Students should practice Overview of Accounting Standards – Corporate and Management Accounting CS Executive MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Overview of Accounting Standards – Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
Question 1.
AS-2 is on:
(A) Disclosure of Accounting Policies
(B) Valuation of Inventories
(C) Revenue Recognition
(D) Depreciation Accounting
Answer:
(B) Valuation of Inventories
Question 2.
Consistency with reference to the application of accounting principles refer to the:
(A) All the companies in the same industries should use identical procedures and methods.
(B) Income and assets have not been overstated.
(C) Accounting methods and procedures used have to be consistently applied from year to year.
(D) Any accounting method or procedure can be utilized.
Answer:
(C) Accounting methods and procedures used have to be consistently applied from year to year.
Question 3.
Accounting Standards_____the statue:
(A) Can over-ride
(B) Cannot over-ride
(C) May over-ride
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B) Cannot over-ride
Question 4.
The global key professional accounting body is the_______
(A) International Accounting Standards Board
(B) Financial Accounting Standards Board
(C) Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
(D) International Accounting Standards Committee
Answer:
(A) International Accounting Standards Board
Question 5.
The original cost at which an asset or liability is acquired is known as –
(A) Carrying cost
(B) Replacement cost
(C) Amortization
(D) Historical cost
Answer:
(D) Historical cost
Question 6.
As per AS-11, the process of converting foreign-subsidiary financial statements into the home currency is known as___
(A) Consolidation
(B) Translation
(C) Transmission
(D) Reconstruction
Answer:
(B) Translation
Question 7.
As per AS-21, the accounting process in which the financial statements of a parent company and its subsidiaries are added together to yield a unified set of financial statements is called____
(A) Amalgamation
(B) Amortization
(C) Consolidation
(D) Translation
Answer:
(C) Consolidation
Question 8.
The council of ICAI has so far issued_____accounting standards. However, AS-8 has been withdrawn. Thus, effectively there are_____accounting standards
(A) 33; 32
(B) 32; 31
(C) 31; 30
(D) 34; 33
Answer:
(B) 32; 31
Question 9.
Which section of the Companies Act, 2013 provides that the financial statements of every company shall comply with the accounting standards?
(A) Section 129
(B) Section 130
(C) Section 131
(D) Section 132
Answer:
(A) Section 129
Question 10.
In the case of charitable trusts and co-operative societies:
(A) If their activities are purely charitable or non-commercial then accounting standards are not applicable.
(B) Even if a very small proportion of the activities of trusts/co-operative societies are considered to be commercial, industrial, or business in nature, then accounting standards are applicable.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 11.
Which of the following is Level-I enterprise?
(A) All commercial, industrial, and business reporting enterprises having borrowings, including public deposits, in excess of ₹ 1 Crore but not in excess of ₹ 10 Crore.
(B) All commercial, industrial, and business reporting enterprises, whose turnover for the immediately preceding accounting period exceeds ₹ 50 Crore.
(C) All commercial, industrial, and business reporting enterprises, whose turnover for the immediately preceding accounting period ₹ 5 Crore but not in excess of ₹ 25 Crore.
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 12.
Which of the following is a Level-II enterprise?
I. Listed enterprises outside India.
II. All commercial, industrial, and business reporting enterprises, whose turnover for the immediately preceding accounting period exceeds ₹ 50 Crore.
III. Financial institutions
IV. Enterprises carrying on insurance business.
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(A) I&III
(B) II&IV
(C) III only
(D) II only
Answer:
(D) II only
Question 13.
Which aspect of Financial Instruments is death by AS-31?
(A) Recognition & Measurement
(B) Presentation
(C) Disclosures
(D) Limited Revision
Answer:
(B) Presentation
Question 14.
Which of the following are fundamental accounting assumptions?
A. Going Concern
B. Matching
C. Consistency
D. Dual Aspect
E. Materiality
F. Accrual
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) A, C & E
(B) B, D&F
(C) A C&F
(D) A D&F
Answer:
(C) A C&F
Question 15.
Which of the following is NON-SMC as per the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules?
(A) Whose equity or debt securities are not listed or are not in the process of listing on any stock exchange, whether in India or outside India
(B) Which is not a bank, financial institution, or an insurance company
(C) Whose turnover excluding other income does exceed ₹ 50 Crore in the immediately preceding accounting year
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(C) Whose turnover excluding other income does exceed ₹ 50 Crore in the immediately preceding accounting year
Question 16.
