Go through this Concept of Auditing – CS Foundation Fundamentals of Accounting and Auditing Notes will help students in revising the entire subject quickly.
Concept of Auditing – CS Foundation Fundamentals of Auditing Notes
Auditing – An introduction:
- The term “audit” has originated from a Latin word “audire” which means to hear.
- Authenticity of accounts is assured with the help of Independent audit.
- Audit is performed to ascertain the validity and reliability of information.
- Auditing is defined as a systematic and independent examination of data, statements, records, operations or performances (financial or non-financial) of an enterprise for a stated purpose.
- The goal of an audit is to express an opinion on financial and non financial matters.
- Audit deals with checking, verification and examination of accounts.
- Traditionally, Audits were associated with gaining information about financial system and financial records of a company or business, but recently it has begun to include non financial subject areas such as Safety,
- Security, Information system performance, Environmental concern.
- Financial statements are said to be true & fair when they are free from material misstatement.
Meaning and Definitions of Auditing:
The word audit means a thorough scrutiny of the books of accounts and its ultimate aim is to verify the financial position disclosed by the balance sheet and the profit and loss account of a company.
The followings are some definitions of audit given by some writers:
Lawrence R. Dicksee: “An audit is an examination of accounting records undertaken with a view to establishing whether they correctly and completely reflects the transactions to which they purport to relate.”
Taylor and Perry: “Audit is defined as an investigation of some statements of figures involving examination of certain evidence, so as to enable an auditor to make a report on the statement.”
F.R.M De Paula: “An audit denotes the examination of Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account prepared by others together with the books of accounts and vouchers relating there to in such manner that the auditor may be able to satisfy himself and honestly report that, in his opinion such Balance Sheet is properly drawn up so as to exhibit a true and correct view of the state of affairs of the particular concern according to the information and explanations given to him and as shown by the books.”
Prof. Montgomery: “Auditing is a systematic examination of the books and records of business or other organization, in order to ascertain or verify and to report upon the facts regulating its financial operations and the result thereof.”
Spicer & Pegler: “Audit such an examination of the books of accounts and vouchers of a business, as will enable the auditor to satisfy himself that the Balance Sheet is properly drawn up, so as to give a true and fair view of the state affairs of the business, and whether the profit and loss account gives a true and fair view of the profit or ioss for the financial period according to the best of his information and explanations given to him and as shown by the books, and if,not, in what respect he is not satisfied.”
Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) defines Auditing as:
“Auditing is defined as a systematic and independent examination of data, statements, records, operations and performance of an enterprise for a stated purpose. In any auditing situation the auditor perceives and recognizes the propositions before him for examination, collect evidences, evaluates the same and on this basis formulates his judgement which is communicated through his audit report.”
The meaning of an Audit contains:
- An intelligent and critical examination of the books of accounts of business.
- It is done by an independent qualified person.
- It is done with the help of vouchers, documents, information and explanations received from the clients.
- The auditor satisfies himself with the authenticity of the financial accounts prepared for a particular period.
Features of Auditing:
(i) It is a systematic examination of books of accounts by an independent person.
(ii) Time, extent and nature of audit depends on the effectiveness of internal control system.
- Internal control system refers to the organisational plan and all methods or procedures adopted by management of an entity to achieve efficient conduct of business, safeguarding assets, preventing frauds and errors, accuracy of accounting records etc.
- This control is exercised by the management of the organisation.
(iii) Auditing may be on test basis or in depth checking of books and accounts.
(iv) Various method and procedures can be used for performing audit.
(v) It involves reporting by the auditor on the accounts examined by him and prepared as per GAAP principle and present true and fair view.
(vi) Auditing is not limited only to examination of financial records but it also includes other areas like – operational audit, process audit, tax audit, secretarial audit, efficiency audit, social audit etc.
(vii) Auditing has nothing to do with Accounting.
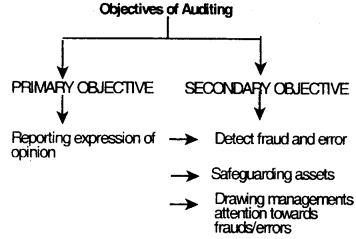
Objectives of Auditing:
Remember:
- Detection of fraud and error is only a secondary objective of auditing.
