Chapter 4 Insolvency Resolution of Corporate Persons – CS Professional Insolvency Law and Practice Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Insolvency Resolution of Corporate Persons – CS Professional Insolvency Law and Practice Study Material
Question 1.
You are appointed as Resolution Professional by Committee of Creditors. You have made a public announcement inviting Expression of Interest. Based on your invitation few Parties have submitted Resolution plans. As per the provisions of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC, 2016) Resolution plans submitted should satisfy few criteria. As a Resolution Professional brief the criteria for a valid Resolution Plan under IBC, 2016. (Dec 2020, 6 marks)
Answer:
Section 30(2) of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 provides that the Resolution Professional shall examine each resolution plan received by him to confirm that each resolution plan fulfils the following criteria:
(a) provides for the payment of insolvency resolution process costs in a manner specified by the Board in priority to the payment of other debts of the corporate debtor:
(b) provides for the payment of the debts of operational creditors in such manner as may be specified by the Board which shall not be less than the amount to be paid to the operational creditors in the event of a liquidation of the corporate debtor under section 53, whichever is higher, and provides for the payment of debts of financial creditors, who do not vote in favour of the resolution plan, in such manner as may be specified by the Board, which shall not be less than the amount to be paid to such creditors in accordance with sub-section (1) of Section 53 in the event of a liquidation of the corporate debtor.
(c) provides for the management of the affairs of the Corporate debtor after approval of the resolution plan;
(d) the implementation and supervision of the resolution plan;
(e) does not contravene any of the provisions of the law for the time being in force,
(f) conforms to such other requirements as may be specified by the Board
Explanation: For the purposes of clause (e), if any approval of shareholders is required under the Companies Act, 2013 or any other lawfor the time being in force for the implementation of actions under the resolution plan, such approval shall be deemed to have been given and it shall not be a contravention of that Act or law.
If the Resolution Professional is satisfied that the resolution plan fulfils the above criteria, he shall present such resolution plan to the committee of creditors for its approval.
![]()
Question 2.
ESI Ltd. filed Corporate Insolvency Resolution Plan (CIRP) with the Adjudicating Authority, which was accepted, and Expression of Interest (EOI) was invited. One N Ltd. filed EOI. It was noticed that N Ltd was incorporated just 7 days before submission of the EOI as joint venture between AE Ltd. and other two companies. It was further come to the notice that AE Ltd. was completely held by Sawant Seth (through various companies and a trust), said Sawant Seth was son of Ravi Seth, who was promoter of ESI Ltd.
You as a Resolution Professional in this case, what would you suggest the Committee of Creditors and Adjudicating Authority about the acceptance or rejection of the EOI. Give reasons and quote the decided case law. (June 2019, 6 marks)
Answer:
Persons not Eligible to be Resolution Applicant:
Section 29A of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 provides the list of persons who are not eligible to be resolution applicant. Sub-clause (c) of Section 29A provides as under:
A person shall not be eligible to submit a resolution plan, if such person, or any other person acting jointly or in concert with such person:
(c) at the time of submission of the resolution plan has an account, or an account of a corporate debtor under the management or control of such person or of whom such person is a promoter, classified as non¬performing asset in accordance with the guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India issued under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 or the guidelines of a financial sector regulator issued under any other law for the time being in force, and at least a period of one year has lapsed from the date of such classification till the date of commencement of the corporate insolvency resolution process of the corporate debtor.
Provided that the person shall be eligible to submit a resolution plan if such person makes payment of all overdue amounts with interest thereon and charges relating to non-performing asset accounts before submission of resolution plan.
The case is similar to Arcelormittal India (P.) Ltd.v. Satish Kumar Gupta & Others, decided by the Supreme Court, dated 4th October, 2018. The Apex Court in the case had opined as under:
(a) Section 29A(c) is a see-through provision; therefore, great care must be taken to ensure that persons who are in-charge of corporate debtor for whom such resolution plan is made, do not come back in some other form to regain control of company without first paying off its debts.
(b) Any person who wishes to submit a resolution plan acting jointly or in concert with other persons who happens to either manage or control or be promoters of a corporate debtor which is classified as an NPA and whose debts have not been paid off for a period of at least one year before commencement of corporate insolvency resolution process, will be ineligible to submit a resolution plan; and in order to become eligible under section 29A(c), he or it must ‘pay off debt’ before submission of the resolution plan.