Consider the following cases:
(i) A (P) Ltd., a subsidiary of a multinational company listed on the London Stock Exchange. Does it have a turnover of ₹ 12 Crores and borrowings of ₹ 5 Crores?
(ii) B (P) Ltd. has a turnover of ₹ 45 Crores, other income of ₹ 7 Crores, and bank borrowings of ₹ 9 Crores.
(zzz) C Ltd. has appointed Merchant Bankers to prepare a Red-herring prospectus for the purpose of filing the same with SEBI.
Classify above enterprises as SMC or NON-SMC and select the correct option given below:
(i) (ii) (iii)
(A) Non-SMC Non-SMC SMC
(B) SMC Non-SMC Non-SMC
(C) Non-SMC SMC Non-SMC
(D) Non-SMC SMC SMC
Answer:
(C) Non-SMC SMC Non-SMC
Question 17.
As per the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, an existing company, which was previously Non-SMC and subsequently becomes an SMC, shall not be qualified for exemption or relaxation in respect of Accounting Standards available to an SMC until the company remains an SMC for:
(A) Three consecutive accounting periods
(B) Four consecutive accounting periods
(C) Two consecutive accounting periods
(D) Five consecutive accounting periods
Answer:
(C) Two consecutive accounting periods
Question 18.
AS-20 deals with:
(A) Earnings Per Share
(B) Lease
(C) Segment Reporting
(D) Taxes on Income
Answer:
(A) Earnings Per Share
Question 19.
Which of the following is treated as Potential Equity Share as per AS-20?
(A) Convertible debentures
(B) Share warrants
(C) Employee Stock Options
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 20.
If rights and beneficial interest in property are transferred but documentation and legal formalities are pending then seller & purchaser should record in their accounts as sale & purchase. This the example of –
(A) Prudence
(B) Substance over from
(C) Materiality
(D) Realization
Answer:
(B) Substance over from
Question 21.
Which of the following is included in the cost of inventory as per AS-2?
(A) Duties and taxes subsequently re-coverable from taxing authorities
(B) Freight inwards
(C) Rebates
(D) Duty drawbacks
Answer:
(B) Freight inwards
Question 22.
Payment of penalties/fines for violation of law should be disclosed separately. It should not be clubbed with “Office Expenses” or “Miscellaneous Expenses”. This the example of –
(A) Prudence
(B) Substance over from
(C) Materiality
(D) Realization
Answer:
(C) Materiality
Question 23.
As per AS-3, unrealized gains and losses arising from changes in foreign exchange rates are –
(A) Cash flows
(B) Cash equivalents
(C) Cash inflows
(D) Not cash flows
Answer:
(D) Not cash flows
Question 24.
Provisions for doubtful debts, provision for discount on debtors are based on:
(A) Prudence
(B) Substance over from
(C) Materiality
(D) Realization
Answer:
(A) Prudence
Question 25.
Which of the following required to be disclosed as per AS-1?
(A) Significant accounting policies
(B) Fundamental accounting as-sumptions
(C) Change in accounting policies
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 26.
As per AS-2, inventories should be valued at:
(1) Cost
(2) Net Realizable Value
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(A) (1) only
(B) Higher of (1) and (2)
(C) (2) only
(D) Lower of (1) and (2)
Answer:
(D) Lower of (1) and (2)
Question 27.
As per AS-2, the historical cost of inventories should normally be determined by using ……………………
(A) FIFO and LIFO Method
(B) LIFO and Weighted Average Cost Method
(C) FIFO and Weighted Average Cost Method
(D) FIFO and Simple Average Cost Method
Answer:
(C) FIFO and Weighted Average Cost Method
Question 28.
As per AS-3, an investment normally qualifies as a cash equivalent only when it has a short maturity of, say,_____from the date of acquisition.
(A) Two months or less
(B) Four months or less
(C) Three months or less
(D) Six months or less
Answer:
(C) Three months or less
Question 29.
NRV or net realizable value of inventory is the expected selling price or market value less………………….
(A) Carry value of the inventory
(B) Expenses necessary to complete the sale
(C) Cost of the stock
(D) replacement cost
Answer:
(B) Expenses necessary to complete the sale
Question 30.
AS-6: Depreciation applies to:
(A) Goodwill and other intangible assets
(B) Forests, plantations, and similar regenerative natural resources
(C) Wasting assets including expenditure on the exploration for and extraction of minerals, oils, natural gas, and similar non-regenerative resources
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 31.
