Students should practice Cost Accounting Records & Cost Audit under the Companies Act, 2013 – Corporate and Management Accounting CS Executive MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Cost Accounting Records & Cost Audit under the Companies Act, 2013 – Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
Question 1.
June 2015: The objective of CAS-1 is
(A) Collection, allocation, apportionment, and absorption of over-heads
(B) Determination of capacity
(C) Preparation of cost statement
(D) Determination of average / equal¬ized transportation cost
Answer:
(C) Preparation of cost statement
Question 2.
June 2015: Which section of the Companies Act, 2013 deals with an audit of cost accounting records –
(A) Section 158
(B) Section 148
(C) Section 168
(D) Section 139
Answer:
(B) Section 148
Question 3.
June 2015: Which of the following is an objective to be achieved through Cost Accounting Standards –
(A) To assist cost accountants in the preparation of uniform cost statements
(B) To provide better guidelines on standard cost accounting practices
(C) To help Indian industry and the Government towards better cost management
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 4.
Dec 2015: The functions of a cost auditor involve___
(A) Examining the inventory records
(B) Capacity utilization
(C) Proper utilization of labor
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 5.
June 2016: Cost Accounting Standard is related to bringing uniformity and consistency in the principles and methods of determining the selling and distribution overheads with reasonable accuracy.
(A) 10
(B) 12
(C) 15
(D) 4
Answer:
(C) 15
Question 6.
June 2016: Section of the Companies Act, 2013 gives the cost auditor the same power as the financial auditor has under the section of the Companies Act, 2013.
(A) 148, 143
(B) 143, 148
(C) 147, 148
(D) 143, 144
Answer:
(A) 148, 143
Question 7.
June 2016: Match the following statements with prescribed forms:
| Statements | Forms |
| (i) Cost Audit Report to Central Government by the company | (a) CRA3 |
| (ii) Cost Auditor to submit a report to the Board of Directors | (b) CRA2 |
| (iii) Intimation of appointment of Cost Auditor to MCA by the company | (c) CRA4 |
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
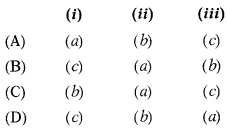
Answer:
(B)
Question 8.
June 2016: Which one is not the objective of Cost Accounting Standards
(A) To bring uniformity and consistency in the principles and methods
(B) To help industry and the Government towards better cost management
(C) To control accounting policies of companies so as to protect investors’ interest
(D) To determine the pollution control costs with reasonable accuracy.
Answer:
(C) To control accounting policies of companies so as to protect investors’ interest
Question 9.
June 2016: Which one of the following is not a statistical technique of cost audit —
(A) Monte-Carlo simulation
(B) Inter-firm comparison
(C) Network analysis
(D) Exponential smoothing
Answer:
(C) Network analysis
Question 10.
Dec 2016: Which one is NOT the objective of Cost Accounting Standards?
(A) To bring uniformity and consistency in the principles and methods,
(B) To help industry and the Government towards better cost management.
(C) To control accounting policies of companies so as to protect investors’ interest
(D) To determine the pollution control costs with reasonable accuracy.
Answer:
(C) To control accounting policies of companies so as to protect investors’ interest
Question 11.
June 2017: The chief objective of cost accounting is to:
(A) Earn more profit
(B) Increase production
(C) Provide information for management for planning and control
(D) Fix the price
Answer:
(C) Provide information for management for planning and control
Question 12.
June 2017: Cost accounting differs from financial accounting in respect of:
(A) Recording Cost
(B) Ascertaining Cost
(C) Control of Cost
(D) Reporting of Cost
Answer:
(D) Reporting of Cost
Question 13.
June 2017: The branch of accoun¬ting which primarily deals with processing and accounting data for internal use in concern is:
(A) Financial accounting
(B) Cost accounting
(C) Management accounting
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Financial accounting
Question 14.
