Financing Decisions-Capital Structure – CA Inter FM Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Financing Decisions-Capital Structure – CA Inter FM Notes
1. Capital Structure: Capital structure is the combination of capitals from different sources of finance.
2. Capital Structure Theories:
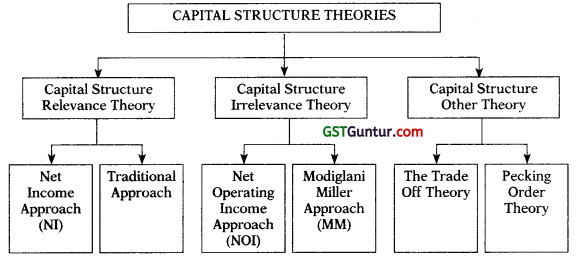
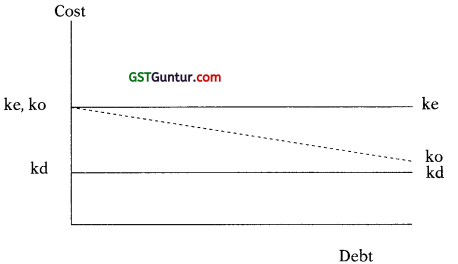
3. Net Income Approach (NI): According to this approach, capital structure decision is relevant to the value of the firm. An increase in financial leverage (Debt Proportion) will lead to decline in the weighted average cost of capital (WACC), while the value of the firm as well as market price of ordinary share will increase.
As per NI Approach:
- Kd and Ke will remain constant.
- K0 will decrease with the help of use of Debt.
- MV of Equity and Firm will increase with the help of use of Debt.
Formulae:
Value of Share (S) = \(\frac{(\mathrm{EBIT}-\mathrm{I})(1-\mathrm{t})}{\mathrm{K}_e}\) Or = V – D
Value of Debt (D) = Face Value of Debt
Value of Firm (V) = S + D Or = \(\frac{\mathrm{EBIT}(1-\mathrm{t})}{\mathrm{K}_0}\)
Cost of Capital (Ko) = \(\frac{\mathrm{EBIT}(1-\mathrm{t})}{\mathrm{K}_0}\) × 100 Or = KoWo + KdWd
Cost of Equity (Ke) = \(\frac{\text { EBIT }(1-t)}{V}\) × 100
Note: Ke and Ko of unlevered firm are same.
![]()
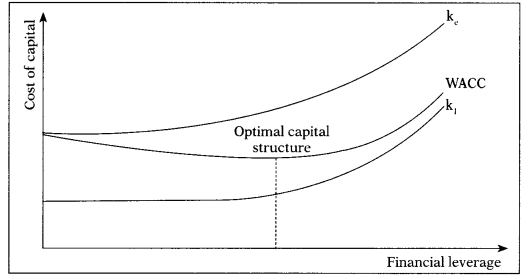
4. Traditional Approach: This approach favours that as a result of financial leverage up to some point, cost of capital comes down and value of firm increases. However, beyond that point, reverse trends emerge.
As per Traditional Approach:
- Kd, Ke, Ko and MV of Equity and MV of Firm are variable
- Company has to select capital structure with lowest Ko or highest MV of Firm
5. Net Operating Income Approach (NOI): According to this approach, capital structure decisions of the firm are irrelevant. Any change in the leverage will not lead to any change in the total value of the firm and the market price of shares, as the overall cost of capital is independent of the degree of leverage.
As per NOI Approach:
- K<sub>d</sub>, K<sub>0</sub> and MV of Firm will remain constant in case of without tax structure.
- K<sub>d</sub> will remain constant in case of with tax structure, with the increase in Debt, MV of firm will increase and K<sub>0</sub> will decrease
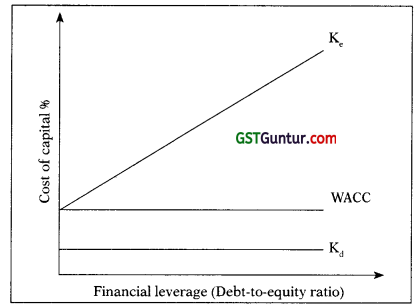
Value of Firms as per NOl Approach:
Step 1 : Calculate Value of Unlevered Firm:
Value of Unlevered Firm (V<sub>0</sub>) = \(\frac{\mathrm{EBIT}(1-\mathrm{t})}{\mathrm{K}_{\circ}}\)
Step 2: Calculate Value of Levered Firm:
Value of Levered Firm (VL) = VU + DT
![]()
6. Modiglani-Miller Approach (MM): The NOI approach is definitional or conceptual and lacks behavioral significance. However, Modigliani-Miller approach provides behavioural justification for constant overall cost of capital and therefore, total value of the firm.
Assumptions of MM Approach
- Capital markets are perfect
- All information is freely available
- There are no transaction costs
- All investors are rational
- Firms can be grouped into ‘Equivalent risk classes’
- Non-existence of corporate taxes
Note: Solution of practical problems are same under NOI and MM Approaches
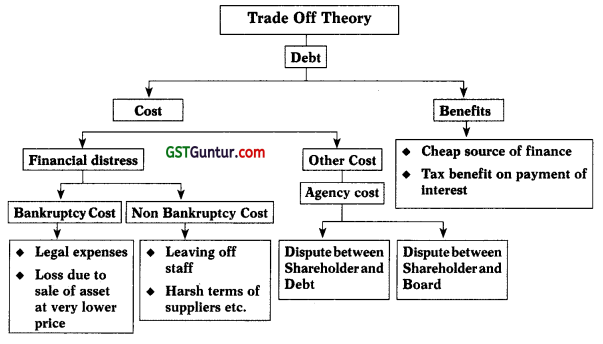
7. The Trade Off Theory:
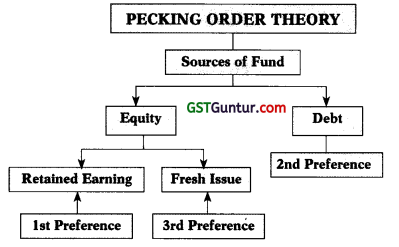
8. Pecking Order Theory:
9. Arbitrage Process: Capital structure arbitrage refers to a strategy used by companies and individual where they take advantage of the existing market mispricing across all securities to make profits.
