks)
![]()
Question 21.
Osaka Tea Co. manufactures and distributes finest quality black tea to hotels, restaurants and retailers. The company has wide presence in tea market. It has become one of the largest premium brands. The customers are very happy with the finest quality of tea. (Nov 2020)
Osaka Tea Co. never compromise with the quality of the tea. The aim of the company is to deliver finest black tea to keep the customers’happy. It has tied up with big tea estates for procurement of finest tea leaves directly from the estate for processing in its own plants. The tea leaves go through various processes like plucking, withering, brushing, oxidising, grading, drying, sorting and shaping etc. Then these are packed in beautiful plastic jars for distribution to the hotels, restaurants and retailers.
During the meeting of the management, it has been decided to reduce the price per kg by 5% to increase the volume of sales. The following variances pertain to last month’s operations, arose as a consequence of implementation of above decision.
| Sales Price Variance | 24,500 (A) |
| Sales Volume Variance | 20,600 (F) |
| Purchase Price Variance | 15,500 (A) |
| Labour Efficiency Variance | 14,300 (A) |
| Fixed Cost Expenditure Variance. | 11,100(A) |
Required :
(i) Identify the ‘Critical Success Factor’ for Osaka Tea Co. (1 mark)
(ii) Evaluate the management’s decision with the ‘Overall Corporate Strategy’ and ‘Critical Success Factors’. (9 marks)
![]()
Question 22.
Mr. Benn, oversees the diverse operations of Bennsys, a large multinational company by using a much decentralized management structure. According to its 2019 annual report, Bennsys had 1,25,000 employees and earned over $100 billion in revenue. Mr. Benn managed this empire from his headquarters in London, that consists of 20 employees and occupies only 10,000 square feet, although the company’s vice-chairman, Simon, who works out of London, occupies another 600 square feet.
The total payroll, including benefits, of both locations was only just above $2 million in 2019. Mr. Benn was invited as the chief guest in a business summit organized at New Delhi during March, 2020. Asked about how an organization of that magnitude could be managed with such a small resources as to space and manpower. Mr. Benn’s own description about his and Mr. Simon’s management style is, “we delegate almost to the point of abdication (renouncing everything).”
An exaggeration perhaps, but clearly a decentralized style and he and his deputy are the stable believers of FOUR recognized levels of decentralization. In the context of responsibility accountings discuss th levels of decentralization which Mr. Benn was referring to and do you concede to the view that Mr. Benn is exaggerating the success of his Divisional organization structure. (Jan 2021, 10 marks)