Students should practice Methods of Valuation – Corporate and Management Accounting CS Executive MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Methods of Valuation – Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
Question 1.
Beta is a measure of __
(A) Non-diversifiable risk
(B) Diversifiable risk
(C) Total risk
(D) Covariance
Answer:
(A) Non-diversifiable risk
Question 2.
Investors should be agreeing to invest in riskier investments merely –
(A) If a return is short
(B) If there are no safe alternatives except for holding cash
(C) If the expected return is adequate for risk level
(D) If there are true speculators
Answer:
(C) If the expected return is adequate for risk level
Question 3.
A beta of 1.15 for security would indicate that –
(A) Security is trading 15% higher than a market index
(B) Security is 15% riskier than index/ market.
(C) Security is 15% less risky than index/market.
(D) Security and market have a covariance of 0.15.
Answer:
(B) Security is 15% riskier than index/ market.
Question 4.
A beta of 0.8 for security would indicate that –
(A) Security is 20% riskier than index/ market.
(B) Security is 80% less risky than index/market.
(C) Security is 20% less risky than index/market.
(D) Securityis80%riskierthanindex/ market
Answer:
(C) Security is 20% less risky than index/market.
Question 5.
Which of the following is the correct formula to calculate beta (β)
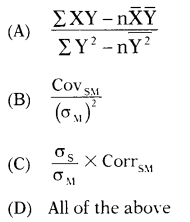
Answer:
(D)
Question 6.
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) provides the link between –
(A) Return and total risk
(B) Risk and covariance
(C) Return and non-diversifiable risk
(D) Return and diversifiable risk
Answer:
(C) Return and non-diversifiable risk
Question 7.
Which of the following investment advice will you provide to your client investor if CAPM Return < Expected return?
(A) Sell
(B) Hold
(C) Buy
(D) Short
Answer:
(C) Buy
Question 8.
Which of the following investment advice will you provide to your client investor if CAPM Return > Expected return?
(A) Sell
(B) Buy
(C) Hold
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Sell
Question 9.
If the expected return is more than the required return as per CAPM, then –
(A) Security is overvalued and hence can be bought
(B) Security is correctly priced and hence should behold
(C) Security is undervalued and hence can be sold
(D) Security is undervalued and hence can be bought
Answer:
(C) Security is undervalued and hence can be sold
Question 10.
The Security Market Line (SML) is a line drawn on a chart that serves as a graphical representation of the Capital Asset Pricing Model, which shows different levels of ____ of various marketable securities plotted against the expected return.
(A) Systematic risk
(B) Unsystematic risk
(C) Total risk
(D) Free risk
Answer:
(A) Systematic risk
Question 11.
Market risk is also called:
(A) Systematic risk and unique risk.
(B) Unique risk & non-diversifiable risk.
(C) Systematic risk & diversifiable risk.
(D) Non-diversihable risk & systematic risk.
Answer:
(D) Non-diversihable risk & systematic risk.
Question 12.
Which of the following investment advice will you provide to your client investor if CAPM Return = Expected return?
(A) Sell
(B) Buy
(C) Hold
(D) Put
Answer:
(C) Hold
Question 13.
If the required return as per CAPM is more than the expected return, then –
(A) Security is undervalued and can be sold
(B) Security is correctly priced and hence should behold
(C) Security is overvalued and hence can be bought
(D) Security is undervalued and hence can be bought
Answer:
(A) Security is undervalued and can be sold
Question 14.
According to the CAPM, overpriced securities have:
(A) Negative alphas
(B) Positive alphas
(C) Zero betas
(D) Zero alphas
Answer:
(A) Negative alphas
Question 15.
The beta of the risk-free asset is:
(A) 0
(B) 0.5
(C) 2.0
(D) 1.0
Answer:
(A) 0
Question 16.
Capital asset pricing theory asserts that portfolio returns are best explained by:
(A) Economic factors
(B) Systematic risk
(C) Specific risk
(D) Diversification
Answer:
(B) Systematic risk
Question 17.
Alpha is an indicator of the extent to which the –
(A) Actual return of security deviates from those predicated by market experts.
