Cost of Capital – CA Inter FM Notes is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Cost of Capital – CA Inter FM Notes
1. Cost of Capital: Cost of capital is the return expected by the providers of capital (i.e. shareholders, lenders and the debt-holders) to the business as a compensation for their contribution to the total capital. Cost of capital is also known as ‘cut-off’ rate, ‘hurdle rate’, ‘minimum rate of return’ etc.
2. Components of Cost of Capital:
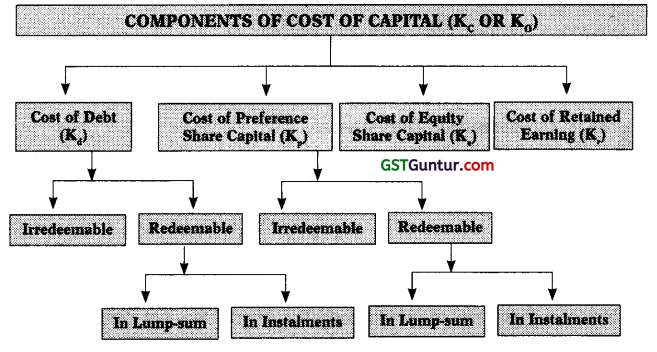
3. Cost of Debt (Kd):
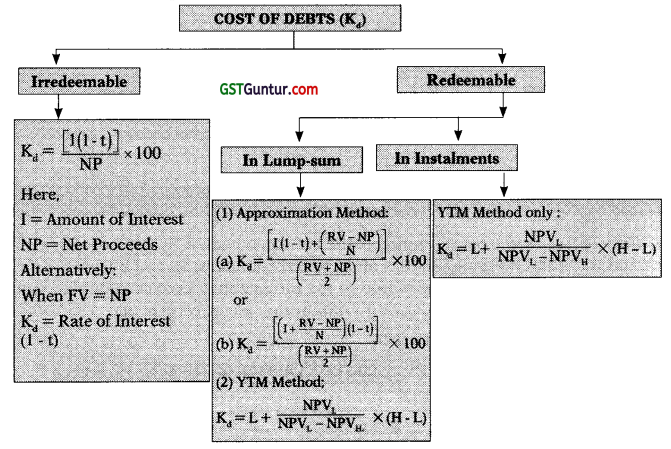
(a) Cost of Irredeemable Debenture:
Kd = \(\frac{\mathrm{I}(1-\mathrm{t})}{\mathrm{NP}}\) × 100
Where,
I = Amount of Interest
t = Tax rate
NP = Net Proceeds of Debenture or Current Market Price
Note: If Face Value of Debenture equal to Net Proceeds then
Kd = Rate of Interest (1 – t)
![]()
(b) Cost of Redeemable Debenture (in Lump sum):
Approximation Method:
Kd = \(\frac{\mathrm{I}(1-\mathrm{t})+\left(\frac{\mathrm{RV}-\mathrm{NP}}{\mathrm{n}}\right)}{\frac{\mathrm{RV}+\mathrm{NP}}{2}}\) × 100 0r \(\frac{\left(I+\frac{R V-N P}{n}\right)(1-t)}{\frac{R V+N P}{2}}\) × 100
Where, I = Amount of Interest.
RV = Redemption value of Debenture
NP = Net Proceeds of Debenture or Current Market Price
n = Remaining Life of Debenture
Present Value Method (PV)/Yield to Maturity Method (YTM):
Kd = IRR = L + \(\frac{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}-\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{H}}}\) × (H – L)
(c) Cost of Redeemable Debenture (in Instalments):
Kd = IRR = L + \(\frac{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}-\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{H}}}\) × (H – L)
(d) Cost of Zero Coupon Bonds (ZCB):
Kd = \(\sqrt[n]{\frac{\mathrm{RV}}{\mathrm{IP}}}\) – 1
Where, I = Amount of Interest.
RV = Redemption value of Debenture
IP – Issue Price of Bond
n = Life of Bond
Note:
- In case of convertible debenture use convertible value in place of redemption value of debenture.
- If nothing is specified, issue price, redemption value etc. assumed to be equal to face value.
- If nothing is specified, floatation cost assumed to be linked with “face value or issue price whichever is higher”.
![]()
4. Cost of Preference Share Capital (Kp):
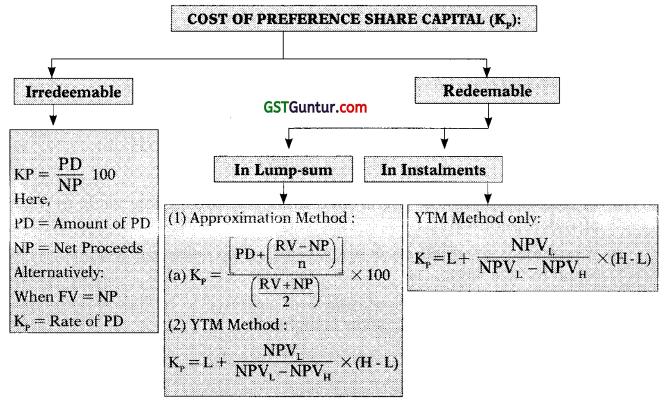
(a) Cost of Irredeemable Preference Share:
Kp = \(\quad \frac{\mathrm{PD}}{\mathrm{NP}}\) × 100
Where,
PD = Amount of Preference Dividend
NP = Net Proceeds of Preference Share or Current Market Price of Preference Share
Note: If Face Value of Preference Share equal to Net Proceeds then
Kp = Rate of Preference Dividend
(b) Cost of Redeemable Preference Share (in Lump sum):
Approximation Method:
Kp = \(\frac{\mathrm{PD}+\left(\frac{\mathrm{RV}-\mathrm{NP}}{\mathrm{n}}\right)}{\frac{\mathrm{RV}+\mathrm{NP}}{2}}\) × 100
Where,
PD = Amount of Preference Dividend
RV = Redemption value of Preference Share
NP = Net Proceeds of Preference Share or Current Market Price of Preference Share
n = Remaining Life of Preference Share
Present Value Method (PV)/Yield to Maturity Method (YTM):
Kp = IRR = L + \(\frac{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}-\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{H}}}\) × (H – L)
![]()
(c) Cost of Redeemable Preference Share (in Instalments):
Kd = IRR = L + \(\frac{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{L}}-\mathrm{NPV}_{\mathrm{H}}}\) × (H – L)
Note:
- In case of convertible preference share use convertible value in place of redemption value.
