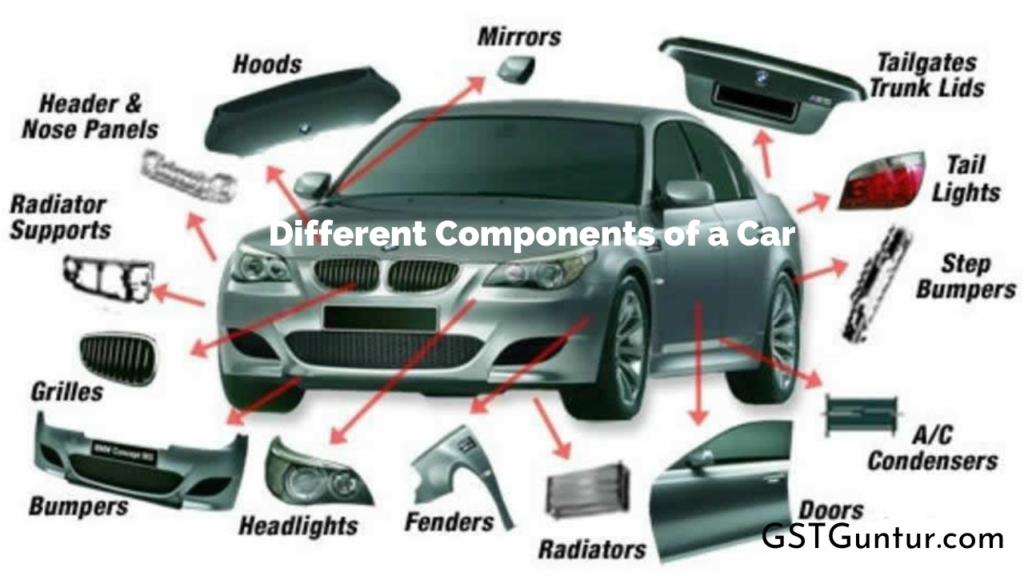
A Detailed Look at the Different Components of a Car: Before purchasing a vehicle, the prospective buyer should be mindful of the other car areas and be familiar with them.
Most Critical Components of a Car
A few of the most critical components are specified below:
A Car’s Body Type
There are countless alternatives for size, style and shape in today’s Indian car market. Carmakers in India are exploring and designing new models to suit a wide range of different needs of Indian customers. Referenced underneath are a couple of the body types.
Sedan
The car’s framework provides four doors, three compartments, and three columns (column A, column B, and column C).
The car has three compartments. The compartments individually are the engine compartment, the passenger compartment, and the baggage compartment, distinctly distinguished from each other.
The cargo compartment is discrete from the passenger compartment, and the boot lid opens upwards.
This prototype has a seating capacity of 4 + 1.
The 2-door configuration can likewise be seen in some sedans. The Audi A5, for example, has two doors.
Any sedan-shaped sports car, namely the Mercedes-Benz CLS-Class, can indeed be marketed as a roadster by the seller.
Hatchback
Hatchbacks are broadly accessible in two fundamental configurations:
- Three doors (2 passengers + 1 luggage) or
- Five doors (4 passengers + 1 luggage).
A classic sedan has three compartments (engine, passenger, and luggage), while a hatchback car has two compartments (engine, passenger, and baggage).
All in all, the traveller and baggage compartment of the Hatchback vehicles are consolidated, and the passengers can get the rear compartment from the back seat.
The fundamental contrast between a hatchback and a sedan is that the passenger cabin (rear seat) and the baggage compartment are not distinctly segregated. Furthermore, the vehicle’s back is perpendicularly lowered (down to the bumper).
The hatchback design is a scaled-down variation of the sedan design. For instance, the Corolla hatchback version is advertised as a sedan.
Station Wagon
The station wagon cars are vast and spacious, with three or five doors and a piece of massive luggage carrying extra room. For congested households, it is the ideal vehicle plan for regular travel and long excursions with many belongings.
The sedan framework style is a higher version of the model of the station wagon type. The motor, equipment, and mid-front body arrangement are similar to the sedan, even though C-D columns and compartments in the rear have been supplanted.
SUV
It refers to vehicles outfitted with sports performance features. SUVs can accommodate both on-street and rough terrain vehicles.
