Cost Accounting System – CA Inter Costing Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Cost Accounting System – CA Inter Costing Study Material
Theory Questions
Question 1.
Explain integrated accounting system and state its advantages. fCA Inter Nov. 2019, May 2019, May 2015, May 2012, May 2010, 5 Marks]
Answer:
Integrated Accounting System:
Integrated Accounting System is a system of accounting, where the cost and financial accounts are kept in the same set of books. Integrated accounts provide or meet out fully the information requirement for Costing as well as for Financial Accounts. For Costing purposes, it provides information useful for ascertaining the cost of each product, job, and process, operation of any other identifiable activity and for carrying necessary analysis.
Integrated accounts provide relevant information which is necessary for preparing profit and loss account and the balance sheets as per the requirement of law and also helps in exercising effective control over the liabilities and assets of its business.
The main advantages of Integrated Accounting System are as follows:
- No need for Reconciliation: The question of reconciling costing profit and financial profit does not arise, as there is only one figure of profit.
- Less efforts: Due to use of one set of books, there is a significant saving in efforts made.
- Less Time consuming: No delay is caused in obtaining information as it is provided from books of original entry.
- Economical process: It is economical also as it is based on the concept of ‘Centralisation of Accounting function’.
Question 2.
Explain essential pre-requisites for Integrated Accounting System. [CA Inter Nov, 2020, May 2018, Nov. 2007, Nov. 2006, Nov. 2001, 5 marks]
Answer:
Essential pre-requisites for integrated Accounting System are following:
(a) The management’s decision about the extent of integration of the two sets of books.
(b) A suitable coding system must be made available so as to serve the accounting purposes of financial and cost accounts.
(c) An agreed routine, with regard to the treatment of provision for accruals, prepaid expenses, other adjustment necessary for preparation of interim accounts.
(d) Perfect coordination should exist between the staff responsible for the financial and cost accounts and an efficient processing of accounting document should be ensured.
(e) Under this system there is no need for a separate cost ledger. Of course, there will be a number of subsidiary ledgers; in addition to the useful Customers’ Ledger and the Purchase Ledger, there will be:
(a) Stores Ledger;
(b) Stock Ledger; and
(c) Job Ledger.
Question 3.
Discuss the reconciliation of Profit as per Cost Accounts and Financial Accounts. [CA Inter May 2007, May 2006, 6 Marks]
Answer:
When the cost and financial accounts are kept separately, it is imperative that these should be reconciled to make the cost accounts reliable. It is necessary for reconciliation of the two sets of accounts that sufficient details are available to locate the differences and the reasons for the same.
Causes of differences in Financial and Cost Accounts:
1. Items included in Financial Accounts only:
- Interest on loans or bank mortgages
- Expenses and discounts on issue of shares, debentures etc.
- Other capital losses i.e., loss by fire not covered by insurance etc.
- Losses on the sales of fixed assets and investments
- Goodwill written off
- Preliminary expenses written off
- Income tax, donations, subscriptions
- Expenses of the company’s share transfer office, if any.
2. Purely Financial Income:
- Interest received on bank deposits, loans and investments
- Dividends received
- Profits on the sale of fixed assets and investments
- Transfer fee received
- Rent receivables
3. Item included in Cost Accounts only (notional expenses):
- Charges in lieu of rent where premises are owned
- Interest on capital at notional figure though not incurred
- Salary for the proprietor at notional figure though not incurred
- Notional Depreciation on the assets fully depreciated for which book value is nil.
![]()
Question 4.
List the Financial expenses which are not included in cost. [CA Inter Nov. 2009, 2 Marks]
Answer:
Financial expenses which are not included in cost accounting are as follows:
- Interest on loans or bank mortgages
- Expenses and discounts on issue of shares, debentures etc.
- Other capital losses Le., loss by fire not covered by insurance etc.
- Losses on the sales of fixed assets and investments
- Goodwill written off
- Preliminary expenses written off .
- Income tax, donations, subscriptions
- Expenses of the company’s share transfer office, if any.
Question 5.
When is the reconciliation statement of Cost and Financial accounts not required? [CA Inter Nov. 2009, 2 Marks]
Answer:
When the Cost and Financial Accounts are integrated, there is no need to have a separate reconciliation statement between the two sets of accounts. Integration means that the same set of accounts fulfil the requirement of both Le., Cost and Financial Accounts.
Question 6.
“Is reconciliation of cost accounts and financial accounts necessary in case of integrated accounting system?” [CA Inter May 2013, 4 Marks]
Answer:
- In integrated accounting system, cost and financial accounts are kept in the same set of books. Such a system will have to afford full information required for Costing as well as for Financial Accounts.
- For Costing purposes, it must provide information useful for ascertaining the cost of each product, job, process and operation of any other identifiable activity and for carrying necessary analysis.
- It also provide relevant information which is necessary for preparing profit and loss account and the balance sheet as per the requirement of law and also helps in exercising effective control over the liabilities and assets of its business.
Since, only one set of books are kept for both cost accounting and financial accounting purpose so there is no necessity of reconciliation of cost and financial accounts.
Question 7.
What are the motivational factors for adopting a reconciliation process? Explain. [CA Inter Nov. 2017, 4 Marks]
Answer:
When the cost and financial accounts are kept separately, it is imperative that these should be reconciled, otherwise the cost accounts would not be reliable.
The reconciliation of two set of accounts can be made, if both the sets contain sufficient detail as would enable the causes of differences to be located. It is therefore, important that in the financial accounts, the expenses should be analysed in the same way as in cost accounts.
Motivation for reconciliation is:
- To ensure reliability of cost data
- To ensure ascertainment of correct product cost
- To ensure correct decision making by the management based on Cost & Financial data.
Question 8.
Which are the types of management accounting systems used for controlling costs? [ICAI Module]
Answer:
For cost control purpose, following are the two main types of management accounting systems which are followed on the basis of timing of variance analysis:
(i) Single Plan: Under this system, the variances in costs from the set standards are reported at its happenings without waiting for books closing.
- Timely analysis is done so that much time is not lost in taking corrective action wherever needed.
- The single plan system envisages the posting of all items in the debit side of the work-in-process account at the standard cost leaving the credit side to represent.
- This system enables the ascertainment of variances as and when the transaction is posted to work-in-process account. This method of analysis is known as analysis at source.
(ii) Partial Plan: In the partial plan, variances are analysed at the end of period. Under this method the work-in-process account is charged at the actual cost of production for the period and is credited with the standard cost of the period’s production of finished product.
- The closing balance of work-in-process is also shown at standard cost.
- The balance after making the credit entries represents the variance from standard for the period. The analysis of the variances is done after the end of the period.
![]()
Practical Questions
Question 1.
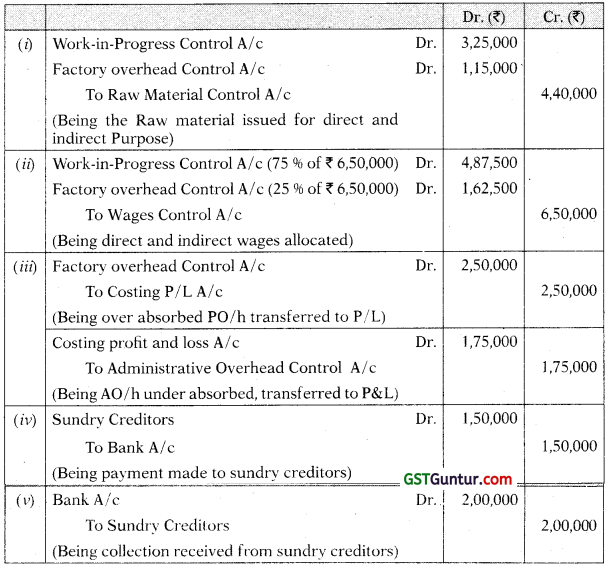
Pass journal entries in the cost books, maintained on non-integrated system, for the following:
(i) Issue of materials: Direct ₹ 5,50,000; Indirect ₹ 1,50.000
(ii) Allocation of wages: Direct ₹ 2,00,000; Indirect ₹ 40,000
(iii) Under/Over absorbed overheads: Factory (over) ₹ 20,000; Administration (under) ₹ 10,000 [CA Inter Now 2000. 6 Marks]
Answer:
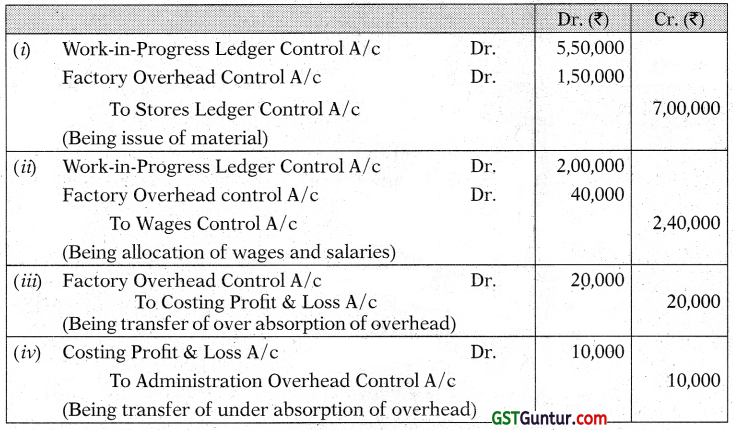
Question 2.
Journalise the following transactions in cost books under Non-Integraled system of Accounting.
(i) Credit Purchase of Material ₹ 27,000
(ii) Manufacturing overhead charged to Production ₹ 6,000
(iii) Selling and Distribution overheads recovered from Sales ₹ 4,000
(iv) Indirect wages incurred ₹ 8,000
(v) Material returned from production to stores ₹ 9,000 [CA Inter Nov. 2019, 5 Marks]
Answer:
Journal entries are as follows:
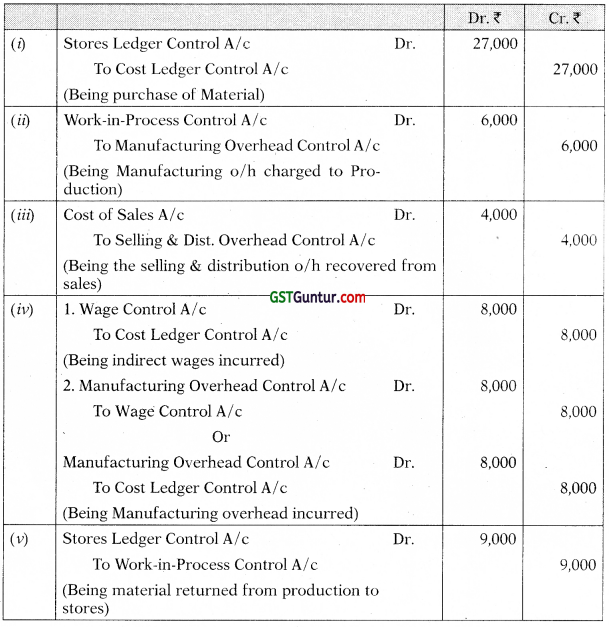
Question 3.
