Organisation and Strategic Leadership – CA Inter SM Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Organisation and Strategic Leadership – CA Inter SM Study Material
Question 1.
Manoj started his telecom business in 2010. Over next five years, he gradually hired fifty people for various activities such as to keep his accounts, administration, sell his products in the market, create more customers, provide after sales service, coordinate with vendors.
Draw the organization structure Manoj should implement in his organization and name it. {Nov. 2018; 5 Marks)
Answer:
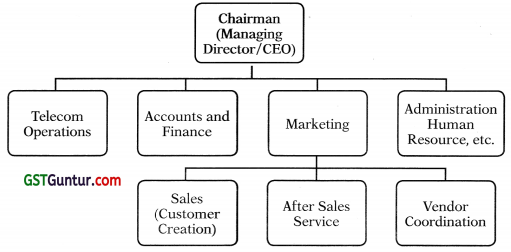
Manoj has started a telecom business. Accounts, Administration, Marketing (customer creation, after sales service, vendor coordination) are the functional areas that are desired in the organisational structure. Further there is inherent need to have a department for the management of telecom services/operations.
Thus, the functional structure in the telecom business of Manoj can be as follows:
Question 2.
Discuss the concept of Multi Divisional Structure. (RTP May 2019)
Answer:
- The multi divisional (M- form) structure:
- is composed of operating divisions
- where each division represents a separate business
- to which the top corporate officer delegates responsibility for day-to-day operations and business unit strategy to division managers.
- By such delegation, the corporate office is responsible for formulating and implementing overall corporate strategy and manages divisions through strategic and financial controls.
- The multi divisional or M-form structure was developed in the 1920s, in response to coordination and control related problems in large firms. Functional departments often had difficulty dealing with distinct product lines and markets, especially in coordinating conflicting priorities among the products. Costs were not allocated to individual products, so it was not possible to assess an individual product’s profit contribution. Loss of control meant that optimal allocation of firm resources between products was difficult (if not impossible).
- Top managers became over-involved in solving short-run problems (such as coordination, communications, conflict resolution) and neglected long-term strategic issues.
- The new, innovative structure called for
- Creating separate divisions, each representing a distinct business;
- Each division would house its functional hierarchy;
- Division managers would be given responsibility for managing day-to-day operations;
- A small corporate office that would determine the long-term strategic direction of the firm and exercise overall financial control over the semi-autonomous divisions.
![]()
Question 3.
What is a strategic business unit? What are its advantages? (RTP May 2020)
Answer:
A strategic business unit (SBU) is any part of a business organization which is treated separately for strategic management purposes. The concept of SBU is helpful in creating an SBU organizational structure. It is discrete element of the business serving product markets with readily identifiable competitors and for which strategic planning can be concluded. It is created by adding another level of management in a divisional structure after the divisions have been grouped under a divisional top management authority based on the common strategic interests
Advantages of SBU are:
- Establishing coordination between divisions having common strategic interests.
- Facilitates strategic management and control on large and diverse organizations.
- Fixes accountabilities at the level of distinct business units.
- Allows strategic planning to be done at the most relevant level within the total enterprise.
- Makes the task of strategic review by top executives more objective and more effective.
- Helps allocate corporate resources to areas with greatest growth opportunities.
Question 4.
Describe the three distinct phases proposed by Davis and Lawrence for development of matrix structure. (RTP Nov 2018)
Answer:
For development of matrix structure Davis and Lawrence, have proposed three distinct phases:
- Cross-functional task forces: Temporary cross-functional task forces are initially used when a new product line is being introduced. A project manager is in charge as the key horizontal link.
- Product/brand management. If the cross-functional task forces become more permanent, the project manager becomes a product or brand manager and a second phase begins. In this arrangement, function is still the primary organizational structure, but product or brand managers act as the integrators of semi permanent products or brands.
- Mature matrix: The third and final phase of matrix development involves a true dual authority structure. Both the functional and product structures are permanent. All employees are connected to both a vertical functional superior and a horizontal product manager. Functional and product managers have equal authority and must work well together to resolve disagreements over resources and priorities.
Question 5.
‘A network structure is suited to unstable environment.’ Elaborate.
Answer:
- Network structure is a newer and somewhat more radical organizational design.