- Auditor’s duty is to examine the accounts and report those fraud and errors which comes to his knowledge during such examination.
- Auditor is a watchdog and not a blood hound. In India the Companies Act, 2013 made audit of company account compulsory. Recently Companies Act, 2013 has been implemented w.e.f. 1st April, 2014 and this contain provision about statutory audit, cost audit, internal audit and secretarial audit.
Functions of Auditing:
- Examination of books of accounts to detect and prevent errors and frauds with supporting vouchers and documents.
- Express opinion on financial or non-financial area.
- Safeguarding the financial interest of persons not associated with management like partners, shareholders etc.
- To act as a moral check on the employees and prevents from committing fraud.
- Providing a reasonable assurance that the statements are free from material error.
- To state that whether the books and accounts show a true and fair picture.
Basic Principle Governing Audit:
- Integrity, objectivity and independence
- Confidentiality
- Skill and competence
- Worked performed by other
- Documentation
- Planning
- Audit evidence
- Accounting System and Internal Control
- Auditing conclusions and reporting.
Principal aspects to be covered in Auditing/ Functions of Audit:
- Review of systems and procedures: adopted by the entity – primary function of auditing.
- Review of internal control system: If the internal control system is stronger then the extent of checking can be reduced and vice versa.
- Routine checking/arithmetical accuracy.
- Review of the accounting principles followed by the entity.
- Comparison of financial statements with books and accounts.
- Verification of assets by physically inspecting the assets.
- Verification of liabilities by verifying legal and official documents.
- Ensuring that financial statements shows a true and fair view.
- Ensuring statutory compliances has been complied by the entity.
- Reporting to the authority appointing him for conducting audit.
Benefits of Auditing:
- It provides satisfaction to the owner.
- It detects and prevents occurrence of frauds and errors.
- It helps in verification of books.
- The auditor is independent and hence, his opinion on financial statements is unbiased.
- Auditing keeps a moral check on the employees and prevents them to commit fraud or error.
- Auditing involves examination of all records whereas investigation involves deep & special examination of a particular record.
- It gives assurance to the shareholders that the books and accounts are managed in proper way.
- If the firm is audited, more reliance is placed by the outsiders on it.
- Auditing ensures compliance with legal requirements.
- By keeping a check on internal control system, auditing helps to strengthen internal control system.
- On the basis of audited balance sheet, it becomes easy to obtain loan/credit facility
Limitations of Audit:
- It involves huge cost however, sometimes the benefits from auditing may not make up for the cost.
- When auditing is performed on test check basis, the results may not be reliable.
- There are insufficient time deadlines to complete audit which may leave scope for errors.
- Evidence obtained by auditor are not conclusive rather they are persuasive.
- Certain Information is based on estimates, which cannot be checked by the auditors.
- If information provided by the management is faulty, the result of auditing will also be incorrect.
Investigation:
- It refers to the critical checking of particular records.
- In simple words, it is the deep examination of those points on which auditor’s suspicion has arisen while conducting audit.
- Auditing and investigation have different purposes
Differences between auditing and investigation:
- Investigation is voluntary while auditing is mandatory for companies though voluntary for others.
- Auditing covers generally a period of one financial year whereas investigation has no fixed duration.
- The evidences obtained under auditing are persuasive whereas under investigation are conclusive.
- An investigator can be engaged by owners or management or even by third parties while auditor can be appointed by owners or shareholders.
- Investigation is carried out for the appointing agency while auditing is carried out on behalf of the owners.
- Investigation is not restricted to any number of financial year though auditing is generally for one financial year.
- Scope of auditing is specific and seeks to answer only those questions laid down in the engagement letter whereas investigation in general seeks to form opinion on the financial statement.
- Audit is not based on suspicion unless circumstances exist to arouse suspicion whereas in investigation its essence lies in going into the matter with some pre-conceived notion suited to the objective.
