Cost Management for Specific Sector – CA Final SCMPE Question Bank is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Cost Management for Specific Sector – CA Final SCMPE Question Bank
Question 1.
Write short note on Structure of Power Sector in India.
Answer:
Power is one of the most critical components of infrastructure crucial for the economic growth and welfare of nations. The existence and development of adequate infrastructure is essential for sustained growth for the Indian economy.
India’s power sector is one of the most diversified in the world. Sources of power generation range from conventional sources such as coal, lignite, natural gas, oil, hydro and nuclear power to viable non-conventional sources such as wind, solar and agricultural and domestic waste. Electricity demand in the country has increased rapidly and is expected to rise further in the years to come. In order to meet the increasing demand for electricity in the country, massive addition to the installed generating capacity is required.
India ranks third among 40 countries in EY’s Renewable Energy Country Attractiveness Index, on back of strong focus by the government on promoting renewable energy and implementation of projects in a time bound manner. India has moved up 73 spots to rank 26,h in the World Bank’s list of electricity accessibility in 2017.
In September 2017, the Government of India launched the Saubhagya Scheme to provide electricity connections to over 40 million families in rural and urban areas by_December 2018 at a cost of US$ 2.5 billion.
![]()
The power sector in India is mainly governed by the Ministry of Power. There are three major pillars of power sector. These are Generation, Transmission, and Distribution. As far as generation is concerned it is mainly divided into three sectors. These are Central Sector, State Sector, and Private Sector. Major PSUs involved in the generation of electricity include NHPC Ltd., NTPC Ltd., and Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL).
Besides PSUs, several state-level corporations are there such as Jharkhand State Electricity Board (JSEB), Maharashtra State Electricity Board (MSEB), Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB), in Gujarat MGVCL, PGVCL, DGVCL, UGVCL four distribution Companies and one controlling body GU VNL, and one generation company GSEC), are also involved in the generation and intra-state distribution of electricity.
Other than PSUs and state level corporations, private sector enterprises also play a major role in generation, transmission and distribution.
The Power Grid Corporation of India is responsible for the inter-state transmission of electricity and the development of national grid.
The Ministry of Power is the apex body responsible for the development of electrical energy in India. This ministry started functioning independently from 2 July 1992; earlier, it was known as the Ministry of Energy.
![]()
Question 2.
Write short note on:
Application of Cost Management Technique in Power Sector.
Answer:
Cost Management Technique in Power Sector is required for:
- Determining Prices
- Regulation tariffs
- Developing a flexible cost allocation system
- Distribution loss and inefficiency gap analysis
- Multi dimensional costing calculations
- Overall analysis and reporting.
Question 3.
Write short note on Activity Based Costing in Agriculture.
Answer:
ABC in Agriculture:
Activity Based Costing is a costing methodology that identifies activities in an organisation and assigns the cost of each activity with resources to all products and services according to actual consumption by each.
Activity Based Costing provides a better manner in which the Indirect costs associated with the processes carried out in the agricultural sector can be carried out in an efficient manner.
It is a step up from the target cost management technique where the fluctuation in the anticipated price which forms part of the formula might not result in appropriate determination of the target costs.
ABC costing helps in allocation of the costs in relation to the various activities associated with the production based upon the cost drives identified in relation to each production activity.
Benefits of using ABC for cost management in the agricultural sector:
- Adjustable costing technique
- Faster and more accurate
- Enables carrying out a more detailed cost analysis.
![]()
Question 4.
State the components of Agri supply Chain.
Answer:
Components of an Agri supply chain
Agribusiness, supply chain management (SCM) implies managing the relationships between the businesses responsible for the efficient production and supply of products from the farm level to the consumers to meet consumers’ requirements reliably in terms of quantity, quality and price.
In practice, this often includes the management of both horizontal and vertical alliances and the relationships and processes between firms. Agri-supply chains are economic systems which distribute benefits and apportion risks among participants. Thus, supply chains enforce internal mechanisms and develop chain wide incentives for assuring the timely performance of production and delivery commitments.
They are linked and interconnected by virtue of shared information and reciprocal scheduling, product quality assurances and transaction volume commitments. Process linkages add value to agricultural products and require individual participants to coordinate their activities as a continuous improvement process.