(c) The antecedent facts reasonably proximate to point of time of submitting resolution plan is to be seen and if at a reasonably proximate point of time before submission of resolution plan, affairs of persons referred to in section 29A are so arranged as to avoid paying off debts of non¬performing asset concerned, such persons must be held to be ineligible to submit a resolution plan.
(d) The term ‘connected person’ covers (i) a promoter or a person in management and control of resolution applicant, (ii) promoter or a person in management or control of business of corporate debtor during implementation of resolution plan and (iii) holding companies, subsidiary companies and associate companies or related parties of persons.
In view of the above, the Committee of Creditors and the Adjudicating Authority shall reject the Expression of Interest (EOI) filed by N Ltd.
![]()
Question 3.
National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) has initiated CIRP on application of one of Operational Creditors of DOP Ltd. A Resolution Professional was appointed after all processes as per the Law. Two viable Resolutions Plans (Plan A and Plan B) were received. Committee of Creditors comprises of Three Financial Creditors. As per Regulations of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Persons) Regulations, 2016, what is the approval status of Resolution Plans (Plan A and Plan B) for various instances of Voting outcome as mentioned below ?
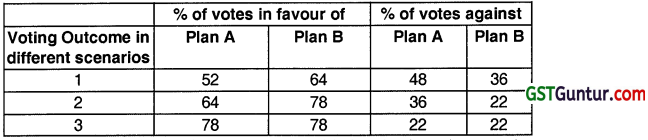
Also clarify the requisite voting percentage and tie-breakerformula as per the aforesaid Regulations. (Aug 2021, 6 marks)
Answer:
Status of Voting outcome:
Voting outcome 1:
No Plan is approved, as neither of the Plan received requisite votes. The committee shall vote again on Plan B, which received the higher votes, subject to the timelines under the code.
Voting outcome 2:
Plan B is approved, as it received higher votes, which is not less than requisite votes.
Voting outcome 3:
The committee shall approve either Plan A Or Plan B, as per the tie-reaker epression announced before voting.
As per the amended Provision of Regulation 39 of IBBI (CIRP) Regulationterequisite vote for approving the Resolution plan is 66% (Reduced from 75%). Tie-breaker formula is a method to break the equality in votes. This has to be decided prior to the meeting and should be communicated to all CoC Members.
Question 4.
What is a resolution plan?
Answer:
- A resolution plan is a proposal that aims to provide a resolution to the problem of the corporate debtor’s insolvency and its consequent inability to pay-off debts.
- It needs to be approved by the committee of creditors (COC), and comply with some mandatory requirements prescribed in the Code.
- After approval, the Resolution Professional needs to send the plan to the NCLT after certifying that the plan meets the requirements of the Code.
- If the NCLT is also satisfied that the plan meets the requirements, it will pass an order approving the plan.
Question 5.
Explain Section 31(1) of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code.
Answer:
- After approval by the NCLT, Section 31(1) makes the resolution plan binding on the corporate debtor and its employees, members, creditors, guarantors and other stakeholders involved in the resolution plan.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 provides a time-bound process for insolvency resolution for a corporate debtor.
- Thus, by avoiding liquidation, the inherent business value in the debtor is preserved.
Question 6.
Explain the process of Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP).
Answer:
- As soon as the Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) is triggered a moratorium is applicable on all proceedings against the Corporate Debtor till the expiry of 180 days (which is extendable to 270 days) or earlier till a resolution plan is approved by the adjudicating authority.
- The Resolution Professional (RP) appointed by the Committee of Creditors (CoC), in its first meeting is required to prepare an Information Memorandum and invite Resolution Applicants (RAs) to present a resolution plan for the revival of the Corporate Debtor.
- In case if a resolution plan is not received or is disapproved by the CoC or the Adjudicating Authority, the resolution process fails and a liquidation order is passed under the provision of Section 33 of the Code.
- RP will then invite prospective lenders, investors and ‘any other persons’ to submit Resolution Plans for the revival of the Corporate Debtor.
- In effect, any financial institution, private investors, competitors and even the ex-management of the Corporate Debtor can obtain the Information Memorandum from the RP and submit a plan.
- The mandatory requirement to be fulfilled by a plan is laid down under Section 30 of the code and included details of insolvency resolution process costs, liquidation value to operational creditors and dissenting financial creditors, its supervision and implementation schedule, and the management and control of the corporate debtor during its term.