(B) Actual return of security deviates from those predicated by derivative market
(C) Actual return of security deviates from those predicated by its beta value.
(D) Actual return of security deviates from those predicated by its probable distribution value.
Answer:
(C) Actual return of security deviates from those predicated by its beta value.
Question 18.
Alpha is denoted by the symbol –
(A) A
(B) ¥
(C) α
(D) Δ
Answer:
(C) α
Question 19.
The negative alpha value indicates that –
(A) Expected return is less than required return as per CAPM and hence security is overvalued. Such security should be sold.
(B) Expected return is less than required return as per CAPM and hence security is undervalued. Such security should be bought.
(C) Expected return is more than required return as per CAPM and hence security is undervalued. Such security should be bought.
(D) Expected return is equal to required return as per CAPM and hence security is correctly valued. Such security should behold.
Answer:
(A) Expected return is less than required return as per CAPM and hence security is overvalued. Such security should be sold.
Question 20.
Systematic Risk is –
(A) Uncontrollable
(B) Controllable
(C) Avoidable
(D) Voidable
Answer:
(A) Uncontrollable
Question 21.
The positive alpha value indicates that –
(A) Expected return is less than required return as per CAPM and hence security is overvalued. Such security should be sold.
(B) Expected return is more than required return as per CAPM and hence security is undervalued. Such security should be bought.
(C) Expected return is equal to required return as per CAPM and hence security is correctly valued. Such security should behold.
(D) Expected return is more than required return as per CAPM and hence security is overvalued. Such security should be sold.
Answer:
(B) Expected return is more than required return as per CAPM and hence security is undervalued. Such security should be bought.
Question 22.
Systematic risk =?
(A) Beta × SD of market
(B) Total risk – SD of market
(C) Total risk – Beta
(D) Beta ÷ SD of market
Answer:
(A) Beta × SD of market
Question 23.
____is also called specific risk.
(A) Systematic risk
(B) Unsystematic risk
(C) Covariance
(D) Coefficient
Answer:
(B) Unsystematic risk
Question 24.
In contrast to the capital asset pricing model, arbitrage pricing theory:
(A) Uses risk premiums based on micro variables.
(B) Requires normally distributed security returns.
(C) Has fewer restrictive assumptions.
(D) Specifies the number and identities of specific factors that determine expected returns.
Answer:
(C) Has fewer restrictive assumptions.
Question 25.
The APT is an equilibrium model developed by:
(A) Stephen Ross and Richard Roll
(B) Stephen Ross
(C) Richard Roll
(D) Harry Markowitz
Answer:
(B) Stephen Ross
Question 26.
Following details are available for two securities:
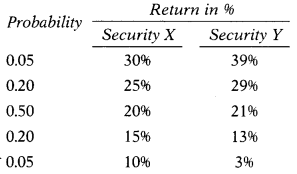
Calculate the expected return.

Hint:
X: (0.05 × 30) + (0.20 × 25) + (0.50 × 20) + (0.20 × 15) + (0.05 × 10) = 20%
Y: (0.05 × 39) + (0.20 × 29) + (0.50 × 21) + (0.20 × 13) + (0.05 × 3) = 21%
Answer:
(C)
Question 27.
Suppose the risk-free rate is 4% and k is 2.5%. If an investor takes 13% risk, he can expect a return of –
(A) 32.5%
(B) 52%
(C) 10%
(D) 36.5%
Hint:
The risk-free rate is 4% and λ is 2.5%. Thus, for every 1% increase in the risk, the investor can expect a 2.5% above risk-free return. Thus, if an investor takes 13% risk, he can expect a return of 36.5% [(13 × 2.5) + 4]
Answer:
(D) 36.5%
Question 28.
Yogesh invests ₹ 1,25,000 in shares of BABA Ltd., a listed company. At the end of the period investment value is ₹ 1,32,000. He gets a dividend of ₹ 8,000. Return from investment is –
(A) 11%
(B) 12%
(C) 13%
(D) 14%
Hint:
[(1,32,000 – 1,25,000) + 8,000]/1,25,000 × 100 = 12%
Answer:
(B) 12%
Question 29.