- The network structure could be termed a “non-structure” as it virtually eliminates in-house business functions and outsource many of them.
- An organisation organized in this manner is often called a virtual organization because it is composed of a series of project groups or collaborations linked by constantly changing non-hierarchical, cobweb-like networks.
- The network structure becomes most useful when the environment of a firm is unstable and is expected to remain so. Under such conditions, there is usually a strong need for innovation and quick response. Instead of having salaried employees, it may contract with people for a specific project or length of time.
- Long-term contracts with suppliers and distributors replace services that the company could provide for itself.
- Example: Companies like Airtel use the network structure in their operations function by sub-contracting manufacturing to other companies in low cost.
![]()
Question 6.
What is an Hourglass structure? How is it beneficial for an organization? (May 2019; 3 Marks)
OR
Discuss the concept of Hourglass Structure. (RTP Nov. 2019)
Answer:
- In the recent years information technology and communications have significantly altered the functioning of organizations. The role played by middle management is diminishing as the tasks performed by them are increasingly being replaced by the technological tools.
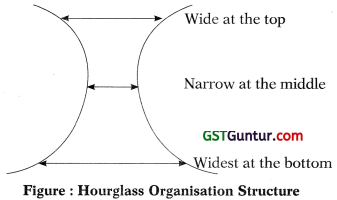
- Hourglass organization structure consists of three layers with constricted middle layer. The structure has a short and narrow middle-management level.
- Information technology links the top and bottom levels in the organization taking away many tasks that are performed by the middle level managers.
- A shrunken middle layer coordinates diverse lower level activities. Contrary to traditional middle level managers who are often specialist, the managers in the hourglass structure are generalists and perform wide variety of tasks.
- They would be handling cross-functional issues emanating such as j those from marketing, finance or production.
- Hourglass structure has obvious benefit of reduced costs. It also helps in enhancing responsiveness by simplifying decision making.
- Decision making authority is shifted close to the source of information so that it is faster.
- However, with the reduced size of middle management the promotion opportunities for the lower levels diminish significantly.
- Continuity at same level may bring monotony and lack of interest and to overcome these problems by assigning challenging tasks, transferring laterally and having a system of proper rewards for performance.
Question 7.
Delta is an organization specializing in Information Technology en-ables Services (ITeS) and Communications business. Previous year the organization had successfully integrated an Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool named ‘Zeus’ into the existing ERP system.
The AI tool using Deep Learning technique provided a digital leap trans-formation in various business processes and operations. It has significantly diminished the role played by specialist managers of the middle management. This technological tool in addition to saving organisational costs by replacing many tasks of the middle management, has also served as a link between top and bottom levels in the organization and assists in faster decision making. The skewed middle level now perform cross-functional duties. Which type of organisational structure is the company transitioning into? (RTPNov 2020)
Answer:
The company Delta is transitioning into the Hourglass organization structure because it has used technological tools to transform various business processes and operations and has significantly diminished the role played by specialist managers of the middle management.
The technological tool in addition to savings organisational costs by replacing many tasks of the middle management has also served as a link between top and bottom levels in the organization and assists in faster decision making. The skewed middle level managers now perform cross-functional duties. All these factors indicate towards Hourglass organization structure.
Question 8.
Discuss the leadership role played by the managers in pushing for good strategy execution. (May 2019; 5 Marks)
OR
Suresh Sinha has been recently appointed as the head of a strategic busi-ness unit of a large multiproduct company. Advise Mr Sinha about the leadership role to be played by him in execution of strategy. (RTP May 2018)
Answer:
A strategy manager has many different leadership roles to play: vision-ary, chief entrepreneur and strategist, chief administrator, culture builder, resource acquirer and allocator, capabilities builder, process integrator, crisis solver, spokesperson, negotiator, motivator, arbitrator, policy maker, policy enforcer, and head cheerleader.
Managers have five leadership roles to play in pushing for good strategy execution:
- Staying on top of what is happening, closely monitoring progress, fer-reting out issues, and learning what obstacles lie in the path of good execution.
- Promoting a culture and esprit de corps that mobilizes and energizes organizational members to execute strategy in a competent fashion and perform at a high level.