- Earlier, the RP had no discretion in rejecting any plan received, now with the amended section 25(h) any plan by a person not meeting the specified criteria is liable to be rejected by the RP and will not be presented before the CoC.
![]()
Question 7.
Define “Resolution Applicant”.
Answer:
Section 5 (25) of the code has defined “resolution applicant” as a person, who individually or jointly with any other person, submits a resolution plan to the resolution professional pursuant to the invitation made under clause (h) of sub-section (2) of section 25.
Question 8.
What is the eligibility criteria of becoming Resolution Applicant?
Answer:
The newly added section 29A of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Act, 2018 declares certain persons ineligible to be a resolution applicant and prohibits such persons from submitting a resolution plan.
It provides that a person shall not be eligible to submit a resolution plan, if such person, or any other person acting jointly or in concert with such person
(a) is an undischarged insolvent;
(b) is a wilful defaulter in accordance with the guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India issued under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949;
(c) at the time of submission of the resolution plan has an account, or an account of a corporate debtor under the management or control of such person or of whom such person is a promoter, classified as non-performing asset in accordance with the guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India issued under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 or the guidelines of a financial sector regulator issued under any other law for the time being in force, and at least a period of one year has lapsed from the date of such classification till the date of commencement of the corporate insolvency resolution process of the corporate debtor.
(d) has been convicted for any offence punishable with imprisonment –
(i) for two years or more under any Act specified under the 12th
Schedule; or
(ii) for seven years or more under any law for the time being in force.
(e) is disqualified to act as a director under the Companies Act, 2013
(f) is prohibited by the Securities and Exchange Board of India from trading in securities or accessing the securities markets;
(g) has been a promoter or in the management or control of a corporate debtor in which a preferential transaction, undervalued transaction, extortionate credit transaction or fraudulent transaction has taken place and in respect of which an order has been made by the Adjudicating Authority under this Code.
(h) has executed a guarantee in favour of a creditor in respect of a corporate debtor against which an application for insolvency resolution made by such creditor has been admitted under this Code and such guarantee has been invoked by the creditor and remains unpaid in full or part;
(i) is subject to any disability, corresponding to clauses (a) to (h), under any law in a jurisdiction outside India;
(j) has a connected person not eligible under clauses (a) to (i).
Question 9.
Who can be referred to as a connected person?
Answer:
- any person who is the promoter or in the management or control of the resolution applicant; or
- any person who shall be the promoter or in management or control of the business of the corporate debtor during the implementation of the resolution plan; or
- the holding company, subsidiary company, associate company or related party of a person referred to in clauses (i) and (ii)
Question 10.
Explain the provisions of section 25 (2).
Answer:
- The resolution professional, under clause (h) of sub-section (2) of section 25, invites prospective resolution applicants, who fulfil such criteria as may be laid down by him with the approval of committee of creditors, having regard to the complexity and scale of operations of the business of the corporate debtor and such other conditions as may be specified by the Board, to submit a resolution plan or plans.
- An information memorandum containing all relevant information required by the resolution applicant to make the resolution plan for the corporate debtor is prepared by the resolution professional.
- Such information includes information relating to the financial position of the corporate debtor, all information related to disputes by or against the corporate debtor as well as any other matter pertaining to the corporate debtor as may be specified.
Section 29(2) provides that the resolution professional shall provide to the resolution applicant access to all relevant information in physical and electronic form, provided such resolution applicant undertakes
(a) to comply with provisions of law for the time being in force relating to confidentiality and insider trading;
(b) to protect any intellectual property of the corporate debtor it may have access to; and
(c) not to share relevant information with third parties unless clauses (a) and (b) above are complied with.
![]()
Question 11.
Explain the process of submission of the resolution plan by a resolution applicant.
Answer:
- Section 30 of the Code prescribes the manner in which a resolution plan may be submitted by a resolution applicant.
- The resolution professional is required to submit each resolution plan, which conforms to the criteria in section 30(2), to the committee of creditors who shall approve a resolution plan by a vote of not less than sixty-six percent of voting share of the financial creditors, after considering its feasibility and viability, and such other requirements as may be specified by the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India.
- Once the resolution plan is approved by the committee of creditors, it is then presented to the adjudicating authority for its approval.
- Section 30(1) of the Code provides that a resolution applicant may submit a resolution plan along with an affidavit stating that he is eligible under section 29A to the resolution professional prepared on the basis of the information memorandum plan.
Question 12.