Costs incurred in one link in the chain are determined in significant measure by actions taken or not taken at other links in the chain. Extensive pre-planning and co-ordination are required up and down the entire chain to affect key control processes such as forecasting, purchase scheduling, production and processing programming, sales promotion, and new market and product launches etc.
![]()
Following are the components of an organised agri-suppiy chain:
1. Procurement or sourcing
2. Logistic management
(a) Transportation
(b) Material management
(c) On the premise of supplying mostly from production not stock
(d) Warehousing
(e) Logistics Network modelling
3. Organizational management
(a) Contracting
(b) Strategic alliances and partnerships
(c) Vertical integration
- Long term storage
- Packaging technology
- Cold chain management
- Energy efficient transport
- Quality and safety
4. Application of Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) System
(a) Electronic scanning of price and product at the point of sale
(b) Streamline the entire distribution chain
![]()
Question 5.
Discuss the features of Power Sector in India.
Answer:
Features of Power Sector
- Limited number of suppliers of electricity.
- Tariff determination is based upon the rationality to determine the cost incurred at various points of operation.
- Stakeholders are existing and future consumers, industries, government, regulators, and investors.
- Continuous growing demand of electricity.
- Flexible Cost allocation.
- Distribution loss and inefficiency gaps between generation and consumption of electricity.
- In-disciplined consumer.
- Continuous network between generators, transmitters, distributors, and consumers.
- Mostly public sector undertakings closely regulated by government.
- Energy subsidies having direct impact on national treasury affecting long term growth potential of the economy.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the 4D IT Cost Optimization Framework.
Answer:
4D IT Cost Optimization Framework Defining Organization Vision
Any amount of spending carried out in relation to the Information Technology requirements of the organization needs to be aligned to the organizational vision and long term objectives. Business owners should have a sense of ownership and thereby control the IT costs in an effective manner. The perspectives of the key stakeholders i.e. CEO, CFO and directors must be taken into consideration when deciding upon the IT consumption within the organization.
The additional visibility through the model needs to determine the appropriate method of cost allocation in relation to the IT cost burden. Thus, the allocation model that is chosen needs to be both flexible and at the same time avoid being too complex in nature. The organization can either opt for a simple method of dividing the entire IT cost by the number of hours consumed by each department or a more complex but accurate method of ABC costing could be used for allocation of the costs based upon the associated cost drivers associated with each set of activities.
Documentation of the current state
The next step involves documentation of the current state of the IT department implemented within the organization in order to identify gaps and potential weaknesses identified in relation to the current state for the purpose of identification of the appropriate pain points as well as identification of areas for potential automation.
Delineation of target business architecture
Once the current state of the IT architecture has been documented, the next step is developing a target business architecture for the purpose of addressing the gaps and limitations identified and laying down the foundation with regards to the formation of the crux of the IT cost management framework.
Decision: Build v/s Buy
The last step understands whether the framework built is bought or custom built internally. The answer to the question involves a great amount of brainstorming and research taking into consideration the view point of all the strategic stakeholders involved.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the challengers associated with IT expenditure in MNCs? Which IT cost framework should be adopted?
Answer:
There are a number of challenges associated with the management of the costs associated with the Information Technology expenditures incurred by the Multi-National corporations. Thus, the complexity of the operating structure and the difficulty seen in the implementation of the cost allocation models, it is seen that in order to manage the IT costs, most organizations tend to develop centralized IT departments acting as cost centers for the purpose of managing the IT budgets as well as allocation of costs associated with along with the charging back of expenses that are incurred by the business units.
IT Organization’s Engagement Model
The question that needs to be addressed under the same is that whether the IT organization should be organized as a cost center to the organization or whether it should be seen as a strategic partner to the business. With more and more organizations whether large or small in nature, opting for third party allocation or opting for cloud computing services it can be seen that the internal IT departments are fighting hard for remaining relevant for the organization. In order to stay relevant, what the IT department needs is a better visibility towards the IT needs of the organization. In order to do the same, organizations operating in the given sector can adopt what is referred as to the 4D framework.
![]()
Question 8.
Draw a diagram to show the Value Chain Analysis in Power Sector in India.
