Chapter 3 Documentation & Maintenance of Records – Secretarial Audit Compliance Management and Due Diligence ICSI Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Documentation & Maintenance of Records – Secretarial Audit, Compliance Management and Due Diligence Study Material
Question 1.
Differentiate Physical Data Room and Virtual Data Room. (June 2022, 5 marks)
Question 2.
What are the disadvantages of Electronic records ? (June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
The followings are the disadvantages of Electronic records:
- Software risk: Storing records in an electronic document management system, have a risk that since the system being no longer supported by the software company the company will cease to exist.
- Format risk: When storing the records as an electronic record, a person run the risk of not being able to read them at some point.
- Media compatibility: Maintaining images on media which the person can access at a iater date is a big challenge. For example, the documents are also stored in floppy disks. But the floppy disk drive is no longer available.
- Reliability: It’s a good idea to have most vital documents imaged, but keeping a paper copy assures that the person have access to them anytime.
- Portability: The portability is an advantage for digital images. It’s very easy to misplace or accidentally delete large amounts of data or to duplicated and transported outside of any organization.
- Conversion expense: It’s very expensive to convert paper documents to digital images. The amount of labour it takes to prepare documents and analyze them so that they can be identified and indexed correctly is very large.
![]()
Question 3.
Privacy of records and its control is the most important function for the Secretarial Department of an organization. Records of Contracts and Commercial Documents and Trade Secretes are to be kept confidentially. Describe the alertness to be observed with respect to keeping of said records. (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
The alertness to be observed with respect to keeping records of Contracts & Commercial Documents and Trade Secretes is described as under:
1. In case of the business contracts, every detail of the arrangement should
be treated with utmost confidentiality for both organization itself and also for the benefit of third party. If the contract has a confidentiality agreement, it could be breach of terms if an unauthorised person gets his hands on the physical copy of the contract. The contracts are full of commercially sensitive information such as the nature of the arrangement, the value of the services offered/received in the agreement, the names of the main contracting parties, etc.
2. The business should avoid sharing contracts unless strictly required, and limit physical copies. Business may consider using digital signatures for signing contracts in order to reduce unnecessary print-outs thereby ensuring confidentiality. While these are some of the most important documents required to be stored securely, the easiest and safest way to reduce the risk of a data breach is to implement a secure document retention policy specific to needs of the organisation.
3. The confidential business information such as “proprietary information” or “trade secrets” shall not be generally known to the public and would not ordinarily be available to competitors. Common examples of “trade secrets” include manufacturing processes and methods, business plans, financial data, budgets and forecasts, computer programs and data compilation, client/customer lists, ingredient formulas and recipes, membership or employee lists, supplier lists, etc. “Trade secrets” do not include information that a company voluntarily gives to potential customers, posts on its website or otherwise freely provides to others outside the company. If such confidential information is available in the wrong hands, it can be misused to commit illegal activity (e.g., fraud or discrimination), which can in turn result in costly lawsuits for the Company. The disclosure of sensitive employee and management information can lead to a loss of employee trust, confidence and loyalty. This will almost always result in a loss of productivity.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Good Documentation? Give some examples of Good Documentation Practices as well as Poor Documentation Practices. (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
The good documentation promotes good corporate governance practices and compliance level of the company and also improves communication and dissemination of information between and across various stakeholders.
The following are the some of the examples of good documentations practices:
- Records should be completed at time of activity or when any action is taken;
- Superseded documents should be retained for a specific period of time;
- Concise, legible, accurate and traceable;
- Picture is worth a thousand words;
- Clear examples;
- Don’t assume knowledge
The following are the some of the examples of poor documentations practices:
- Document with errors, correction, not signed/dated, and didn’t include a reason for the correction; ‘
- Write-overs, multiple line-through and use of “White-out” or other masking device;
- Recording of events is not in sequence & tabled;
- Standards operating procedures as adopted by the professional is not authorised;
- The delegation of work is not recorded / documented;
- Out-of-specification procedure not detailed enough;
- Flow chart and /or check list not available.
![]()
Question 5.
The Board of Directors of Bee & Bee Ltd. was of the view that as the company was diversifying its operations, it should evaluate digitizing the books of accounts and other records. The Board sought views from the Company Secretary about the same and asked him to appraise them about the Document Management System including good documentation practices. Advise the Board as the Company Secretary. (Aug 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
Document management refers to the process of managing and tracking of documents and records through an electronic or physical source of documents.