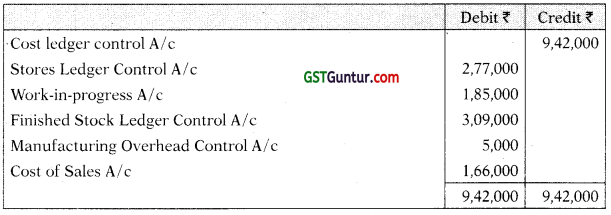
As of 31st March 2021, the following balances existed in a firm’s cost ledger, which is maintained separately on a double-entry basis:
| Debit ₹ | Credit ₹ | |
| Stores Ledger Control A/c | 3,00,000 | – |
| Work-in-progress Control A/c | 1,50,000 | – |
| Finished Goods Control A/c | 2,50,000 | – |
| Manufacturing Overhead Control A/c | 15,000 | |
| Cost Ledger Control A/c | 6,85,000 | |
| 7,00,000 | 7,00,000 |
During the next quarter, the following items arose:
| ₹ | |
| Finished Product (at cost) | 2,25,000 |
| Manufacturing overhead incurred | 85,000 |
| Raw material purchased | 1,25,000 |
| Factory wages | 40,000 |
| Indirect labour | 20,000 |
| Cost of sales | |
| Materials issued to production | |
| Sales returned (at cost) | 9,000 |
| Materials returned to suppliers | 13,000 |
| Manufacturing overhead charged to production | 85,000 |
You are required to prepare the Cost Ledger Control A/c, Stores Ledger Control A/c, Work-In-progress Control A/c. Finished Stock Ledger Control A/c, Manufacturing Overhead Control A/c, Wages Control A/c, Cost of Sales A/c and the Trial Balance at the end of the quarter. [CA Inter Nov. 2008, 15 Marks]
Answer:
Cost Ledger Control Account
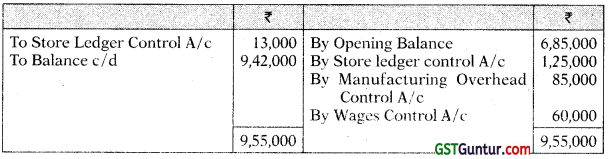
Stores Ledger Control Account
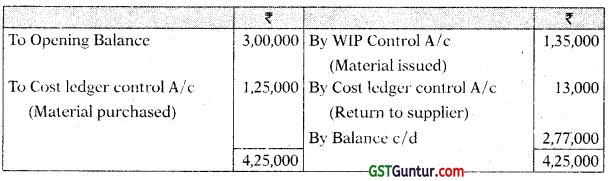
Work-in-progress Control Account
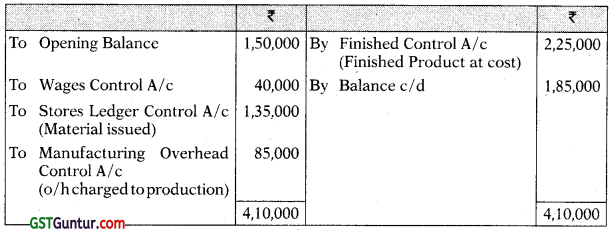
Finished Stock Ledger Control Account
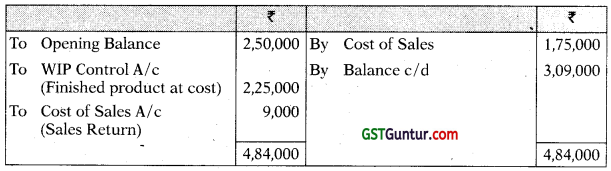
Manufacturing Overhead Control Account
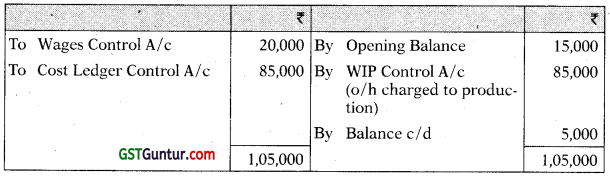
Wages Control Account
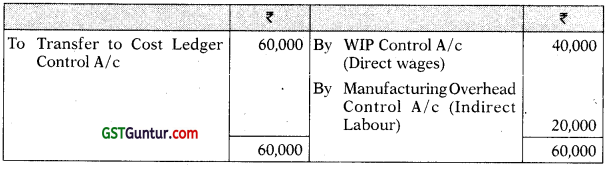
Cost of Sales Account
![]()
Question 4.
The following balances were extracted from a Company’s ledger as on 30th June, 2021:
| Debit (₹) | Credit (₹) | |
| Raw material control a/c | 2,82,450 | |
| Work-in-progress control a/c | 2,38,300 | |
| Finished stock control a/c | 3,92,500 | |
| General ledger adjustment a/c | 9,13,250 | |
| Total | 9,13,250 | 9,13,250 |
The following transactions took place during the quarter ended 30th September, 2021:
(i) Factory overheads – allocated to work-in-progress ₹ 1,36,350
(ii) Goods furnished – at cost ₹ 13,76,200
(iii) Raw materials purchased ₹ 12,43,810
(iv) Direct wages – allocated to work-in-progress ₹ 2,56,800
(v) Cost of goods sold ₹ 14,56,500
(vi) Raw materials – issued to production ₹ 13,60,430
(vii) Raw materials – credited by suppliers ₹ 27,200
(viii) Raw materials losses – inventory audit ₹ 6,000
(ix) Work-in-progress rejected (with no scrap value) ₹ 12,300
(x) Customer’s returns (at cost) of finished goods ₹ 45,900
You are required to prepare:
(i) Raw material control a/c
(ii) Work-in-progress control a/c
(iii) Finished stock control a/c
(iv) General ledger adjustment a/c [CA Inter Nov. 2018, 10 Marks]
Answer:
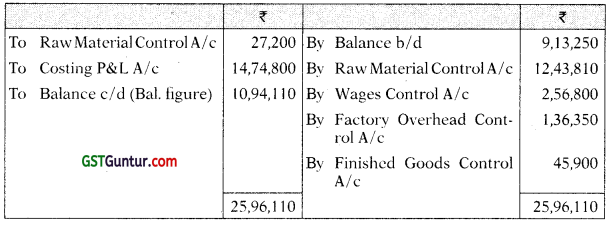
(i) Raw Material Control A/c
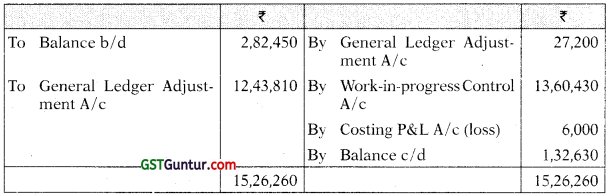
(ii) Work-in-Progress Control A/c
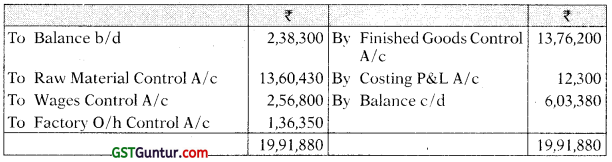
(iii) Finished Goods Control A/c
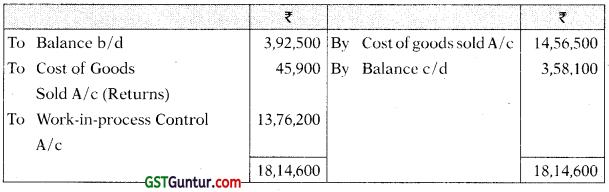
(iv) General Ledger Adjustment A/c
Question 5.
The following information has been extracted from the cost records of a manufacturing company:
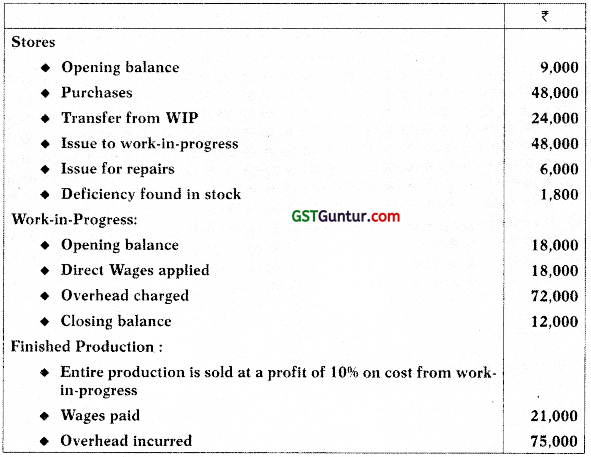
Draw the Stores Leger Control A/c, Work-in-Progress Control A/c, Overheads Control A/c and Costing Profit and Loss A/c. [CA Inter May 2017, Nov. 2014, Nov. 2011, 8 Marks]
Note: General Ledger Adjustment A/c may also be written as Cost Ledger Control A/c
Answer:
Stores Ledger Control A/c
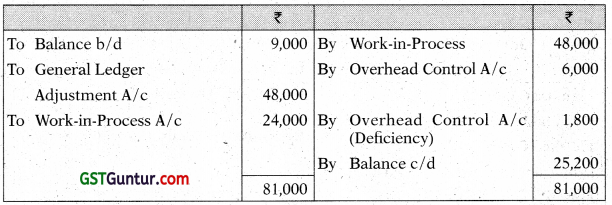
Note: Deficiency is assumed to be normal.
Work-in-Progress Control A/c
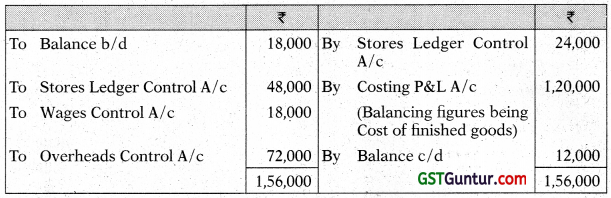
Overheads Control A/c
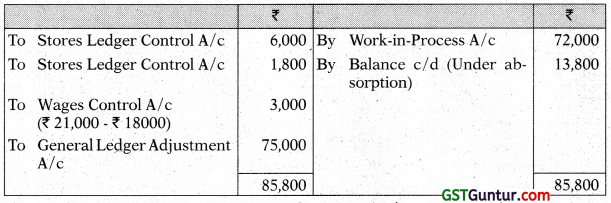
Costing Profit & Loss A/c
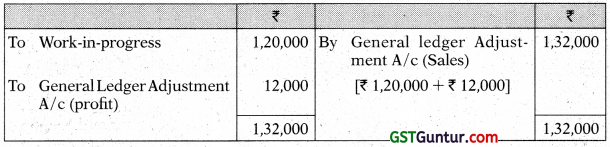
Note: General Ledger Adjustment A/c may also be written as Cost Ledger Control A/c
Question 6.