Concept of Auditing MCQ Questions
1. The term audit originated from a __________ word “audire” which means to hear.
(a) Latin
(b) French
(c) Greek
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Latin
2. The goal of audit is to express an opinion on _________ areas.
(a) Only financial
(b) Financial and operational
(c) Financial or non financial
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Financial or non financial
3. “Accounting begins where auditing ends” This statements is _________.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Partly true
(d) None.
Answer:
(b) False
4. Auditor is a _________ person.
(a) Dependent
(b) Independent
(c) Sometimes dependent sometimes independent
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Independent
5. Principal aspects covered in an audit refers to the _________ of audit.
(a) Features
(b) Functions
(c) Essentials
(d) Advantages.
Answer:
(b) Functions
6. Compliance and substantive procedures will determine the:
(a) Effectiveness of internal control system
(b) Extent of errors and frauds
(c) Role of management in the organisation
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
7. Principal aspects to be covered in an audit involves.
(a) Review of system and procedures
(b) Review of internal control system
(c) Ensuring statutory compliance
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
8. Stronger the internal control, _________ will be the checking by the auditor.
(a) Stronger
(b) Lesser
(c) Any of these
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Lesser
9. Verification of assets is done to ascertain.
(a) Existence of asset
(b) Ownership of asset
(c) Possession of asset
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
10. Auditor is a _________.
(a) Watchdog
(b) Blood hound
(c) Investigator
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Watchdog
11. Which of these is not a benefit of auditing?
(a) Moral check on employees
(b) Strengthening internal control
(c) Protection of interest of shareholders
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(d) None of these.
12. The primary objective of auditing is:
(a) Detection of fraud
(b) Expression of opinion
(c) Checking efficiency of internal control
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(b) Expression of opinion
13. Evidence obtained by audit are _________ whereas of investigation are _________.
(a) Conclusive, persuasive
(b) Persuasive, conclusive
(c) Persuasive, persuasive
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Persuasive, conclusive
14. An investigator _________ be a Chartered Accountant.
(a) Must
(b) May or may not
(c) Should
(d) None.
Answer:
(b) May or may not
15. Investigation is done _________.
(a) Mandatory
(b) Voluntary
(c) As per the statute
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Voluntary
16. Auditing assures that financial statements are _________.
(a) True and fair
(b) True and correct
(c) Free from errors
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) True and fair
17. Time, extent and nature of audit depends upon:
(a) Fees paid to the auditor
(b) Effectiveness of internal control
(c) Report of previous auditor
(d) Time available with the auditor
Answer:
(b) Effectiveness of internal control
18. Internal Control is exercised by _________.
(a) Management
(b) Auditor
(c) Special investigators
(d) Any of these
Answer:
(a) Management
19. _________ is the responsibility of management.
(a) Accounting
(b) Auditing
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Accounting
20. _________ are the test designed to obtain evidence as to completeness, accuracy and validity of data produced by accounting system.
(a) Substantive procedures
(b) Compliance procedures
(c) In depth examination
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Substantive procedures
21. _________ is referred as a special purpose examination.
(a) Auditing
(b) Investigation
(c) Test checks
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Investigation
22. Primary responsibility for the adequacy of financial statements rests with:
(a) Auditor
(b) Management
(c) Auditor’s staff
(d) Central Government.
Answer:
(b) Management
23. Weakness in internal control system, _________ the risk of fraud and error.
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Does not affect
(d) None.
Answer:
(a) Increases
24. Who appoints internal auditor?
(a) Management
(b) Shareholder
(c) Government
(d) Stock exchange.
Answer:
(a) Management
25. An audit is _________ examination of financial or non-financial information of any entity.
(a) A true
(b) A true and fair
(c) An independent
(d) A dependent
Answer:
(c) An independent
26. ‘Investigation’ is done for __________.