In an electronic repository, Document Management Systems (DMS) works by using a computer system and software to store, manage and track electronic documents and electronic images of paper-based information captured through the use of a scanner.
The term document management system can be defined as the software that controls and organizes documents of an organization. It incorporates document and content capture, work flow, document repositories.and output systems, and information retrieval systems. Also, the processes used to track, store and control documents.
Advantages of DMS are as follows:
- Tracking on check-in/check-out by various officers
- Locking and unlocking of Document
- Simultaneous editing
- Document Version Control
- Roll-back options / Retrieve option
- Ease in Audit trail
- Annotation and Stamps
Good Documentation Practices:
The term documentation includes any and all forms of documentation recorded by a person in professional capacity in relation to his professional duties and includes written and electronic records. Good documentation promotes good corporate governance practices and can help in improving the compliance level of the company and also the communication and dissemination of information between and across various stakeholders.
The following are the some of the examples of good documentations practices:
- Records should be completed at time of activity or when any action is taken;
- Superseded documents should be retained for a specific period of time;
- Concise, legible, accurate and traceable;
- Picture is worth a thousand words;
- Clear examples;
- Don’t assume knowledge.
Legal Compliance: In case the documentation process involves maintenance of documents and records in electronic format then such documentation system shall additionally comply with the requirements mentioned in Sec 120 of the Companies Act, 2013 and applicable Rules issued thereunder. The System shall also be in compliance with the Information Technology Act, 2000.
Question 6.
In naming of a document, briefly explain the concept of Descriptive file and Non- Descriptive file. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
The Descriptive file names are useful for small, well-defined projects with existing identification schemes that link the digital object to the source material. However, inconsistent application of terms or typos will increase to indexing and sorting errors.
Non-descriptive file names are usually system-generated sequential numerical string or the system based, such as a digital ID number, combination of Date and time, name of original file and are often linked to meta data stored elsewhere. Non-descriptive file names are often created for large scale digitization projects and may employ a digital ID number and numerical sequences to indicate batch or parent-child relationships. The advantage of non-descriptive names is that there is less chance of repeated or non unique file names within a data structure.
![]()
Question 7.
The Chairman of ABC Limited, a listed company, seeks your opinion for framing a policy for preservation of documents to avoid stringent penal provisions for non-compliance of the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 and the Rules made there under. Write a note to the Chairman stating classification of documents under specific period of preservation with specific reference to the Securities and Exchange Board t of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015. (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
To,
The Chairman
ABC Limited
Re: Classification of documents for period of preservation under SEBI (LODR) Regulations, 2015
Dear Sir,
The legal requirements of preservation of documents in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 and Regulation 9 of the SEBI (LODR) Regulations, 2015 are as under:
(a) Documents whose preservation shall be permanent in nature:
- Property records including purchase and sale deeds, licences, copyrights, patents & trademarks
- Corporate Records including Certificate of Incorporation, Common Seal, Minutes of Board, Committee and Shareholders’ Meetings, Register Of Members and other Statutory Records
- Personal files of all live employees
- Any other record as may be decided by the Chief Executive Officer of the Company from time to time.
(b) Documents whose preservation period shall not be less than eight years after completion of the relevant transactions:
- Books of Account, Bank Statements and vouchers
- Filings with Stock Exchanges, Registrar of Companies and other statutory authorities.
- Payroll Records, Employee deduction authorisations, attendance records, employee medical records, leave records, Pension and retiral related Records, etc.
- Corporate Social Responsibility Records
- Sponsorship Projects Records
- Correspondence and Internal Memoranda
- Any other record as may be decided by the Chief Executive Officer of the Company from time to time.
(c) Documents whose preservation shall be for a minimum period of three years after completion of the event:
- Tender Documents
- Lease Deeds and Contracts
- Legal files
- Insurance Records including policies and claims
- All e-mail correspondence, internal & external
- Documents under Secretarial Standards
- Proof of sending Notice of the meetings of the Board / Committee and General meetings and its delivery
- Proof of sending Agenda and Notes on Agenda and their delivery
- Proof of sending and delivery of the draft of the Resolution
- Proof of sending draft Minutes and its delivery
- Proof of sending signed Minutes and its delivery
- Any other record as may be decided by the Chief Executive Officer of the Company from time to time.