Process of examination of resolution plan by resolution professional.
Answer:
Section 30(2) further provides that the resolution professional shall examine
each resolution plan received by him to confirm that each resolution plan:
(a) provides for the payment of insolvency resolution process costs in a manner specified by the Board in priority to the payment of other debts of the corporate debtor;
(b) provides for the payment of the debts of operational creditors in such manner as may be specified by the Board which shall not be less than the amount to be paid to the operational creditors in the event of a liquidation of the corporate debtor under section 53;
(c) provides for the management of the affairs of the Corporate debtor after approval of the resolution plan;
(d) The implementation and supervision of the resolution plan;
(e) does not contravene any of the provisions of the law for the time being in force.
(f) confirms to such other requirements as may be specified by the Board.
Question 13.
In what manner the Resolution plans are to be submitted to committee of creditors?
Answer:
- The resolution professional shall present to the committee of creditors for its approval such resolution plans which confirm the conditions referred to in sub section (2) of section 30. [Section 30(3)].
- Approval by committee of creditors – Section 30(4) of the Code provides that the committee of creditors may approve a resolution plan by a vote of not less than sixty-six percent of voting share of the financial creditors, after considering its feasibility and viability, and such other requirements as may be specified by the Board.
- Provided that the committee of creditors shall not approve a resolution plan, submitted before the commencement of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Ordinance, 2017 where the resolution applicant is ineligible under section 29A and may require the resolution professional to invite a fresh resolution plan where no other resolution plan is available with it.
- Provided further that where the resolution applicant referred to in the first proviso is ineligible under clause (c) of section 29A, the resolution applicant shall be allowed by the committee of creditors such period, not exceeding thirty days, to make payment of overdue amounts in accordance with the proviso to clause (c) of section 29A.
- Provided also that nothing in the second proviso shall be construed as extension of period for the purposes of the proviso to sub-section (3) of section 12, and the corporate insolvency resolution process shall be completed within the period specified in that subsection].
- Provided also that the eligibility criteria in section 29A as amended by the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Ordinance, 2018 shall apply to the resolution applicant who has not submitted resolution plan as on the date of commencement of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Ordinance, 2018.
- The resolution applicant may attend the meeting of the committee of creditors in which the resolution plan of the applicant is considered but shall not have a right to vote at the meeting of the committee of creditors unless such resolution applicant is also a financial creditor.
- After approval by the committee of creditors, the resolution professional shall submit the resolution plan to the Adjudicating Authority. [Section 30(6)].
![]()
Question 14.
How to obtain the approval of Resolution Plan by the Adjudicating Authority.
Answer:
- As per Section 31(1), if the Adjudicating Authority is satisfied that the resolution plan as approved by the committee of creditors under sub-section (4) of section 30 meets the requirements as referred to in sub-section (2) of section 30, it shall by order approve the resolution plan.
- Such resolution plan shall be binding on the corporate debtor and its employees, members, creditors, guarantors and other stakeholders involved in the resolution plan.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Second Amendment) Act, 2018 added to a proviso to sub-section (1) of section 31. The newly added proviso provides that the Adjudicating Authority, before passing an order for approval of resolution plan under sub-section (1) to section 31, shall satisfy that the resolution plan has provisions for its effective implementation.
- Where the Adjudicating Authority is satisfied that the resolution plan does not confirm to the requirements referred to in sub-section (1), it may, by an order, reject the resolution plan. [Section 31(2)].
- Section 31 (3) provides that if the adjudicating authority passes an order of approval under sub-section (1) of section 31,
(a) the moratorium order passed by the Adjudicating Authority under section 14 shall cease to have effect; and
(b) the resolution professional shall forward all records relating to the conduct of the corporate insolvency resolution process and the resolution plan to the Board to be recorded on its database.
Question 15.
Explain the grounds of filing an appeal against the order approving the resolution plan.
Answer:
According to section 61(3), an appeal against an order approving a resolution plan under section 31 may be filed on the following grounds:
- the approved resolution plan is in contravention of the provisions of any law for the time being in force,
- there has been material irregularity in exercise of the powers by the resolution professional during the corporate insolvency resolution period,
- the debts owed to operational creditors of the corporate debtor have not been provided for in the resolution plan in the manner specified by the Board,
- the insolvency resolution process costs have not been provided for repayment in priority to all other debts, or
- the resolution plan does not comply with any other criteria specified by the Board.