Its trademark distinguishing feature is the four-wheel drive. The four-wheel-drive system can be set to be permanent or discretionary.
Being high provides a sense of safety while also providing a decent view and fast driving in challenging road conditions. Big luggage and interior space offer luxury and flexibility with a sense of solace.
Crossover
It’s a blend of an SUV and a hatchback. Crossover trucks, which are the smallest SUVs, are likewise called Crossover SUVs.
It offers ease of driving in city traffic, user-friendly parking, a huge luggage capacity, and compact skeletal anatomy.
It pretty much exclusively comes with two compartments: the engine compartment and the passenger + baggage compartment. The traveller and the baggage compartment are consolidated.
The baggage can be made available from the rear seat of this type of care and the rear seats to the traveller and baggage compartment.
Car Segments
Cars in A Segment (MINI CLASS VEHICLES)
The term “mini-vehicle” refers to a vehicle that is much less than 370 cm in length. The vehicle’s body is slim, and the distance between the driver’s head and the knee is limited.
Extended tours are not strongly advised. They are compact and light in weight. As a consequence, their ability to respond to troublesome situations is often minimal and exceptionally low.
Cars in The B Segment (SMALL CLASS VEHICLES)
The B section is similar to the A-segment but vastly more significant in size. The dimensions vary from 370 cm to 400 cm.
To compare, they are technically better than section A. These comprise of more strong body systems. The bodywork choices, like the A-segment, are extensive.
There are numerous alternatives like the hatchback, sedan, station wagon, coupe, cabriolet, roadster, SUV, and CUV and MVP, which are essentially available.
Cars in the C segment (SUB-MEDIUM CLASS VEHICLES)
It is one of the most manufactured and delivered segments. Since it is classified as compact or lower middle class, we broadly classify it as a family vehicle. They are ideal for both family and independent use on account of their size.
Vehicle efficiency is excellent, and they can comfortably travel long distances. Since they get high marketing projections, competition is fierce, and it is relatively easy to find a low-cost vehicle model in this category.
Cars in the D segment (TOP-MIDDLE CLASS VEHICLES)
They are often attributed to extended family cars. They contrast from the C section because their proportions are more incredible, and their efficiency is significantly higher.
This section, also known as the upper-middle class, has large cabins, comfortable cabins, and robust motor and power efficiency.
Cars in the E Segment (UPPER-CLASS VEHICLES)
It belongs to the top-tier vehicle market. The vehicles in this segment are otherwise referred to as administrator vehicles. They are more efficient in terms of comfort and performance, and their fuel consumption is much lower than just about every other class.
In the meantime, pricing patterns are still very high contrasted to other segments.
Cars in the F Segment (LUXURY CLASS VEHICLES)
F segment cars, also widely recognized as luxurious segment vehicles, are characterized by their outstanding technical features and facilities and their efficiency details and physical highlights.
Cars in the G Segment (SUPER LUXURY VEHICLES)
Of necessity, car admiration is not constrained to utilitarian vehicles. A sports car, such as a bird, has a distinct niche in the market both inside and outside the city.
The G segment comprises vehicle types that are performance-dependent.
They are made available in coupe, roadster, sedan, and grand tourer body styles.
SUV Cars in the J SEGMENT
The J-Segment cars, usually widely recognized as terrain sports cars, integrate the speed of a sports car with the power of a rough terrain vehicle. SUV is the acronym for Sports Utility Vehicle.
These prototypes, which have a high fuel consumption, are more sustainable in the last century, and the developers are prompted to two towing systems from four towers.
J-segment vehicles come in many different frame configurations, including small SUVs, mid-SUVs, big SUVs, and luxury SUVs.
MPV Cars in the M segment
As discussed earlier, M-segment cars, also known as multi-purpose vehicles, happened to come together in a variety of different segments. MPV is an acronym that stands for Multi-Purpose Vehicles.
The Ford brand was the first to produce M segment cars, which sold well throughout the globe.
Other Specifications of a Car
Engine
The engine is the backbone of the car. It is a machine that transforms electricity into momentum or develops the energy that forces the vehicle forward. Engines are generally categorized into two types:
petrol (which runs on gasoline)
Diesel (which runs on diesel)
The echo of a massive engine sounds like vroom vroom. The aggregate volume of all the cylinders in a car’s engine is communicated in cubic centimetres (cc) or litres more often.