Acme Manufacturing Co. Ltd. opens the costing records, with the balances as on 1st July as follows:
| (₹) | (₹) | |
| Material Control A/c | 1,24,000 | |
| Work-in-Process Control A/c | 62,500 | |
| Finished Goods Control A/c | 1,24,000 | |
| Production Overhead Control A/c | 8,400 | |
| Administrative Overhead Control A/c | 12,000 | |
| Selling & Distribution Overhead Control A/c | 6,250 | |
| Cost Ledger Control A/c | 3,13,150 | |
| 3,25,150 | 3,25,150 |
The following are the transactions for the quarter ended 30th September:
| (₹) | |
| Materials purchased | 4,80,100 |
| Materials issued to jobs | 4,77,400 |
| Materials to works maintenance | 41,200 |
| Materials to administrative office | 3,400 |
| Materials to sales department | 7,200 |
| Wages direct | 1,49,300 |
| Wages indirect | 65,000 |
| Transportation for indirect materials | 8,400 |
| Production overheads incurred | 2,42,250 |
| Absorbed production overheads | 3,59,100 |
| Administrative overheads incurred | 74,000 |
| Administrative overheads allocated to production | 52,900 |
| Administrative overheads allocated to sales department | 14,800 |
| Selling & Distribution overheads incurred | 64,200 |
| Selling & Distribution overheads absorbed | 82,000 |
| Finished goods produced | 9,58,400 |
| Finished goods sold | 9,77,300 |
| Sales; | 14,43,000 |
Make up the various accounts as you envisage in the Cost Ledger and prepare a Trial Balance as at 30th September. [ICAI Module]
Answer:
Cost Ledgers
Material Control A/c
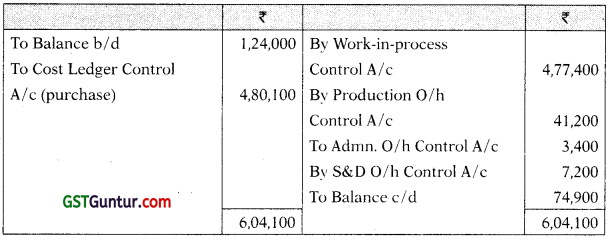
Wages Control A/c
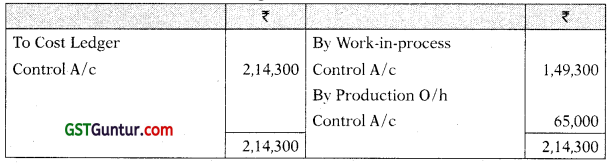
Production Overhead Control A/c
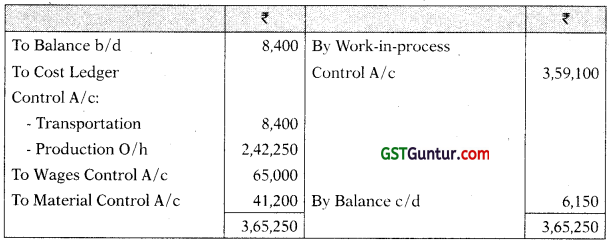
Administrative Overhead Control A/c
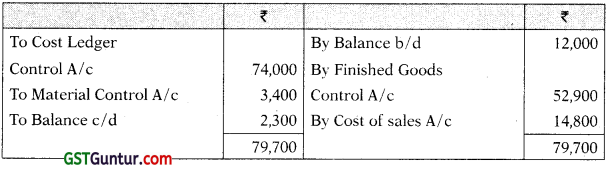
Work-in-Process Control A/c
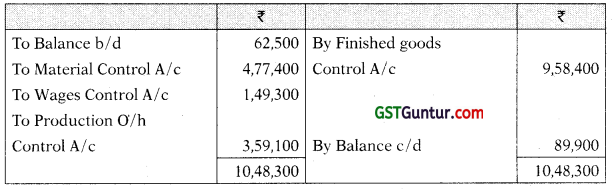
Finished Goods Control A/c
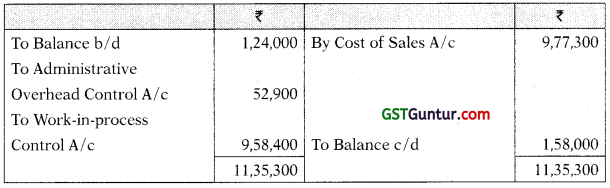
Selling and Distribution Overhead Control A/c
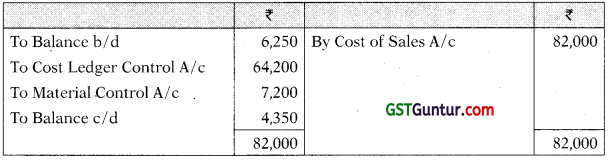
Cost of Sales A/c
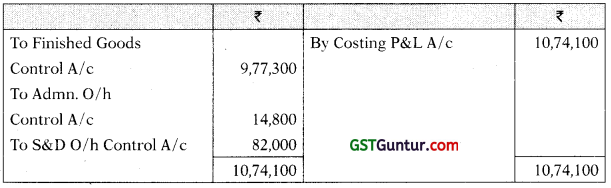
Cost Ledger Control A/c
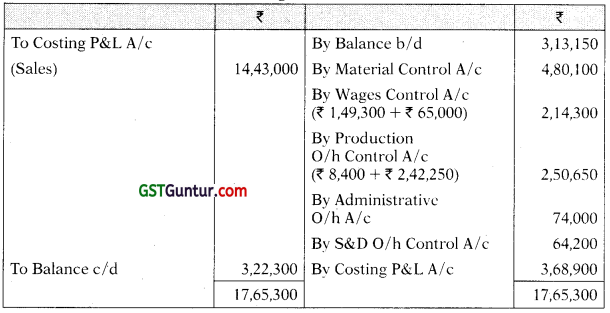
Costing Profit & Loss A/c
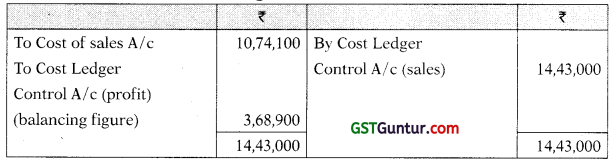
Trial Balance as at 30th September
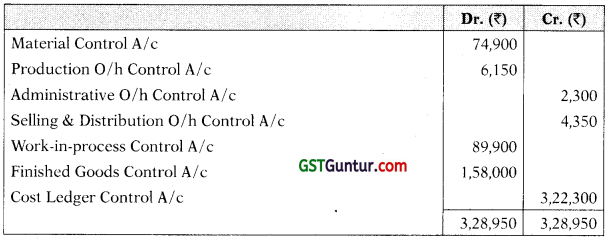
![]()
Question 7.
A company operates on historic job cost accounting system, which is not integrated with the financial accounts. At the beginning of a month, the opening balances in cost ledger were:
| (₹ in lakhs) | |
| Stores Ledger Control Account | 80 |
| Work-in-Process Control Account | 20 |
| Finished Goods Control Account | 430 |
| Building Construction Account | 10 |
| Cost Ledger Control Account | 540 |
During the month, the following transactions took place:
| (₹ in lakhs) | ||
| Materials | Purchased | 40 |
| Issued to production | 50 | |
| Issued to factory maintenance | 6 | |
| Issued to building construction | 4 | |
| Wages | Gross wages paid | 150 |
| Indirect wages | 40 | |
| For building construction | 10 | |
| Works Overheads | Actual amount incurred (excluding items shown above) |
160 |
| Absorbed in building construction | 20 | |
| Under absorbed | 8 | |
| Royalty paid (related to production) | 5 | |
| Selling, distribution and administration overheads | 25 | |
| Sales | 450 | |
At the end of the month, the stock of raw material and work-in-process was f 55 lakhs and ₹ 25 lakhs respectively. The loss arising in the raw material accounts is treated as factory overheads. The building under construction was completed during the month. Company’s gross profit margin is 20% on sales.
You are required to prepare the Cost Ledger Control A/ c, Stores Ledger Control A/c, Wages Control A/c, Works Overhead Control A/c, Work-in-Process Control A/c, Finished Goods Control A/c, Cost of Sales A/c, Costing P&L A/c, Building Construction A/c and Trial Balance at the end of the month. [CA Inter Nov. 2021, RTPJ
Answer:
Cost Ledger Control A/c
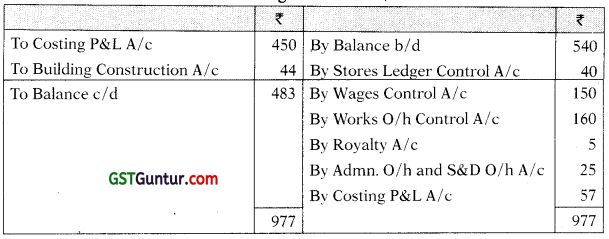
Stores Ledge Control A/c
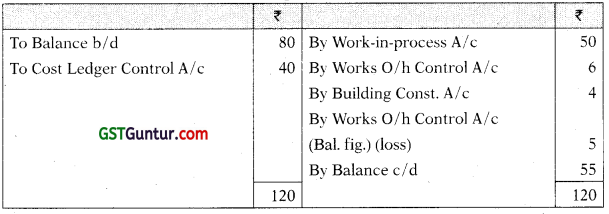
Wages Control A/c
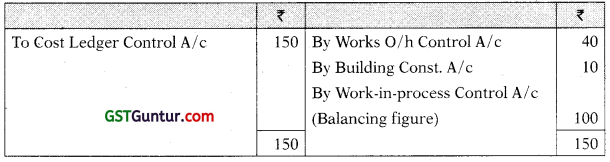
Works Overhead Control A/c
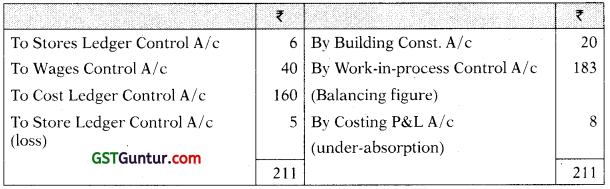
Work-in -Process Control A/c
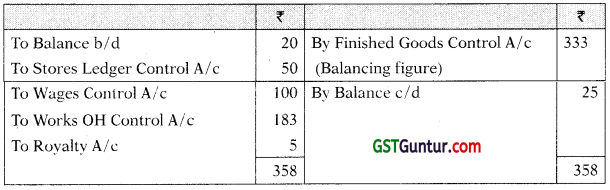
Finished Goods Control A/c
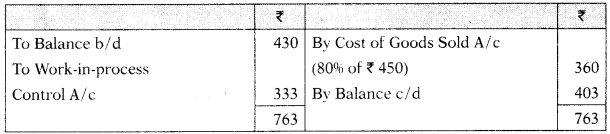
Cost of Sales A/c
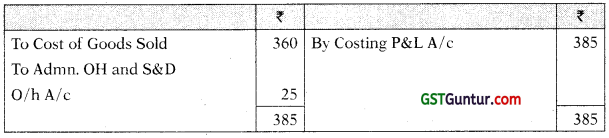
Costing P & L A/c
Building Construction A/c
Trial Balance

Question 8.
A Company operates separate cost accounting and financial accounting systems. The following is the list of opening balances as on 1.04.2021 in the Cost Ledger:
| Debit (₹) | Credit (₹) | |
| Stores Ledger Control Account | 53,375 | …… |
| WIP Control Account | 1,04,595 | …… |
| Finished Goods Control Account | 30,780 | …… |
| General Ledger Adjustment Account | ….. | 1,88,750 |
Transactions for the quarter ended 30.06.2021 are as under:
| Materials purchased | 26,700 |
| Materials issued to production | 40,000 |
| Materials issued to factory for repairs | 900 |
| Factory wages paid (including indirect wages ₹ 23,000) | 77,500 |
| Production overheads incurred | 95,200 |
| Production overheads under- absorbed and written-off | 3,200 |
| Sales | 2,56,000 |
The Company’s gross profit is 25% on Cost of Sales. At the end of the quarter, WIP stocks increased by ₹ 7,500.