Due to which of the following concept inventory is valued at cost or net realizable value, whichever is less?
(A) Going Concern
(B) Separate Entity
(C) Prudence
(D) Matching
Answer:
(C) Prudence
Question 32.
AS-7: Construction Contracts should be applied in accounting for construction contracts in the financial statements of:
(A) Contractor
(B) Contractors
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Only (A) not (B)
Answer:
(B) Contractors
Question 33.
While finalizing the current year’s profit, the company realized that there was an error in the valuation of closing stock of the previous year. In the previous year, the closing stock was overvalued. As a result……………
(A) Previous year profit is overstated and current year profit is also overstated.
(B) Previous year profit is understated and current year profit is overstated
(C) Previous year profit is understated and current year profit is also understated.
(D) Previous year profit is overstated and current year profit is under-stated.
Answer:
(D) Previous year profit is overstated and current year profit is under-stated.
Question 34.
As per AS-7: Construction Con-tracts, an expected loss on the construction contract should be –
(A) Charged to other profitable contracts
(B) Charged to that contract itself
(C) Recognized as an expense immediately Le. debited to P & L A/c.
(D) Should be carried forward.
Answer:
(C) Recognized as an expense immediately Le. debited to P & L A/c.
Question 35.
Which of the following method of inventory valuation is not recommended by AS – 2?
(A) Specific Identification Method
(B) Last-in-First Out Method
(C) Weighted Average Cost Method
(D) First-in-First Out Method
Answer:
(B) Last-in-First Out Method
Question 36.
Which of the following is not a method of determining the stage of completion of a contract as per AS-7?
(A) Physical completion method
(B) Residual completion method
(C) Surveys of work performed method
(D) Proportionate cost method
Answer:
(B) Residual completion method
Question 37.
If closing stock is overstated…………………
(A) Profit will increase and current assets will decrease
(B) Profit will decrease and current assets will increase
(C) Both profit & current assets will increase
(D) Both profit & current assets will decrease
Answer:
(C) Both profit & current assets will increase
Question 38.
AS-9 is concerned with the recognition of revenue arising in the course of the ordinary activities of the enterprise from:
(A) Sale of goods
(B) Rendering of services
(C) Use by others of enterprise resources yielding interest, royalties, and dividends
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 39.
Which of the following is ‘revenue’ as per AS-9?
(A) Realized gains from the disposal of non-current assets
(B) Natural increases in herds and agricultural and forest products
(C) Realized or unrealized gains resulting from changes in foreign exchange rates
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 40.
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to inventories?
(A) The FIFO method assumes that the costs of the earliest goods acquired are the last to be sold.
(B) It is generally good business management to sell the most recently acquired goods first.
(C) Under FIFO, the ending inventory is based on the latest units purchased.
(D) FIFO seldom coincides with the actual physical flow of inventory.
Answer:
(C) Under FIFO, the ending inventory is based on the latest units purchased.
Question 41.
Revenue from service transactions is usually recognized as the service is performed, by the:
(A) Proportionate completion method
(B) Completed service contract method
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 42.
As per AS-9, revenue from interest should be recognized –
(A) On-time proportion basis.
(B) On an accrual basis as per the term of the agreement
(C) When the right to receive is established
(D) Any of the above
Answer:
(A) On-time proportion basis.
Question 43.
AS-13 deals with:
(A) Accounting for borrowings
(B) Accounting for investments
(C) Finance lease
(D) Operating lease
Answer:
(B) Accounting for investments
Question 44.
As per AS-13 shares, debentures and other securities held for sale in the ordinary course of business are –
(A) Disclosed as stock-in-trade under the head Current Assets.
(B) Disclosed as temporary investments under the head Current Assets.
(C) Debited to Investment A/c
(D) Disclosed as long-term investments under the head Non-Current Assets.
Answer:
(A) Disclosed as stock-in-trade under the head Current Assets.
Question 45.
As per AS-13, where, long-term investments are reclassified as current investments, transfers are made at the:
(A) Higher of Cost or Fair Value at the date of transfer.
(B) Lower of Cost or Carrying Amount at the date of transfer.
(C) Lower of Cost or Fair Value at the date of transfer.
(D) Higher of Cost or Carrying Amount at the date of transfer.
Answer:
(B) Lower of Cost or Carrying Amount at the date of transfer.
Question 46.