- If nothing is specified, issue price, redemption value etc. assumed to be equal to face value.
- If nothing is specified, floatation cost assumed to be linked with “face value or issue price whichever is higher”.
5. Cost of Equity Share Capital (Ke):
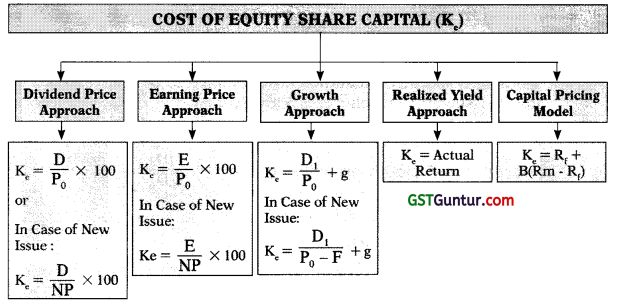
(a) Dividend Price /Yield Approach:
Ke = \(\frac{\mathrm{D}}{\mathrm{P}_0}\) × 100
Where,
D = Expected/Current Dividend
P0 = Current Market Price of Equity Share
Assumption: Constant Dividend
(b) Earning Price /Yield Approach:
Ke = \(\frac{\mathrm{E}}{\mathrm{P}_0}\) × 100
Where,
E = Expected/Current EPS
P0 = Current Market Price of Equity Share
Assumption: Constant EPS
![]()
(c) Growth Approach or Gordon’s Model:
Ke = \(\frac{\mathrm{D}_1}{\mathrm{P}_0}\) + g or \(\frac{\mathrm{D}_0(1+\mathrm{g})}{\mathrm{P}_0}\) + g
Where,
D1 = D0 (1 + g) = Expected DPS
P0 = Current Market Price of Equity Share
g = Constant Growth Rate of Dividend
Note:
- In case of fresh issue of Equity shares (New Shares), Net Proceeds from equity share {(Issue price – Issue expenses/Floatation cost) or (P – F)} is used in place of current price of share.
- If nothing is specified, floatation cost assumed to be linked with “face value or issue price whichever is higher”.
- Estimation of Growth Rate:
(a) Average Method: Growth rate = \(\sqrt[n]{\frac{D_0}{D_n}}\) – 1
D0 = Current Dividend
Dn = Dividend in n years ago
(b) Gordon’s Growth Model: g = b × r
r = Rate of return on fund invested
b = Earning retention ratio
(c) Realised Yield Approach:
Ke = Average rate of return realised in past few years
= IRR or Geometric mean
![]()
(d) Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM);
Ke = Rf + B (Rm – Rf)
Rf = Risk Free Rate of Return
Rm = Rate of Return on Market Portfolio
Rm – Rf = Market Risk Premium
β = Beta coefficient
6. Cost of Retained Earnings (Kr): After tax return to shareholder if he invest elsewhere.
Formulae:
Kr = Ke (of existing investors)
Kr = Ke (1 – tp) (In case of personal tax)
Kr = Ke (1 – tp) (1 – f) (f is rate of floatation cost)
7. Weighted Average Cost of Capital (K0): WACC is also known as the overall cost of capital of having capitals from the different sources as explained above. WACC of a company depends on the capital structure of a company. Weighted average cost of capital is the weighted average after tax costs of the individual components of firm’s capital structure. That is, the after tax cost of each debt and equity is calculated separately and added together to a single overall cost of capital. It can be calculated by using either Book Value weights or Market Value weights.
Proforma Statement of WACC
| Capital Structure (a) | Amount (b) | Weight (c) | Specific Cost (d) | Cost of Capital (e) = c × d |
| Equity Share Capital | XXX | 0.XXX | 0.XX | 0.0XX |
| Retained Earnings | XXX | 0.XXX | 0.XX | 0.0XX |
| Preference Share Capital | XXX | 0.XXX | 0.XX | 0.0XX |
| Debentures | XXX | 0.XXX | 0.XX | 0.0XX |
| Total | XXX | 1.000 | WACC | 0.0XXX |
Note: Market Value of equity has been apportioned in the ratio of Book Value of equity and retained earnings when Market Value weights are used.
![]()
8. Marginal Cost of Capital (MCC): The marginal cost of capital may be defined as the cost of raising an additional rupee of capital. Marginal cost of capital is derived, when the average cost of capital is calculated using the marginal weights.