Prepare the relevant Control Accounts, Costing Profit & Loss Account and General Ledger Adjustment Account to record the above transactions for the quarter ended 30.06.2021. [CA Inter Nov. 2001, 10 Marks]
Answer:
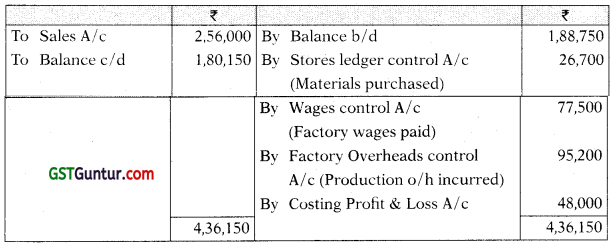
General Ledger Adjustment A/c
Stores Ledger Control A/c
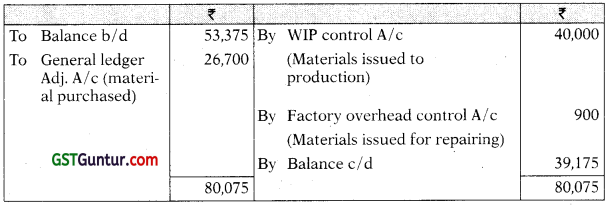
WIP Control A/c
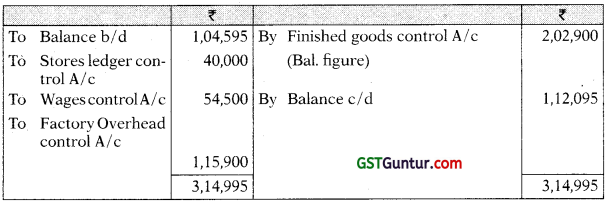
Finished Goods Control A/c
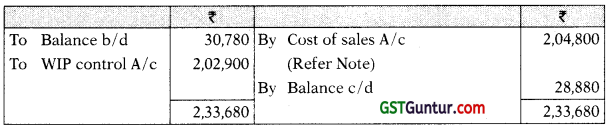
Note: Gross profit is 25% of Cost of Sales or 20% on sales.
Hence cost of sales = ₹ 2,56,000 – 20% of ₹ 2,56,000 = ₹ 2,04,800
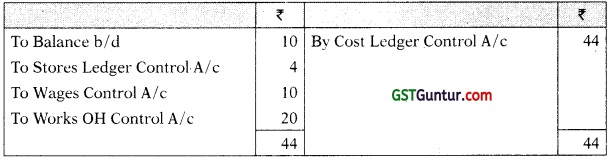
Factory Overhead Control A/c
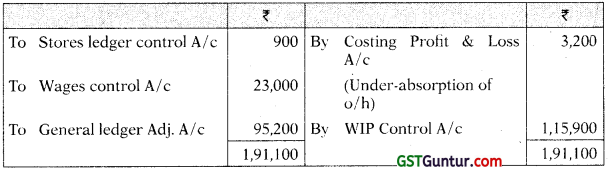
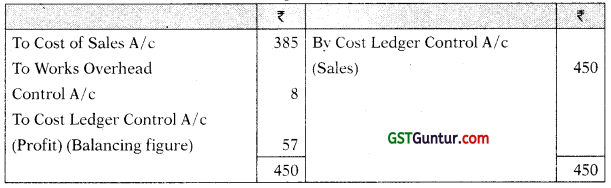
Cost of Sales A/c
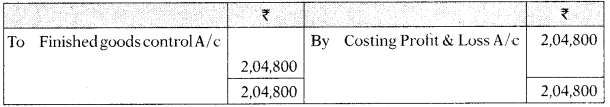
Sales A/c
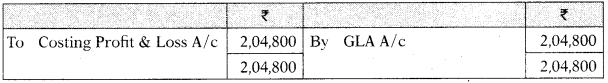
Wages Control A/c
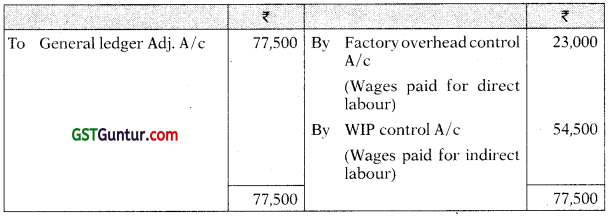
Costing Profit & Loss A/c
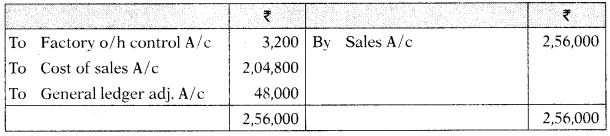
Trial Balance (as on 30.06.2021)
| (₹) | (₹) | |
| Stores ledger control A/c | 39,175 | |
| WIP control A/c % | 1,12,095 | |
| Finished goods control A/c | 28,880 | |
| General ledger adjustment A/c | 1,80,150 | |
| 1,80,150 | 1,80,150 |
![]()
Question 9.
The following information is available from a company’s records for March, 2021:
(a) Opening Balance of Creditors Account ₹ 25,000
(b) Closing Balance of Creditors Account ₹ 40,000
(c) Payment made to Creditors ₹ 5,80,000
(d) Opening Balance of Stores Ledger Control Account ₹ 40,000
(e) Closing Balance of Stores Ledger Control Account ₹ 65,000
(f) Wages paid (for 8,000 hours) 20% relate to indirect workers ₹ 4,00,000
(g) Various indirect expenses incurred ₹ 60,000
(h) Opening balance of W1P control account ₹ 50,000
(i) Inventory of WIP at the end of the month includes material worth on which 400 labour hours have been booked. ₹ 35,000
(j) Factory overhead is charged to production at budgeted rate based on direct labour hours.
(k) j Budgeted overhead cost is ₹ 20,80,000 for budgeted direct labour hours 1,04,000.
You are required to prepare Creditors A/c, Stores Ledger Control A/c, WIP Control A/c, Wages Control A/c and Factory Overhead Control A/c. [CA Inter May 2016, 8 Marks]
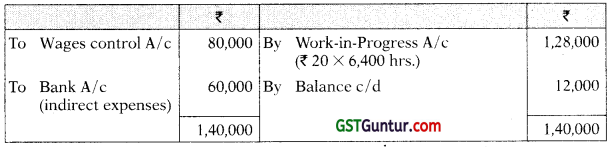
Answer:
Creditors A/c
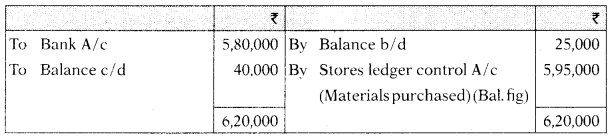
Stores Ledger Control A/c
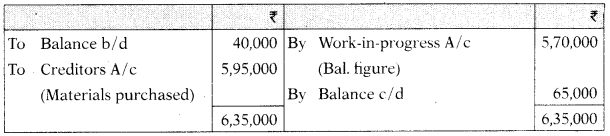
Work-in-Process Control A/c
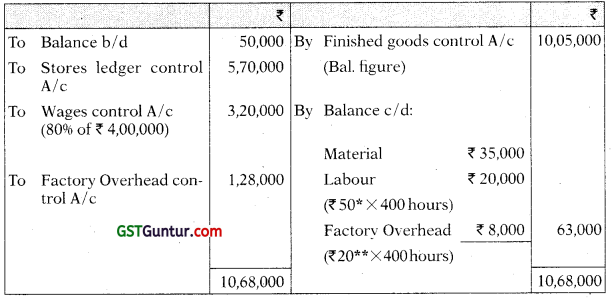
*Direct Labour Hour Rate = ₹ 3,20,000/ 6,400 hours = ₹ 50
**Factory Overhead Rate = ₹ 20,80,000/ 1,04,000 = ₹ 20
Wages Control A/c
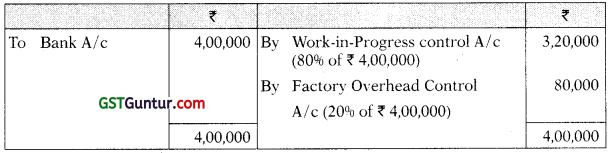
Factory Overhead Control A/c
Question 10.
Journalise the following transactions assuming cost and financial accounts are integrated: [CA Inter Nov. 2013, 5 Marks]
| ₹ | ||
| (i) | Materials issued: | |
| Direct: | 3,25,000 | |
| Indirect | 1,15,000 | |
| (ii) | Allocation of wages (25% indirect) | 6,50,000 |
| (iii) | Under/Over absorbed overheads: | |
| Factory (Over) | 2,50,000 | |
| Administration (Under) | 1,75,000 | |
| (iv) | Payment to Sundry Creditors | 1,50,000 |
| (v) | Collection from Sundry Debtors | 2,00,000 |
Answer:
Journal Entries under Integrated system of accounting
Question 11.
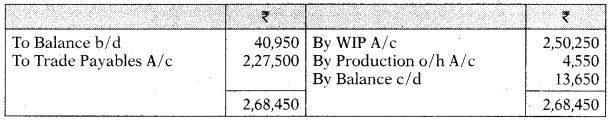
BPR Limited keeps books on integrated accounting system. The following balances appear in the books as on April 1, 20?