- Keeping the organization responsive to changing conditions, alert for new opportunities, bubbling with innovative ideas, and ahead of rivals in developing competitively valuable competencies and capabilities.
- Exercising ethics leadership and insisting that the company conduct its affairs like a model corporate citizen.
- Pushing corrective actions to improve strategy execution and overall strategic performance.
Question 9.
What are the different responsibilities of a Strategic Leader?
OR
KaAthens Ltd., a diversified business entity having business operations across the globe. The company leadership has just changed as Mr. D. Bandopadhyay handed over the pedals to his son Aditya Bandopadhyay, due to his poor health. Aditya is a highly educated with an engineering degree from IIT, Delhi. However, being very young he is not clear about his role and responsibilities.
In your view, what are the responsibilities of Aditya Bandopadhyay as CEO of the company. (RTP Nov 2018; RTP May 2020)
Answer:
Aditya Bandopadhyay, an effective strategic leader of KaAthens Ltd. must be able to deal with the diverse and cognitively complex competitive situations that are characteristic of today’s competitive landscape.
A Strategic leader has several responsibilities, including the following:
- Making strategic decisions.
- Formulating policies and action plans to implement strategic decision.
- Ensuring effective communication in the organisation.
- Managing human capital (perhaps the most critical of the strategic leader’s skills).
- Managing change in the organisation.
- Creating and sustaining strong corporate culture.
- Sustaining high performance over time.
![]()
Question 10.
Distinguish between Transformational Leadership Style and Trans-actional Leadership Style. (Nov. 2019; 5 Marks) (RTP Nov. 2020)
OR
Ram and Shyam are two brothers engaged in the business of spices. Both have different approaches to management. Ram prefers the conventional and formal approach in which authority is used for explicit rewards and punishment. While, on the other hand, Shyam believes in democratic par-ticipative management approach, involving employees to give their best.
Analyse the leadership style followed by Ram and Shyam. (May 2018)
OR
Ramesh is owner of a popular brand of Breads. Yashpal, his son after completing Chartered Accountancy stated assisting his father in running of business.
The approaches followed by father and son in management were very different.
While Ramesh preferred to use authority and having a formal system of defining goals and motivation with explicit rewards and punishments, Yashpal believed in involving employees and generating enthusiasm to inspire people to deliver in the organization.
Discuss the difference in leadership style of father and son. (RTP May 2019)
Answer:
[Ramesh is a follower of transactional leadership style, while Yashpal is follower of transformational leadership style.]
1. TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP STYLE
- Use charisma and enthusiasm to inspire people to exert them for the good of the organization.
- Transformational leadership style may be appropriate in turbulent environments, in industries at the very start or end of their life-cycles, in poorly performing organizations when there is a need to inspire a company to embrace major changes.
- Transformational leaders offer excitement, vision, intellectual stimu-lation and personal satisfaction.
- They inspire involvement in a mission, giving followers a ‘dream’ or ‘vision’ of a higher calling so as to elicit more dramatic changes in organizational performance.
- Such a leadership motivates followers to do more than originally af-fected to do by stretching their abilities and increasing their self-con-fidence, and also promote innovation throughout the organization.
2. TRANSACTIONAL LEADERSHIP STYLE
- Focus more on designing systems and controlling the organization’s activities and are more likely to be associated with improving the current situation.
- Transactional leaders try to build on the existing culture and enhance current practices.
- Transactional leadership style uses the authority of its office to exchange rewards, such as pay and status.
- They prefer a more formalized approach to motivation, setting clear goals with explicit rewards or penalties for achievement or non-achievement.
- Transactional leadership style may be appropriate in settled environ-ment, in growing or mature industries, and in organizations that are performing well.
- The style is better suited in persuading people to work efficiently and run operations smoothly.
Question 11.
Define corporate culture. Also elucidate the statement “Culture is a strength that can also be a weakness”. (Nov 2018; 5 Marks)
OR
How can a corporate culture be both strength and weakness of an organ-isation?
Answer:
The phenomenon which often distinguishes good organizations from bad ones could be summed up as ‘corporate culture’.
Corporate culture refers to a company’s values, beliefs, business principles, traditions, ways of operating and internal work environment.