The actual return of GK Ltd. for the last four years is 20%, 14%, 17%, and 18%. GK Ltd. has a beta of 1.15. Return on the market portfolio is 15%. The risk-free rate of return is 6%. Compute Alpha value and decide whether to hold, buy, or sell the security?
(A) Alpha value is +0.8 and hence it is advised to sell the security.
(B) Alpha value is -0.9 and hence it is advised to buy the security.
(C) Alpha value is -0.8 and hence it is advised to short sell the security
(D) Alpha value is +0.9 and hence it is advised to buy the security.
Hint:
ER = Rf + β (Rm – Rf)
= 6 + 1.15(15 – 6)
= 16.35%
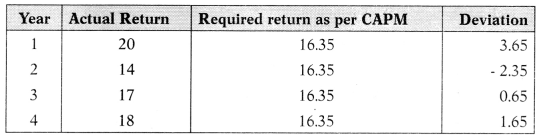
α = \(\frac{3.65-2.35+0.65+1.65}{4}\) = 0.9
Answer:
(D) Alpha value is +0.9 and hence it is advised to buy the security.
Question 30.
Return of last 5 years of listed security is 16.2%, 19.8%, 18%, 15% & 21%. Five years ago the price of the security was 120 per share. What is its average return?
(A) 18%
(B) 19%
(C) 20%
(D) 21%
Answer:
(A) 18%
Question 31.
Return of last 5 years of listed security is 16.2%, 19.8%, 18%, 15% & 21%. Five years ago the price of the security was 120 per share.
What is its holding period return?
(A) 135.55%
(B) 128.58%
(C) 145.64%
(D) 154.45%
Hint:
120 × 1.162 × 1.198 × 1.18 × 1.15 × 1.21 = 274.29
(274.29 – 120)/120 × 100 = 128.58%
Answer:
(B) 128.58%
Question 32.
Dividend for the last 4 years of Tara Ltd. was ₹ 7, ₹ 5, 12.8 & ₹ 10, and the market price was ₹ 120, ₹ 80, ₹ 130 & ₹ 150 respectively. What is the average return of the last 3 years considering capital gain and dividend?
(A) 19.28%
(B) 14.48%
(C) 10.84%
(D) 16.65%
Hint:
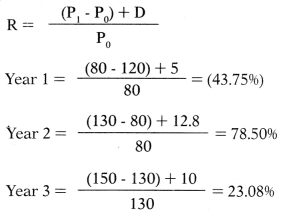
Average return = – 43.75 + 78.50 + 23.08/3 = 19.28%
Answer:
(A) 19.28%
Question 33.
Return on XM Ltd. shares has a standard deviation of 23%, as against the standard deviation of the market at 19%. The correlation coefficient between the market and the stock of XM Ltd. is 0.8. Compute the systematic risk of XM Ltd.’s shares.
(A) 96.84%
(B) 18.4%
(C) 25.78%
(D) 64.85%
Hint:
β = \(\) × CorrSM
= \(\) × 0.8
= 0.9684
Systematic risk = Beta × SD of market
= 0.9684 × 19
= 18.4%
Answer:
(B) 18.4%
Question 34.
Return on Lucky Ltd. shares has a standard deviation of 2096, as against the standard deviation of the market at 1596. The correlation coefficient between the market and stock of XM Ltd. is 0.9. Compute the unsystematic risk of Lucky Ltd.’s shares.
(A) 5%
(B) 2%
(C) 18%
(D) 20%
Hint:
β = \(\frac{\sigma_{\mathrm{S}}}{\sigma_{\mathrm{M}}}\) × CorrSM
= \(\frac{20}{15}\) × 0.9
= 1.2
Systematic risk = Beta × SD of market
= 1.2 × 15 = 18%
Unsystematic risk = Total risk – Systematic risk
= 20 – 18 = 2%
Answer:
(B) 2%
Question 35.
You are analyzing the beta for ABC Ltd. and have divided the Company into four broad business groups, with market values and betas for each group.