June 2017: A good costing system gives equal emphasis on cost ascertainment and cost
(A) Reduction
(B) Control
(C) Maximization
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B) Control
Question 15.
Dec 2017: Match the following Cost Accounting Standards with the titles:
| CAS | Title |
| (a) CAS-2 | (1) Material Cost |
| (b) CAS-6 | (2) Direct Expenses |
| (c) CAS-10 | (3) Pollution Cost Control |
| (d)CAS-14 | (4) Capacity Determination |
Codes:

Answer:
(D)
Question 16.
Dec 2017: Management Accounting and Cost Accounting are to each other.
(A) Complementary
(B) Supplementary
(C) Opposite
(D) Independent
Answer:
(B) Supplementary
Question 17.
Dec 2017: Practical difficulty in the installation of a costing system is:
(A) Lack of support from top management
(B) Shortage of trained staff
(C) Resistance from existing staff
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 18.
Dec 2017: A PSU company shall within 30 days from the date of receipt of the report of the cost auditor furnish an explanation on every reservation or qualification contained therein to:
(A) The Registrar
(B) Central Government
(C) The Shareholders
(D) The Parliament
Answer:
(B) Central Government
Question 19.
Dec 2017: The social purpose of cost audit is:
(A) Detection of errors and frauds
(B) Facilitating the fixation of prices of goods and services
(C) Promoting corporate governance
(D) Inculcation of cost-consciousness
Answer:
(B) Facilitating the fixation of prices of goods and services
Question 20.
Dec 2017: Every PSU company, within a period of 30 days from the date of receipt of cost audit report, furnish to the Central Government with such report full explanation on every reservation or qualification contained in the report in:
(A) Form CRA-3
(B) Form CRA-4
(C) Form CRA-5
(D) Form CRA-6
Answer:
(B) Form CRA-4
Question 21.
Dec 2017: Section 148 of the Companies Act, 2013 gives:
(A) No powers to the cost auditor as the financial auditor has u/s 143 of Companies Act, 2013
(B) Same powers to the cost auditor as the financial auditor has u/s 143 of Companies Act, 2013
(C) More powers to the cost auditor than the financial auditor has u/s 143 of Companies Act, 2013
(D) Lesser powers to the cost auditor than the financial auditor has u/s 143 of Companies Act, 2013
Answer:
(B) Same powers to the cost auditor as the financial auditor has u/s 143 of Companies Act, 2013
Question 22.
Dec 2017: Profitability and productivity measurement technique used by cost auditor while doing cost audit is categorized under:
(A) Economic Techniques
(B) Statistical Techniques
(C) Personnel Techniques
(D) General Techniques
Answer:
(C) Personnel Techniques
Question 23.
Dec 2017: Non-compliance of which attribute of financial statements makes a company, besides invoking penalties, impairs the confidence of the public investors:
(A) Authenticity
(B) Compliance with Law
(C) Freedom from Bias
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(B) Compliance with Law
Question 24.
June 2018: Every cost auditor, shall submit the cost audit report along with his or its reservation or qualification or suggestions, if any, in the form:
(A) CRA-1
(B) CRA-2
(C) CRA-3
(D) CRA-4
Answer:
(C) CRA-3
Question 25.
June 2018: Which of the following statement is not correct?
(A) Cost audit helps the Government in the fixation of ceiling price of essential commodities.
(B) Cost audit helps in improvement if the productivity of human, physical, and financial resources of the enterprises.
(C) The cost auditor submits the report in an annual general meeting organized by shareholders.
(D) Cost auditor is appointed by the board of directors with the previous approval of the Central Government.
Answer:
(C) The cost auditor submits the report in an annual general meeting organized by shareholders.
Question 26.
June 2018: Every cost auditor shall forward his duly signed report to the board of directors of the company within a period from the closure of the financial year to which the report relates.
(A) 30 days
(B) 120 days
(C) 90 days
(D) 180 days
Answer:
(D) 180 days
Question 27.