| Dr. (₹) | Cr. (₹) | |
| Stores Control A/c | 40,950 | – |
| Work-in-progress A/c | 38,675 | – |
| Finished Goods A/ c | 52,325 | – |
| Bank A/c | – | 22,750 |
| Trade Payables A/c | – | 18,200 |
| Non-Current Assets A/c | 1,47,875 | – |
| Trade Receivables A/c | 27,300 | – |
| Share Capital A/c | – | 1,82,000 |
| Provision for Depreciation A/c | – | 11,375 |
| Provision for Doubtful Debts A/c | – | 3,721 |
| Factory Overheads Outstanding A/c | – | 6,250 |
| Pre-Paid Administration Overheads A/c | 9,975 | – |
| Profit & Loss A/c | – | 72,800 |
| 3,17,100 | 3,17,100 |
The transactions for the year ended March 31, 2021, were as given below:
| ₹ | ₹ | |
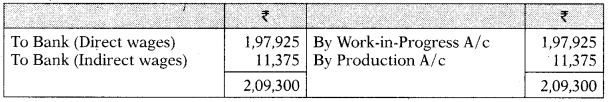
| Direct Wages | 1,97,925 | |
| Indirect Wages | 11.375 | 2,09,300 |
| Purchase of materials (on credit) | 2,27,500 | |
| Materials issued to production | 2,50,250 | |
| Material issued for repairs | 4,550 | |
| Goods finished during the year (at cost) | 4,89,125 | |
| Credit Sales | 6,82,500 | |
| Cost of Goods sold | 5,00,500 | |
| Production overheads absorbed | 1,09,200 | |
| Production overheads paid during the year | 91,000 | |
| Production overheads outstanding at the end of year | 7,775 | |
| Administration overheads paid during the year | 27,300 | |
| Selling overheads incurred | 31,850 | |
| Payment to Trade Payables | 2,29,775 | |
| Payment received from Trade Receivables | 6,59,750 | |
| Depreciation of Machinery | 14,789 | |
| Administration overheads outstanding at the end of year | 2,225 | |
| Provision for doubtful debts at the end of the year | 4,590 |
Required:
Write up accounts in the integrated ledger of BPR Limited and prepare a Trial balance. ]CA Inter Nov. 2003, 10 Marks]
Answer:
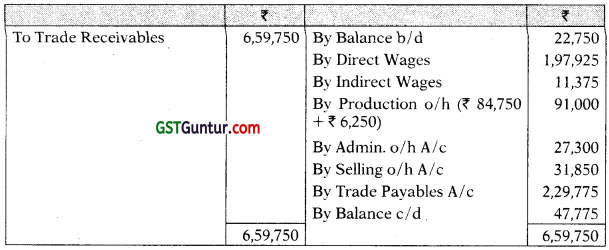
Stores Control A/c
Wages Control A/c
Work-in-Progress A/c
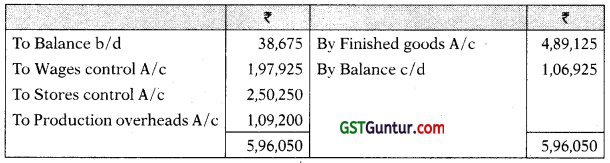
Production Overheads A/c
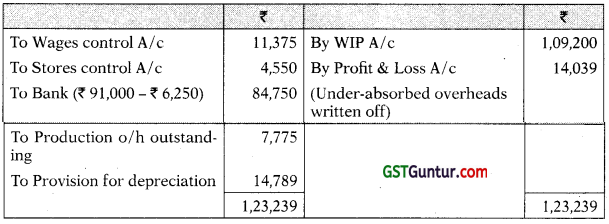
Finished Goods A/c
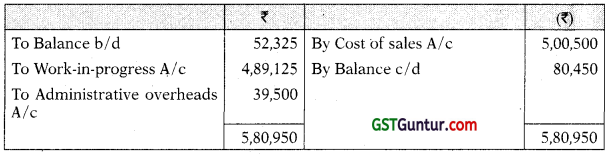
Administration Overheads A/c
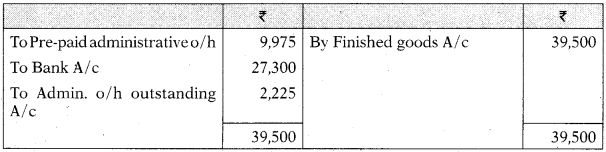
Cost of Sales A/c
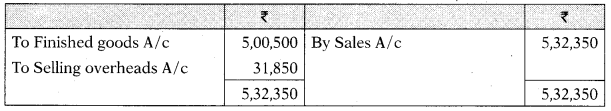
Sales A/c
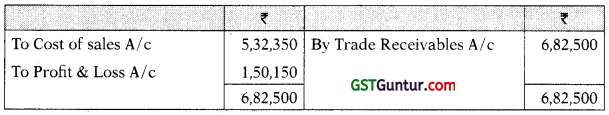
Factory Overheads/Production Overheads Outstanding A/c
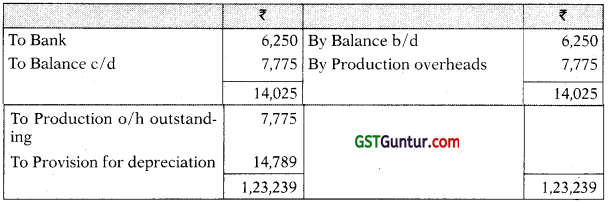
Finished Goods A/c
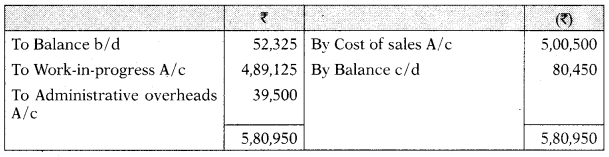
Administration Overheads A/c
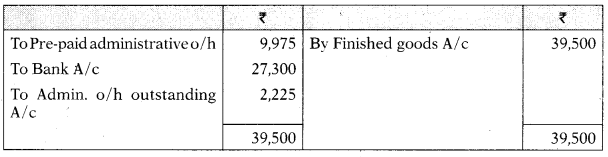
Cost of Sales A/c
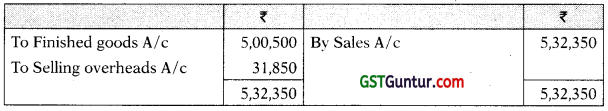
Sales A/c
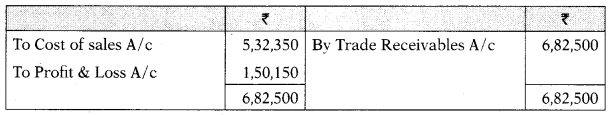
Factory Overheads/Production Overheads Outstanding A/c
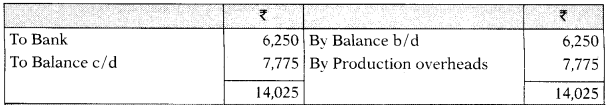
Prepaid Administration Overheads A/c
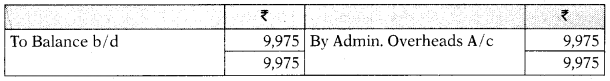
Provision for Depreciation A/c
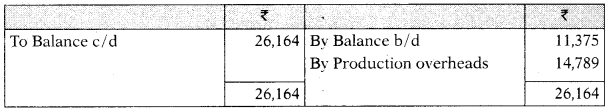
Provision for Doubtful Debts A/c
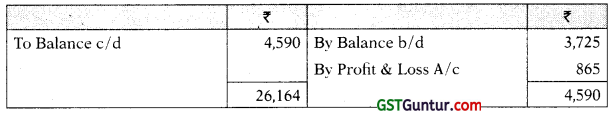
Profit & Loss A/c
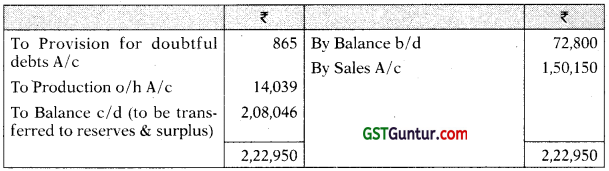
Trade Receivables A/c
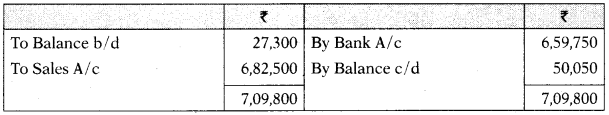
Trade Payables A/c
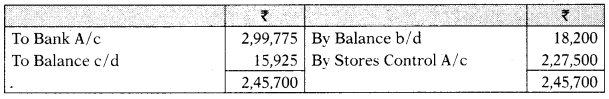
Non-Current Assets A/c
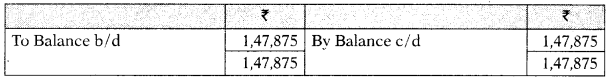
Bank A/c
Trial Balance as on 31.03.2021
| Debit ₹ | Credit ₹ | |
| Stores Control A/c | 13,650 | |
| WIP A/c | 1,06,925 | |
| Finished goods A/c | 80,450 | |
| Bank A/c | 47,775 | |
| Trade Payables A/c | 15,925 | |
| Non-Current Assets A/c | 1,47,875 | |
| Trade Receivables A/c | 50,050 | |
| Share Capital A/c | 1,82,000 | |
| Provision for Depreciation A/c | 26,164 | |
| Reserve And Surplus (Profit & loss A/c ) | 2,08,046 | |
| Production o/h outstanding A/c | 7,775 | |
| Administration o/h outstanding A/c | 2,225 | |
| Provision for doubtful debts A/c | 4,590 | |
| 4,46,725 | 4,46,725 |
![]()
Question 12.
A fire destroyed some accounting records of a company. You have been able to collect the following from the spoilt papers/records and as a result of consultation with accounting staff for the month of January:
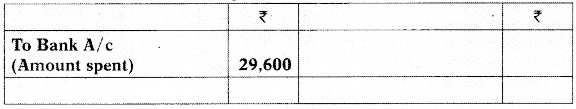
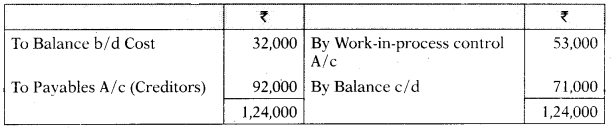
(i) Incomplete Ledger Entries:
Materials Control A/c
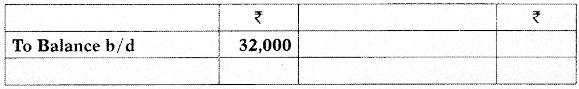
Work-In-Process Control A/c
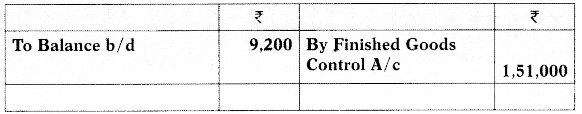
Payables (Creditors) A/c

Manufacturing Overheads Control A/c
Finished Goods Control A/c

(ii) Additional Information:
(1) The bank-book showed that ₹ 89,200 have been paid to creditors for raw-material.
(2) Ending inventory of work-in-process included materials of ₹ 5,000 on which 300 direct labour hours have been booked against wages and overheads.
(3) The job card showed that workers have worked for 7,000 hours. The wage rate is ₹ 10 per labour hour.
(4) Overhead recovery rate was ₹ 4 per direct labour hour.
You are required to complete the above accounts in the cost ledger of the company. [ICAI Module]
Answer:
Materials Control A/c
Manufacturing Overheads A/c
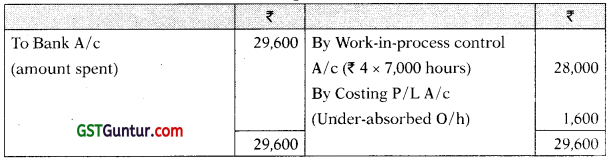
Work-in-Process Control A/c
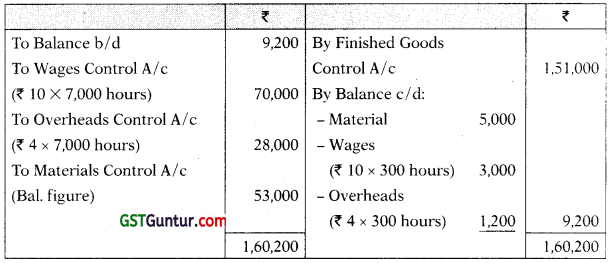
Finished Goods Control A/c
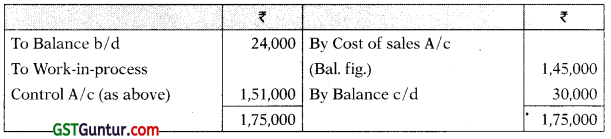
Payables (Creditors) A/c
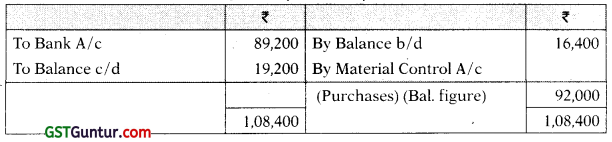
Question 13.