In this strategy, there is buying share of undervalued firms and sell shares of overvalued firm. The main objective is to make use of the pricing inefficiency to make a profit. There is anticipation that the pricing difference, will at some point cancel out or reach at equilibrium.
![]()
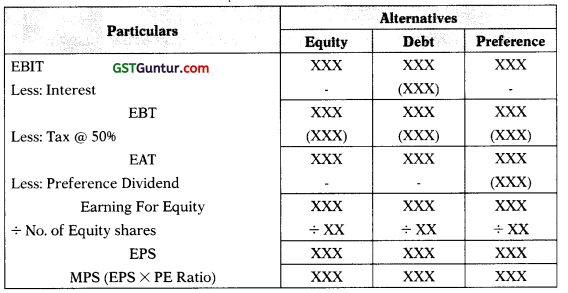
10. Proforma Statement Showing EBIT, EPS & MPS:
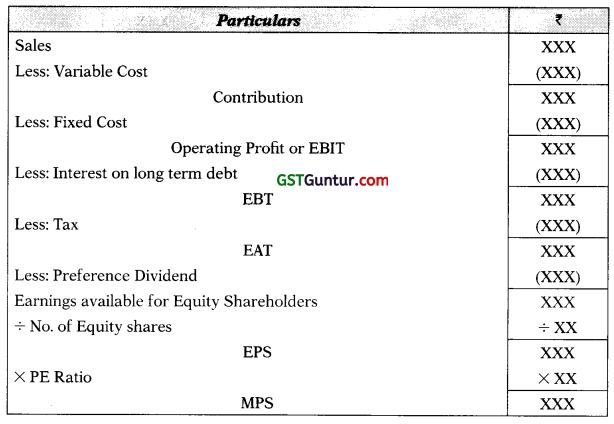
Note:
- MPS = EPS × PE Ratio
- Number of Equity Shares = Existing Shares + New Shares
- New Equity Shares = \(\frac{\text { Additional Funds Raised through Equity }}{\text { Net Proceeds from One Equity Share }}\)
- Net Proceeds from Share = Issue Price – Issue Expenses
Note: If nothing is specified in the question, MPS is assumed to be Issue Price.
![]()
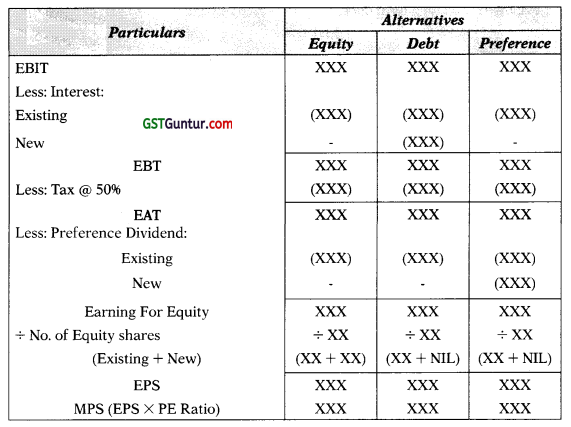
11. Selection of plan on the basis of EPS or MPS (New company):
Statement of EPS & MPS
12. Selection of plan on the basis of EPS or MPS (Existing company):
Statement of EPS & MPS
![]()
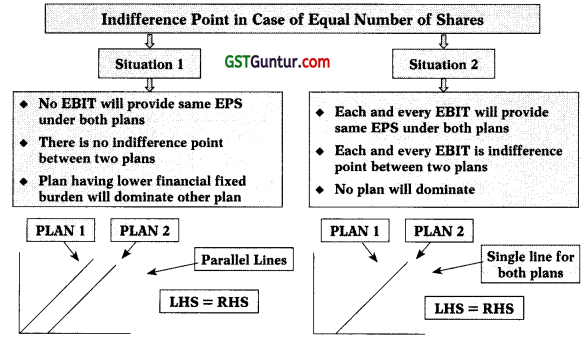
13. Indifference Point: Indifference point refers the level of EBIT at which EPS under two different options are same.
EPS under option 1 = EPS under option 2
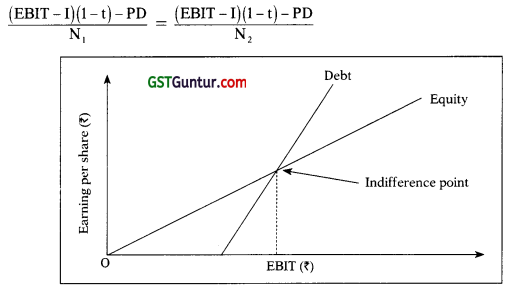
Course of Action
| Situations | Action |
| If expected EBIT < Indifference Point | Select option having lower Fixed Financial Burden |
| If expected EBIT = Indifference Point | Select any option |
| If expected EBIT > Indifference Point | Select option having higher Fixed Financial Burden |
14. FinanclaiBreakEven Point: It is the level of EBIT at which EPS will be zero.
EBIT = Interest + \(\frac{\text { Preference Dividend }}{(1-t)}\)
![]()
15. Indifference Point in case of Equal Number of Share: