Students should practice Corporate Financial Reporting – Corporate and Management Accounting CS Executive MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Corporate Financial Reporting – Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
Question 1.
Which of the following action can be taken to improve EVA?
(A) Improve Asset Turnover Ratios
(B) Change the capital structure by substituting lower-cost debt for higher-cost equity.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 2.
Which of the following matters are required to be covered in Management Discussion & Analysis Report?
I. Industry Structure & Developments
II. Opportunities and threats
III. Auditors negative remarks
IV. Product-wise performance
V. Risks and concerns
VI. Notes to financial statements
VII. SEBI Directions
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) IV, III, V & I only
(B) I, II, III & VI only
(C) IV, II, V & I only
(D) I, II, IV, VI & VI only
Answer:
(C) IV, II, V & I only
Question 3.
Market value added is the difference between
(A) EPS and Price Earning per share
(B) Cost of capital and economic value added
(C) The Company’s adjusted value for inflation and book value of various assets
(D) The Company’s market and book value of shares.
Answer:
(D) The Company’s market and book value of shares.
Question 4.
In the audit report, the auditor expresses his opinion of whether the financial statement of the company gives in conformity with the accounting principles.
(A) True & fair view
(B) Full & fair view
(C) True & reasonable view
(D) Full & reasonable view
Answer:
(A) True & fair view
Question 5.
_______ represents the economic profits generated by a business above and beyond the minimum return required by all providers of capital.
(A) Shareholder Value Added (SVA)
(B) Economist Value Added (EVA)
(C) Market Makers Value Added (MMVA)
(D) Debt holders Value Added (DVA)
Answer:
(A) Shareholder Value Added (SVA)
Question 6.
Match List-I with List-II:
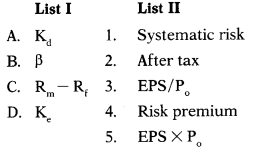
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
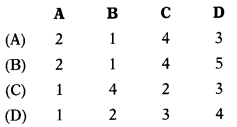
Answer:
(A)
Question 7.
The auditor of a company is required to give his report in accordance with the provisions of______of the Companies Act, 2013.
(A) Section 148
(B) Section 143
(C) Section 149
(D) Section 147
Answer:
(B) Section 143
Question 8.
Which of the following is not an objective of financial reporting given by the Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB)?
(A) The information should be useful to both, the present and potential investors.
(B) It should provide information about how the management of an enterprise has discharged its stewardship responsibilities to owners for the use of enterprise resources entrusted to it.
(C) It should provide information about the enterprise’s financial performance during a period.
(D) It should forecast the future performance and financial position of the enterprise using past data.
Answer:
(D) It should forecast the future performance and financial position of the enterprise using past data.
Question 9.
____can be defined as the value created by the activities of a firm, that is, sales less the cost of bought-in goods and services.
(A) Economic value added
(B) Value added,
(C) Market value-added
(D) Shareholders value-added
Answer:
(B) Value added,
Question 10.
Value-added can be defined as
(A) Wealth generated by the owners and shareholders of the business entity
(B) Value added by increasing net profit of the company
(C) Wealth generated by the entity through the collective efforts of capital providers, management, and employees
(D) Net increasing in assets of the business organization.
Answer:
(C) Wealth generated by the entity through the collective efforts of capital providers, management, and employees
Question 11.
Which of the following is the advantage of the Value Added Statement?
(A) It helps in judging the productivity of the company.
(B) It helps in ascertaining result le. profit earned or loss suffered in business during a particular period.
(C) It provides up-to-date information about the various assets that the firm possesses and the liabilities the firm owes.
(D) It measures the past performance of the business entity and depicts its current financial position.
Answer:
(A) It helps in judging the productivity of the company.
Question 12.
Which of the following is deducted in Value Added Statement in the ‘Value Added’ section?
(A) Other Income
(B) Replacement Reserve
(C) Deferred tax account
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 13.
Which of the following is appears in the ‘Value Applied’ section in the value-added statement?
(A) Decrease in stock
(B) Manufacturing & Other Expenses
(C) Depreciation
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(C) Depreciation
Question 14.
Statement I: EWA measures whether the operating profit is sufficient enough to cover the cost of capital.
Statement II: If a company’s EVA is negative it is destroying shareholder’s wealth even though it may be reporting positive and growing EPS or return on capital employed.
Which statement is correct and which statement is false?
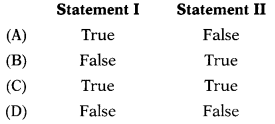
Answer:
(C)
Question 15.
If we add ‘Cost of Capital’ ‘Economic Value Added’ we get
(A) Profit After Tax
(B) Net Operating Profit After Tax
(C) Gross Value Added
(D) Earnings before Interest and tax
Answer:
(B) Net Operating Profit After Tax
Question 16.
To which type of company the Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2016 (CARO) applies?
(A) Banking company
(B) The Insurance company
(C) One Person Company
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 17.
CARO, 2016 applies to a private limited company being a subsidiary or holding company of a public company, having a paid-up capital and reserves and surplus not more than____as on the balance sheet date
(A) ₹ 5 Crore
(B) ₹ 1 Crore
(C) ₹ 2 Crore
(D) ₹ 10 Crore
Answer:
(B) ₹ 1 Crore
Question 18.
CARO, 2016 applies to a private limited company that has total revenue as disclosed in Scheduled El to the Companies Act, 2013 including revenue from discontinuing operations exceeding____during the financial year as per the financial statements.
(A) ₹ 15 Crore
(B) ₹ 100 Crore
(C) ₹ 10 Crore
(D) ₹ 25 Crore
Answer:
(C) ₹ 10 Crore
Question 19.
To which type of company the Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2016 (CARO) applies?
1. A private limited company is a subsidiary or holding company of a public company, having a paid-up capital and reserves & surplus of more than ₹ 2 Crore as on the balance sheet date.
2. A private limited company that has total borrowings exceeding ₹ 2 Crore from any bank or financial institution at any point of time during the financial year.
3. A private limited company that has a total revenue as disclosed in Scheduled III to the Companies Act, 2013 (including revenue from discontinuing operations) less than ₹ 10 Crore during the financial year as per the financial statements.
Select the correct answer from the options given below
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) None of the 1, 2 or 3
Answer:
(A) 1 and 2 only
Question 20.
CARO, 2016 shall not apply to the auditor’s report on
(A) Income statement
(B) Financial statements
(C) Consolidated financial statements
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) Consolidated financial statements
Question 21.
As per CARO, 2016 auditor’s report must state whether the company has entered into any non-cash transactions with directors or persons connected with him as contained in___ of Companies Act, 2013
(A) Section 192
(B) Section 195
(C) Section 292
(D) Section 295
Answer:
(A) Section 192
Question 22.
The Board of every company referred to Section 135(1), shall ensure that the company spends, in every financial year, at least___ of the company made during the 3 immediately preceding financial years, in pursuance of its Corporate Social Responsibility Policy.
(A) 1% of the profits
(B) 2% of the profit before depreciation
(C) 2% of the average net profits
(D) 5% of the EBIT
Answer:
(C) 2% of the average net profits
Question 23.
Financial statement and Board’s Report shall be sent to every member of the company, to every trustee for the debenture-holder of any debentures issued by the company, and to all persons other than such member or trustee, being the person so entitled, not less than before the date of the meeting.
(A) 10 days
(B) 30 days
(C) 7 days
(D) 21 days
Answer:
(D) 21 days
Question 24.
A copy of the financial statements and Board’s report duly adopted at the AGM shall be filed with the Registrar within_____of the date of AGM.
(A) 60 days
(B) 30 days
(C) 90 days
(D) 21 days
Answer:
(B) 30 days
Question 25.
The Board of Directors of a company shall approve the financial statement and the Board’s report by means of resolutions passed:
(A) By circulation
(B) Shareholders ordinary resolution
(C) At meetings of the Board
(D) E-meeting
Answer:
(C) At meetings of the Board
Question 26.
As per Rule 8 of the Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014, the Report of the Board shall contain the particulars of contracts or arrangements with related parties Section 188 (1) in the:
(A) Form AOC-1A
(B) Form AOC-2
(C) Form AOC-3
(D) Form AOC-4A
Answer:
(B) Form AOC-2
Question 27.
Every listed company and every other public company having a paid-up share capital calculated at the end of the preceding financial year shall include, in the report by its Board of directors, a statement indicating the manner in which formal annual evaluation has been made by the Board of its own performance and that of its committees and individual directors.
(A) ₹ 5 Crore or more
(B) ₹ 50 Crore or more
(C) ₹ 25 Crore or more
(D) ₹ 10 Crore or more
Answer:
(C) ₹ 25 Crore or more
Question 28.
Which of the following is not one of the underlying principles of Corporate Governance?
(A) Openness
(B) Integrity
(C) Accountability
(D) Acceptability
Answer:
(D) Acceptability
Question 29.
Directors’ responsibilities are unlikely to include:
(A) A duty of care
(B) A duty to propose high dividends for shareholders
(C) A fiduciary duty
(D) A duty to keep proper accounting records
Answer:
(B) A duty to propose high dividends for shareholders
Question 30.
A director of a limited company may not be liable for wrongful trading if he
(A) Introduced into the balance sheet an asset based on a valuation of its brands sufficient to meet any shortfall.
(B) Took every step to minimize the potential loss to creditors.
(C) Increased the valuation of its inventories to cover any potential shortfall.
(D) Brought in some expected sales from next year into the current year.
Answer:
(B) Took every step to minimize the potential loss to creditors.
Question 31.
Which of the following actions will not help directors to protect themselves from non-compliance with their obligations and responsibilities?
(A) Keeping themselves fully informed about company affairs.
(B) Including a disclaimer clause in their service contracts.
(C) Ensuring that regular management accounts are prepared by the company.
(D) Seeking professional help
Answer:
(B) Including a disclaimer clause in their service contracts.
Question 32.
The corporate governance structure of a company reflects the individual company’s:
(A) Cultural and economic system
(B) Legal and business system
(C) Social and regulatory system
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 33.
CSR stands for
(A) Company Social Responsibility
(B) Corporate Social Rights
(C) Corporate Social Responsibility
(D) Company Social Rights
Answer:
(C) Corporate Social Responsibility
Question 34.
CSR and corporate governance represent a_____between business and society.
(A) Social climate
(B) Special contract
(C) Special climate
(D) Social contract
Answer:
(D) Social contract
Question 35.
Who are the stakeholders of the business that are concerned with CSR?
(A) Governments, employees, communities, partners, competitors
(B) Employees, research agencies, Governments, communities, trade organizations
(C) Suppliers, partners, employees, communities, investors, education institutions
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 36.
Corporate governance can be defined as:
(A) The system used by firms to control the actions of their employees.
(B) The election process used to vote in a new Board of Directors.
(C) The corporate compliance system used by the firm.
(D) The system used by firms to identify who the critical stakeholders are for the firm.
Answer:
(C) The corporate compliance system used by the firm.
Question 37.
The company shall obtain a certificate from either the ____ regarding the compliance of conditions of corporate governance of the listing agreement and annex the certificate with the director’s report, which is sent annually to all the shareholders of the company.
(A) Auditors
(B) Practicing Company Secretary
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Answer:
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Question 38.
Which type of director should be the head of the Stakeholders Grievance Committee?
(A) Executive director
(B) Non-executive director
(C) Senior most director
(D) Chairman appointed for share-holders meetings
Answer:
(B) Non-executive director
Question 39.
Which type of committee is not required to form for compliance with provisions of Corporate Governance under the Companies Act, 2013 and SEBI Regulations?
(A) Audit Committee
(B) Nomination & Remuneration Committee
(C) Stakeholders Grievance Commit-tee
(D) Corporate Governance Commit-tee
Answer:
(D) Corporate Governance Commit-tee
Question 40.
R Ltd. has disbursed a dividend of ₹ 75 on each equity share of ₹ 25. The market price of a share is ₹ 200. The corporate tax rate is 40%. Its cost of equity is
(A) 30.0%
(B) 37.5%
(C) 35.7%
(D) 33.5%
Hint:
75/200 = 0.375 i.e. 37.5% .
Answer:
(B) 37.5%
Question 41.
P Ltd. has 1,50,000 equity shares of ₹ 25 each and its current market value is ₹ 150 each. The before-tax profit of the company for the year just ended is ₹ 36,36,363. The tax rate is 34%. Cost of equity of P Ltd.
(A) 10.76%
(B) 12.72%
(C) 10.67%
(D) 13.48%
Hint:
Profit after tax = 36,36,363 – 12,36,363 = 24,00,000.
EPS = 24,00,000/1,50,000 = 16 per share
Price Earning Method:

Answer:
(C) 10.67%
Question 42.
NSZ Ltd. has equity of 15 Million and 10% debentures of 20 Million. The cost of equity is 18% and the pre-tax cost of debt is 10%. The company estimates its EBIT at 7 Million. The applicable tax rate is 30%. What is the Economic value added of NSZ Ltd?
(A) 0.088 Million
(B) 0.678 Million
(C) 0.798 Million
(D) 0.533 Million
Hint:
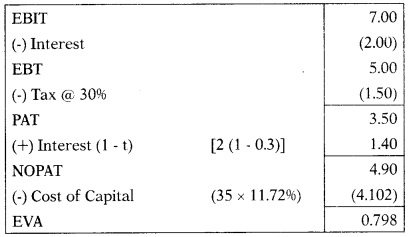
Kd = I(1 – t)
= 10(1 – 0.3)
= 7%

WACC = 1,171.46/100 = 11.72%
Answer:
(C) 0.798 Million
Question 43.
Maya Ltd.’s shares beta factor (P) is 1.1214. The dividend paid by the company last year was ₹ 3.60 per share on a face value of ₹ 20. The risk-free rate of interest on government bonds is 7.5%. The expected rate of return on company equity shares is 13%. What is the cost of equity (Ke) of Maya Ltd.?
(A) 12.89%
(B) 13.67%
(C) 14.52%
(D) 13.03%
Hint:
K = Rf + p(Rm – Rf)
= 7.5 + 1.1214(13 – 7.5)
= 13.67%
Answer:
(B) 13.67%
Question 44.
H Ltd. p is 1.8025. The dividend paid by the company last year was ₹ 9 per share on the face value of ₹ 30. The risk-free rate is 0.061275. The risk premium is 0.0825. Calculate cost of equity capital.
(A) 21%
(B) 6.28%
(C) 14.77%
(D) 12%
Hint:
Ke = Rf + p (Rm – Rf) Note: Risk Premium = (Rm – Rf)
= 6.1275 + 1.8025 × 8.25 = 21%
Answer:
(A) 21%
Question 45.
Rao Ltd. earns proRt after tax ₹ 3,96,000. Corporate tax is 0.4. Its capital structure consist of equity shares ₹ 9,60,000; 15% Term loan ₹ 4,80,000. Cost of equity is 0.12. its economic value added is
(A) ₹ 2,66,400
(B) ₹ 2,80,800
(C) ₹ 2,08,800
(D) ₹ 2,80,008
Hint:
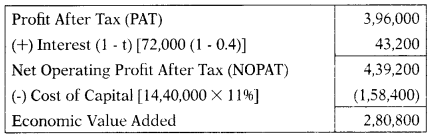
Calculation of cost of debts:
Kd = I (1 – t)
= 15 (1 – 0.4) = 9%
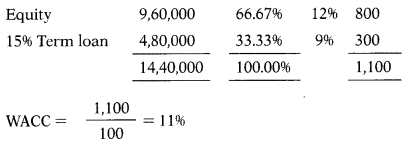
Answer:
(B) ₹ 2,80,800
Question 46.
Following details are submitted by Rajlakhami Ltd.:
| EBIT | ₹ 350 lakh |
| Equity Capital | ₹ 400 lakh |
| Reserves & Surplus | ₹ 325 lakh |
| 10% Debentures | ₹ 1,000 lakh |
| Current Assets | ₹ 82 lakh |
| Cost of Equity | 17.5% |
| Income Tax Rate | 30% |
Economic Value Added =?
(A) ₹ 43.75 lakh
(B) ₹ 40.75 lakh
(C) ₹ 43.57 lakh
(D) ₹ 45.37 lakh
Hint:
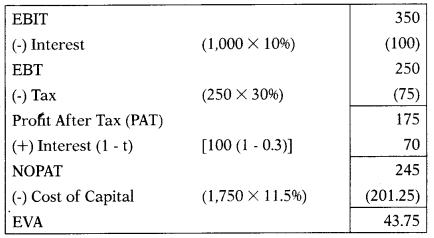
Kd = 1(1 – t)
= 10(1 – 0.3)
= 7%
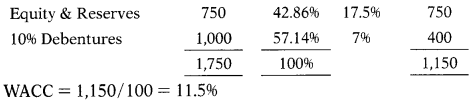
Answer:
(A) ₹ 43.75 lakh
Question 47.
An analyst has calculated the economic value added of ₹ 43,750 for Z Ltd. WACC of the company is 11.5% and the applicable tax rate is 30%. The company paid interest of ₹ 1,00,000 during the year. The total assets of the company are ₹ 17,50,000. What is the profit after tax (PAT) of the company?
(A) ₹ 2,45,000
(B) ₹ 1,45,000
(C) ₹ 1,75,000
(D) ₹ 3,15,000
Hint:
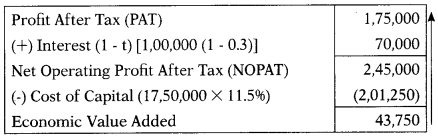
Perform reverse working.
Answer:
(C) ₹ 1,75,000
Question 48.
Ramola Ltd. report its NOPAT ₹ 25,00,000. Its capital employed and economic value added is ₹ 60,00,000 & 7 19,00,000 respectively. What is the overall cost of capital of Ramola Ltd.?
(A) 10.9%
(B) 11%
(C) 10%
(D) 9.8%
Hint:
EVA = NOPAT – (Capital Employed × WACC)
19,00,000 = 25,00,000 – (60,00,000 × x)
– 6,00,000 = – 60,00,000x
x = 0.1 i.e. 10%
Answer:
(C) 10%
Question 49.
Compute the EVA with the help of the following information:
|
|
₹ |
| Equity | 10,00,000 |
| Debt (10%) | 5,00,000 |
| Profit after tax | 2,00,000 |
Risk-free rate of return is 7%. Beta (p) = 0.9, Market rate of return = 15% Applicable tax rate is 40%.
(A) ₹ 57,950
(B) ₹ 57,590
(C) ₹ 57,905
(D) ₹ 59,750
Hint:
K = Rf + p(Rm – Rf)
= 7 + 0.9 (15 – 7)
= 14.2% = 6%
Kd = I (1 -1)
= 10(1 – 0.4)
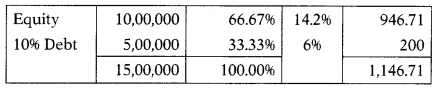
WACC = 1,146.71/100= 11.47%
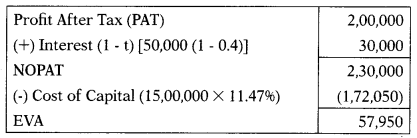
Answer:
(A) ₹ 57,950
Question 50.
Compute the EVA with the help of the following information:
| Equity | ₹ 15,00,000 |
| Debt (10%) | ₹ 7,00,000 |
| Profit after tax | ₹ 4,00,000 |
The risk-free rate of return is 7%. Beta (P) = 0.9 Market rate of return =15%. The applicable tax rate is 40%.
(A) ₹ 1,87,020
(B) ₹ 1,78,020
(C) ₹ 1,87,200
(D) ₹ 1,85,200
Hint:
K = Rf + p(Rm – Rf)
= 7 + 0.9 (15 – 7)
= 14.2%
Kd = I (1 – t) = 10 (1 – 0.4) = 6%

WACC = 1159.08/100 = 11.59%

Answer:
(A) ₹ 1,87,020