R Limited showed a net loss of ₹ 35,400 as per their cost accounts for the year ended 31.03.2021. However, the financial accounts disclosed a net profit of ₹ 67,800 for the same period. The following information was revealed as a result of scrutiny of the figures of cost accounts and financial accounts: [CA Inter Nov. 2012, June 2009, 8 Marks]
| ₹ | |
| (j) Administrative overhead under recovered | 25,500 |
| (ii) Factory overhead over recovered | 1,35,000 |
| (iii) Depreciation undercharged in Cost Accounts | 26,000 |
| (iv) Dividend received | 20,000 |
| (v) Loss due to obsolescence charged in Financial Accounts | 16,800 |
| (vi) Income tax provided | 43,600 |
| (iv) Bank interest credited in Financial Accounts | 13,600 |
| (viii) Value of opening stock: | |
| In Cost Accounts | 1,65,000 |
| In Financial Accounts | 1,45,000 |
| (ix) Value of closing stock: | |
| In Cost Accounts | 1,25,500 |
| In Financial Accounts | 1,32,000 |
| (x) Goodwill written-off in Financial Accounts | 25,000 |
| (xi) Notional rent of own premises charged in Cost Accounts | 60,000 |
| (xii) Provision for doubtful debts in Financial Accounts | 15,000 |
| Prepare a reconciliation statement by taking costing net loss as base. |
Answer:
Statement of Reconciliation
| ₹ | ₹ | |
| Net loss as per Cost Accounts Additions |
(35,400) | |
| Factory overhead over recovered | 1,35,000 | |
| Dividend Received | 20,000 | |
| Bank Interest received | 13,600 | |
| Difference in Value of Opening Stock (? 1,65,000-? 1,45,000) | 20,000 | |
| Difference in Value of Closing Stocky 1,32,000-₹ 1,25,500) | 6,500 | |
| Notional Rent of own Premises | 60,000 | 2,55,100 |
| Deductions | ||
| Administration overhead under recovered | 25,500 | |
| Depreciation under charged | 26,000 | |
| Loss due to obsolescence | 16,800 | |
| Income tax Provided | 43,600 | |
| Goodwill written-off | 25,000 | |
| Provision for doubtful debts | 15,000 | (1,51,900) |
| Net Profit as per Financial Accounts | 67,800 |
Question 14.
GK Ltd. showed net loss of ₹ 2,43,300 as per their financial accounts for the year ended 31.03.2021. However, cost accounts disclosed net loss of ₹ 2,48,300 for the same period. On scrutinizing both the set of books of account, the following information were revealed:
| ₹ | ||
| (i) | Works overheads over recovered 30,400 | 30,000 |
| (ii) | Selling overheads under recovered | 20,300 |
| (iii) | Administrative overheads under recovered | 27,700 |
| (iv) | Depreciation over charged in cost accounts | 35,100 |
| (v) | Bad debts w/off in financial accounts | 15,000 |
| (vi) | Preliminary Exp. w/off in financial accounts | 5,000 |
| (vii) | Interest credited during the year in financial accounts | 7,500 |
Prepare a reconciliation statement reconciling losses shown by financial and cost accounts by taking costing net loss as base. [CA Inter May 2018, 5 Marks]
Answer:
Reconciliation Statement
| ₹ | ₹ | |
| Loss as per Cost Accounts | (2,48,300) | |
| Add: Works overheads over recovered | 30,400 | |
| Depreciation over charged in cost accounts | 35,100 | |
| Interest credited during the year in financial accounts | 7,500 | 73,000 |
| Less: Selling overheads under recovered | 20,300 | |
| Administrative overheads under recovered | 27,700 | |
| Bad debts written off in financial accounts Preliminary Exp. written off in financial accounts |
15,000 5,000 |
68,000 |
| Loss as per Financial Accounts | (2,43,300) |
Question 15.
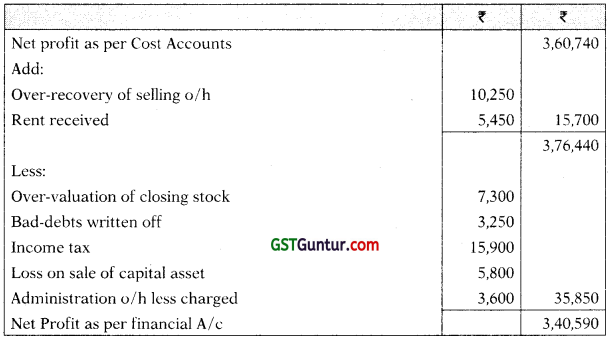
R Ltd. showed a Net Profit of ₹ 3,60,740 as per their cost accounts for the year ended 31st March, 2021.
The following information was revealed as a result of scrutiny of the figures from the both sets of accounts;
| Sr. No. | Particulars | ₹ |
| i. | Over recovery of selling overheads in cost accounts | 10,250 |
| ii. | Over valuation of closing stock in cost accounts | 7,300 |
| iii. | Rent received credited in financial accounts | 5,450 |
| iv. | Bad debts provided in financial accounts | 3,250 |
| V. | Income tax provided in financial accounts | 15,900 |
| vi. | Loss on sale of capital asset debited in financial accounts | 5,800 |
| vii. | Under recovery of administration overheads in cost accounts | 3,600 |
Prepare a reconciliation statement showing the profit as per financial records. [CA Inter Dec. 2021, 5 Marks]
Answer:
Question 16.
A manufacturing company has disclosed net loss of ₹ 48,700 as per their cost accounting records for the year ended 31st March, 2021. However their financial accounting records disclosed net profit of ₹ 35,400 for the same period. A scrutiny of data of both the sets of books of account revealed the following information:
| ₹ | |
| (i) Factory overheads under absorbed | 30,500 |
| (ii) Administrative overheads over absorbed | 65.000 |
| (iii) Depreciation charged in financial accounts | 2,25,000 |
| (iv) Depreciation charged in cost accounts | 2,70,000 |
| (v) Income-tax provision | 52,400 |
| (vi) Transfer fee (credited in financial accounts) | 10,200 |
| (vii) Obsolescence loss charged in financial accounts | 20,700 |
| (vili) Notional rent of own premises charged in cost accounts | 54,000 |
| (ix) Value of opening stock: | |
| (a) in cost accounts | 1,38,000 |
| (b) in financial accounts | 1,15,000 |
| (c) Value of closing stock | |
| (d) in cost accounts | 1,22,000 |
| (e) in financial accounts | 1,12,500 |
Prepare a Memorandum Reconciliation Account by taking costing loss as base. [CA Inter May 2014, Nov. 2010, 5 Marks]
Answer:
Memorandum Reconciliation Accounts
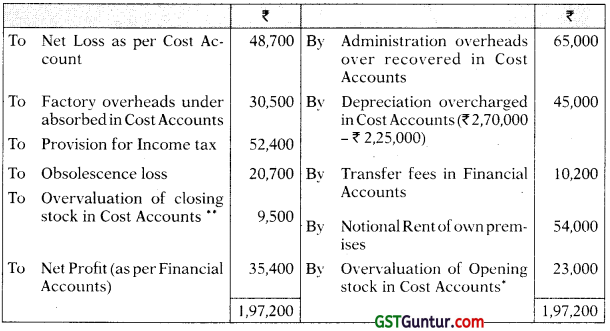
“Overvaluation of Opening Stock as per Cost Accounts
= Value in Cost Accounts – Value in Financial Accounts
= ₹ 1,38,000 – ₹ 1,15,000 = ₹ 23,000
“Overvaluation of Closing Stock as per Cost Accounts
= Value in Cost Accounts – Value in Financial Accounts
= ₹ 1,22,000 – ₹ 1,12,500 = ₹ 9,500
![]()
Question 17.
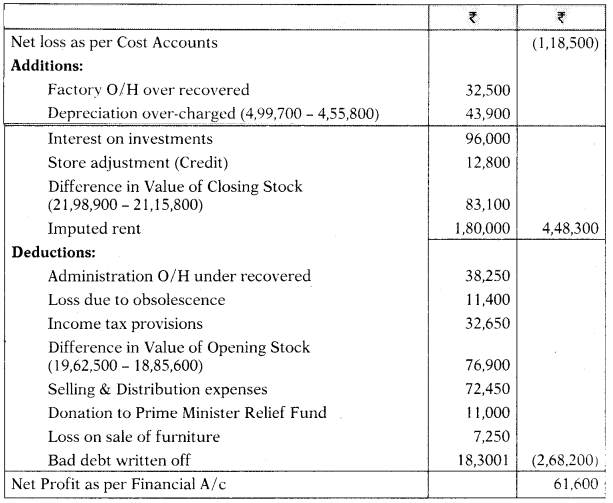
The net loss of Waywell Ltd. appeared at ₹ 1,18,500 as per cost records for the year ending 31.03.2021. The following information was revealed as a result of scrutiny of the figures of financial and cost records:
| ₹ | |
| Factory overheads over absorbed in cost accounts | 32,500 |
| Administrative overheads under absorbed in cost accounts | 38,250 |
| Depreciation charged in financial accounts | 4,55,800 |
| Depreciation recovered in cost accounts | 4,99,700 |
| Loss due to obsolescence charged in financial accounts | 11,400 |
| Income tax provision made in financial accounts | 32,650 |
| Interest on investments not included in cost accounts | 96,000 |
| Store adjustment (Credit) in financial accounts | 12,800 |
| Value of opening stock in: Cost accounts | 18,85,600 |
| Financial accounts | 19,62,500 |
| Value of closing stock in: Cost accounts | 21,15,800 |
| Financial accounts | 21,98,900 |
| Imputed rent charged in cost accounts | 1,80,000 |
| Selling and distribution expenses not charged in cost accounts | 72,450 |
| Donation to Prime Minister Relief Fund | 11,000 |
| Loss on sale of furniture | 7,250 |
| Bad debts written off | 18,300 |
Prepare a reconciliation statement and arrive at the profit or loss as per financial accounts. [CA Inter May 2019, 8 Marks]
Answer:
Statement of Reconciliation
Question 18.
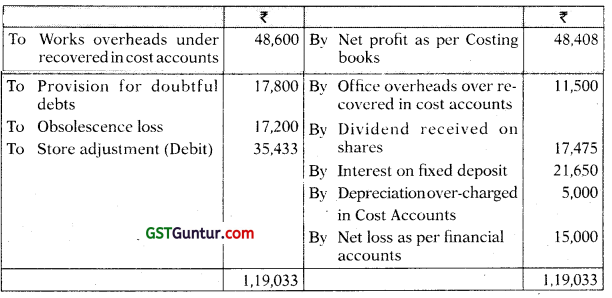
M/s Abid Private Limited disclosed a net profit of ₹ 48,408 as per cost books for the year ending 31st March 2021. However, financial accounts disclosed net loss of ₹ 15,000 for the same period. On scrutinizing both the set of books of account, the following information was revealed:
| Works Overheads under- recovered in Cost Books | 48,600 |
| Office Overheads over- recovered in Cost Books | 11,500 |
| Dividend received on Shares | 17,475 |
| Interest on Fixed Deposits | 21,650 |
| Provision for doubtful debts | 17,800 |
| Obsolescence loss not charged in Cost Accounts | 17,200 |
| Stores adjustments (debited in Financial Accounts) | 35,433 |
| Depreciation charged in financial accounts | 30,000 |
| Depreciation recovered in Cost Books | 35,000 |
Prepare a Memorandum Reconciliation Account. [CA Inter May 2019, 5 Marks]
Answer:
Memorandum Reconciliation Account
Question 19.