(a) Satisfaction
(b) An opinion
(c) Special purpose
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Special purpose
27. Tick the best statement related to word “Corroborative”
(a) Agreement on a secret plot
(b) An action or motion that stops expression
(c) Improver or developer
(d) To strengthen or support with additional evidence
Answer:
(d) To strengthen or support with additional evidence
28. The statement “As per my opinion, the books and accounts show a true and fair picture” is a part of _________.
(a) Audit plan
(b) Audit report
(c) Audit programme
(d) Audit evidence
Answer:
(b) Audit report
29. Which of the following is not a benefit of auditing?
(a) Moral check
(b) Increasing the sales volume
(c) Compliance with legal requirements
(d) Loan facility
Answer:
(b) Increasing the sales volume
30. Owners or management or even third party may appoint the _________.
(a) Auditor
(b) Investigator
(c) Financial auditor
(d) All of them
Answer:
(b) Investigator
31. The authenticity of the accounts can be ensured by conducting _________.
(a) Independent audit
(b) Audit by the internal management
(c) Management audit
(d) Cost audit
Answer:
(a) Independent audit
32. The main objective of audit is to _________.
(a) Gain information about the financial system
(b) Improving the efficiency of the management
(c) Increasing the profitability
(d) Express an opinion on the financial statement
Answer:
(d) Express an opinion on the financial statement
33. Audit is performed to ascertain _________.
(a) Validity of information
(b) Reliability of information
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
34. Which of the following statement is False?
(a) Audit is conducted by an independent person
(b) Nature, time and extent of audit depends upon the effectiveness of internal control
(c) Audit includes maintenance of books of accounts
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Audit includes maintenance of books of accounts
35. GAAP stands for _________.
(a) Generally accepted auditing principles
(b) Generally accepted accounting principles
(c) Globally accepted accounting principles
(d) Globally accepted auditing principles
Answer:
(b) Generally accepted accounting principles
36. The systematic, critical and special examination of the records for a special purpose is called _________.
(a) Auditing
(b) Inspection
(c) Investigation
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Investigation
37. An investigator can be appointed by __________.
(a) Owners
(b) Management
(c) Third parties
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
38. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Investigator seeks conclusive and corroborative evidence
(b) Auditor seeks persuasive rather than conclusive evidence
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
39. Auditing provides a complete guarantee that the books of accounts are free from errors and there is no chance of any fraud.
(a) True
(b) Partly true
(c) False
(d) Partly false
Answer:
(c) False
40. A valuation certificate issued by some authority is _________.
(a) Persuasive audit evidence
(b) Conclusive audit evidence
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(a) Persuasive audit evidence
41. The auditor submits his audit report to the _________.
(a) Government
(b) Appointing authority
(c) Directors
(d) Registrar of companies
Answer:
(b) Appointing authority
42. _________ are not legally required to get their financial statements audited.
(a) Companies
(b) Banks
(c) Partnership firms
(d) Insurance companies
Answer:
(c) Partnership firms
Auditing refers to systematic and independent examination of date, statements, records, operations or performances of an enterprise for a stated purpose. Auditing is mandatory for companies whereas it is voluntary for others. Moreover, banks and insurance companies are a form of company form of organisation.
Thus, among the following only partnership firms are not legally required to get their financial statements audited.
43. In audit, investigation exercise is _________.
(a) Mandatory
(b) Recommendatory
(c) Voluntary
(d) Voluntary but recommendatory in all cases
Answer:
(c) Voluntary
The difference between audit and investigation lies in the fact that- Audit is mandatory for companies but voluntary for others whereas Investigation is a voluntary exercise.
44. The format of investigation report is _________.
(a) Prescribed by law
(b) Not prescribed by any law
(c) Standardized
(d) Neither standardized nor prescribed by any law
Answer:
(d) Neither standardized nor prescribed by any law
Auditing and investigation differs from each other in point that – The format of audit report has been prescribed by law whereas there is no statutory form of investigation report neither any form has been prescribed by law.
45. Which of the following is true about audit?
(a) Audit starts after accounting ends
(b) Accounting starts after auditing ends
(c) Accounting and auditing exercise are parallel
(d) Accounting is complementary to auditing.
Answer:
(a) Audit starts after accounting ends
Relationship exists between accounting and auditing :
- Accounting is the art of recording the transactions whereas auditing is the independent examination of such recorded information.