Like that of a reference, a 1598cc engine would be referred to as a 1.6-litre unit. Generally, For the most part, the higher the power of an engine, the greater its output.
Distinctions Between A Petrol Engine And A Diesel Engine
There are some distinctions between a petrol engine and a diesel engine:
- Petrol engines burn through too much fuel than diesel engines.
- Petrol engines also provide torque but supply more power than diesel engines.
- Since diesel engines have broader flywheels, they gauge more than petrol cars.
- Petrol engines need no or significantly fewer maintenance expenses.
- Diesel engines are somewhat tougher to sustain, not because of the cost, but rather because a skilled mechanic is not always accessible worldwide. Since diesel engines have a higher compression ratio than gasoline engines, running them is more problematic.
- Because of their high thermal efficiency, diesel engines have much fewer challenges with the issue caused due to overheating.
- A diesel engine’s thermal efficiency is about 40%. Owing to their poor thermal performance, petrol engines are more highly susceptible to getting too hot. Thermal performance in gasoline engines is only about 25%.
Petrol engines are more often than not used in lighter vehicles such as motorcycles, scooters, and automobiles. In contrast, diesel engines are used in much heavier equipment such as tractors, trucks, and buses.
Displacement
The estimation of the volume of the engine’s cylinders or “chambers” is measured in litres or cubic centimetres and is termed as displacement. So, whenever you see “x cc,” it indicates that the amount of the total volume of the cylinders is x cubic centimetres. “Y-litre” on a spec sheet is just yet another way of doing the same thing, but less pretty much precisely, which demonstrates that the actual capacity of the cylinders is Y litres.
Transmissions of 5 or 6 speeds
Similarly to how you can choose various gears on a bicycle with differing inclines and velocity, you would have to select gears centred on the vehicle’s speed or the traffic conditions or the street circumstances. A 5-speed transmission has five gears or speeds from which to choose when driving or riding. Manual transmission allows you to adjust speed individually, while an automatic gearbox doesn’t allow you to do it manually, as the name suggests.
Power of a car- expressed through horsepower
The unit of power, i.e., horsepower, is the most straightforward key to understanding this. Colloquially, one horsepower is calculated as the amount of power one-horse provides when pulling.
So, if your car has 75 horsepower, it will drive the equivalent of 75 thoroughbred horses. To be a little more concise, the amount of force used only to elevate 550 pounds one foot in one second.
Torque – For example, 200 Nm
Torque is the motor’s ability to do work or a force that appears to produce wheel rotation in the case of an automobile or bike.
Torque is assessed in Newton Metres (Nm) and is substantially larger in diesel engines than in equivalent spaced petrol engines. Vehicles with higher torque usually allow for fewer gear shifts if properly configured efficiently used.
The capacity of the fuel tank – for illustration, 35 litres
The fuel tank capacity of any vehicle is the estimated amount of fuel it can incorporate, which generally contains the reserve volume and is represented in litres. One can approximate the operational range of the vehicle by multiplying its capability by its mileage.
The size of the wheelbase
The difference between a vehicle’s front and rear axles (the poles interfacing the focuses of the wheels) is known as its wheelbase. In particular, the longer the wheelbase, the bigger the cabin will be, resulting in more interior space. In almost all of the cases, the wheelbase is assessed in millimetres.
Width of the tread/track
The distance evaluated width-of-the-vehicle astute from Tyre centre to Tyre centre is identified as tread or road width. Primarily, the longer the track diameter, the more secure and survivable a car is around bent. The tread is accurately estimated in millimetres as well.
Airbags are a safety feature.
In case of occurrence of a collision or a dangerous crash, quickly inflatable padding is constructed to safeguard the driver or passenger(s).
After quite a while of being behind the remainder of the world in such a manner, even cars in lower-priced segments are now starting to have airbags (at least for the driver) in the country.
Brakes
A car’s brakes assist it with easing back down and stop. As a consequence, it is the most critical safety device and main wellbeing highlight on a vehicle. When you click on the brake pedal, brake fluid is transferred to the braking clamps.
Keep in mind that the brake mechanism relies on the driver constantly engaging the peddle to bring the vehicle to a complete halt.