The Trading and Profit & Loss Account of a company for the year ended 31.03.2021 is as under:
Trading and Profit and Loss Account
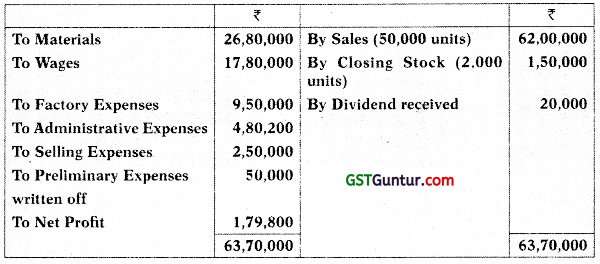
In the Cost Accounts:
(i) Factory expenses have been allocated to production at 20% of Prime Cost.
(it) Administrative expenses absorbed at 10% of factory cost.
(iii) Selling expenses charged at ₹ 10 per unit sold.
Prepare the Costing Profit and Loss Account of the company and reconcile the Profit/Loss with the profit as shown in the Financial Accounts.
[CA Inter Nov. 2016, 8 Marks]
Answer:
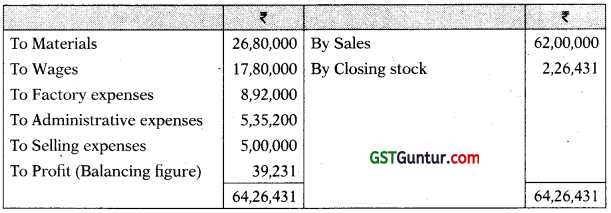
Preparation of Cost Sheet
| ₹ | |
| Materials | 26,80,000 |
| Wages | 17,80,000 |
| Prime Cost | 44,60,000 |
| Add: Factory expenses (20% of ₹ 44,60,000) | 8,92,000 |
| Factory Cost | 53,52,000 |
| Add: Administrative expenses (10% of ₹ 53,52,000) | 5,35,200 |
| Cost of Production | 58,87,200 |
| Less: Closing stock [(₹ 58,87(200 T- 52,000 units) × 2,000 units) | (2,26,431) |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 56,60,769 |
| Add: Selling expenses (₹ 10 × 50,000 units) | 5,00,000 |
| Cost of Sales | 61,60,769 |
| Profit (Balancing figure) | 39,231 |
| Sales Value | 62,00,000 |
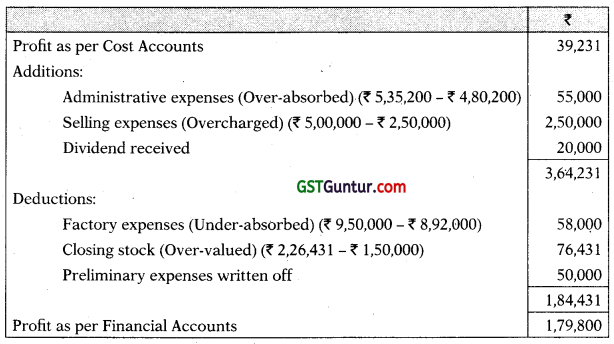
Note: It has been assumed that administrative expenses are related with production activities
Costing Profit and Loss Account
Reconciliation of profit as per Cost Accounts and as per Financial Accounts
![]()
Question 20.
You are given the following information of the cost department of a manufacturing company:
| ₹ | |
| Stores | |
| Opening Balance | 12,60,000 |
| Purchases | 67,20,000 |
| Transfer from work-in-progress | 33,60,000 |
| Issue to work-in-progress | 67,20,000 |
| Issue to repairs and maintenance | 8,40,000 |
| Shortage found in stock taking | 2,52,000 |
| Work-in-progress: | |
| Opening Balance | 25,20,000 |
| Direct wages applied . | 25,20,000 |
| Overhead applied | 90,08,000 |
| Closing Balance | 15,20,000 |
Finished products:
Entire output is sold at a profit of 12% on actual cost from work-in-progress Other information:
| Wages incurred | 29,40,000 |
| Overhead incurred | 95,50,000 |
| Income from Investment | 4,00,000 |
| Loss on sale of fixed assets | 8,40,000 |
Shortage in stock taking is treated as normal loss.
You are required to prepare:
(i) Stores control account
(ii) Work-in-progress control account
(iii) Costing Profit and Loss account
(iv) Profit and Loss account and
(v) Reconciliation statement [CA Inter May 2011, May 2005, 12 Marks]
Answer:
Stores Ledger Control Account
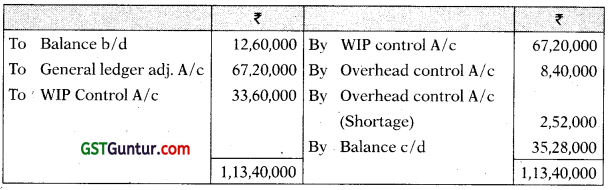
WIP control Account
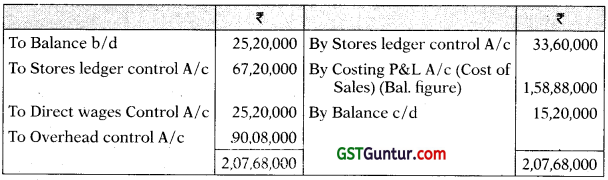
Costing Profit and Loss A/c
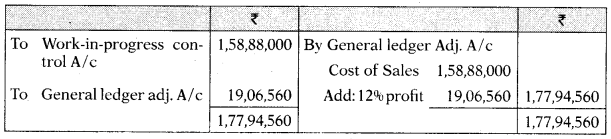
Financial Profit and Loss A/c
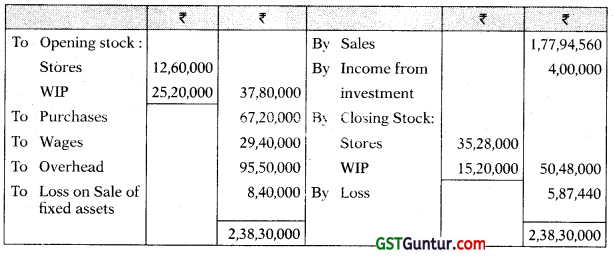
Reconciliation Statement

Working Notes:
Overhead Control Account
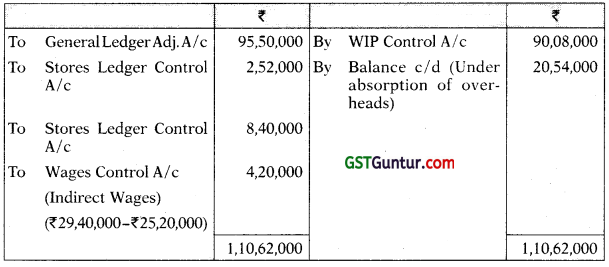
Question 21.
The following is the Trading and Profit & Loss Account of Omega Limited:
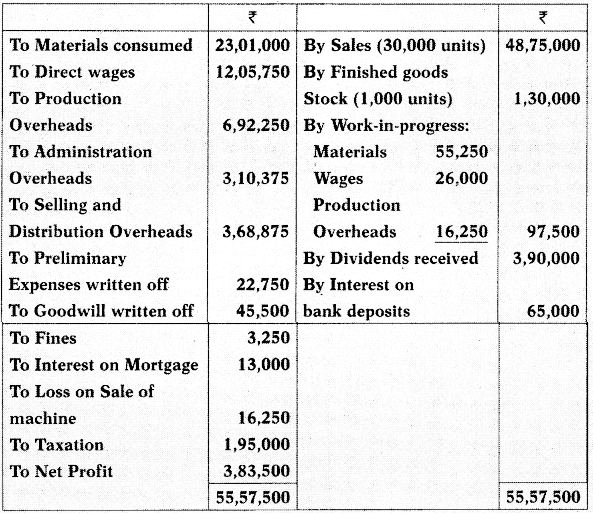
Omega Limited manufactures a standard unit.
The Cost Accounting records of Omega Ltd. Show the following:
(i) Production overheads have been charged to work-in-progress at 20% on Prime cost.
(ii) Administration Overheads have been recovered at ₹ 9.75 per finished Unit.
(iii) Selling & distribution Overheads have been recovered at ₹ 13 per Unit sold.
(iv) The Under-absorption or Over-absorption of Overheads has not been transferred to costing P & L A/c.
Required:
(i) Prepare a proforma Costing Profit & Loss account, indicating net profit.
(ii) Prepare Control accounts for production overheads, administration Overheads and selling & distribution Overheads.
(iii) Prepare a statement reconciling the profit disclosed by the cost records with that shown in Financial accounts. [CA Inter Nov. 2005, 10 Marks]
Answer:
(i) Costing Profit & Loss A/c
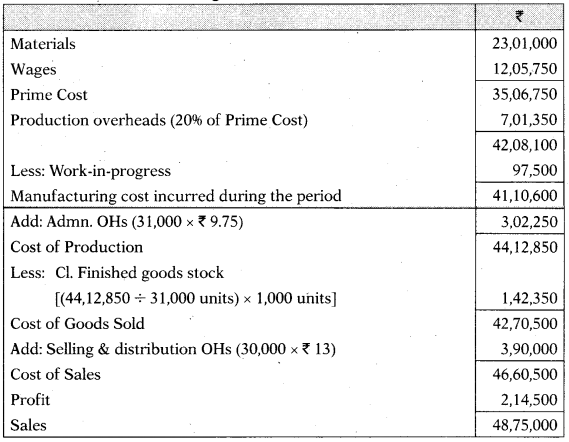
(ii) Production OH A/c
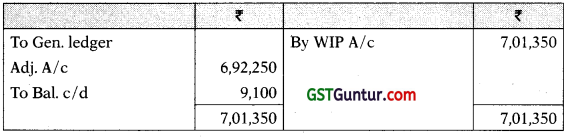
Administration OH A/c
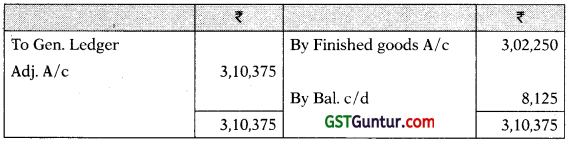
Selling & Distribution OH A/c
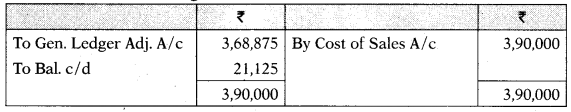
(iii) Reconciliation Statement
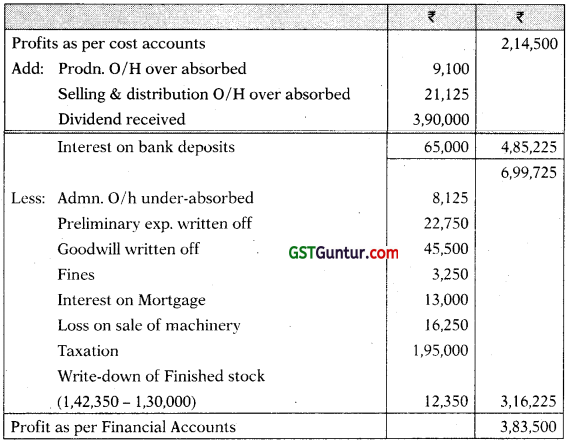
Question 22.