- Accounting is the management’s responsibility whereas auditing is the auditor’s responsibility appointed by the owner.
- Auditing starts where accounting ends.
Thus, only the statement, “Audit starts after accounting ends” is true about audit.
46. Which of the following is a type of persuasive audit evidence for the auditor?
(a) Client’s Bank statements
(b) Documents obtained by auditor directly from third parties
(c) Carbon copies of sales invoices
(d) Computations made by the auditor himself.
Answer:
(c) Carbon copies of sales invoices
The evidences obtained by the auditor are persuasive rather than conclusive. Persuasive means intended or having the power to induce action or belief. E.g. an architects, certificate of valuation for a newly constructed building of a client is a persuasive evidence of the correct value of building; carbon copies of sales invoice etc.
47. For an auditor, to check arithmetical accuracy is _________.
(a) Not required
(b) Mandatory
(c) Voluntary
(d) Recommendatory
Answer:
(b) Mandatory
It is the duty of the auditor to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts by checking the proper posting and balances of the books of accounts. Thus, checking of arithmetical accuracy is mandatory.
48. Verification of assets is done to ascertain _________.
(X) Existence of asset
(Y) Ownership of asset
(Z) Possession of asset
The correct option is:
(a) (X) and (Y)
(b) (Y) and (Z)
(c) (X) and (Z)
(d) (X), (Y) and (Z).
Answer:
(d) (X), (Y) and (Z).
It is the duty of the auditor to physically inspect the assets and their recording in the books of accounts and verify the legal and official documents to ascertain the existence, ownership, possession, classification and valuation of assets of an entity.
49. Which of the following is not correct about investigation?
(a) Investigation may be done by any person having the knowledge of entity’s business
(b) Investigation is mandatory in nature and needs to be done on yearly basis
(c) The scope of investigation is decided by the appointing authority
(d) There is no standard format of investigation report.
Answer:
(b) Investigation is mandatory in nature and needs to be done on yearly basis
The investigation is the critical checking of particular records of business for specific purpose.
It has following features:
- It is voluntary in nature.
- It can be conducted by any person who may not be a CA.
- He is appointed by the owners or management or even by third parties.
- Work is carried out from the viewpoint of the appointing agency.
- It answers those questions as laid down in the engagement letter.
- It is not restricted to one financial year,
- It seeks conclusive and corroborative evidence.
- There is no statutory form of investigation report.
Thus, the option that investigation is mandatory in nature and needs to be done on yearly basis is not correct about investigation.
50. Principal aspects to be covered in an audit involves:
(X) Review of system and procedures
(Y) Review of internal control system
(Z) Ensuring statutory compliance The correct option is:
(a) (X) and (Y)
(b) (Y) and (Z)
(c) (X) and (Z)
(d) (X), (Y) and (Z)
Answer:
(d) (X), (Y) and (Z)
The following principal aspects also known as functions of audit are required to be covered by an auditor while doing audit of an organisation:
- Review of system and procedures
- Review of internal control system
- Routine checking/arithmetical accuracy
- Accounting principles
- Books and statements
- Verification of assets
- Verification of liabilities
- True and fair view
- Statutory compliance
- Reporting.
Thus, the correct option is (d) which means all three are the principle aspects of audit
51. Detection and prevention of fraud is the _________ objective of auditing activity.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Single
(d) Specific.
Answer:
(b) Secondary
“Auditing is defined as a systematic and independent examination of data, statements, records, operations and performances of an enterprise for a stated purpose, on the basis of which he formulates his judgement which is communicated through his audit report”. Thus, primary purpose of auditing is to examine the company’s financial statement and form an opinion. During this process, auditor comes across various frauds and errors which help in their detection and prevention. This is the secondary objective of audit.
52. Quality of auditor to be free from influence is defined by which term?
(a) Independence
(b) Confidentiality
(c) Skill
(d) Integrity
Answer:
(a) Independence
Auditing is very useful in obtaining the independent opinion of the auditor about business condition. If the accounts are audited by an independent auditor, the report of the auditor will be true and fair in all respects and it will be of extreme importance for the management of the company. Thus, quality of auditor to be free from influence is defined by Independence.