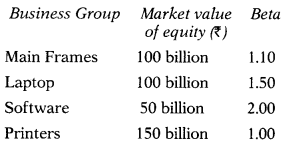
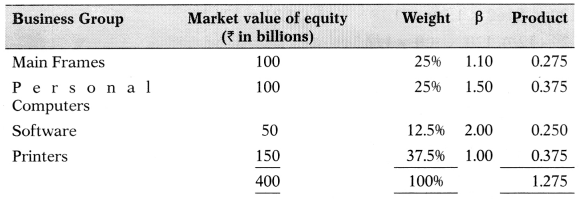
Estimate the beta for ABC Ltd. as a company.
(A) 1.275
(B) 1.825
(C) 1.645
(D) 0.895
Hint:
Answer:
(A) 1.275
Question 36.
Pavan has invested in four securities. Amount invested and a beta of each security is as follows:
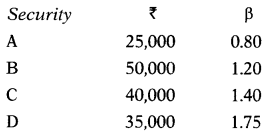
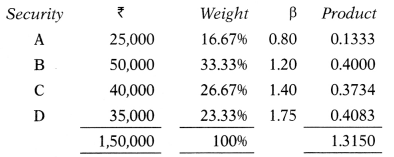
Compute portfolio beta.
(A) 1.524
(B) 1.874
(C) 0.789
(D) 1.315
Hint:
Answer:
(D) 1.315
Question 37.
ABC Ltd. beta is 1.45. The rate of market return is 1696. The rate of return on government securities is 8%. What is the expected return as per Capital Asset Pricing Model? If the risk premium on the market goes up by 2.5% points, what would be the revised expected return on this stock?
(A) 16.9%;32.32%
(B) 18.7%;24.28%
(C) 19.6%:23.23%
(D) 19.6%; 16.7%
Hint:
ER = Rf + β (Rm – Rf)
= 8 + 1.45(16 – 8)
= 19.6%
Revised expected return if the risk premium on the market goes up by 2.5%:
ER = Rf + β (Rm – Rf)
= 8 + 1.45 (10 – 5)
= 23.23%
Note: Risk Premium = (Rm – Rf)
Revised risk premium = 8 + 2.5 = 10.5
Answer:
(C) 19.6%: 23.23%
Question 38.
A financial consultant has gathered the following facts for H Ltd.
The systematic risk of the firm is 1.4.
182 days Treasury bill yield is 8%
The expected yield on the market portfolio is 13%. Calculate expected returns based on the capital asset pricing model (CAPM).
(A) 18%
(B) 17%
(C) 16%
(D) 15%
Hint:
ER = Rf + β(Rm – Rf)
= 8 + 1.4(13 – 8)
= 15%
Answer:
(D) 15%
Question 39.
Calculate the required return on the security from the following information:
Standard deviation 2.5%
Market standard deviation 2.0%
The risk-free rate of return 13%
Expected rate of return on market portfolio 15%
The correlation coefficient of the portfolio with the market 0.8
(A) 16%
(B) 15%
(C) 14%
(D) 12%
Hint:
β = \(\frac{\sigma_{\mathrm{S}}}{\sigma_{\mathrm{M}}}\) × CorrSM
= \(\frac{2.5}{2}\) × 0.8
= 1
ER = Rf + β (Rm – Rf)
= 13 + 1 (15 – 13)
= 15%
Answer:
(B) 15%
Question 40.
The expected return of Security A is 22% while that of Security B is 24%. The beta of Security A is 0.86 while that of Security B is 1.24. What is a risk-free rate?
(A) 14.74%
(B) 17.47%
(C) 14.71%
(D) 14.00%
Hint:
Let the be Rf ‘x’ and (Rm – Rf) be ‘y’

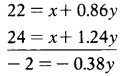
y = 2/0.38 = 5.2632
y = Rm – Rf =5.2632
Putting value of ‘y’ in first equation we can get value of ‘x’.
22 = x + 0.86y
22 = x + 0.86 × 5.2632
22 = x + 4.5264
x = Risk free rate = 17.47%
Answer:
(B) 17.47%