![]()
Question 8.
‘R’ was appointed as Managing Director of P Mart Limited recently. During the meeting of the Board, he desires that all agenda files should be sent by email encrypted by password. He also desires that to protect the file from hacking, there should be some special name to the file. As a company secretary, kindly highlight any eight best practices for file naming. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
The following are best practices for file naming. The File names should:
- Limit the character length to no more than 25-35 characters;
- Be unique and consistently structured;
- Be persistent and not tied to anything that changes over time or location;
- Use leading Os to facilitate sorting in numerical order if following a numeric scheme “001,002, 010,011 … 100,101, etc.” instead of “1,2, …10,11 … 100,101, etc.”;
- Contain a file format extension;
- Use a period followed by a file extension (for example, .tif, .jpg, .gif, .pdf, .wav, .mpg);
- Use lowercase letters. However, when a name has more than one word, start each word with an uppercase letter for example, “File_Name_Convention_001 .doc”;
- Use numbers and/or letters but not characters such as symbols or spaces that could cause complications across operating platforms;
- Use hyphens or underscores instead of spaces;
- Use standard date notation (YYYY-MM-DD or YYYYMMDD);
- Avoid blank spaces anywhere within the character string; and
- Not use an overly complex or lengthy naming scheme that is susceptible to human error during manual input, such as “file name convention joes final version edited final, doc”.
The strength of a folder and file naming convention is dependent on the proposed naming structure and the quality and quantity of the data elements chosen to build it. It should be of no surprise that for any business activity there is always an ideal naming structure. However, any structured naming convention that attempts to be all encompassing may result in overkill and unwieldiness.
Question 9.
Write a short note on The Data (Privacy and Protection) Bill, 2017
Answer:
The Data (Privacy And Protection) Bill, 2017 is an proposed law to avoid situations like a country-wide hack like in the case of Estonia in 2007 and the recent global ransom ware attack ‘WannaCry’ in 2017. Globally, data is being considered the new oil and in the coming years, our international trade and economic relations will depend on the health and bargaining power of the data economy.
The bill intends to provide rights of persons vis-a-vis their own information, as well as procedures for data collection, data processing, reasonable and targeted surveillance, and means of redress in case of breaches and violations.
The bill provides that the collection and processing of data is important, there is an overwhelming need to secure personal data and ensure better security by creating a statutory obligation to safeguard data and individuals. To that effect, this Bill seeks to establish Inter alia, a balance between rights , of individuals and legitimate intervention by the State.
The bill seeks to codify and safeguard the right to privacy for all juristic persons in the digital age, balanced with the need for data protection in the interests of national security.
Question 10.
Write a short note on Electronic Repository of Documents.
Answer:
Document management refer the process of managing and tracking of the ; documents and records through an electronic or physical source of documents.
In an electronic repository, Document Management Systems (DMS) works by using a computer system and software to store, manage and track electronic documents and electronic images of paper based information captured through the use of a document scanner.
The term document management system can be defined as the software that controls and organizes documents of an organization. It incorporates document and content capture, work flow, document repositories and output systems, and information retrieval systems. Also, the processes used to track, store and control documents.
![]()
Question 11.
Define the difference between virtual and physical data room.