The financial books of a company reveal the following data for the year ended 31st March, 2021:
| ₹ | |
| Opening Stock: | |
| Finished goods 625 units | 1,06,250 |
| Work-in-process | 92,000 |
| 01.04.2020 to 31.03.2021 | |
| Raw materials consumed | 16,80,000 |
| Direct Labour | 12,20,000 |
| Factory overheads | 8,44,000 |
| Administration overheads (production related) | 3,96,000 |
| Dividend paid | 2,44,000 |
| Bad Debts | 36,000 |
| Selling and Distribution O verheads | 1,44,000 |
| Interest received | 76,000 |
| Rent received | 92,000 |
| Sales 12,615 units | 45,60,000 |
| Closing Stock: Finished goods 415 units | 91,300 |
| Work-in-process | 82,400 |
The cost records provide as under:
- Factory overheads are absorbed at 70% of direct wages
- Administration overheads are recovered at 15% of factory cost.
- Selling and distribution overheads are charged at 16 per unit sold.
- Opening Stock of finished goods is valued at ? 240 per unit.
- The company values work-in-process at factory cost for both Financial and Cost Profit Reporting.
Required:
(i) Prepare statements for the year ended 31st March, 2021 showing:
- the profit as per financial records
- the profit as per costing records
(ii) Prepare a statement reconciling the profit as per costing records with the profit as per financial records. [CA Inter May 2021 RTP]
Answer:
Statement of Profit as per financial records
(for the year ended March 31, 2021)
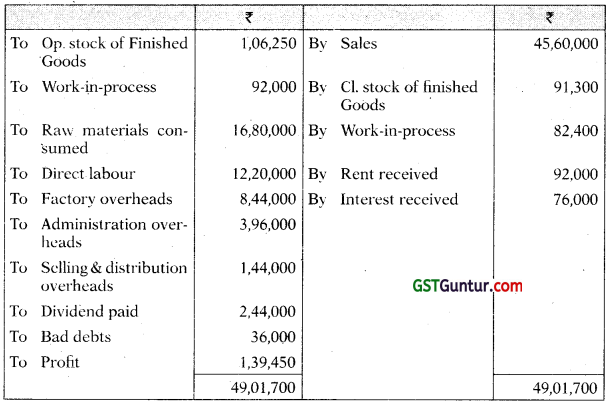
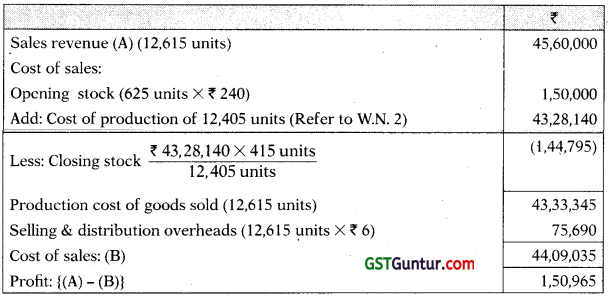
Statement of Profit as per costing records
(for the year ended March 31, 2021)
Statement of Reconciliation
(Reconciling the profit as per costing records with profit as per financial records)
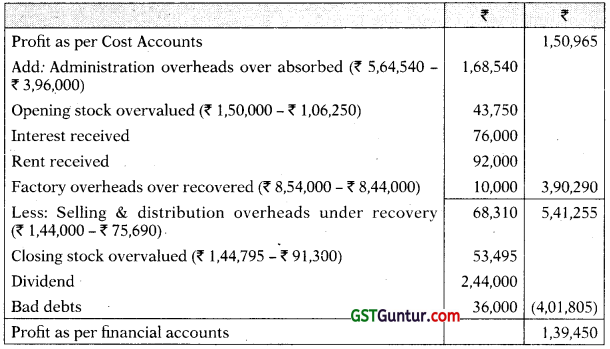
Working notes:
1. Number of units produced
| Units | |
| Sales | 12,615 |
| Add: Closing stock | 415 |
| Total | 13,030 |
| Less: Opening stock | (625) |
| Number of units produced | 12,405 |
2. Cost Sheet
| ₹ | |
| Raw materials consumed | 16,80,000 |
| Direct labour | 12,20,000 |
| Prime cost | 29,00,000 |
| Factory overheads (70% of direct wages) | 8,54,000 |
| Factory cost | 37,54,000 |
| Add: Opening work-in-process | 92,000 |
| Less: Closing work-in-process | (82,400) |
| Factory cost of goods produced | 37,63,600 |
| Administration overheads (15% of factory cost) | 5,64,540 |
| Cost of production of 12,405 units (W.N.l)
Cost of production per unit (₹ 43,25,140 / 12,405 units) = ₹ 348.90 |
43,28,140 |
![]()
Question 23.
The profit and loss account of ABC Ltd. for the year ended 31st March, 2021 is given below:
Profit and Loss account
(For the year ended 31st March, 2021)
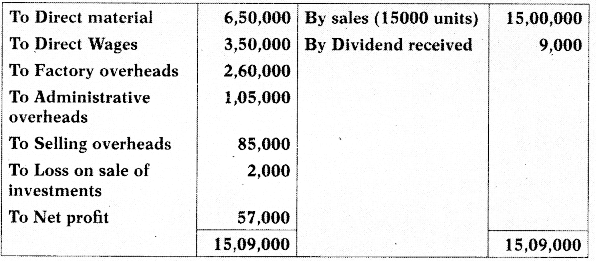
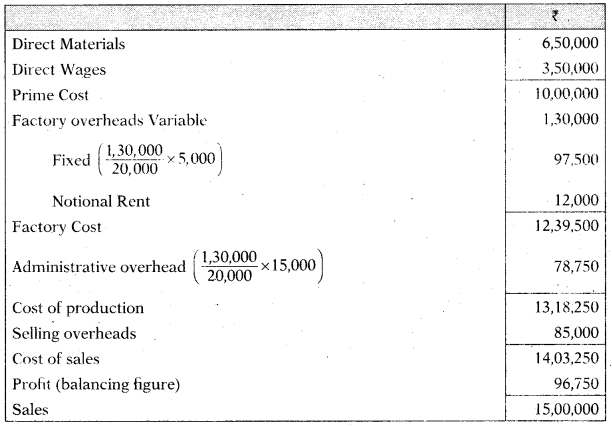
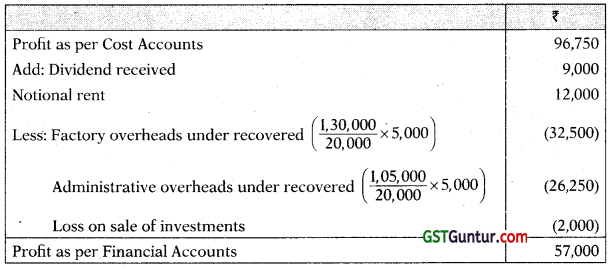
- Factory overheads are 50% fixed and 50% variable.
- Administrative overheads are 100% fixed.
- Selling overheads are completely variable
- Normal production capacity of ABC Ltd. is 20,000 units.
- Indirect Expenses are absorbed in the cost accounts on the basis of normal production capacity.
- Notional rent of own premises charged in cost accounts is amounting to ₹ 12,000
You are required to:
(i) Prepare a cost sheet and ascertain the profit as per cost records for the year ended 31st March, 2021.
(ii) Reconcile the profit as per Financial Records with profit as per Cost Records. [CA Inter July 2021, 10 Marks]
Answer:
Cost Sheet
Reconciliation Statement
Question 24.
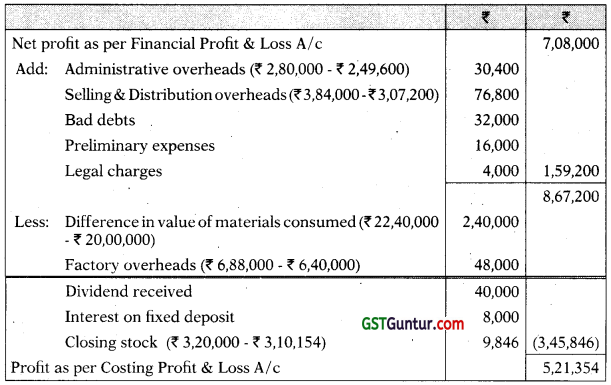
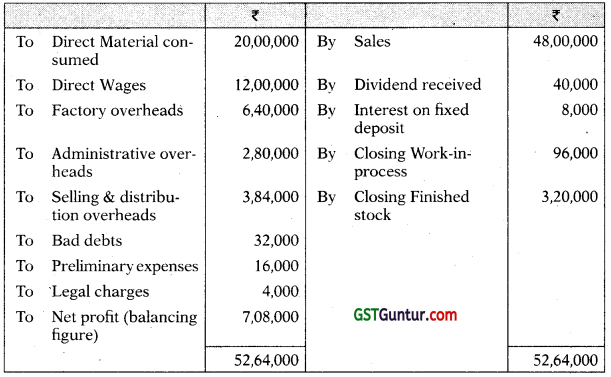
The following figures have been taken from the financial accounts of a manufacturing firm for the year ended 31st March, 2021:
| ₹ | |
| Direct material consumption | 20,00,000 |
| Direct wages | 12,00,000 |
| Factory overheads | 6,40,000 |
| Administrative overheads | 2,80,000 |
| Selling and distribution overheads | 3,84,000 |
| Bad debts | 32,000 |
| Preliminary expenses written off | 16,000 |
| Legal charges | 4,000 |
| Dividend received | 40,000 |
| Interest on fixed deposit | 8,000 |
| Sales: 48,000 units | 48,00,000 |
| Closing stock: | |
| Finished stock: 4,000 units | 3,20,000 |
| Work-in-process | 96,000 |
The cost accounts for the same period reveal that the Direct Material consumption was ? 22,40,000; Factory overhead is recovered at 20% on prime cost; Administration overhead is recovered @ ? 4.8 per unit of production; and Selling and Distribution overheads are recovered at ? 6.40 per unit sold.
Required:
Prepare Costing and Financial Profit & Loss Accounts and Reconcile the difference in the profit as arrived at in the two sets of accounts. [CA Inter, MTP]
Answer:
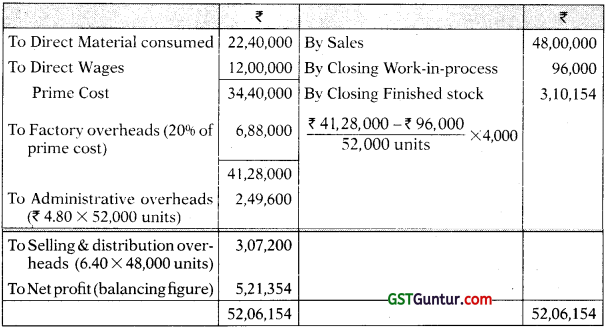
Units produced = Units sold + Closing stock – Opening stock
= 48,000 + 4,000 – 0 = 52,000 units
Financial Profit and Loss Account
Reconciliation Statement