Answer:
Value Chain Analysis is Power Sector:
This involves ensuring value creation in all the activities both inbound and outbound activities undertaken by the power company starting from electricity generation to the point of supply or distribution of the electricity supply.
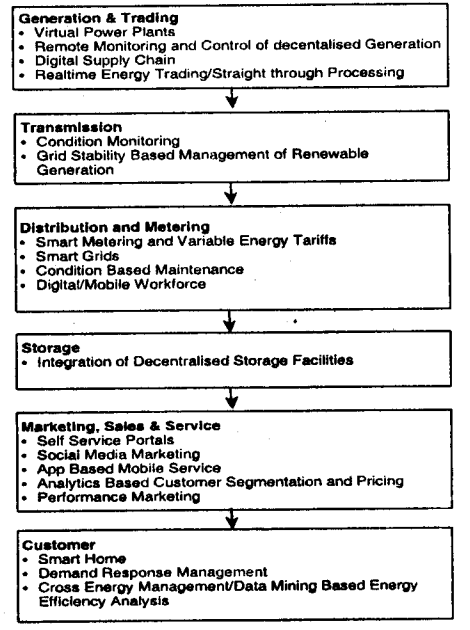
![]()
Question 9.
What are the key risks in Power Sector in India?
Answer:
Key Risks in the Power Sector are:
1. Highly Capital Intensive
Power sector is a highly capital intensive business with long gestation periods before commencement of revenue streams (construction periods of 7-8 years) and an even longer operating period (over 25 years). Since most of the projects have such a longtime frame, there are some inherent risks in both thb internal and external environment.
2. Coal Supply Position
More than 50 percent of India’s generation capacity is coal based. According to the Integrated Energy Policy, by FY 20 – 21, India requires 2,040 million tonnes of coal for power generation, more than 5 times its current consumption levels. The shortage of coal is so acute that most of the power generation companies are looking at imported coal as a viable alternative to domestic coal.
![]()
Question 10.
Discuss the features of Agriculture Sector in India.
Answer:
Features of Agriculture Sector in India:
- Challenges associated with structure of the industry which is fragmented and unorganized
- Lack of understanding of costs
- Understanding the potential of working collaboratively
- Use of target costing techniques for price determination
- Imbalance of power across the supply chain
1. Fragmented Structure of the Industry
The structure of the agriculture sector is seen to be unorganized and fragmented in nature and thus lack of effective regulation in the given sector is also seen as one of the reasons why farmers seem to be exploited and have been operating at very low margins.
2. Lack of understanding of costs and prices by the farmers
One of the key reasons seen for the lack of appropriate cost management in the given sector is with regards to the lack of prioritization of the cost management among farmers because of lack of knowledge with regards to the same.
![]()
3. Understanding the potential to work collaboratively
The farmers need to be open to innovation in cost management and contracting techniques. Though there is scope for cost reduction in order to bring about improvement in the profit margins for the farmers, it is seen that generally the profits tend to get transferred to the customers and the only point of negotiation is in the contract pricing with the retailers which the farmers fail to reach.
4. Target cost. Management
The target costing technique involves determining the cost by subtracting the required margin from the anticipated price for the agricultural produce. However, the anticipated price for the agricultural products fluctuates making the process of cost management using the target cost management system ineffective in the case of the agricultural sector.
5. Imbalance of power distribution
With the fragmentation and the unorganized nature of the farmers operating in the agricultural sector, the power of bargaining seems to lie in the hands of the wholesalers purchasing the produce from the farmers resulting in overall low margins for farmers in comparisons to the margins earned by the wholesalers and the retailers operating in the said sector.
![]()
Question 11.
Write a brief note on Minimum Support Price (MSP).
Answer:
Minimum Support Price (MSP)
In India, Minimum Support Price (MSP) was introduced by the Government of India to protect farmers against sharp dip of agricultural prices, which was usually observed during the harvest seasons. The harvest seasons are associated with huge supply, which overshadows the demand, and hence, in most cases the commodity prices hit the bottom.
This forces the farmers, in necessity of money for repayment of debts, in selling their produce at losses or very little profits. Thus, the government fixes the MSP, as a part of government food grain procurement. Selling at MSP ensures profit margins for farmers and avoids distress selling situations.