53. Auditing exercise includes:
(i) Checking of accounts
(ii) Verification of accounts
(iii) Examination of accounts The options are:
(a) I and III
(b) I, II and III
(c) I and II
(d) II and III
Answer:
(b) I, II and III
Auditing exercise includes:
- Checking of accounts
- Verification of accounts
- Examination of accounts
- Investigation of some statements
- Examination of evidence.
So, the option (b) is correct answer i.e. I, II and III.
54. In case of investigation, the period of investigation coverage _________.
(a) Is 2 years
(b) Is 1 year
(c) Differs on case to case basis
(d) Is 6 months
Answer:
(c) Differs on case to case basis
In case of investigation, the period of investigation coverage is not necessarily restricted to a financial year. It can be extended for a period consisting of a number of years.
Thus, option (c) is the correct answer i.e. it may differs on case to case basis.
55. The primary objective of statutory auditing is to – (x) detect errors (y) prevent errors (z) express an opinion. The options are:
(a) (x) and (y)
(b) (z) only
(c) (y) only
(d) (x), (y) and (z).
Answer:
(b) (z) only
Primary objective of statutory auditing is to ascertain whether financial statement present true and fair view of financial position. Therefore, give an opinion. And secondary objective is to detect and present frauds and errors.
56. Audit working papers are the property of _________.
(a) Income Tax Department
(b) Auditor
(c) Owner
(d) Government
Answer:
(b) Auditor
Audit working papers are property of auditors.
57. Which of the following best describes the primary purpose of audit programme preparation?
(a) To detect errors or fraud
(b) To assets audit risk
(c) Together sufficient appropriate evidence
(d) To comply with GAAP.
Answer:
(c) Together sufficient appropriate evidence
Audit program contains the measures that are generally employed to determine what, and how much evidence must be collected and evaluated.
58. _________ is an independent person who check the companies book:
(a) Auditor
(b) CS
(c) Shareholder
(d) Board
Answer:
(a) Auditor
Auditor is an independent person who check the companies book. Auditor is a watchdog and not a blood hound. Auditor’s duty is to examine the accounts and report those fraud and errors which comes to his knowledge during such examination.
59. Meaning of ‘Audire’:
(a) Audit
(b) Investigation
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Meaning of ‘Audire’ means to hear.
60. _________ evidence are not conclusive.
(a) Investment
(b) Corroboration
(c) Audit
(d) Can’t say
Answer:
(c) Audit
The auditor should obtain sufficient appropriate evidences through the performance of compliance and other substantive procedure to enable him to draw reasonable conclusion to form an opinion on the financial information. The evidences obtained by an auditor are persuasive rather than conclusive.
61. Which of the following is started with some pre-conceived notion suited to the objective?
(a) Audit
(b) Verification
(c) Vouching
(d) Investigation
Answer:
(d) Investigation
Investigation is started with some pre-conceived notion suited to the objective as it is done when a lapse already exist to pin point the reason and person involved in it so that responsibility for such lapse could be fixed.
62. The auditing exercise acts as a moral check for?
(I) Management only
(II) Employee only
(III) Regulation. This option are:
(a) (I), (II) and (III)
(b) (I) and (II)
(c) (II) and (III)
(d) (I) and (III)
Answer:
(b) (I) and (II)
Audit is performed to ascertain the validity and reliability of information. The goal of an audit is to express an opinion on the financial or non-financial areas, as audit safeguards the financial interest of person not associated with the management and thus act as a moral check and prevents from committing fraud.
63. Systematic, critical and special examination of the records of a business for a specific purpose in known as:
(a) Investigation
(b) Audit
(c) Verification
(d) Vouching
Answer:
(a) Investigation
Investigation is systematic, critical and special examination of the business records for a specific purpose.