Answer:
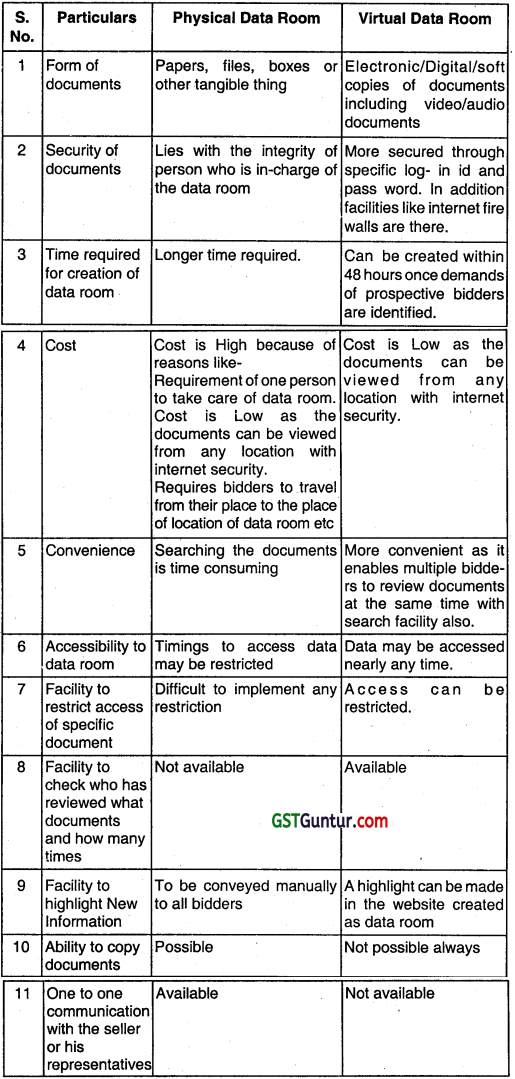
Question 12.
The Justice AP Shah Committee report outlined nine principles that were central to and defined the Right to Privacy. Explain
Answer:
- Principle of Notice
- Principle of Choice and Consent
- Principle of Collection Limitation
- Principle of Access and Correction
- Principle of Disclosure of Information
- Principle of Security
- Principle of Openness
- Principle of Accountability.
Question 13.
What are the suggestive steps for protecting confidential information?
Answer:
For every business/organization it is important to have a written confidentiality describing both the type of information considered confidential and the procedures employees must follow for protecting confidential information and dealing with the confidential information’s. However the company may adopt the following procedures for protecting confidential information:
- All confidential documents should be stored in locked file cabinets or rooms accessible only to those who are authorized.
- All electronic confidential information should be protected via firewalls, encryption and passwords.
- Employees should clear their desks of any confidential information before going home at the end of the day.
- Employees should refrain from leaving confidential information visible on their computer monitors when they leave their work stations.
- All confidential information, whether contained on written documents or electronically, should be marked as “confidential.”
- All confidential information should be disposed of properly (e.g., employees should not print out a confidential document and then throw it away without shredding it first.)
- Employees should refrain from discussing confidential information in public places.
- Employees should avoid using e-mail to transmit certain sensitive or controversial information.
- Limit the acquisition of confidential client data (e.g., social security numbers, bank accounts, or driver’s license numbers) unless it is integral to the business transaction and restrict access on a “need-to-know” basis.
- Before disposing of an old computer, use software programs to wipe out the data contained on the computer or have the hard drive destroyed.
Documentation & Maintenance of Records Notes
The Guiding Principles for Good Documentation are:
- Clear
- Concise
- Complete
- Contemporary
- Consecutive
- Correct
- Comprehensive
- Collaborative
- Client Centric
- Confidential
![]()
Examples of Poor Documentation Practices
- Document with errors, correction, not signed/dated, and didn’t include a reason for the correction;
- Write-overs, multiple line-through and use of “White-out” or other masking device;
- Recording of events is not in sequence and tabled;
- Standards operating procedures as adopted by the professional is not authorised;
- The delegation of work is not recorded/documented;
- Out-of-specification procedure not detailed enough; flow chart and /or check list not available.
Examples of Good Documentation Practices:
- Records should be completed at time of activity or when any action is taken;
- Superseded documents should be retained for a specific period of time;
- Concise, legible, accurate and traceable;
- Picture is worth a thousand words;
- Clear examples;
- Don’t assume knowledge.
Advantages of DMS:
- Tracking on Check-in/check-out by various officers
- Locking and unlocking of Document
- Simultaneous editing
- Document Version Control
- Roll-back options / Retrieve option
- Ease in Audit trail
- Annotation and Stamps
Advantages of the Electronic records:
- Cost Effective
- Ease of use
- Labor savings
- Search ability
- Portability
- Version tracking
Disadvantage of Electronic records:
- Software risk
- Format risk
- Media compatibility
- Reliability
- Portability
- Conversion expense
Physical repository:
The term Physical repository refers to a central place where data is stored and maintained. A repository can be a place where multiple databases or files are located for distribution over a network, or a repository can be a location that is directly accessible to the user without having to travel across a network.