X Ltd. purchased goods at the cost of ₹ 40 lakhs in October 2018. Till March 2019, 75% of the stocks were sold. The company wants to disclose closing stock at ₹ 10 lakhs. The expected sale value is ₹ 11 lakhs and a commission of 10% on sale is payable to the agent. What is the correct closing stock to be disclosed as of 31.3.2019 as per AS-2?.
(A) 10 lakhs
(B) 9.9 lakhs
(C) 11 lakhs
(D) 12 lakhs
Hint:
As per AS -2, Inventories should be valued at the lower of:
- Cost (40 Lakhs × 2596) 10 Lakhs
- Net Realizable Value (11 Lakhs – 1.1 Lakhs) 9.9 Lakhs
Hence, as per AS- 2, Inventory should be valued at Rs. 9.9 Lakhs.
Answer:
(B) 9.9 lakhs
Question 47.
On 31.3.2018 a business firm finds that the cost of a partly finished unit on that date is ₹ 530. The unit can be finished in 2018-2019 by an additional expenditure of ₹ 310. The finished unit can be sold for ₹ 750 subjects to payment of 4% brokerage on the selling price. Does the firm seek your advice regarding the amount at which the unfinished unit should be valued as of 31.3.2019 for the preparation of final accounts?
(A) 530 per unit
(B) 410 per unit
(C) 440 per unit
(D) 720 per unit
Hint:
As per AS -2, Inventories should be valued at the lower of:
– Cost Rs. 530
– Net Realizable Value (750 – 310 – 30) Rs. 410
Hence, as per AS- 2, Inventory should be valued at Rs. 410 per unit.
Answer:
(B) 410 per unit
Question 48.
X Ltd. manufactures a product and details of costs are as under:
| Raw material | ₹ 4,00,000 |
| Direct labor | ₹ 2,50,000 |
| Variable production overheads | ₹ 1,50,000 |
| Fixed production overheads (including interest ₹ 1,00,000) | ₹ 2,90,000 |
The normal production capacity is ₹ 55,000 units. At the year-end closing, the stock was 2,500 units. Compute the value of the closing stock.
(A) ₹ 45,000
(B) ₹ 40,000
(C) ₹ 55,000
(D) ₹ 50,000
Hint:
| Raw material | 4,00,000 |
| Direct labor | 2,50,000 |
| Variable production overheads | 1,50,000 |
| Fixed production overheads (excluding interest ₹ 1,00,000) | 1,90,000 |
| 9,90,000 |
Value of closing stock = 9,90,000 × \(\frac{2,500}{55,000}\) = 45,000
Answer:
(A) ₹ 45,000
Question 49.
In the process, 100 units of raw materials were introduced at a cost of ₹ 1,000. The other expenditure incurred by the process was ₹ 600. Of the units introduced, 10% are normally lost in the course of manufacturing and they possess a scrap value of ₹ 3 each. The output of Process was only 75 units. Calculate the value of the final output.
(A) ₹ 262
(B) ₹ 1,308
(C) ₹ 1,406
(D) ₹ 863
Hint:
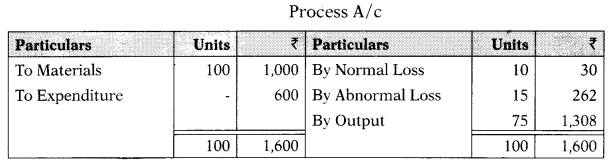
Working Notes:
Cost per unit = \(\frac{1,000+600-30}{100-10}=\frac{1,570}{90}\) = 17.4444
Value of abnormal loss = 15 × 17.4444 = 262
Value of output = 75 × 17.4444 = 1,308
Answer:
(B) ₹ 1,308
Question 50.
Z Ltd. operates retails business. For the financial year following data is given.
At Retail Price At Cost
| Opening stock | ₹ 80,000 | ₹ 60,000 |
| Purchases | ₹ 1,40,000 | ₹ 1,20,000 |
Calculate the cost of closing stock, if sales made during the year are ₹ 2,00,000.
(A) ₹ 16,436
(B) ₹ 14,366
(C) ₹ 16,364
(D) ₹ 14,346
Hint:
The average percentage of the cost to retail price
\(\frac{60,000+1,20,000}{80,000+1,40,000}\) × 100
\(\frac{1,80,000}{2,20,000}\) × 100 = 81.82%
Margin on retail price = 100% – 81.82% = 18.18%
Closing inventory at retail price = 80,000 + 1,40,000 – 2,00,000 = 20,000
Value of closing inventory = 20,000 – 3,636 = 16,364.
Answer:
(C) ₹ 16,364
Question 51.
Best Ltd. deals in five products, P, Q, R, S, and T which are neither similar nor interchangeable. At the time
of closing of its accounts for the year ending 31st March 2019, the historical cost and net realizable value of the items of the closing stock are determined as follows:
| Items | Historical Cost | Net Realizable Value |
| P | 5,70,000 | 4,75,000 |
| Q | 9,80,000 | 10,32,000 |
| R | 3,16,000 | 2,89,000 |
| S | 4,25,000 | 4,25,000 |
| T | 1,60,000 | 2,15,000 |
What will be the value of closing stock for the year ending 31 st March 2019 as per AS – 2 “Valuation of Inventories”?
(A) ₹ 23,29,000
(B) ₹ 24,51,000
(C) ₹ 24,36,000
(D) ₹ 23,42,000
Hint:
4,75,000 + 9,80,000 + 2,89,000 + 4,25,000 + 1,60,000 = 23,29,000
Answer:
(A) ₹ 23,29,000
Question 52.
Books of T Ltd. revealed the following information:
Opening inventory ₹ 6,00,000
Purchases during the year ₹ 34,00,000 Sales during the year ₹ 48,00,000
At year-end, the value of inventory as per physical stock-taking was ₹ 3,25,000. The company’s gross profit on sales has remained constant at 25%. The management of the company suspects that some inventory might have been pilfered by a new employee. What is the estimated cost of missing inventory?
(A) ₹ 75,000
(B) ₹ 25,000
(C) ₹ 1,00,000
(D) ₹ 1,50,000
Hint:
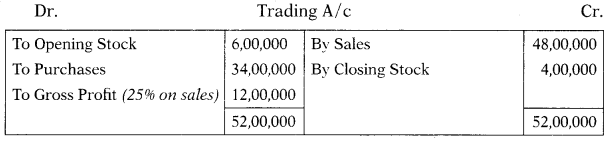
Inventory pilfered by a new employee = 4,00,000 – 3,25,000 = 75,000.
Answer:
(A) ₹ 75,000
Question 53.
NS Ltd., a dealer in second-hand cars has the following five vehicles of different models and makes in their stock at the end of the financial year 2018-2019:
| Car | Cost | NRV |
| Fiat | 90,000 | 95,000 |
| Ambassador | 1,15,000 | 1,55,000 |
| Maruti Esteem | 2,75,000 | 2,65,000 |
| Maruti 800 | 1,00,000 | 1,25,000 |
| Zen | 2,10,000 | 2,00,000 |
Value of stock included in the balance sheet of the company as on March 31, 2019 was:
(A) ₹ 7,62,500
(B) ₹ 7,70,000
(C) ₹ 7,90,000
(D) ₹ 8,70,000
Hint:
The closing stock has to value at cost or NRV whichever is less.
90,000 + 1,15,000 + 2,65,000 + 1,00,000 + 2,00,000 = 7,70,000.
Answer:
(B) ₹ 7,70,000
Question 54.
An amount of ₹ 9,90,000 was incurred on a contract work up to 31.3.2018. Certificates have been received to date to the value of ₹ 12,00,000 against which ₹ 10,80,000 has been received in cash. The cost of work done but not certified amounted to ₹ 22,500. It is estimated that by spending an additional amount of ₹ 60,000 the work can be completed in all respects in another two months. The agreed contract price of work is ₹ 12,50,000. Compute a profit to be taken to the P&L A/c as per AS-7.
(A) ₹ 1,88,625
(B) ₹ 1,65,288
(C) ₹ 1,62,885
(D) ₹ 1,88,562
Hint:
Estimated total cost = 9,90,000 + 60,000 = 10,50,000
% of work completion = \(\frac{\text { Cost incurred }}{\text { Estimated total cost }}\) × 100 = \(\frac{9,90,000}{10,50,000}\) × 100 = 94.29%
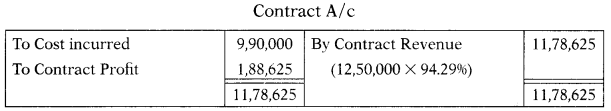
Answer:
(A) ₹ 1,88,625
Question 55.
The following details determine the expected profit or loss that should be recognized in the accounts for the year.
Contract price = ₹ 12,50,000 Cost incurred till date = ₹ 10,90,000
Cost expected to be incurred to complete the contract = ₹ 3,60,000
(A) ₹ 2,00,000 profit
(B) ₹ 49,625 loss
(C) ₹ 2,00,000 loss
(D) ₹ 49,625 profit
Hint:
Estimated total cost = 10,90,000 + 3,60,000 = 14,50,000
| Contract price | 12,50,000 |
| Estimated total cost | (14,50,000) |
| Estimated loss | (2,00,000) |
% of work completion = \(\frac{\text { Cost incurred }}{\text { Estimated total cost }}\) × 100
\(\frac{10,90,000}{14,50,000}\) × 100 = 75.17%
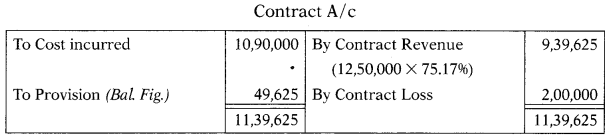
Answer:
(C) ₹ 2,00,000 loss
Question 56.
Z Ltd. purchased 10,000 shares of N Ltd. @ ₹ 300. Brokerage @2% and stamp duty was 10 paisa per ₹ 100. What is the value of the investment as per AS-13?
(A) ₹ 30,63,000
(B) ₹ 30,60,000
(C) ₹ 30,00,000
(D) ₹ 30,93,000
Hint:

Answer:
(A) ₹ 30,63,000
Question 57.
P Ltd. purchased 10,000 shares of Q Ltd. and issued its 5,000 shares. The nominal value of shares of both P Ltd. & Q Ltd. is ₹ 10. The fair value of shares of P Ltd. & Q Ltd. is ₹ 11.5 & ₹ 12 respectively. Calculate the cost of investment acquired as per AS-13.
(A) ₹ 57,500
(B) ₹ 1,15,000
(C) ₹ 60,000
(D) ₹ 1,20,000
Hint:
Cost of investment = 5,000 × 11.5 = 57,500
Answer:
(A) ₹ 57,500
Question 58.
N Ltd. acquired certain investments by giving its machinery having WDV ₹ 47,000 and cash ₹ 16,000. The realizable value of machinery was ₹ 20,000. Calculate the cost of investment acquired as per AS-13.
(A) ₹ 31,000
(B) ₹ 36,000
(C) ₹ 27,000
(D) ₹ 11,000
Hint:
Cost of investment = 20,000 + 16,000 = 36,000
Answer:
(B) ₹ 36,000
Question 59.
An Ltd. is absorbed by B Ltd., the consideration being the takeover of liabilities, the payment of the cost of absorption as part of purchase consideration not exceeding ₹ 20,000, the payment of the 9% Debenture of ₹ 1,00,000 at a premium of 10% to the debenture holders of A Ltd. Equity shareholders of A Ltd. is entitled to ₹ 16 per share in cash and allotment of one 14% Preference Share of ₹ 10 each and 6 equity share of ₹ 10 each fully paid for every 4 shares in A Ltd. The numbers of shares of A Ltd. are 2,00,000 of ₹ 10 each fully paid. Purchases consideration as per AS-14 =?
(A) ₹ 67,00,000
(B) ₹ 62,00,000
(C) ₹ 67,20,000
(D) ₹ 62,20,000
Hint:

Answer:
(A) ₹ 67,00,000
Question 60.
On 1.1.2019, 7,200 equity shares outstanding in the books of X Ltd.
On 31.5.2019, 2,400 shares issued for cash.
1.11.2019, the company made a buyback of 1,200 shares.
Net profit for the year ended 31.12.2019 is ₹ 6,30,000.
Basic EPS as per AS-20 =?
(A) 75 per share
(B) 80 per share
(C) 35 per share
(D) 55 per share
Hint:
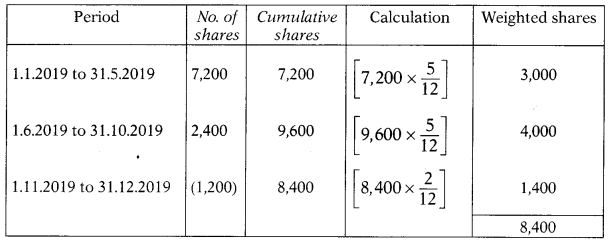
Basic EPS = \(\frac{\text { Profit available for equity shareholder }}{\text { Weighted average number of shares }}\)
= \(\frac{6,30,000}{8,400}\)
= 75 per share
Answer:
(A) 75 per share