64. Which one of the following is primary function of statutory audit? (i) Review of system and procedures (ii) Report whether accounts show true and fair view of entry’s operation (iii) detection of fraud. The options are:
(a) I and II
(b) I, II and III
(c) I and III
(d) II and III
Answer:
(a) I and II
The functions of Statutory Audit are:
- Review of system and procedure
- Review of internal control system
- Routine checking/Arithmetical Accuracy
- Accounting principle are followed
- Books and statement comply with each other
- Verification of Asset
- Verification of Liabilities
- True and fair view
- Statutory compliance
- Reporting
65. Full form-of MIP _________.
(a) Mandatory Inspection Point
(b) Modification Instruction Package
(c) Mobile Internet Package
(d) Monthly Income Ran
Answer:
(a) Mandatory Inspection Point
MIP stands for Mandatory Inspection Point.
66. The purpose of Auditing and Investigation is:
(a) Similar
(b) Contrary
(c) Same
(d) Different
Answer:
(d) Different
Purpose of Auditing + Investigation is Different.
67. The Statutory auditor of a company can act as:
(a) Tax Auditor
(b) Internal Auditor
(c) Concurrent Auditor
(d) Cost Auditor
Answer:
(a) Tax Auditor
The Statutory Auditor can Act as a Tax Auditor.
68. Which of the following is not correct about investigation?
(a) Investigation may be done by any person having the knowledge of entity’s business
(b) Investigation is mandatory in nature and needs to be done on yearly basis
(c) The scope of investigation is decided by the appointing authority.
(d) There is no standard format of Investigation report.
Answer:
(b) Investigation is mandatory in nature and needs to be done on yearly basis
It is not mandatory or compulsory to investige on yearly basis, investigation is not needed to be done annually, it is not of compulsory nature.
69. In Audit assignment, who among the following set the level of materiality?
(a) Shareholders
(b) Board of Directors
(c) Auditor
(d) Manager of the entity/department concerned
Answer:
(c) Auditor
In an audit assignment, the materiality level is set by the auditor of the entity, based on his objectivity and scope of audit. The Management or Board of Director etc. have no role in it.
70. Principals aspect to be covered in an audit involves:
(x) Review of system and procedures
(y) Review of internal control system
(z) Ensuring statutory compliance The correct option is:
(a) (x) and (y)
(b) (y) and (z)
(c) (x) and (z)
(d) (x), (y) and (z)
Answer:
(d) (x), (y) and (z)
Auditing is done on the basis of some principles and audit covers:
- Review of system and procedures
- Review of internal central system
- Ensuring statutory compliance
71. Verification of Assets is done to ascertain
x. Existence of Assets
y. Ownership of Assets
z. Possession of Assets
The Correct option is:
(a) (x) and (y)
(b) (y) and (z)
(c) (x) and (z)
(d) (x), (y) and (z)
Answer:
(d) (x), (y) and (z)
Verification of Assets is done every year to know the existence of assets means asset is in business or not, ownership of asset means asset is sold or not, possession of assets mean asset is transferred to anybody or not.
72. Auditing is compulsory for which organisation _________.
(a) Profit organisation
(b) Non-profit organisation
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Auditing is compulsory for profit organisation as well as for Non¬profit organisation too under certain circumstances, (include capital, turnover limits etc.). Hence, option (c) is correct.
73. In general, the scope of management audit is:
(a) Flexible
(b) Rigid
(c) Prescribed by law
(d) Prescribed by the appointing authority
Answer:
(a) Flexible
In general, the scope of management audit is flexible and incorporates all the needs of the company.
74. Detection and prevention of fraud is the _________ objective of auditing activity.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Single
(d) Specific
Answer:
(b) Secondary
Detection and prevention of fraud is the secondary objective of accounting activity.
75. Investigation is for _________.
(a) 1 year
(b) 2 year
(c) Differ case to case
(d) 4 years
Answer:
(c) Differ case to case
Period covered Under investigation is not necessarily restricted to a financial year. It may be extended to a period more than one year. Even it may be less than one year. It is voluntary and any person, who may not be a Charted Accountant may conduct investigation.
76. Limitations of internal audit _________.
(a) Time log
(b) Duties
(c) Costly
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Limitations of Internal Audit are:
- Staff shortage
- Time Log
- Error
- Responsibility
- Duties
- Lost consuming