June 2018: Which of the following is not a Statistical technique of Cost Audit?
(A) Activity Sampling
(B) Attitude Survey
(C) Exponential Smoothing
(D) Monte Carlo Simulation
Answer:
(B) Attitude Survey
Question 28.
June 2018: Which of the following is not an objective of the Cost Accounting Standards issued by the Institute of Cost and Works Accountants of India?
(A) Provide better guidelines on standard cost accounting practices.
(B) Enable the comparability of financial statements and improve the reliability and usefulness of financial statements.
(C) Assist cost accountants in the preparation of uniform costs statements.
(D) Help Indian industry and the Government towards better cost management
Answer:
(B) Enable the comparability of financial statements and improve the reliability and usefulness of financial statements.
Question 29.
Dec 2018: Which of the following Sections of the Companies Act, 2013 deals with the audit of Cost Accounting Records?
(A) Section 128
(B) Section 145
(C) Section 147
(D) Section 148
Answer:
(D) Section 148
Question 30.
Dec 2018: Remuneration of cost auditor is to be determined in accordance with provisions of:
(A) Section 148(3) of the Companies Act, 2013
(B) Section 143(12) of the companies Act, 2013
(C) Section 147(1) of the Companies Act, 2013
(D) Section 148(5) of the Companies Act, 2013
Answer:
(A) Section 148(3) of the Companies Act, 2013
Question 31.
Dec 2018: The Cost Accounting Standard (CAS) concerned with quality control cost is:
(A) CAS-21
(B) CAS-19
(C) CAS-14
(D) CAS-8
Answer:
(A) CAS-21
Question 32.
Dec 2018: Cost Audit as per the direction of the Central Government shall be conducted by:
(A) A Chartered Accountant in practice
(B) A Cost Accountant in practice
(C) A Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant in practice
(D) The Auditor General of India
Answer:
(B) A Cost Accountant in practice
Question 33.
Dec 2018: Which of the following Cost Accounting Standards (CAS) is related to “Depreciation and Amortization”?
(A) CAS-4
(B) CAS-12
(C) CAS-16
(D) CAS-21
Answer:
(C) CAS-16
Question 34.
June 2019: Maintenance of cost records relating to the utilization of materials, labor, and other items of cost, in the manner as prescribed by specified class of companies engaged in the:
(A) Production of goods only
(B) Providing services only
(C) Production of such goods and providing such services as may be prescribed
(D) Production of such goods or providing such services as may be prescribed
Answer:
(D) Production of such goods or providing such services as may be prescribed
Question 35.
June 2019: Every cost auditor, who conducts an audit of the cost records of a company, shall submit a report in:
(A) General form
(B) Form CRA-1
(C) Form CRA-2
(D) Form CRA-3
Answer:
(D) Form CRA-3
Question 36.
June 2019: ‘Cost-benefit analysis’ falls under:
(A) Scientific techniques
(B) Accounting or economic techniques
(C) Personnel techniques
(D) Statistical techniques
Answer:
(B) Accounting or economic techniques
Question 37.
June 2019: Which is not a social purpose of cost audit?
(A) Promoting corporate governance
(B) Facilitate in fixation of reasonable prices of goods and services
(C) Improvement of human productivity
(D) Pinpointing areas of inefficiency
Answer:
(A) Promoting corporate governance
Question 38.
June 2019: Principles to determine production overheads relates to:
(A) CAS 5
(B) CAS 7
(C) CAS 3
(D) CAS 2
Answer:
(C) CAS 3
Question 39.
June 2019: _____is concerned with historical records, while is concerned with historical cost with pre-determined cost.
(A) Cost Accounting, Financial Ac-counting
(B) Financial Accounting, Cost Ac-counting
(C) Financial Accounting, Manage-ment Accounting
(D) Management Accounting, Cost Accounting
Answer:
(B) Financial Accounting, Cost Ac-counting