Every corporation has a culture that exerts powerful influences on the 2 behaviour of managers. Culture affects not only the way managers behave z within an organization but also the decisions they make about the organi-zation’s relationships with its environment and its strategy.
“Culture is a strength that can also be a weakness”. This statement can be explained by splitting it into two parts.
Culture as a strength:
As a strength, culture can facilitate communication, decision-making & control and create cooperation & commitment. An organization’s culture could be strong and cohesive when it conducts its business according to a clear and explicit set of principles and values, which the management de-votes considerable time to communicating to employees and which values are shared widely across the organization.
Culture as a weakness:
As a weakness, culture may obstruct the smooth implementation of strategy by creating resistance to change. An organization’s culture could be charac-terized as weak when many sub-cultures exist, few values and behavioural norms are shared and traditions are rare. In such organizations, employees do not have a sense of commitment, loyalty and sense of identity.
Question 12.
Write a short note on importance of corporate culture.
OR
Explain briefly the role of culture in promoting better strategy execution.
Answer:
- A culture where creativity, embracing change, and challenging the status quo are pervasive themes is very conducive to successful execution of a product innovation and technological leadership strategy.
- A culture built around such business principles as listening to customers, encouraging employees to take pride in their work, and giving employees a high degree of decision-making responsibility is very conducive to successful execution of a strategy of delivering superior customer service.
- A strong strategy-supportive culture nurtures and motivates people to do their jobs in ways conducive to effective strategy execution; it provides structure, standards, and a value system in which to operate; and it promotes strong employee identification with the company’s vision, performance targets, and strategy.
- All this makes employees feel genuinely better about their jobs and work environment and the merits of what the company is trying to accomplish.
- Employees are stimulated to take on the challenge of realizing the company’s vision, do their jobs competently and with enthusiasm, and collaborate with others as needed to bring the strategy to success.
Question 13.
Jupiter Electronics Ltd, is known for its ability to come out with path-breaking products. Though the work environment at Jupiters is relaxed and casual, yet, there is a very strong commitment to deadlines. The employees believe in “work hard play hard” ethic. The organisation has moved away from formal and hierarchical set up to a more results -driven approach. Employees are committed to strategies and work to-wards achieving them. They guard innovations, maintain confidentiality and secrecy in their working. They are closely related to values, practices, and norms of organisations.
What aspects of an organization that are being discussed? Explain. (RTP Nov. 2019)
Answer:
- The scenario being referred to is culture in Jupiter Electronics.
- Strong culture promotes good strategy execution when there’s fit and impels execution when there’s negligible fit.
- A culture grounded in values, practices, and behavioural norms that match what is needed for good strategy execution helps energize people throughout the organization to do their jobs in a strategy-supportive manner.
- A culture built around such business principles as listening to customers, encouraging employees to take pride in their work, and giving employees a high degree of decision-making responsibility.
- This is very conducive to successful execution of a strategy of delivering superior customer service.
- A strong strategy-supportive culture makes employees feel genuinely better about their jobs and work environment and the merits of what the company is trying to accomplish.
- Employees are stimulated to take on the challenge of realizing the organizational vision, do their jobs competently and with enthusiasm, and collaborate with others.
![]()
Question 14.
Define Entrepreneur. What are the characteristics of an entrepreneur? (RTP May 2018)
Answer:
- Entrepreneurship is the attempt to create value through:
- recognition of business opportunity,
- the management of risk taking appropriate to the opportunity and
- through management skills to mobilize financial, human and material resources necessary to create an enterprise.
- Entrepreneurship involves creation of a business idea and the fusion of capital, technology and human talent to give practical shape to the idea.
- The person who perceives the business idea and take steps to implement the idea is known as an entrepreneur.
- An entrepreneur is an individual who conceives the idea of starting a new venture, takes all types of risks, not only to put the product or service into reality but also to make it an extremely demanding one.
- An entrepreneur is one who:
- Initiates and innovates a new concept.
- Recognises and utilises opportunity.
- Arranges and coordinates resources such as man, material, machine and capital.
- Faces risks and uncertainties.
- Establishes a startup company.
- Adds value to the product or service.
- Takes decisions to make the product or service a profitable one.
- Is responsible for the profits or losses of the company.